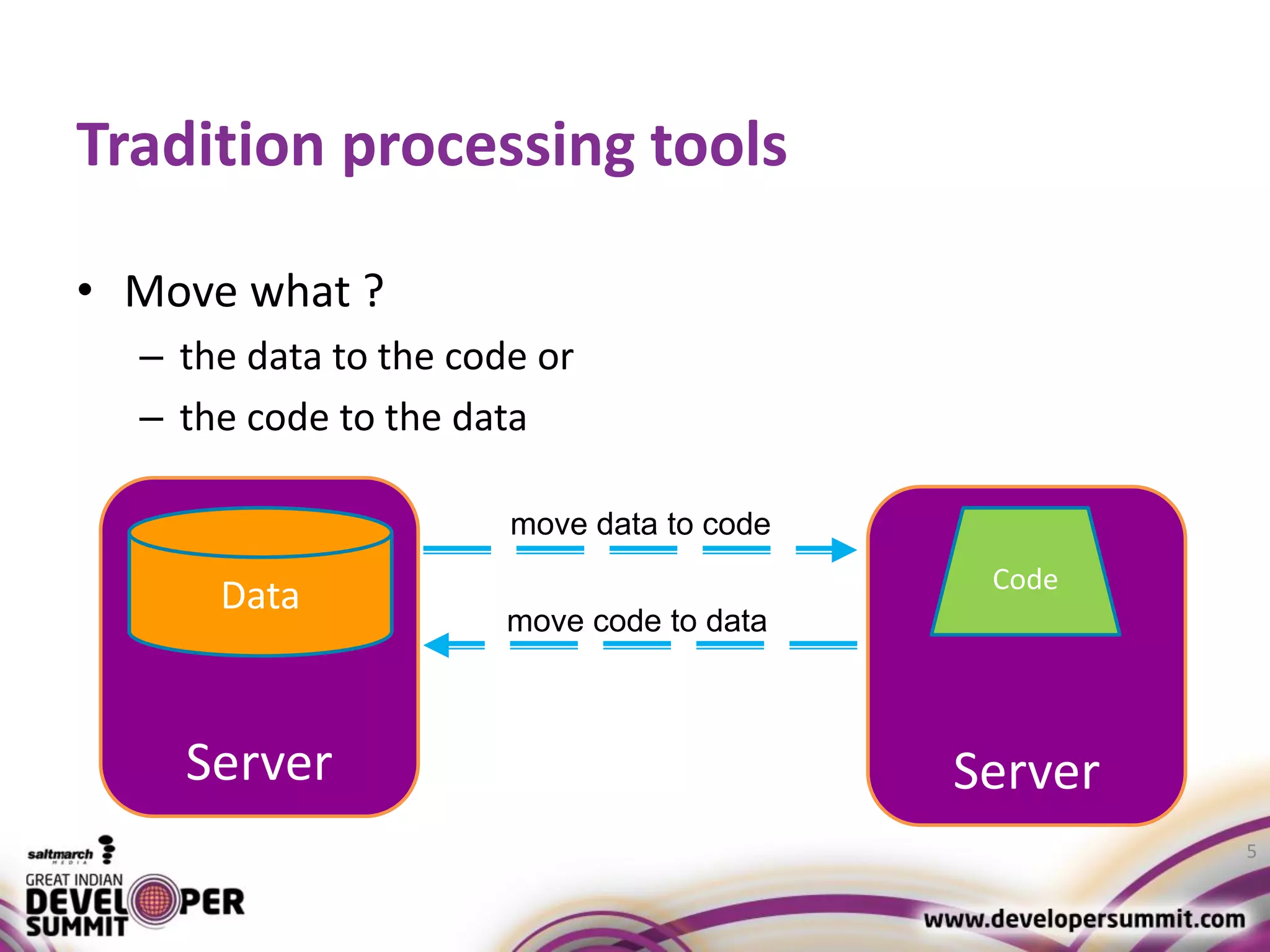
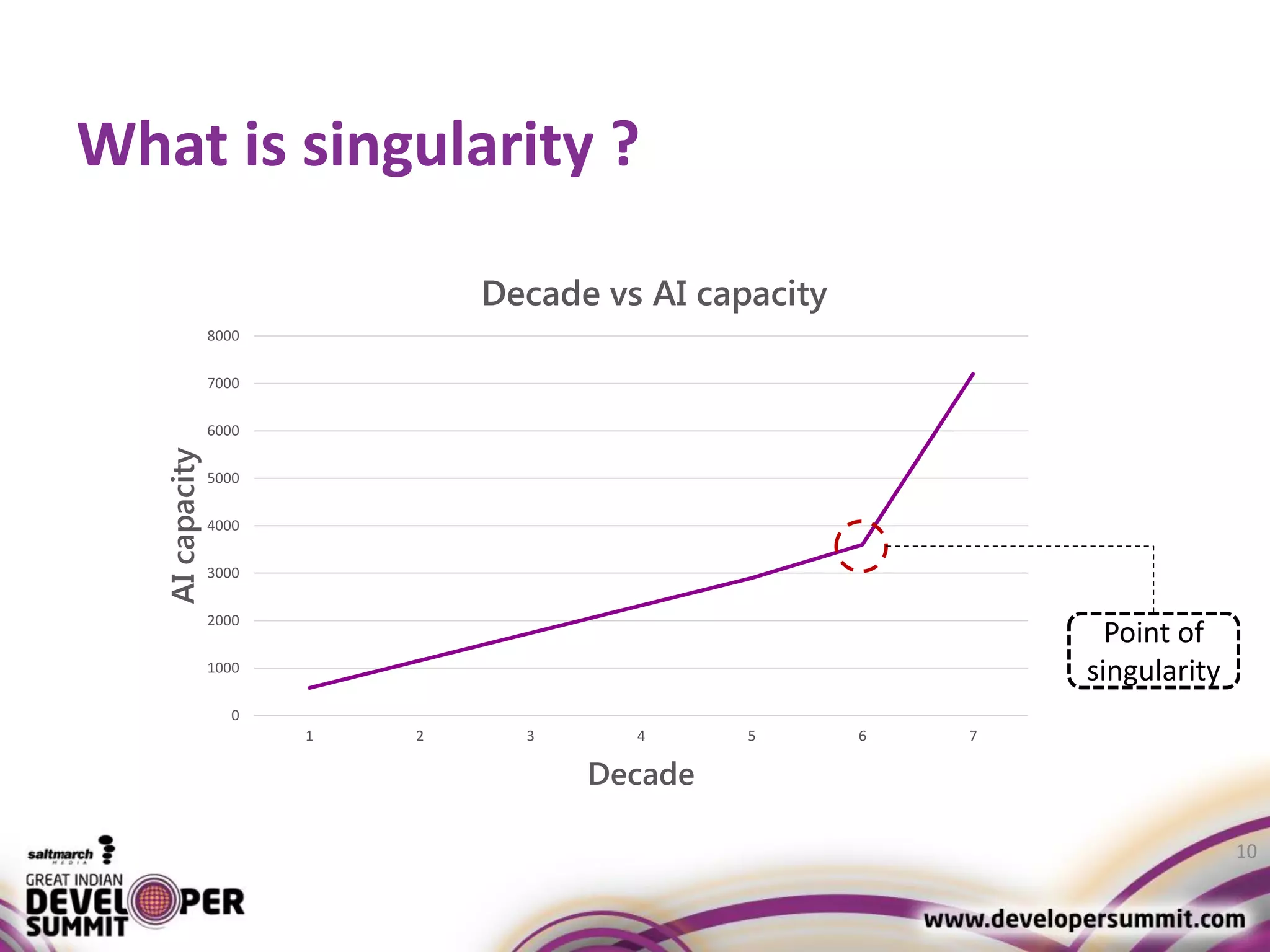
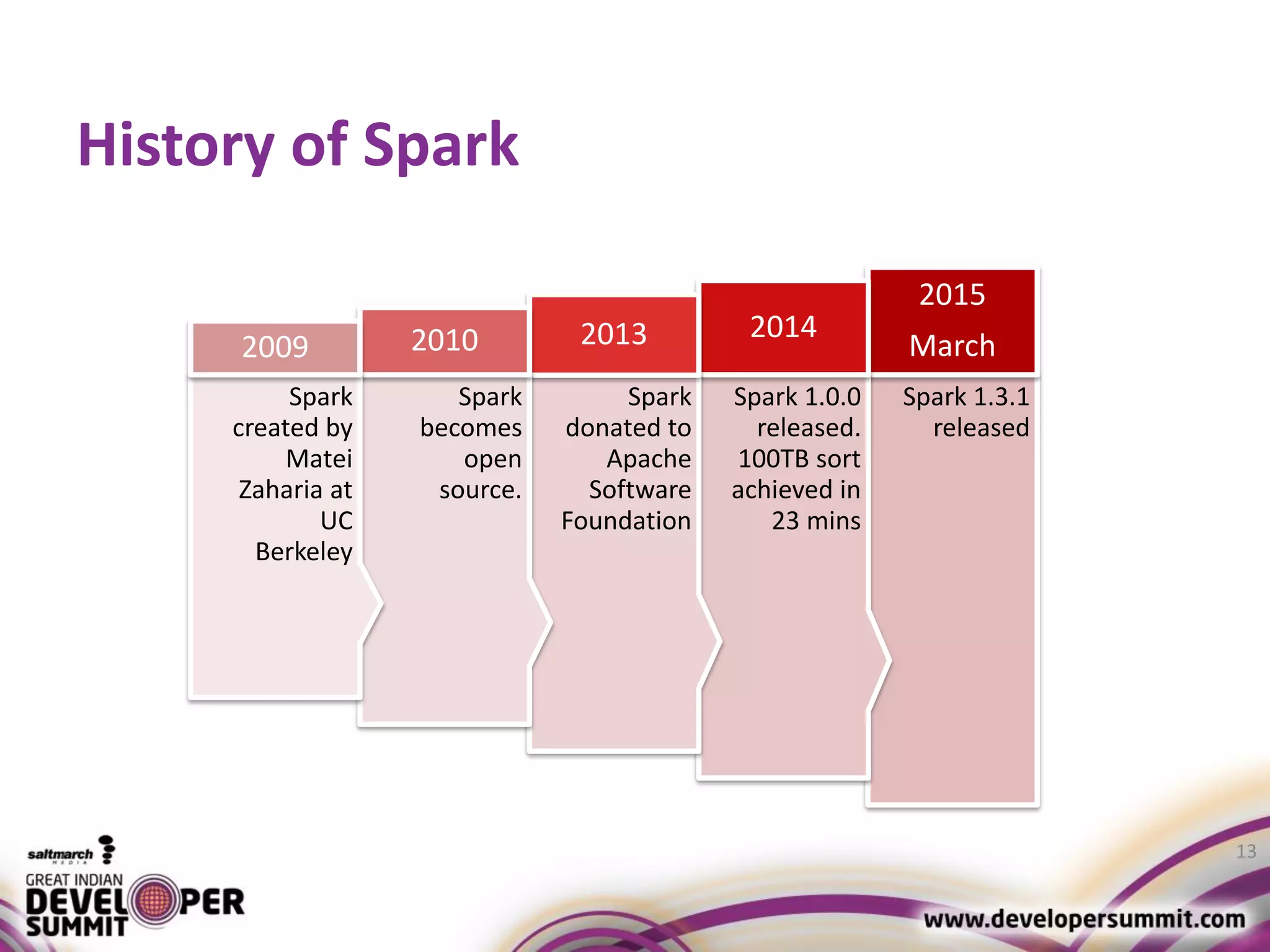
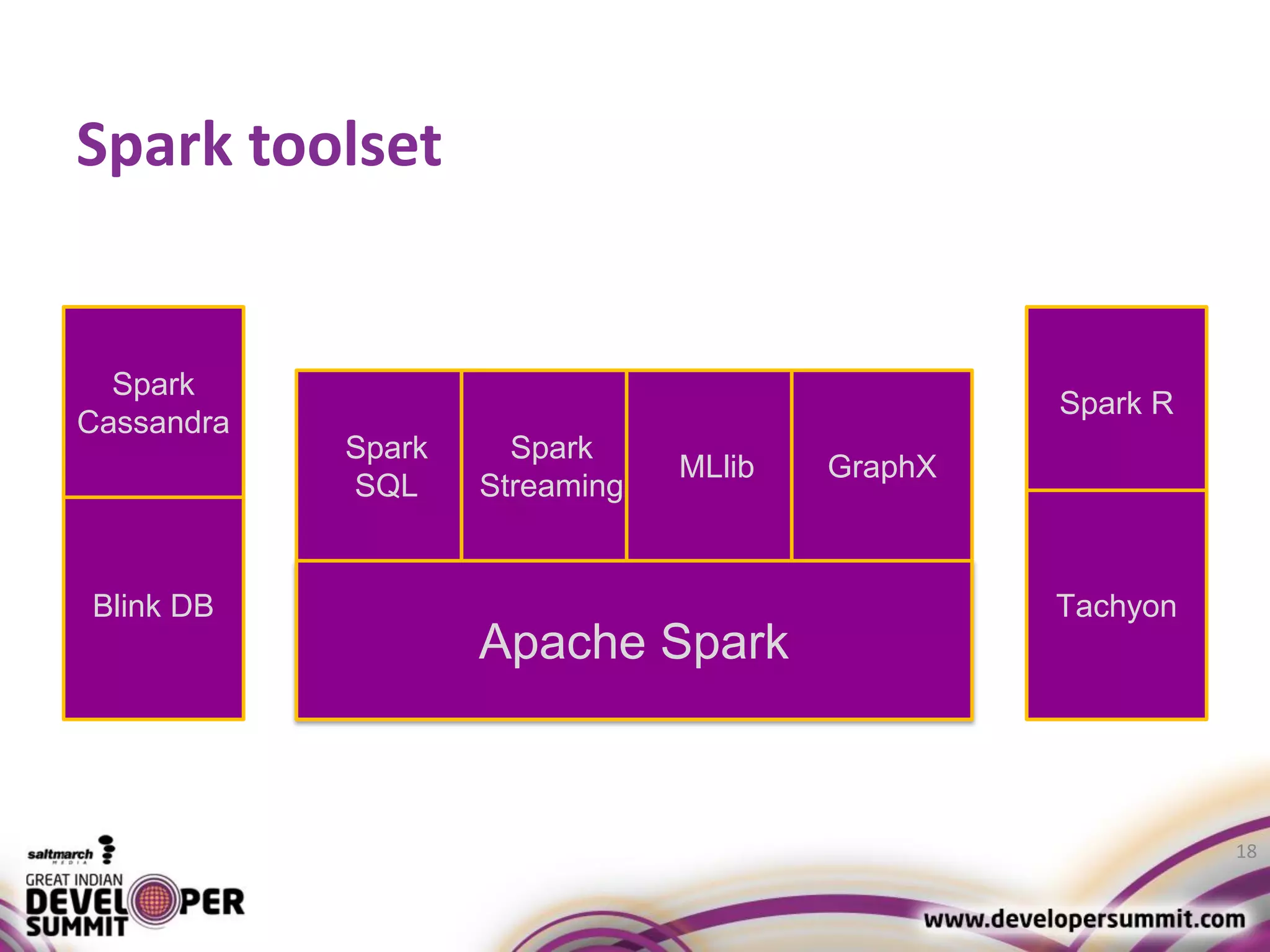
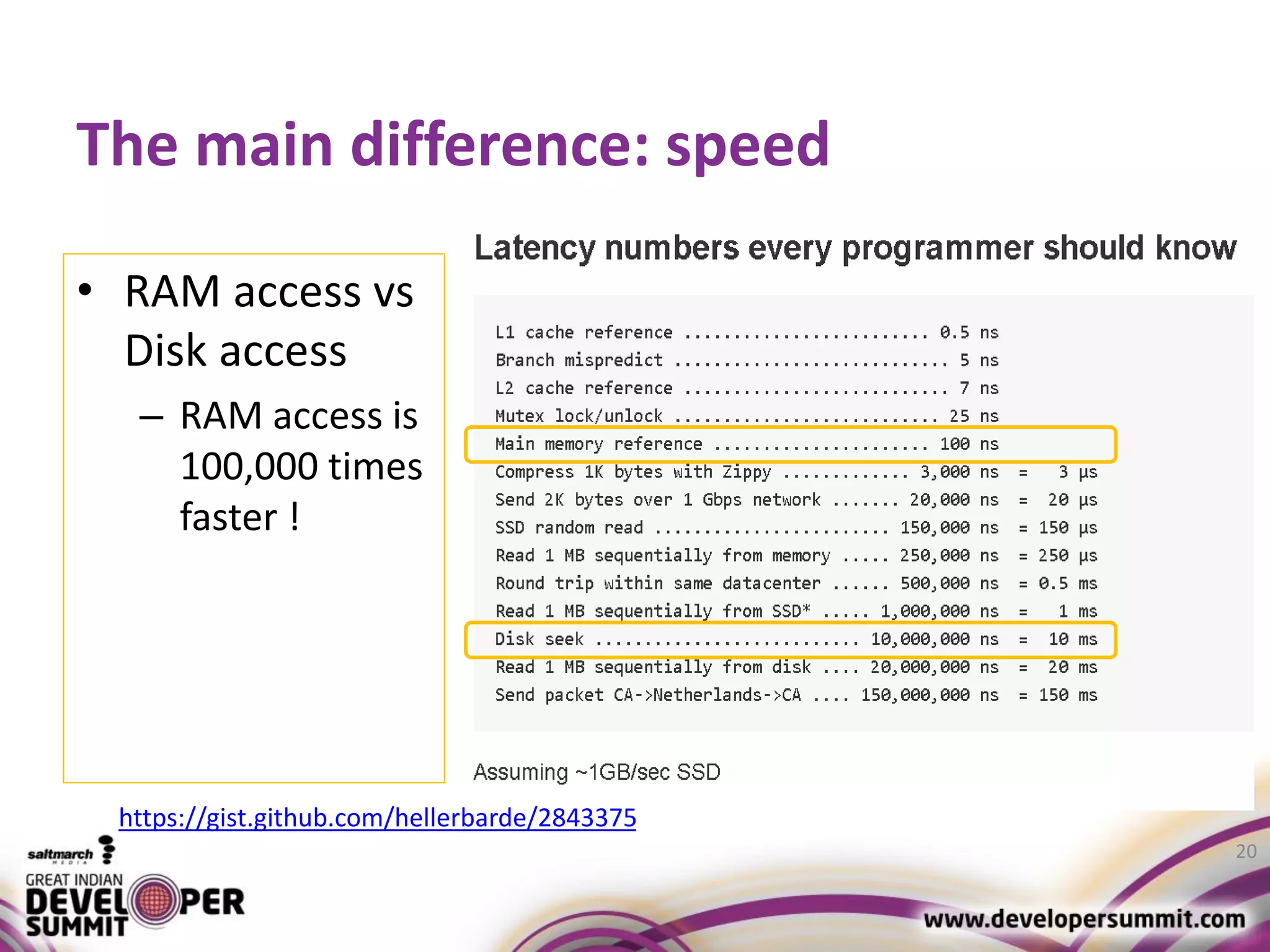
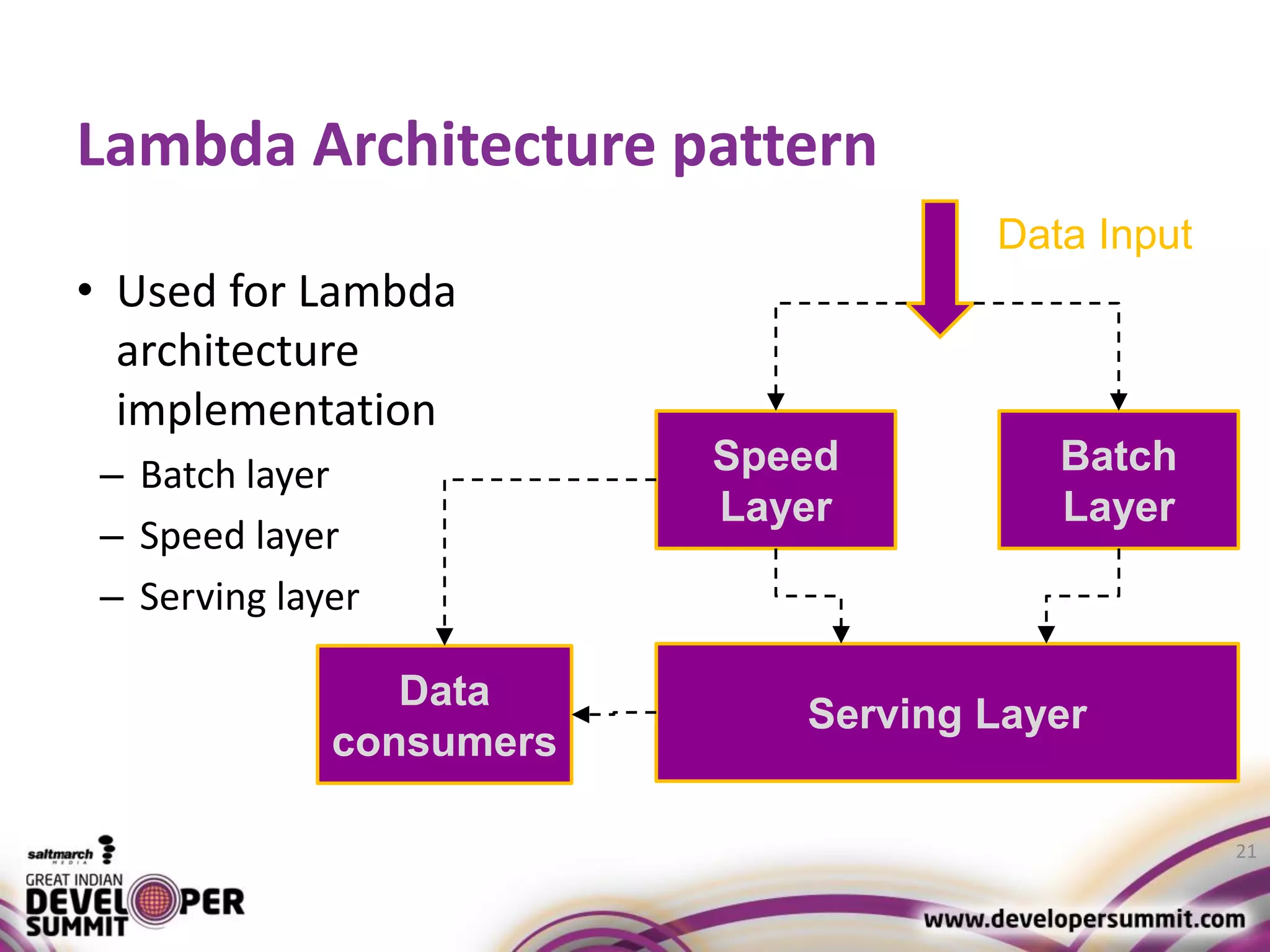
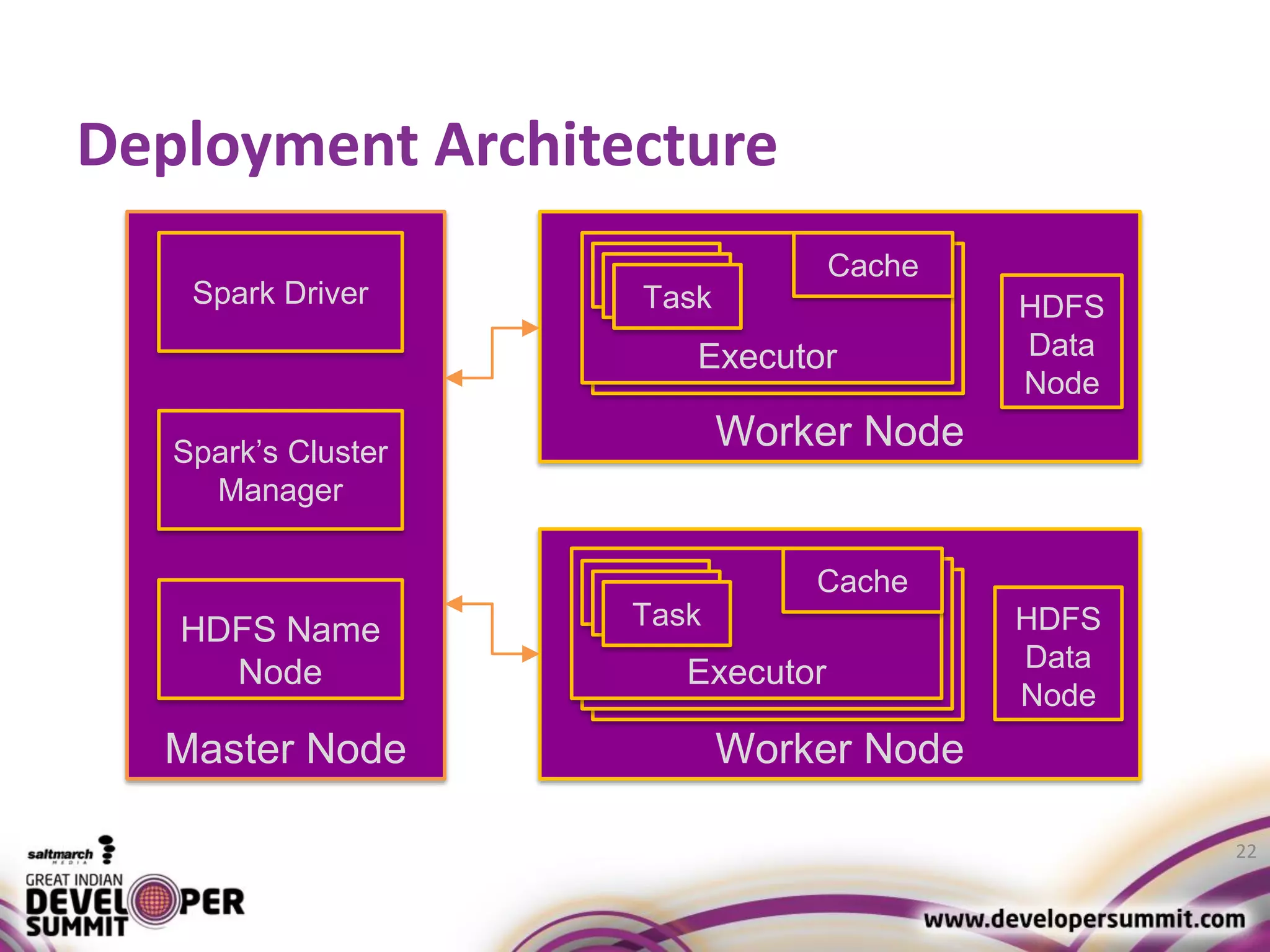
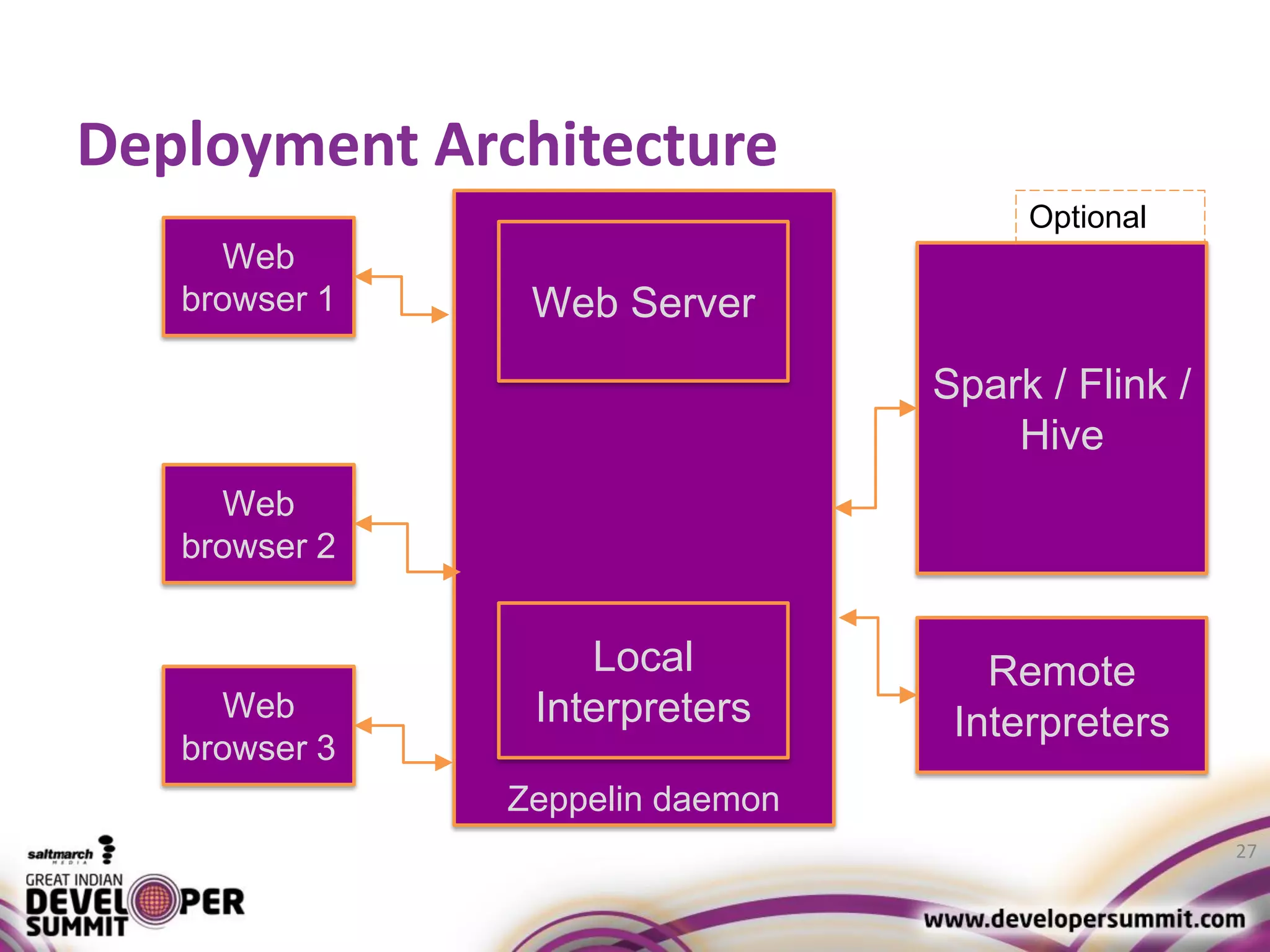
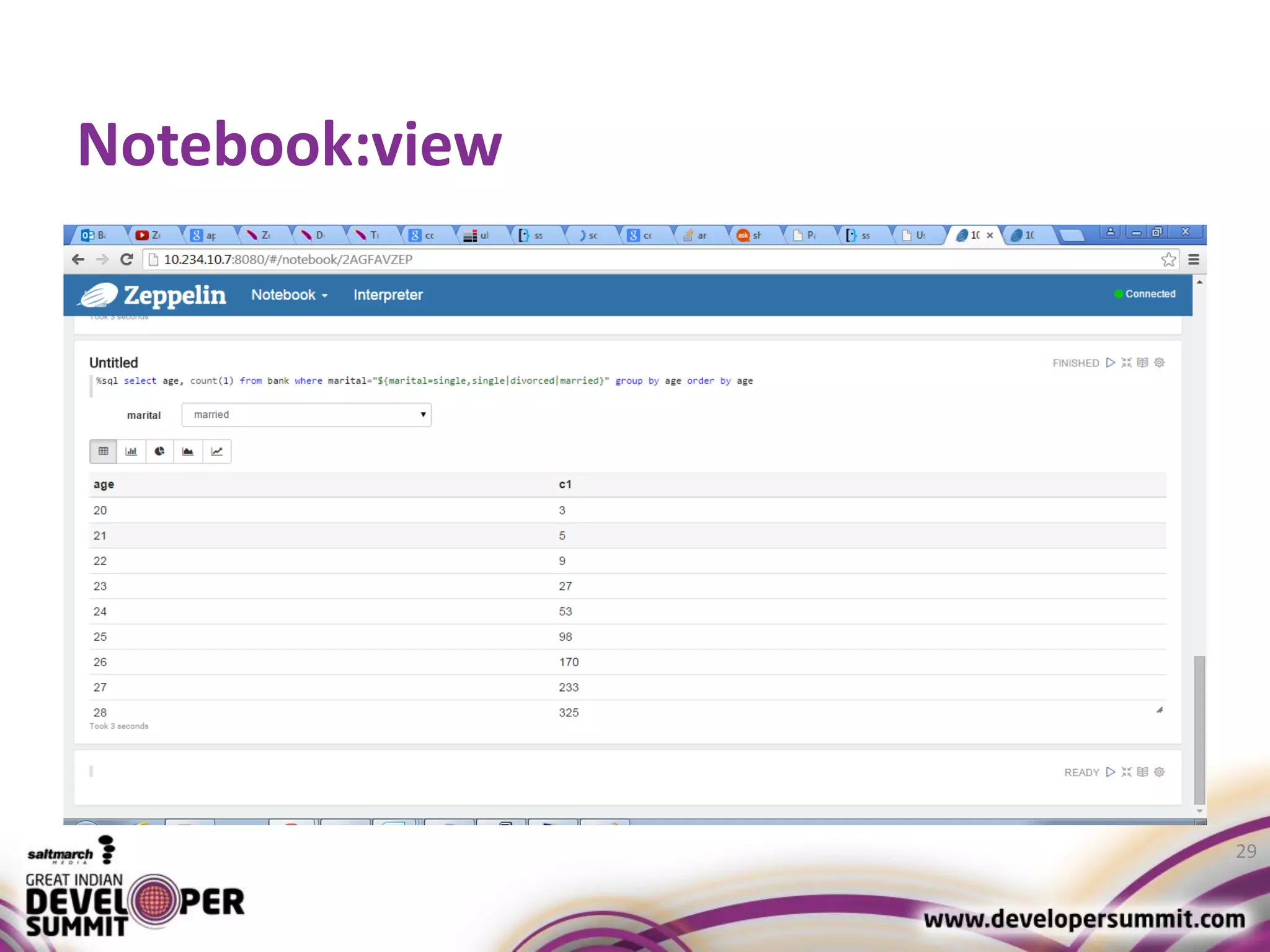
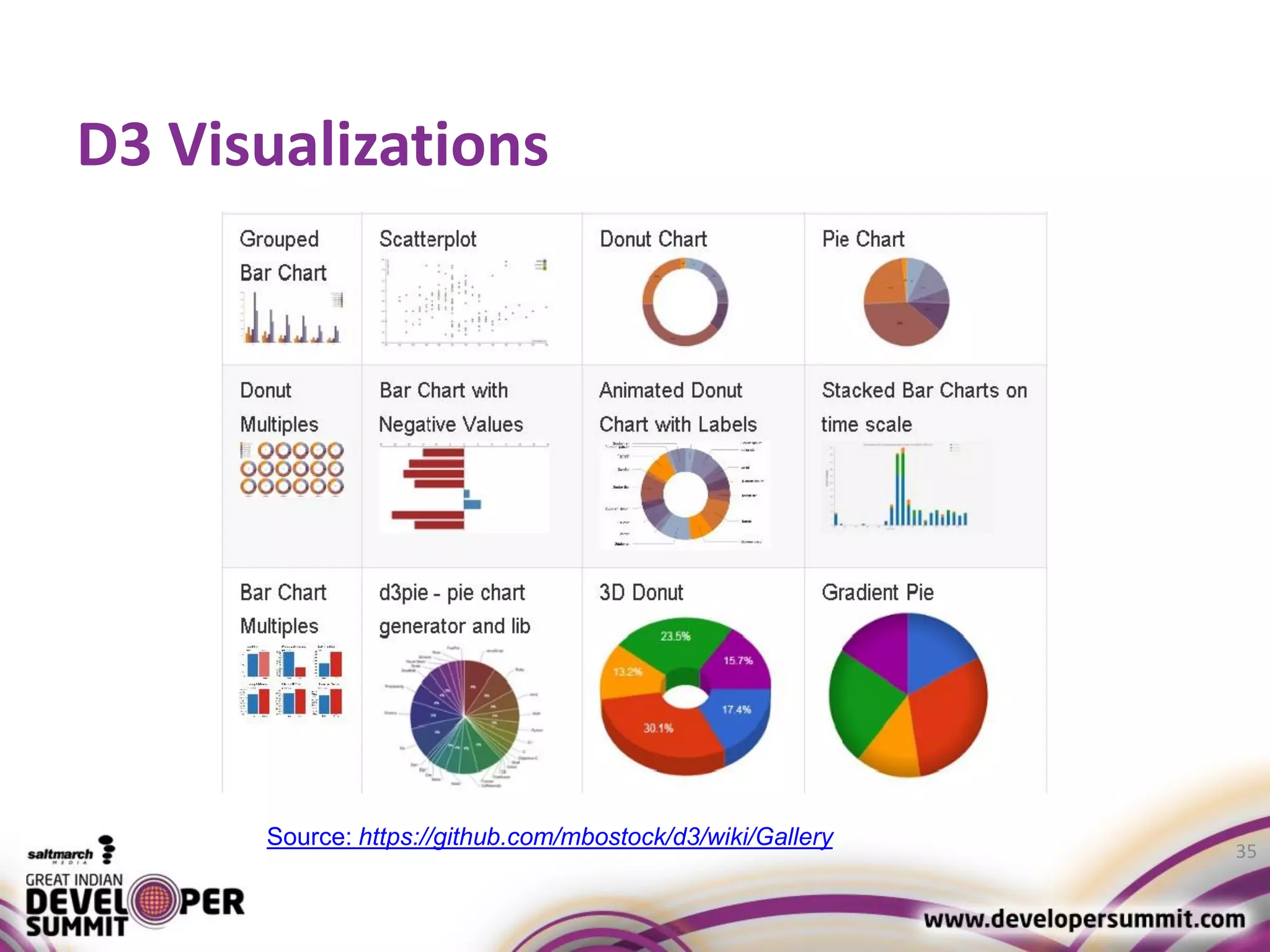
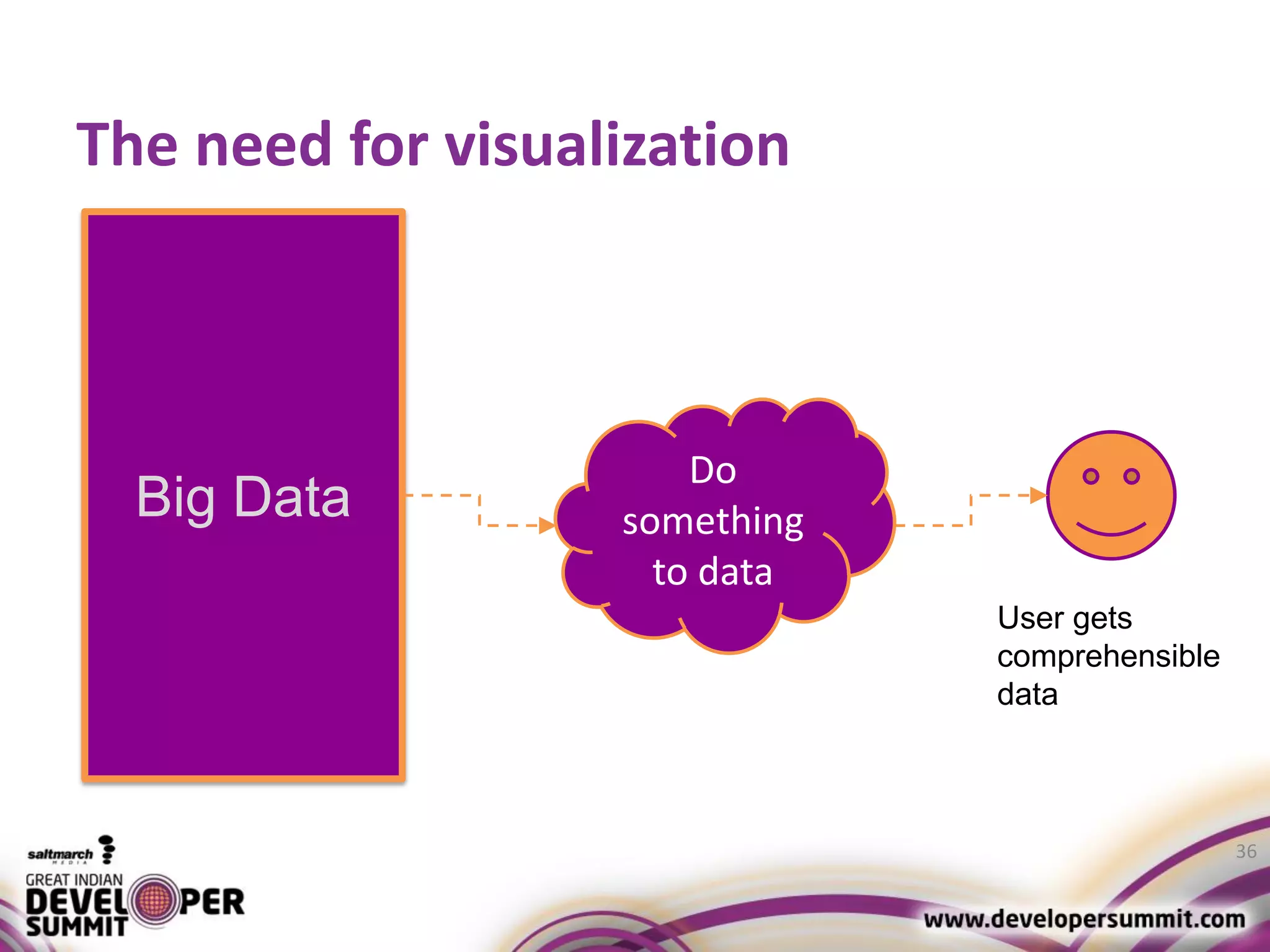
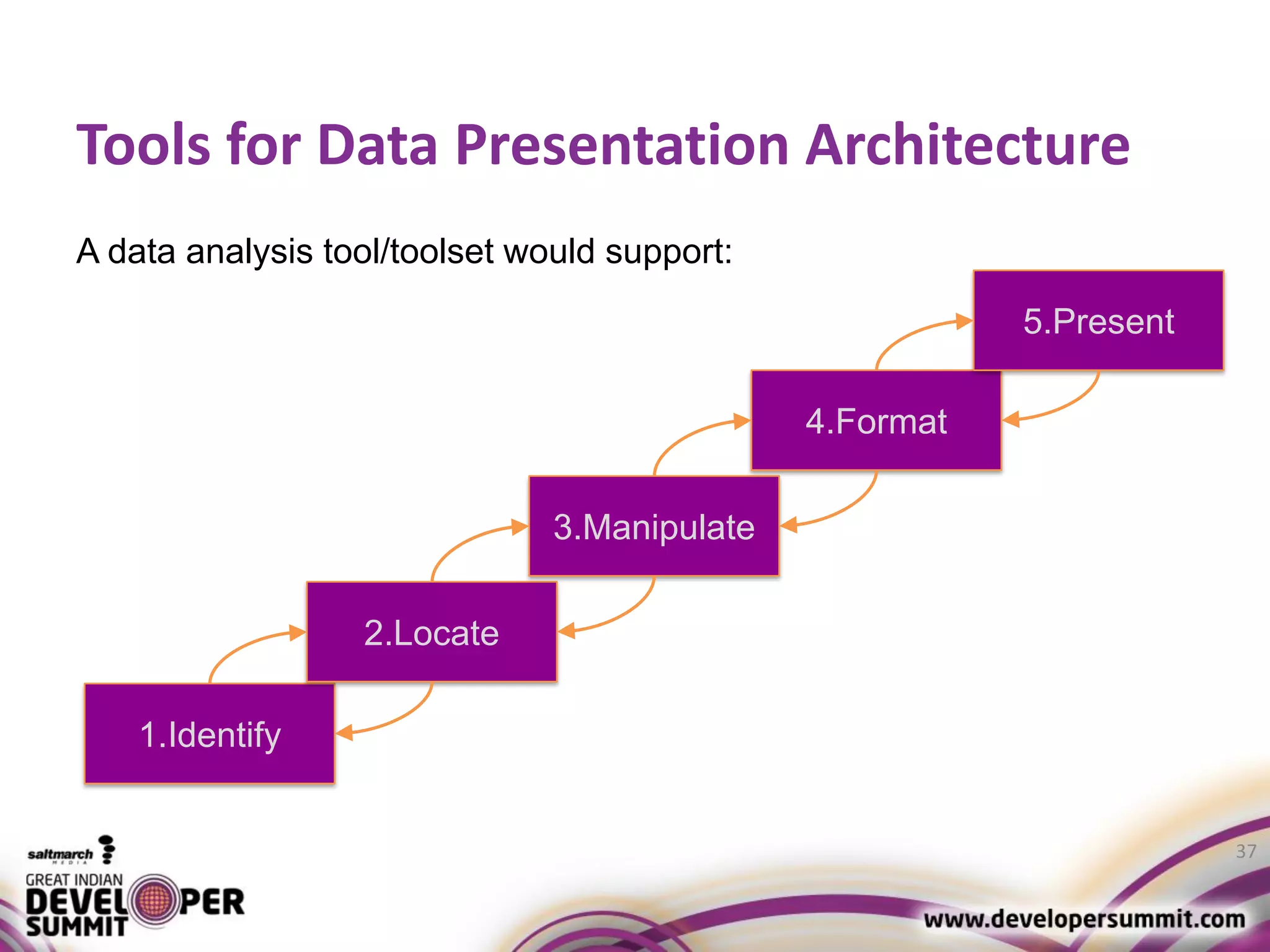
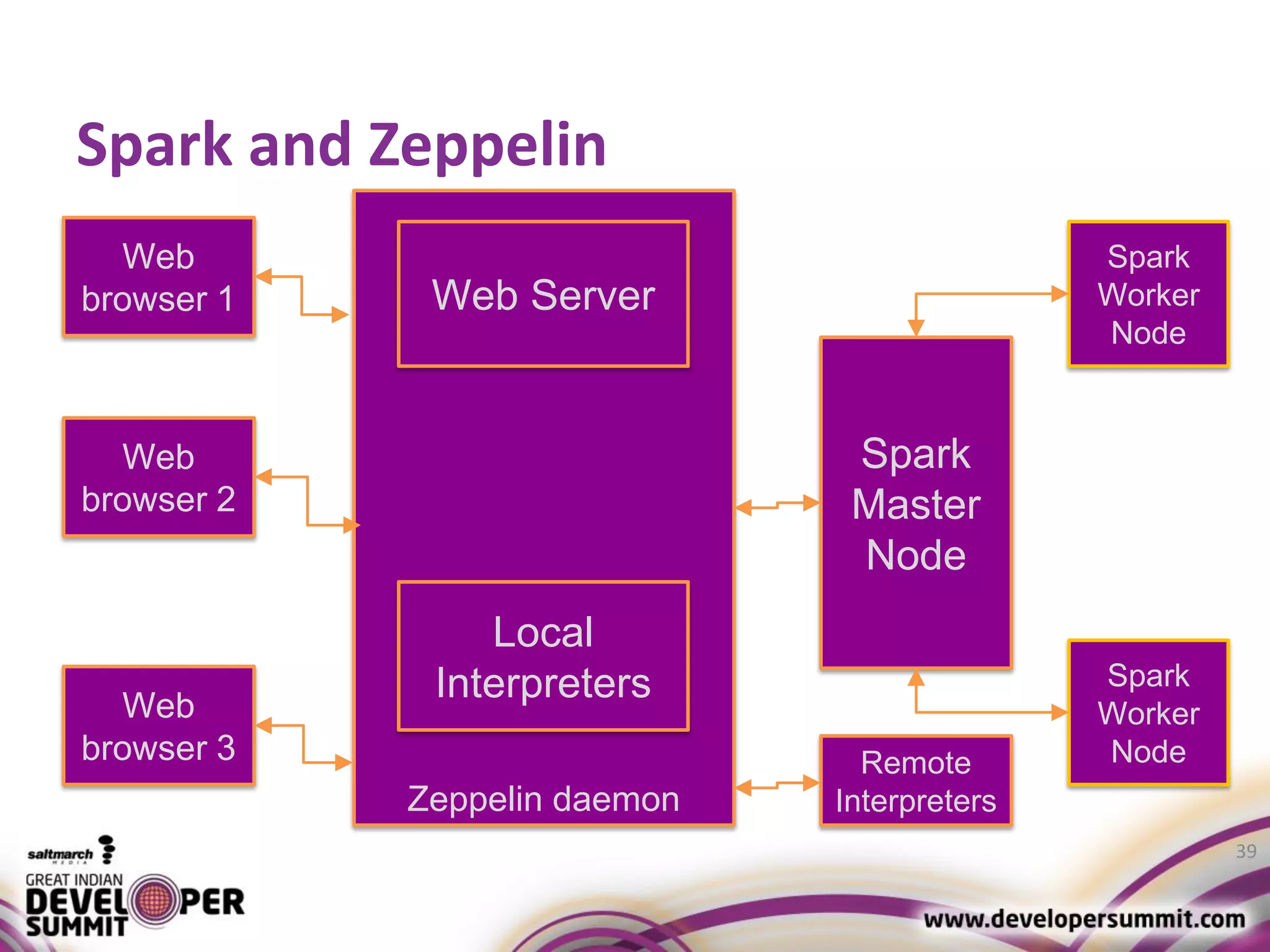
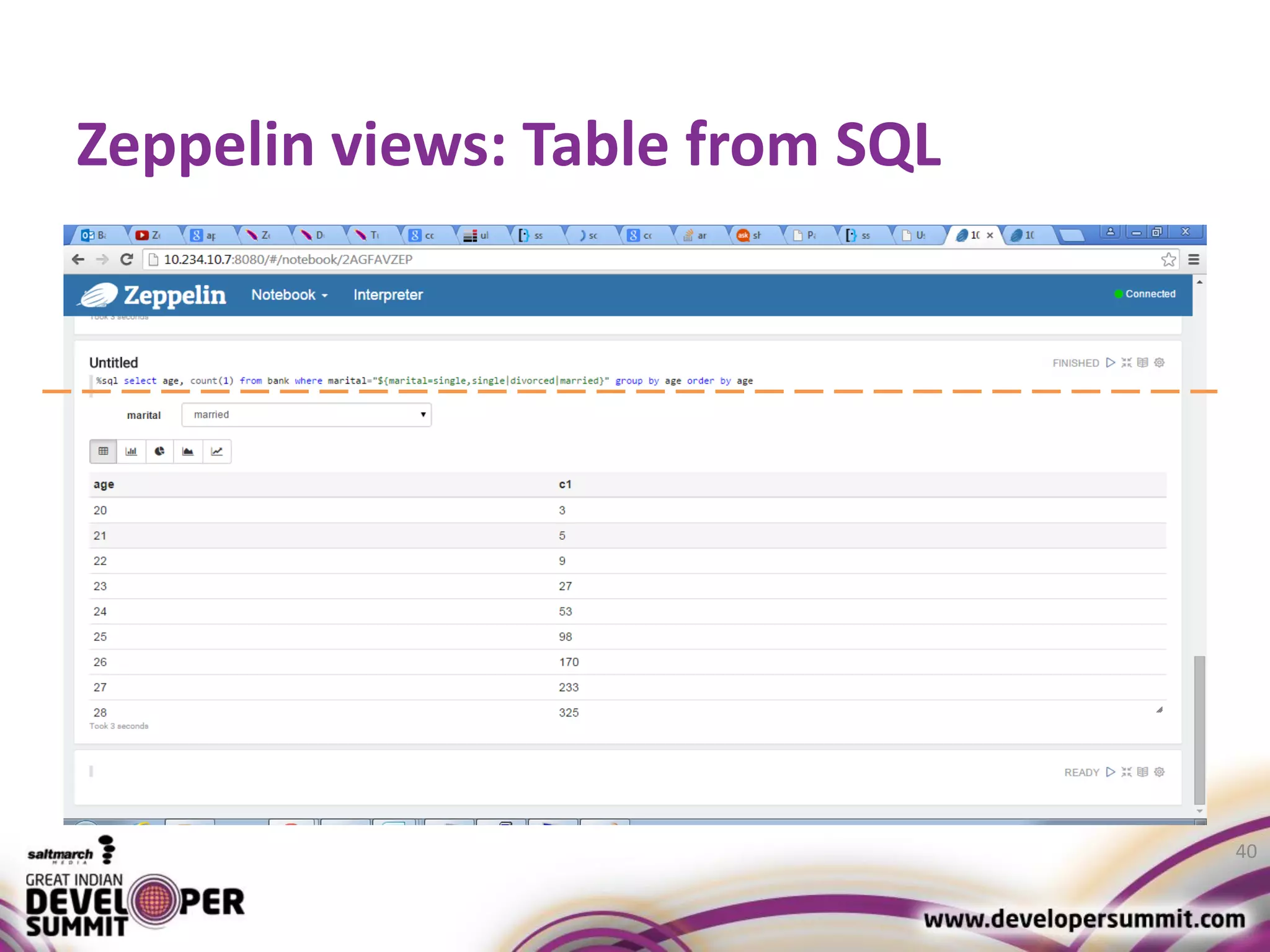
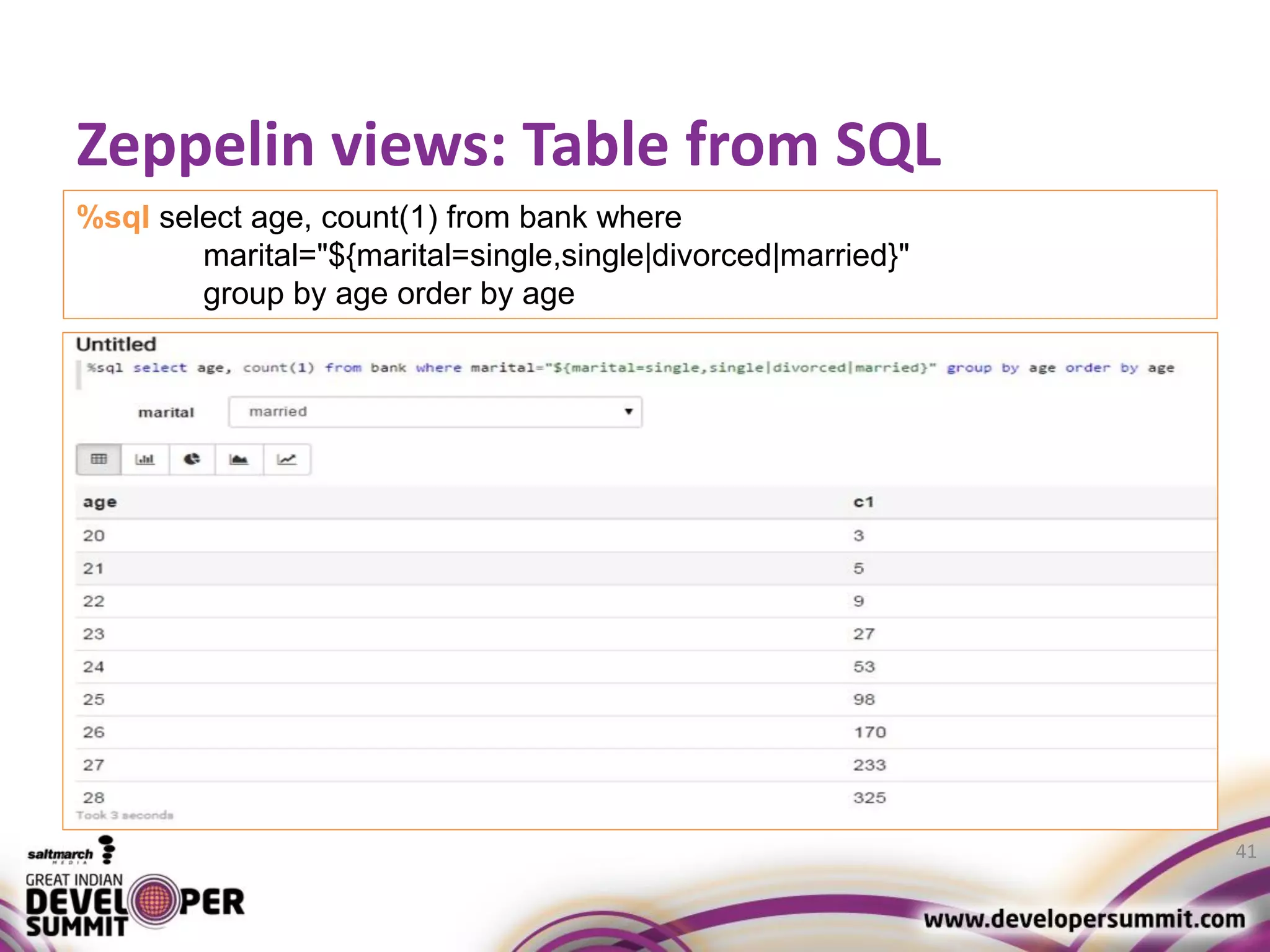
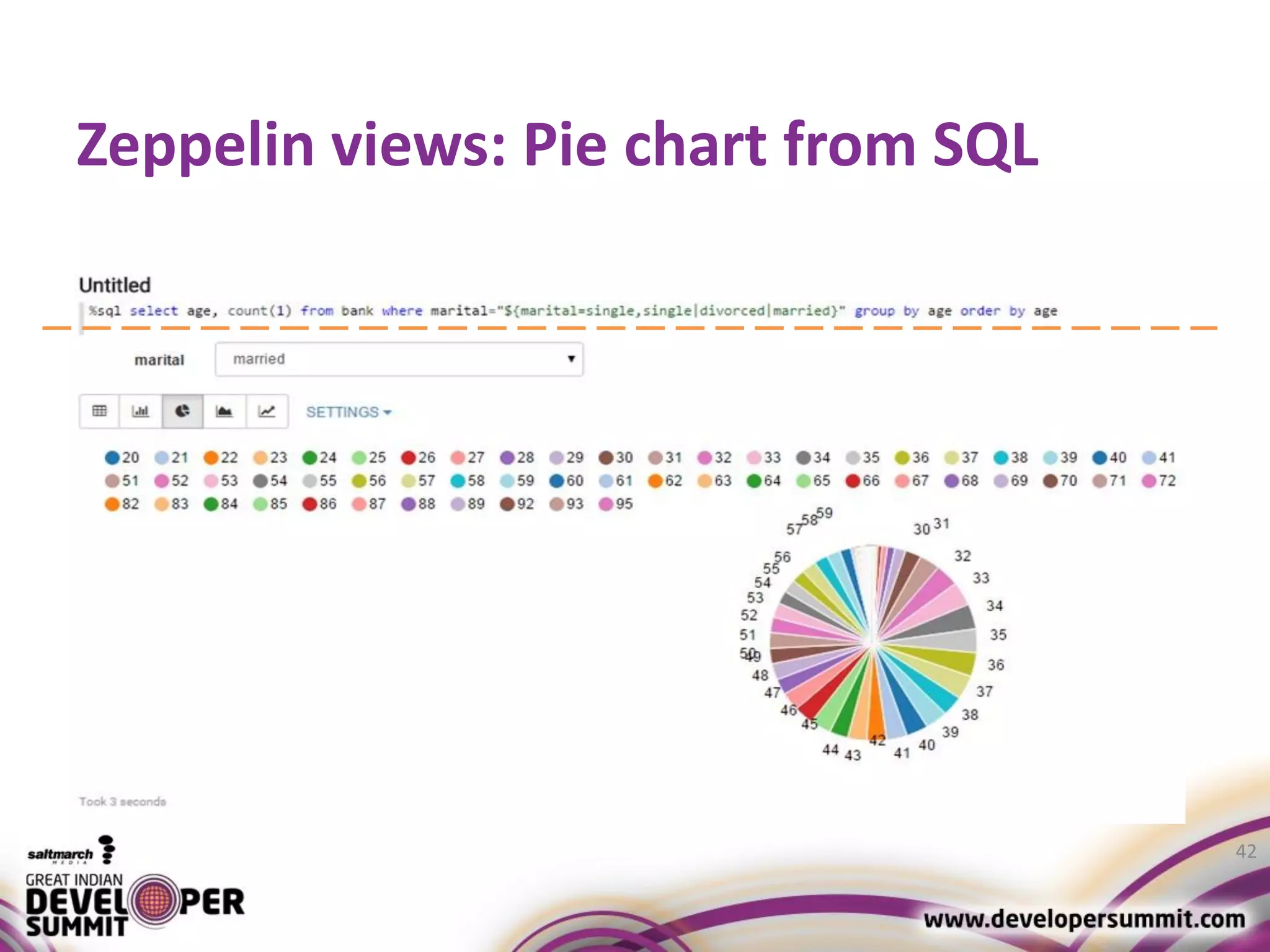
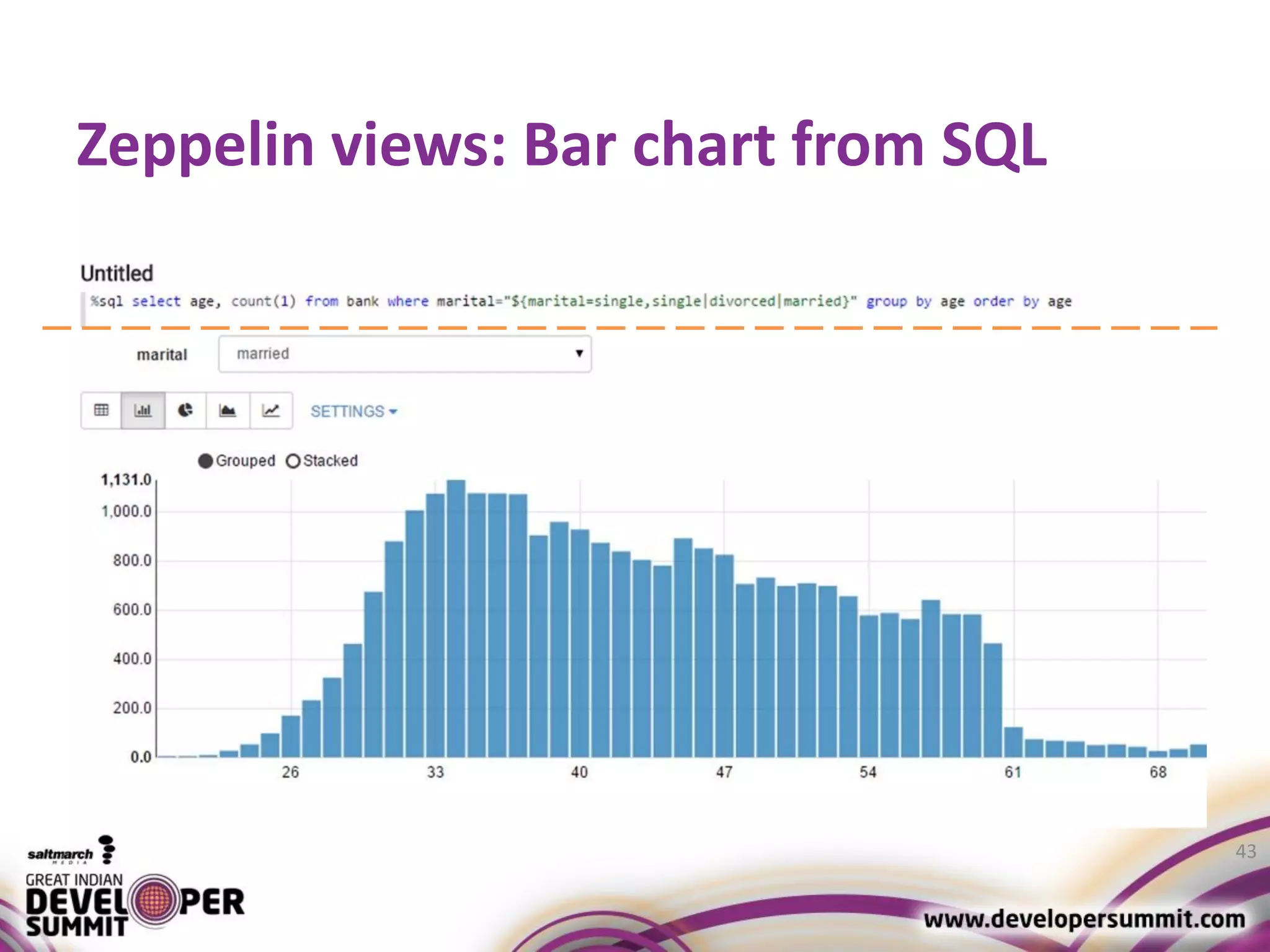
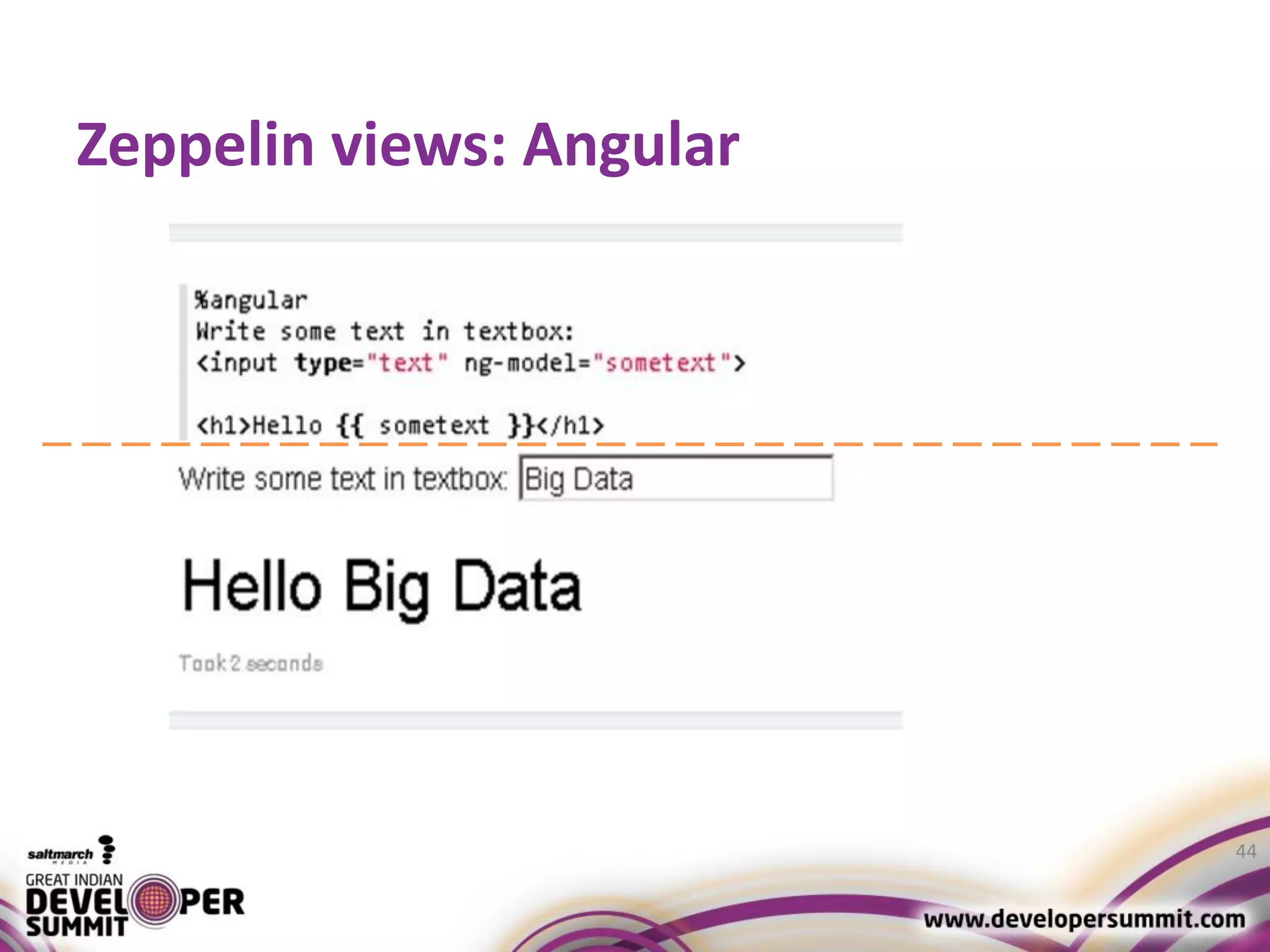
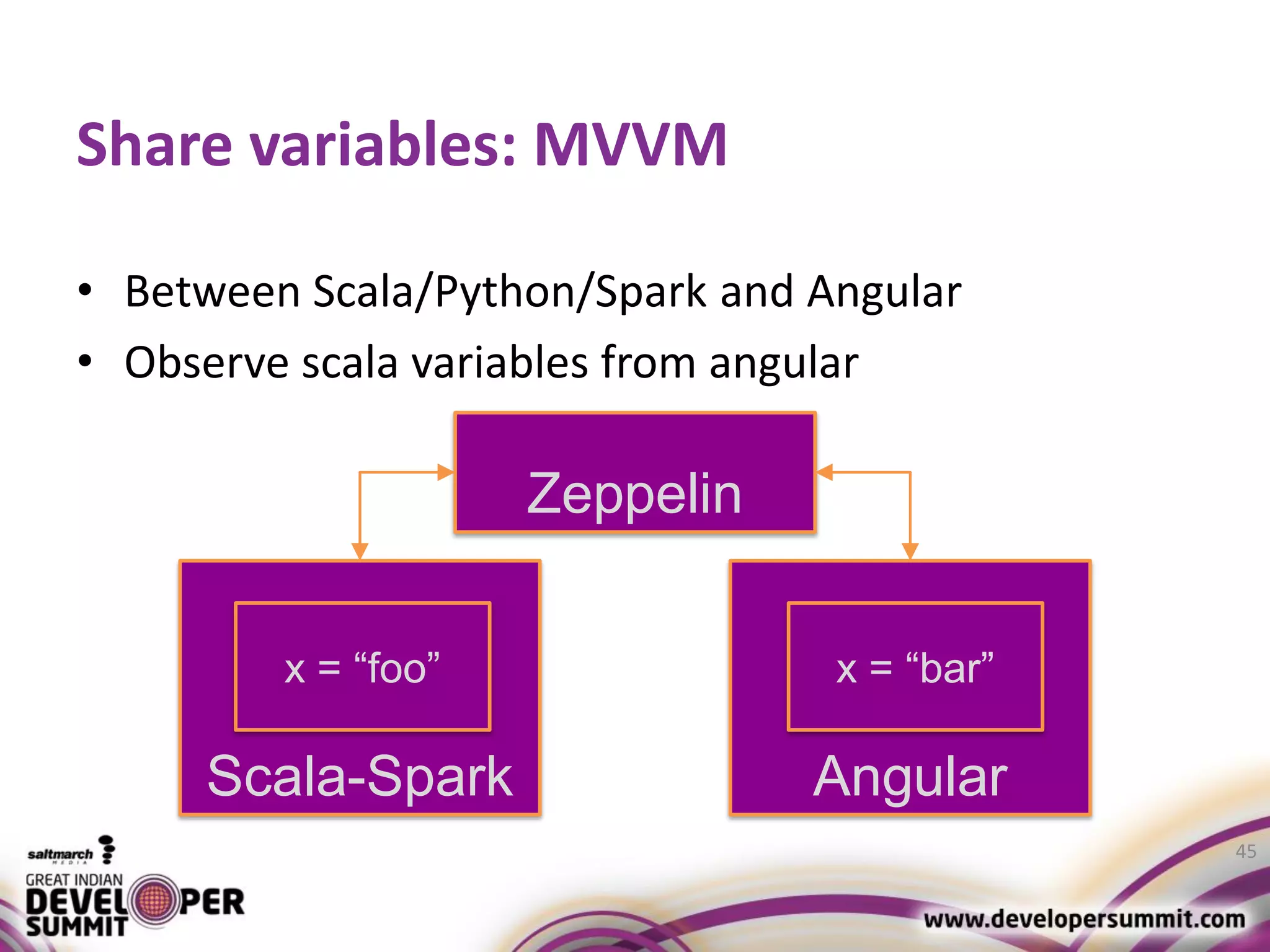
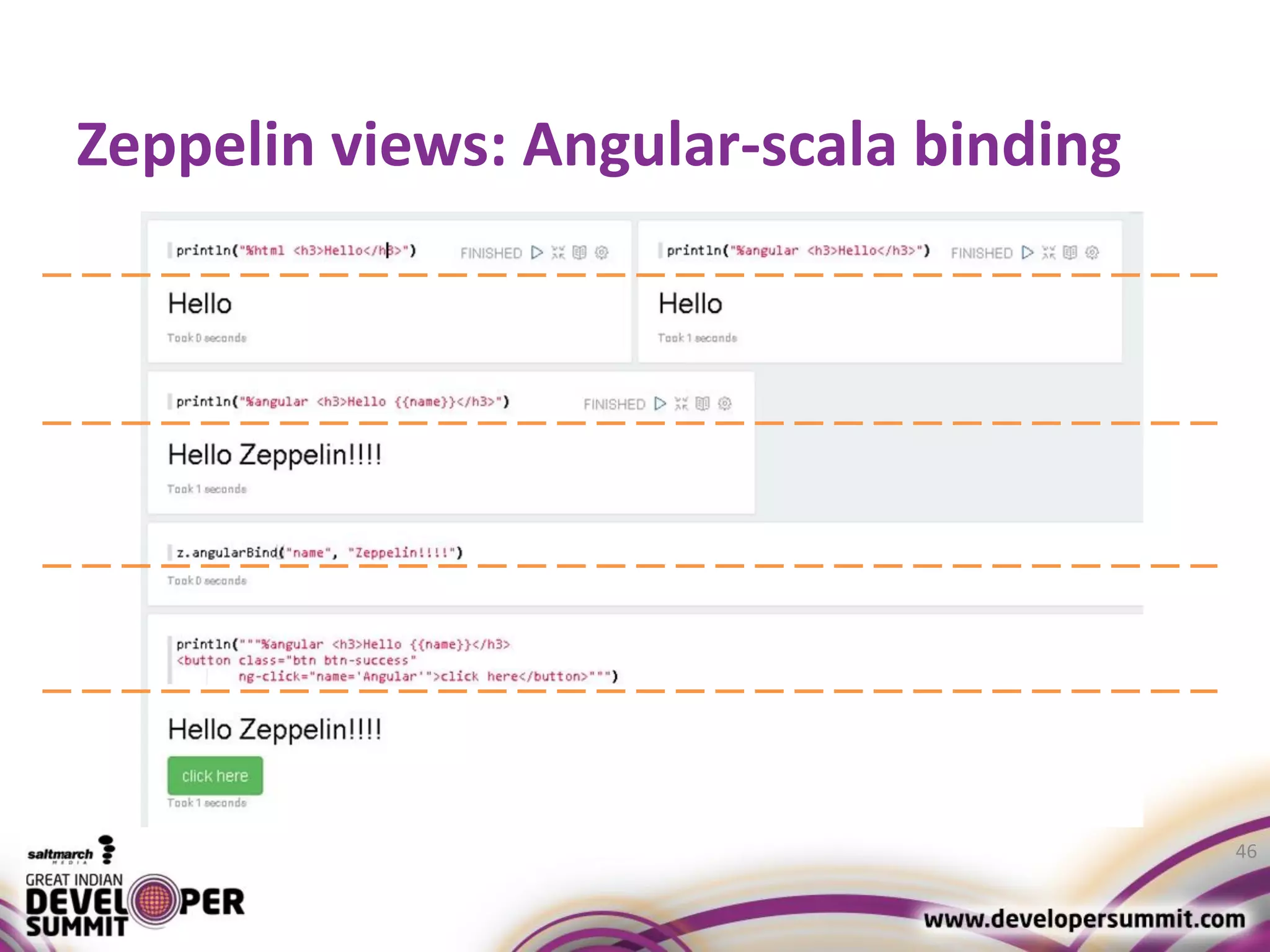
The document discusses big data visualization using Apache Spark and Zeppelin, highlighting the challenges of handling large data sizes and the limitations of traditional processing tools. It details the capabilities of Spark as a complement to the Hadoop ecosystem, including its speed advantages and integration with various data sources. Additionally, it emphasizes Zeppelin's role in interactive data analytics and visualization, providing a web-based interface for data analysis and report sharing.