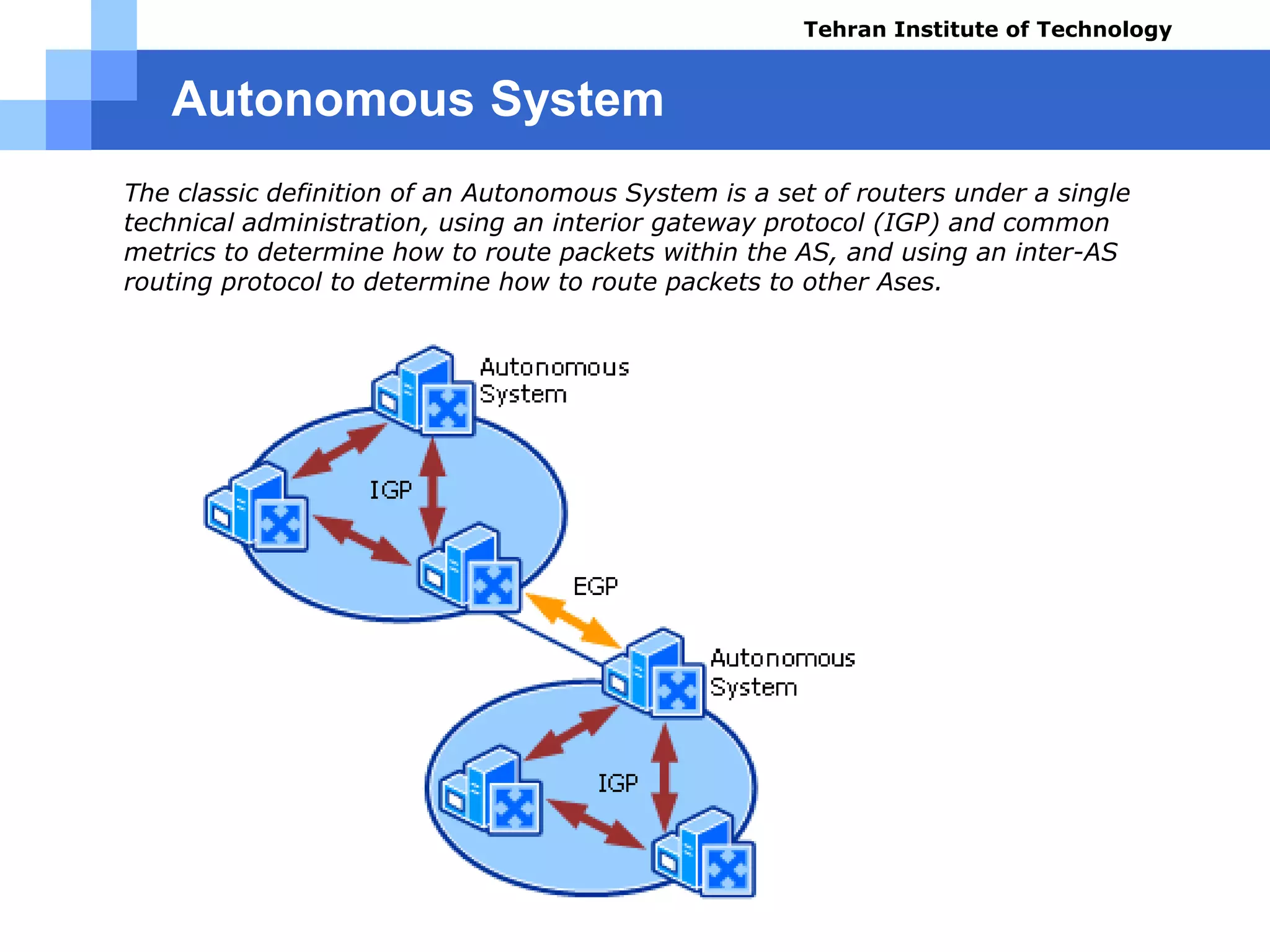
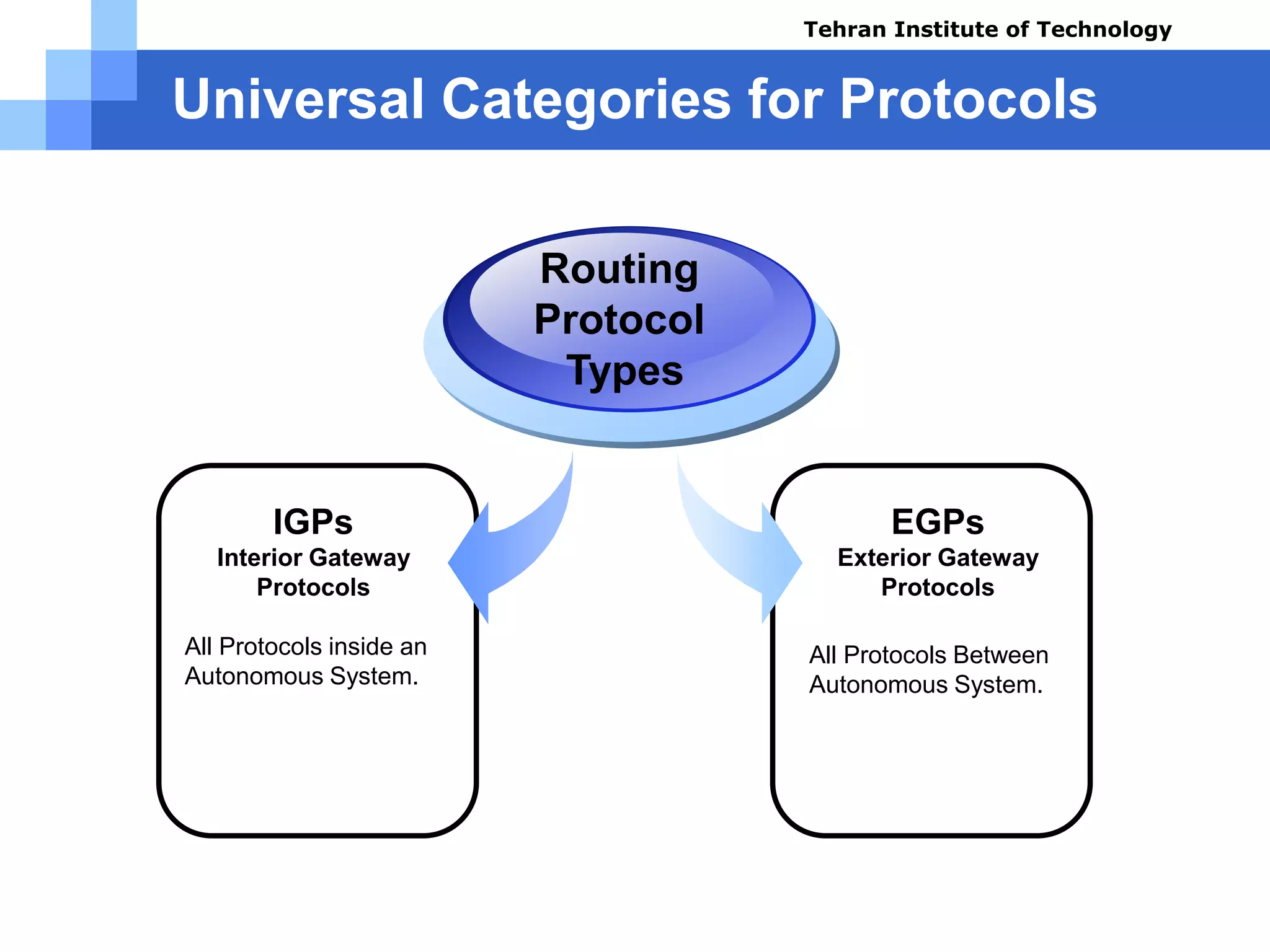
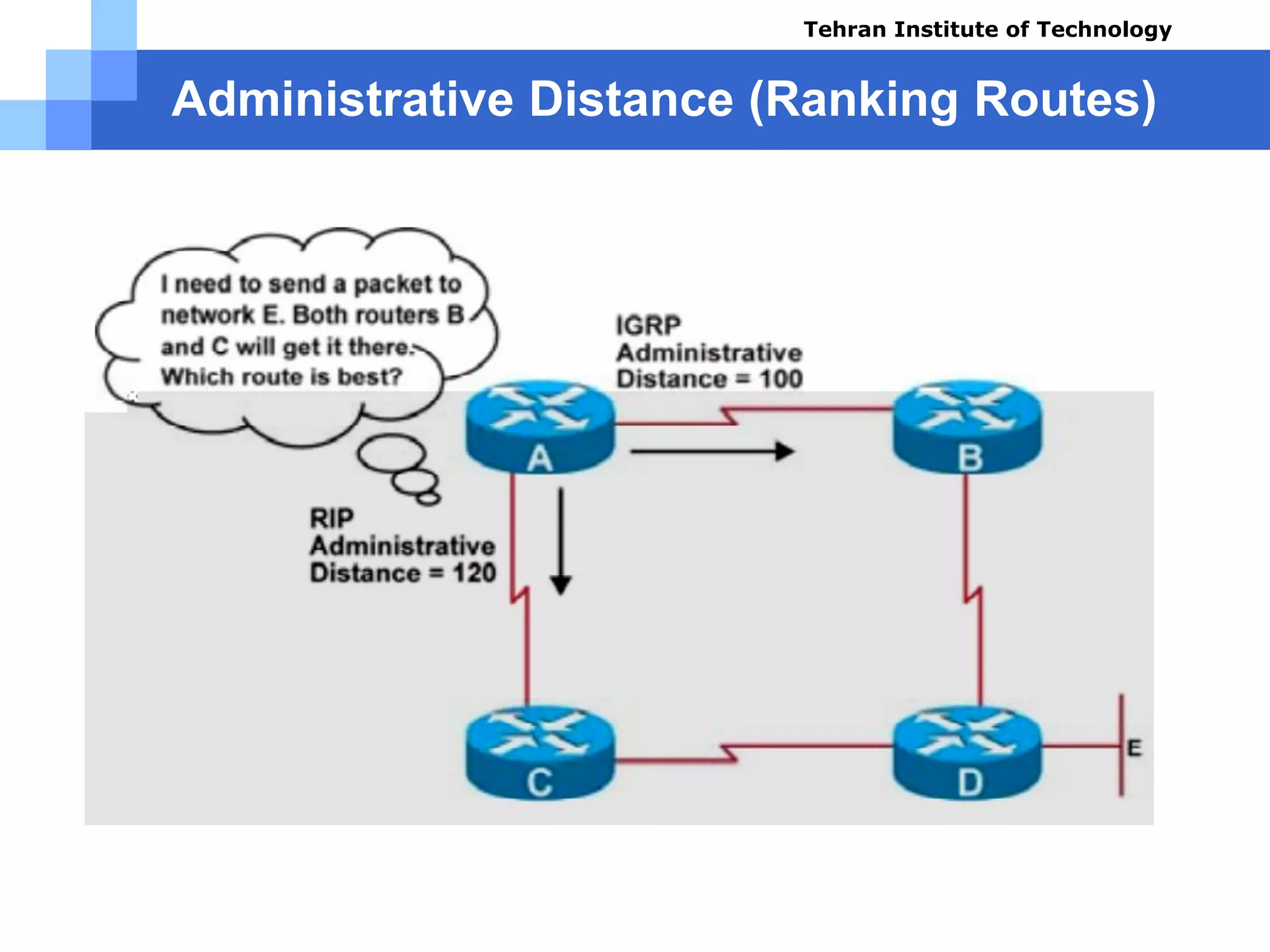
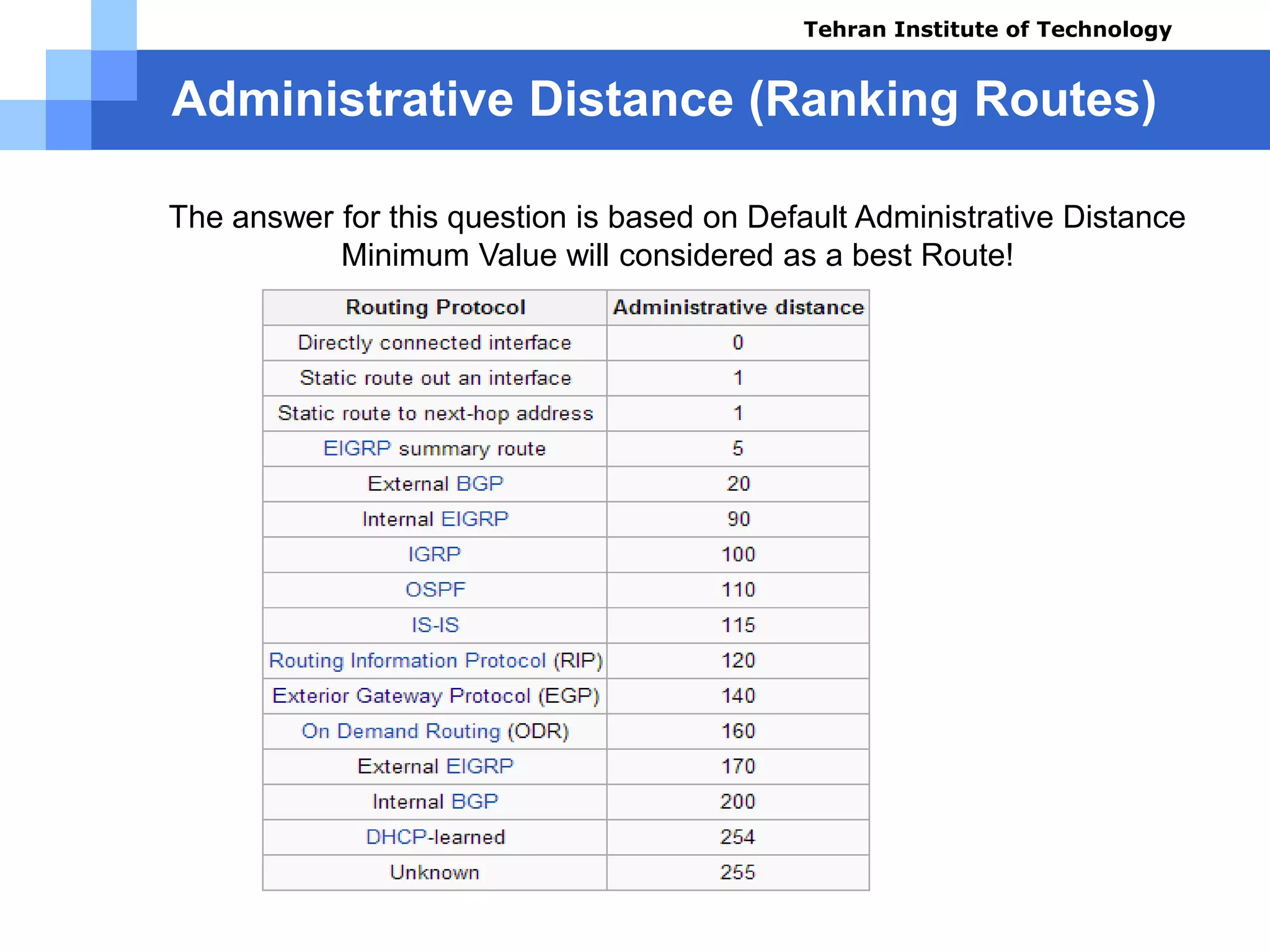
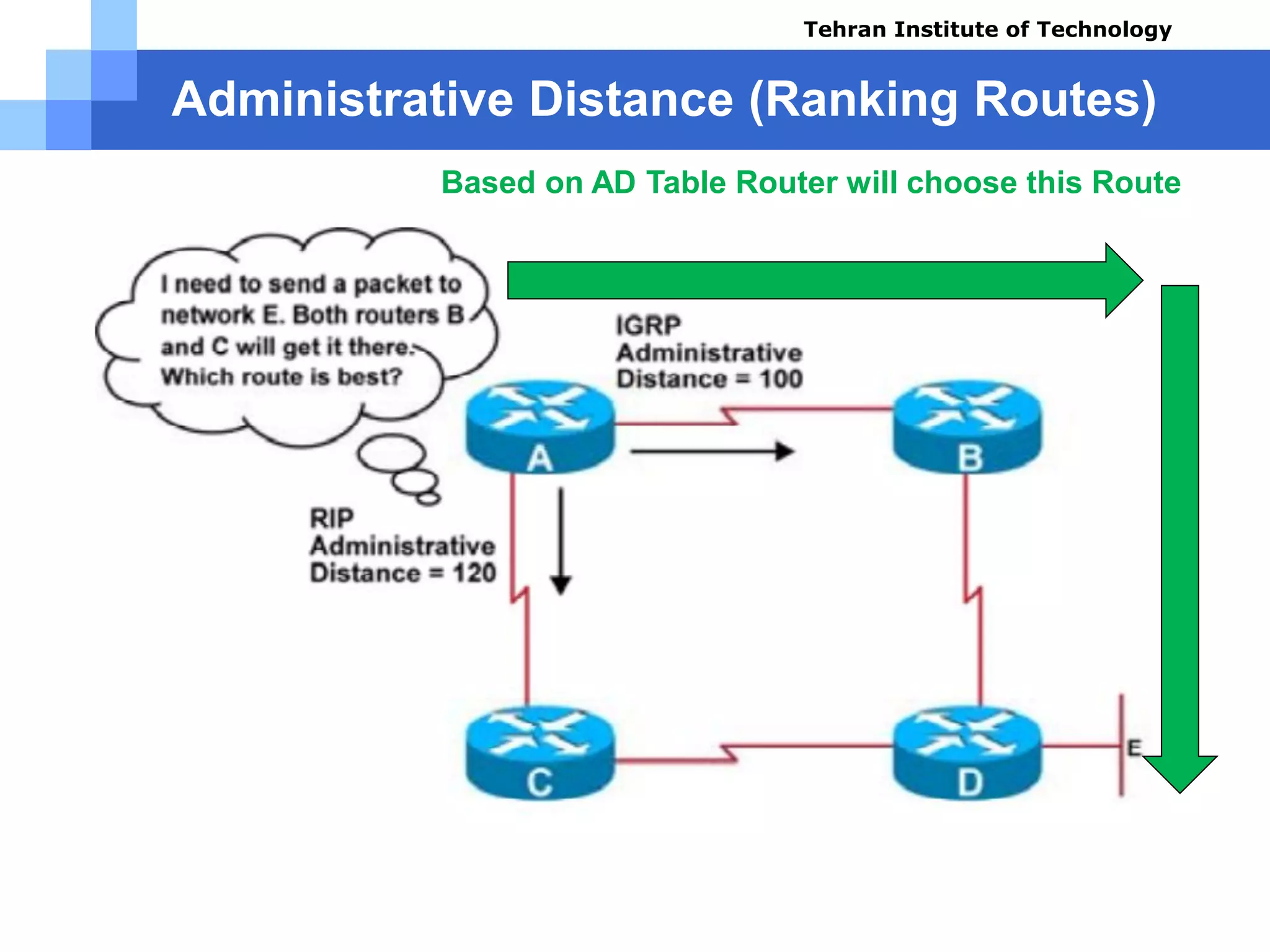
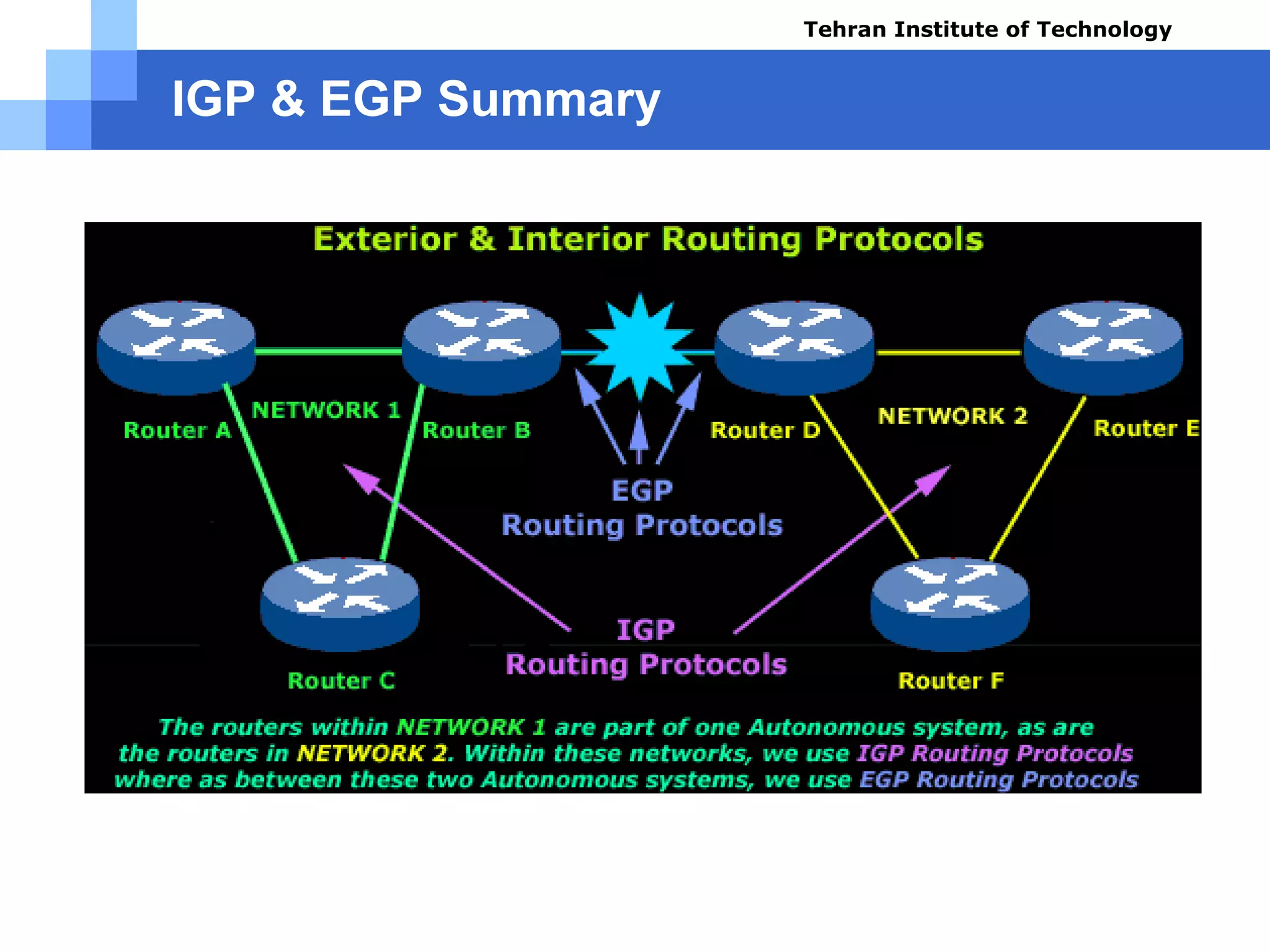
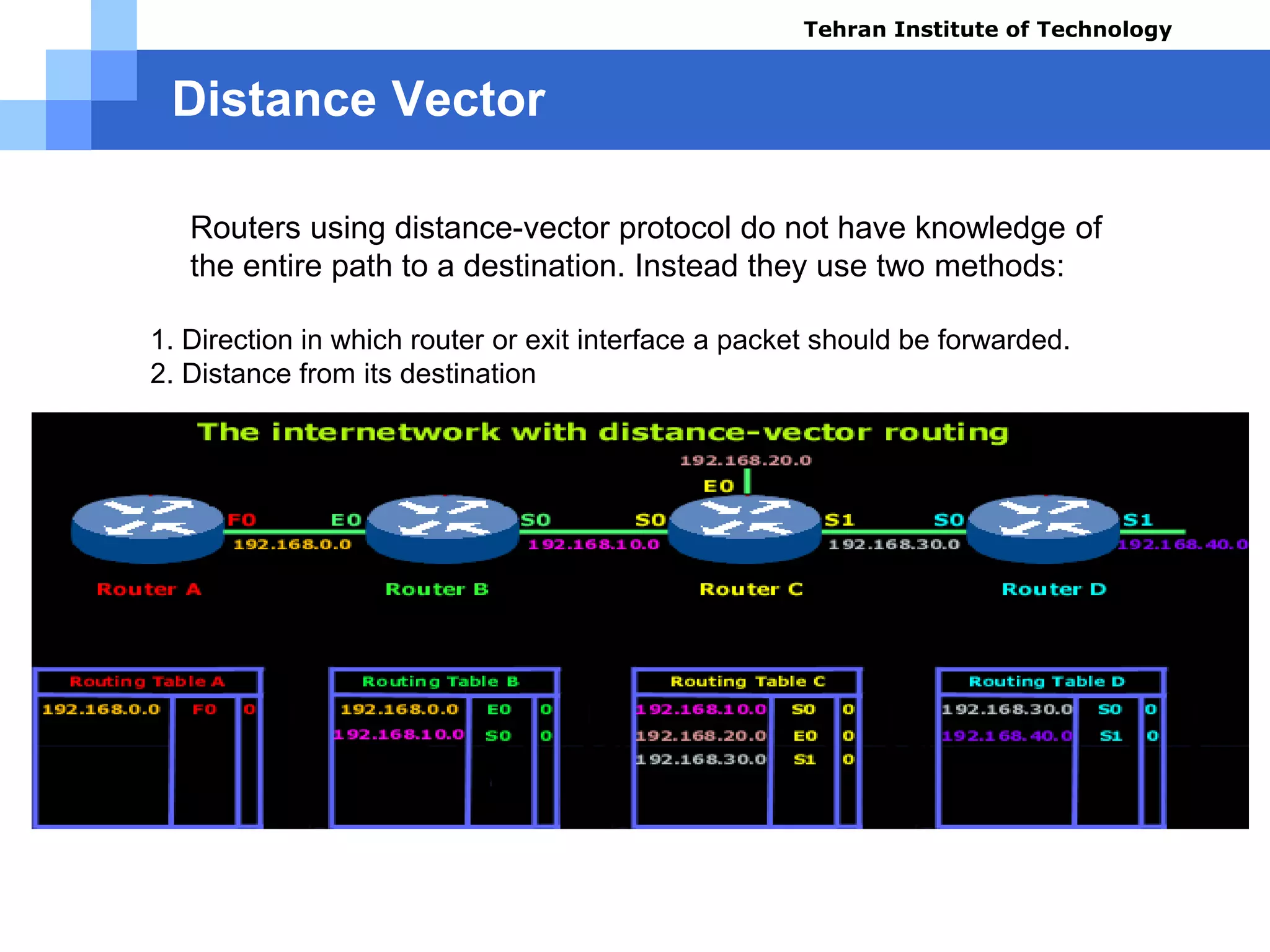
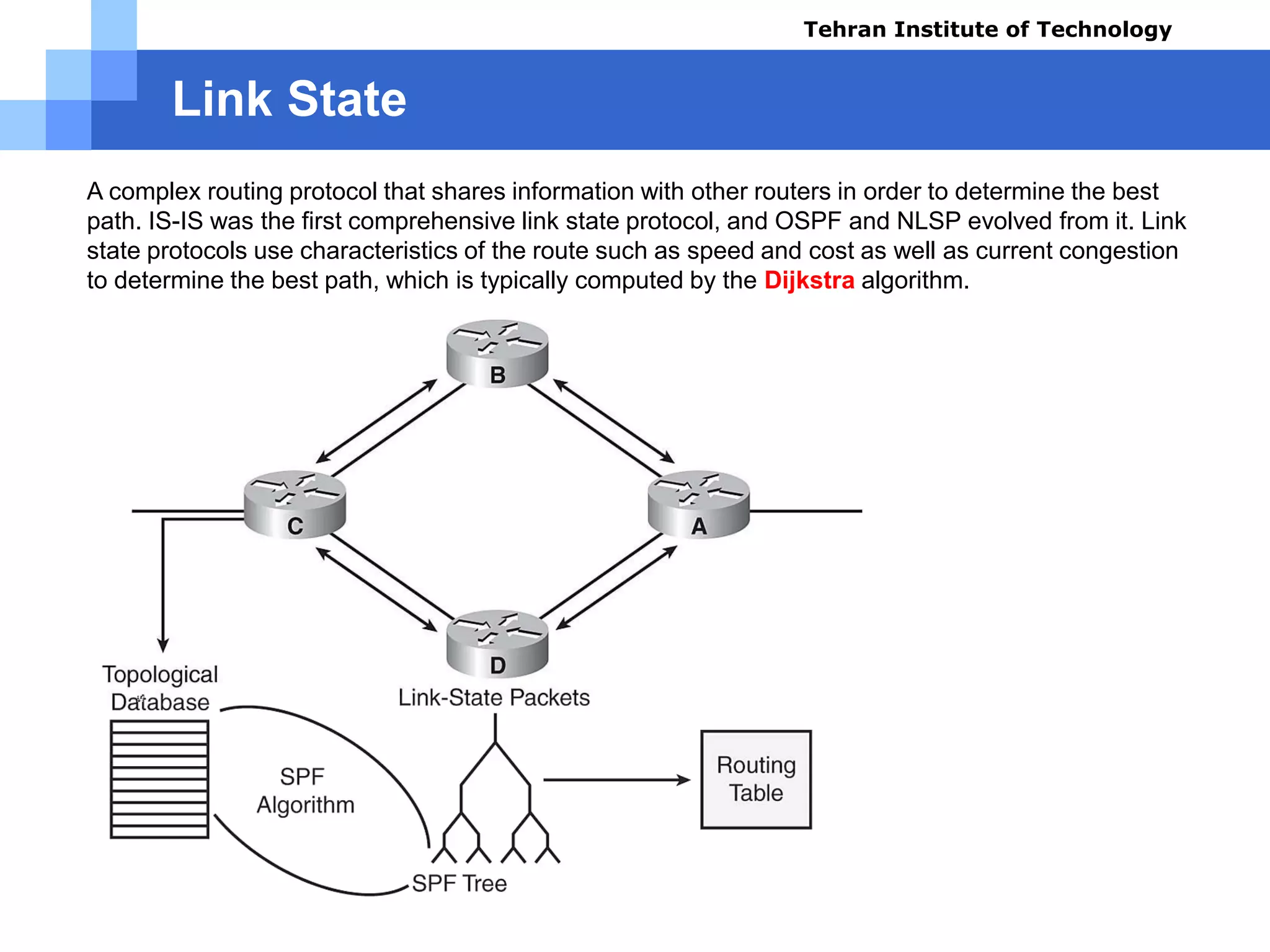
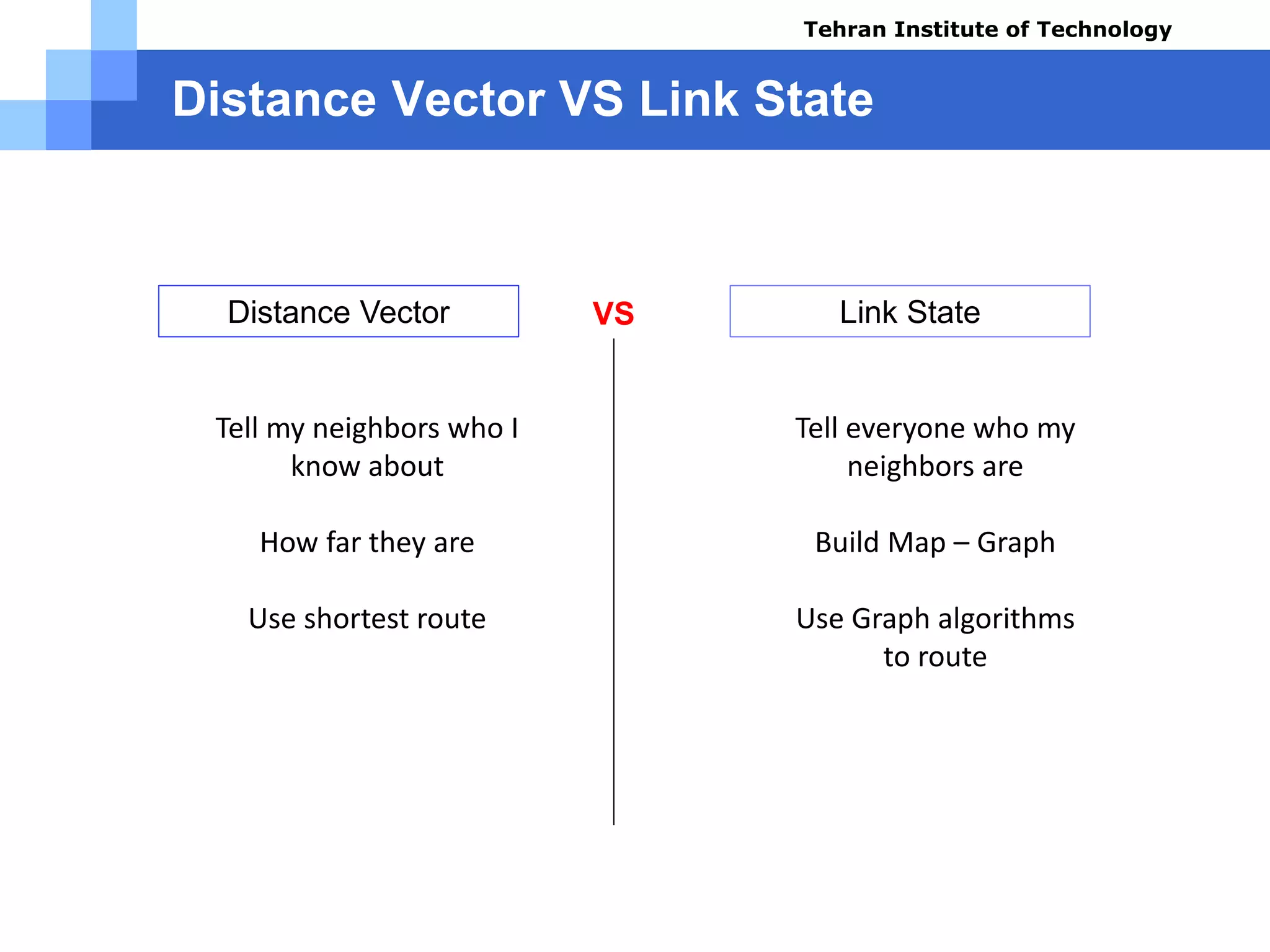
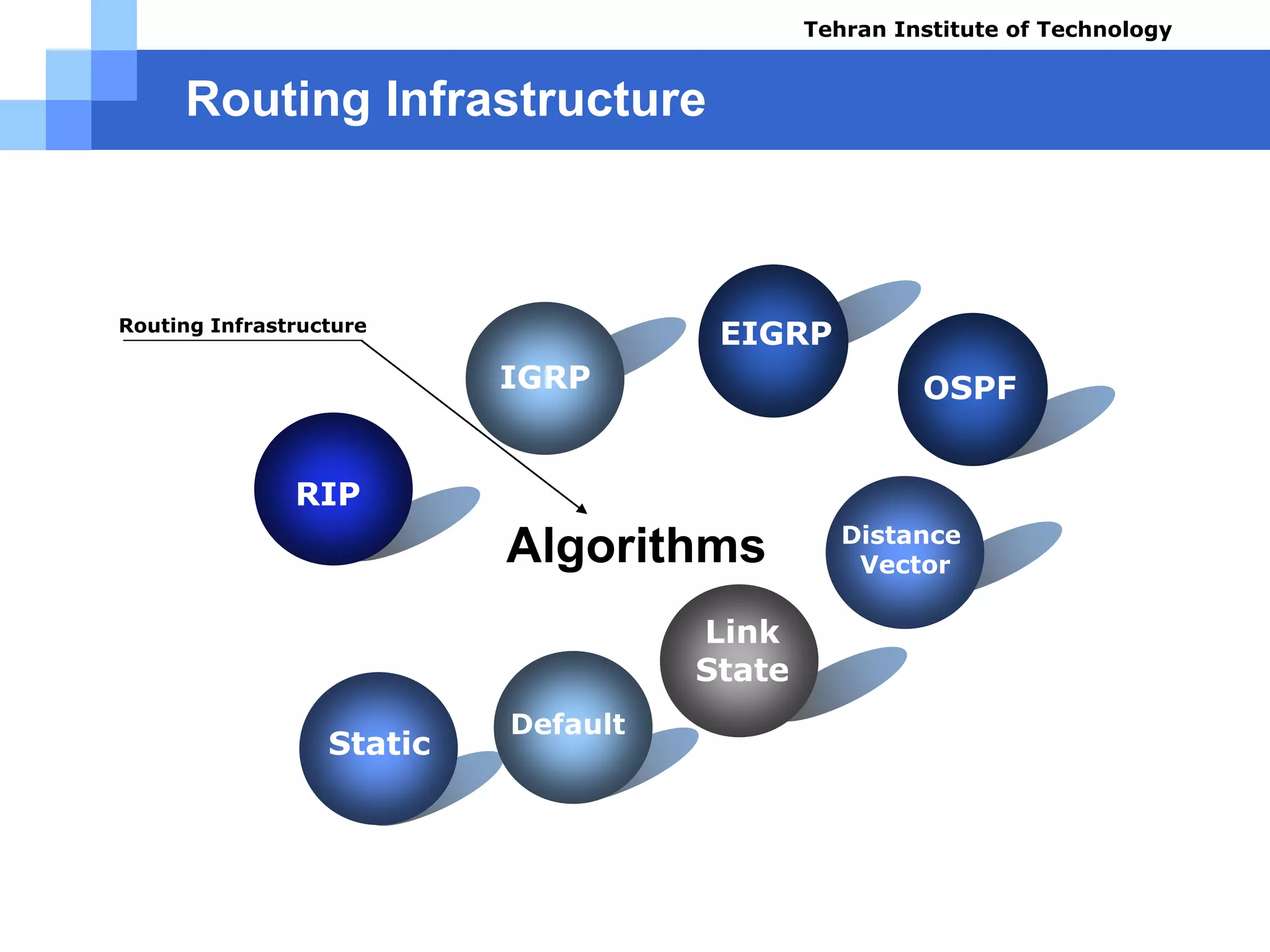
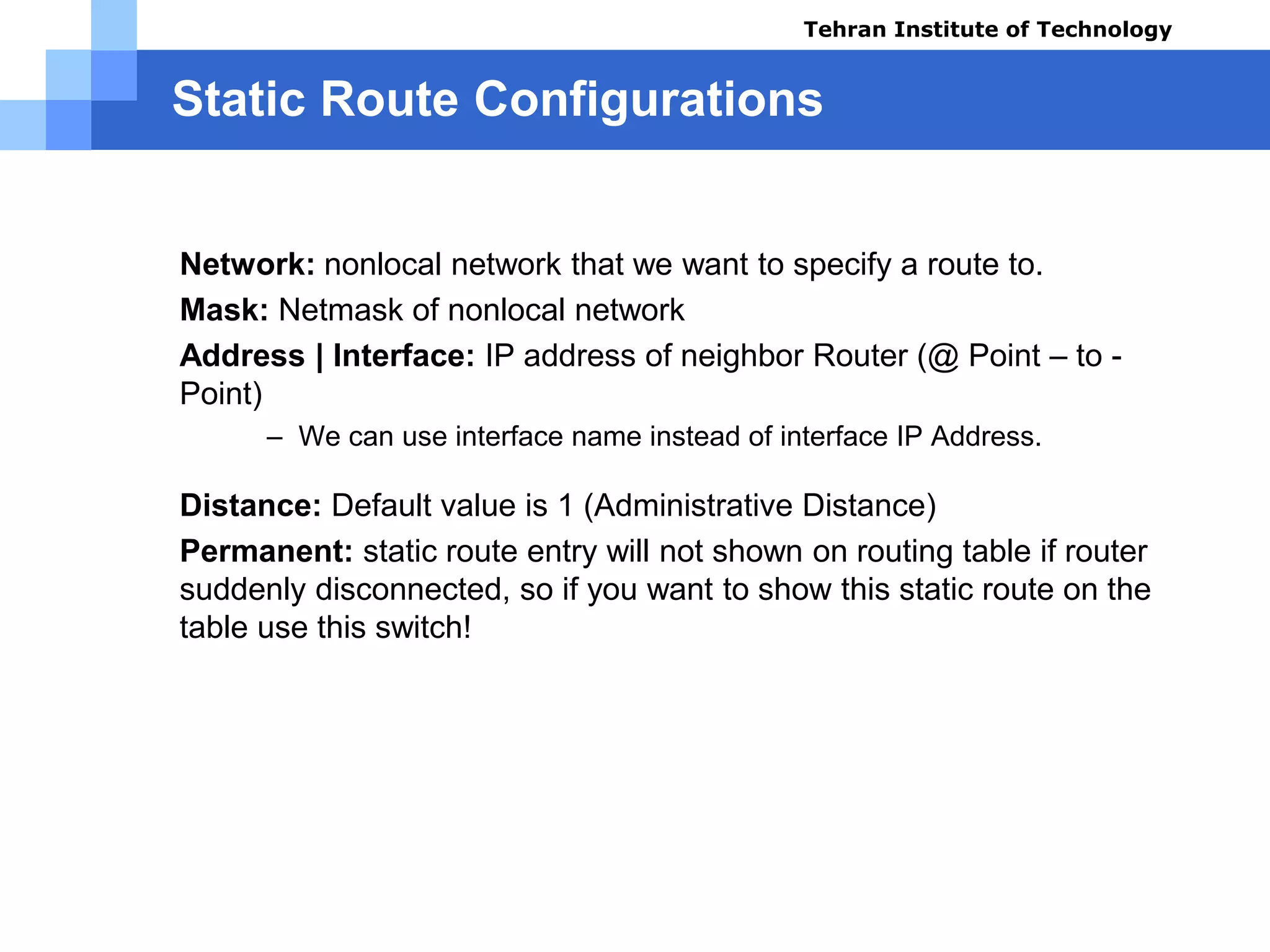
The document covers various aspects of router configuration and network routing theories as part of a Cisco CCNA course. It discusses static and dynamic routing, including the configuration of default routes and administrative distances. Additionally, it contrasts distance vector and link state routing protocols, providing examples and commands for network routing scenarios.



![Default Route
What the purpose of this tiny program?
» For (i=0 ; i<9 ; i++)
» If num[i] == 0
» Cout<< “action Acknowledged!”;
» Else Cout << “action not acknowledged!”;
When the code visits “0” an action will be performed, else it can
not be Done! So the default route acts as same as this code!
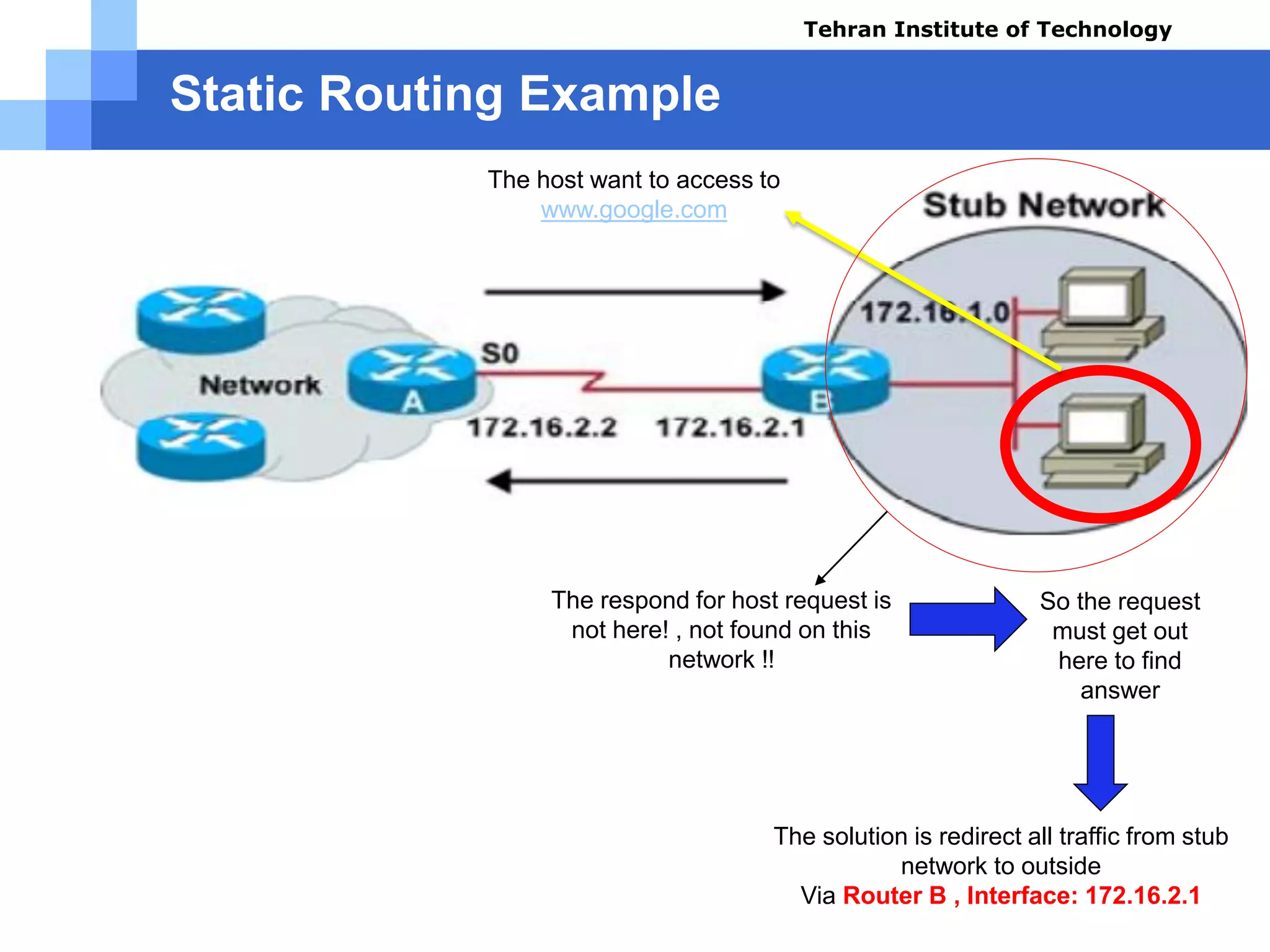
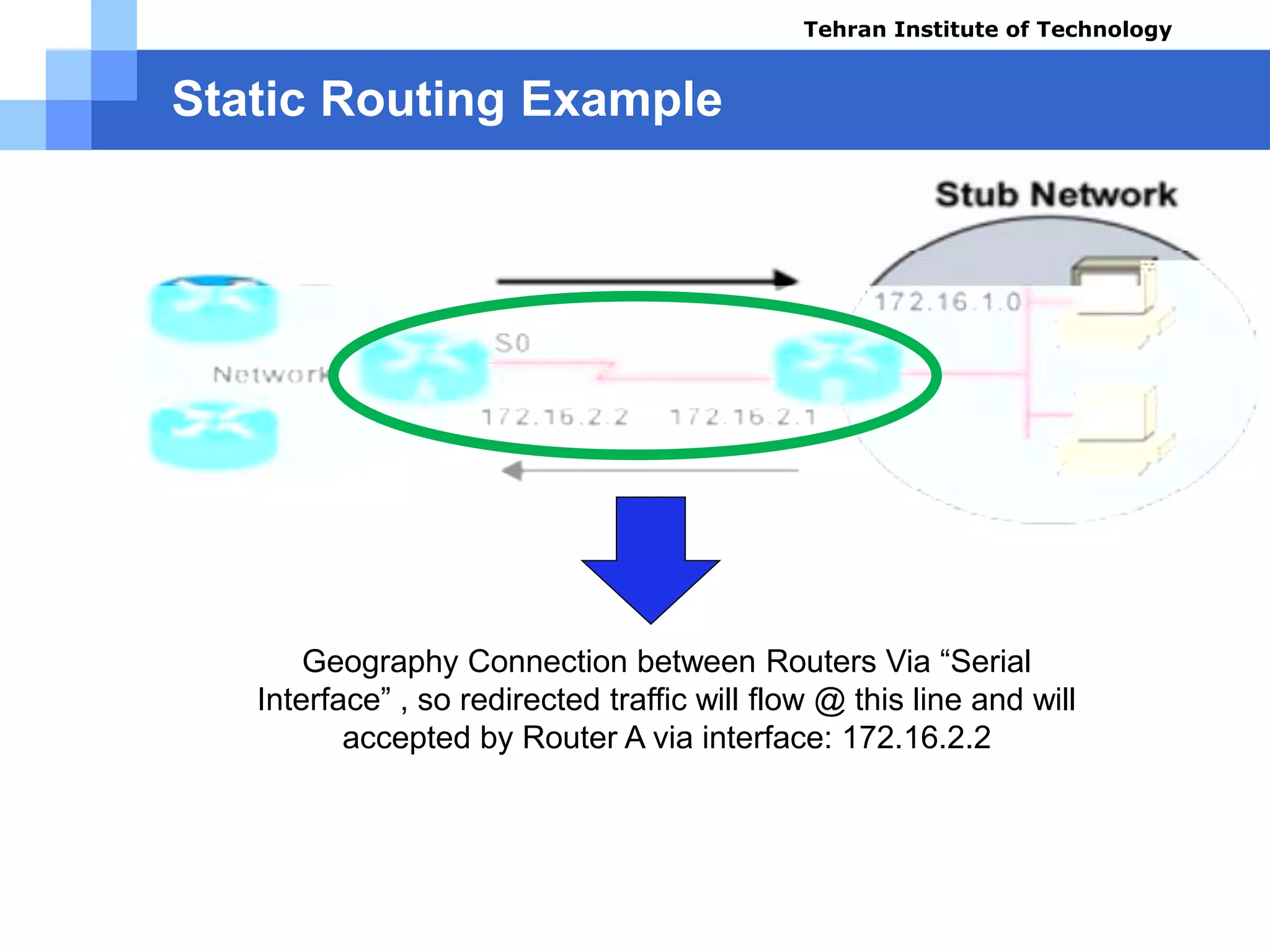
If the host packets destination
don’t match the local address:
172.16.1.0 , it will be forwarded
out of the network Via Router B ,
interface: 172.16.2.1
if requests on this network don’t match
the 172.16.1.0 Network Address
Default Route Acknowledged
else
Default Route not Acknowledged
Tehran Institute of Technology
Course name: Cisco CCNA
Instructor: Mansour.nch
Senior @ Tehran Institute of Technology
Copyright 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingprotocolspart01-140405121314-phpapp02/75/CCNA-Routing-Protocols-14-2048.jpg)
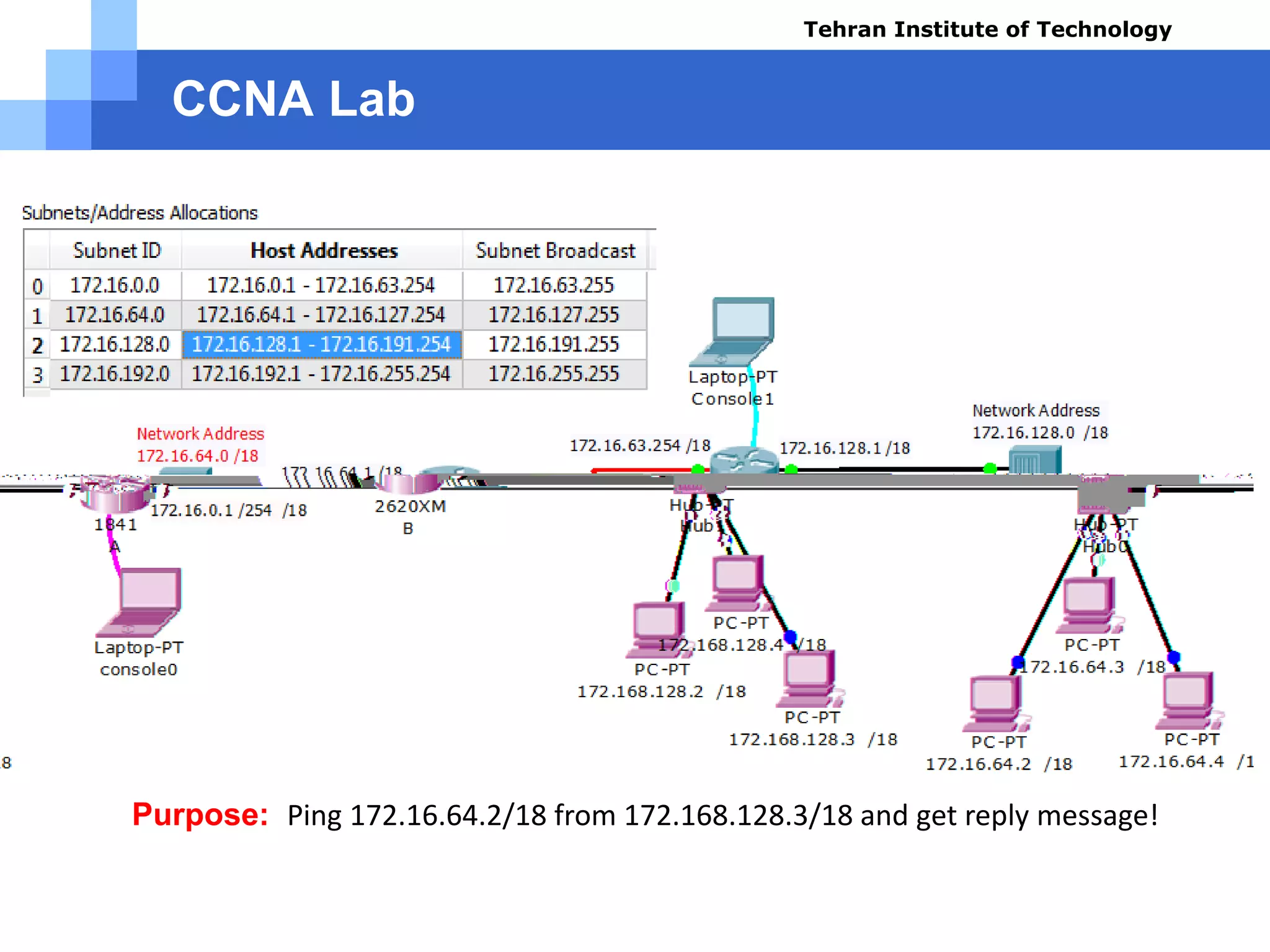
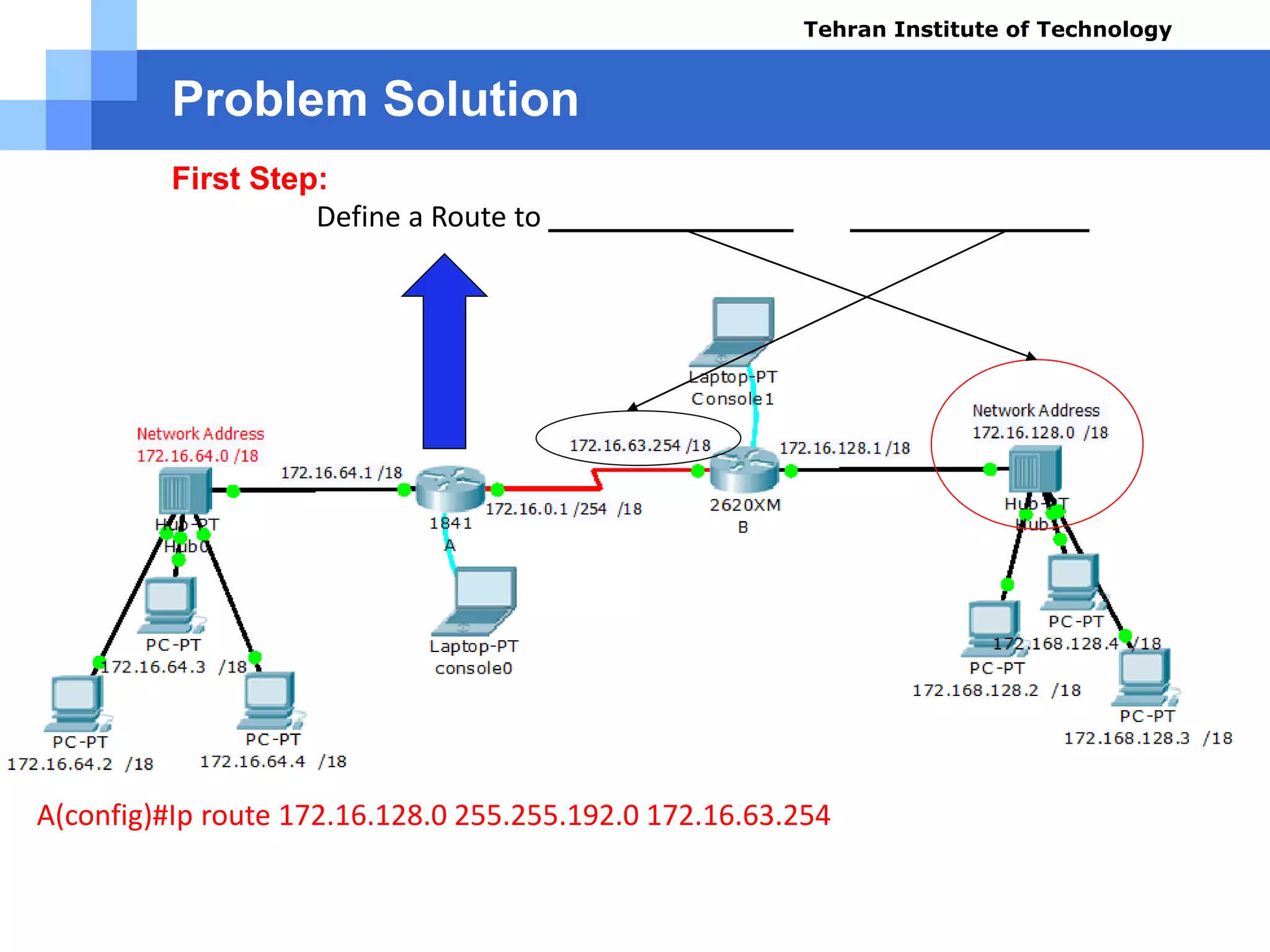
![Problem Solution
Test Results using command (A):
» A#show ip route
» Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
» D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
» N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
» E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
» i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
» * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
» P - periodic downloaded static route
» Gateway of last resort is not set
» 172.16.0.0/18 is subnetted, 3 subnets
» C 172.16.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0
» C 172.16.64.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
» S 172.16.128.0 [1/0] via 172.16.63.254
» A#
Tehran Institute of Technology
Course name: Cisco CCNA
Instructor: Mansour.nch
Senior @ Tehran Institute of Technology
Copyright 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingprotocolspart01-140405121314-phpapp02/75/CCNA-Routing-Protocols-20-2048.jpg)
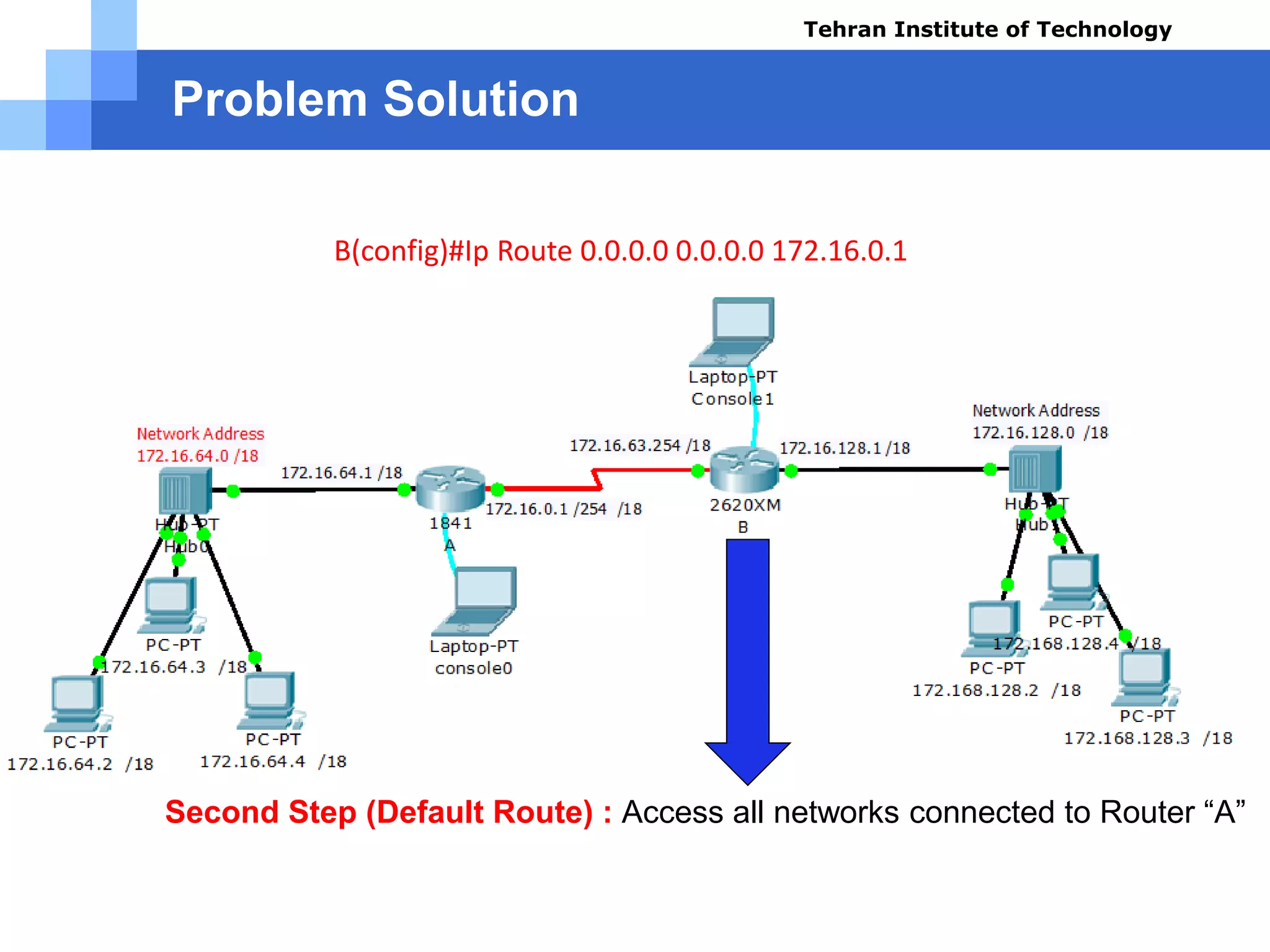
![Problem Solution
Test Results using command (B):
» Router#show ip route
» Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
» D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
» N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
» E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
» i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
» * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
» P - periodic downloaded static route
» Gateway of last resort is 172.16.0.1 to network 0.0.0.0
» 172.16.0.0/18 is subnetted, 2 subnets
» C 172.16.0.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
» C 172.16.128.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
» S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.0.1
Tehran Institute of Technology
Course name: Cisco CCNA
Instructor: Mansour.nch
Senior @ Tehran Institute of Technology
Copyright 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingprotocolspart01-140405121314-phpapp02/75/CCNA-Routing-Protocols-21-2048.jpg)