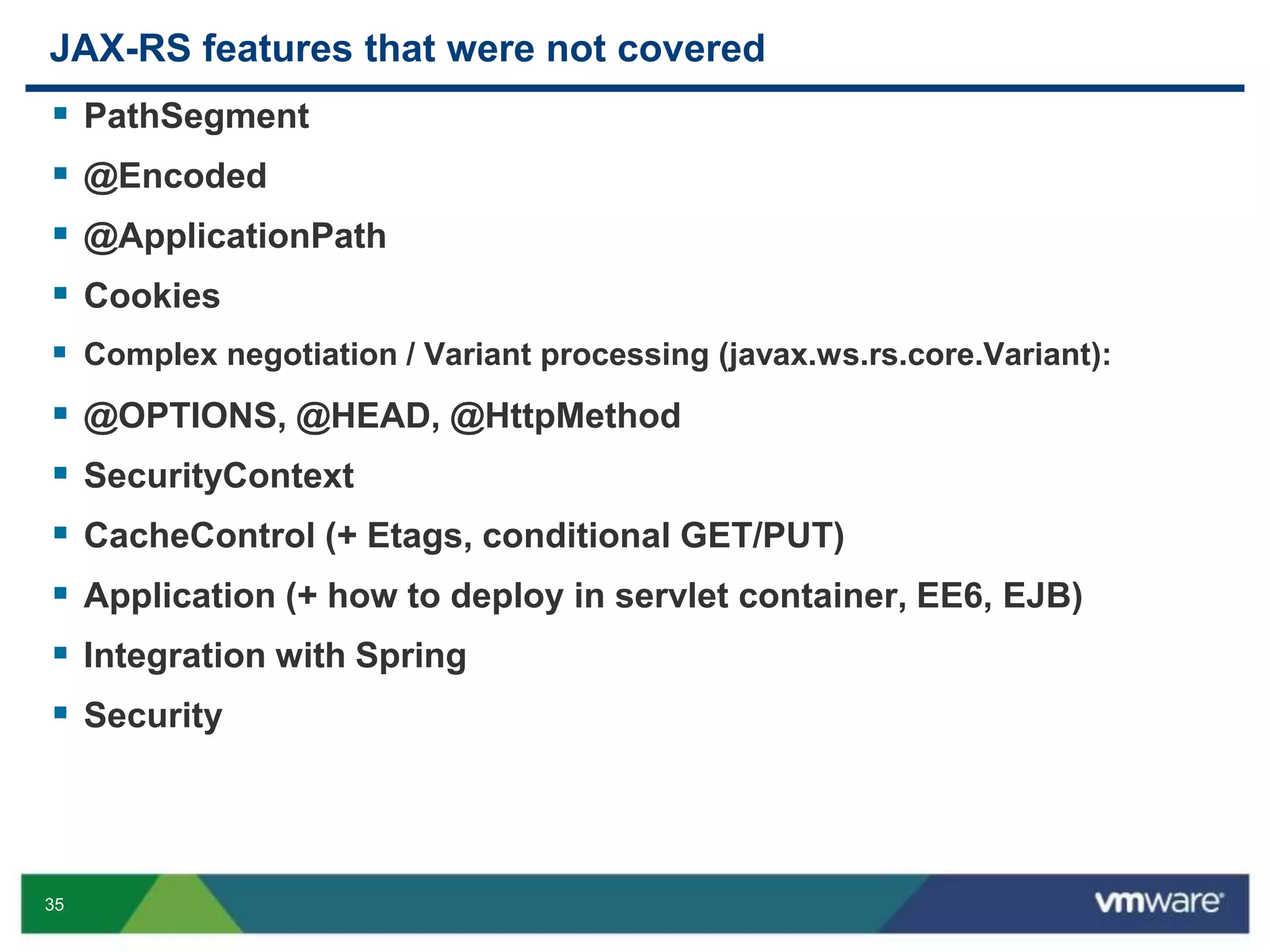
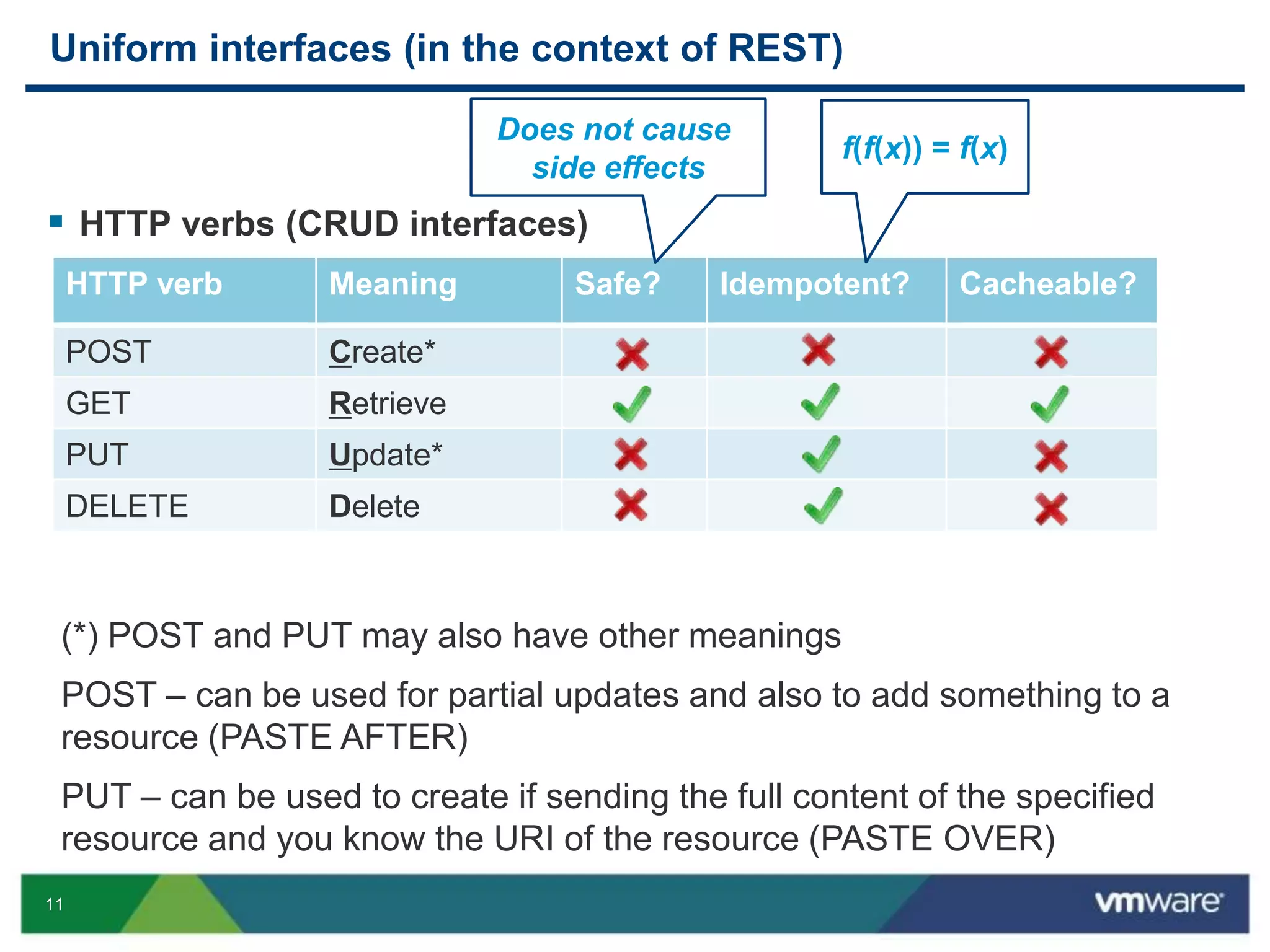
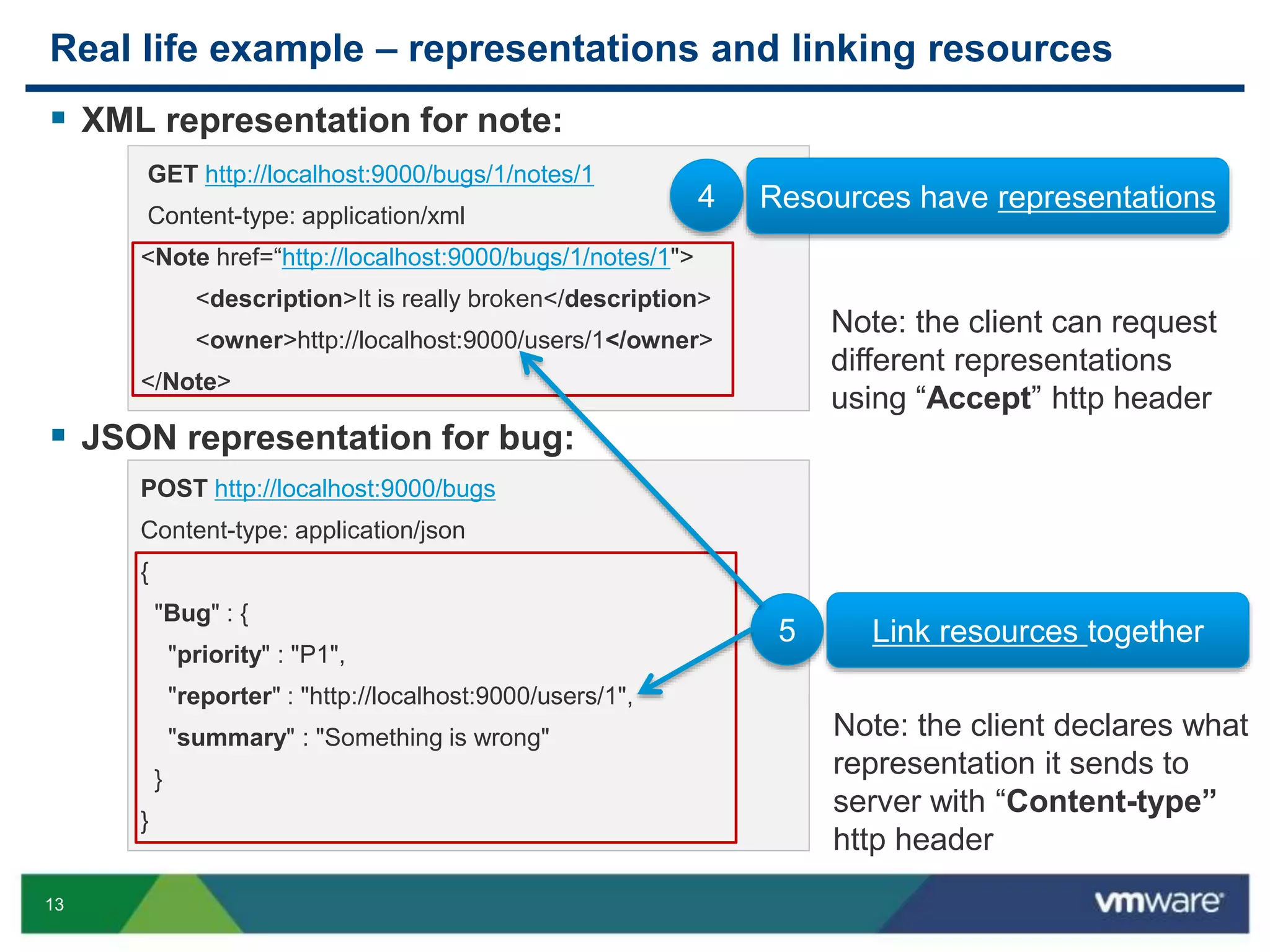
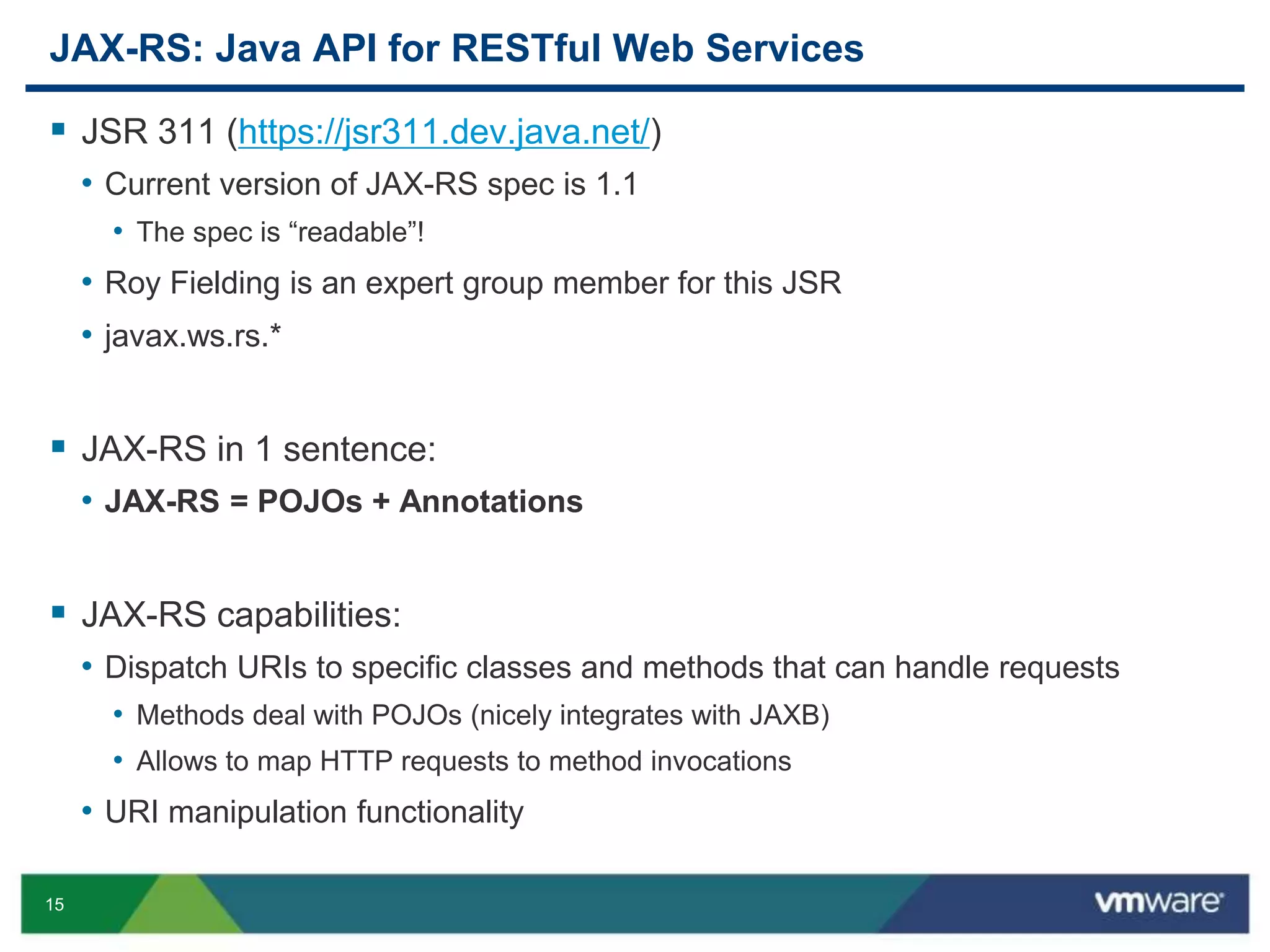
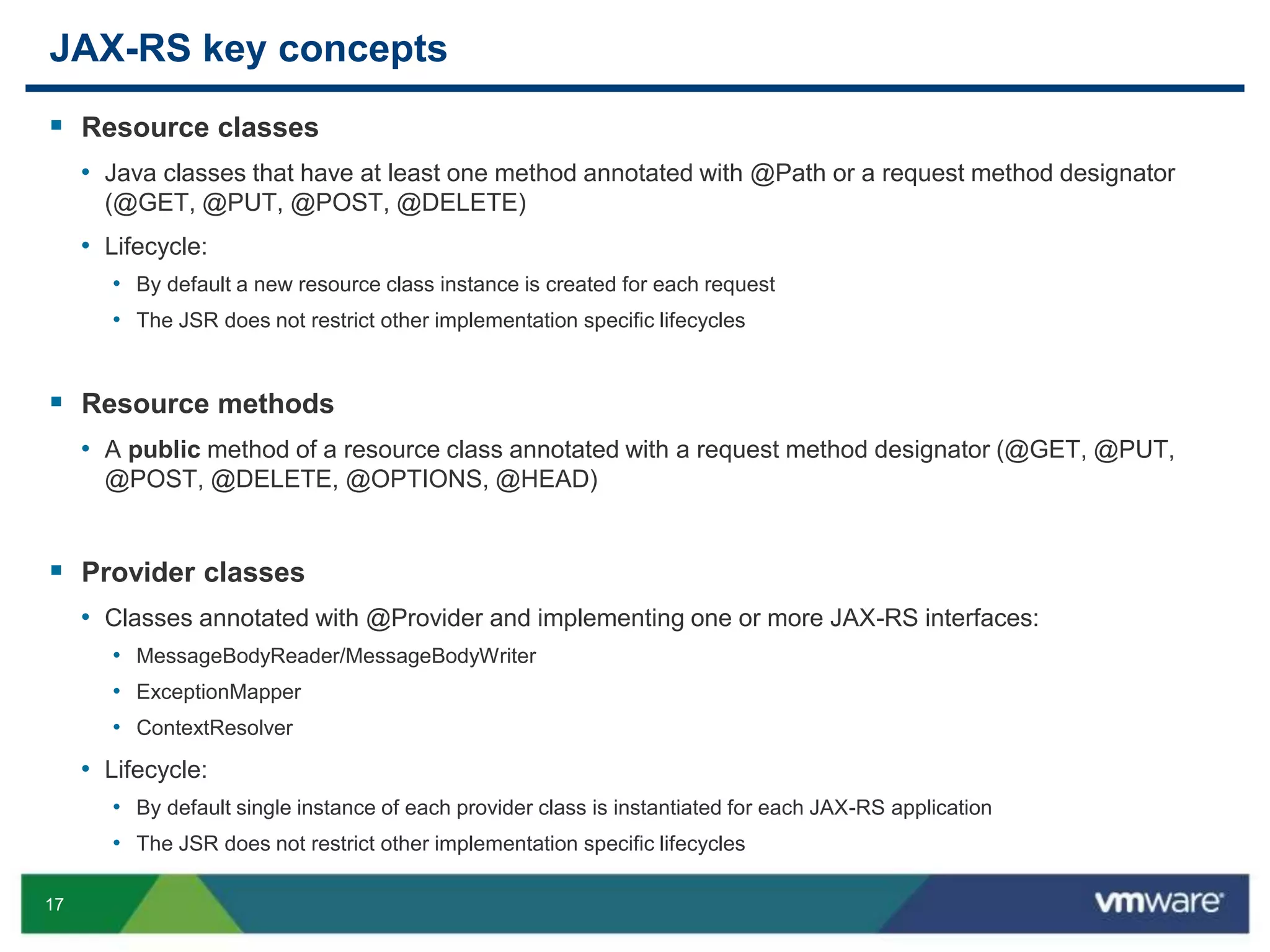
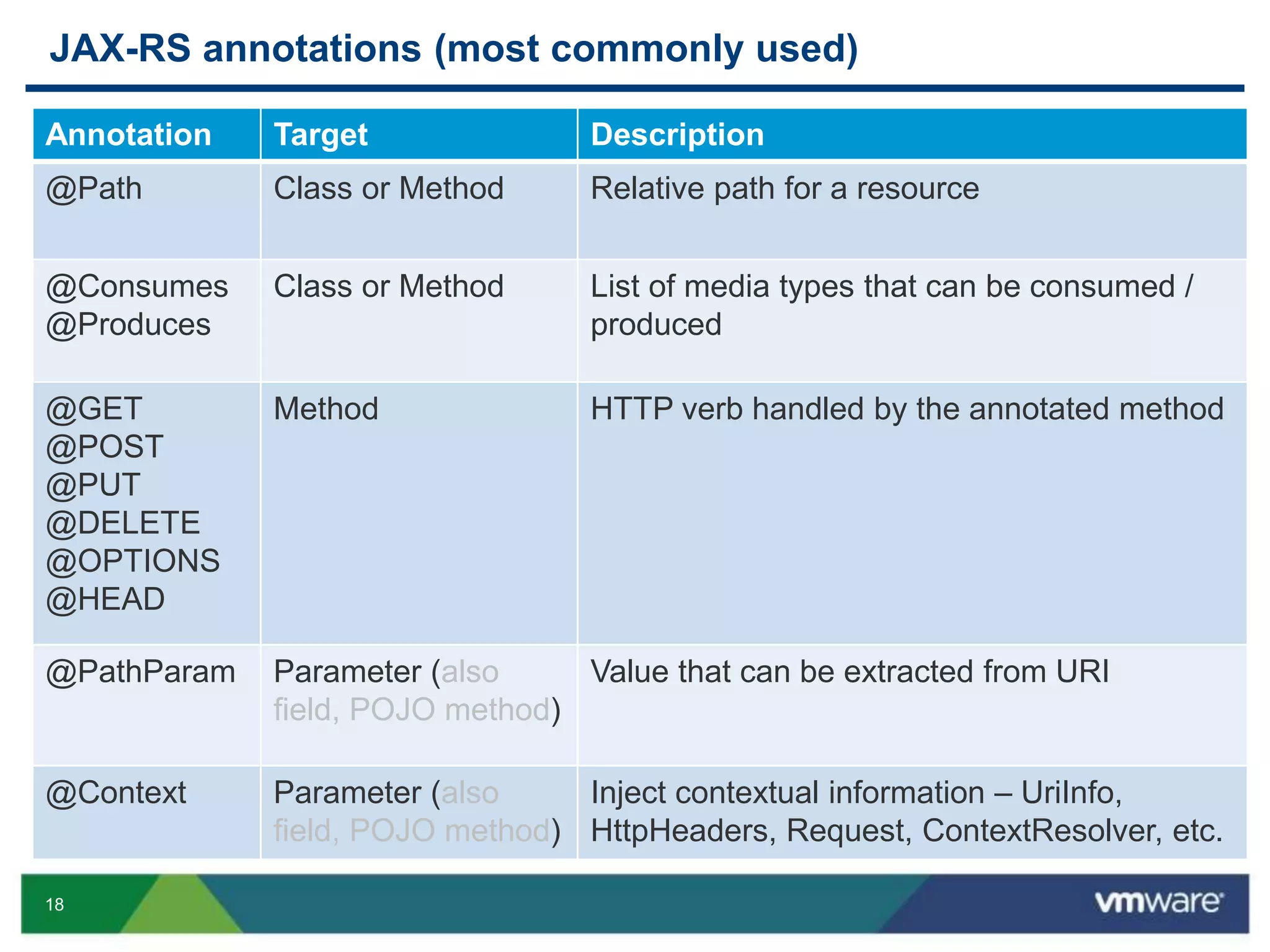
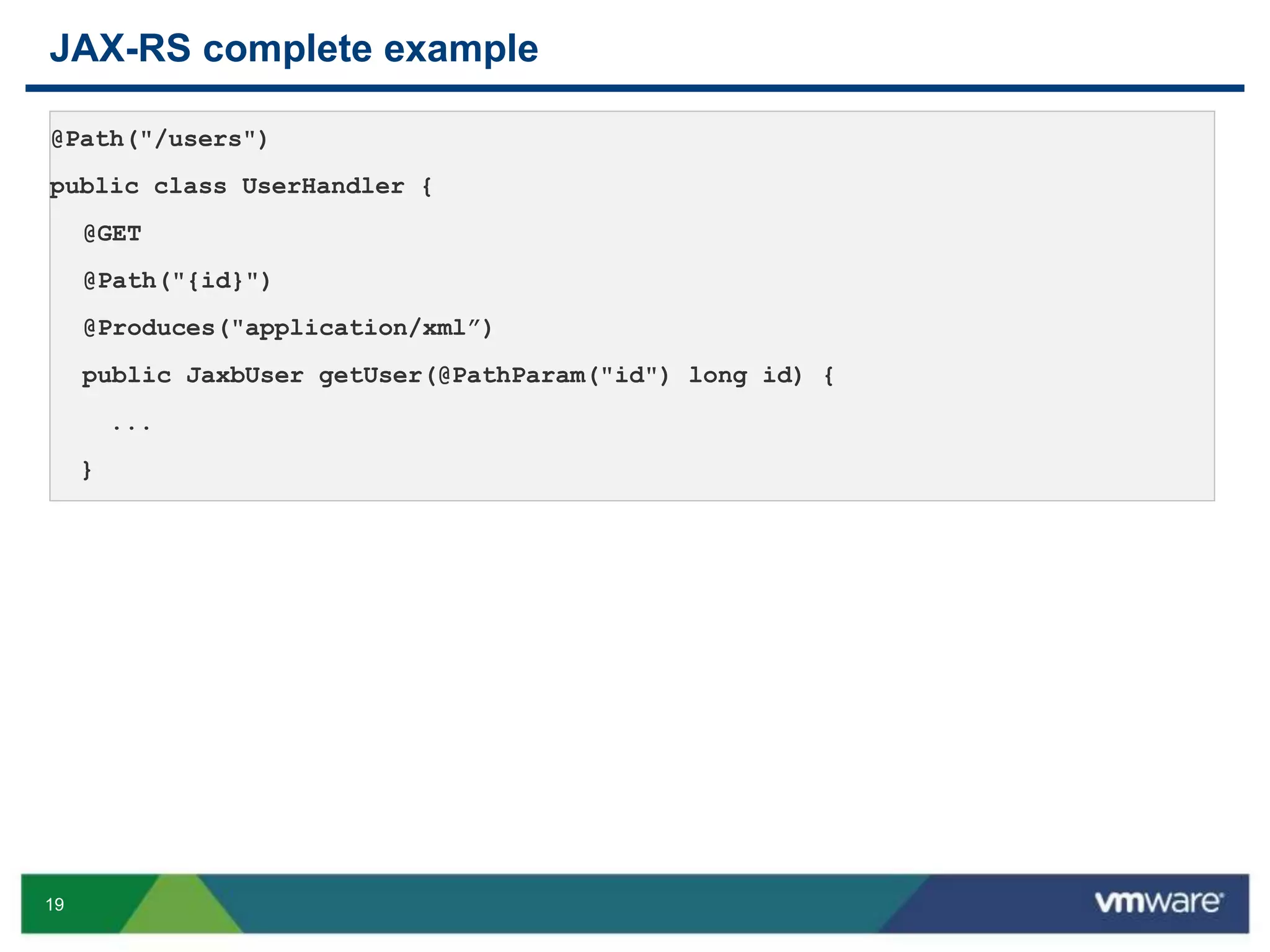
JAX-RS is a Java API that allows building RESTful web services using plain Java objects and annotations. Key concepts include resource classes that define endpoints, resource methods that map to HTTP methods, and annotations like @Path and @GET that define request mappings. The presentation provided an overview of REST principles and JAX-RS, demonstrated a sample application, and discussed advanced topics like regular expressions, parameters, and exception handling.





![12
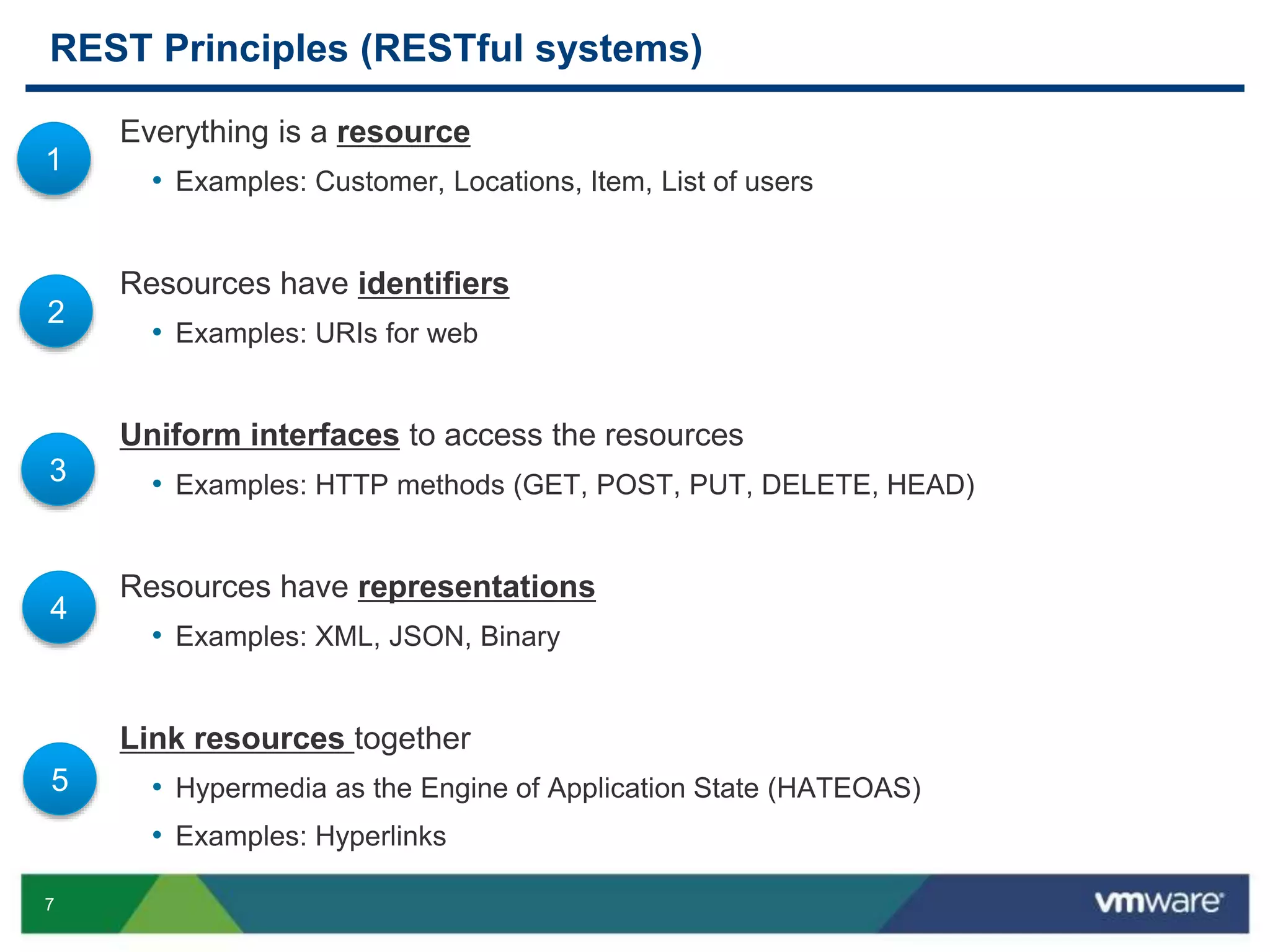
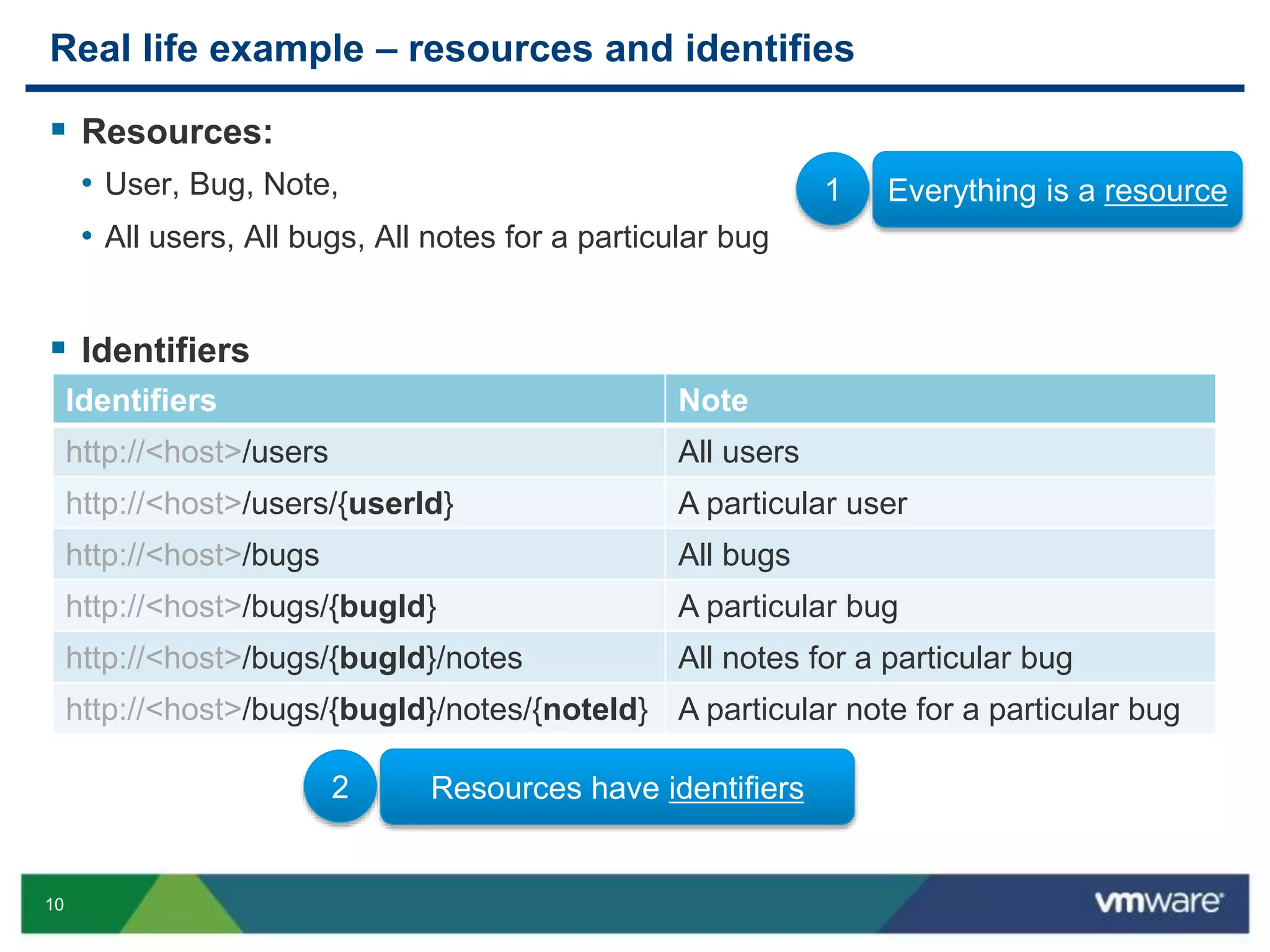
Real life example – uniform interfaces
Operation Description
GET http://<host>/users List all users
POST http://<host>/users Creates a new user
GET http://<host>/users/345 Retrieves a particular user
PUT http://<host>/users/345 Modifies a particular user
DELETE http://<host>/users/345 Deletes a particular user
Operation Description
GET http://<host>/bugs/234/notes List all notes for bug 234
POST http://<host>/bugs/234/notes Creates a new note for bug 234
[GET | PUT | DELETE] .../bugs/234/notes/34 [retrieves | modifies | deletes]
note 34 in bug 234
3 Uniform interfaces to access the resources](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingrestfulwebserviceswithjava-140625030251-phpapp01/75/Building-Restful-Web-Services-with-Java-11-2048.jpg)




![30
@Path and regular expression mappings
@Path(path-expression)
"{" variable-name [ ":" regular-expression ] "}“
Examples
• @Path("example2/{var:.+}") matches following:
• …/example2/a
• …/example2/a/b/c
• @Path("example3/{var:d+}") matches following:
• …/example3/345
• …/example3/23
• @Path(“example4/{name}-{id}”) matches following:
• …/example4/a-1
• …/example4/a----1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingrestfulwebserviceswithjava-140625030251-phpapp01/75/Building-Restful-Web-Services-with-Java-29-2048.jpg)
![31
@[Query|Header|Matrix|Cookie|Form]Param
@QueryParam
• For example …/query?sorted=true
@GET
@Path("query")
public String queryParamExample(@QueryParam(“sorted") String var) {
return var;
}
@MartixParam
• For example …/users;sorted=true
@HeaderParam
• For example “Date” header
@CookieParam / @FormParam
@DefaultValue – can be used with any @*Param to specify the default
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingrestfulwebserviceswithjava-140625030251-phpapp01/75/Building-Restful-Web-Services-with-Java-30-2048.jpg)
![33
MessageBodyReader
MessageBodyReader
MessageBodyWriter
package javax.ws.rs.ext
public interface MessageBodyReader<T> {
boolean isReadable(Class<?> type, Type genericType,
Annotation annotations[], MediaType mediaType);
T readFrom(Class<T> type, Type genericType,
Annotation annotations[], MediaType mediaType,
MultivaluedMap<String, String> httpHeaders,
InputStream entityStream) throws IOException, WebApplicationException;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingrestfulwebserviceswithjava-140625030251-phpapp01/75/Building-Restful-Web-Services-with-Java-32-2048.jpg)
![34
MessageBodyWriter
package javax.ws.rs.ext
public interface MessageBodyWriter<T> {
boolean isWriteable(Class<?> type, Type genericType,
Annotation annotations[], MediaType mediaType);
long getSize(T t, Class<?> type, Type genericType, Annotation annotations[],
MediaType mediaType);
void writeTo(T t, Class<?> type, Type genericType, Annotation annotations[],
MediaType mediaType,
MultivaluedMap<String, Object> httpHeaders,
OutputStream entityStream) throws IOException, WebApplicationException;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingrestfulwebserviceswithjava-140625030251-phpapp01/75/Building-Restful-Web-Services-with-Java-33-2048.jpg)