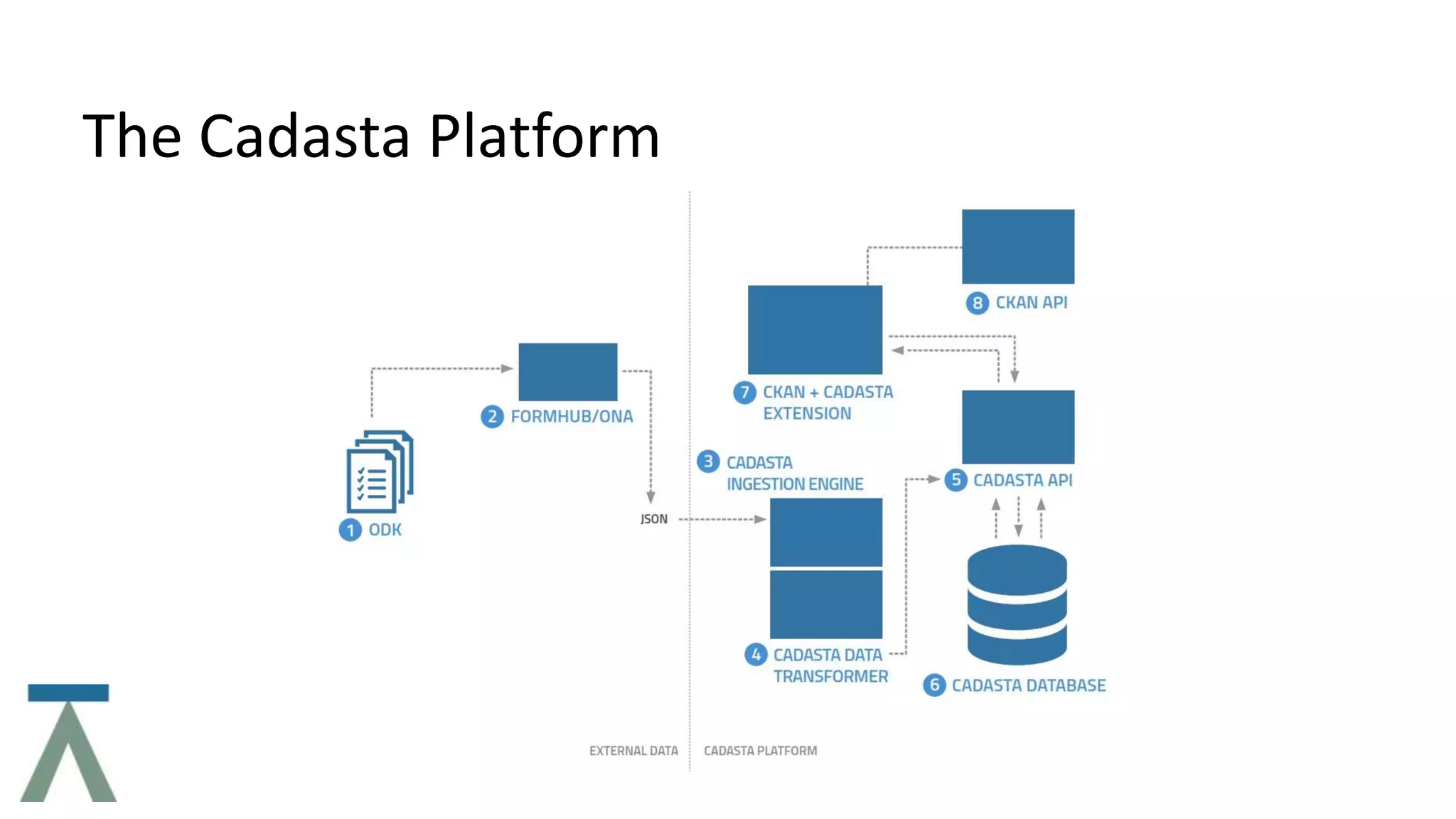
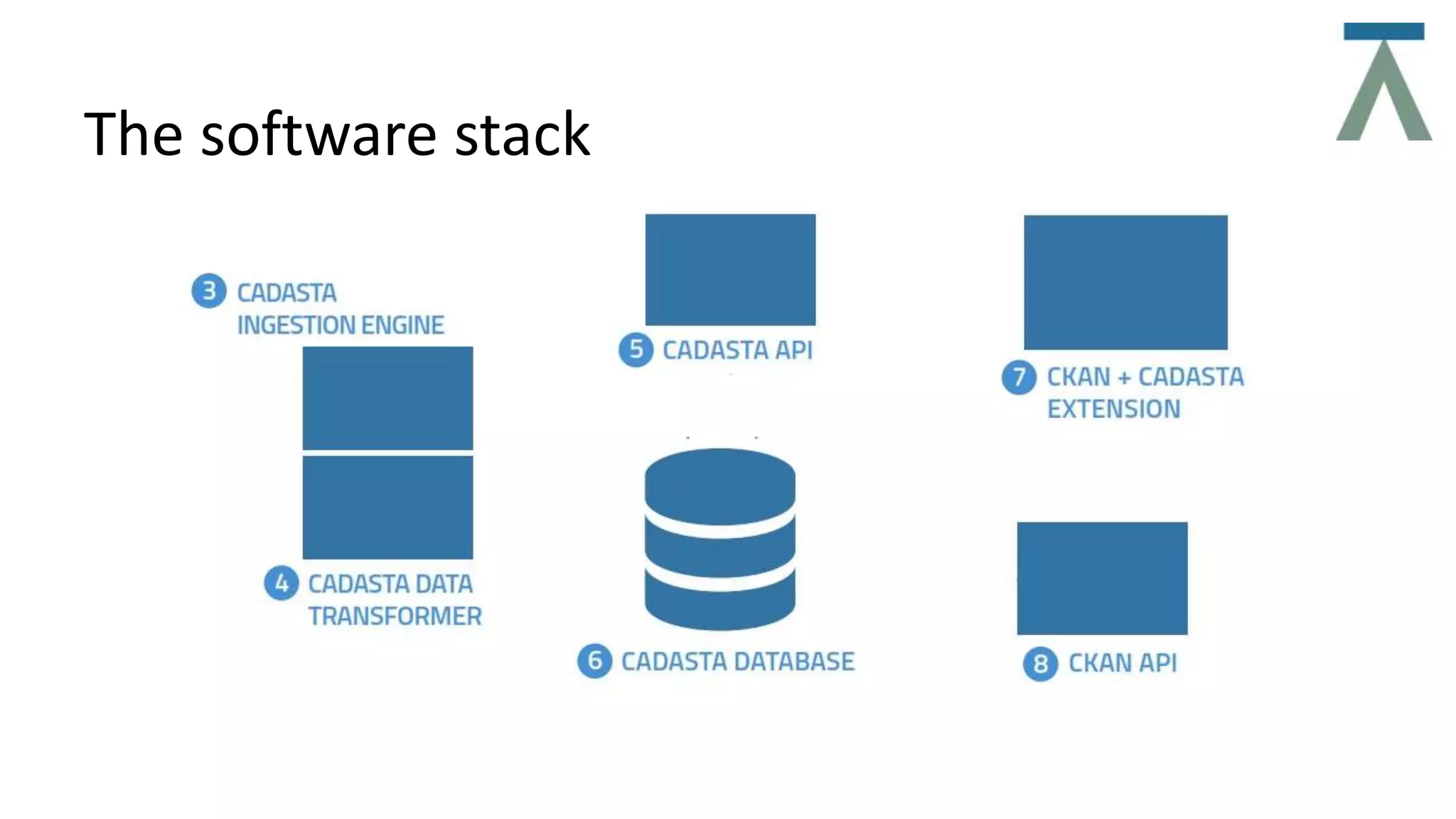
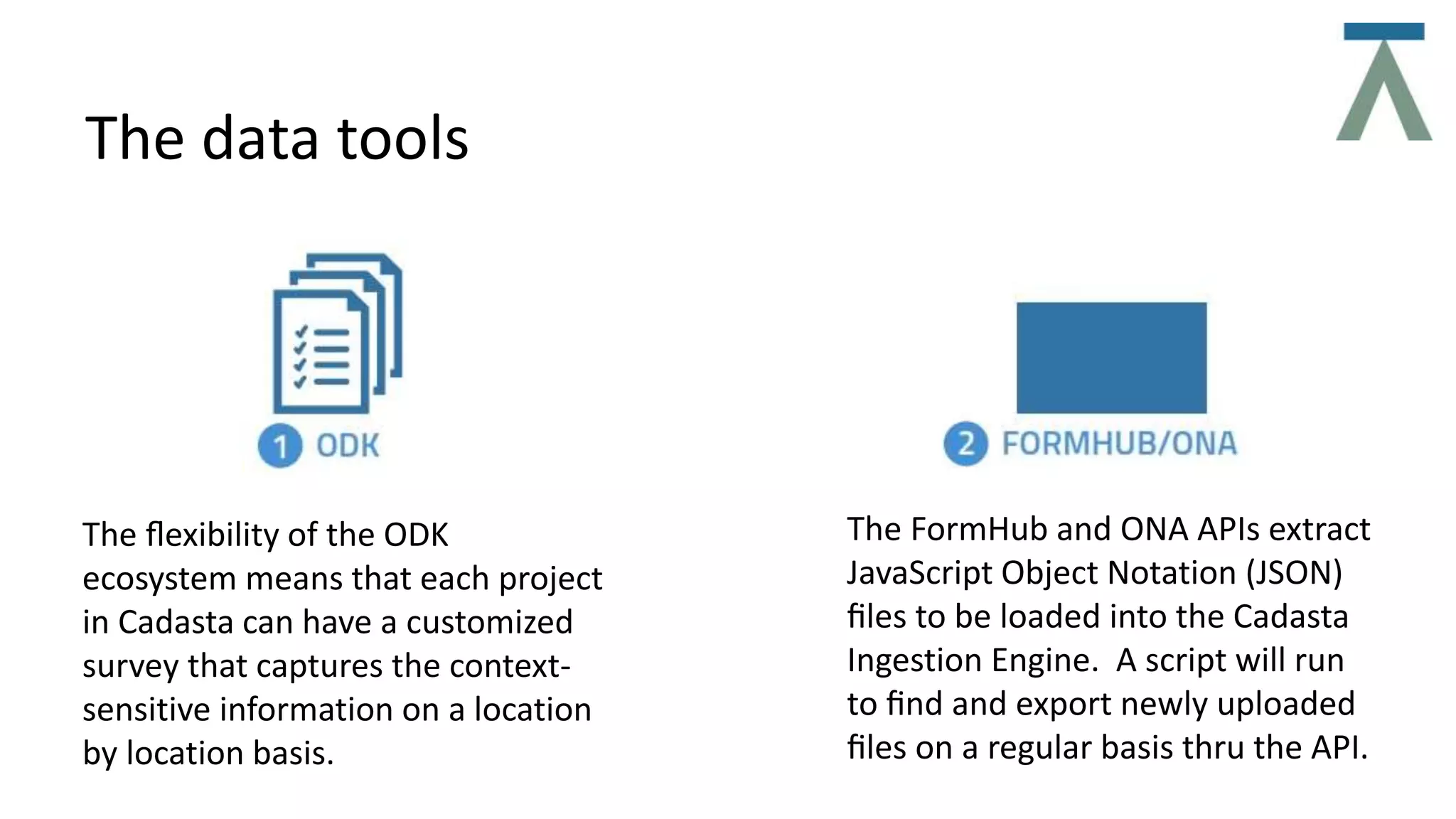
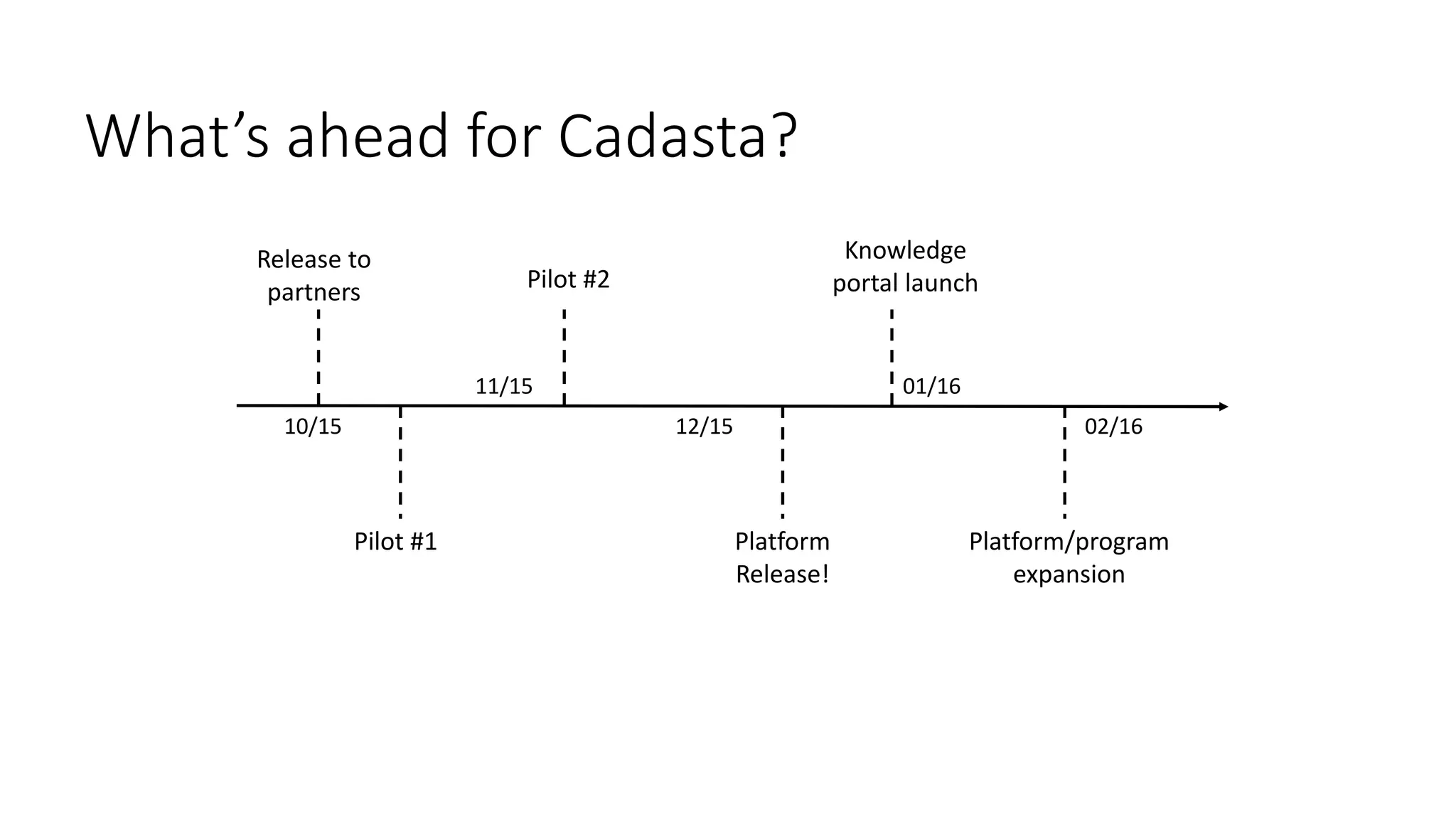
The document discusses Cadasta, an open source platform that aims to simplify, modernize and expedite the documentation of property rights globally. It provides an alternative model for collecting and managing ownership data using open source tools, data, community and maps. The Cadasta platform utilizes customized surveys on a location-by-location basis to capture context-sensitive land tenure information, with the data stored in a PostGreSQL database. It focuses on enabling informed consent and privacy protection, with an emphasis on empowering local communities to sustainably document land rights.