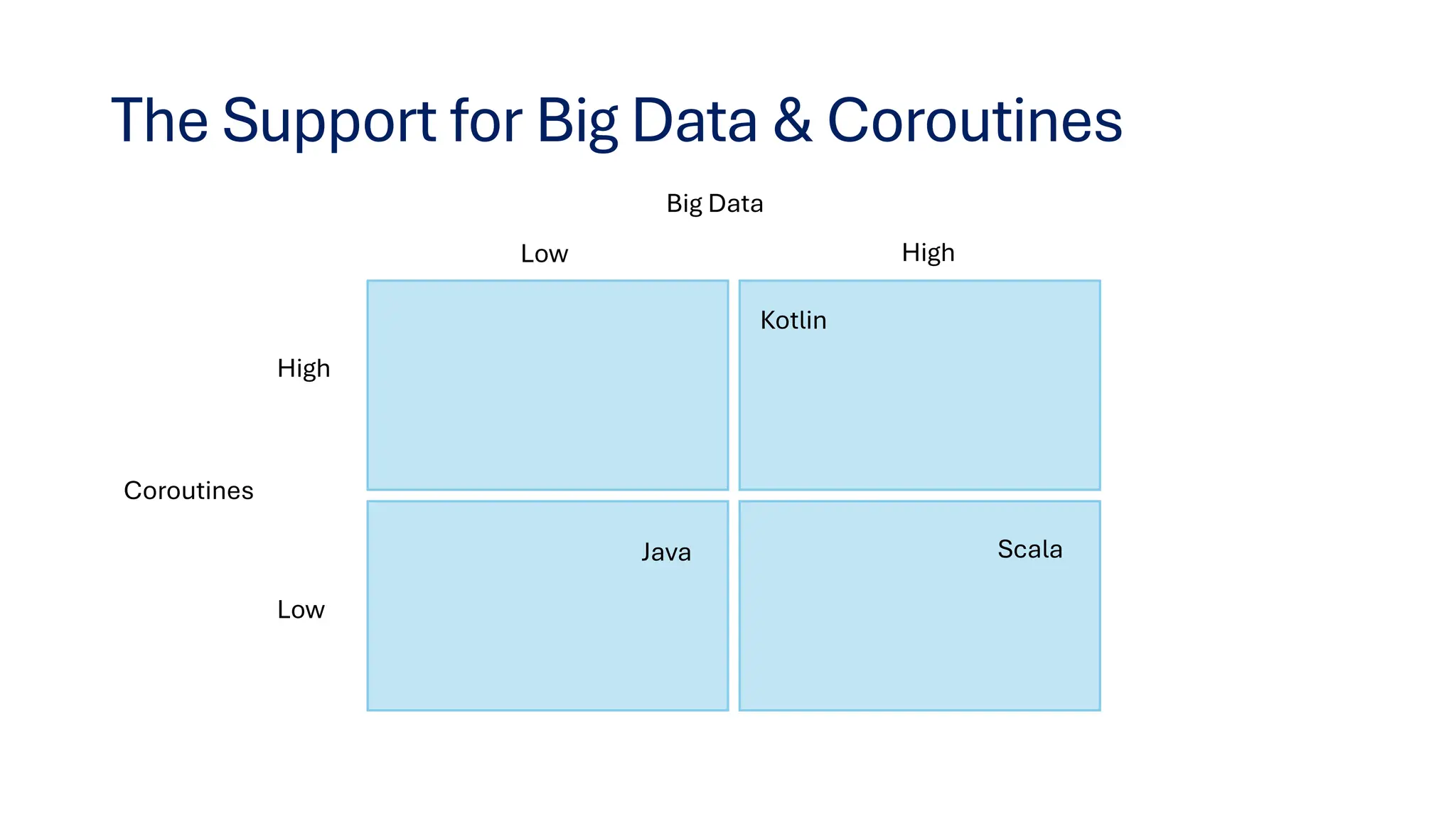
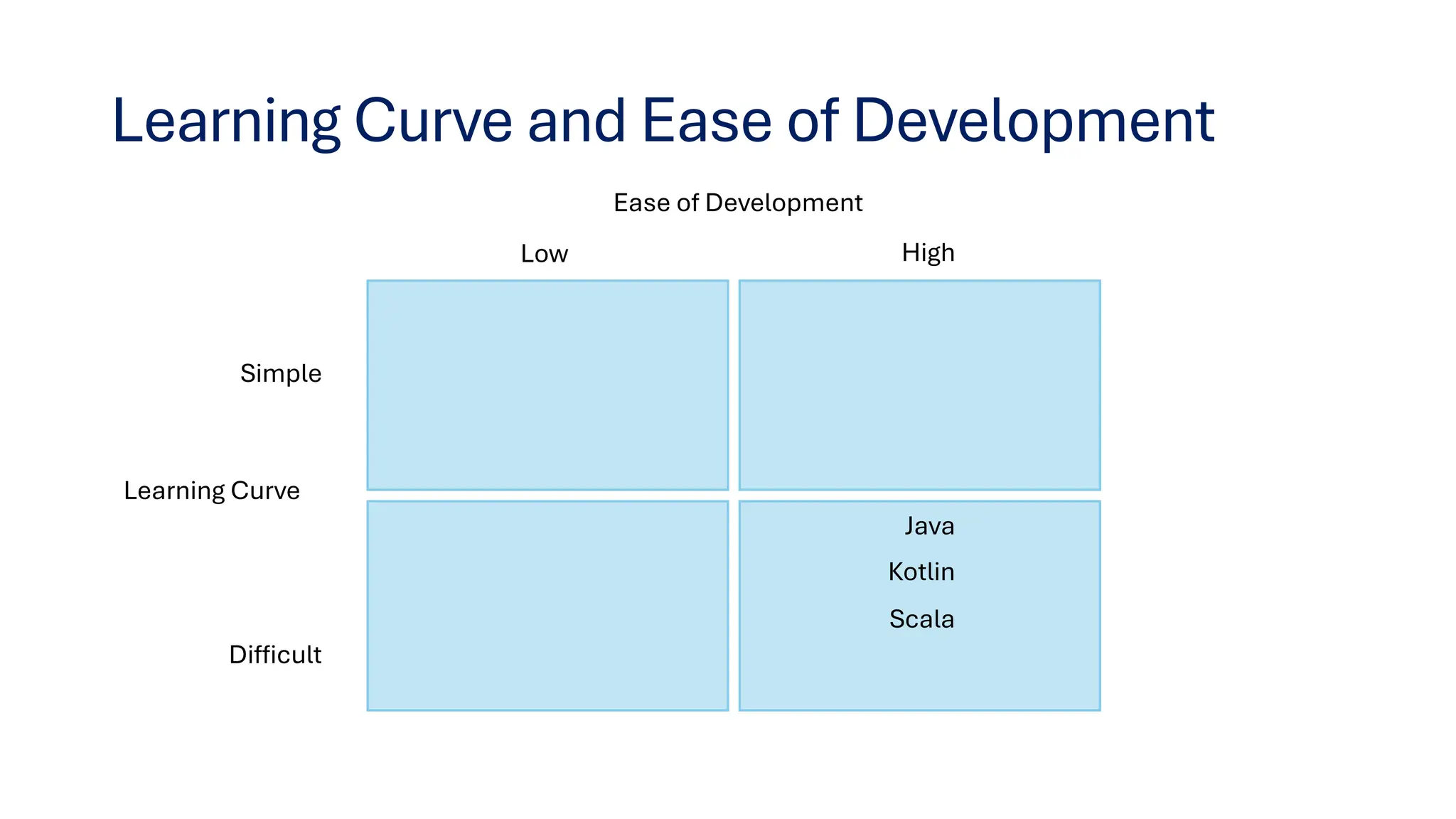
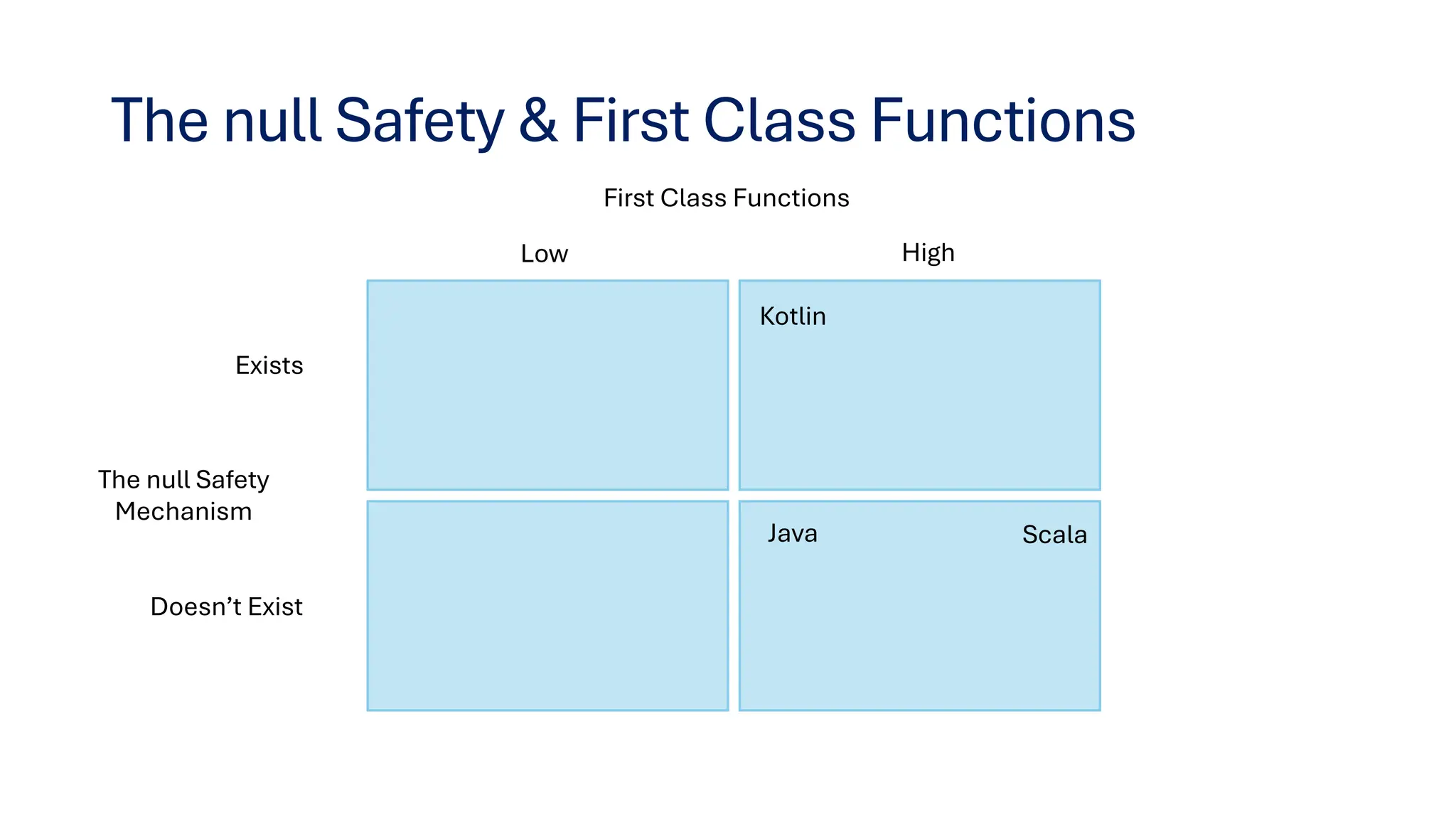
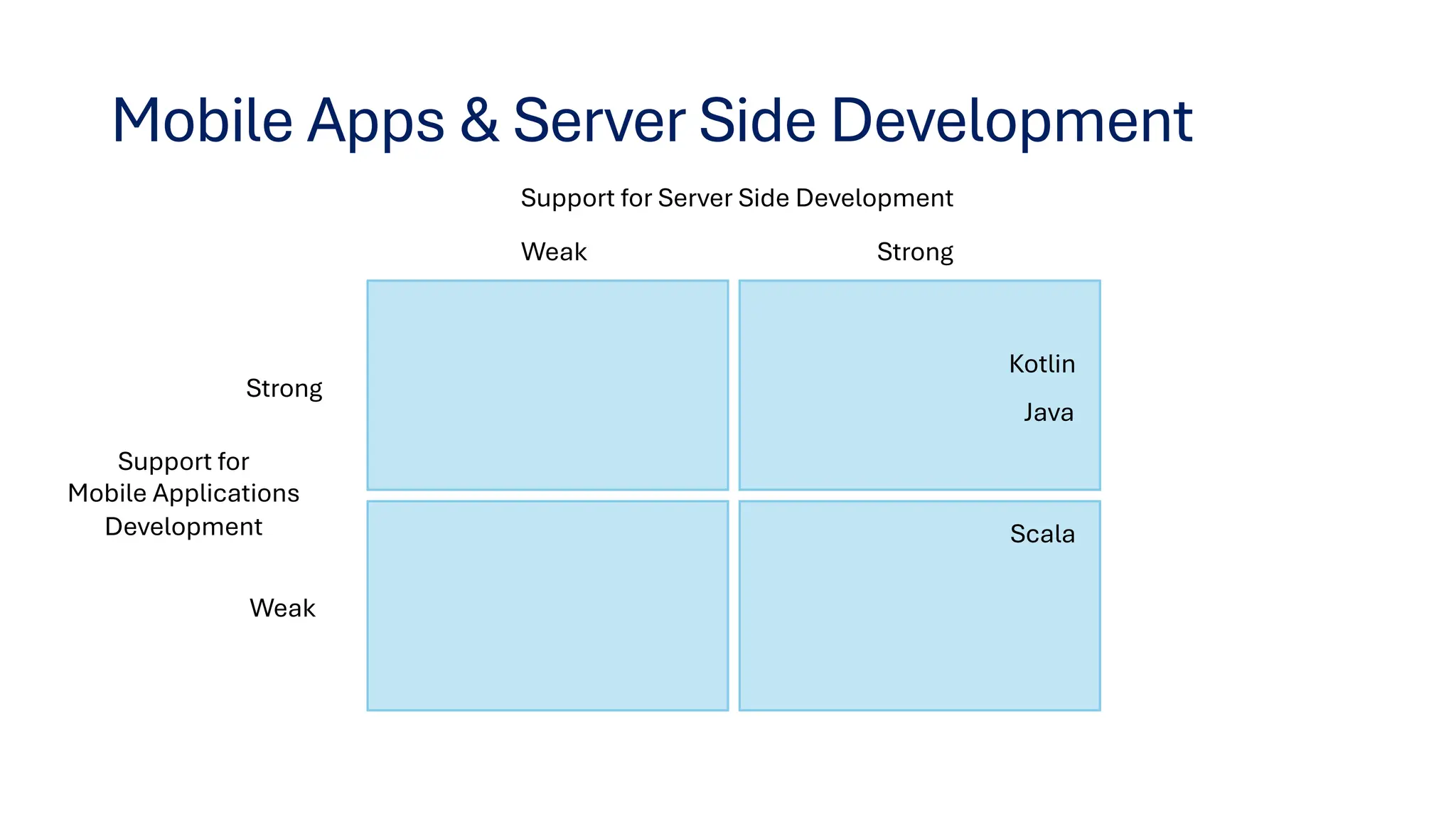
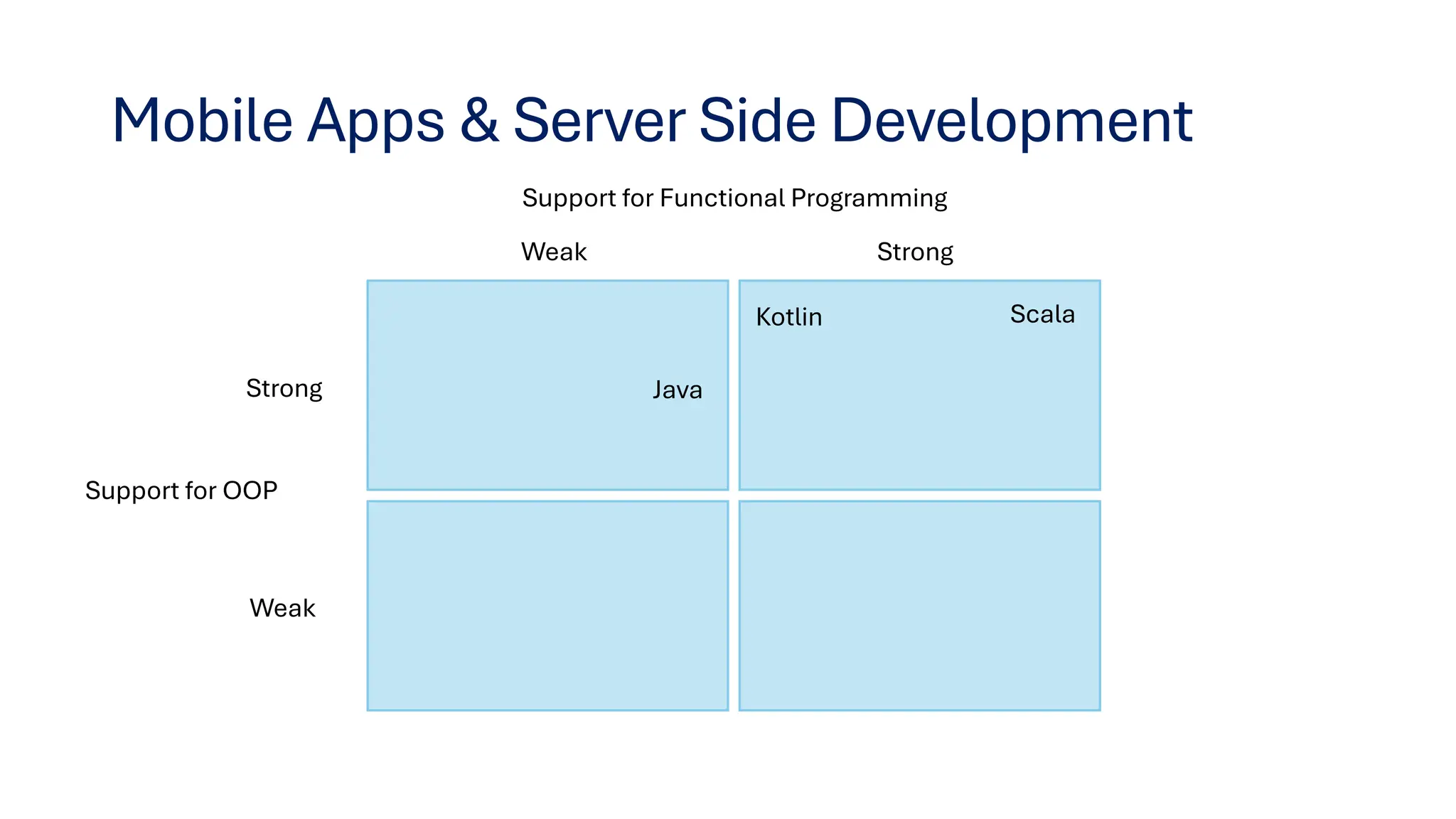
This document provides insights on transitioning from Java to modern JVM languages, specifically Scala and Kotlin, which offer more expressive and functional programming capabilities. Both languages are statically typed and allow smooth integration with Java systems, with Scala being favored for big data support, while Kotlin is easier for Java developers to adopt. The summary highlights similarities, IDE recommendations, and concludes that transitioning between the two languages is straightforward.