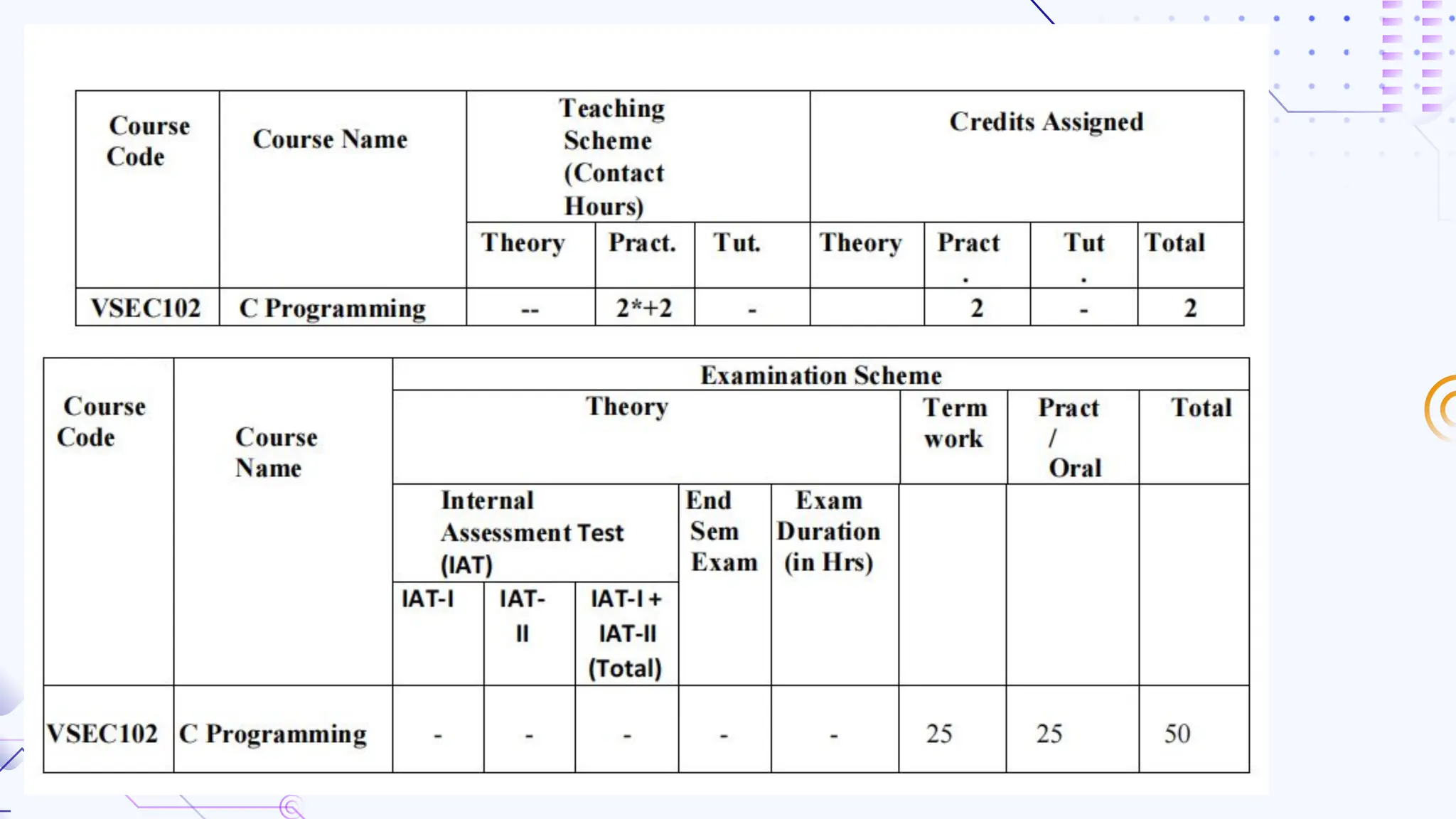
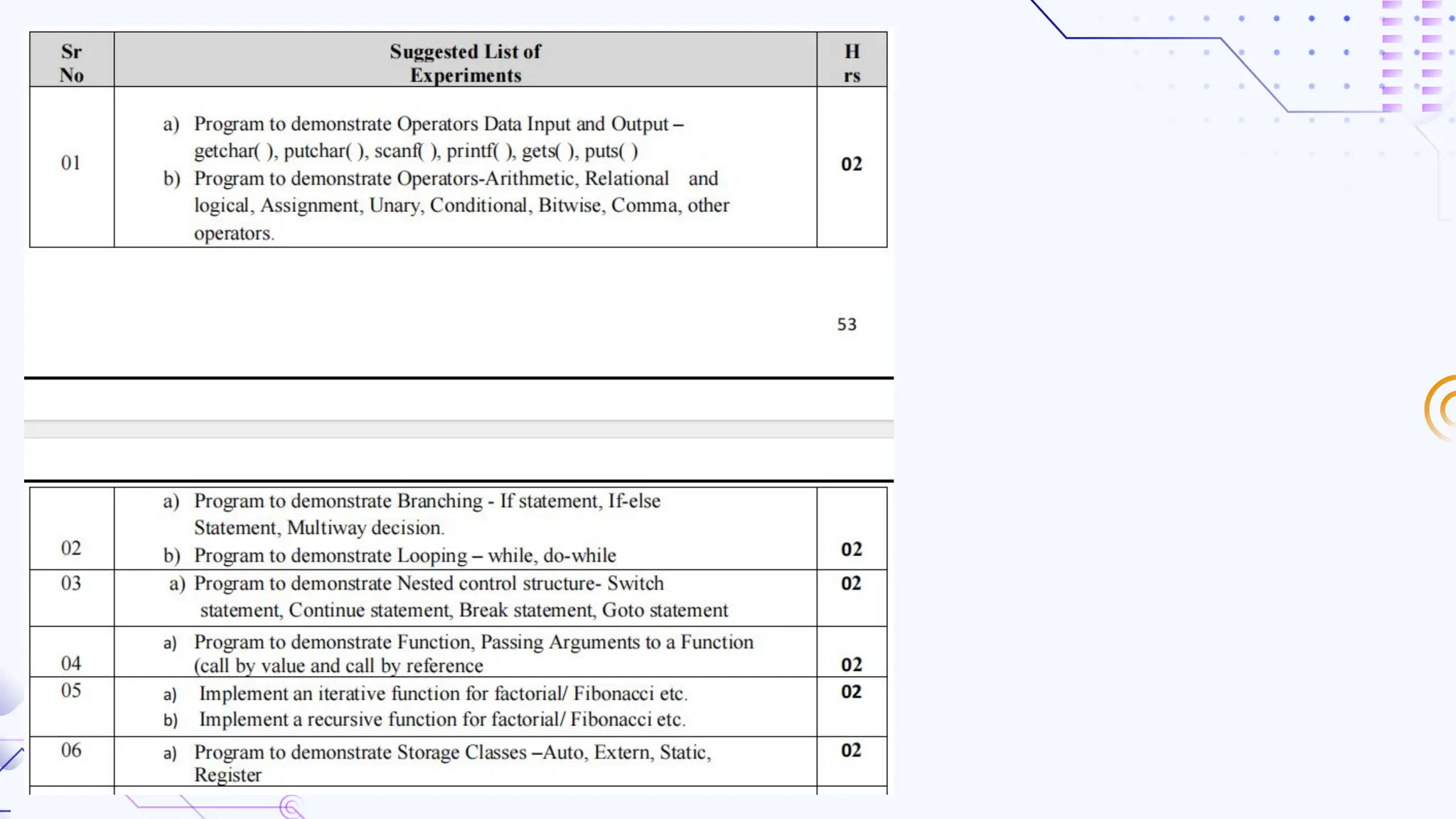
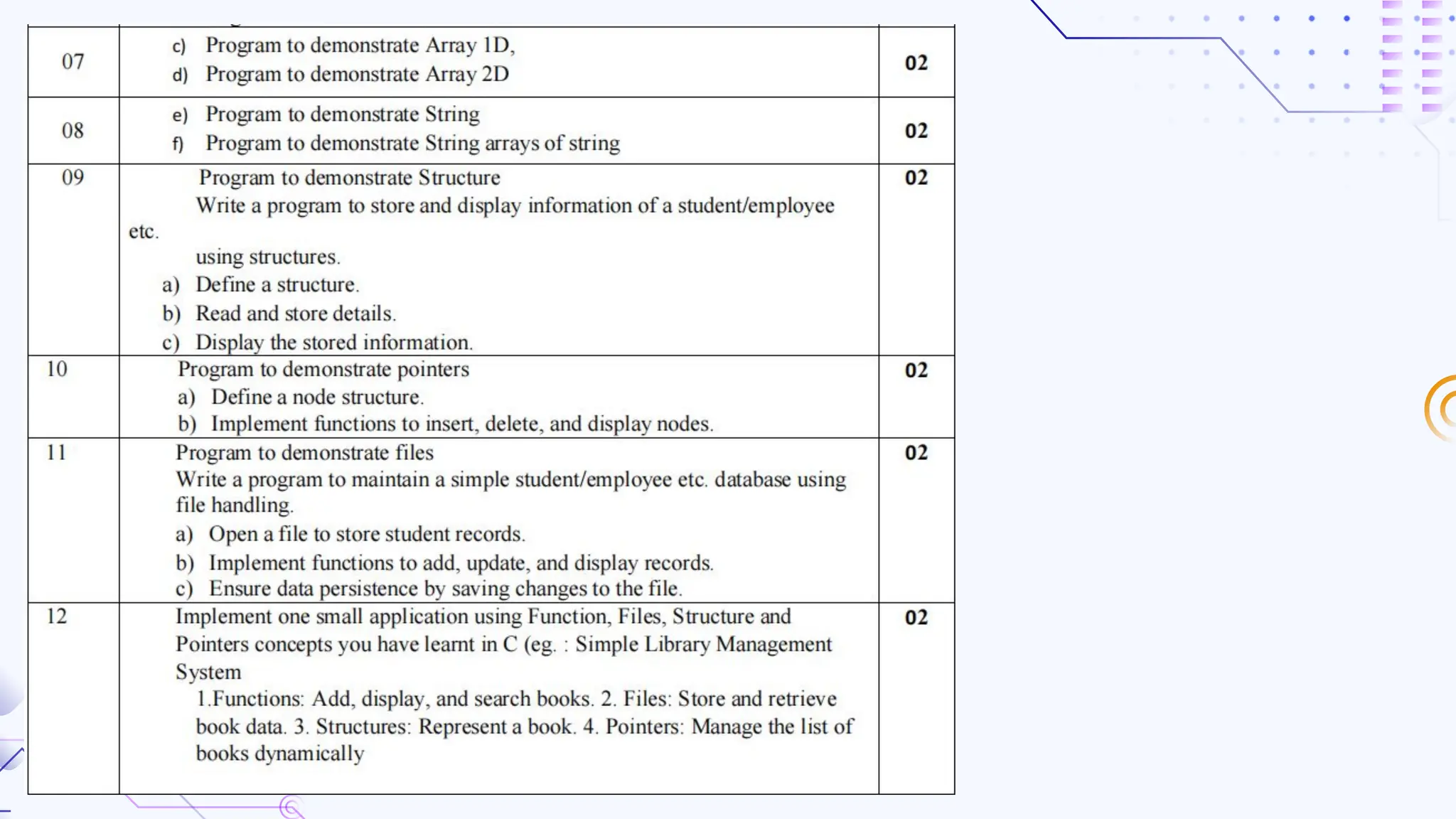
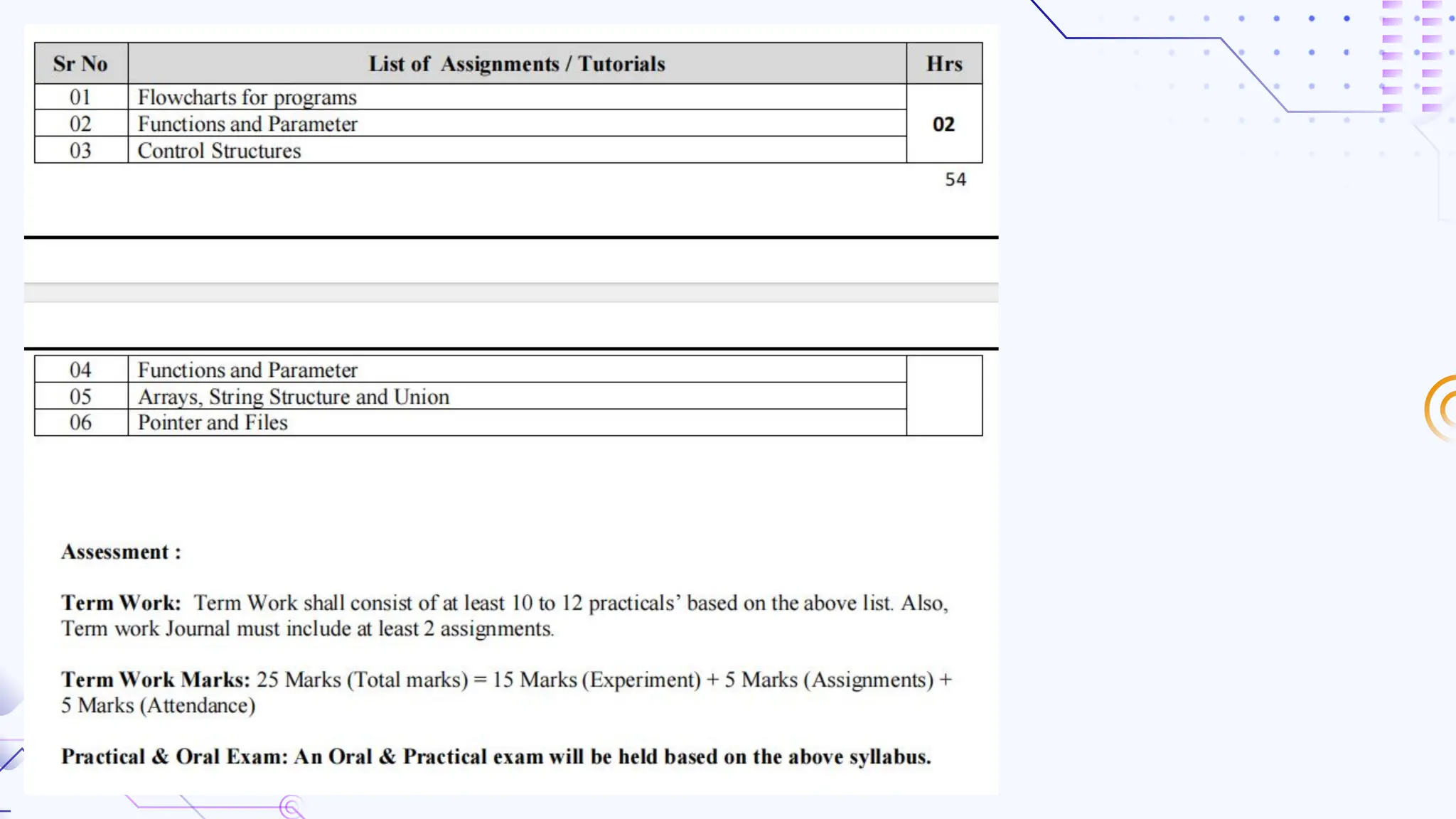
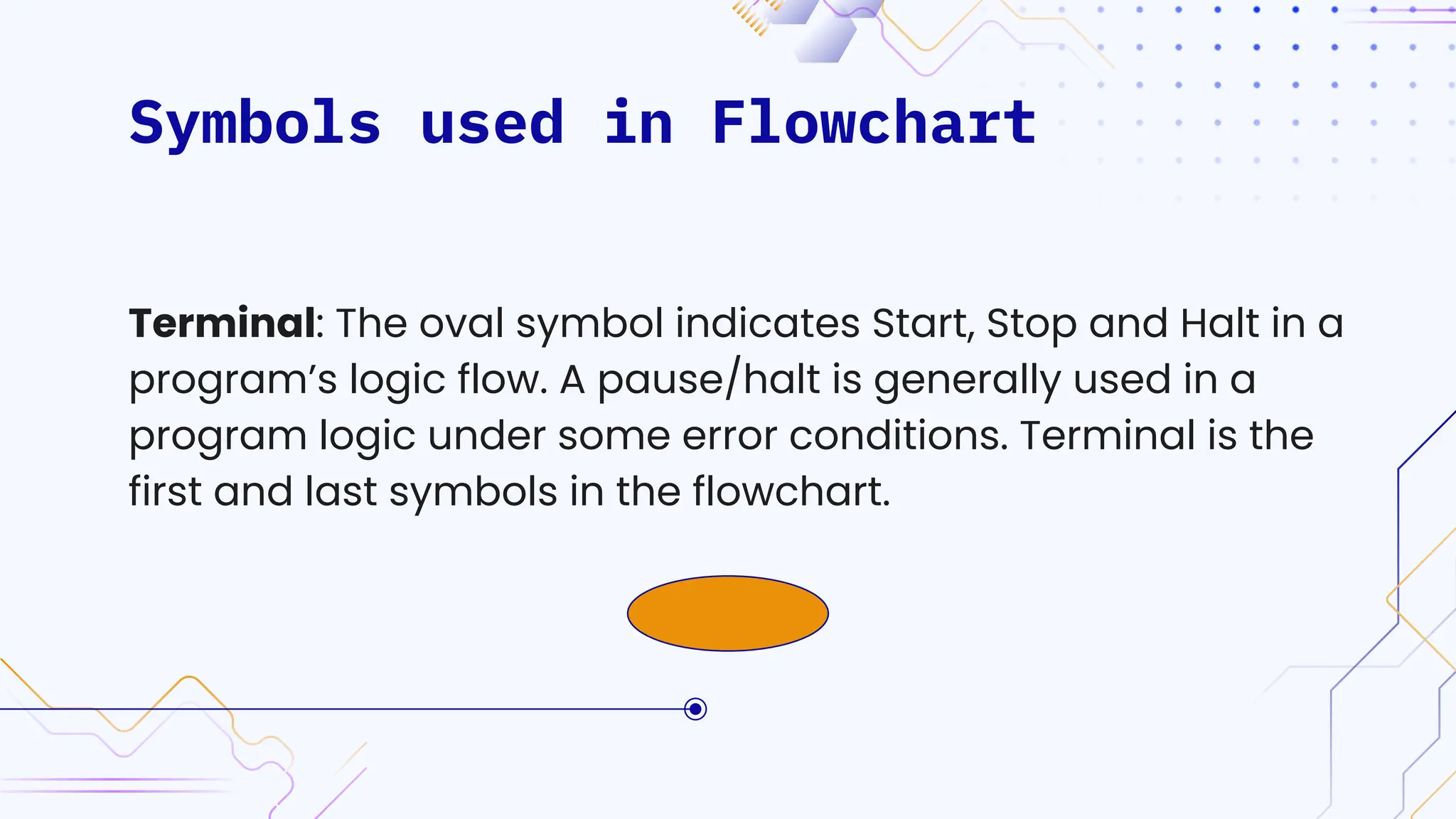
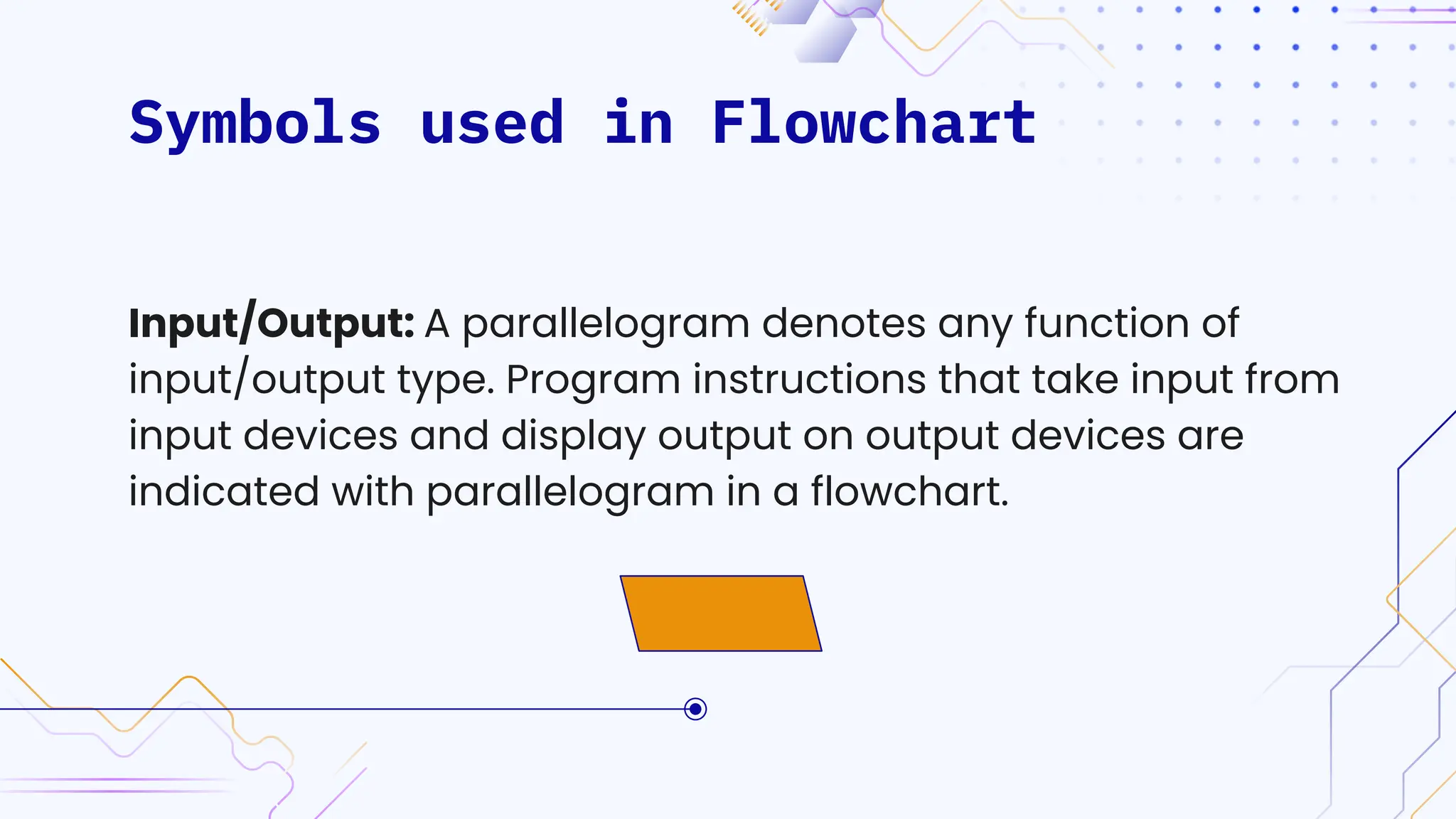
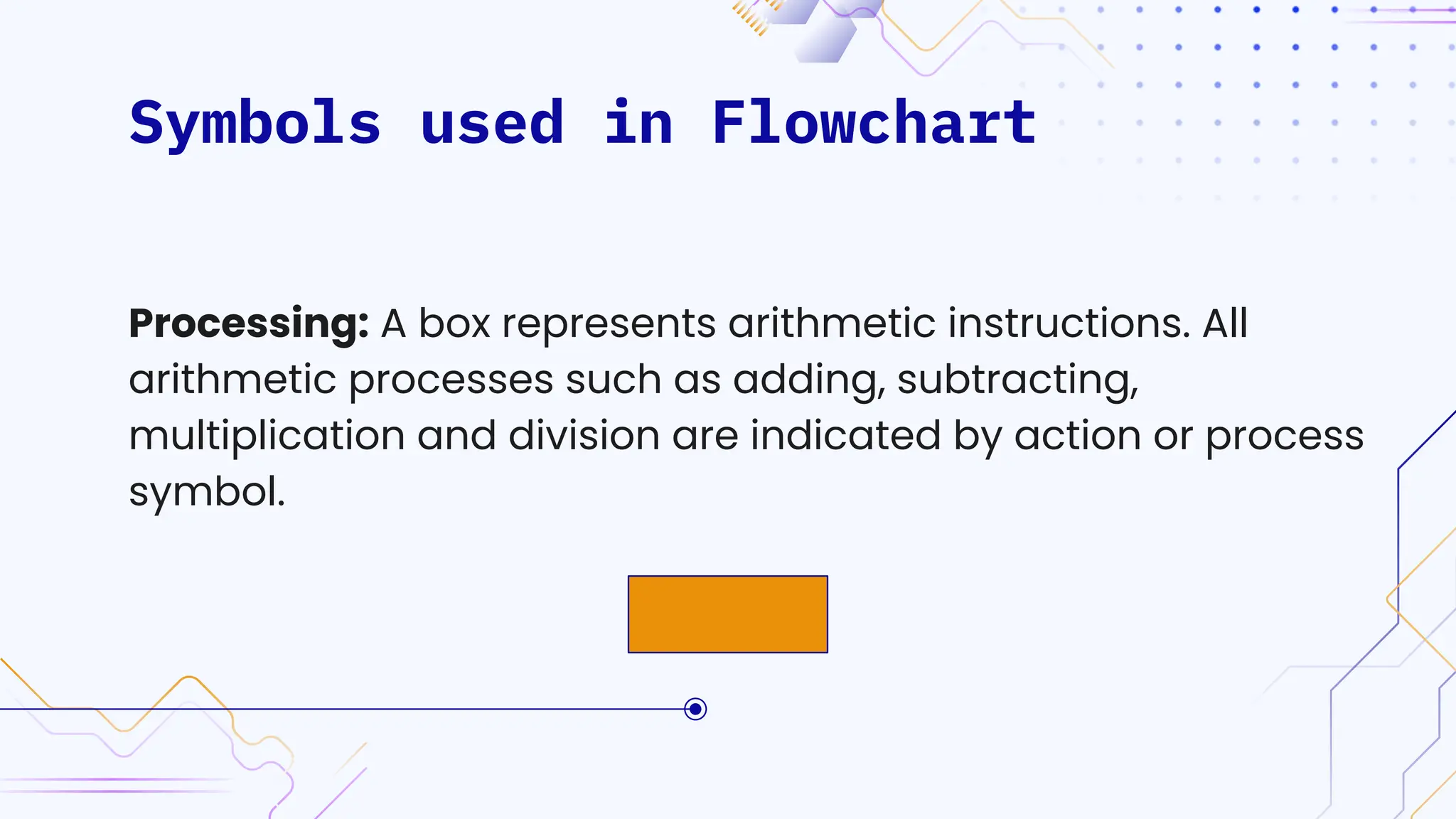
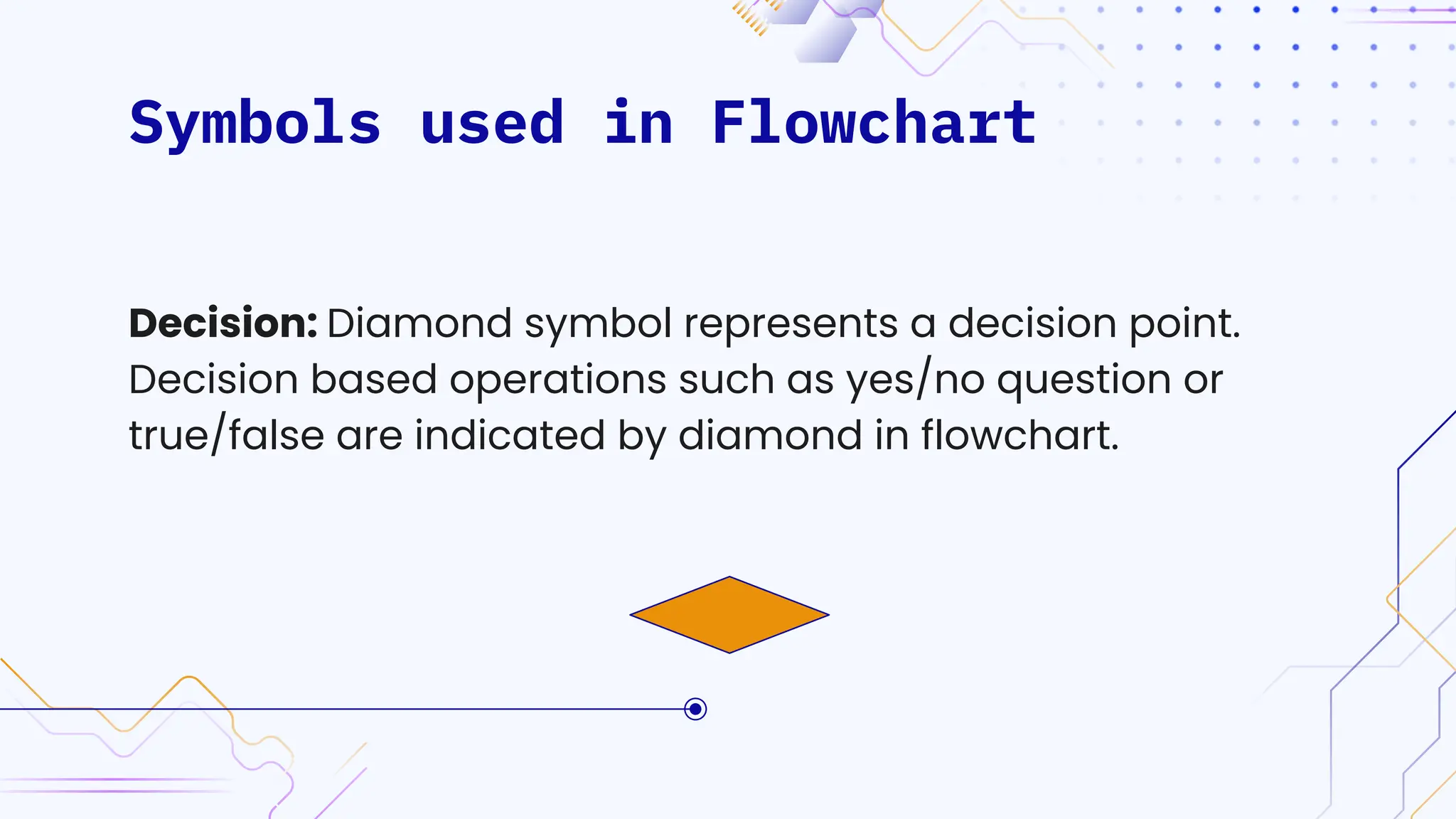
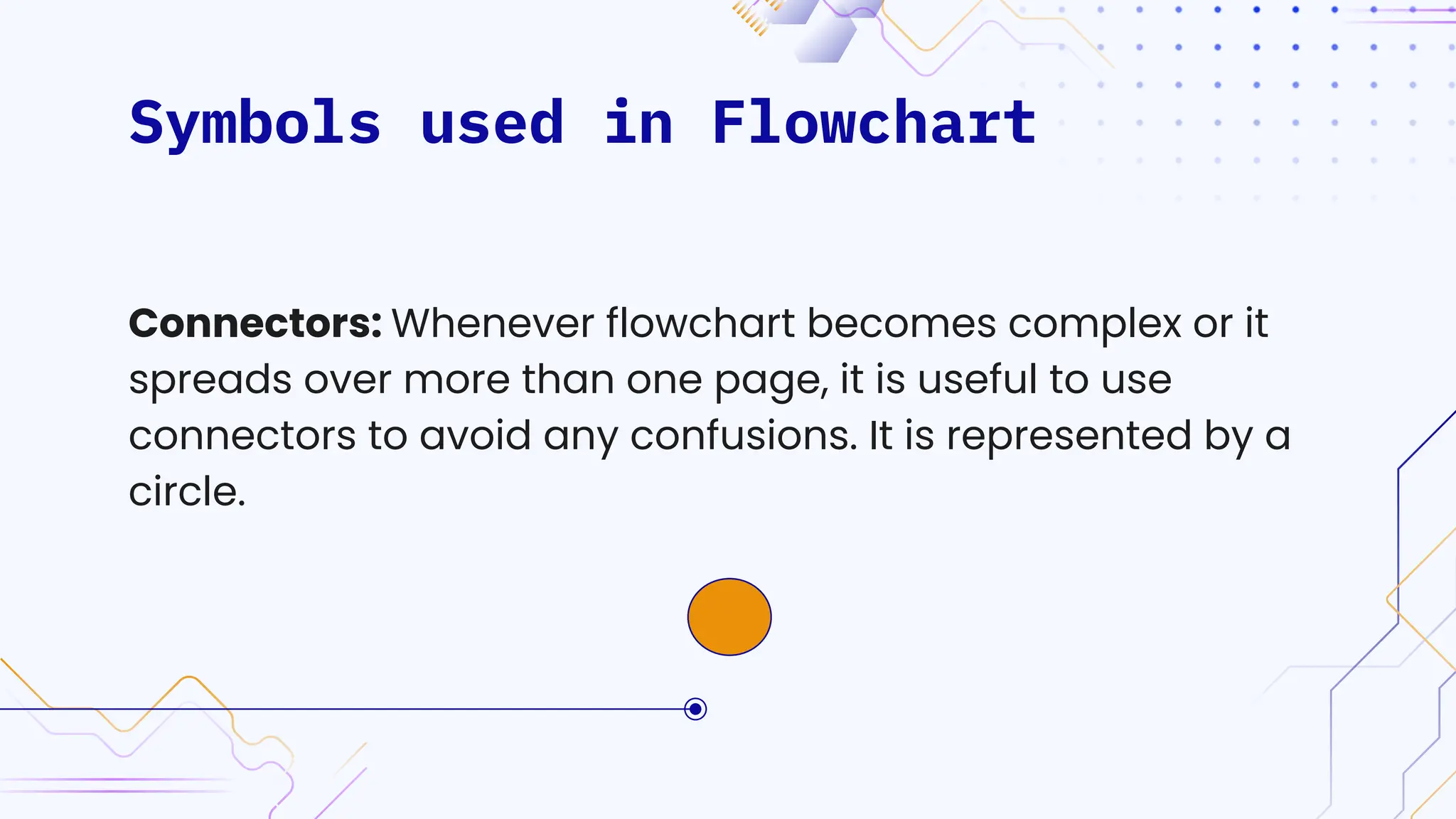
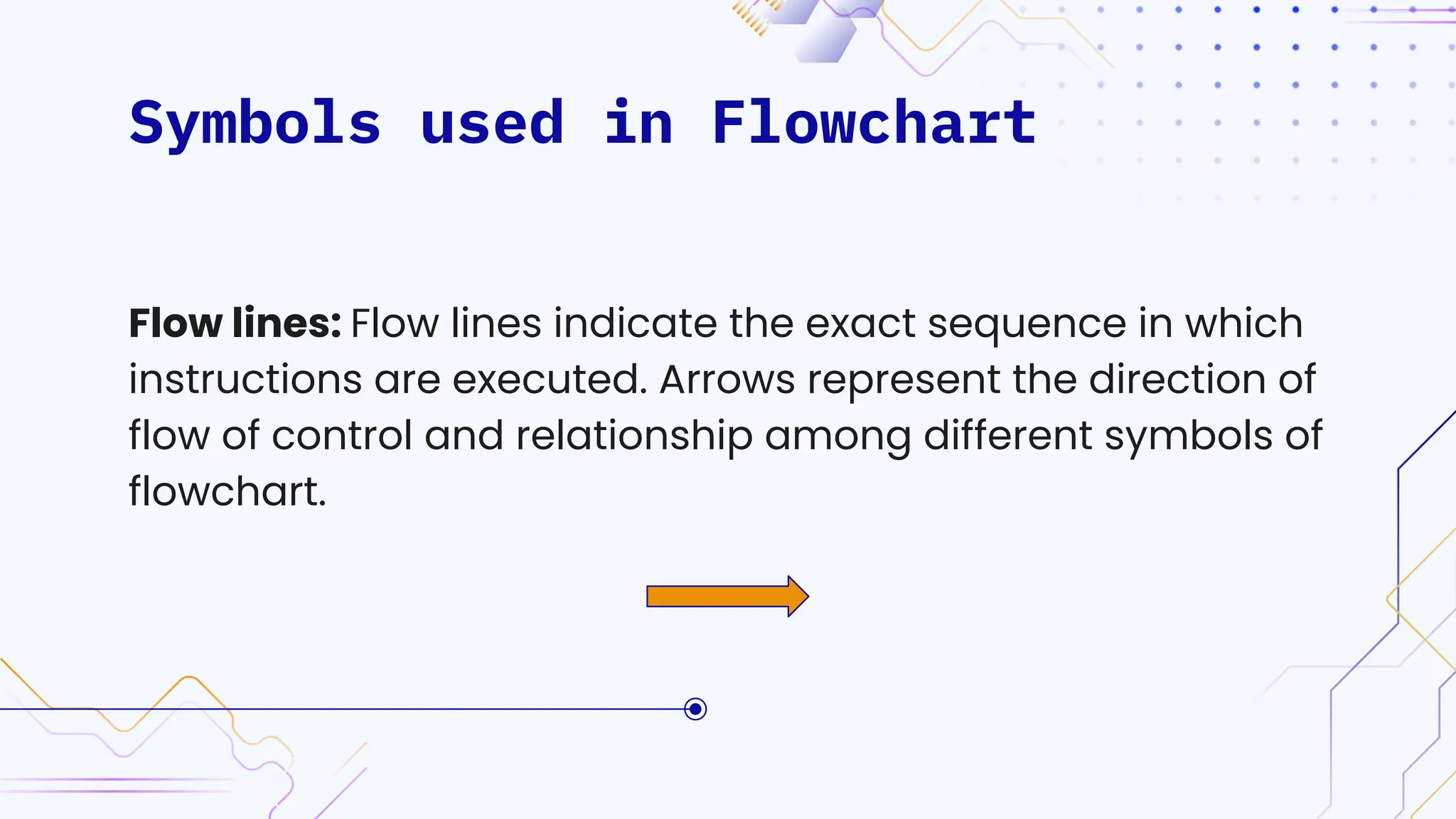
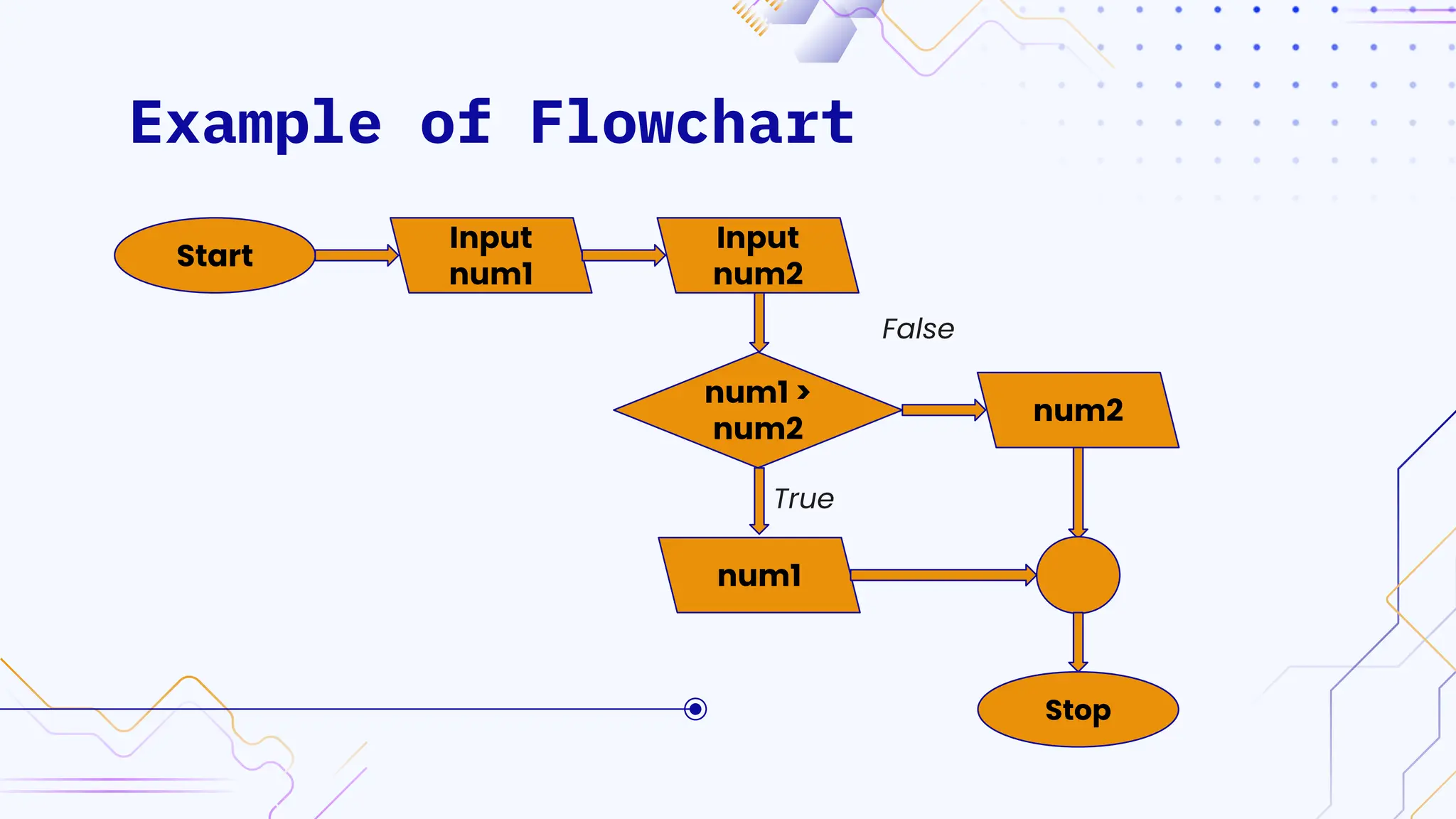
The document provides an overview of programming, including definitions, types of programming languages, and characteristics of low-level and high-level languages. It discusses algorithms, their features, and the significance of flowcharts for program planning, including their symbols, rules for creation, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, it outlines assignment questions related to algorithms and flowcharts provided by Dr. Rohan Dasgupta.