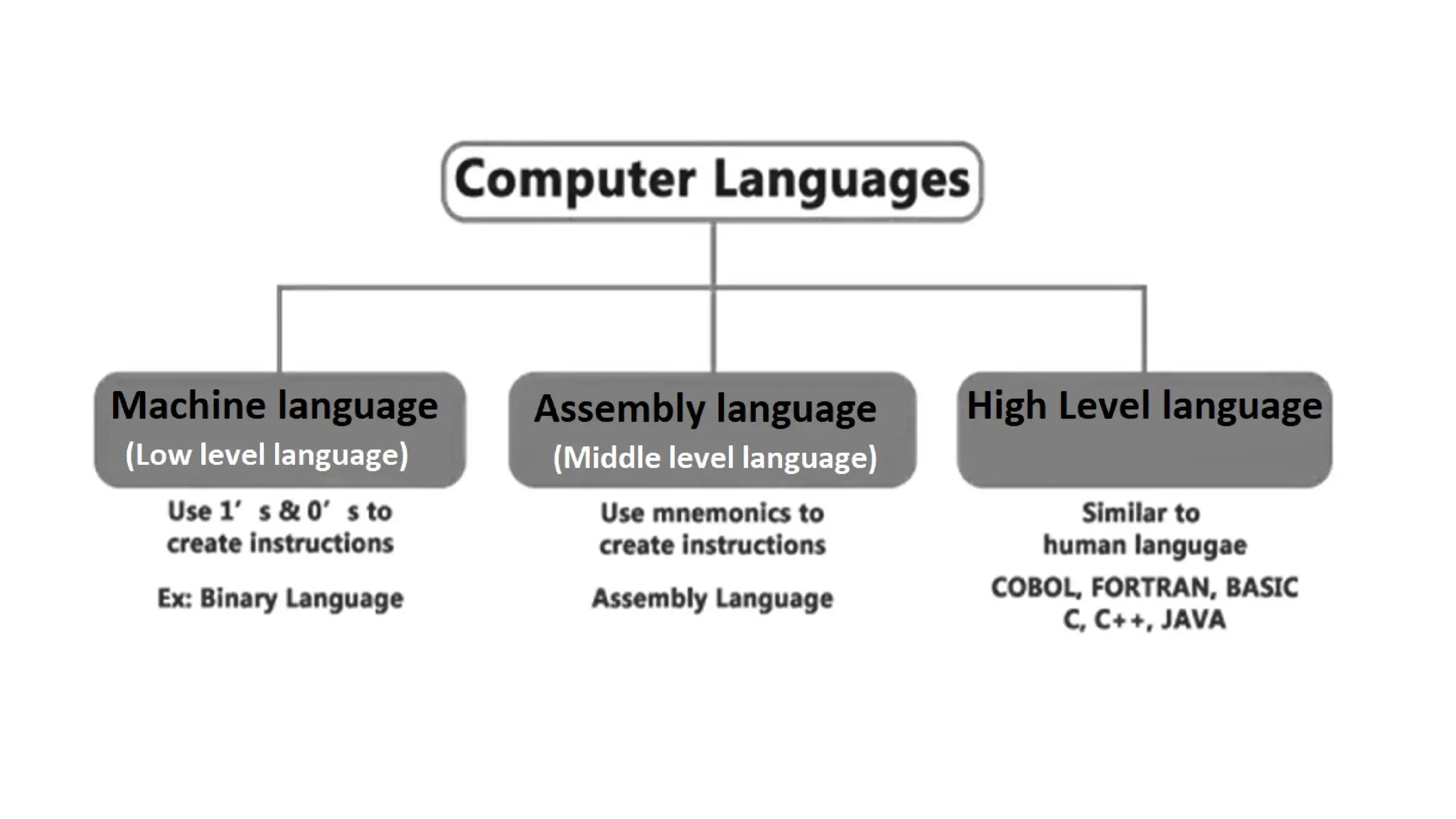
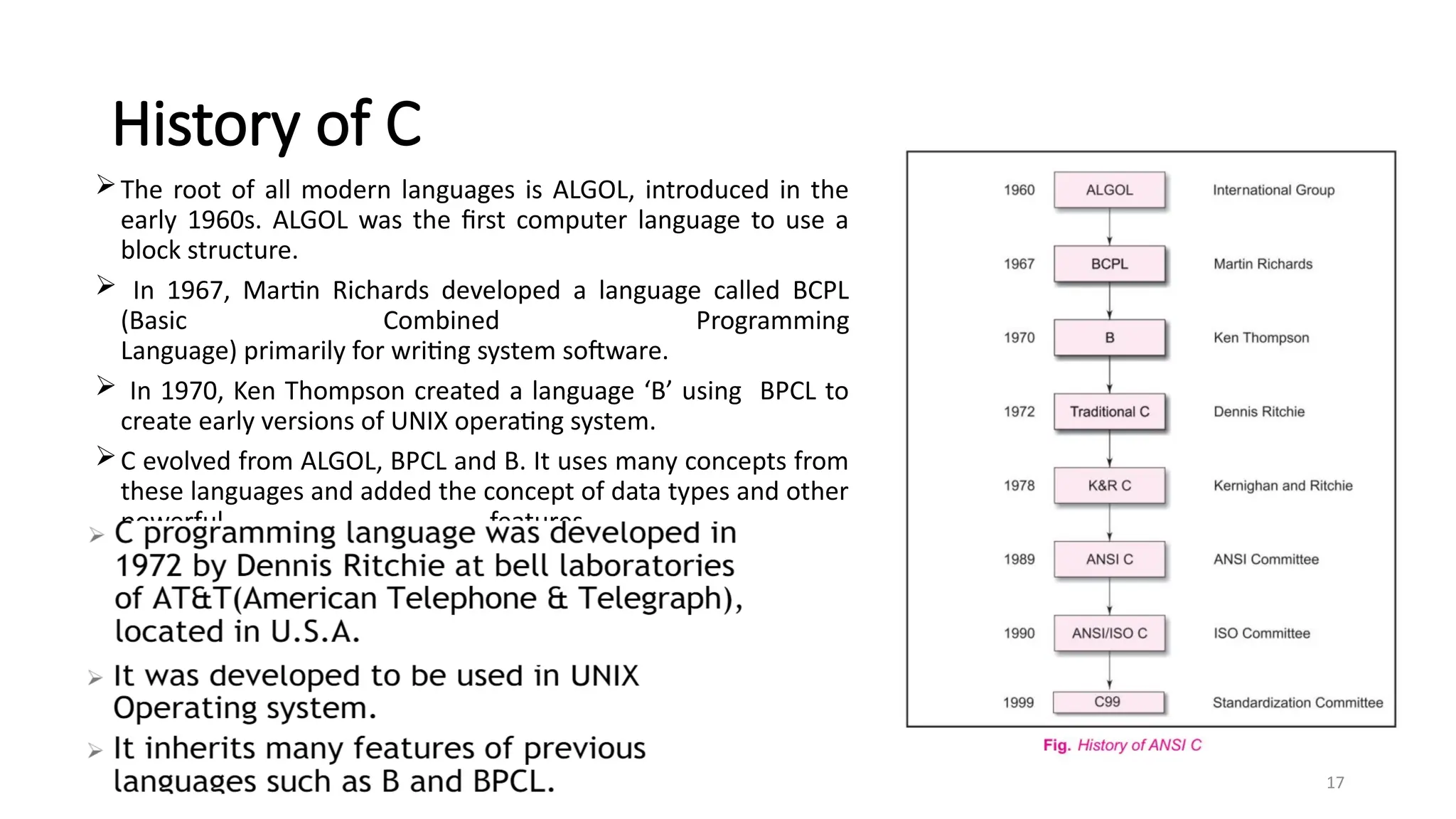
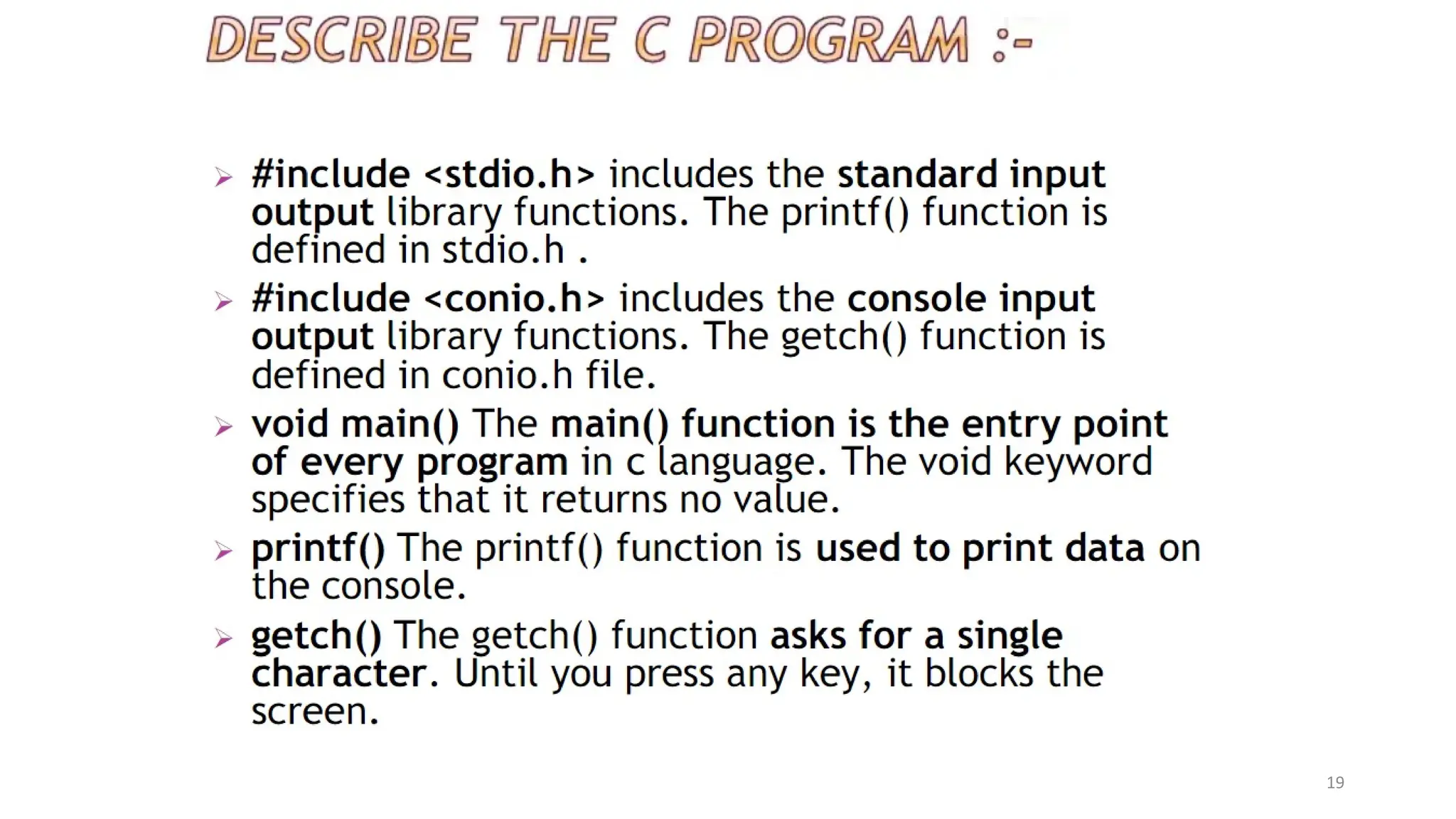
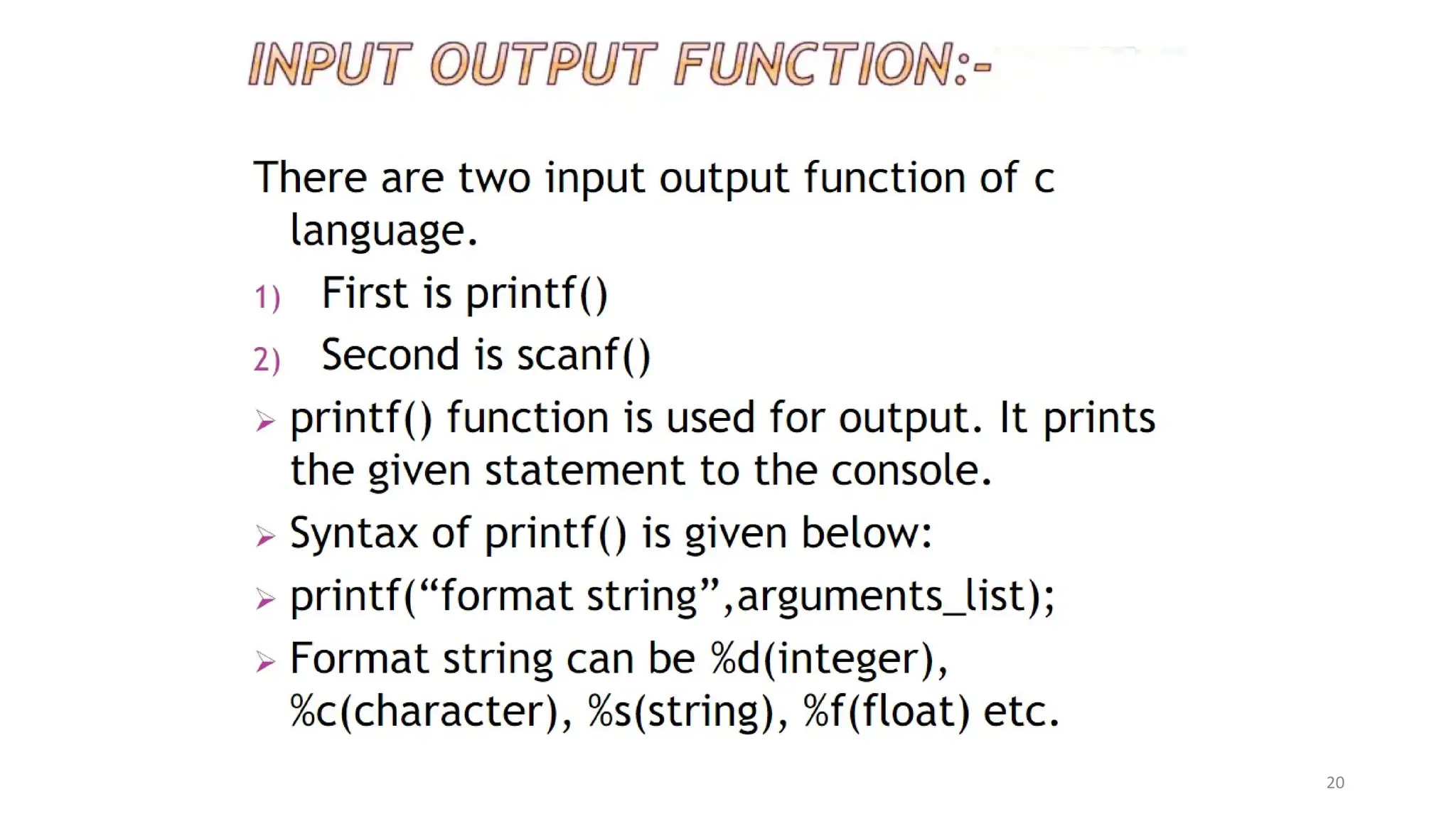
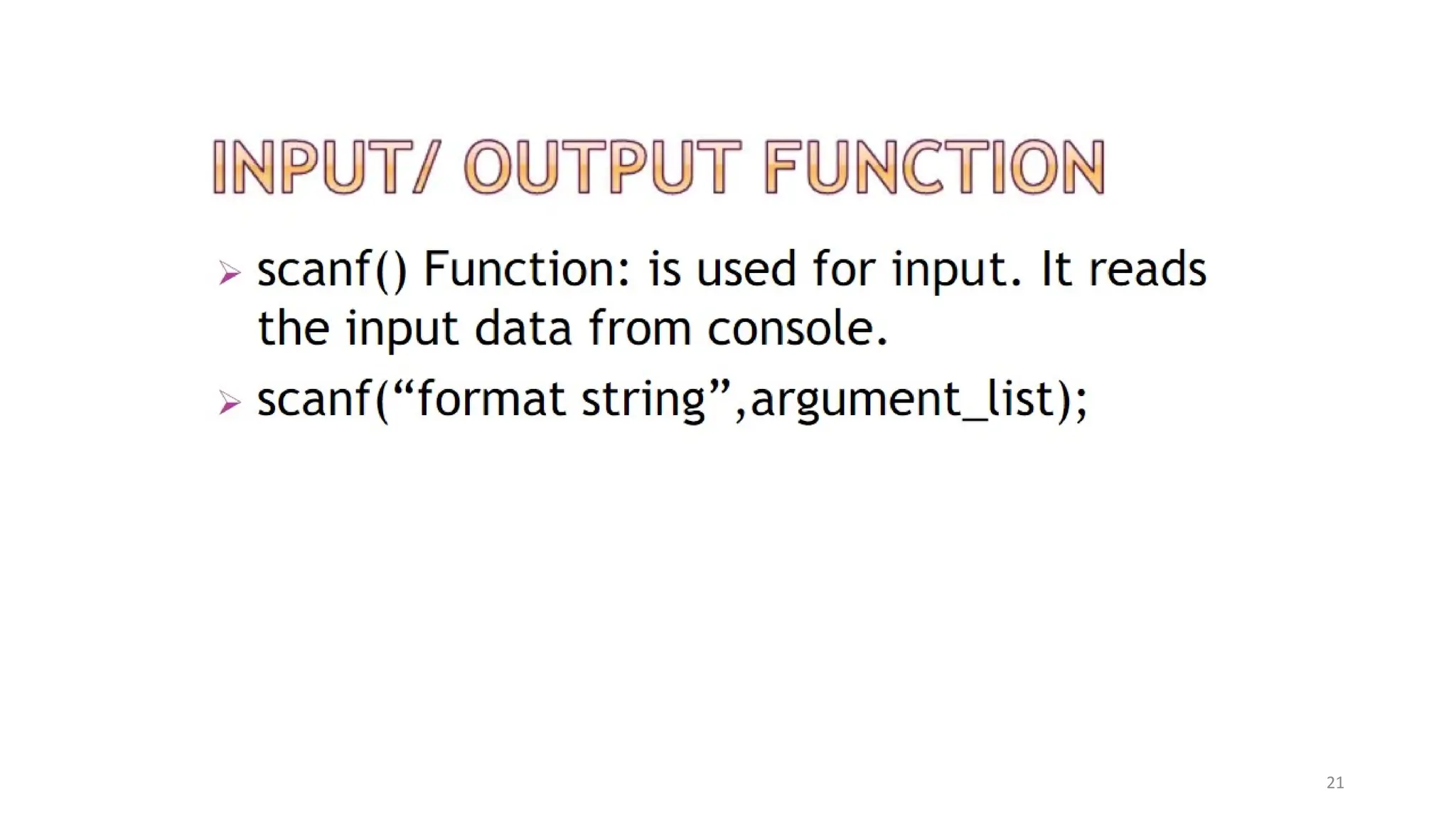
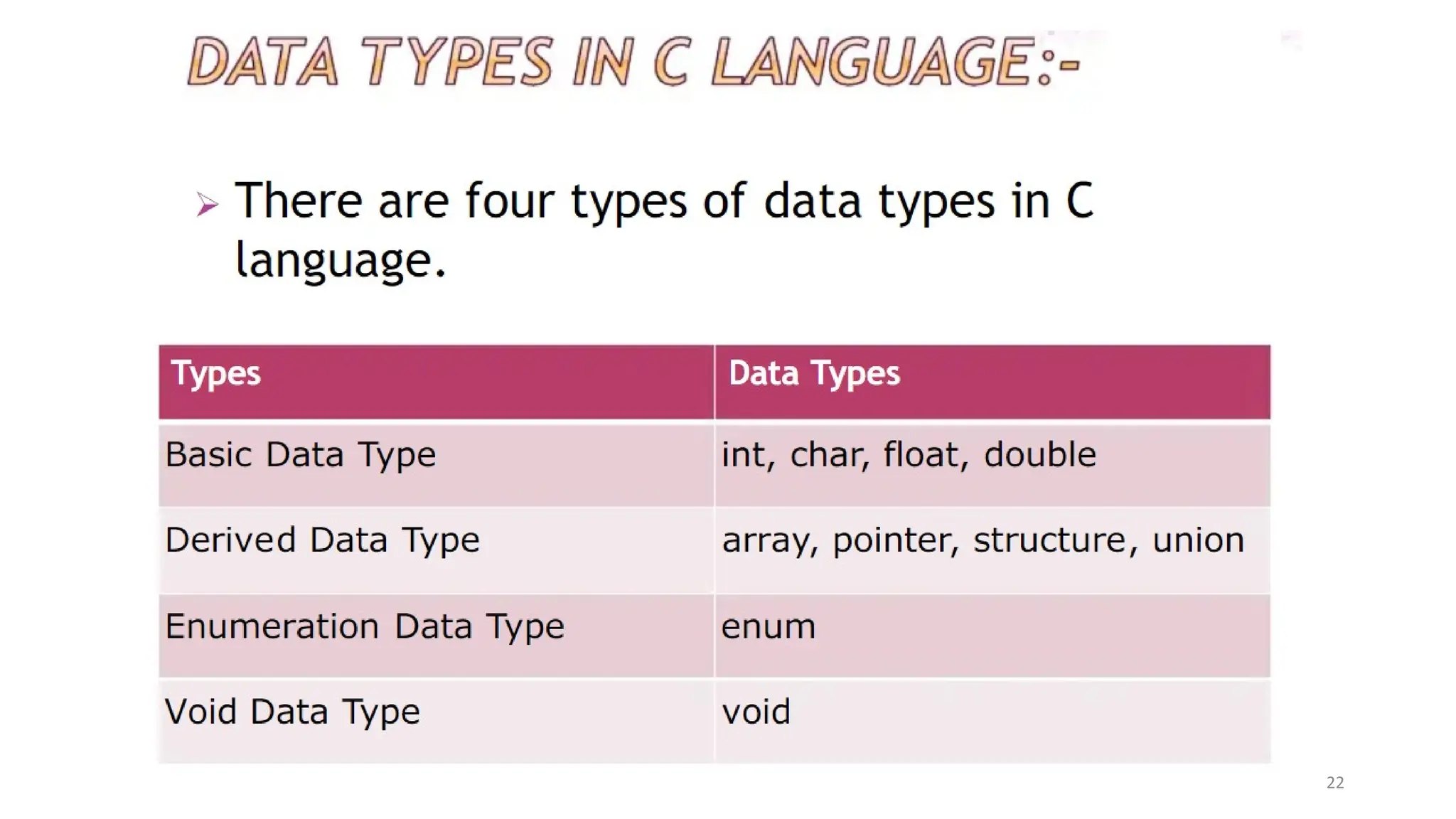
The document outlines a computer programming course at ABV-IIITM Gwalior, focusing on C programming fundamentals and concepts. It covers topics such as control statements, functions, recursion, and file handling, emphasizing the importance and history of C as a high-level programming language. The course aims to develop programming skills and problem-solving abilities through practical application and theoretical knowledge.