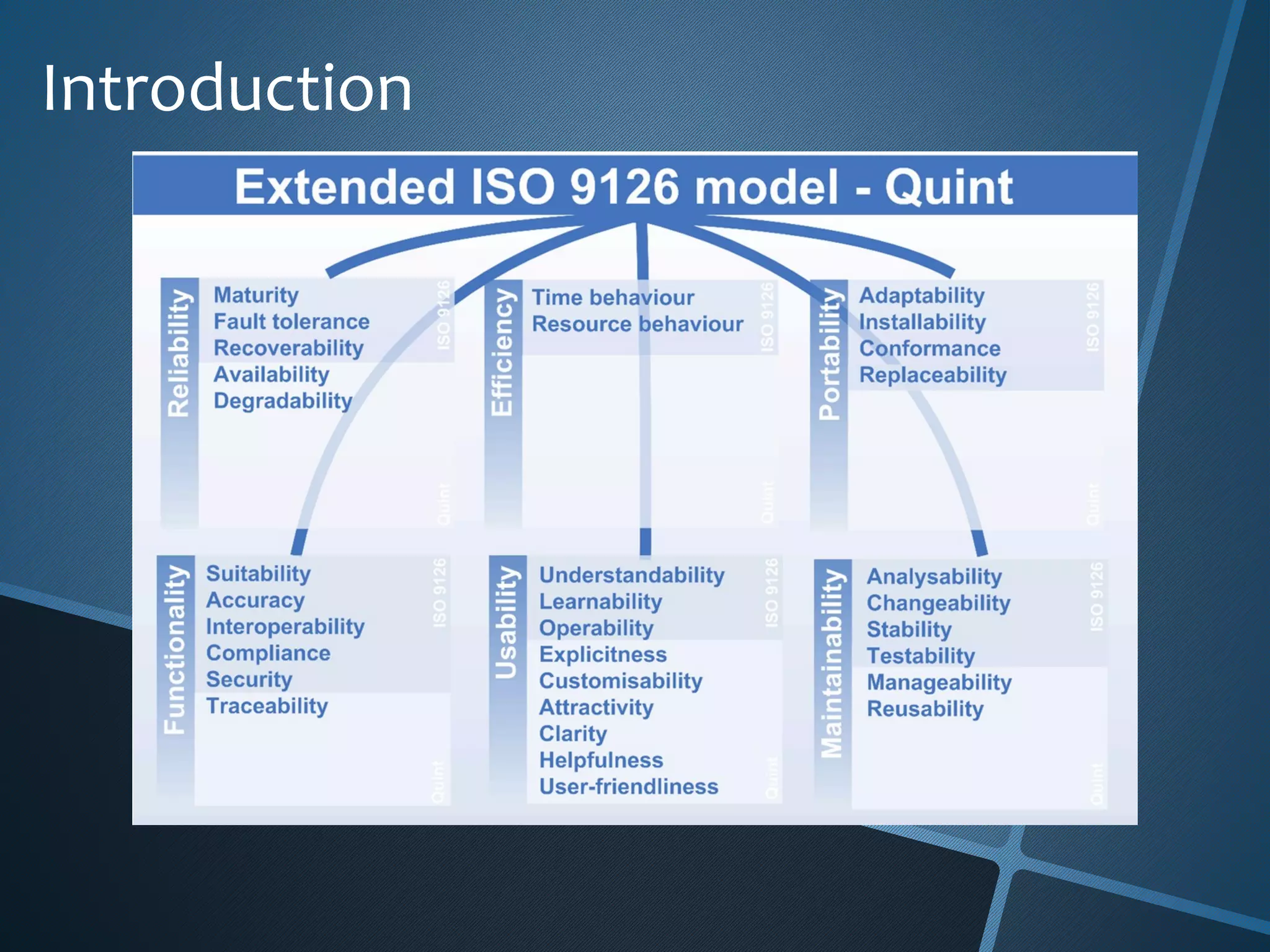
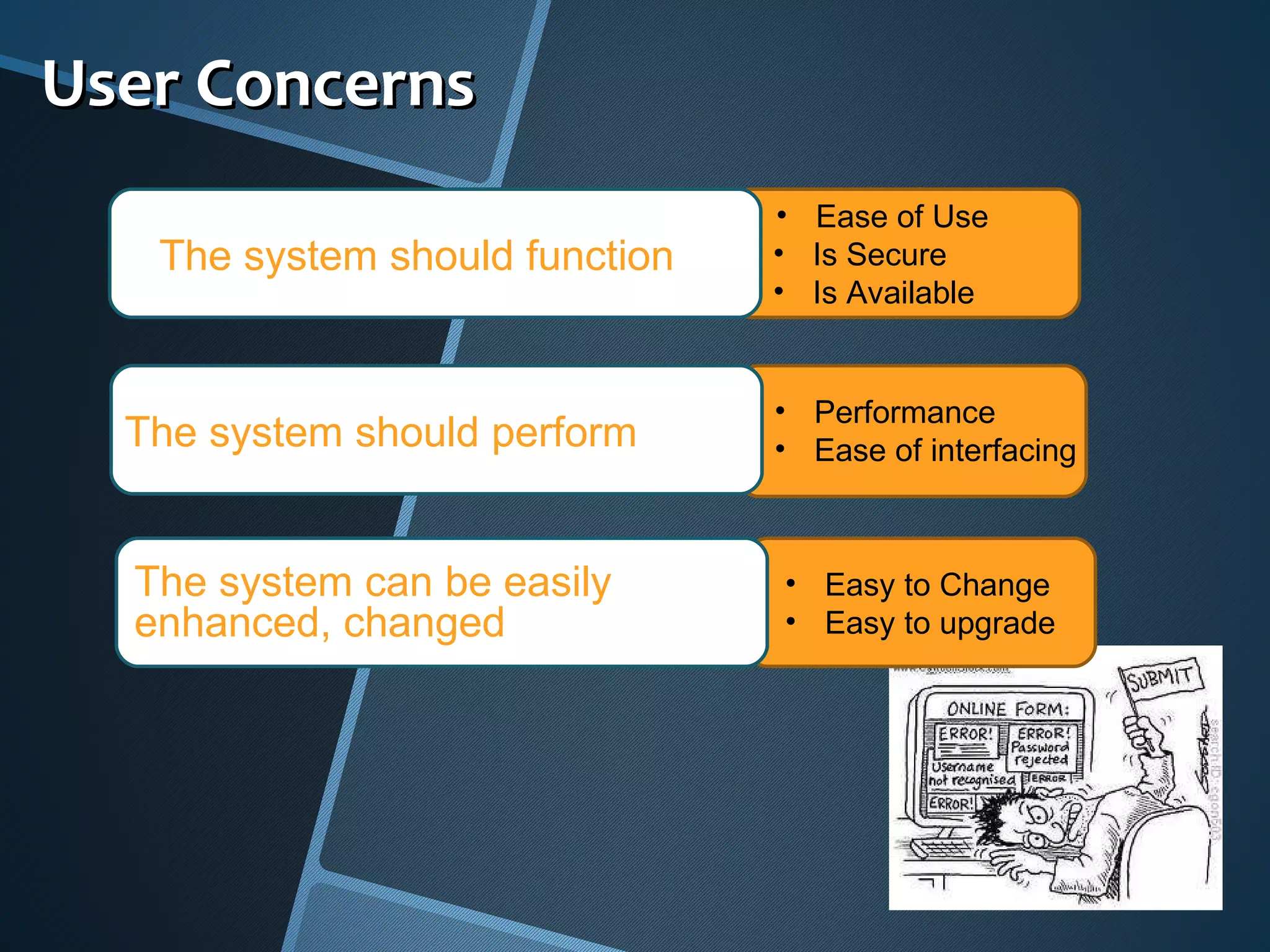
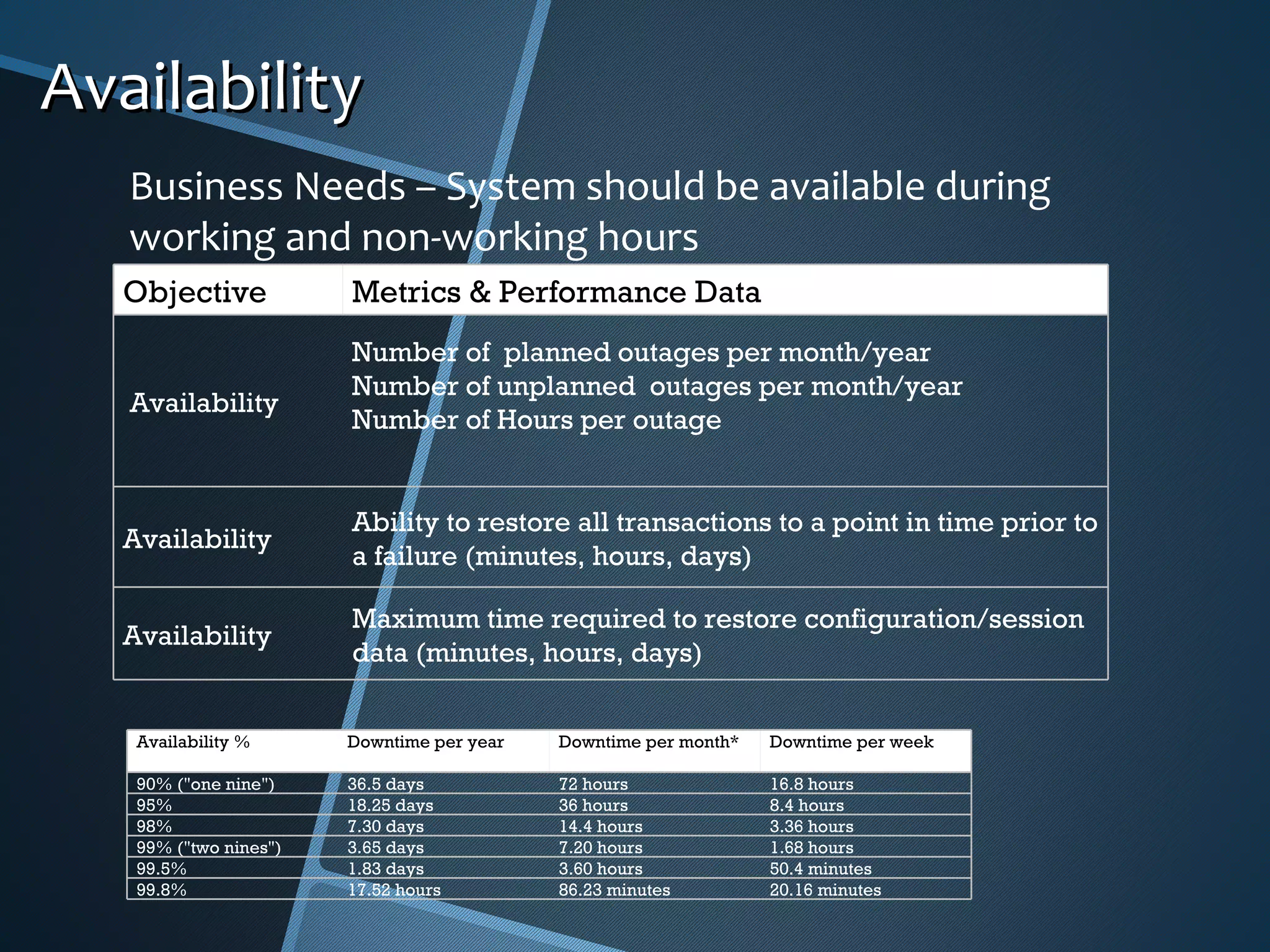
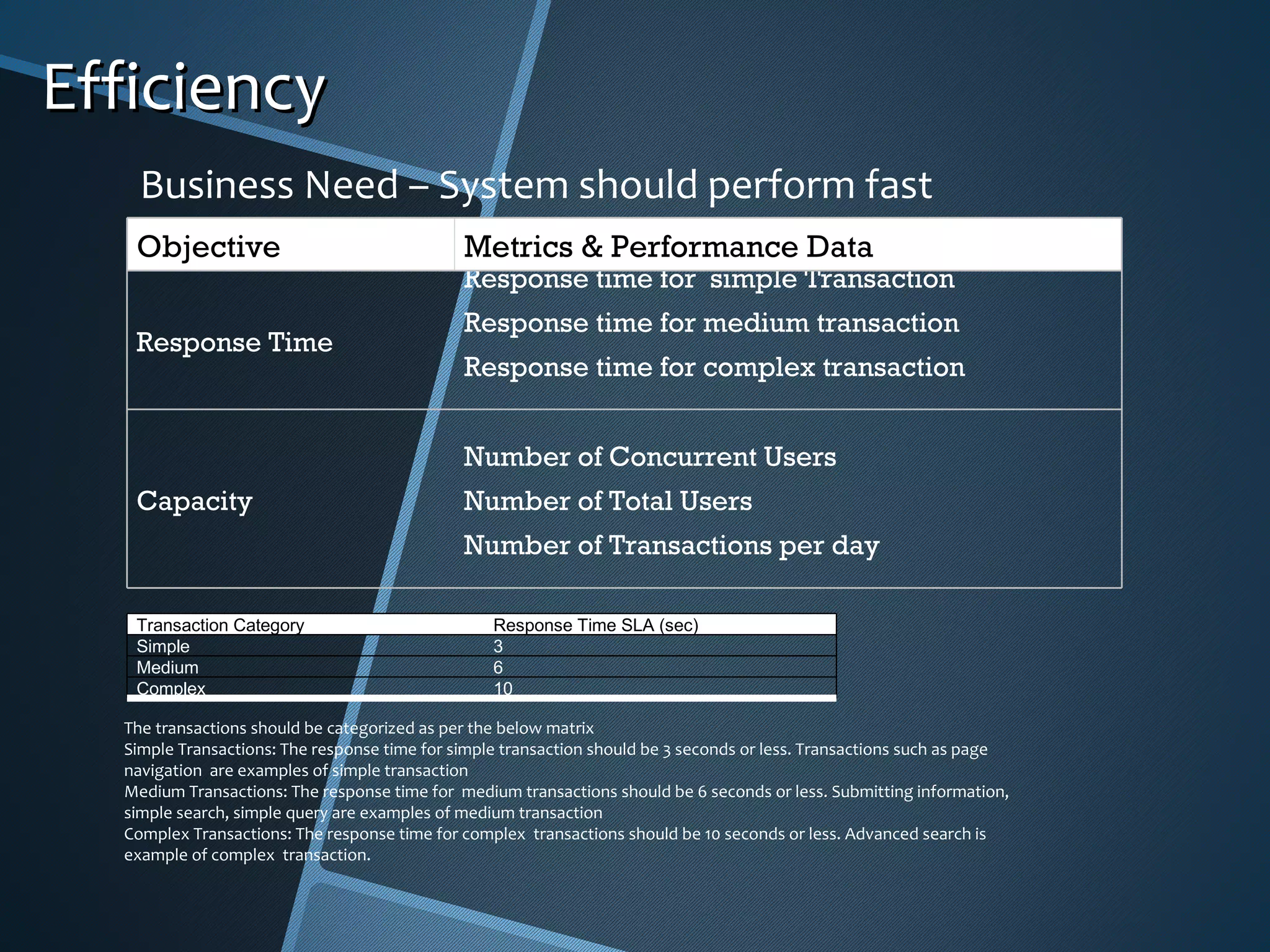
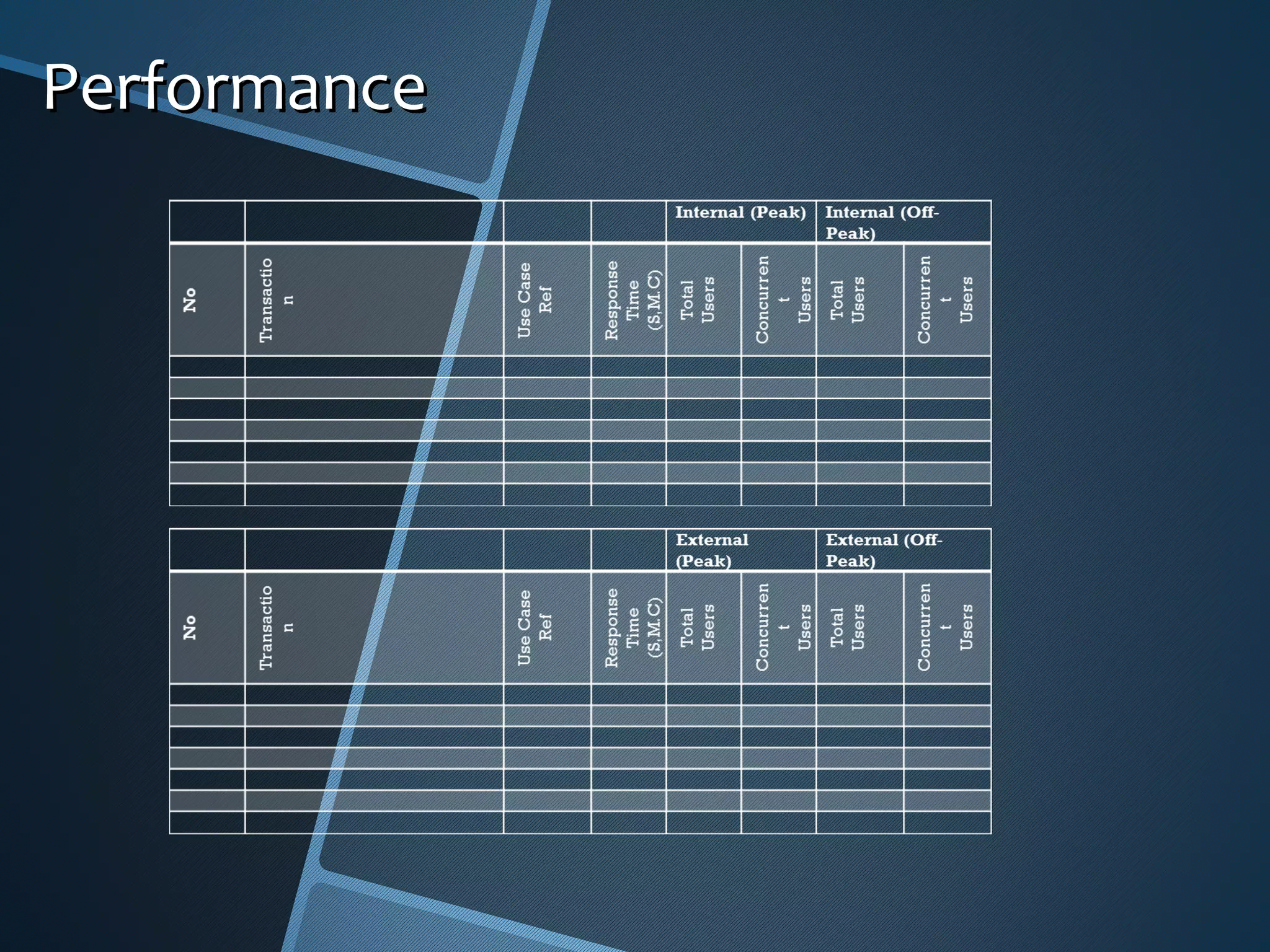
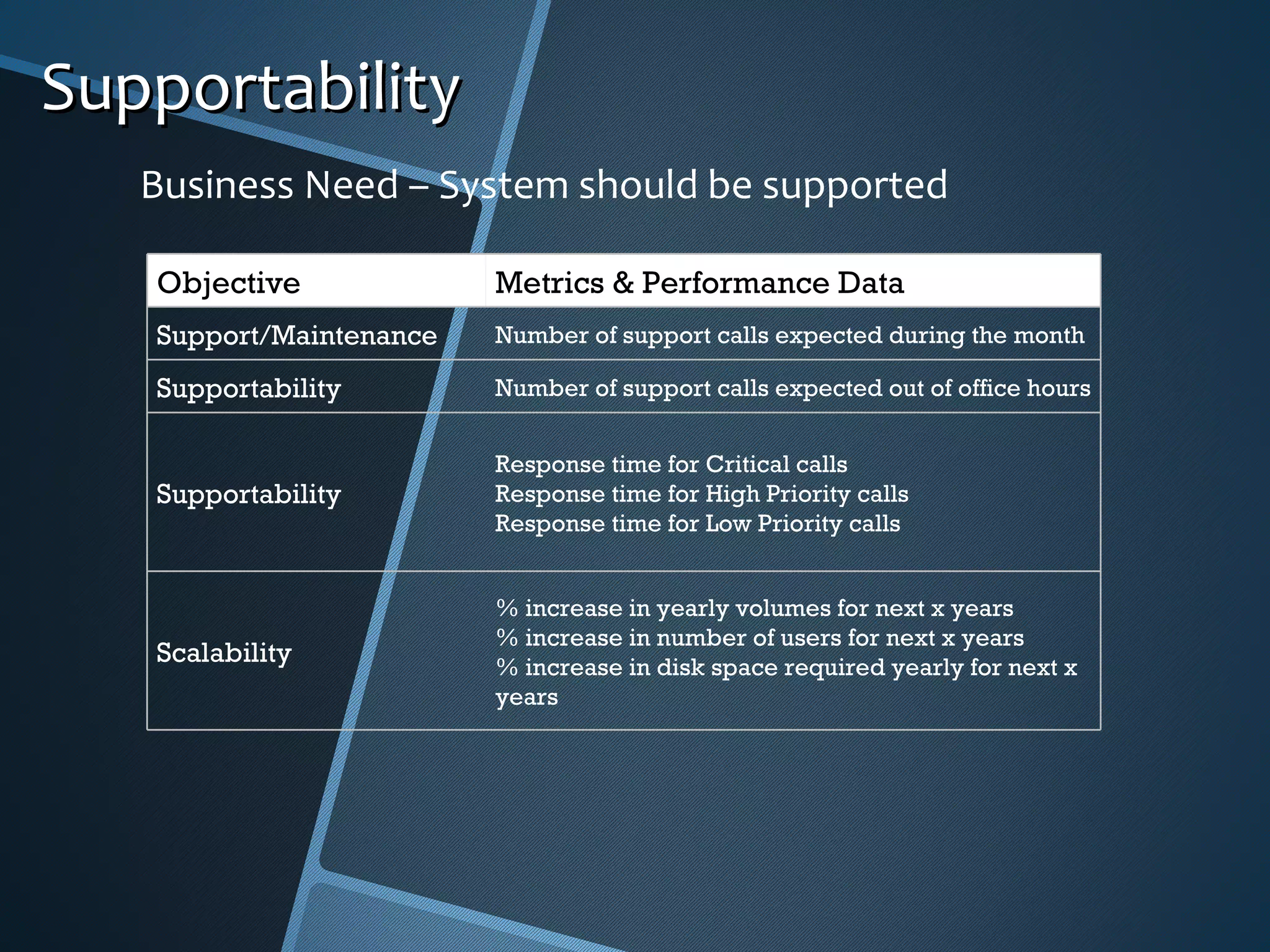
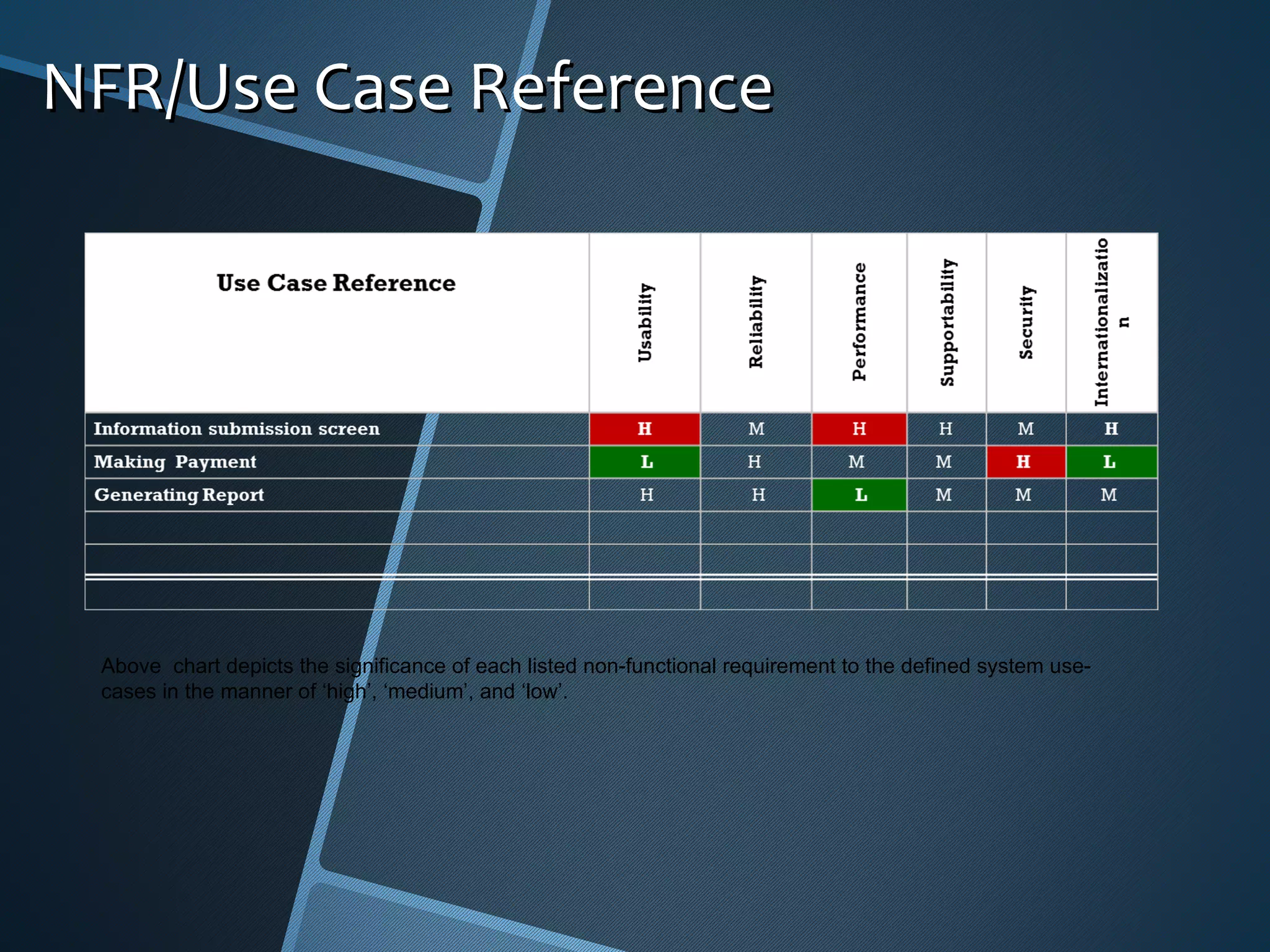
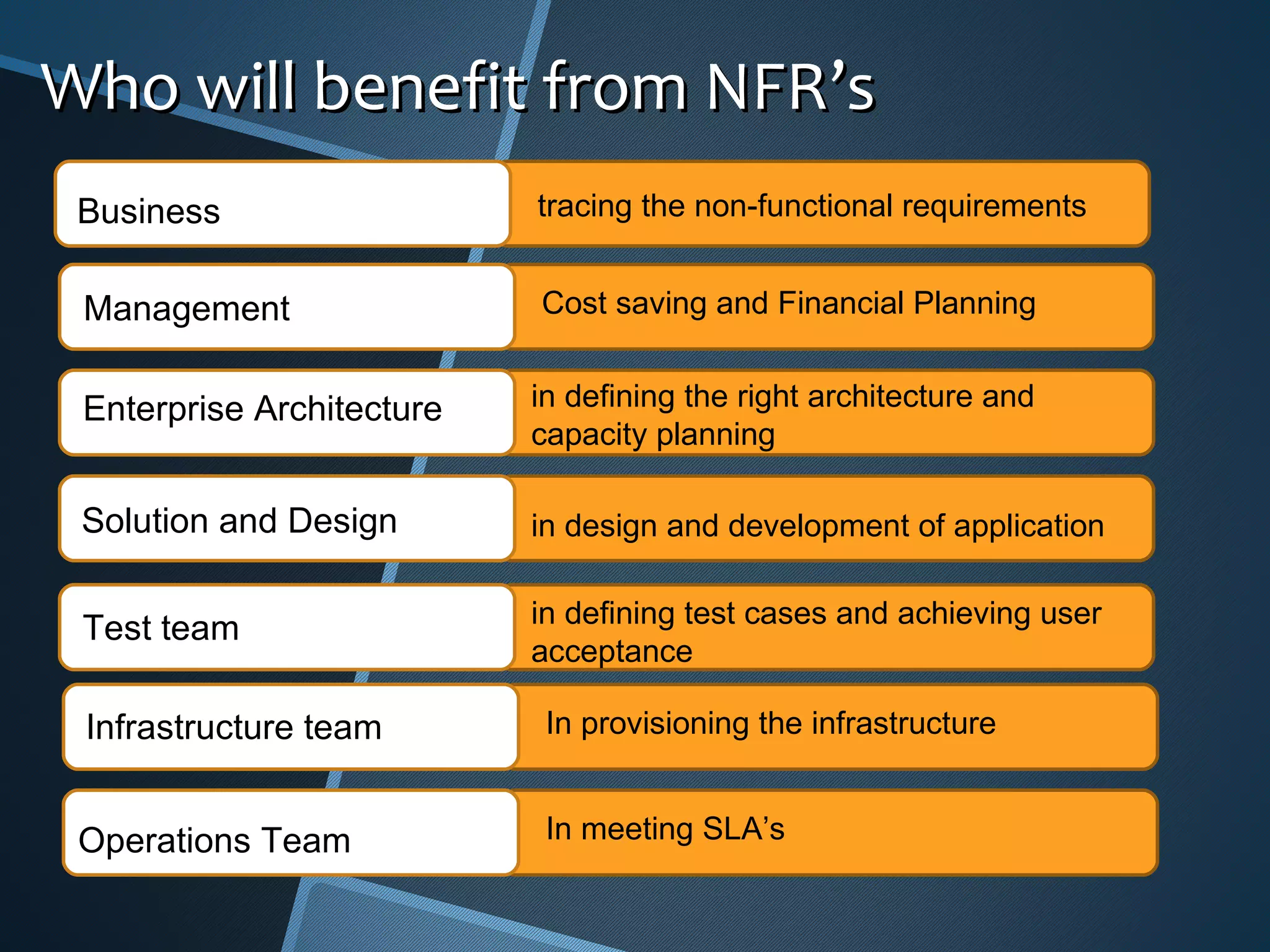
The document outlines the importance of capturing measurable non-functional requirements (NFRs) for system performance, usability, security, and supportability. It differentiates NFRs from functional requirements and provides metrics for evaluating aspects like availability, response times, and compliance standards. Furthermore, it emphasizes how different stakeholders, such as infrastructure and operations teams, can benefit from clear NFRs in their respective roles.
![Capturing Measurable Non-Functional Requirements Shehzad Lakdawala, Enterprise Architect http://ae.linkedin.com/in/shehzadl [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capturingmeasurablenon-functionalrequirements-110926110712-phpapp02/75/Capturing-Measurable-Non-Functional-Requirements-1-2048.jpg)