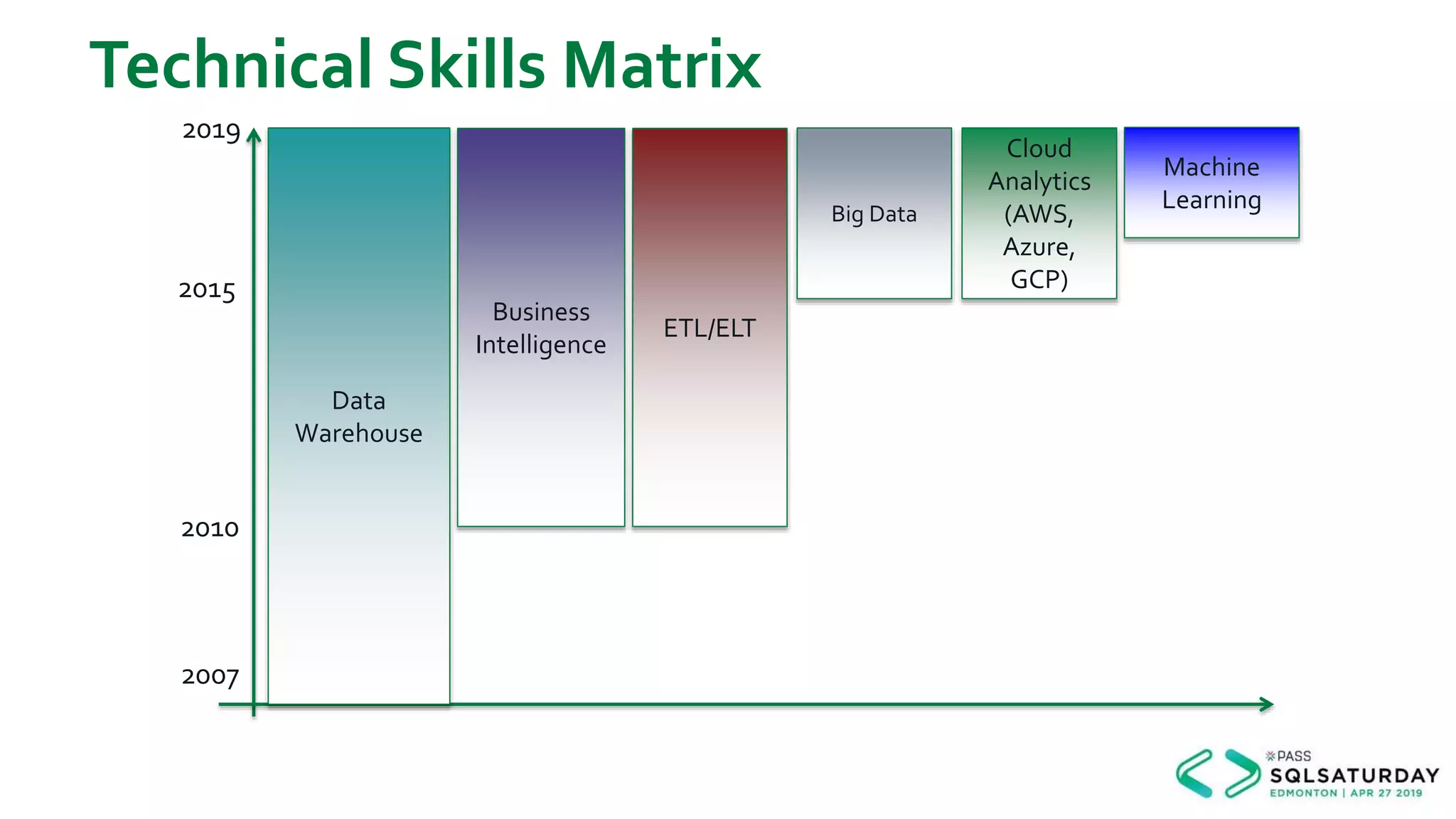
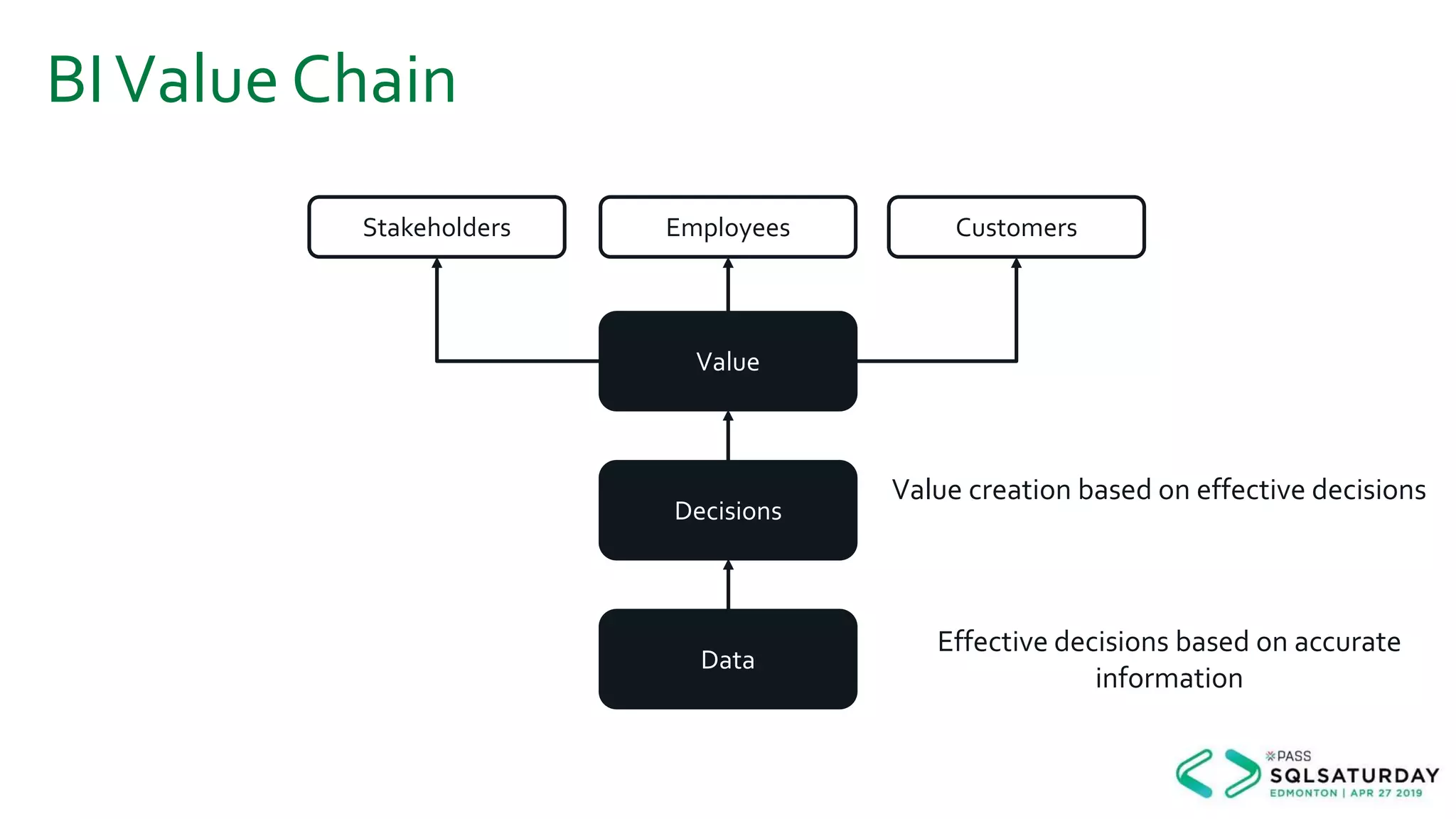
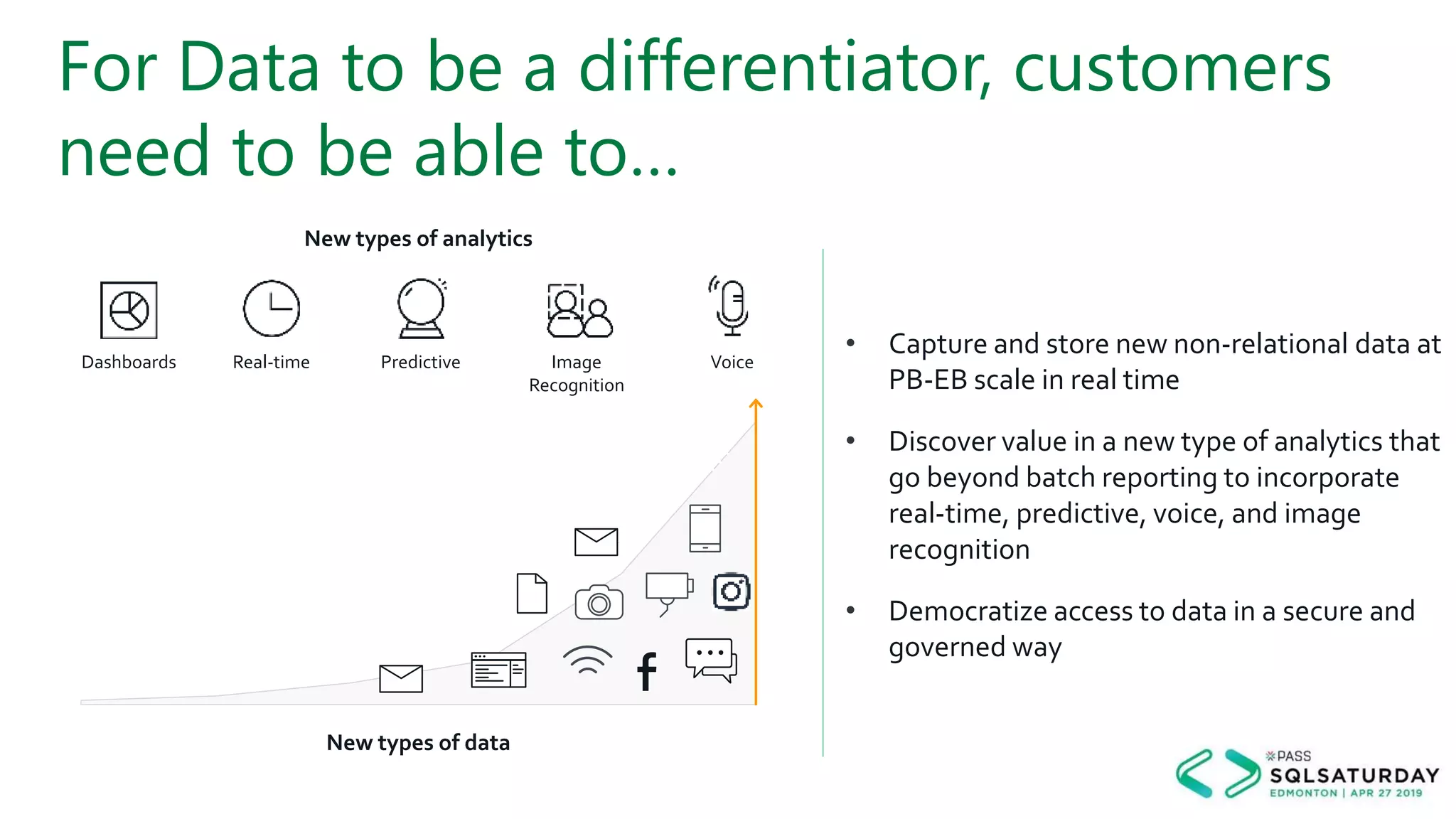
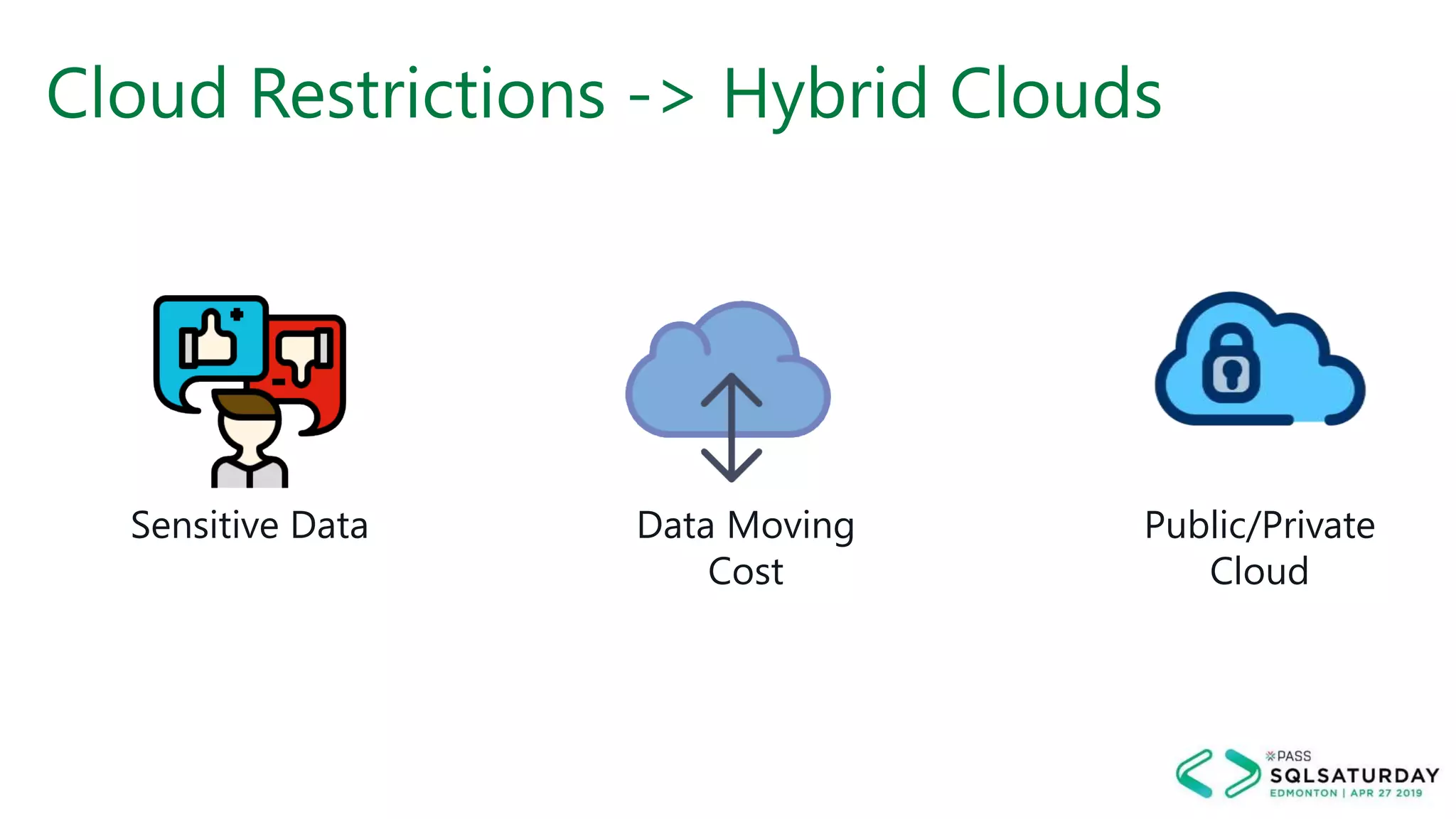
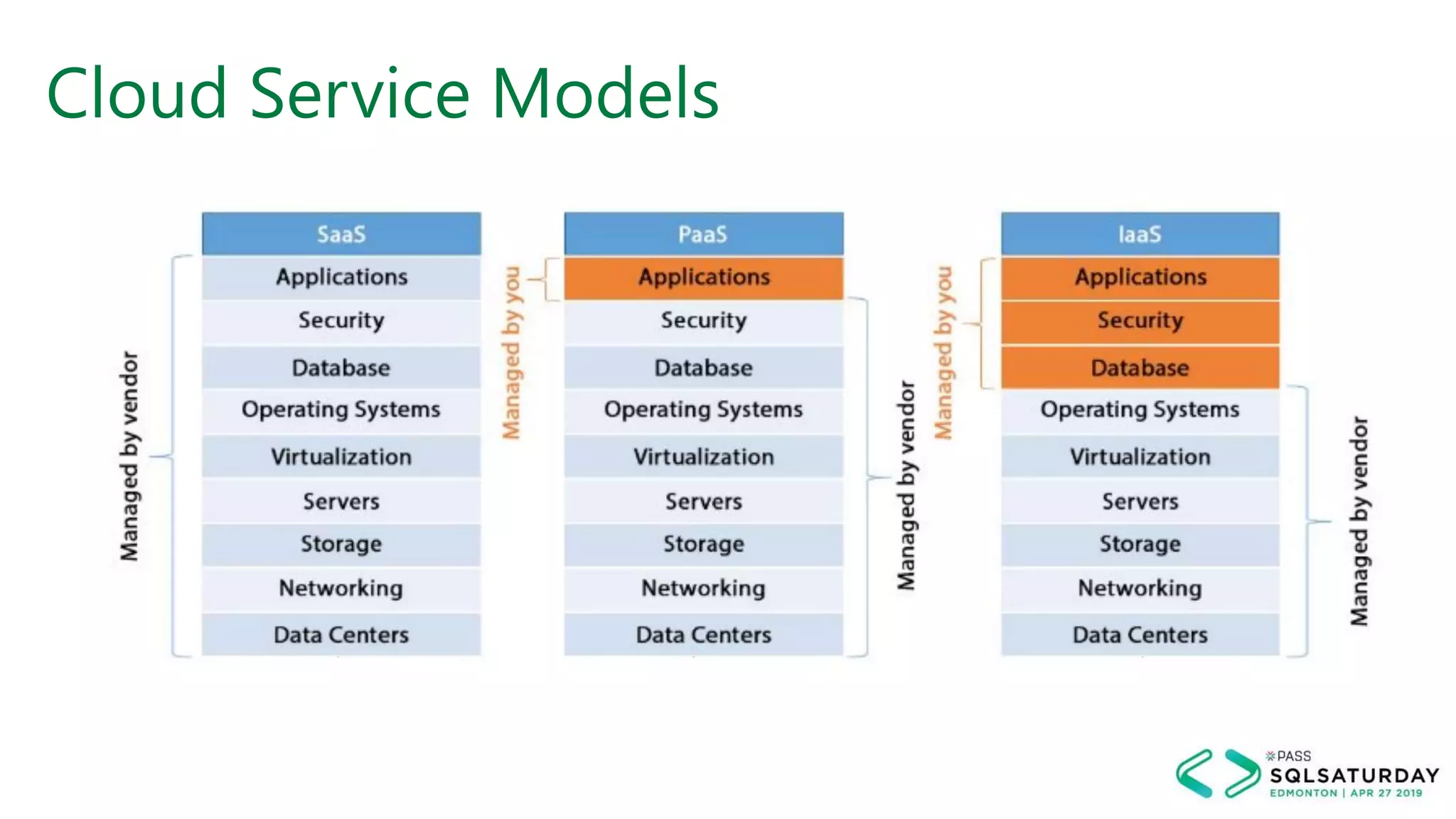
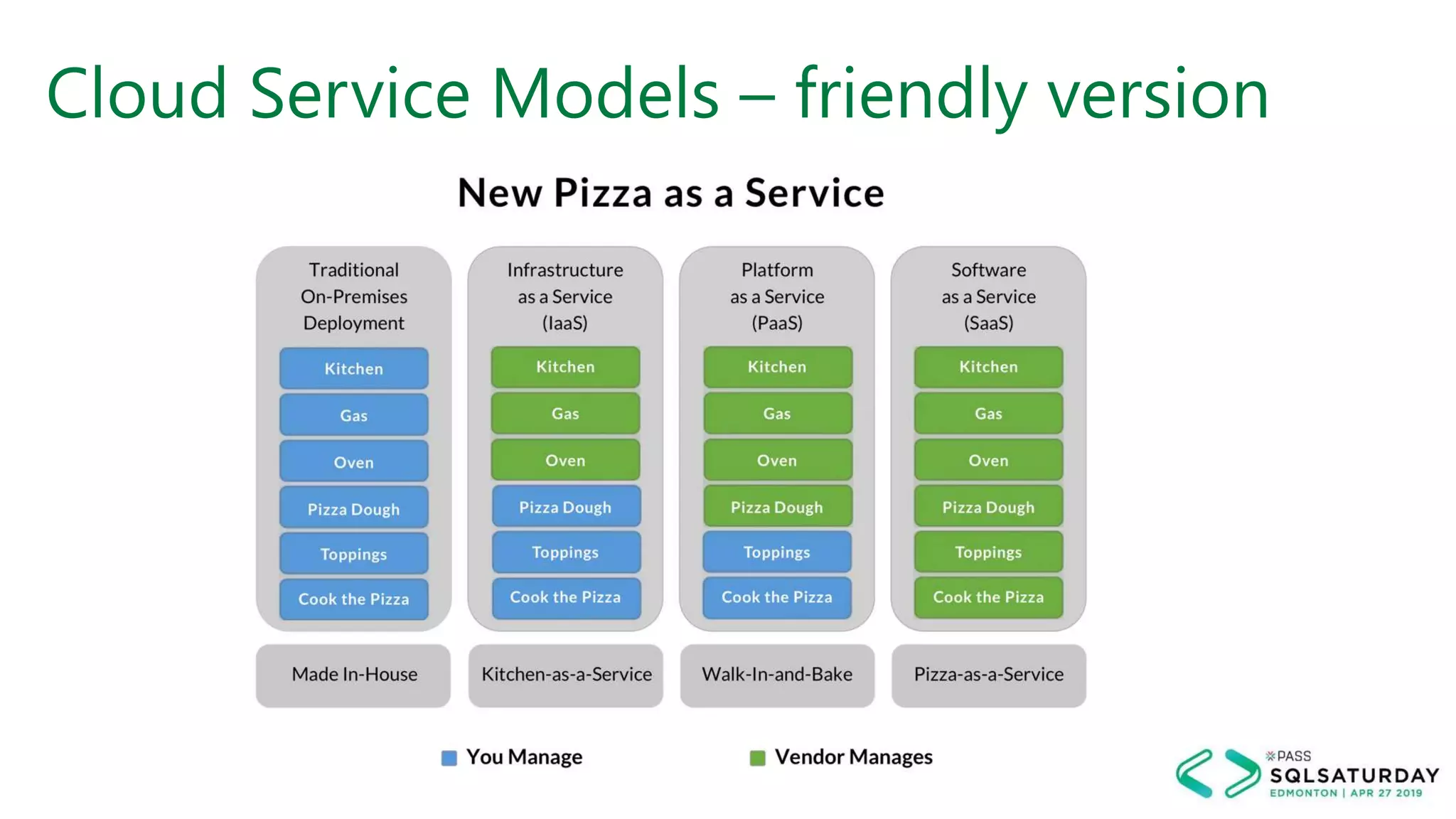
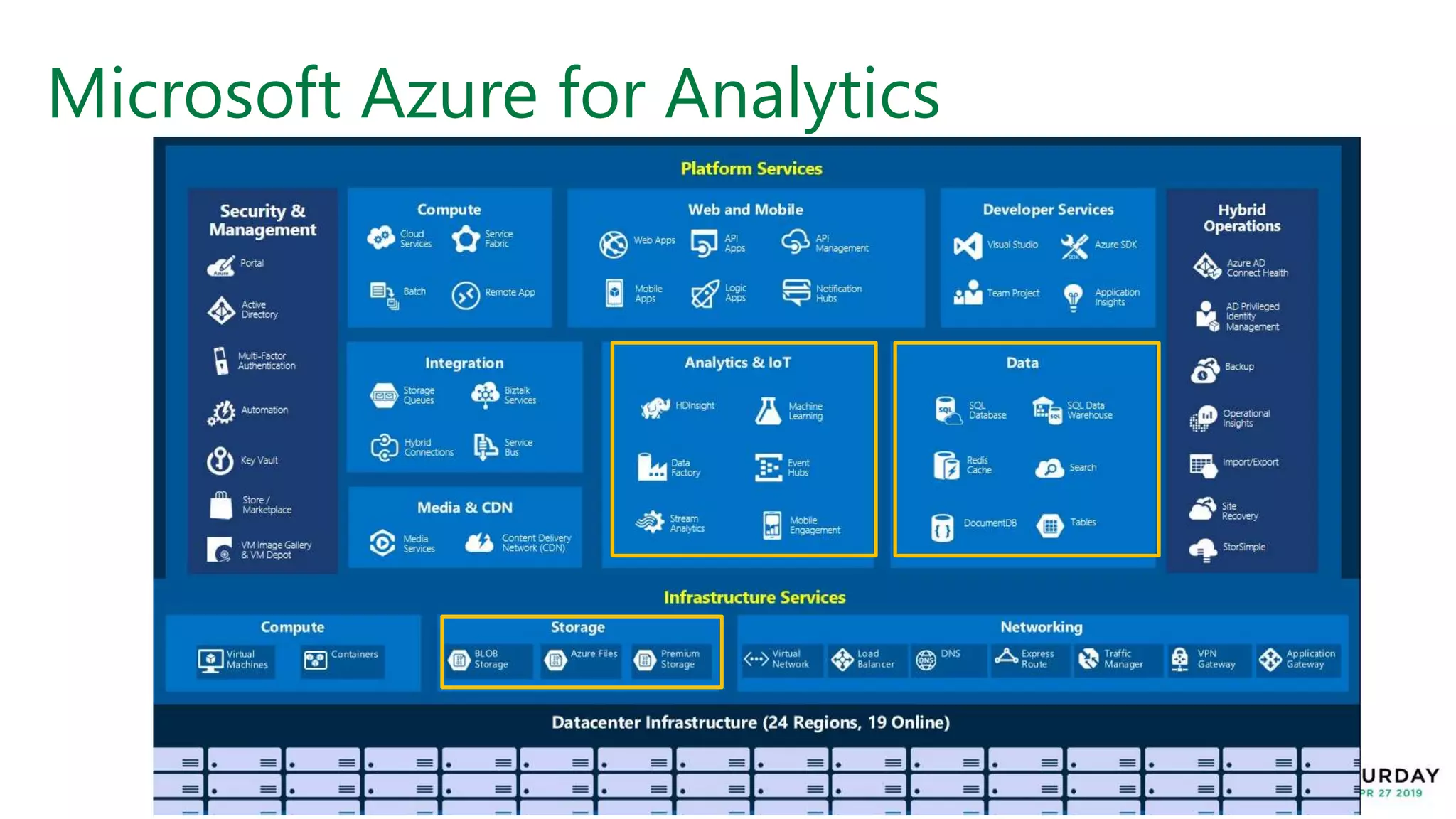
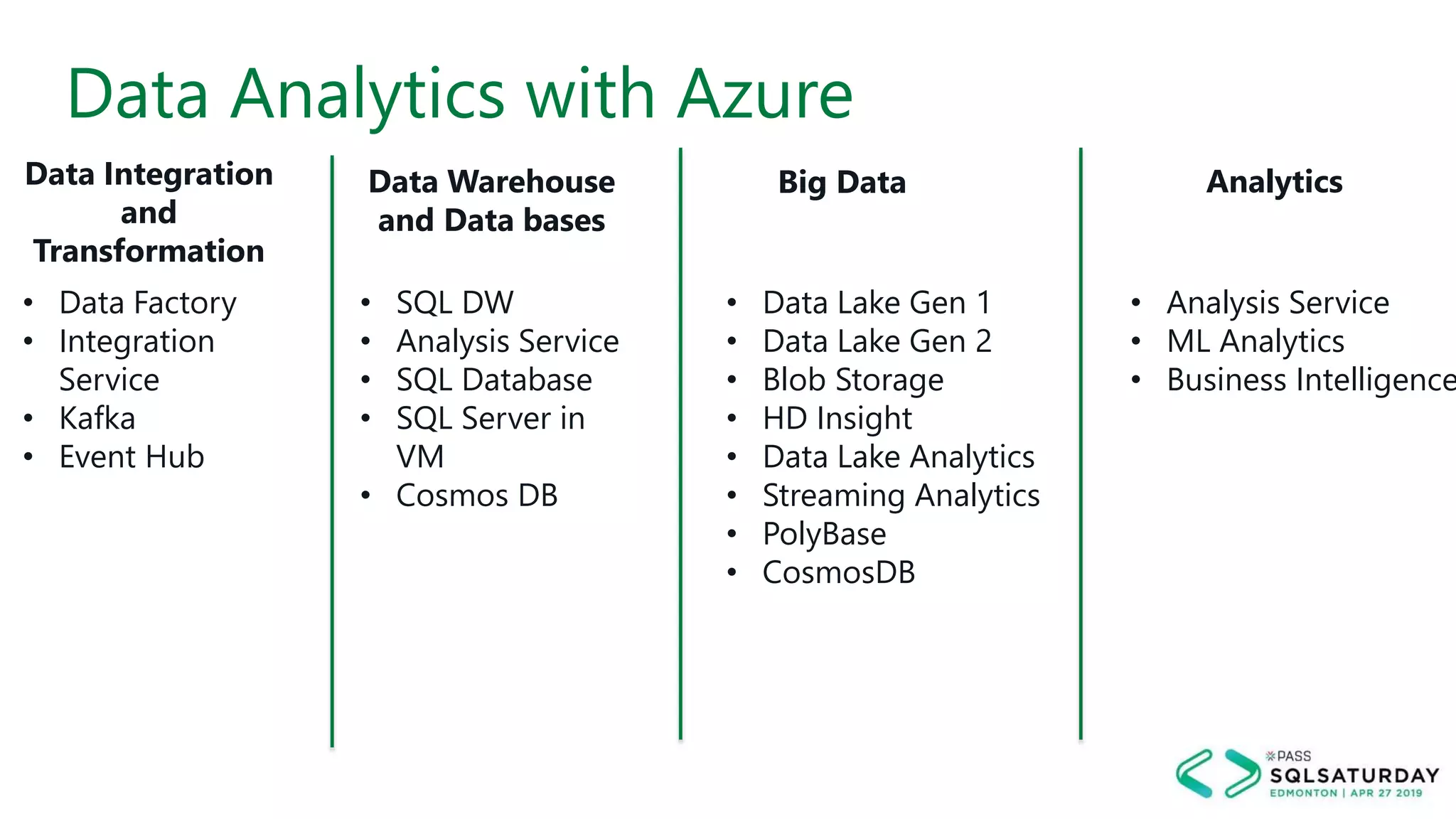
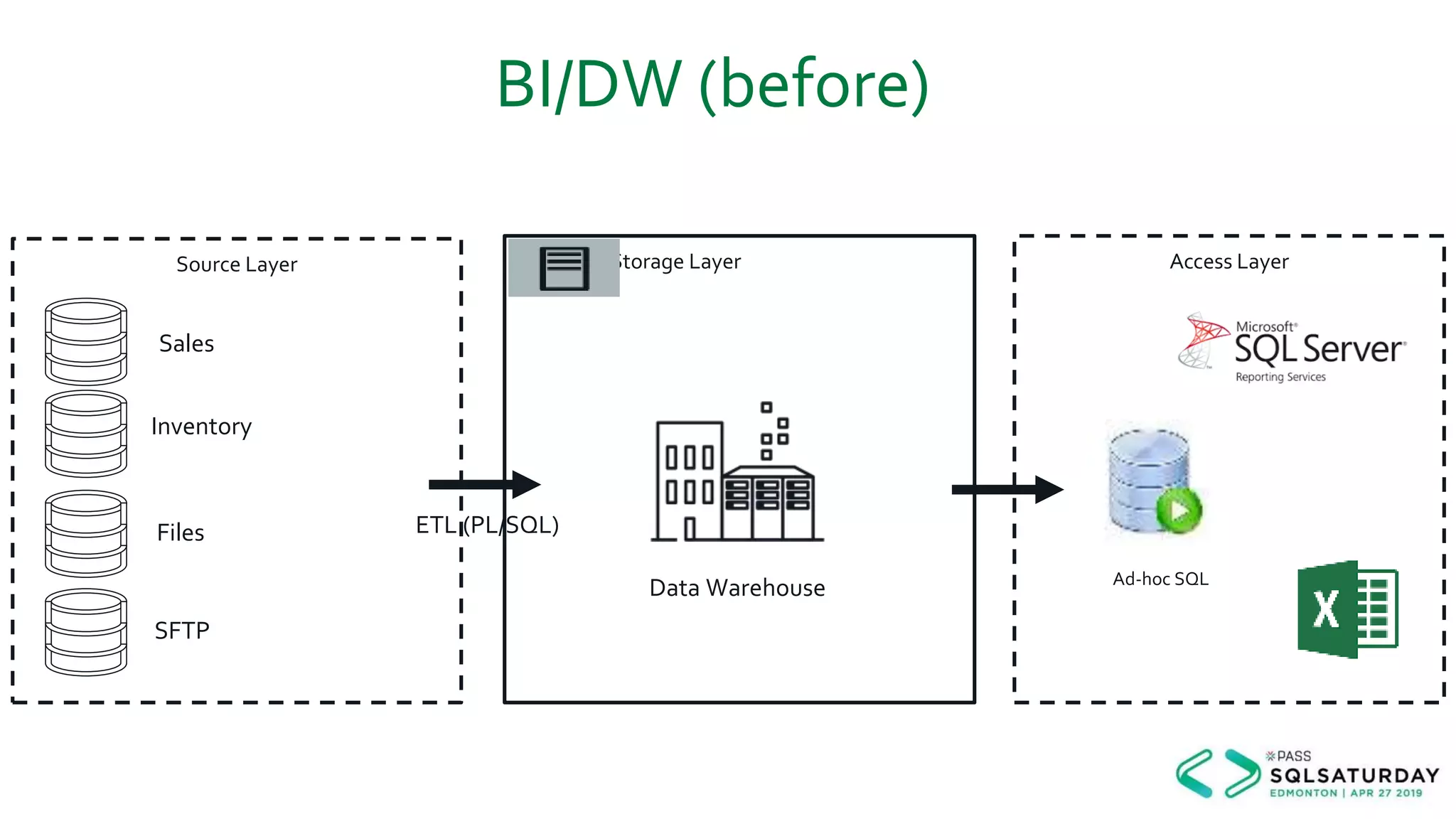
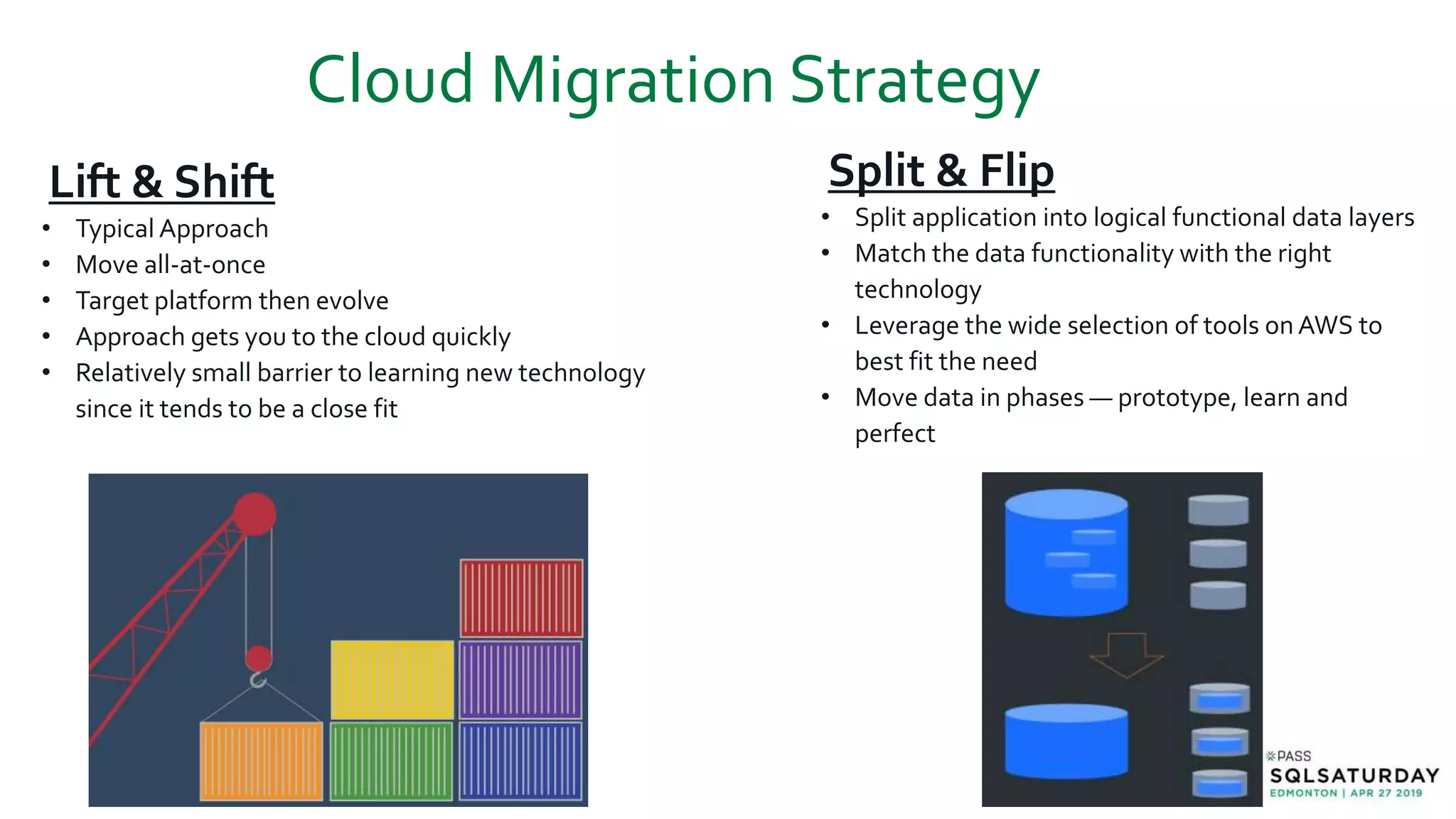
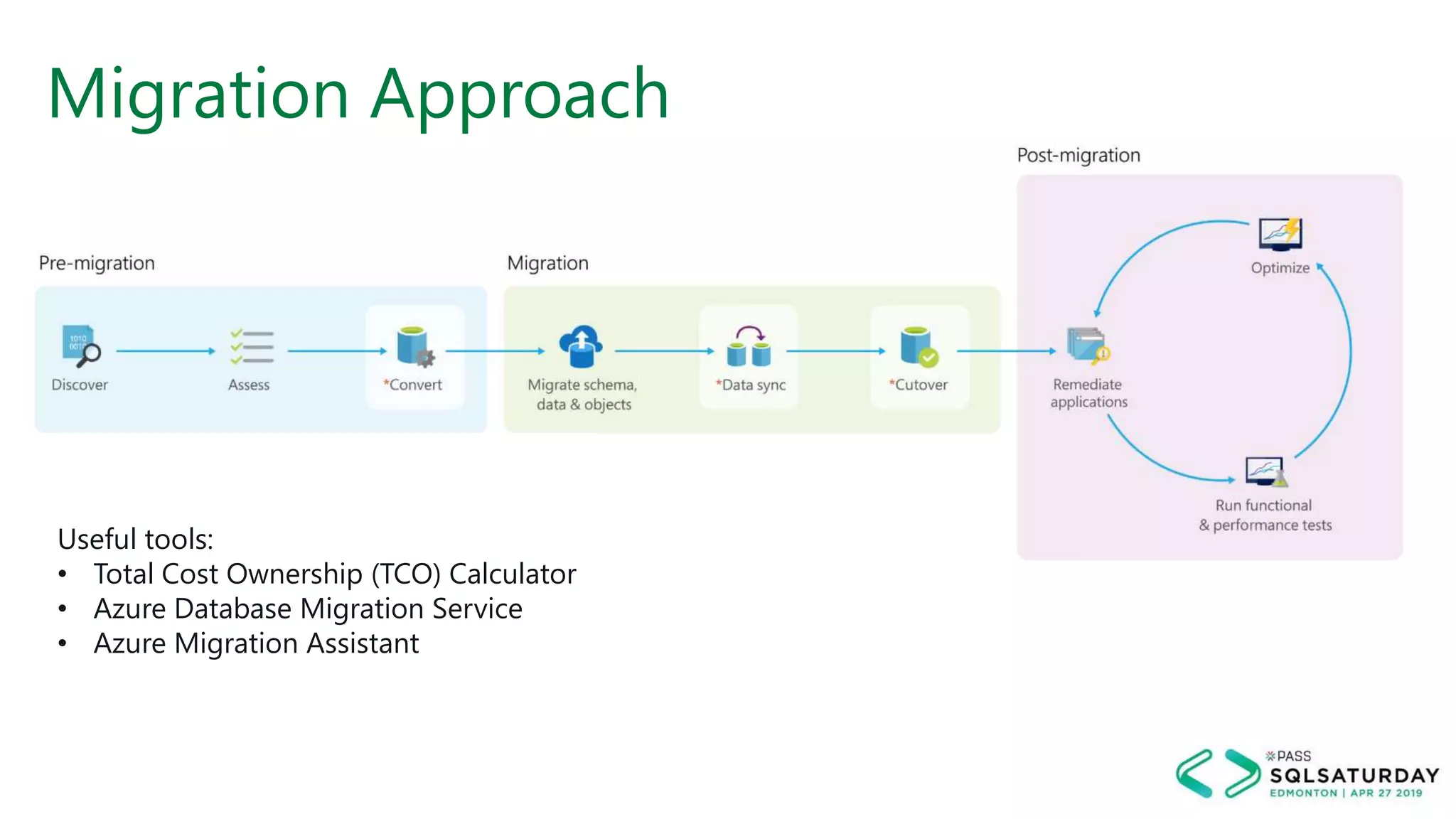
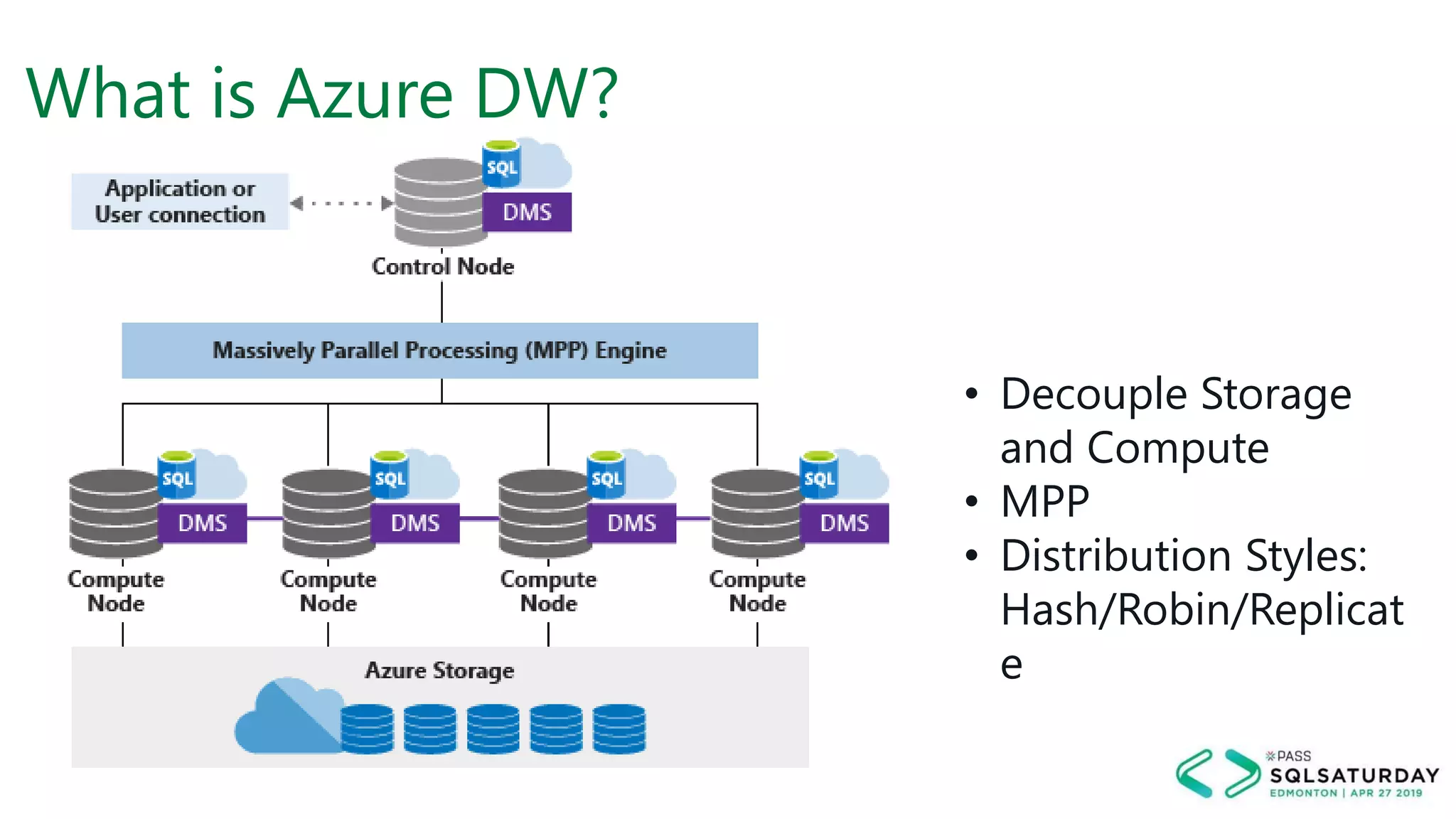
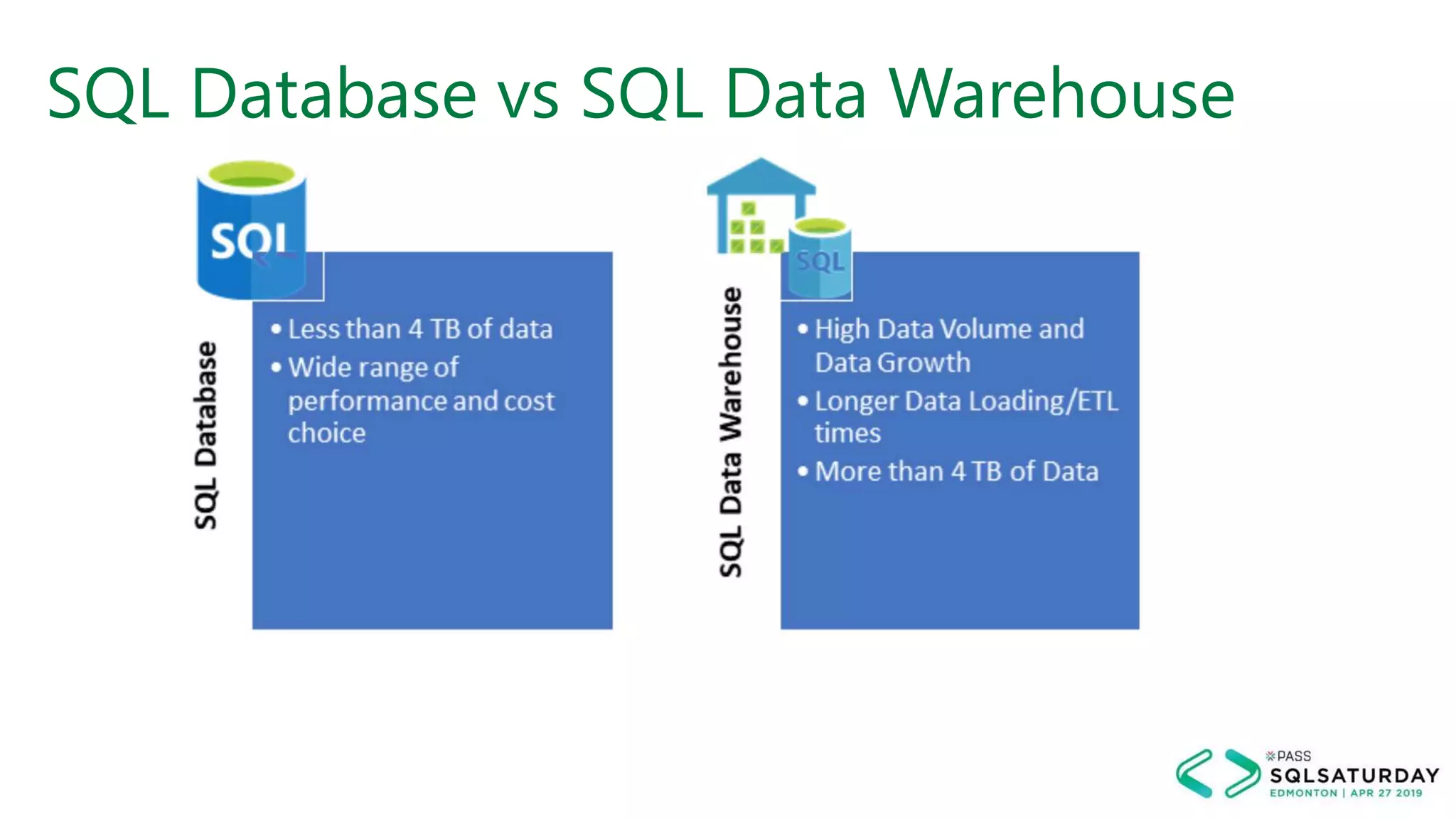
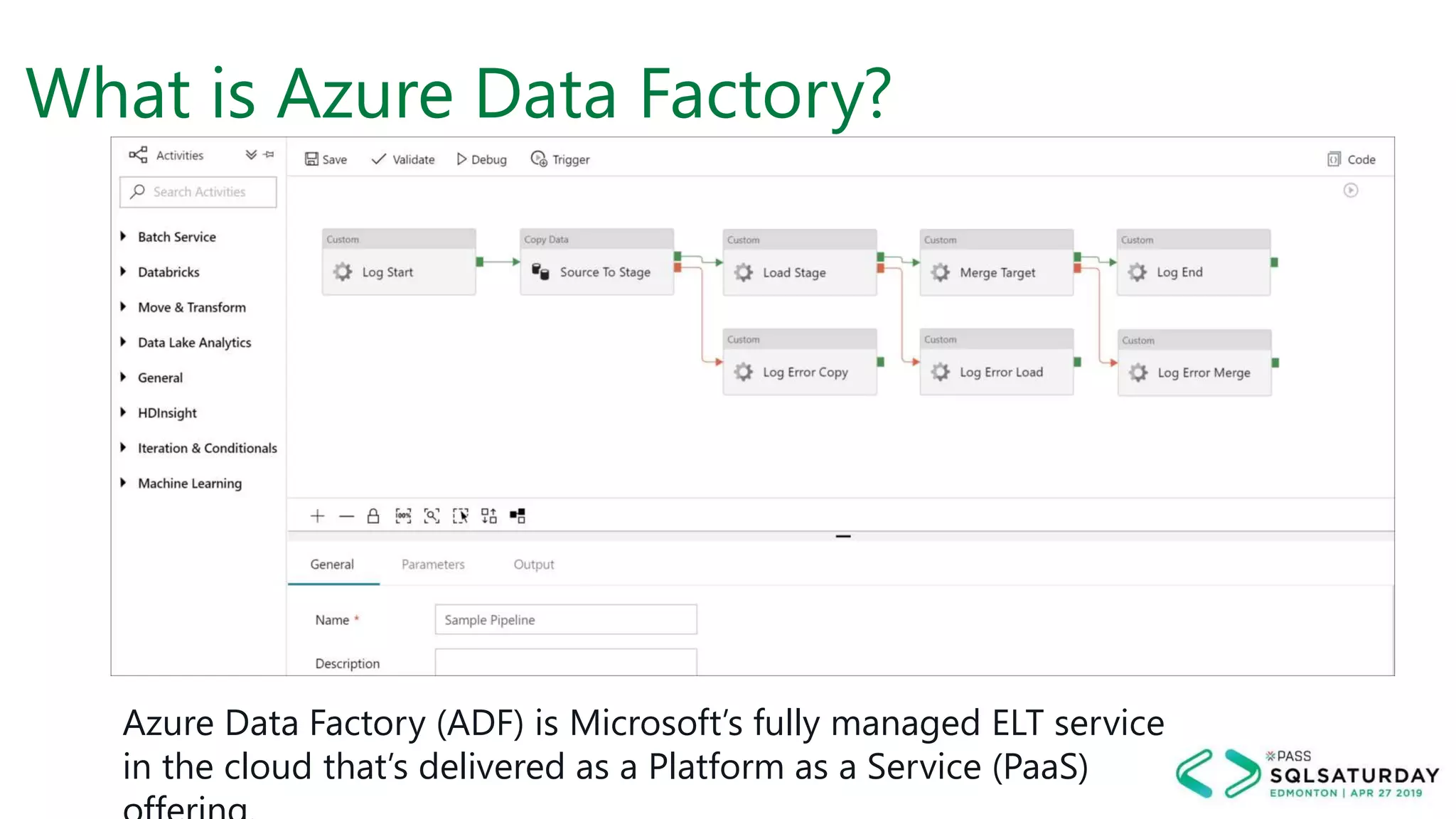
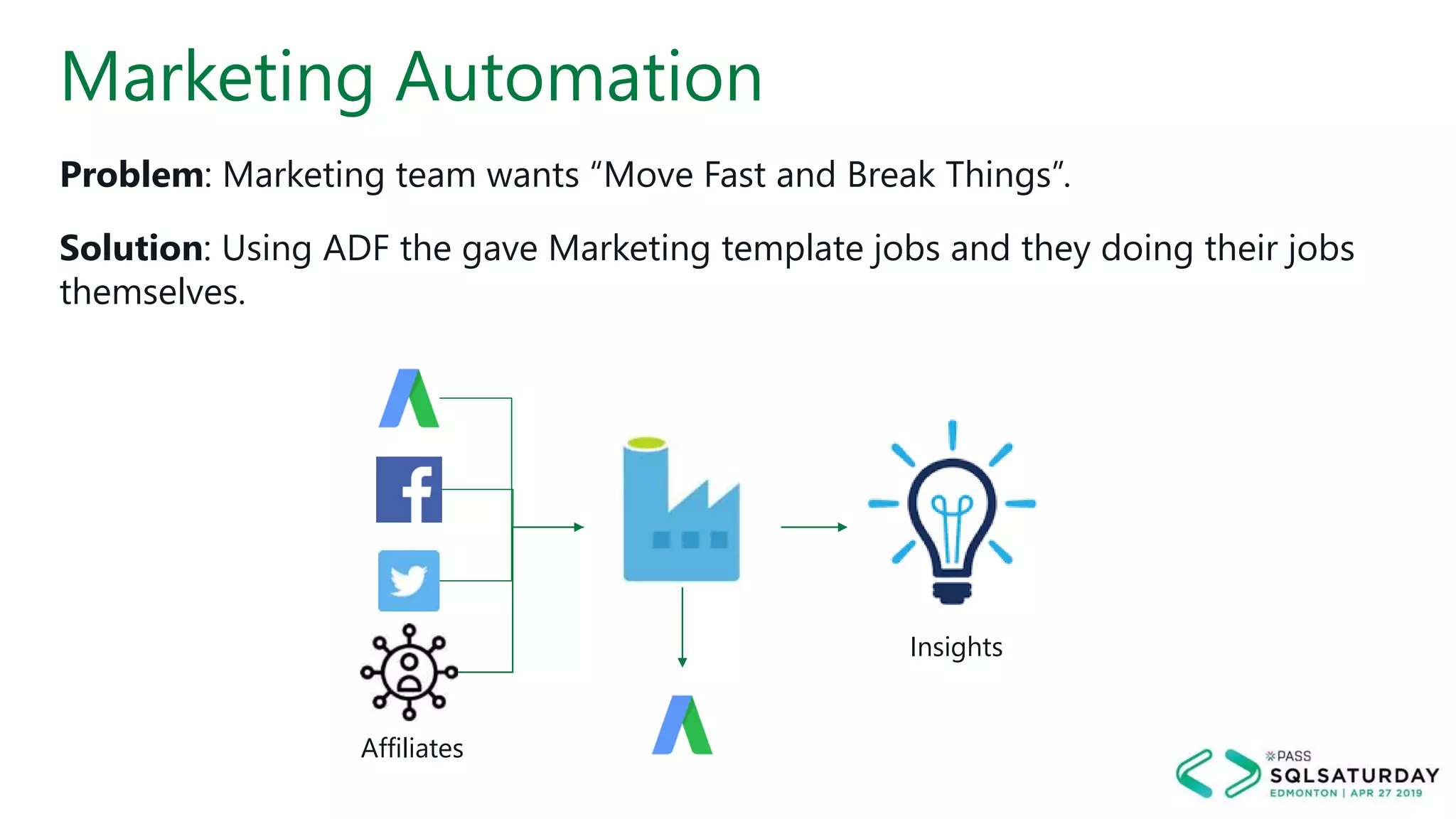
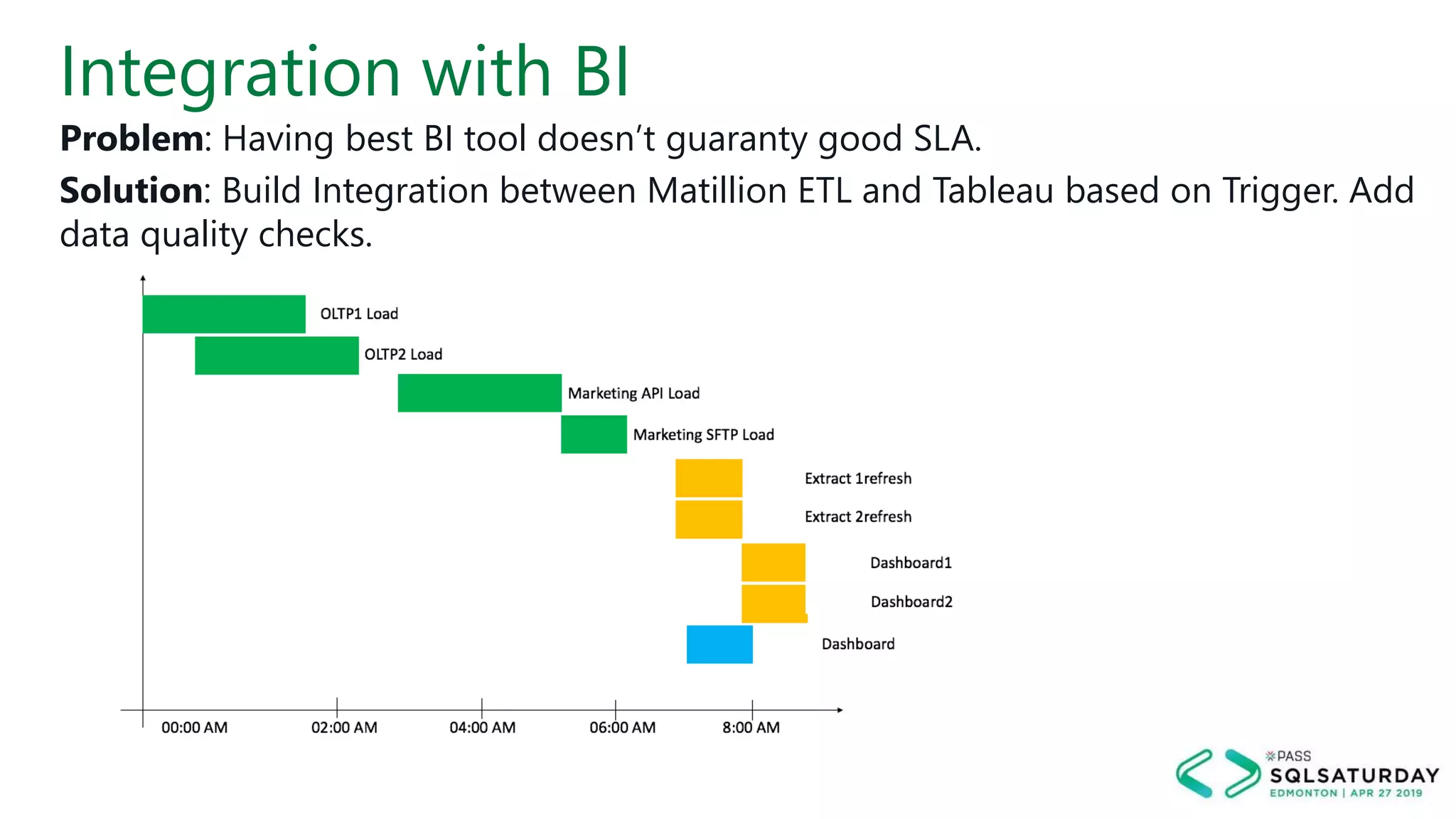
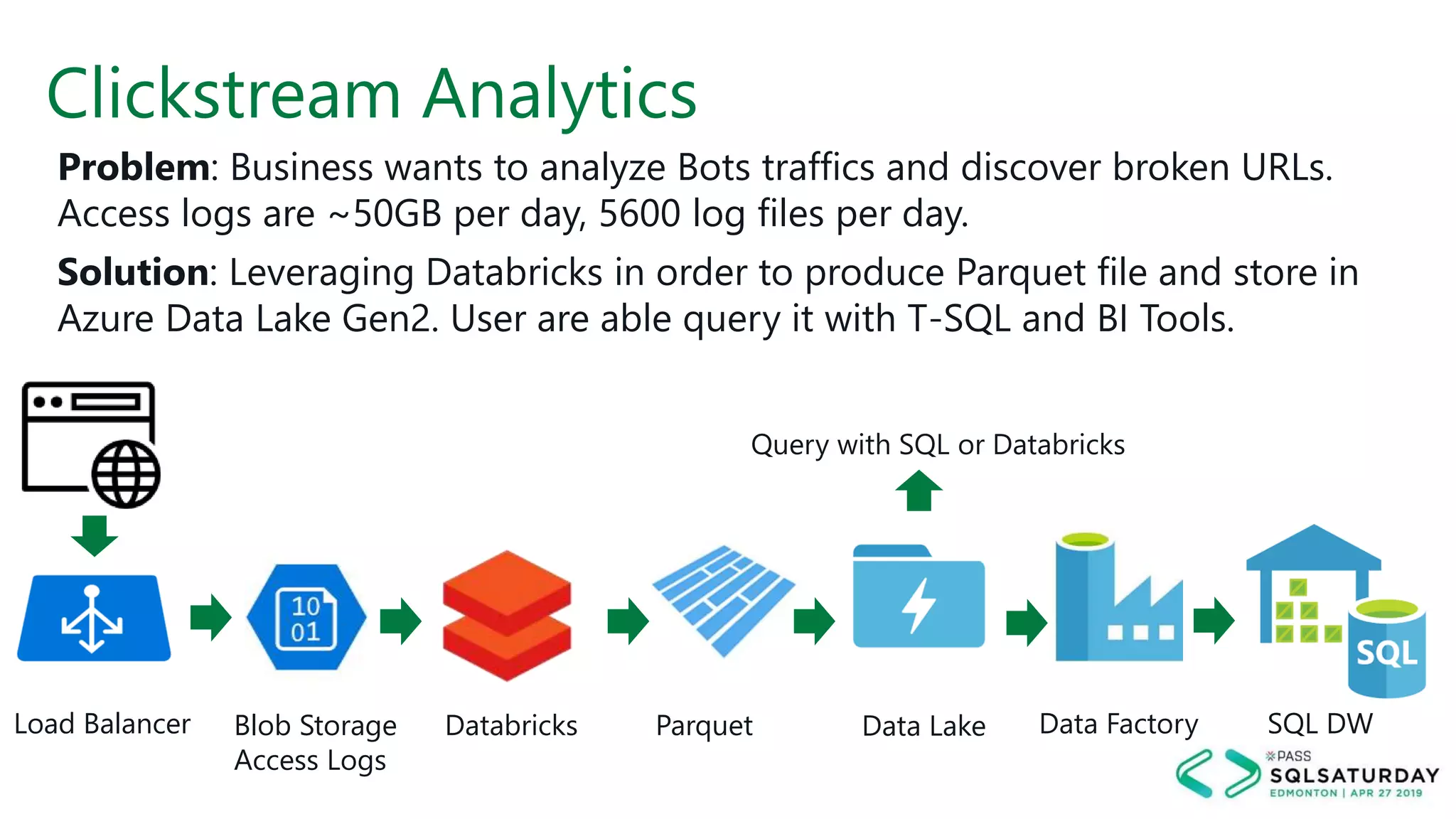
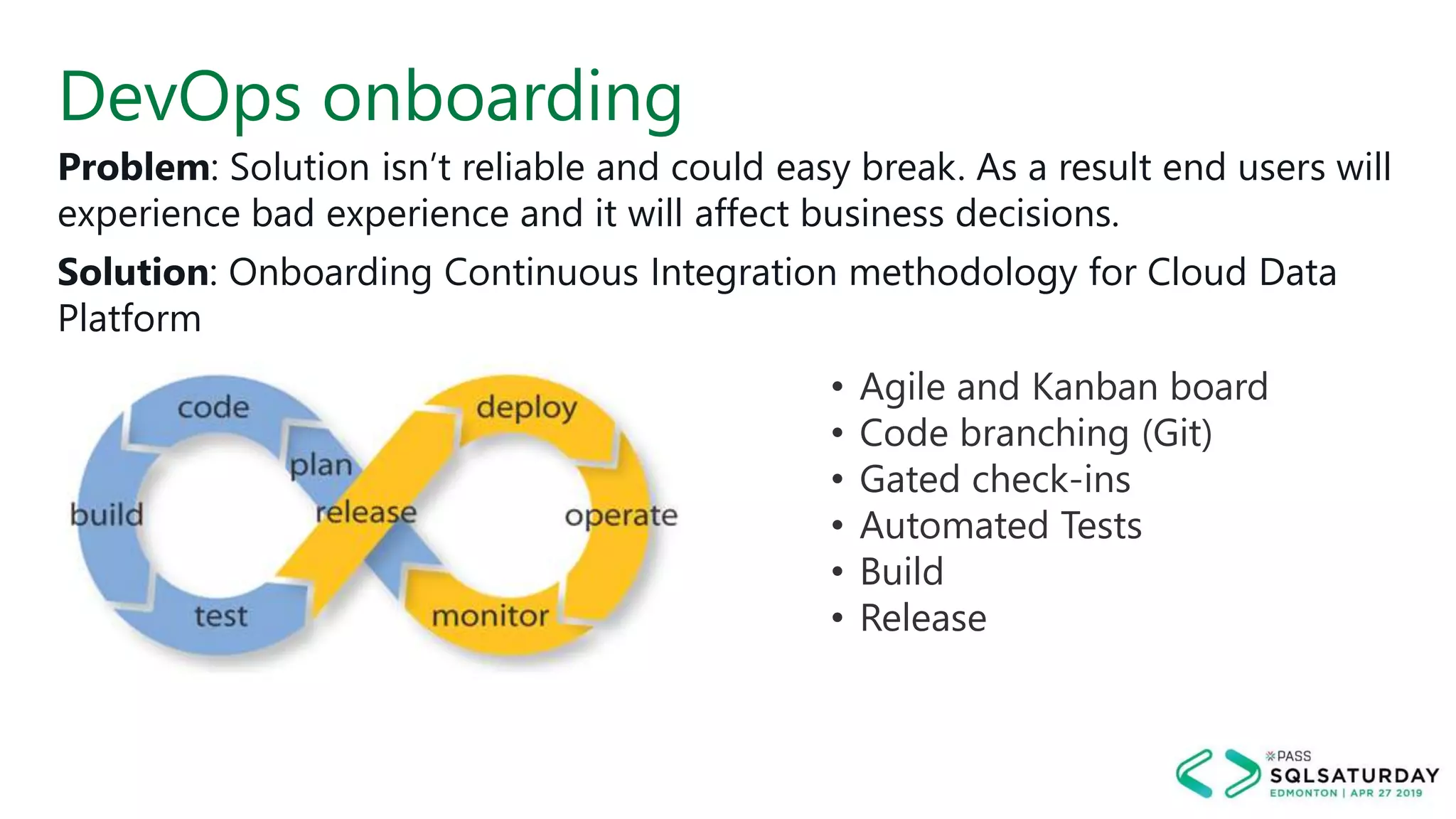
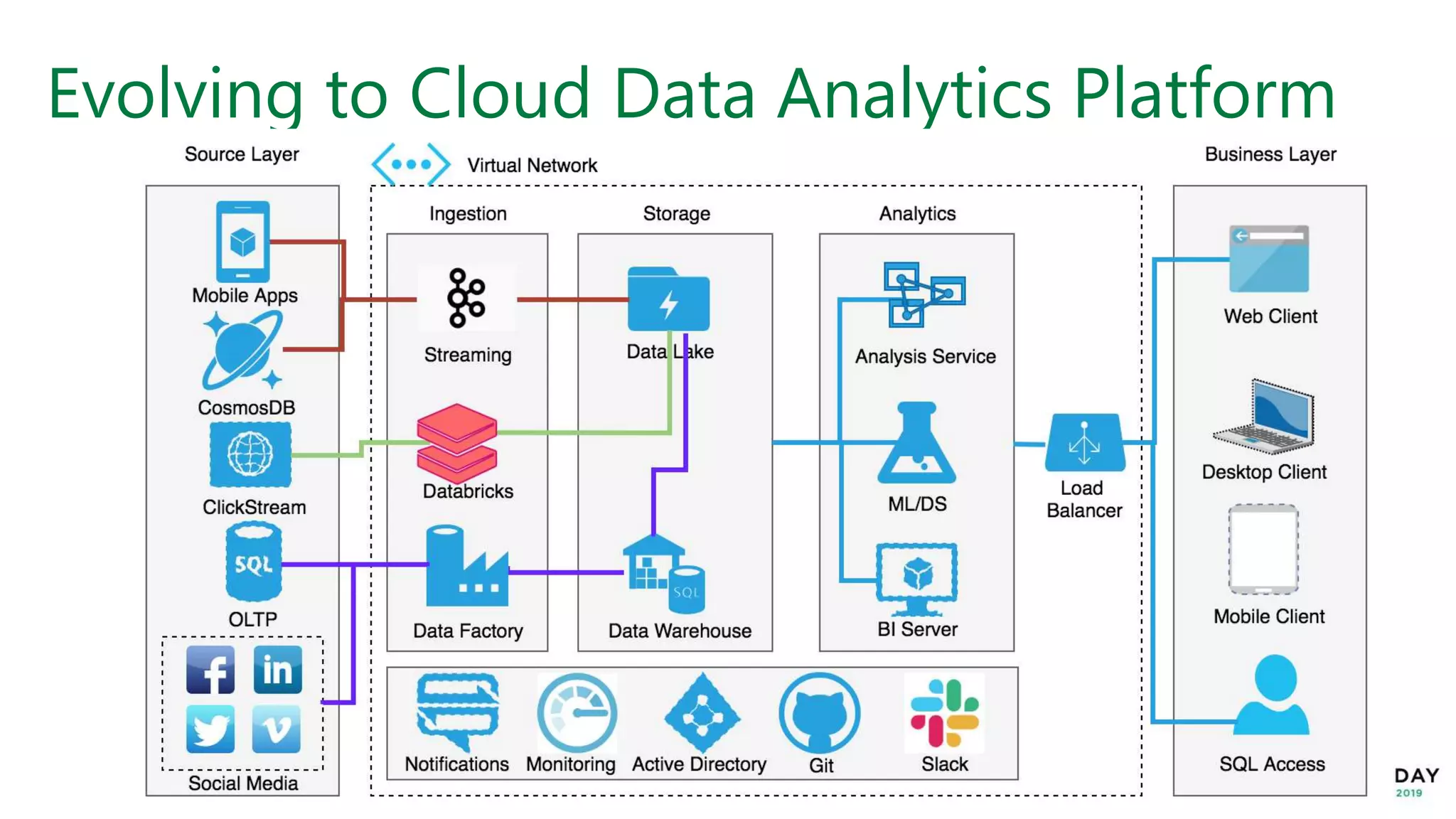
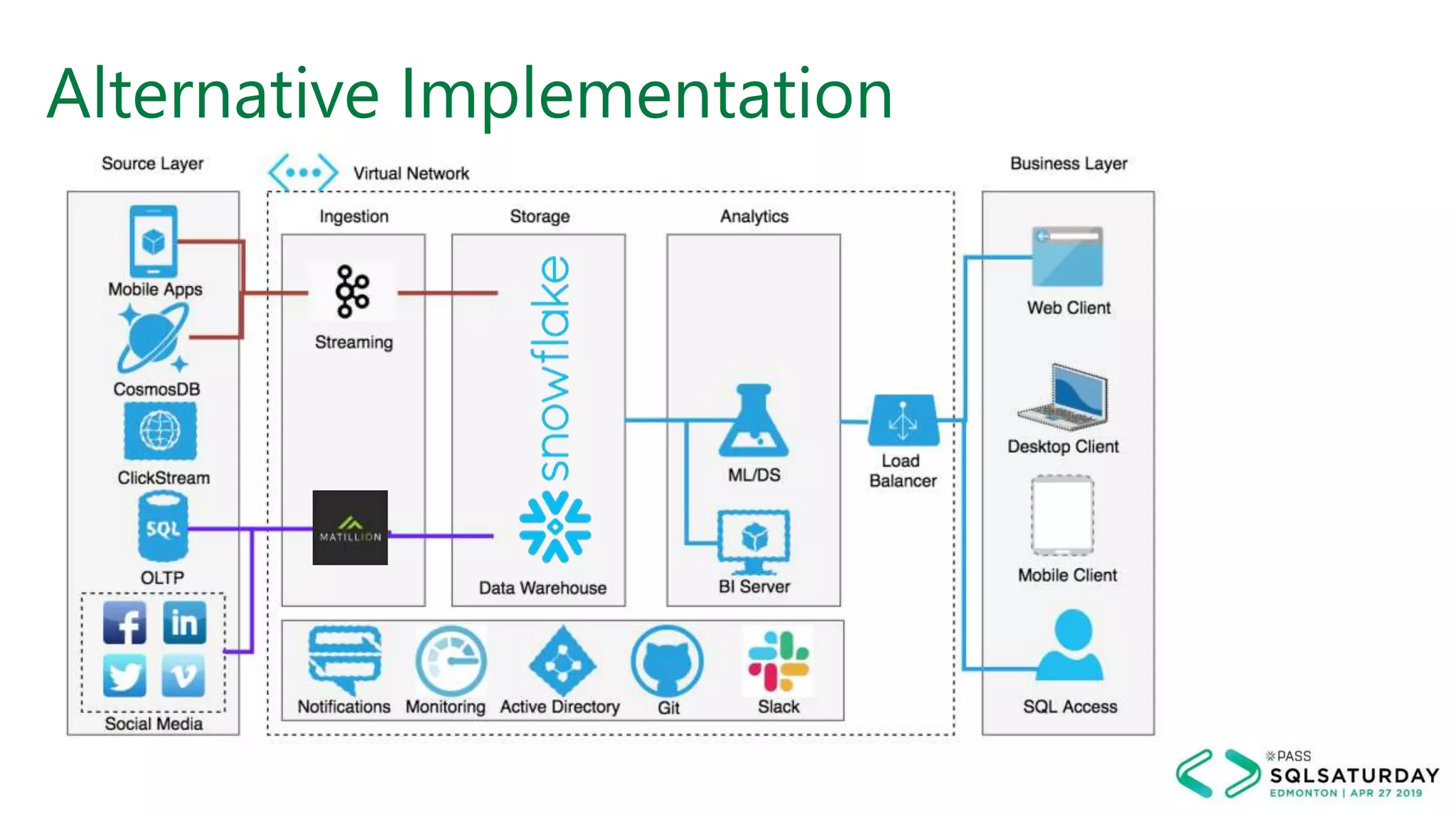
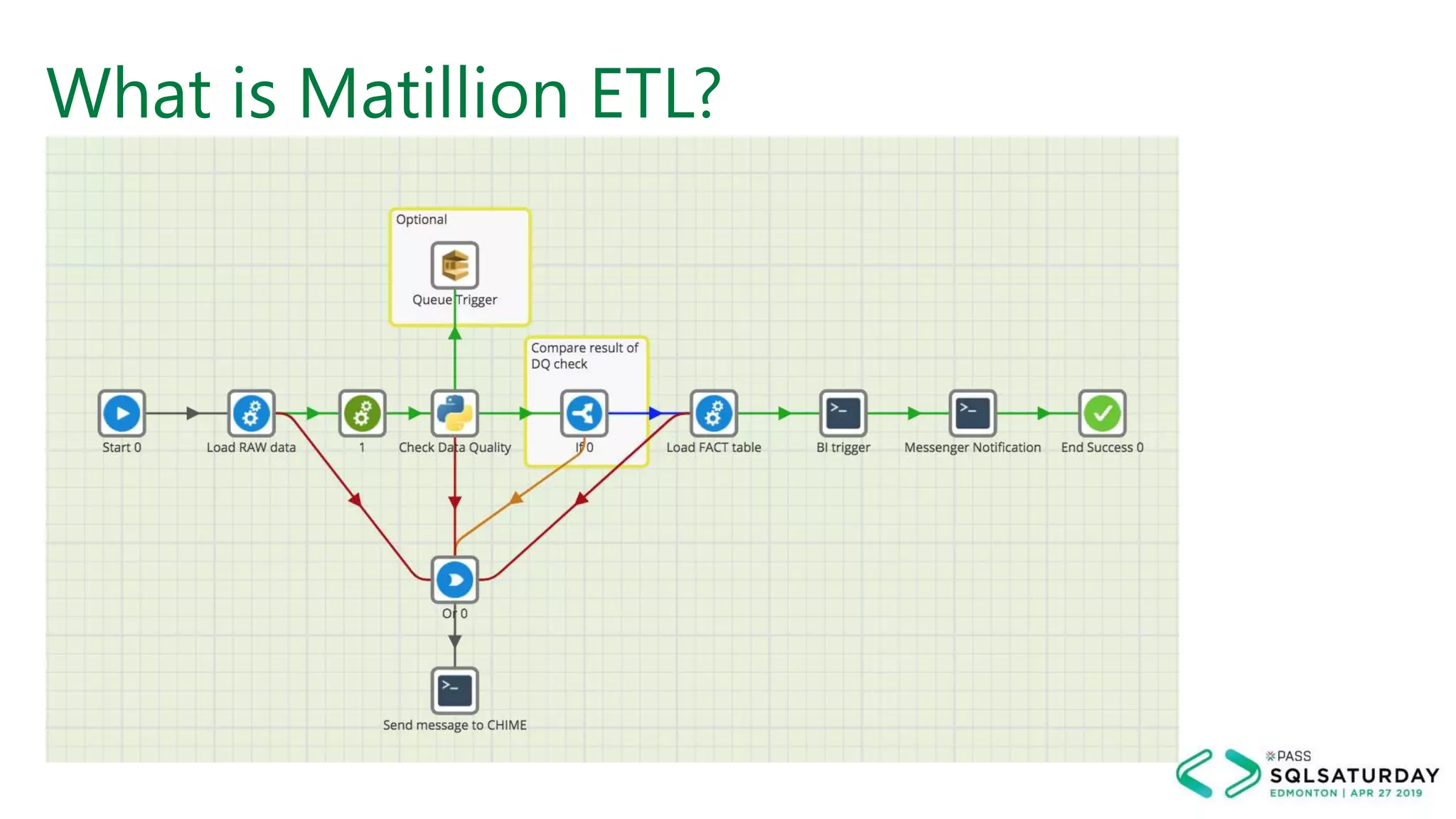
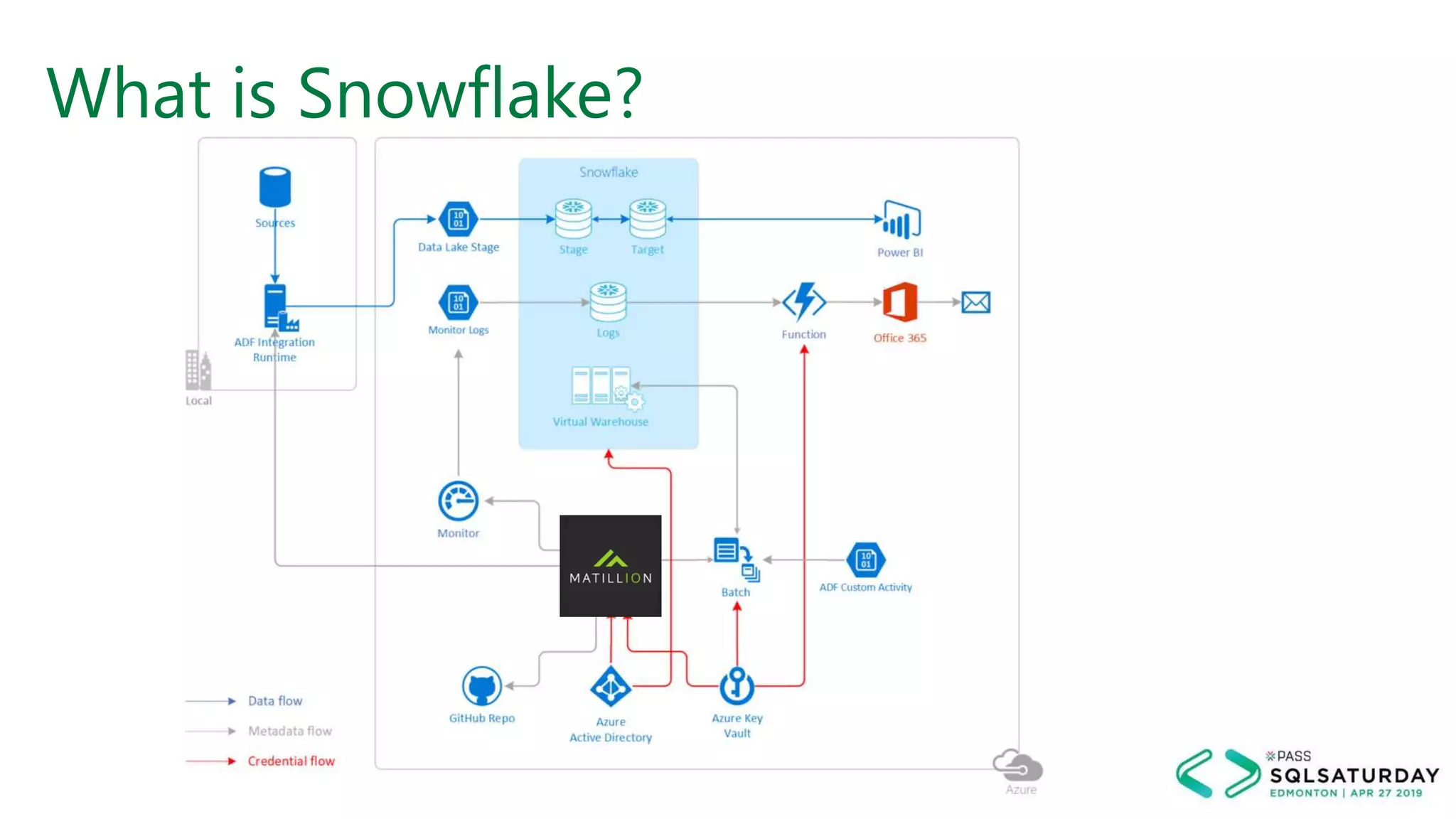
This document provides an overview of building a modern cloud analytics solution using Microsoft Azure. It discusses the role of analytics, a history of cloud computing, and a data warehouse modernization project. Key challenges covered include lack of notifications, logging, self-service BI, and integrating streaming data. The document proposes solutions to these challenges using Azure services like Data Factory, Kafka, Databricks, and SQL Data Warehouse. It also discusses alternative implementations using tools like Matillion ETL and Snowflake.