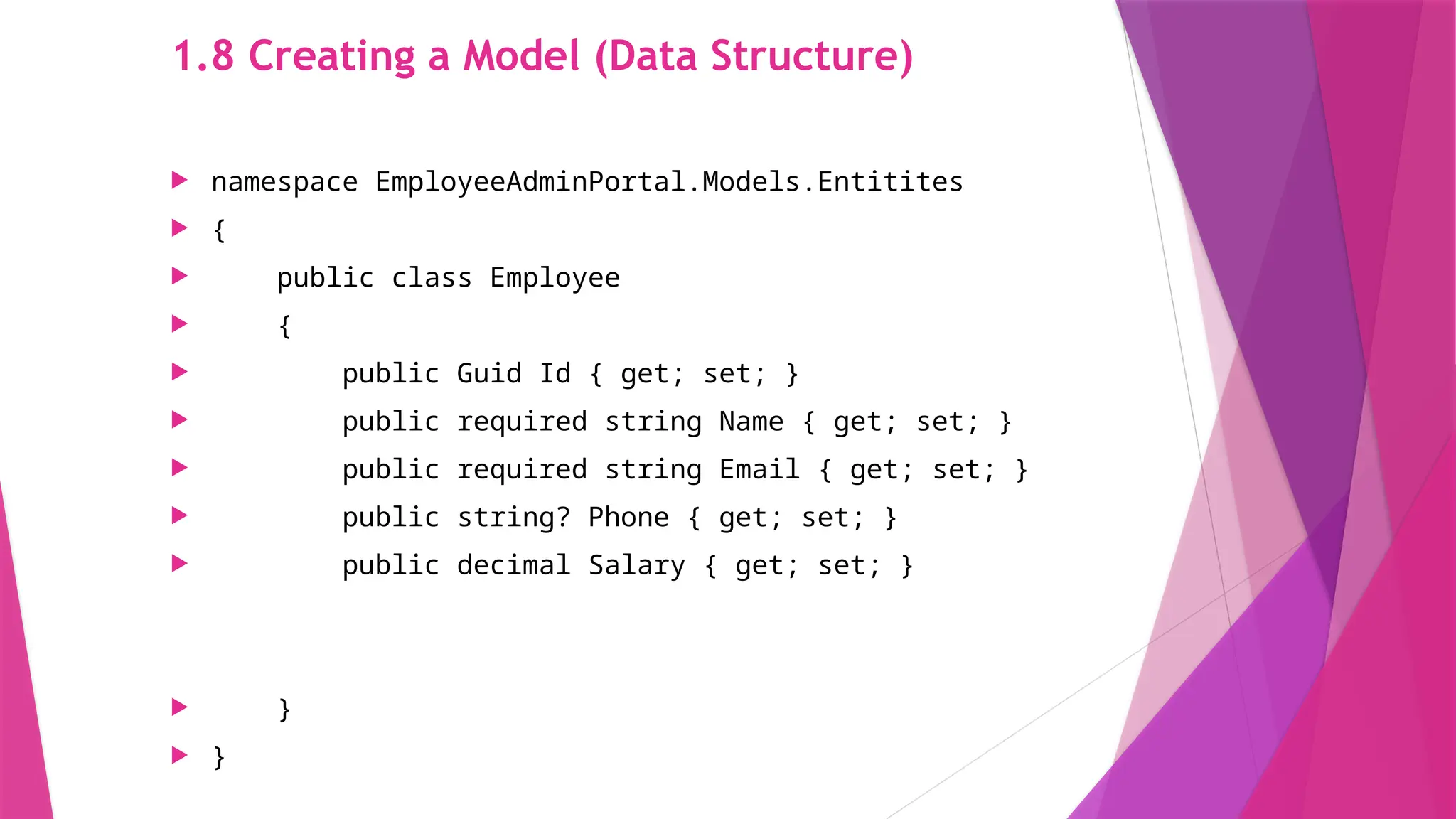
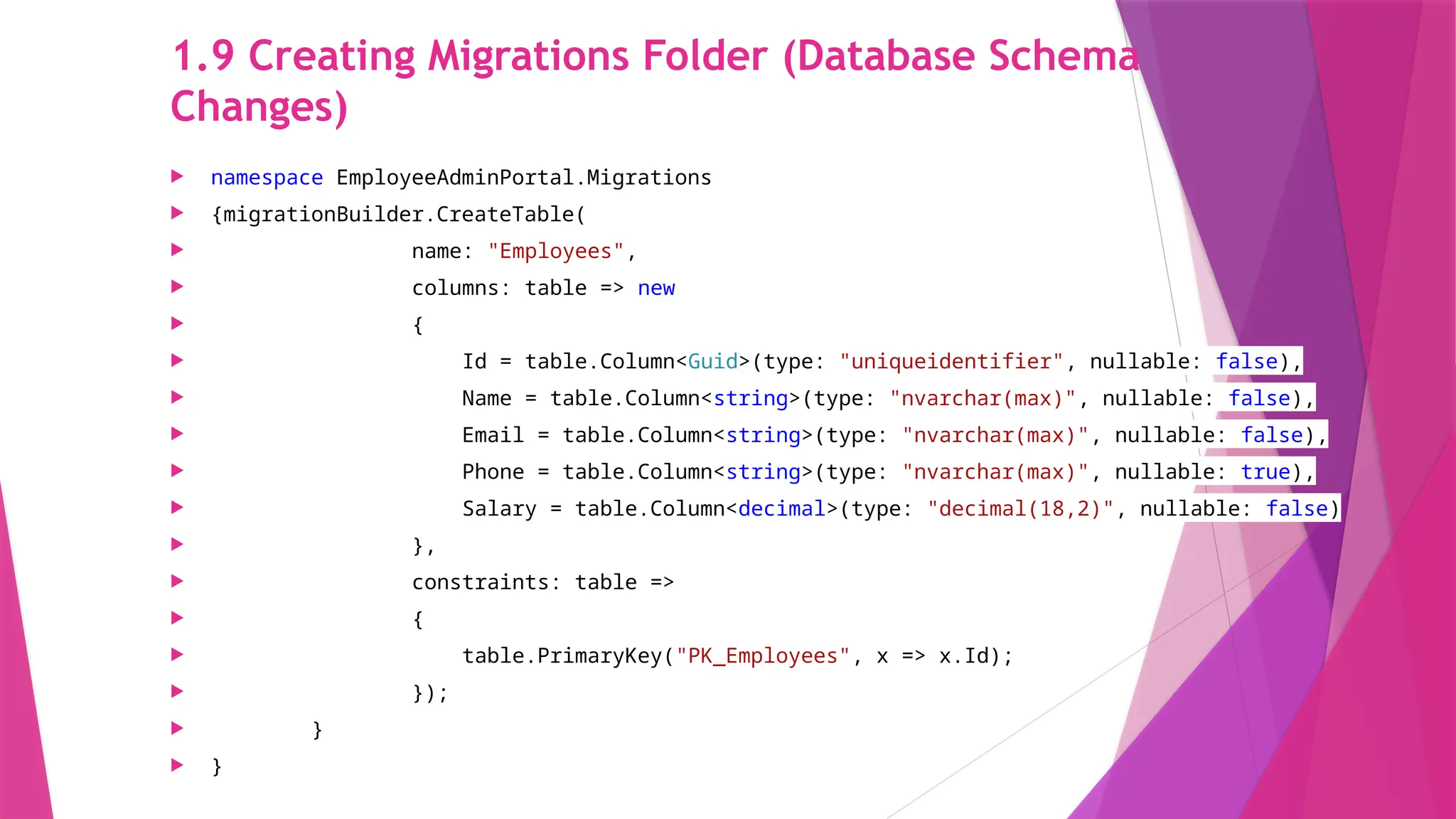
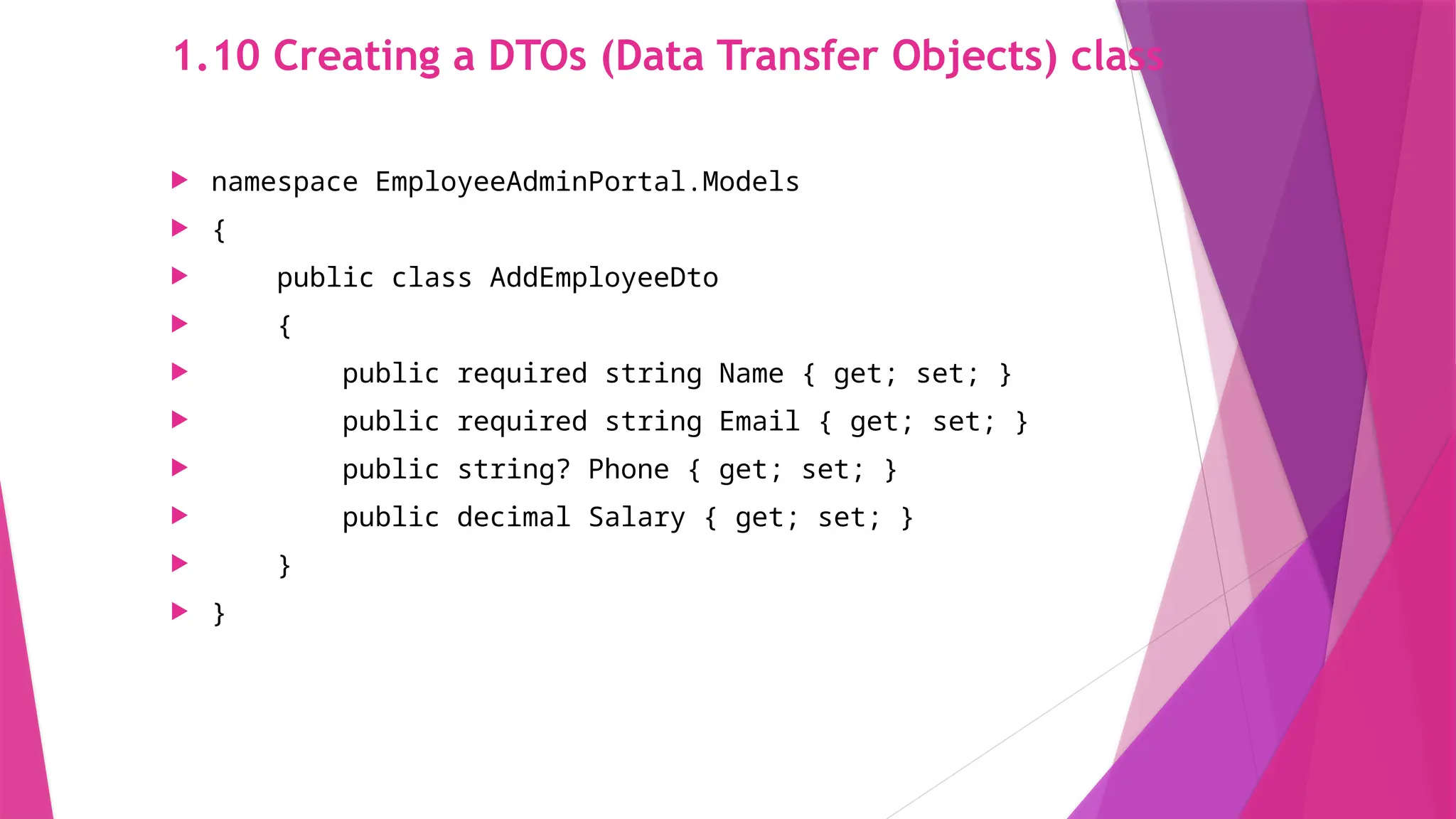
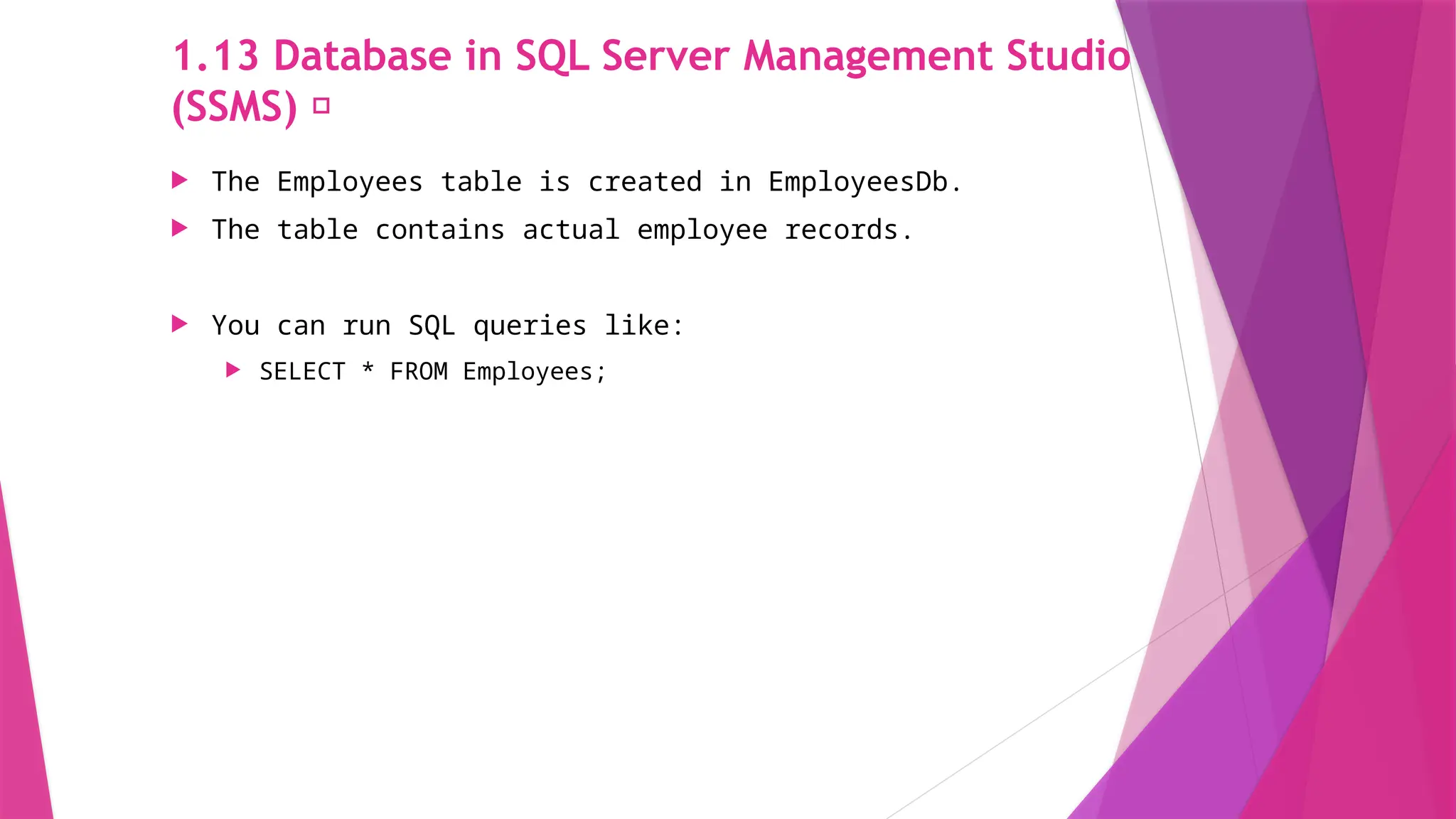
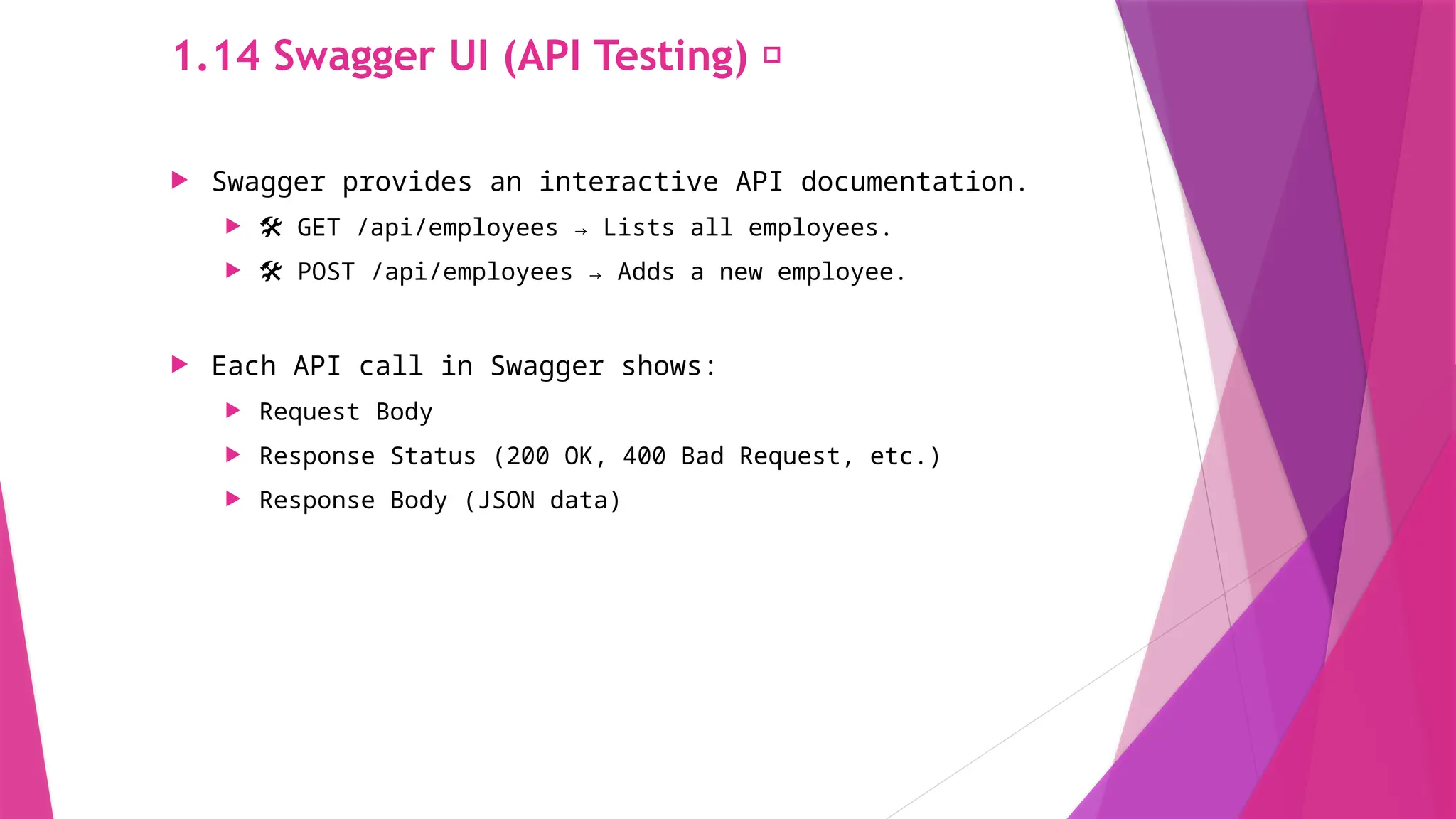
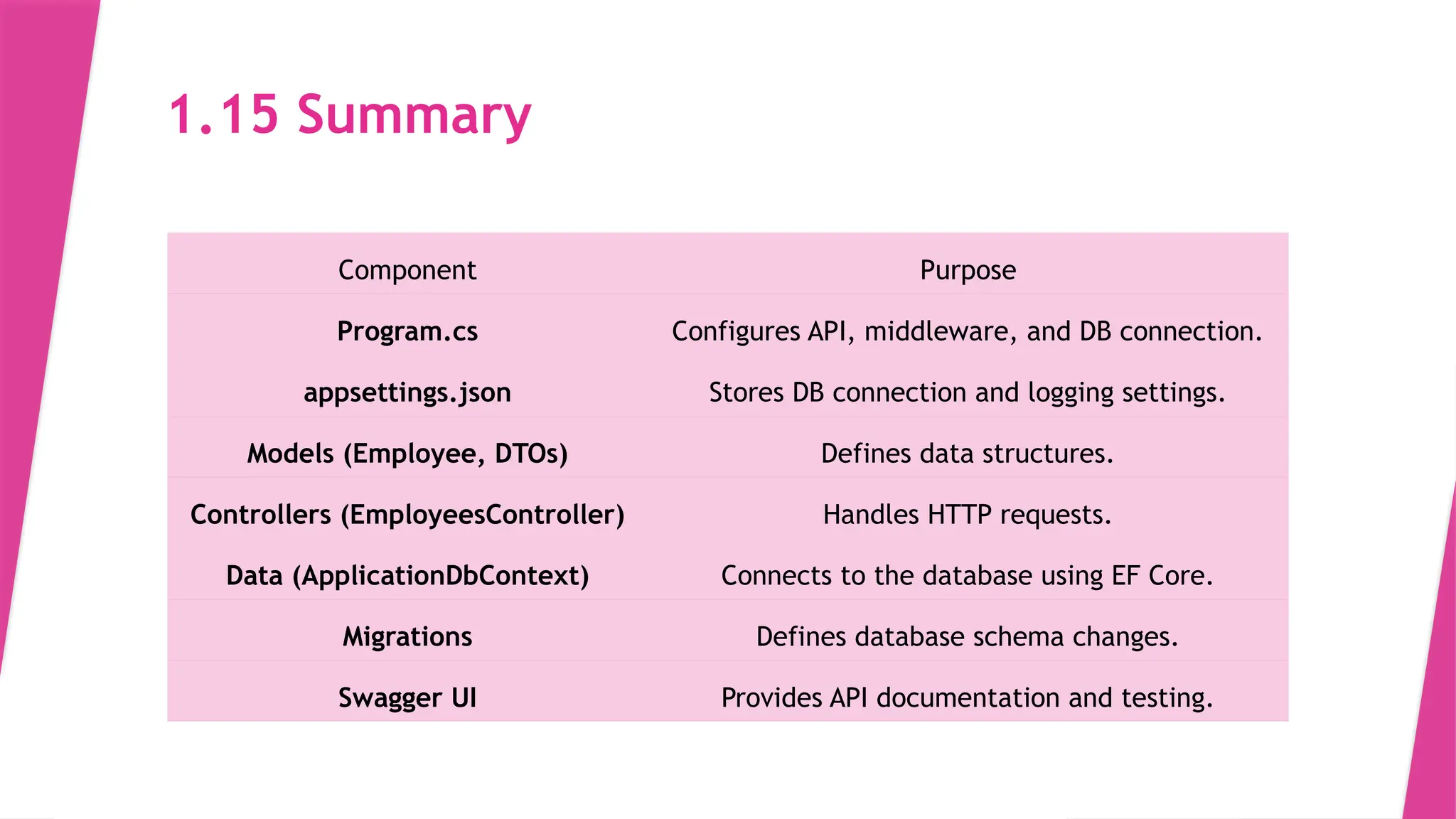
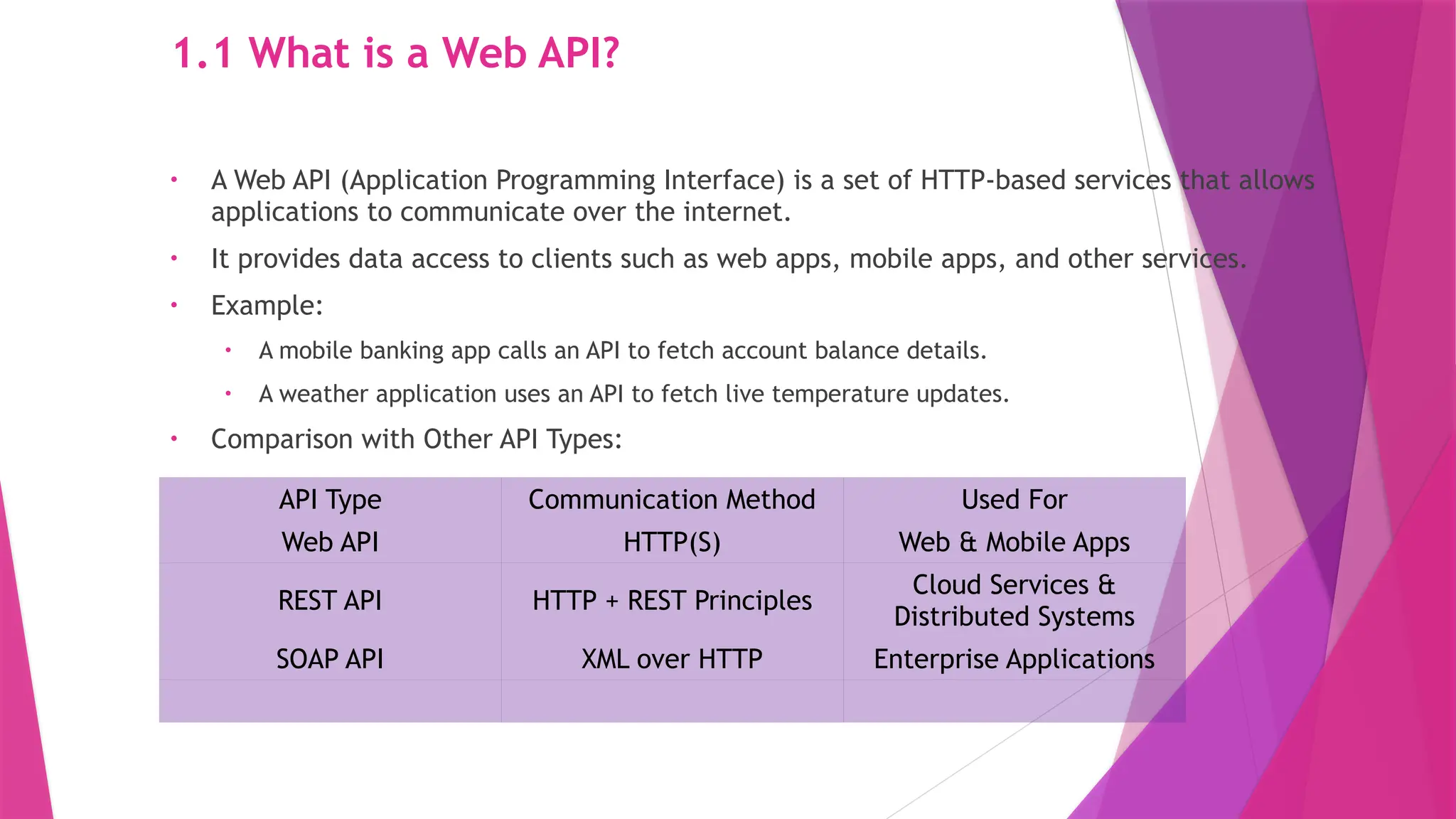
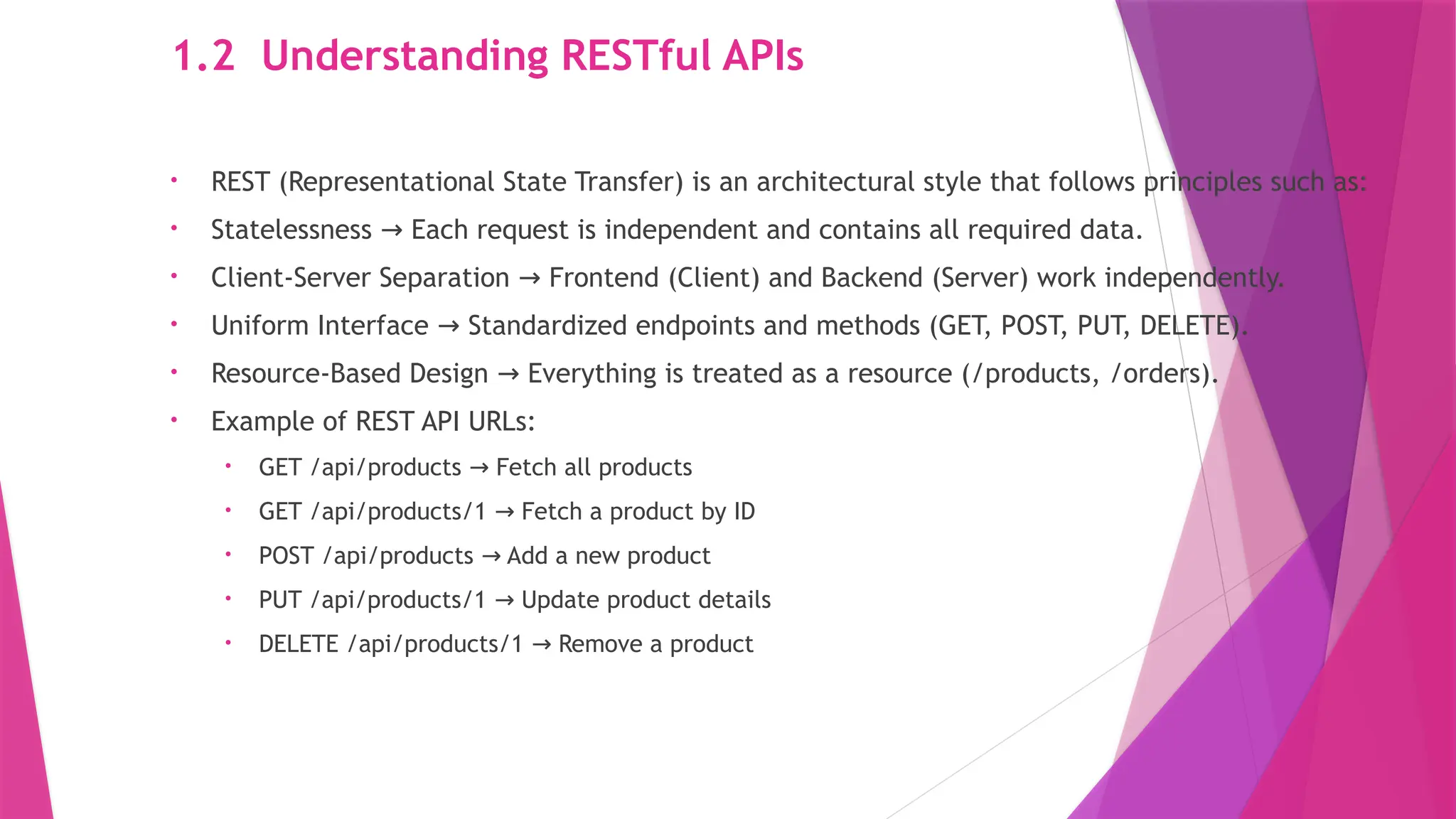
The slides in this presentation cover RESTful APIs, the fundamentals of ASP.NET Core Web API, and how to set up a web API project. First-time readers are encouraged to read this, but a basic understanding of the topic will enable you to fully engage with the presentation. The slides do cover the basic codes for just starting up but watching a tutorial or reading an elaborative article will help in grasping the content much better.


![1.7 Creating a Simple API Controller
namespace EmployeeAdminPortal.Controllers
{
// route url - localhost:xxxx/api/employees
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class EmployeesController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext dbContext;
public EmployeesController(ApplicationDbContext dbContext)
{
this.dbContext = dbContext;
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetAllEmployees()
{
var allEmployees = dbContext.Employees.ToList();
return Ok(allEmployees);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofintroductiontoasp-250408061831-d6ced944/75/Basics-Of-Introduction-to-ASP-NET-Core-pptx-8-2048.jpg)