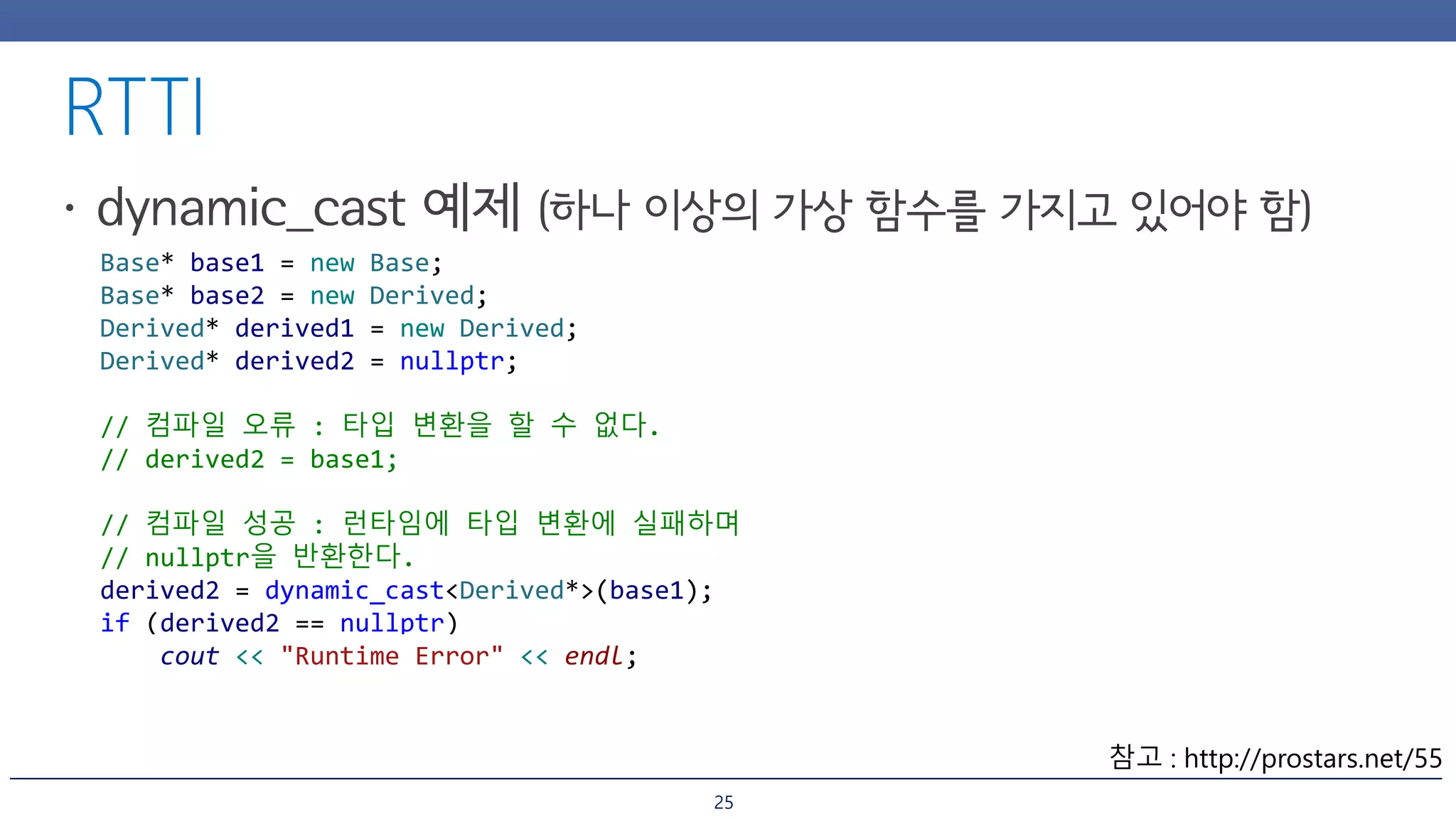
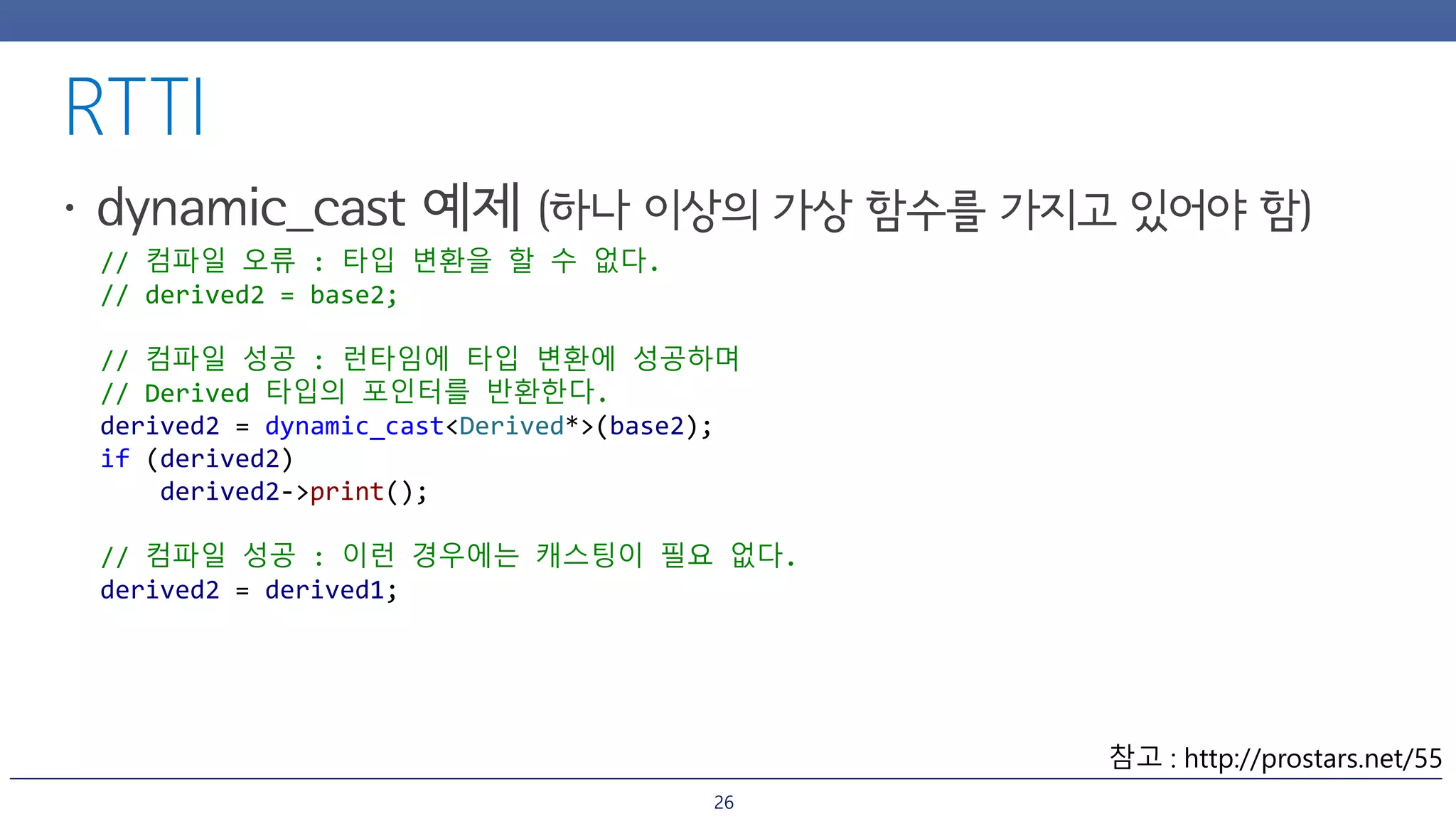
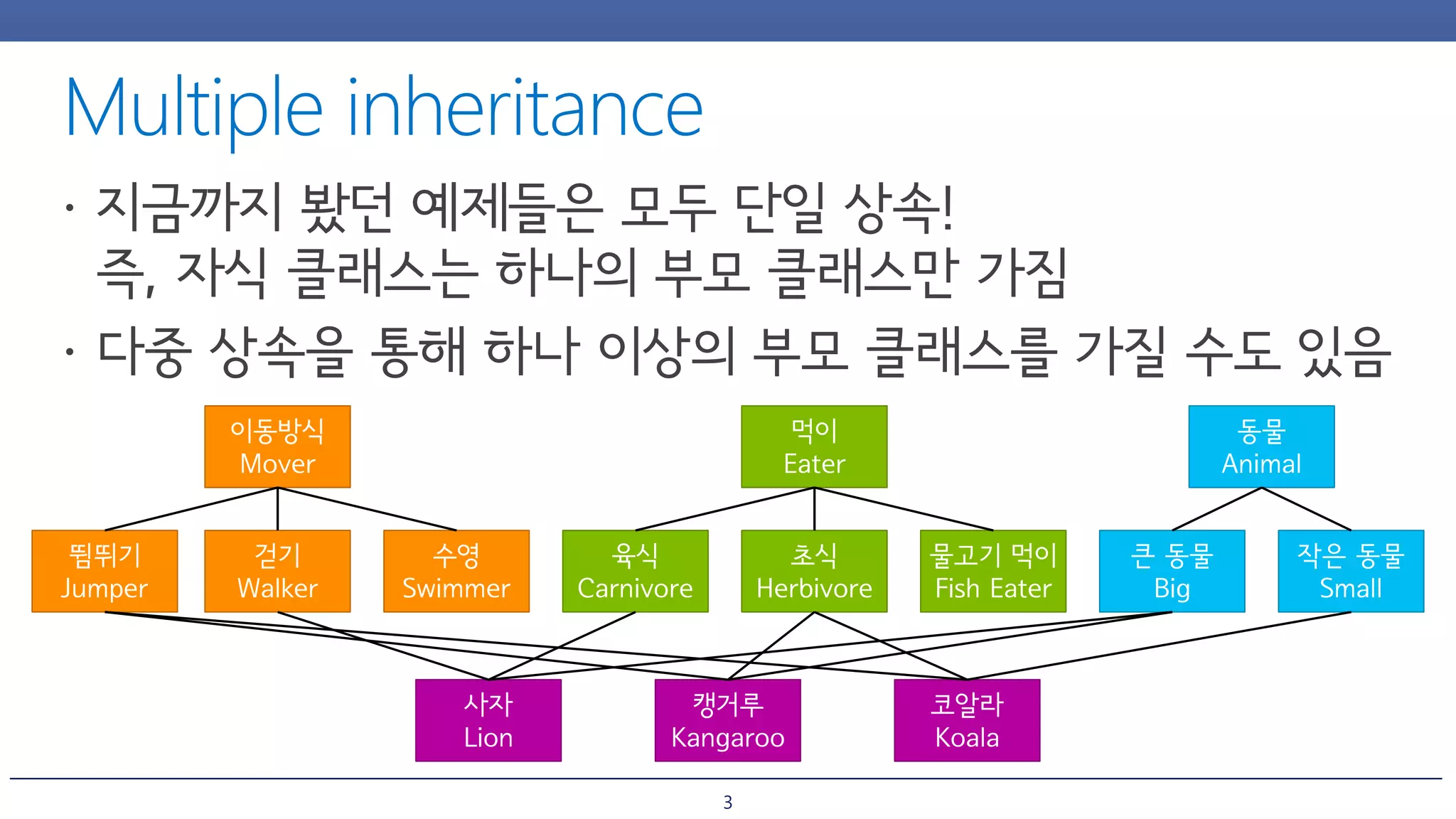
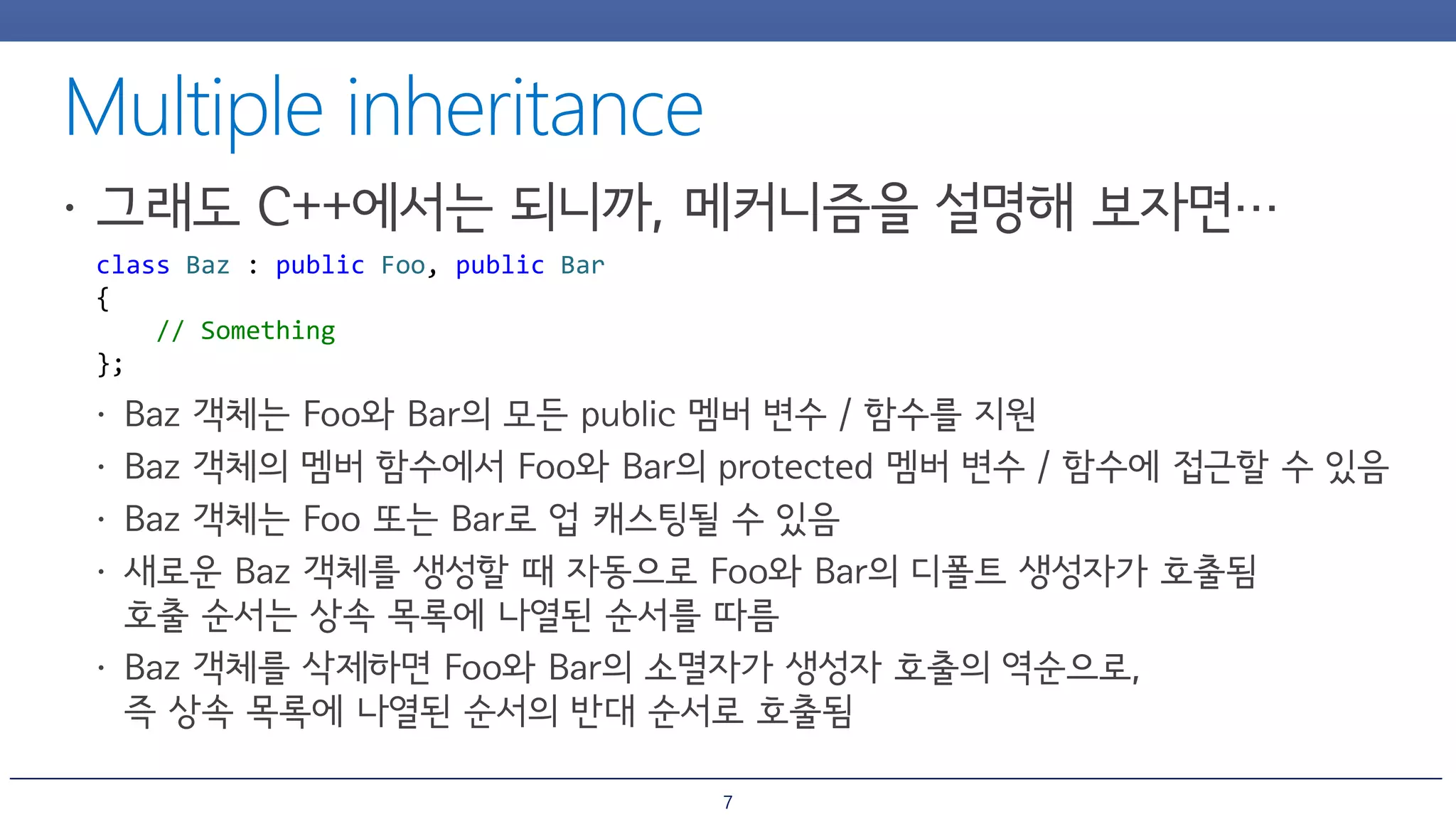
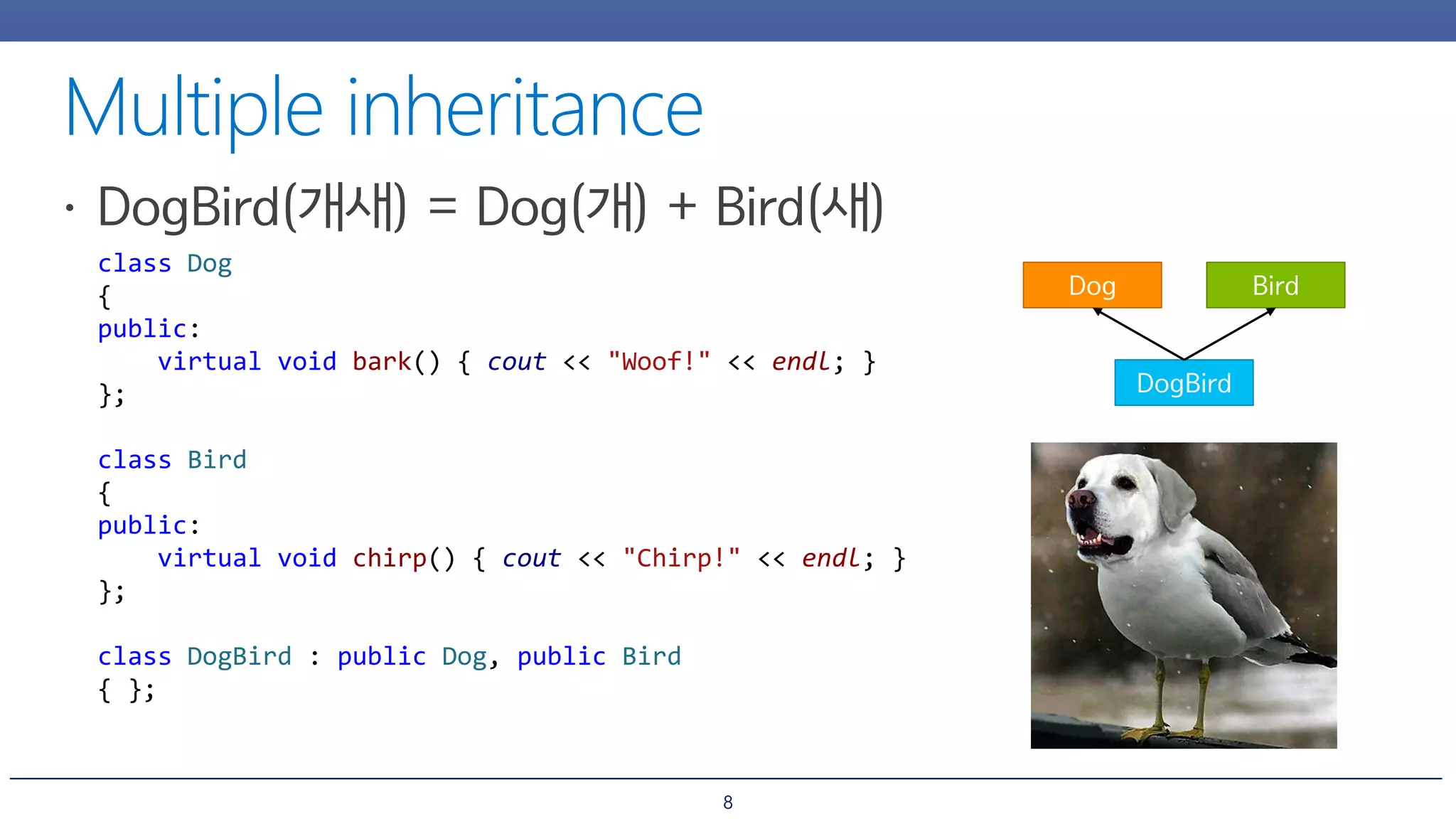
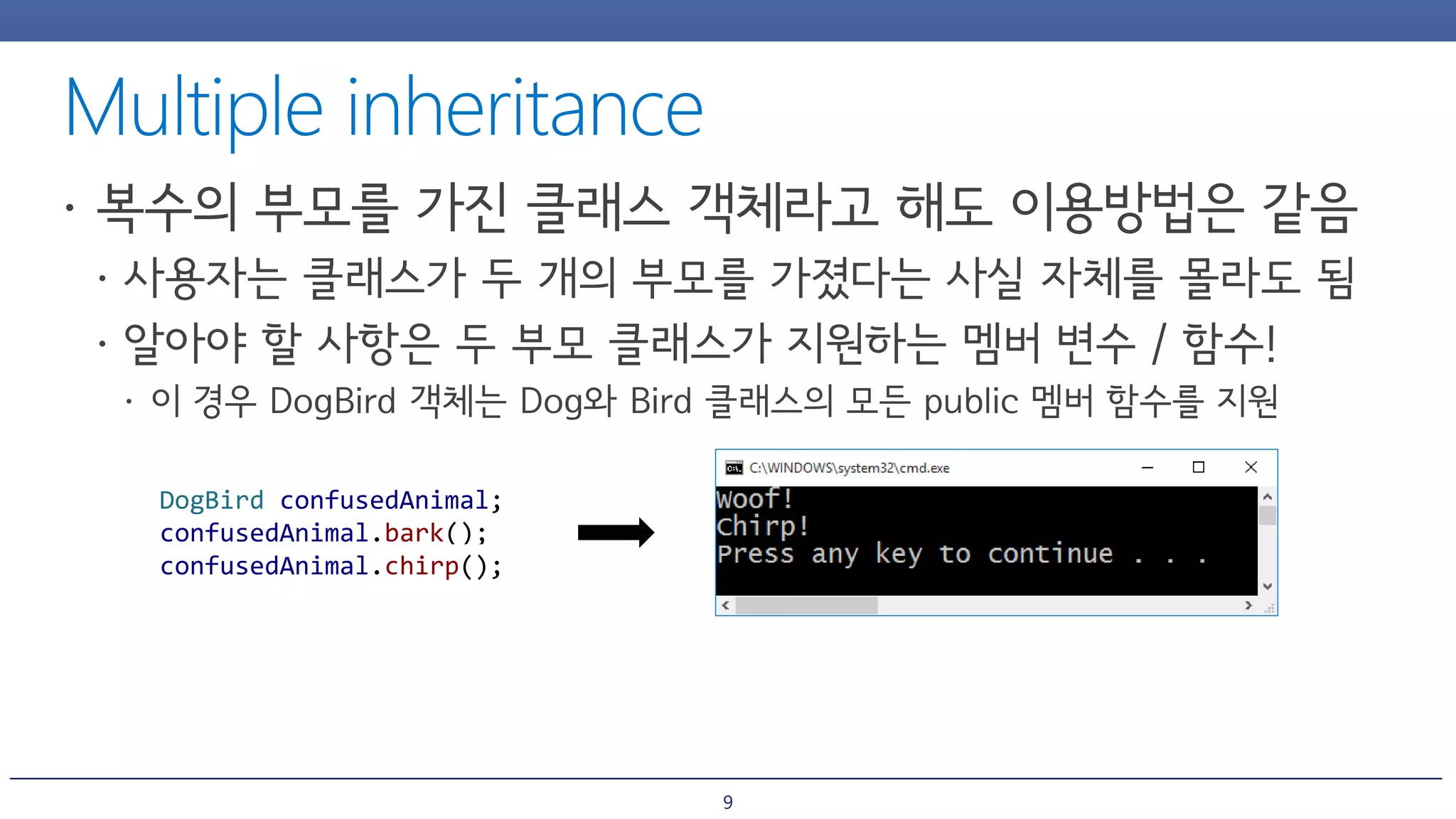
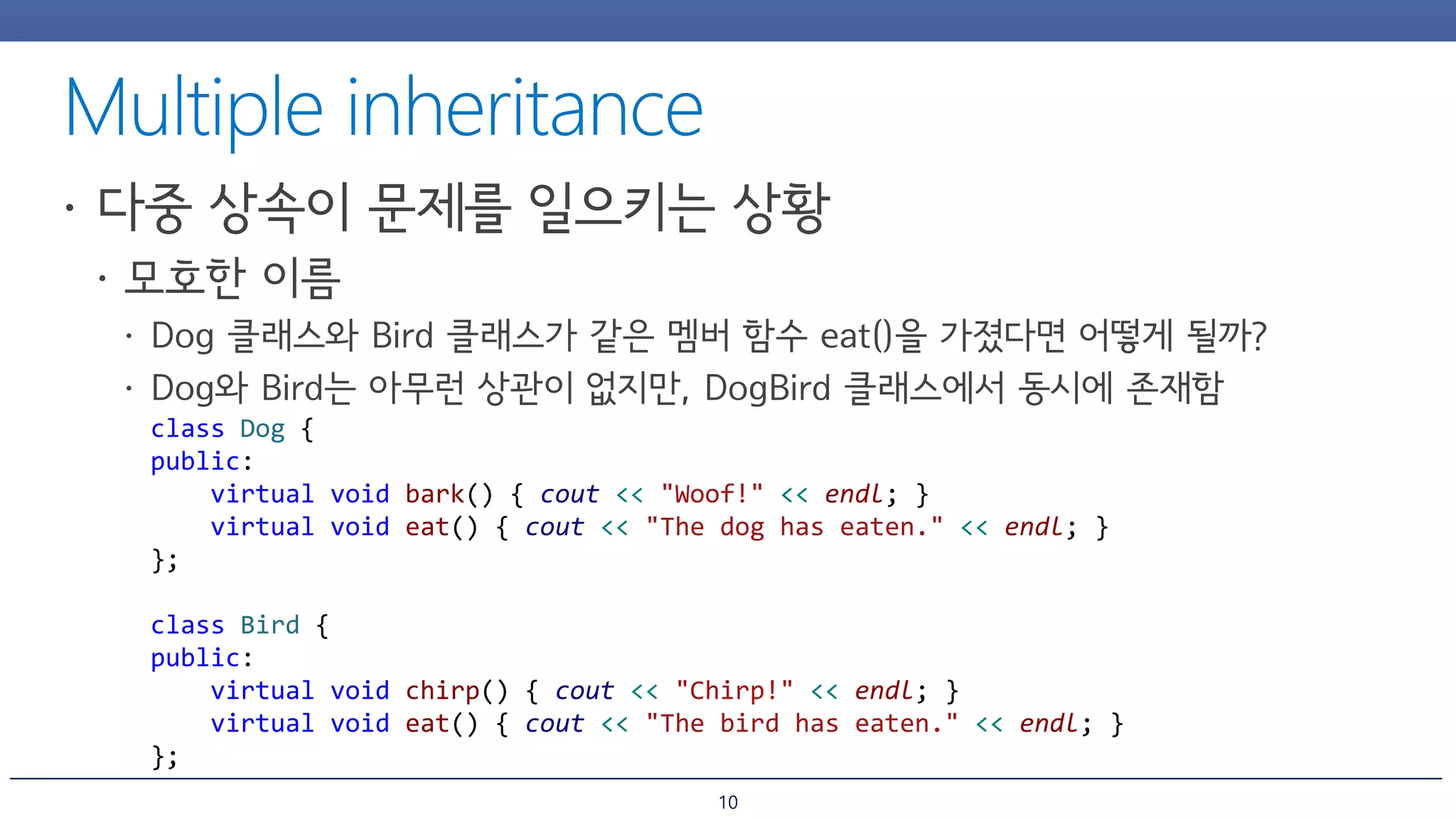
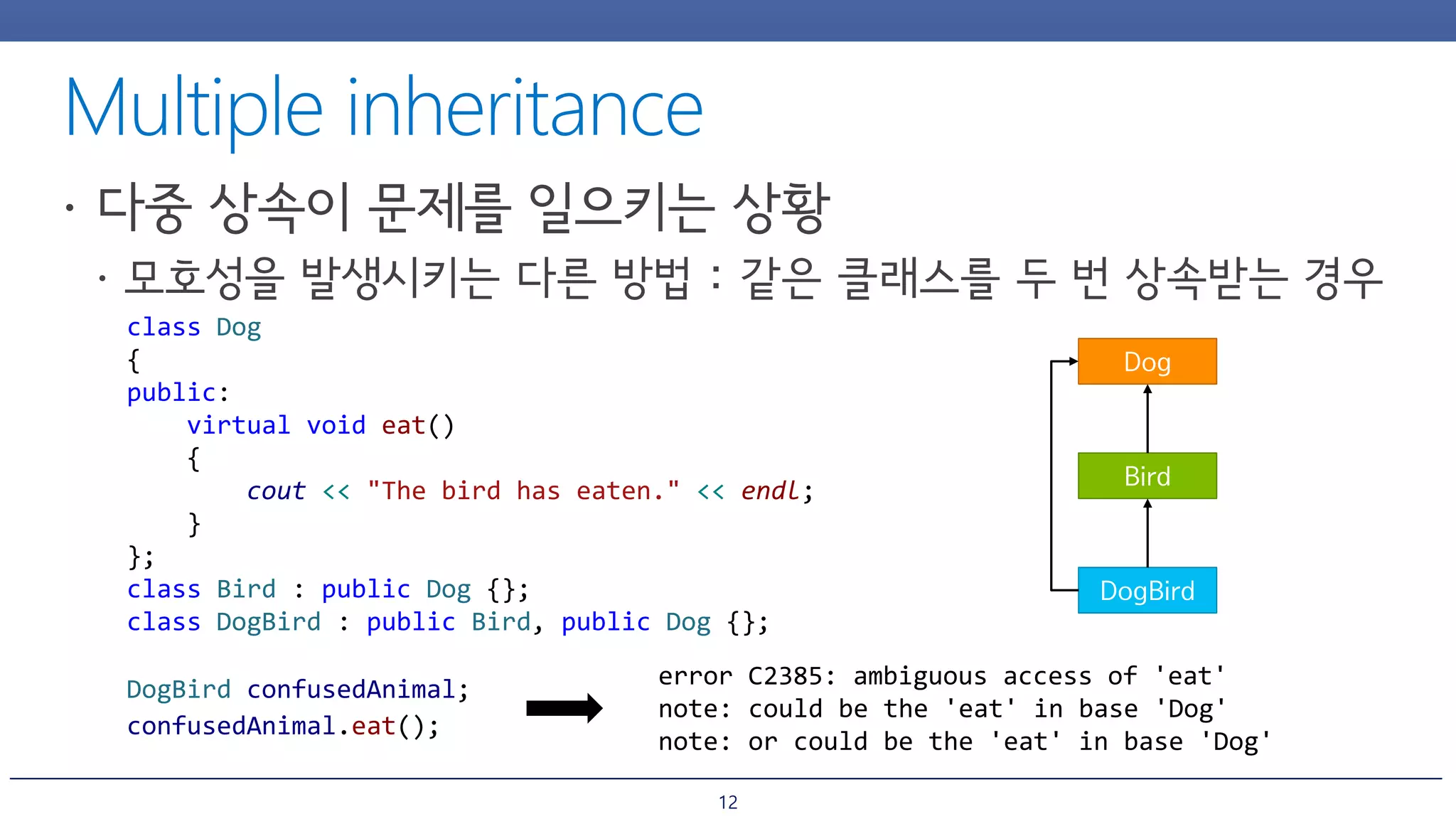
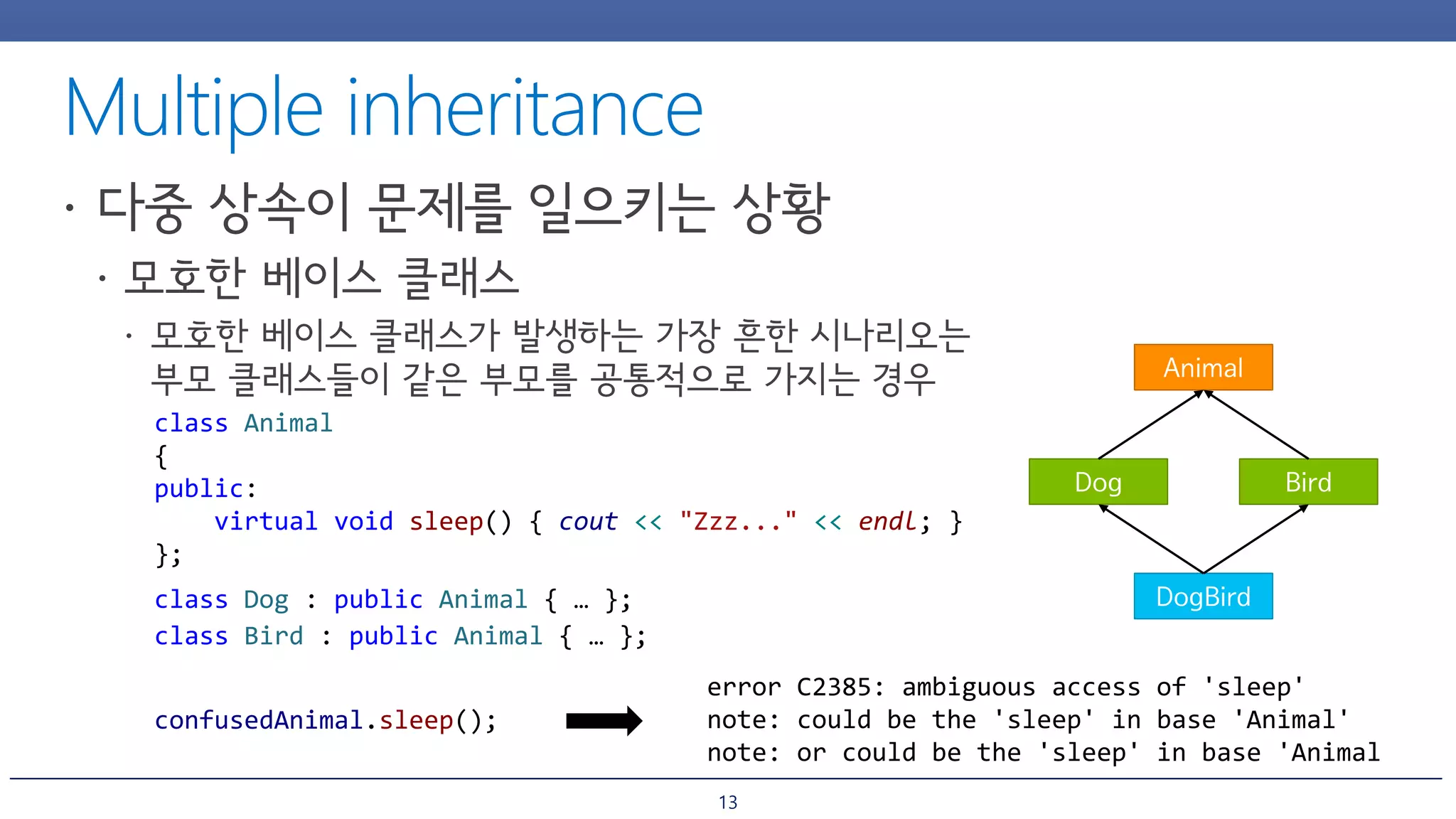
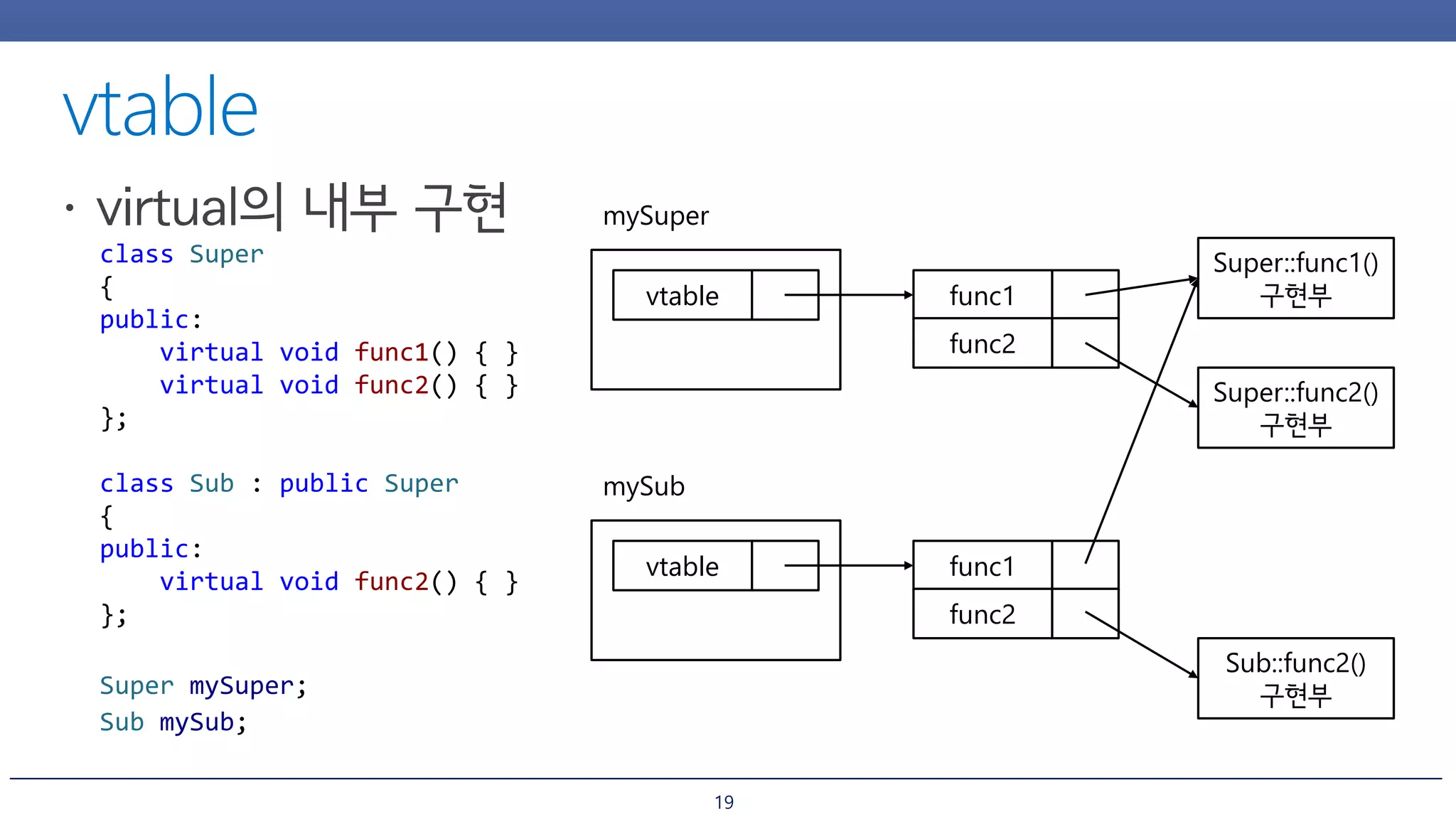
The document discusses inheritance and polymorphism in C++. It shows examples of defining base and derived classes, and using virtual functions to allow polymorphic behavior. It also covers issues that can arise from multiple inheritance like ambiguous function calls, and ways to resolve them like using virtual inheritance or explicitly calling the base class function. Dynamic casting is demonstrated to check an object's type at runtime.












![21
class Super {
public:
Super() { }
~Super() { }
};
class Sub : public Super {
private:
char* mString;
public:
Sub() { mString = new char[30]; }
~Sub() { delete[] mString; }
};
Super* ptr = new Sub(); // mString은 이 시점에 할당됨
delete ptr; // ~Super가 호출되었지만
// virtual이 아니기 때문에
// ~Sub는 호출되지 않음](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-12thstudy-150708143416-lva1-app6892/75/C-Programming-12th-Study-21-2048.jpg)