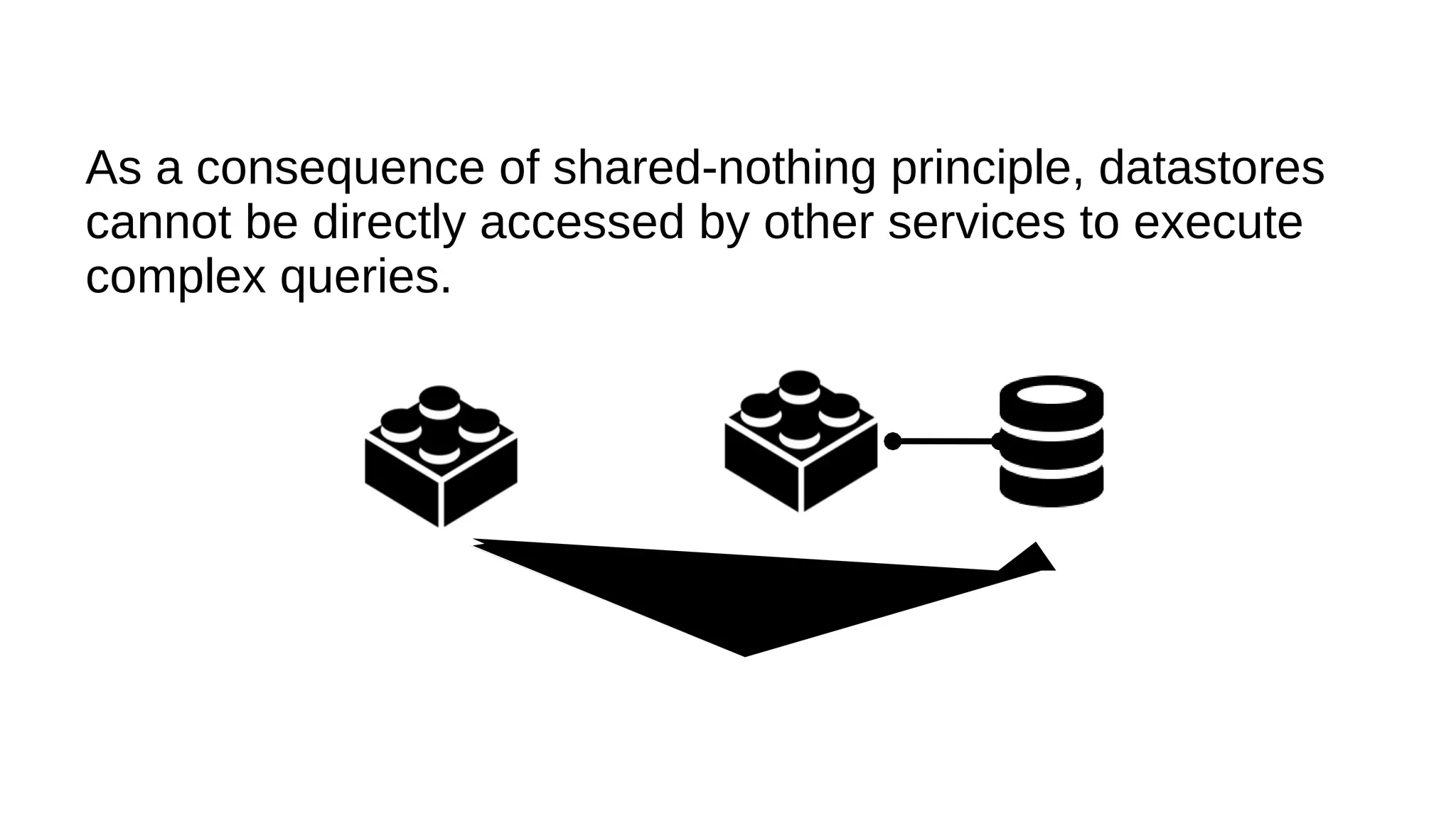
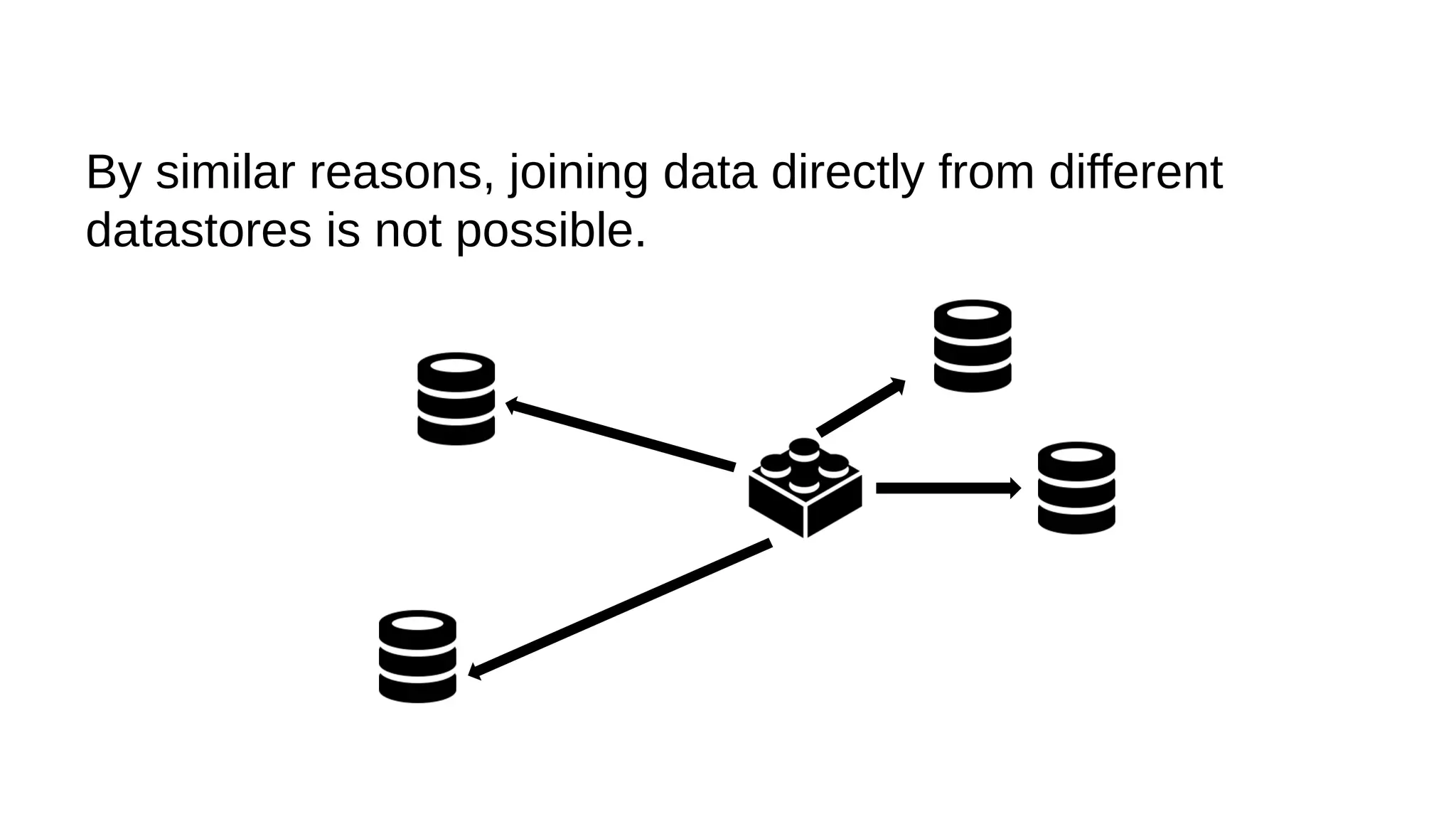
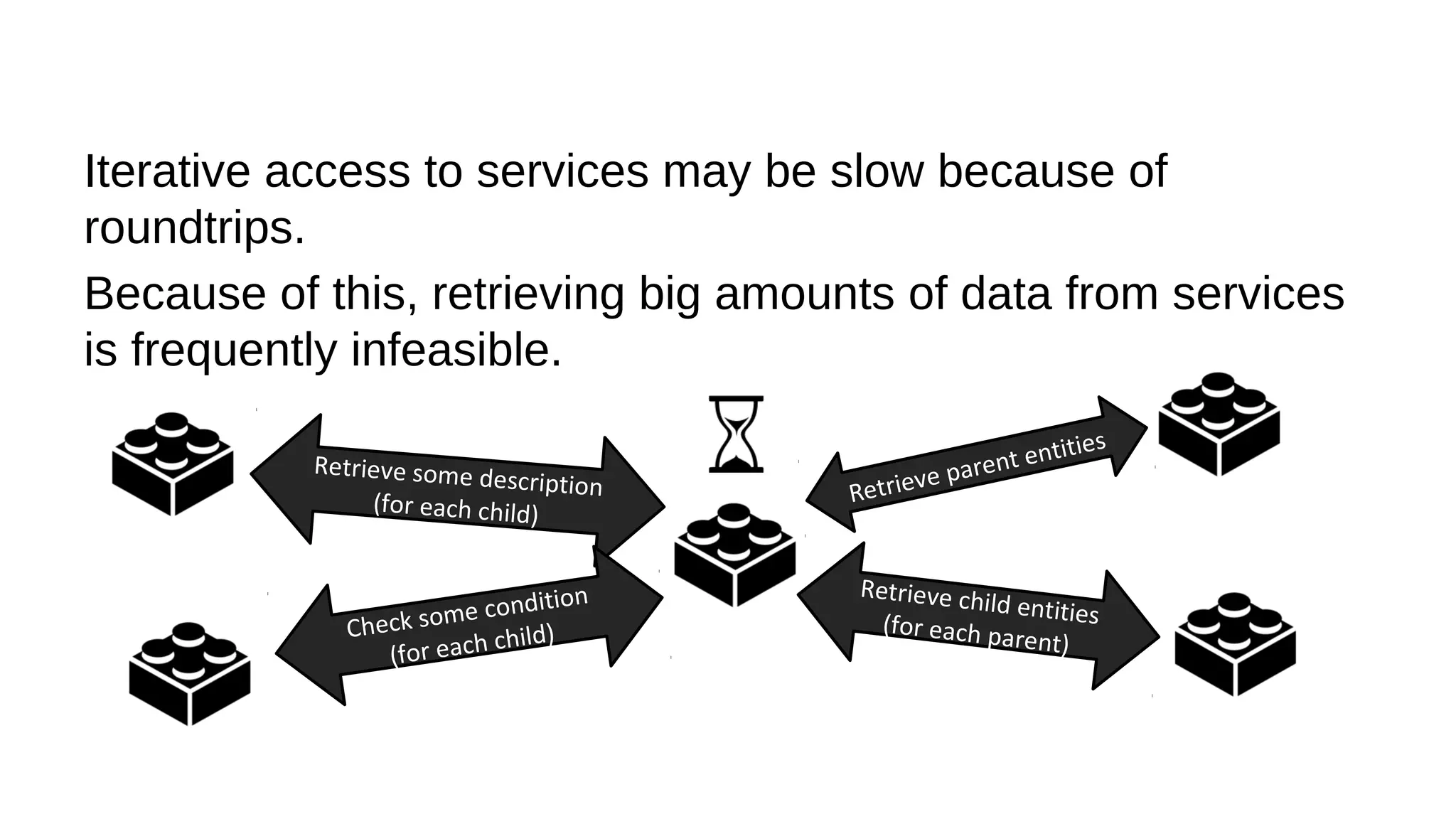
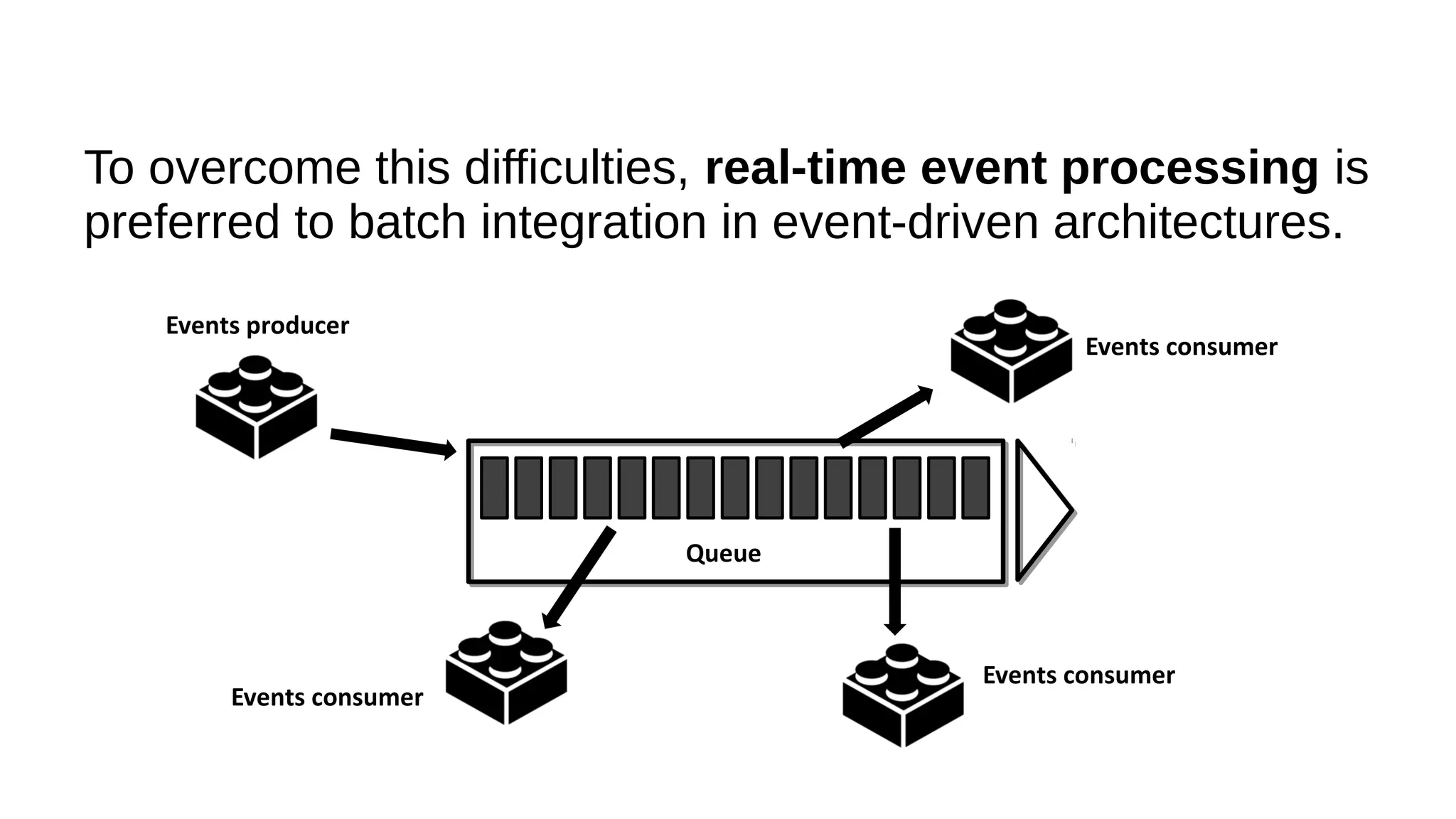
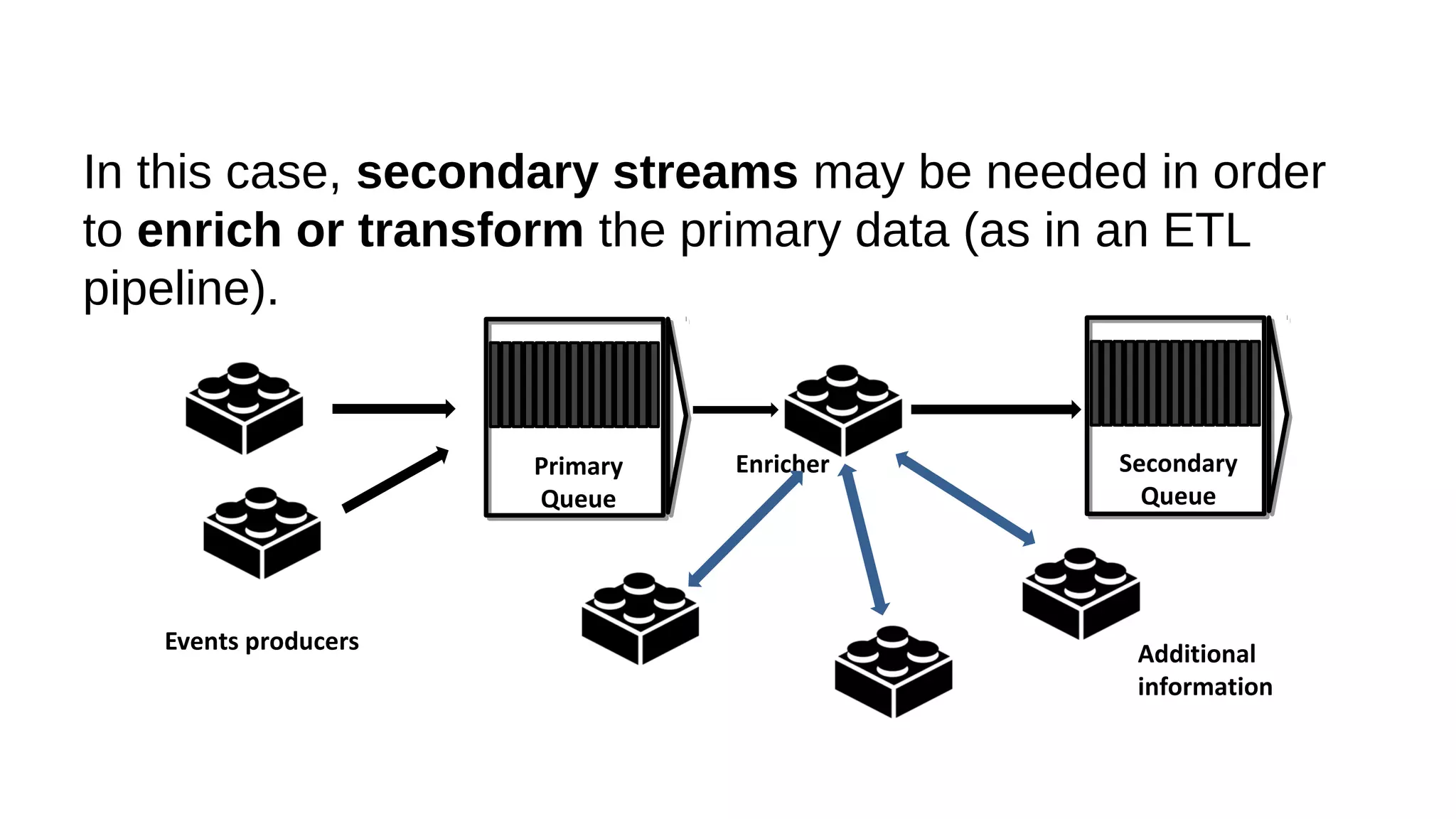
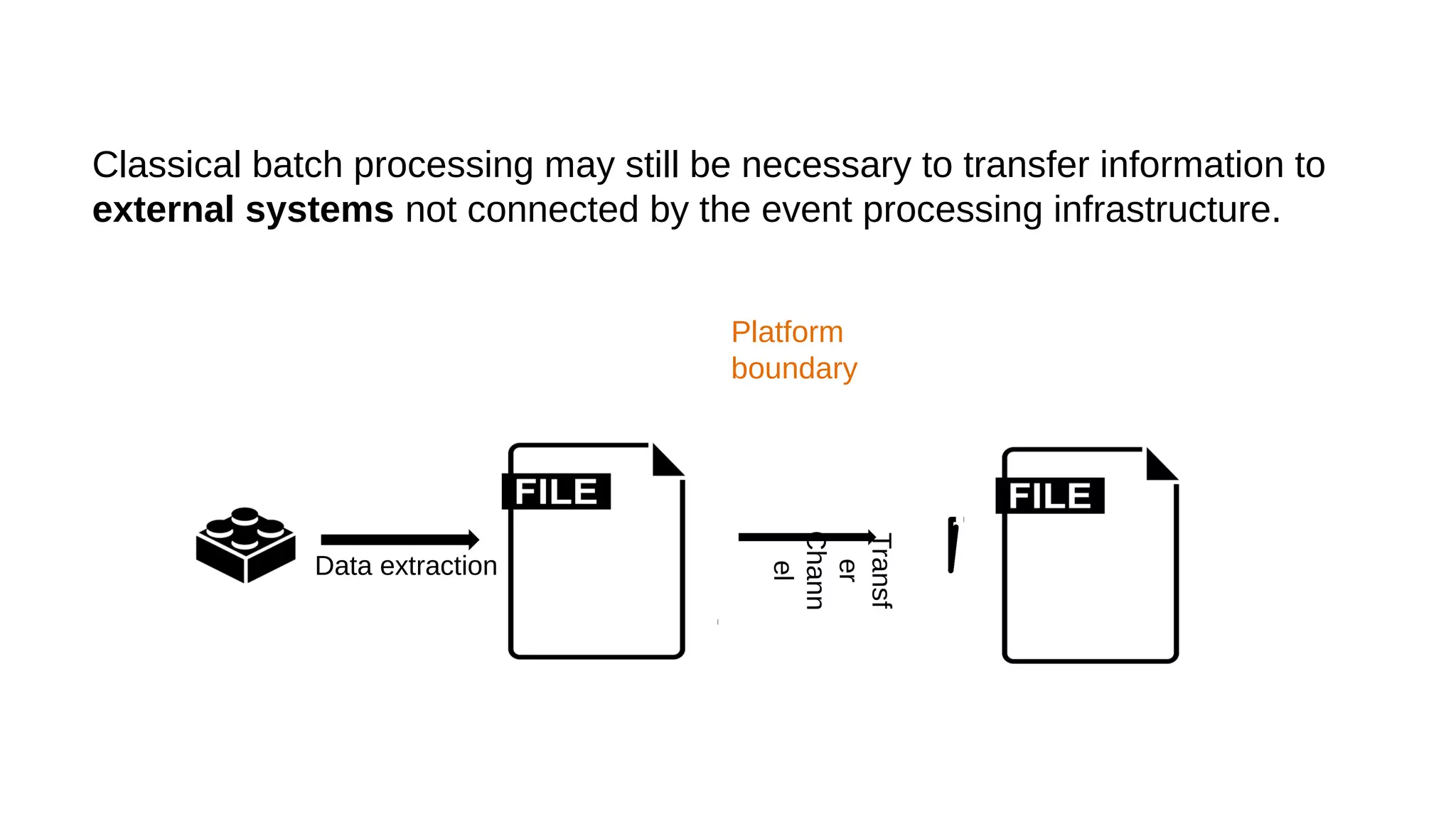
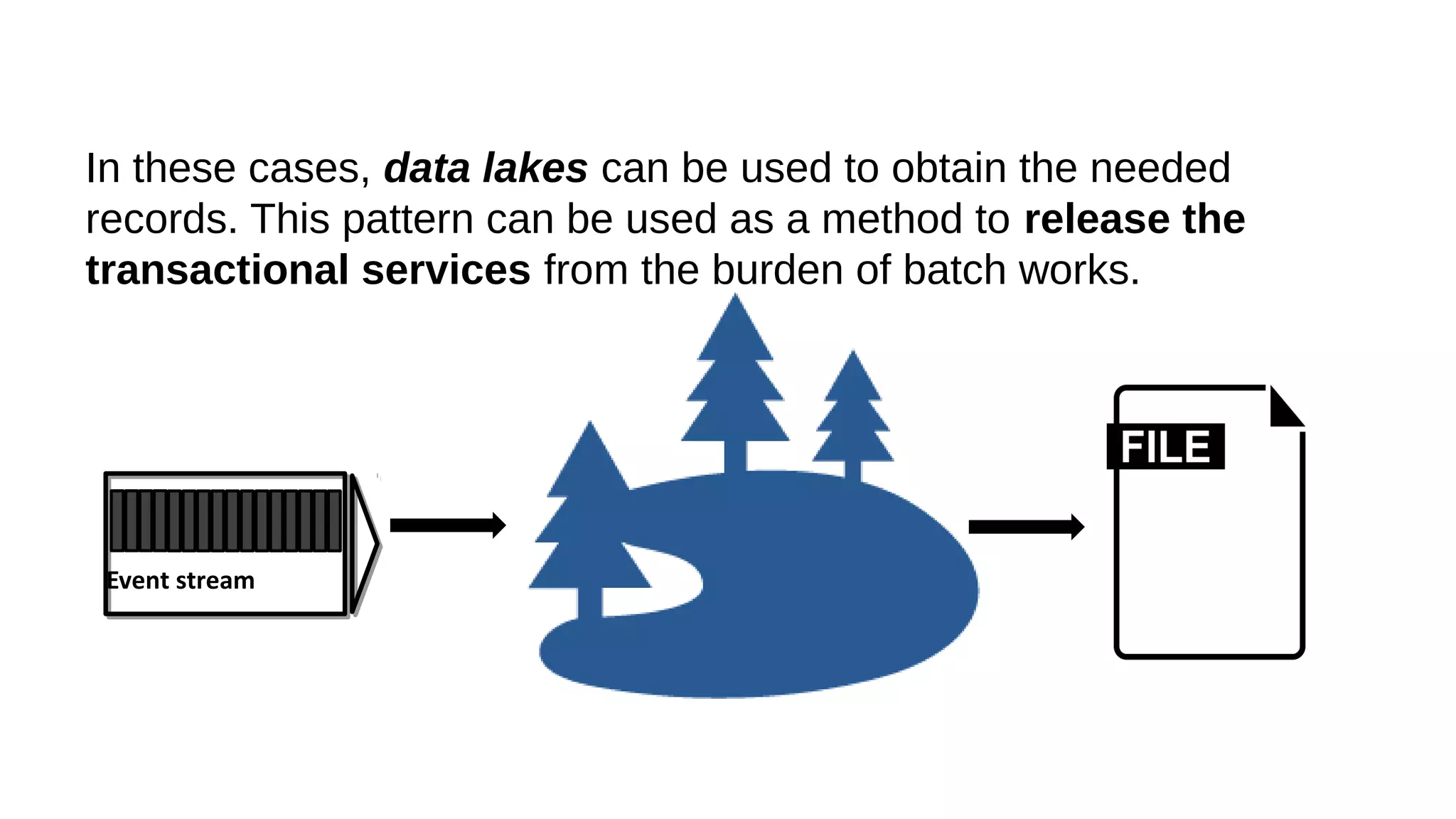
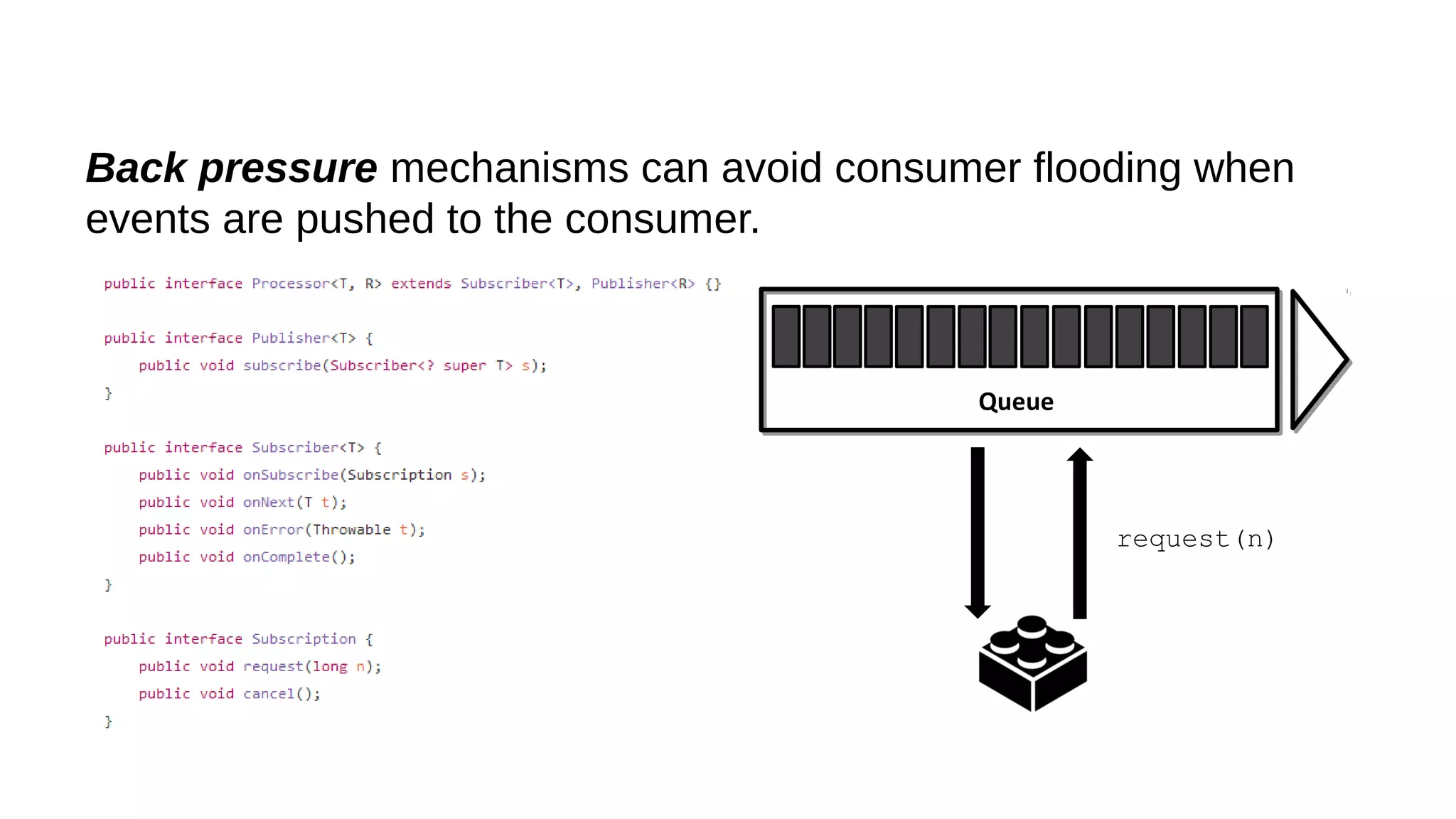
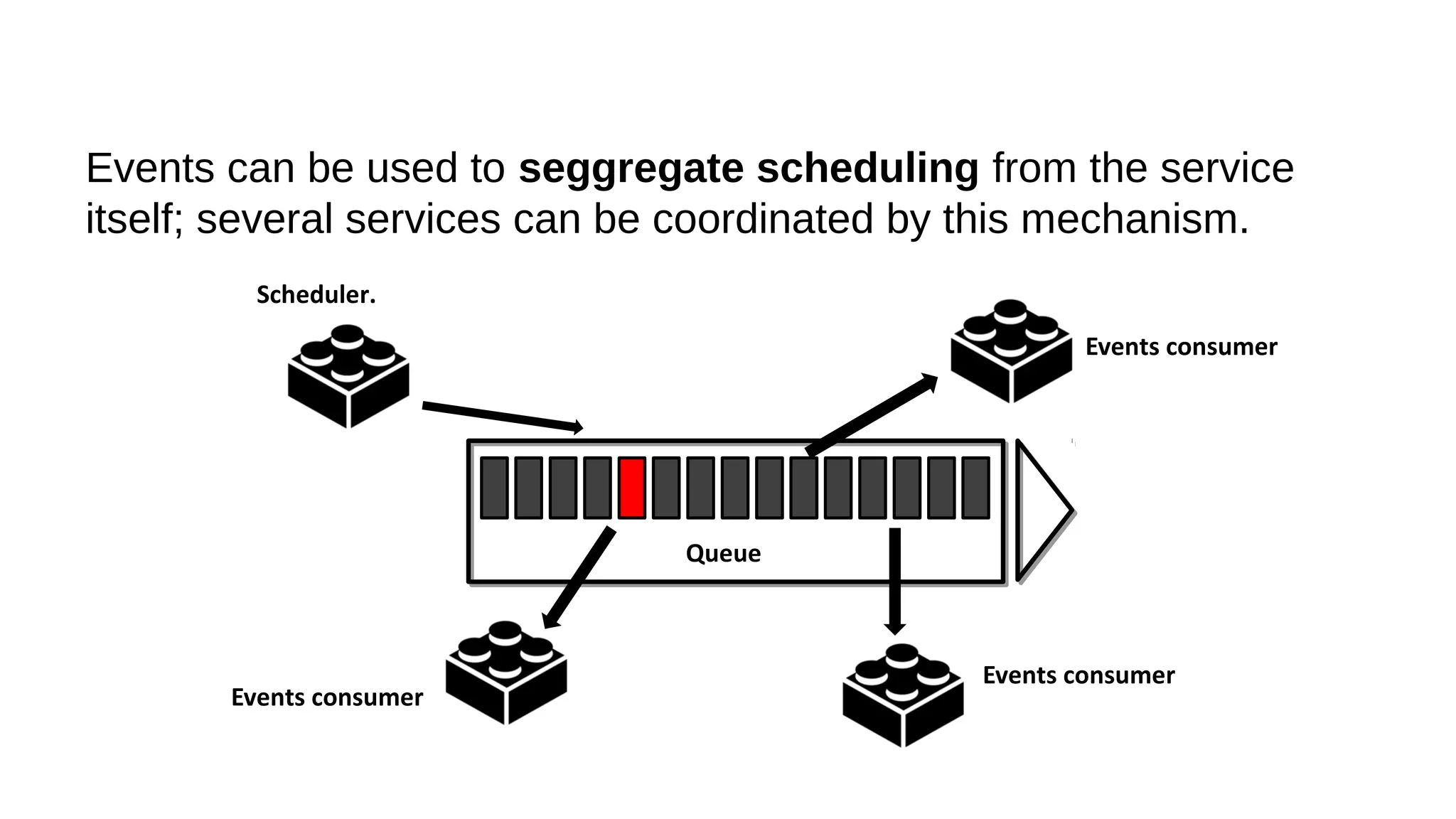
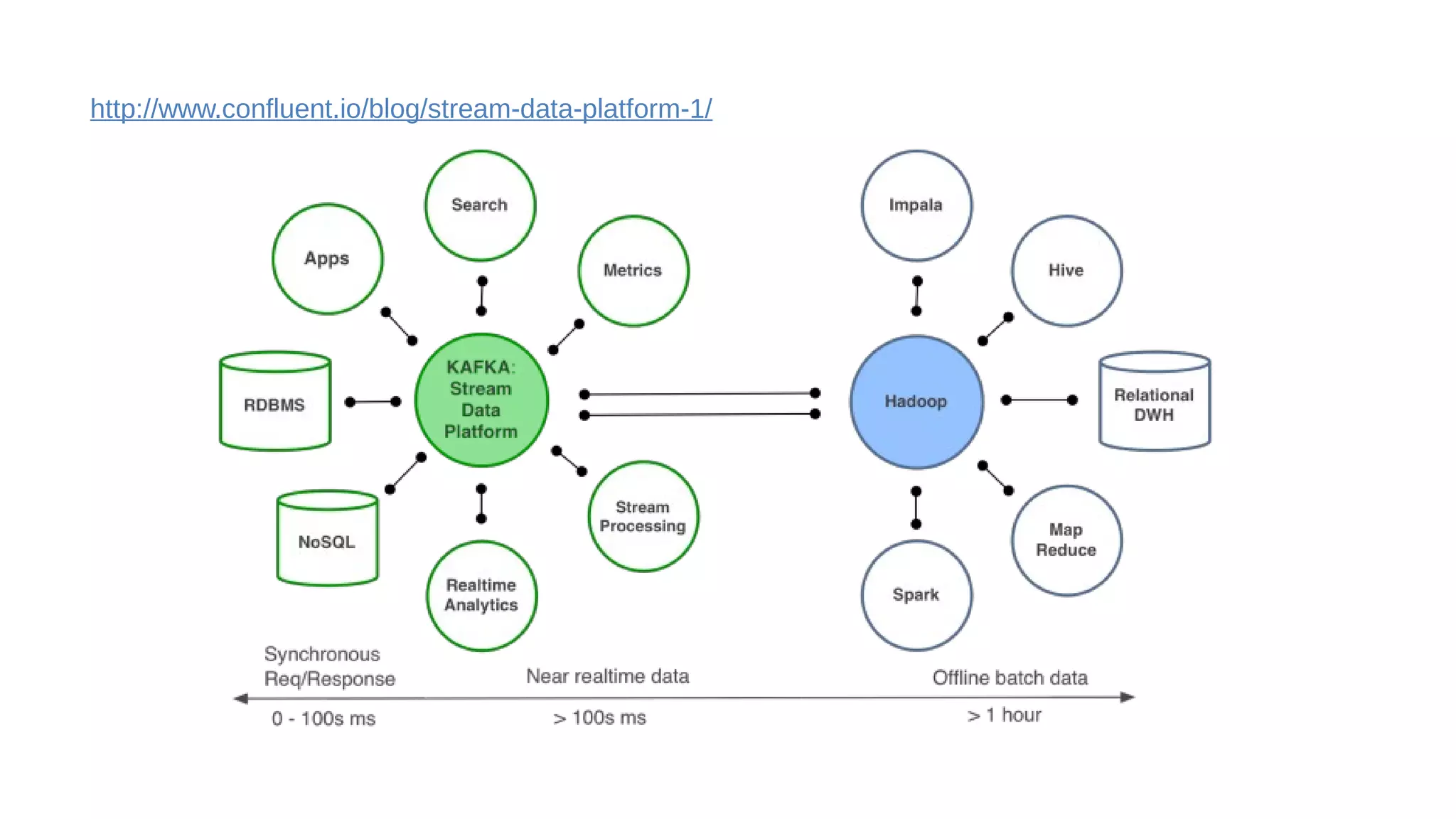
This document discusses the role of batch processing in event-driven architectures. It notes that while classical SOAs are better suited for online processing, batch processing is often used for technical reasons unrelated to business logic, which can force duplicate implementations. The document then explores how event-driven architectures use events and queues to distribute work asynchronously between services, providing advantages over traditional batch-oriented integration like avoiding roundtrips and allowing incremental updates. It also discusses safety mechanisms like back pressure and storing events in queues to prevent consumer flooding.