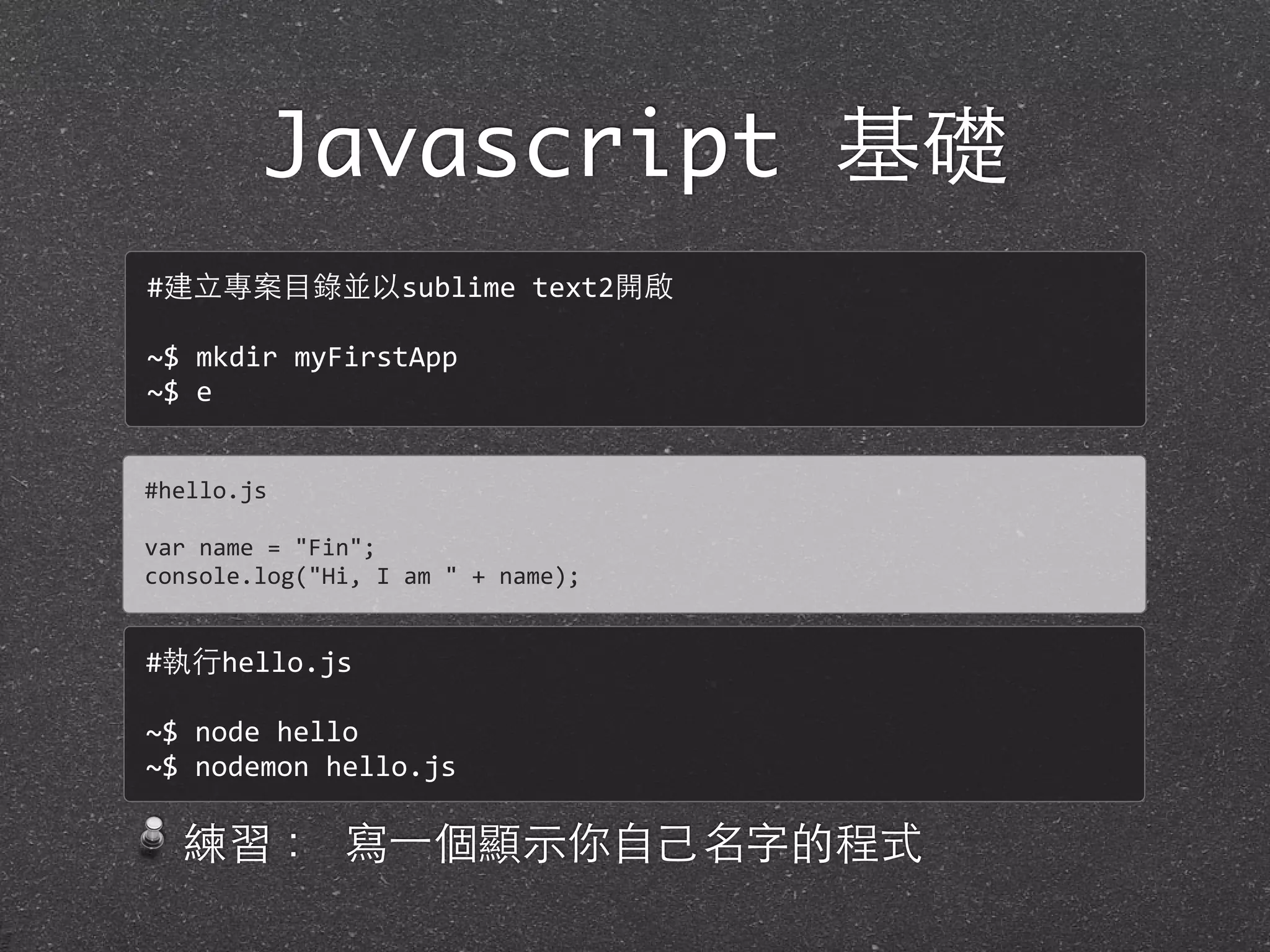
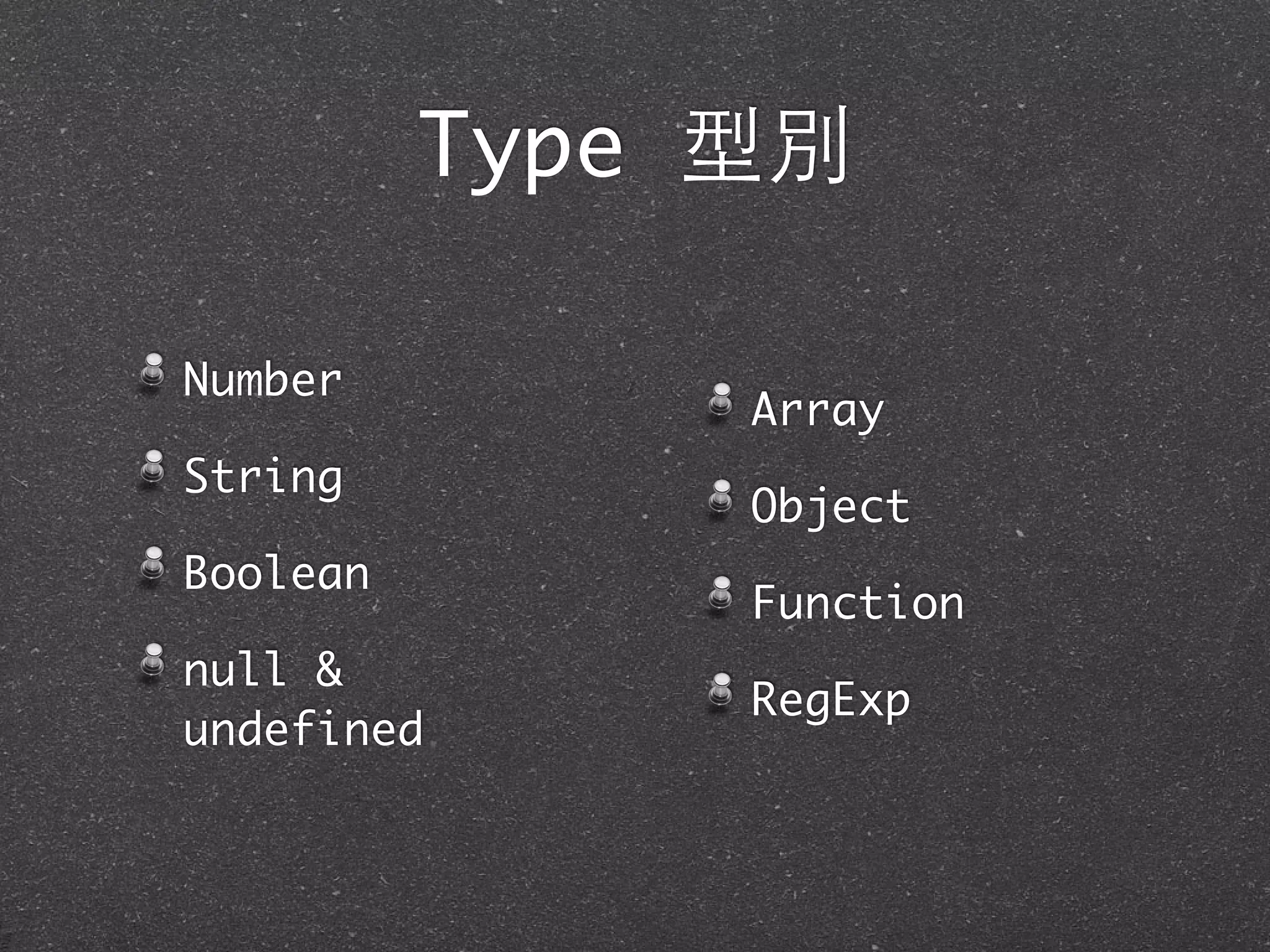
This document provides an introduction to JavaScript basics including data types, variables, operators, flow control, objects, arrays, functions, regular expressions and classes/modules. It begins with an overview of JavaScript and its relationship to ECMAScript. It then covers JavaScript syntax, variables, data types like numbers, strings, Booleans, null/undefined, arrays and objects. Methods for manipulating strings and numbers are demonstrated. The document concludes with examples and exercises for practicing JavaScript fundamentals.












![String 範例
var
s
=
"hello,
world"
//
Start
with
some
text.
s.charAt(0)
//
=>
"h":
the
first
character.
s.charAt(s.length-‐1)
//
=>
"d":
the
last
character.
s.substring(1,4)
//
=>
"ell":
the
2nd,
3rd
and
4th
characters.
s.slice(1,4)
//
=>
"ell":
same
thing
s.slice(-‐3)
//
=>
"rld":
last
3
characters
s.indexOf("l")
//
=>
2:
position
of
first
letter
l.
s.lastIndexOf("l")
//
=>
10:
position
of
last
letter
l.
s.indexOf("l",
3)
//
=>
3:
position
of
first
"l"
at
or
after
3
s.split(",
")
//
=>
["hello",
"world"]
split
into
substrings
s.replace("h",
"H")
//
=>
"Hello,
world":
replaces
all
instances
s.toUpperCase()
//
=>
"HELLO,
WORLD"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-15-2048.jpg)
![ECMAScript 5中,可以把字串當成陣列來操作
String 範例
(ECMAScript 5)
s
=
"hello,
world";
s[0]
//
=>
"h"
s[s.length-‐1]
//
=>
"d"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-16-2048.jpg)


![Boolean
var
myName
=
'Fin';
var
hisName
=
'Ben';
var
equal
=
myName
===
hisName;
console.log("Is
"
+
myName
+
"
and
"
+
hisName
+
"
equal?
"
+
equal);
var
emptyArray
=
[];
var
emptyObject
=
{};
var
emptyString
=
"";
console.log(!!emptyArray,
!!emptyObject,
!!emptyString);
雙重否定轉換為boolean](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-19-2048.jpg)




![Variable Scope
變數的尋找是由內⽽而外
scope
=
"global";
//
編譯器會⾃自動宣告變數
function
checkscope()
{
scope
=
"local";
//
local端沒有此變數,往上⼀一層找
myscope
=
"local";
//
沒有宣告的話會變成全域變數
var
myLocalScope
=
"local";
return
[scope,
myscope];
//
Return
two
values.
}
console.log(myLocalScope);
//這是checkscope的local變數,看不到
console.log(scope,
myscope);
//因為兩個都是全域變數,可以直接取值](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-24-2048.jpg)


![Expression 運算式
能夠讓直譯器理解並執⾏行的程式⽚片段
//primary
expression
"hello"
|
1.23
/pattern/
true
|
false
|
null
|
this
i
|
undefined
//object
and
array
var
ary
=
[1,2,3];
var
obj
=
{x:1,
y:2};
//function
var
square
=
function(x)
{
return
x*x;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-27-2048.jpg)
![Expression 運算式
//property
access
var
o
=
{x:1,
y:{z:3}};
var
a
=
[o,4,[5,6]];
o.y;
a[0].x;
//invocation
expression
f(0);
Math.max(x,y,z);
//object
creation
new
Date();
new
Point(2,3);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-28-2048.jpg)


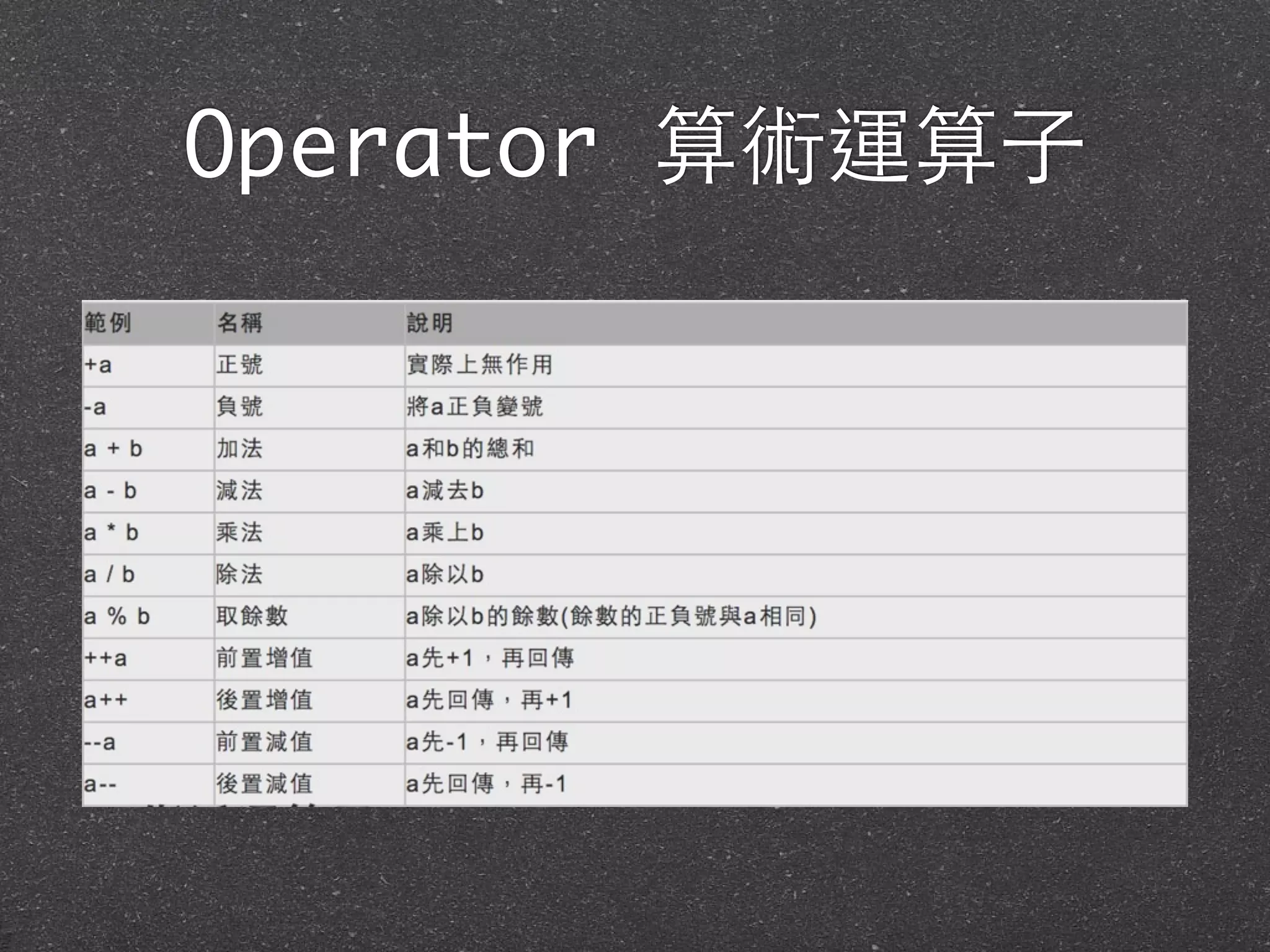
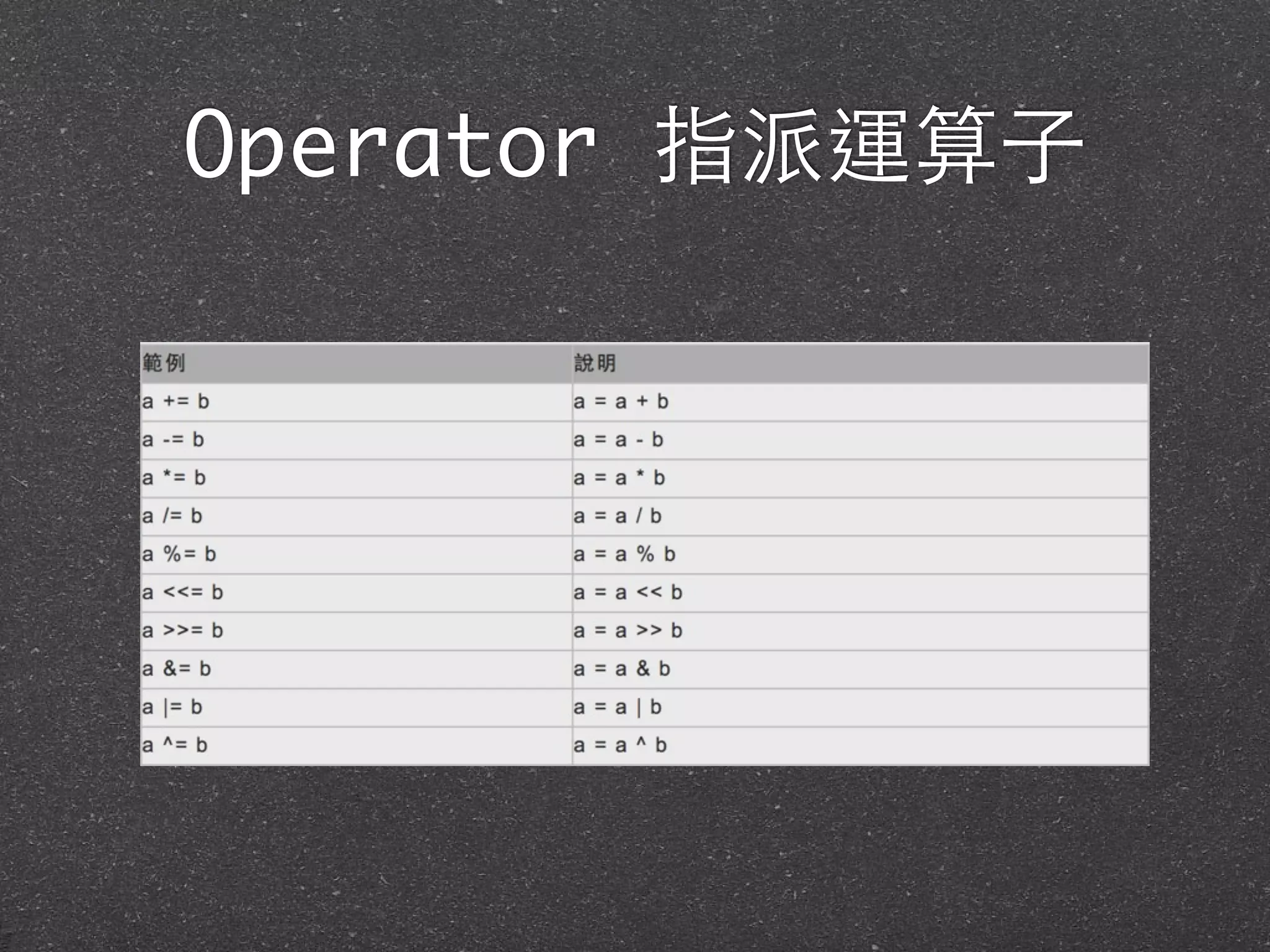



![Operator +
1
+
2
//
=>
3:
addition
"1"
+
"2"
//
=>
"12":
concatenation
"1"
+
2
//
=>
"12":
concatenation
after
number-‐to-‐string
1
+
{}
//
=>
"1[object
Object]":
concatenation
after
object-‐to-‐string
true
+
true
//
=>
2:
addition
after
boolean-‐to-‐number
2
+
null
//
=>
2:
addition
after
null
converts
to
0
2
+
undefined
//
=>
NaN:
addition
after
undefined
converts
to
NaN
1
+
2
+
"
blind
mice";
//
=>
"3
blind
mice"
1
+
(2
+
"
blind
mice");
//
=>
"12
blind
mice"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-36-2048.jpg)









![Statement 迴圈
do while
確定此迴圈⾄至少執⾏行⼀一次時才使⽤用
function
printArray(a)
{
var
len
=
a.length,
i
=
0;
if
(len
==
0)
console.log("Empty
Array");
else
{
do
{
console.log(a[i]);
}
while
(++i
<
len);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-46-2048.jpg)
![Statement 迴圈
for
for/in: ⽤用在列舉物件屬性時
for(var
count
=
0;
count
<
10;
count++)
console.log(count);
for(var
i
=
0,
j
=
10
;
i
<
10
;
i++,
j-‐-‐)
sum
+=
i
*
j;
for(var
p
in
o)
//
Assign
property
names
of
o
to
variable
p
ßconsole.log(o[p]);
//
Print
the
value
of
each
property
var
o
=
{x:1,
y:2,
z:3};
var
a
=
[],
i
=
0;
for(a[i++]
in
o)
/*
empty
*/;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-47-2048.jpg)

![Statement 跳脫
break
for(var
i
=
0;
i
<
a.length;
i++)
{
if
(a[i]
==
target)
break;
}
switch(n)
{
case
1:
//
Start
here
if
n
==
1
//
Execute
code
block
#1.
break;
case
2:
//
Execute
code
block
#2.
break;
case
3:
//
Execute
code
block
#3.
break;
default:
//
Execute
code
block
#4.
break;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-49-2048.jpg)
![Statement 跳脫
continue
return
for(i
=
0;
i
<
data.length;
i++)
{
if
(!data[i])
continue;
//
Can't
proceed
with
undefined
data
total
+=
data[i];
}
function
display_object(o)
{
if
(!o)
return;
console.dir(o);
return;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-50-2048.jpg)





![Object 物件屬性
//get
properties
from
object
var
book
=
{
author:
{firstname:
"J.R.R.",
lastname:
"Tolkien"},
"main
title":
"The
Lord
of
the
Rings"
};
var
author
=
book.author;
//
Get
the
"author"
property
of
the
book.
var
name
=
author.lastname;
//
Get
the
"surname"
property
of
the
author.
var
title
=
book["main
title"];
//
Get
the
"main
title"
property
of
the
book.
console.log(name,
title);
//set
properties
of
object
book["sub
title"]=
"The
Fellowship
of
the
Ring";
book.price
=
131;
console.log(book["main
title"],
book["sub
title"]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-56-2048.jpg)

![移除物件屬性
全域物件無法移除
Object delete
//delete:
remove
props
from
an
object
var
book
=
{
author:
{firstname:
"J.R.R.",
lastname:
"Tolkien"},
"main
title":
"The
Lord
of
the
Rings"
};
delete
book.author;
//
The
book
object
now
has
no
author
property.
delete
book["main
title"];
//
Now
it
doesn't
have
"main
title",
either.
console.dir(book);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-58-2048.jpg)

![Object 列舉屬性
列出此物件的所有屬性
//
在for
loop裡的in只會列出enumerable的屬性
//
ex:
前例的toString不會出現在loop中
for(var
i
in
o)
{
if
(foo.hasOwnProperty(i))
{
console.log(i);
}
}
//
列出物件的屬性,且⾮非函式
for(var
i
in
o)
{
if
(foo.hasOwnProperty(i)
&&
typeof
o[i]
!==
'function')
{
console.log(i);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-60-2048.jpg)

![Array 陣列
基本的陣列宣告:
var myArray = [];
var myArray2 = [1, {}, true];
物件式宣告:(不建議使⽤用)
var a = new Array();
var b = new Array(5);
var c = new Array(4, "1", true);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-62-2048.jpg)
![Iterating Array
//針對⼀一般陣列
for(var
i
=
0;
i
<
a.length;
i++)
{
if
(!(i
in
a))
continue
;
//
跳過未定義的index
//
loop
body
here
}
//針對sparse
array
for(var
index
in
sparseArray)
{
var
value
=
sparseArray[index];
//
Now
do
something
with
index
and
value
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-63-2048.jpg)

![Array Methods
var
a
=
[1,
2,
3];
a.join();
a.join("
");
a.join("");
var
b
=
new
Array(10);
b.join('-‐')
var
a
=
[1,2,3];
a.reverse().join()
//
=>
"3,2,1"
and
a
is
now
[3,2,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-65-2048.jpg)
![Array Methods
//sort
with
alphabetical
order
var
a
=
new
Array("banana",
"cherry",
"apple");
a.sort();
var
s
=
a.join(",
");
//
s
==
"apple,
banana,
cherry"
var
a
=
[1,2,3];
a.reverse().join()
//
=>
"3,2,1"
and
a
is
now
[3,2,1]
var
a
=
[33,
4,
1111,
222];
a.sort();
//
Alphabetical
order:
1111,
222,
33,
4
a.sort(function(a,b)
{
//
Numerical
order:
4,
33,
222,
1111
return
a-‐b;
//
Returns
<
0,
0,
or
>
0,
depending
on
order
});
a.sort(function(a,b)
{return
b-‐a});
//
Reverse
numerical
order](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-66-2048.jpg)
![Array Methods
var
a
=
[1,2,3];
a.concat(4,
5)
a.concat([4,5]);
a.concat([4,5],[6,7])
a.concat(4,
[5,[6,7]])
var
a
=
[1,2,3,4,5];
a.slice(0,3);
//
Returns
[1,2,3]
a.slice(3);
//
Returns
[4,5]
a.slice(1,-‐1);
//
Returns
[2,3,4]
a.slice(-‐3,-‐2);
//
Returns
[3]
//slice可以拿來複製陣列
var
a
=
[1,2,3,4,5];
var
b
=
a.slice(0);
b[4]
=
0;
console.log(a,
b);
//[1,2,3,4,5]
[1,2,3,4,0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-67-2048.jpg)
![Array Methods
var
stack
=
[];
//
stack:
[]
stack.push(1,2);
//
stack:
[1,2]
Returns
2
stack.pop();
//
stack:
[1]
Returns
2
stack.push(3);
//
stack:
[1,3]
Returns
2
stack.pop();
//
stack:
[1]
Returns
3
stack.push([4,5]);
//
stack:
[1,[4,5]]
Returns
2
stack.pop()
//
stack:
[1]
Returns
[4,5]
stack.pop();
//
stack:
[]
Returns
1
var
a
=
[];
//
a:[]
a.unshift(1);
//
a:[1]
Returns:
1
a.unshift(22);
//
a:[22,1]
Returns:
2
a.shift();
//
a:[1]
Returns:
22
a.unshift(3,[4,5]);
//
a:[3,[4,5],1]
Returns:
3
a.shift();
//
a:[[4,5],1]
Returns:
3
a.shift();
//
a:[1]
Returns:
[4,5]
a.shift();
//
a:[]
Returns:
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-68-2048.jpg)

![Array Methods
(ECMAScript 5)
//
forEach()
//
array
iterator
var
data
=
[1,2,3,4,5];
//
An
array
to
sum
//
Compute
the
sum
of
the
array
elements
var
sum
=
0;
//
Start
at
0
data.forEach(function(value)
{
sum
+=
value;
});
//
Add
each
value
to
sum
sum
//
=>
15
//
Now
increment
each
array
element
data.forEach(function(v,
i,
a)
{
a[i]
=
v
+
1;
});
console.log(data);
//
=>
[2,3,4,5,6]
//map
//計算並產⽣生⼀一個新的陣列
a
=
[1,
2,
3];
b
=
a.map(function(x)
{
return
x*x;
});
//
b
is
[1,
4,
9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-70-2048.jpg)
![Array Methods
(ECMAScript 5)
//filter
a
=
[5,
4,
3,
2,
1];
smallvalues
=
a.filter(function(x)
{
return
x
<
3
});
//
[2,
1]
everyother
=
a.filter(function(x,i)
{
return
i%2==0
});
//
[5,
3,
1]
//every
//檢查是否每個元素都符合條件
a
=
[1,2,3,4,5];
a.every(function(x)
{
return
x
<
10;
})
//
=>
true:
all
values
<
10.
a.every(function(x)
{
return
x
%
2
===
0;
})
//
=>
false:
not
all
values
even.
//some
//檢查是否有元素符合條件
a
=
[1,2,3,4,5];
a.some(function(x)
{
return
x%2===0;
})
//
=>
true
a
has
some
even
numbers.
a.some(isNaN)
//
=>
false:
a
has
no
non-‐numbers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-71-2048.jpg)
![Array Methods
(ECMAScript 5)
//array.reduce(callback,
[initialValue])
//callback
=
function(previousValue,
currentValue,
index,
array)
var
a
=
[1,2,3,4,5]
var
sum
=
a.reduce(function(x,y)
{
return
x+y
},
0);
//
Sum
of
values
var
product
=
a.reduce(function(x,y)
{
return
x*y
},
1);
//
Product
of
values
var
max
=
a.reduce(function(x,y)
{
return
(x>y)?x:y;
});
//
Largest
value
//reduceRight()
var
a
=
[2,
3,
4]
//
Compute
2^(3^4).
Exponentiation
has
right-‐to-‐left
precedence
var
big
=
a.reduceRight(function(accumulator,value)
{
return
Math.pow(value,accumulator);
});
練習:使⽤用reduce把陣列[1,2,3,4,5]變成字串
12345](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-72-2048.jpg)
![Array Methods
(ECMAScript 5)
//
Find
all
occurrences
of
a
value
x
in
an
array
a
and
return
an
array
//
of
matching
indexes
function
findall(a,
x)
{
var
results
=
[],
//
The
array
of
indexes
we'll
return
len
=
a.length,
//
The
length
of
the
array
to
be
searched
pos
=
0;
//
The
position
to
search
from
while(pos
<
len)
{
//
While
more
elements
to
search...
pos
=
a.indexOf(x,
pos);
//
Search
if
(pos
===
-‐1)
break;
//
If
nothing
found,
we're
done.
results.push(pos);
//
Otherwise,
store
index
in
array
pos
=
pos
+
1;
//
And
start
next
search
at
next
element
}
return
results;
//
Return
array
of
indexes
}
//array.lastIndexOf(searchElement[,
fromIndex])
a
=
[0,1,2,1,0];
a.indexOf(1)
//
=>
1:
a[1]
is
1
a.lastIndexOf(1)
//
=>
3:
a[3]
is
1
a.indexOf(3)
//
=>
-‐1:
no
element
has
value
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-73-2048.jpg)
![寫⼀一個函式,接收三個參數
between(str, start, end)
str為⼀一字串,start為開始字串,end為結束字
串;回傳為start與end中間的值。舉例:
between("hola [hello] bon", "[", "]")
應回傳 "hello"
tips: 使⽤用String.indexOf以及Array.slice
Array Practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-74-2048.jpg)



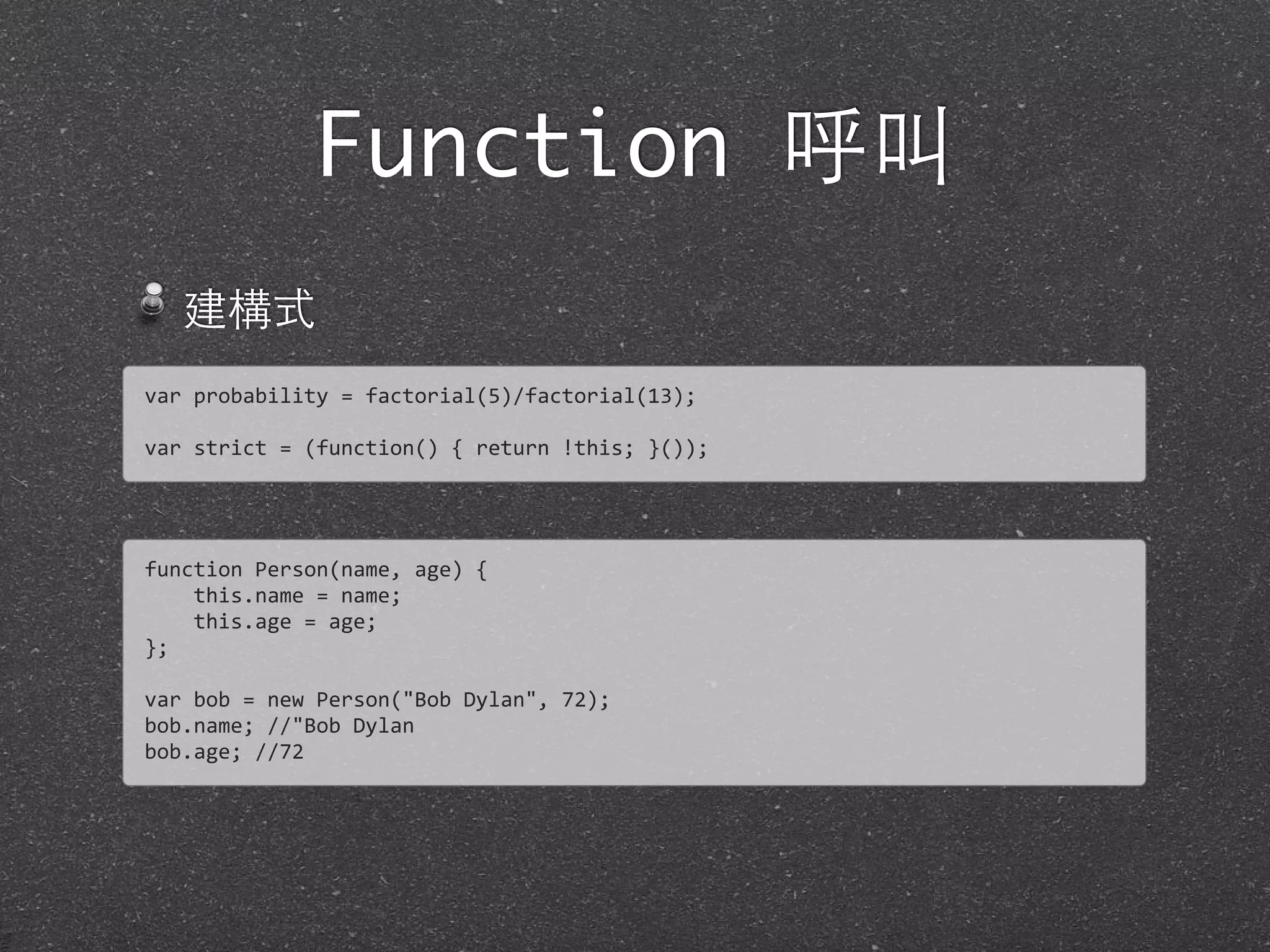
![Function 呼叫
call, apply
function
Person(name,
age)
{
this.name
=
name;
this.age
=
age;
this.greet
=
function(greeter)
{
return
"Hi,
"
+
greeter
+
".
I'm
"
+
this.name;
}
};
var
bob
=
new
Person("Bob
Dylan",
72);
var
hans
=
new
Person("Hans
Zimmer",
55);
bob.greet.call(hans,
"Fin");
hans.greet.apply(bob,
["Fin"]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-79-2048.jpg)
![Function 參數
參數可以是任意數,⽤用arguments來取
function
max(/*
...
*/)
{
var
max
=
Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
//
Loop
through
the
arguments,
looking
for,
and
remembering,
the
biggest.
for(var
i
=
0;
i
<
arguments.length;
i++)
if
(arguments[i]
>
max)
max
=
arguments[i];
//
Return
the
biggest
return
max;
}
var
largest
=
max(1,
10,
100,
2,
3,
1000,
4,
5,
10000,
6);
//
=>
10000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-80-2048.jpg)







![Class 類別
Complex.prototype.toString
=
function()
{
return
"{"
+
this.r
+
","
+
this.i
+
"}";
};
//
Test
whether
this
Complex
object
has
the
same
value
as
another.
Complex.prototype.equals
=
function(that)
{
return
that
!=
null
&&
that.constructor
===
Complex
&&
this.r
===
that.r
&&
this.i
===
that.i;
};
Complex.ZERO
=
new
Complex(0,0);
Complex.ONE
=
new
Complex(1,0);
Complex.I
=
new
Complex(0,1);
Complex.parse
=
function(s)
{
try
{
//
Assume
that
the
parsing
will
succeed
var
m
=
Complex._format.exec(s);
//
Regular
expression
magic
return
new
Complex(parseFloat(m[1]),
parseFloat(m[2]));
}
catch
(x)
{
//
And
throw
an
exception
if
it
fails
throw
new
TypeError("Can't
parse
'"
+
s
+
"'
as
a
complex
number.");
}
};
Complex._format
=
/^{([^,]+),([^}]+)}$/;
如果要把toString改成{1, 5i}這種格式要如何改](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-89-2048.jpg)



![RegExp 正規表⽰示法
[...] 含有[]裡⾯面的任何字元其⼀一
[^...] 不含有[]裡⾯面的任何字元其⼀一
. 任何"⼀一個"字元(不包含換⾏行符號)
w 等同[a-zA-Z0-9_]
W 等同[^a-zA-Z0-9_]
s 任何空⽩白字元,包含t, v
S 任何⾮非空⽩白字元
d [0-9]
D [^0-9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-93-2048.jpg)

![RegExp 正規表⽰示法
| 符合左邊或右邊的物件
(...) 群組,可與{}, *等結合
(?:...) 群組但不儲存
n 與第n個群組相同
^ 含有[]裡⾯面的任何字元其⼀一
$ 不含有[]裡⾯面的任何字元其⼀一](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-95-2048.jpg)

![RegExp in String
search
replace
match
split
console.log("JavaScript".search(/script/i));
console.log("jAvaSCRipt
claZZ".replace(/javascript/gi,
"JavaScript"));
console.log("hello
_there_
and
_here_".replace(/_(.*?)_/g,
"<div>$1</div>"));
var
url
=
/(w+)://([w.]+)/(S*)/;
var
text
=
"https://www.facebook.com/thingsaboutwebdev";
var
result
=
text.match(url);
console.log(result);
var
words
=
'How
are
you
doing,
john?'.split(/[s,?.]+/);
console.log(words);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-97-2048.jpg)
![RegExp 物件
exec: 執⾏行結果像是String.match,但如果有
g flag,則可以連續執⾏行取得多筆結果
test: boolean test
var
pattern
=
/Java/g;
var
text
=
"JavaScript
is
more
fun
than
Java!";
var
result;
while((result
=
pattern.exec(text))
!=
null)
{
console.log("Matched
'"
+
result[0]
+
"'"
+
"
at
position
"
+
result.index
+
";
next
search
begins
at
"
+
pattern.lastIndex);
}
var
pattern
=
/java/i;
pattern.test("JavaScript");
//
Returns
true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-98-2048.jpg)
![常⽤用 RegExp
限制英⽂文字⺟母/數字: /^[a-zA-Z0-9]*$/
⽇日期(YYYY/MM/DD): /^((19|20)?[0-9]{2}[- /.](0?[1-9]|
1[012])[- /.](0?[1-9]|[12][0-9]|3[01]))*$/
Email: /^([a-zA-Z0-9._%-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]
{2,4})*$/
IP: /^((?:(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?).)
{3}(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?))*$/
Password: /^(?=^.{6,}$)((?=.*[A-Za-z0-9])(?=.*[A-Z])(?
=.*[a-z]))^.*$/
VISA Card#: /^(4[0-9]{12}(?:[0-9]{3})?)*$/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascriptbasics-130604065408-phpapp02/75/Javascript-basics-99-2048.jpg)


