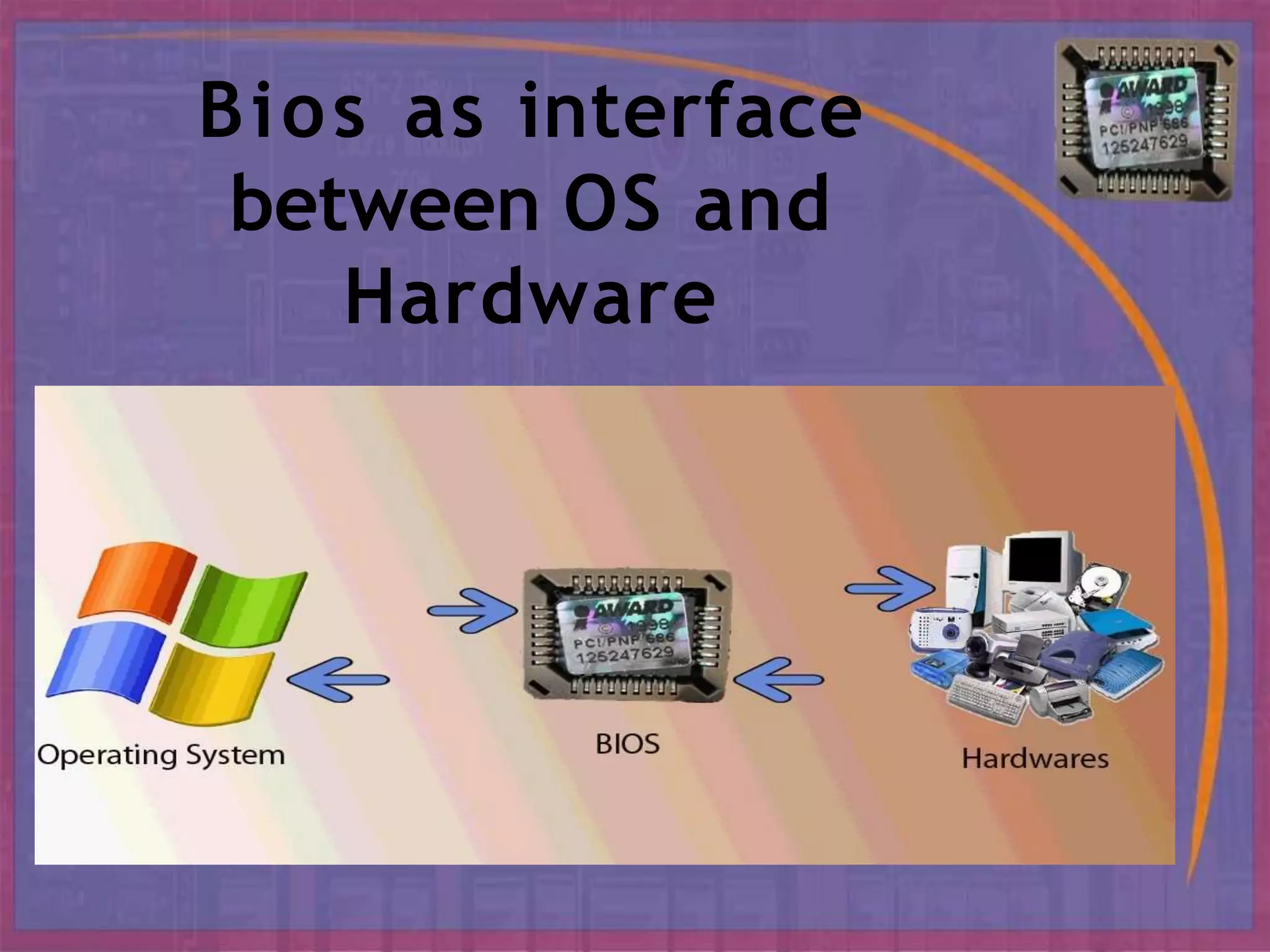
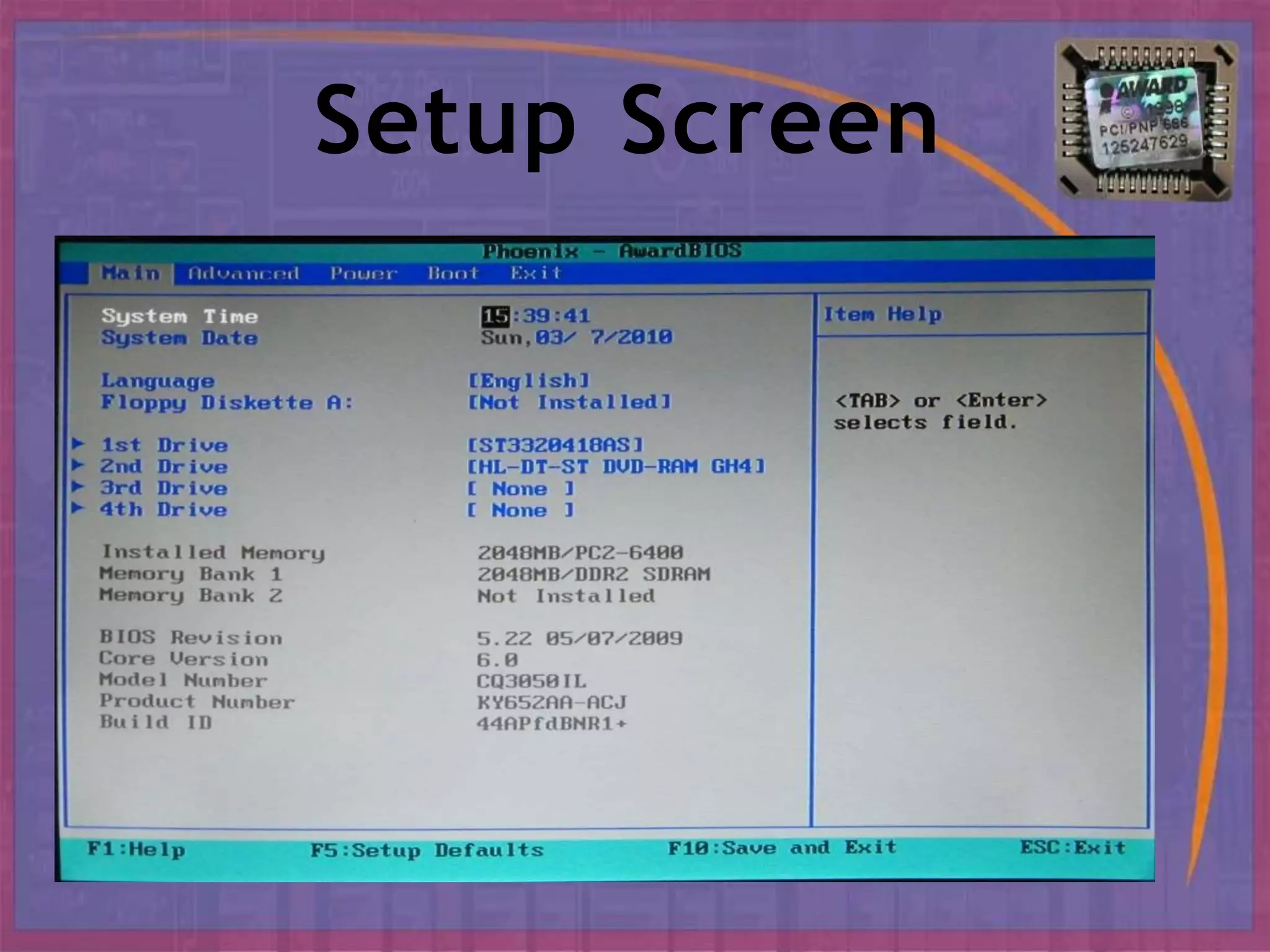
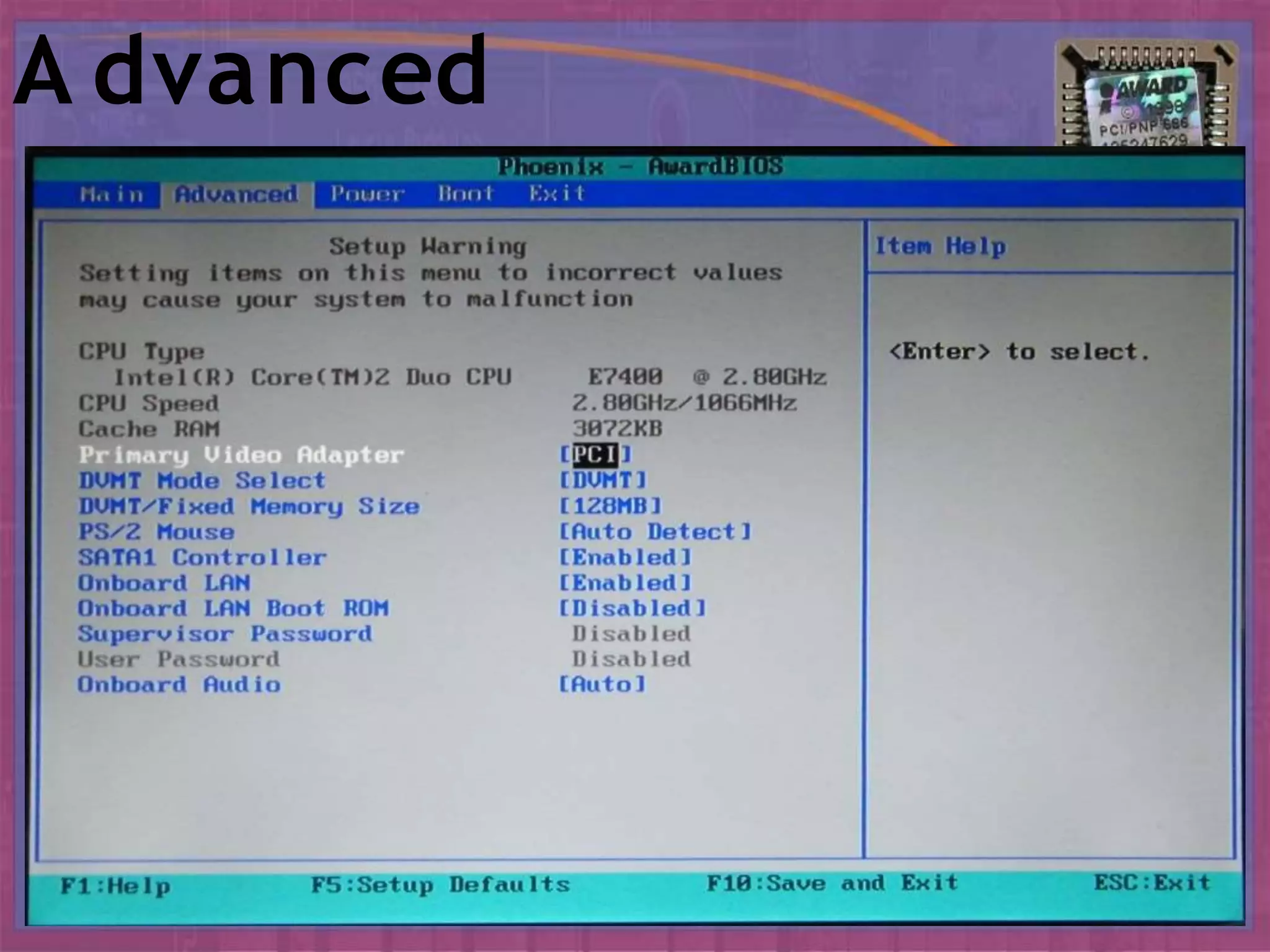
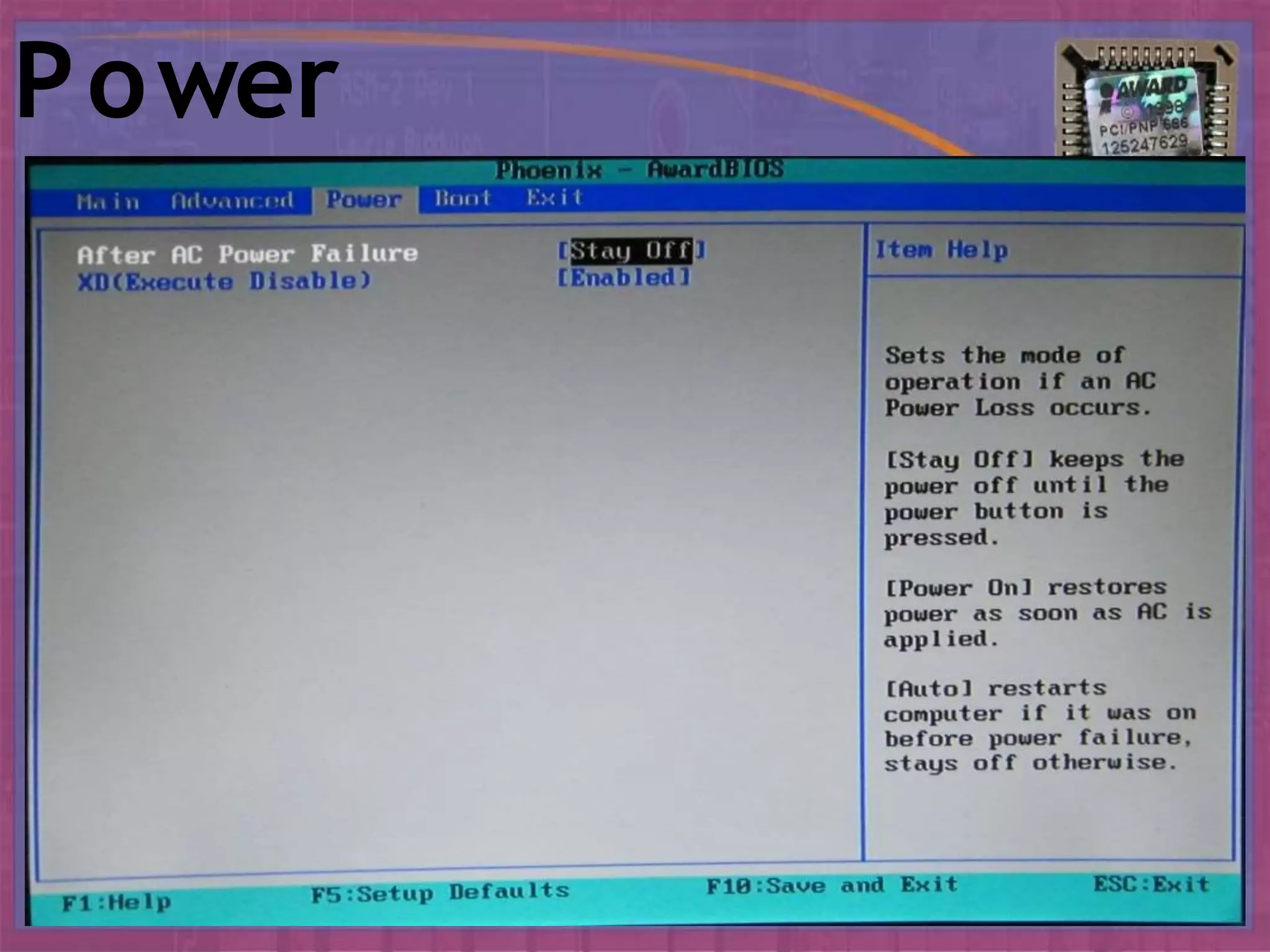
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, is the boot firmware that initializes and tests system hardware upon powering on a computer. It facilitates the loading of the operating system and configuration of hardware settings through a setup program. Common functions include conducting a Power-On Self Test (POST), managing boot options, and allowing configurations of system components and parameters.