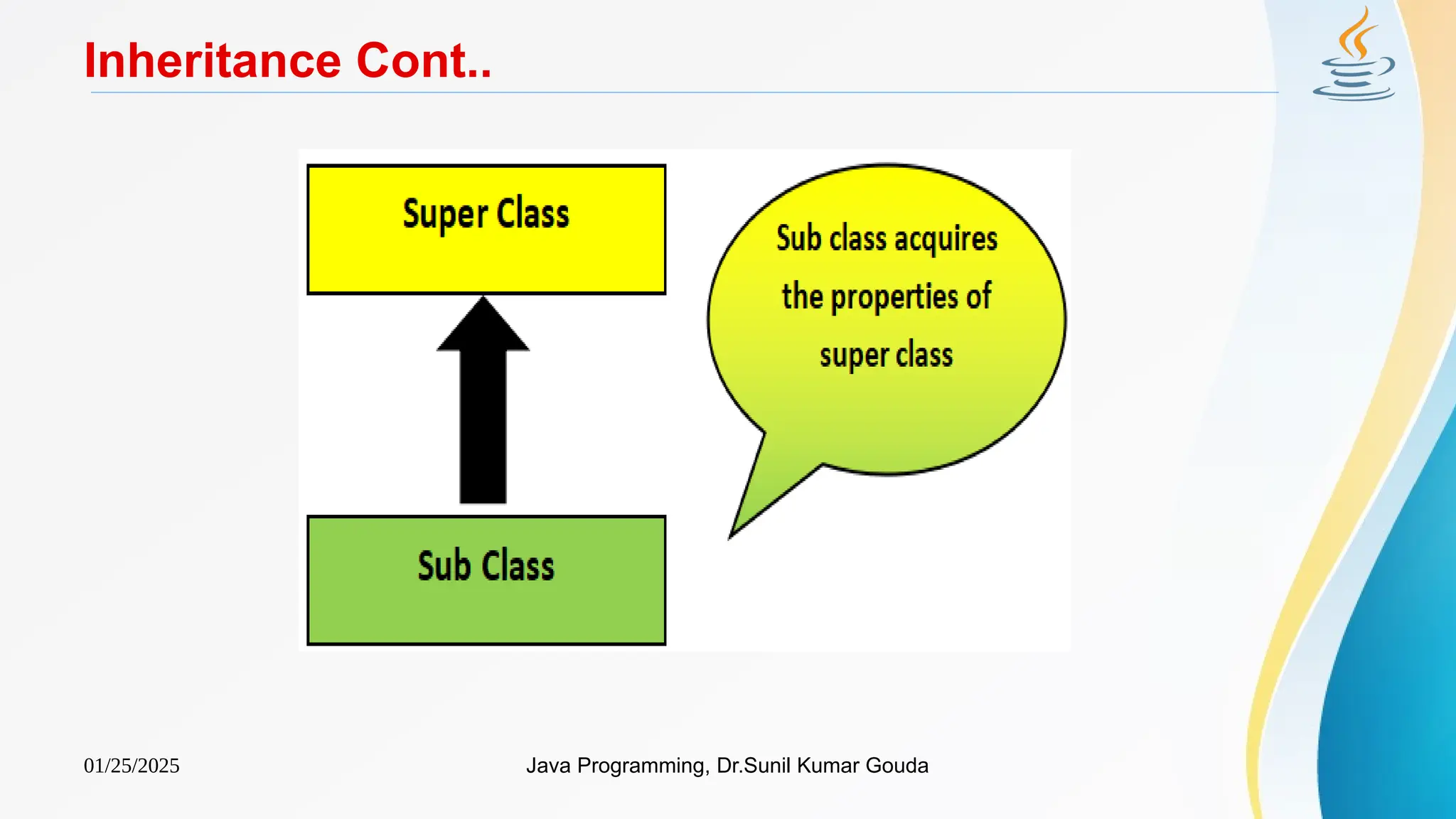
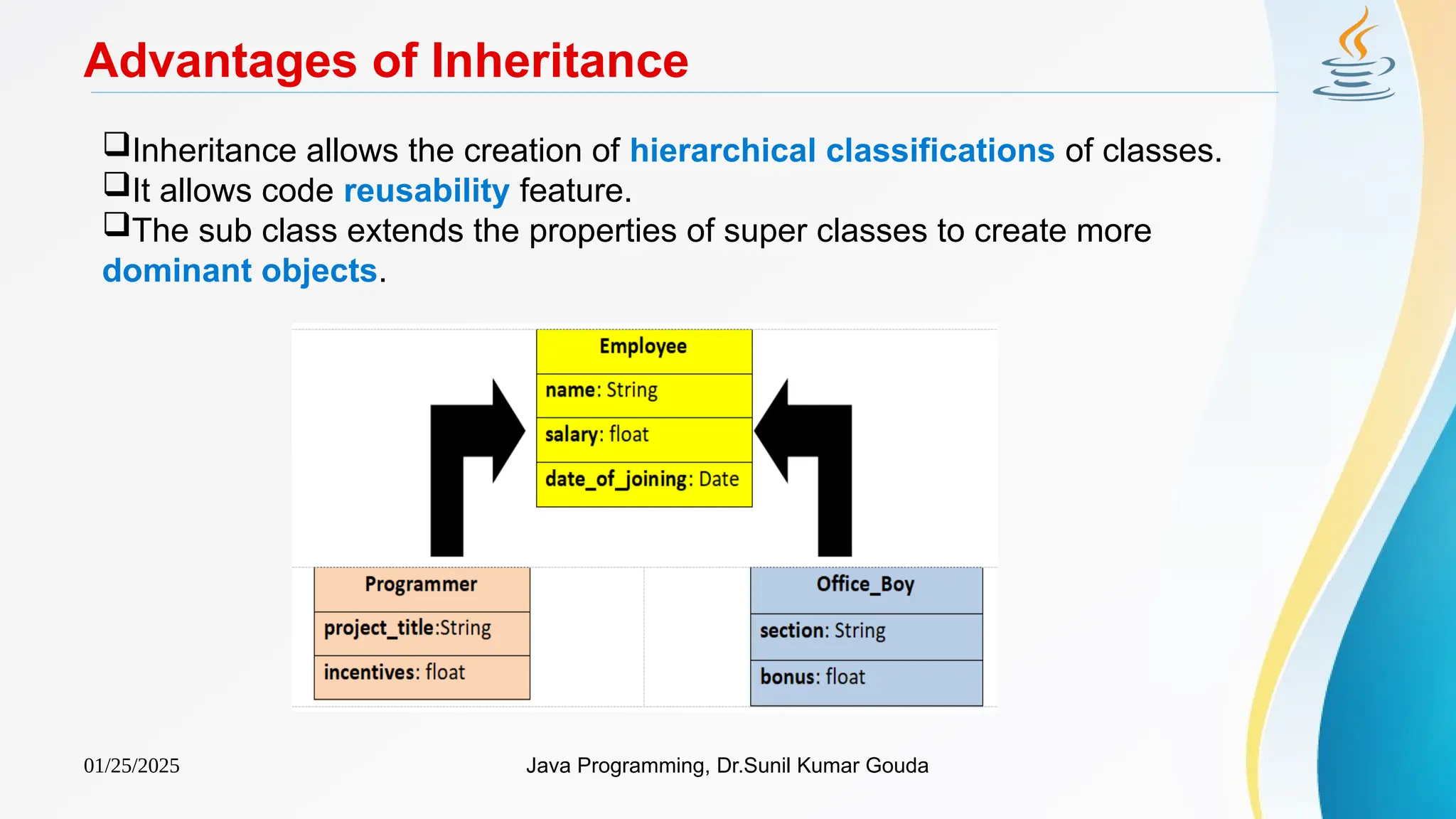
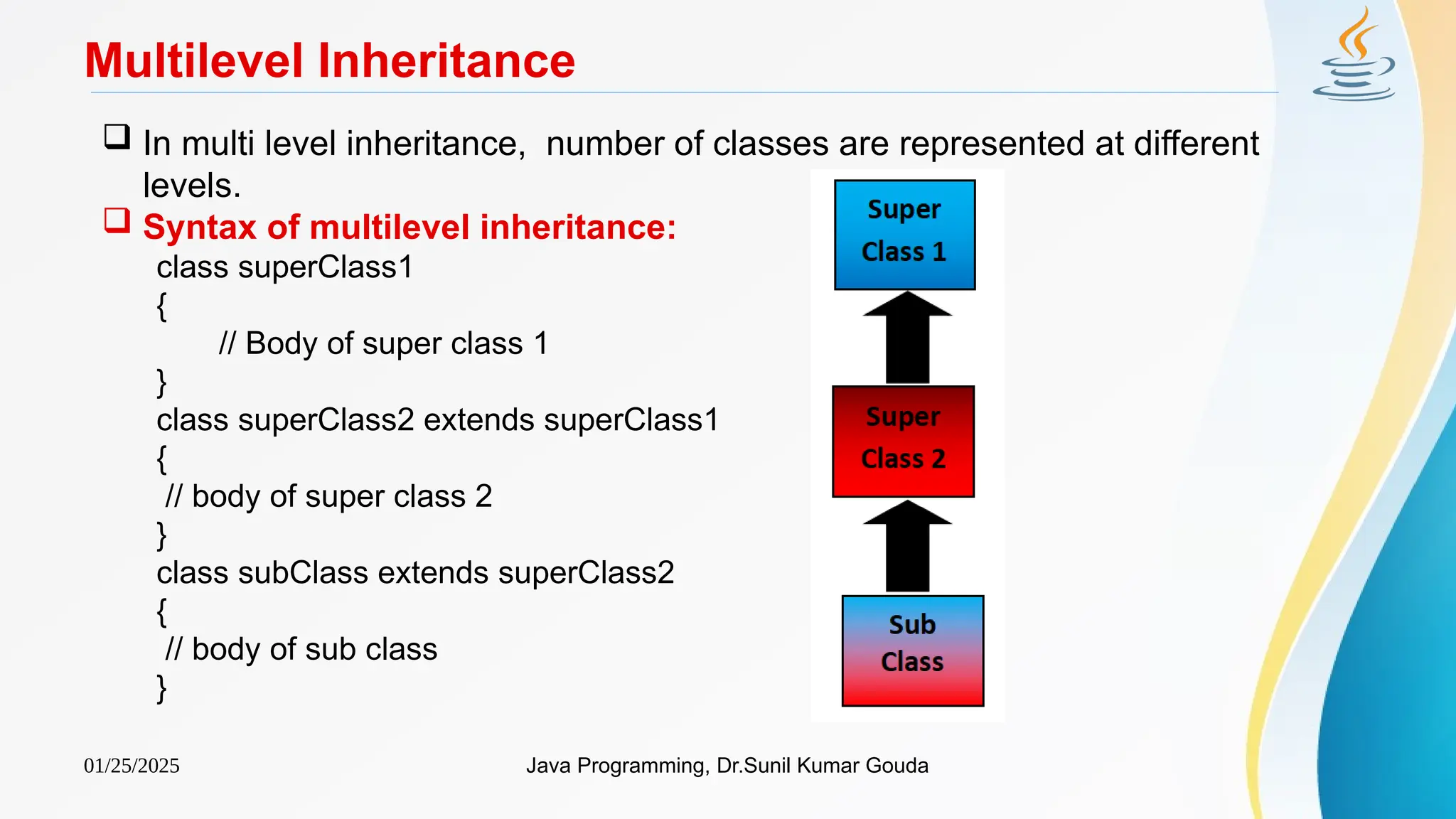
The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in Java, focusing on inheritance, which allows subclasses to acquire properties and methods from superclasses. Key topics include types of inheritance such as single, hierarchical, multilevel, and hybrid inheritance, as well as the syntax for implementing these inheritance types in Java. It also discusses how constructors are called in inheritance hierarchies, including the use of default and parameterized constructors.


![01/25/2025 Java Programming, Dr.Sunil Kumar Gouda
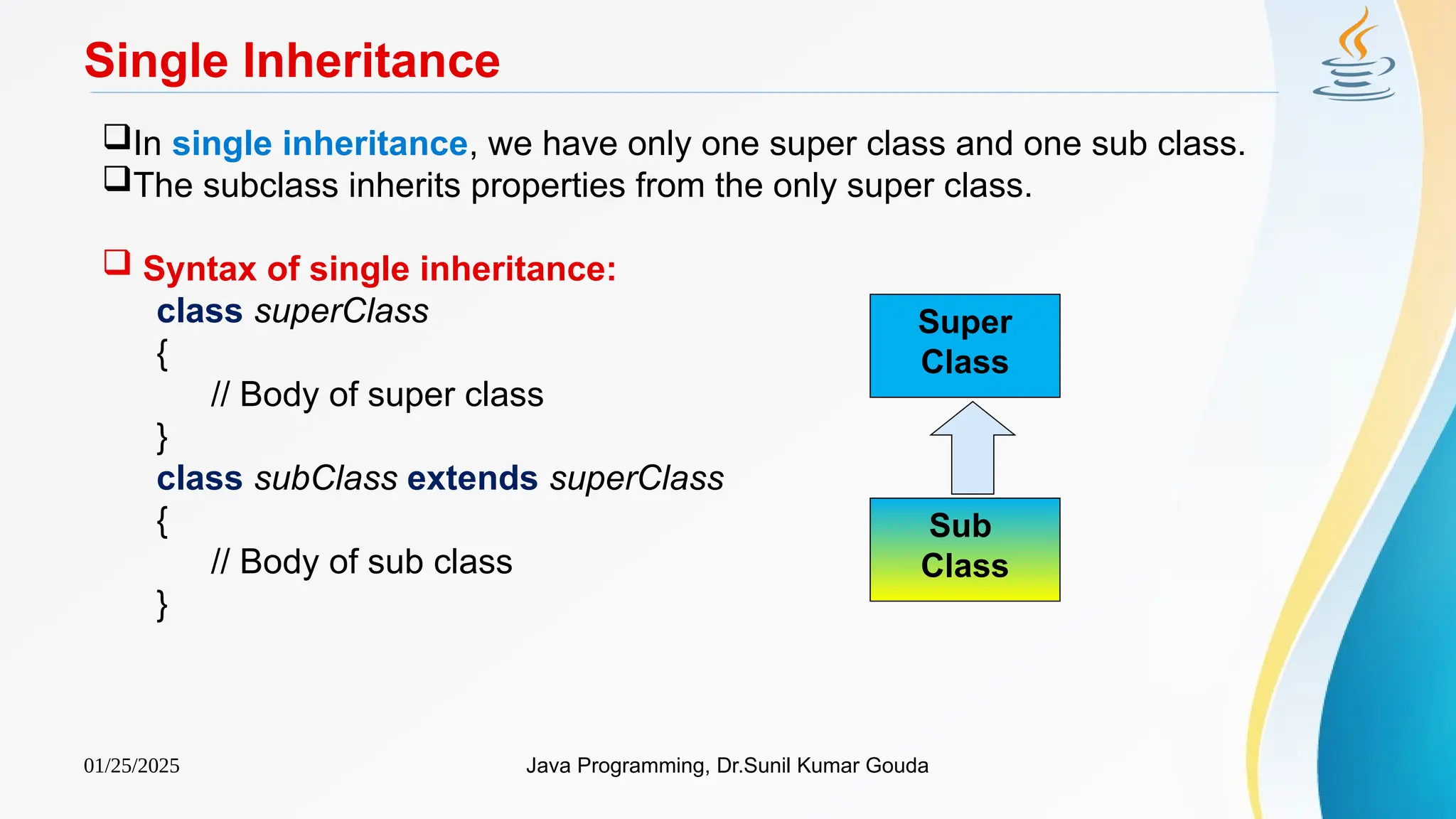
Single Inheritance (Example)
class Rectangle
{
int l, b;
void disp_lb()
{
System.out.println("l= " +l+", b="+b);
}
}
class Cuboid extends Rectangle
{
int h;
void disp_h()
{
System.out.println("h= " +h);
}
void find_volume()
{
System.out.println ("Volume= "+l*b*h);
}
}
class SingleInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cuboid c=new Cuboid();
c.l=9;
c.b=7;
c.h=3;
c.disp_lb();
c.disp_h();
c.find_volume();
}
}
Output:
l=9, b=7
h=3
Volume=189](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5inheritance-250125152833-8126c1af/75/Ch5Inheritance-pptx-Java-program-Java-file-8-2048.jpg)
![01/25/2025 Java Programming, Dr.Sunil Kumar Gouda
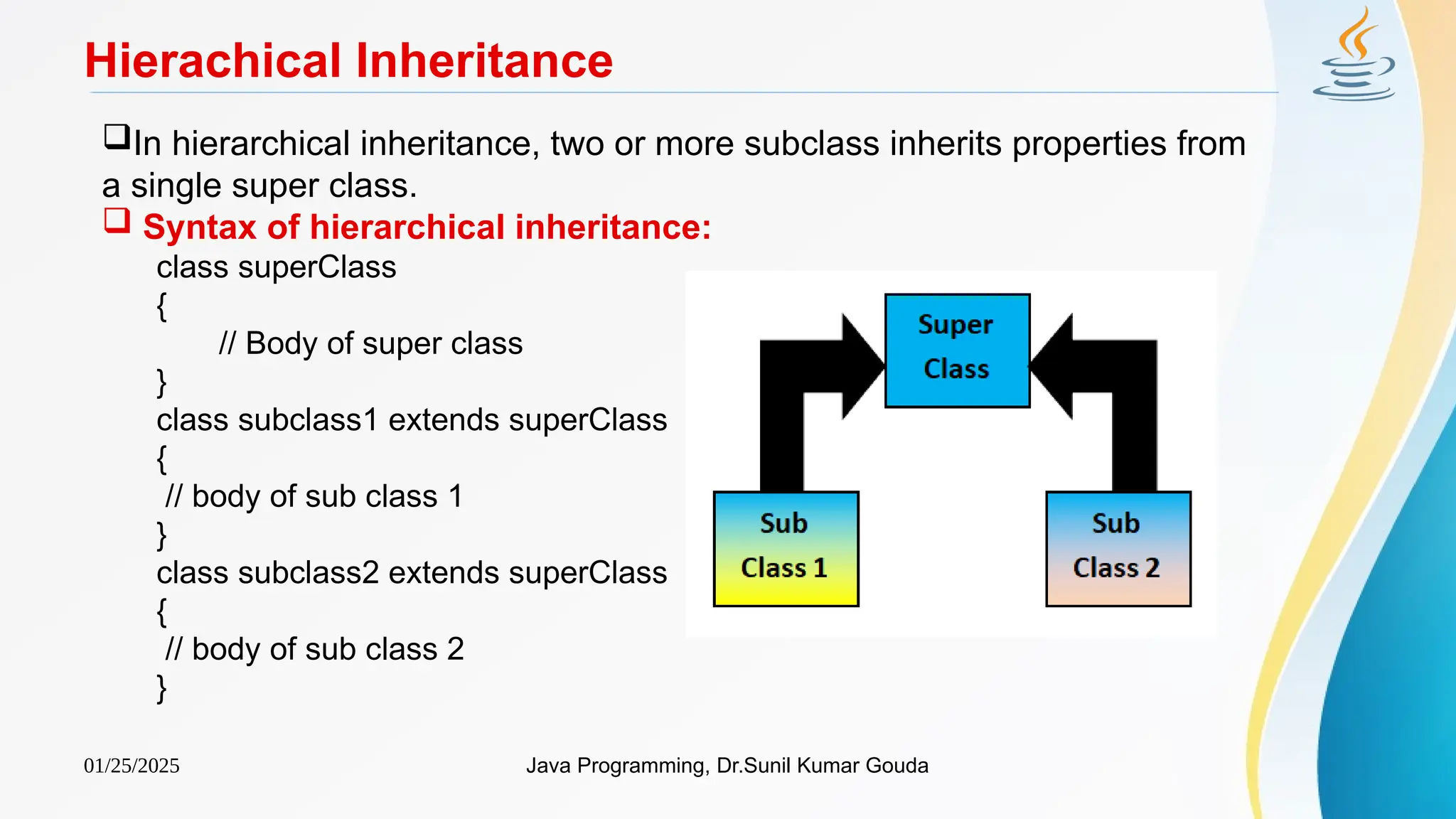
Hierachical Inheritance (Example)
class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal
{
void meow()
{
System.out.println("meowing...");
}
}
class HierarchicalInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cat c=new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
}
}
Output:
meowing...
eating...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5inheritance-250125152833-8126c1af/75/Ch5Inheritance-pptx-Java-program-Java-file-10-2048.jpg)
![01/25/2025 Java Programming, Dr.Sunil Kumar Gouda
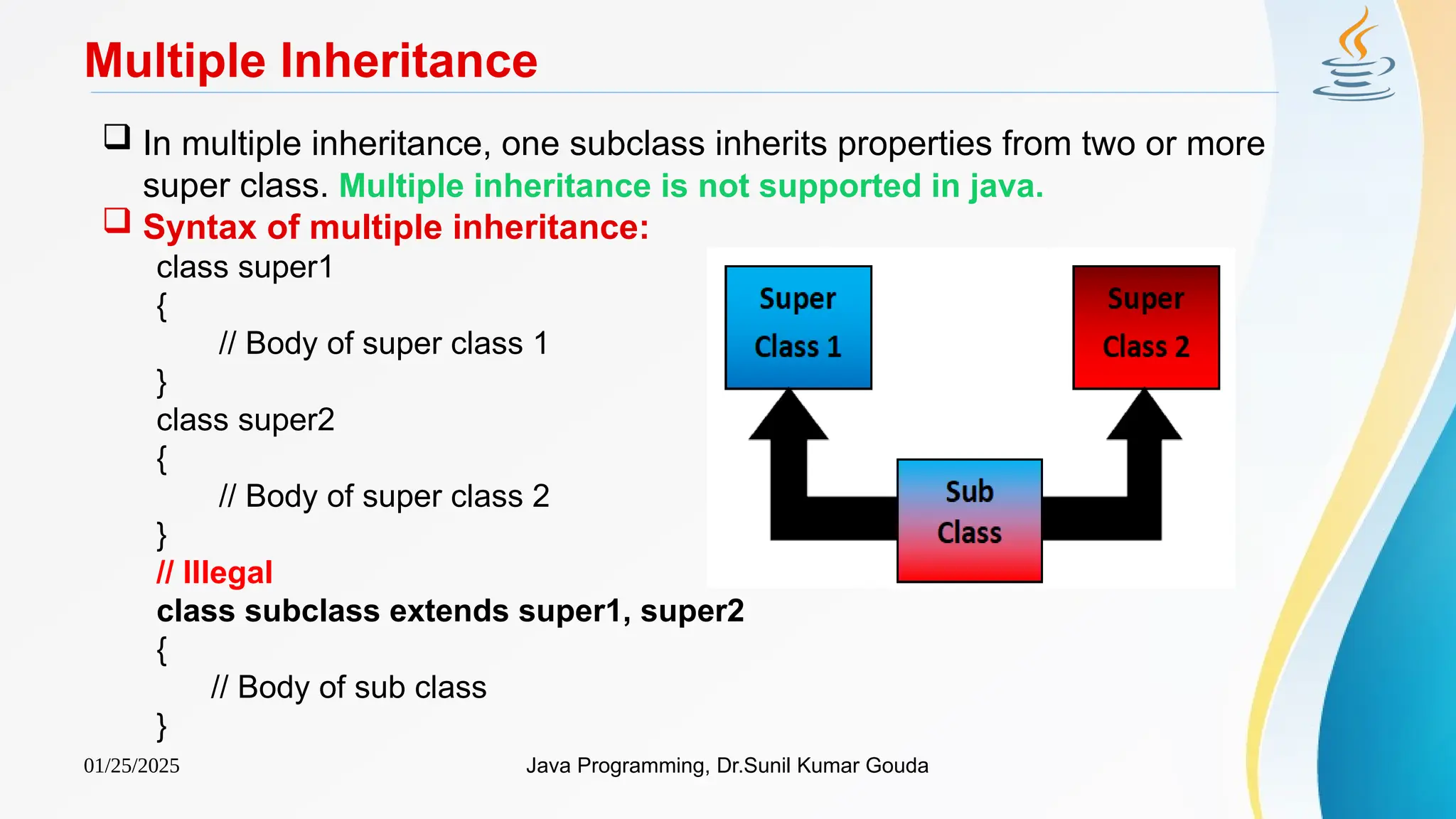
Multilevel Inheritance (Example)
class Shape
{
public void display()
{
System.out.println("Inside display");
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
public void area()
{
System.out.println("Inside area");
}
}
class Cube extends Rectangle
{
public void volume()
{
System.out.println("Inside volume");
}
}
public class Tester
{
public static void main(String[] arguments)
{
Cube cube = new Cube();
cube.display();
cube.area();
cube.volume();
}
}
Output:
Inside display
Inside area
Inside volume](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5inheritance-250125152833-8126c1af/75/Ch5Inheritance-pptx-Java-program-Java-file-14-2048.jpg)


![01/25/2025 Java Programming, Dr.Sunil Kumar Gouda
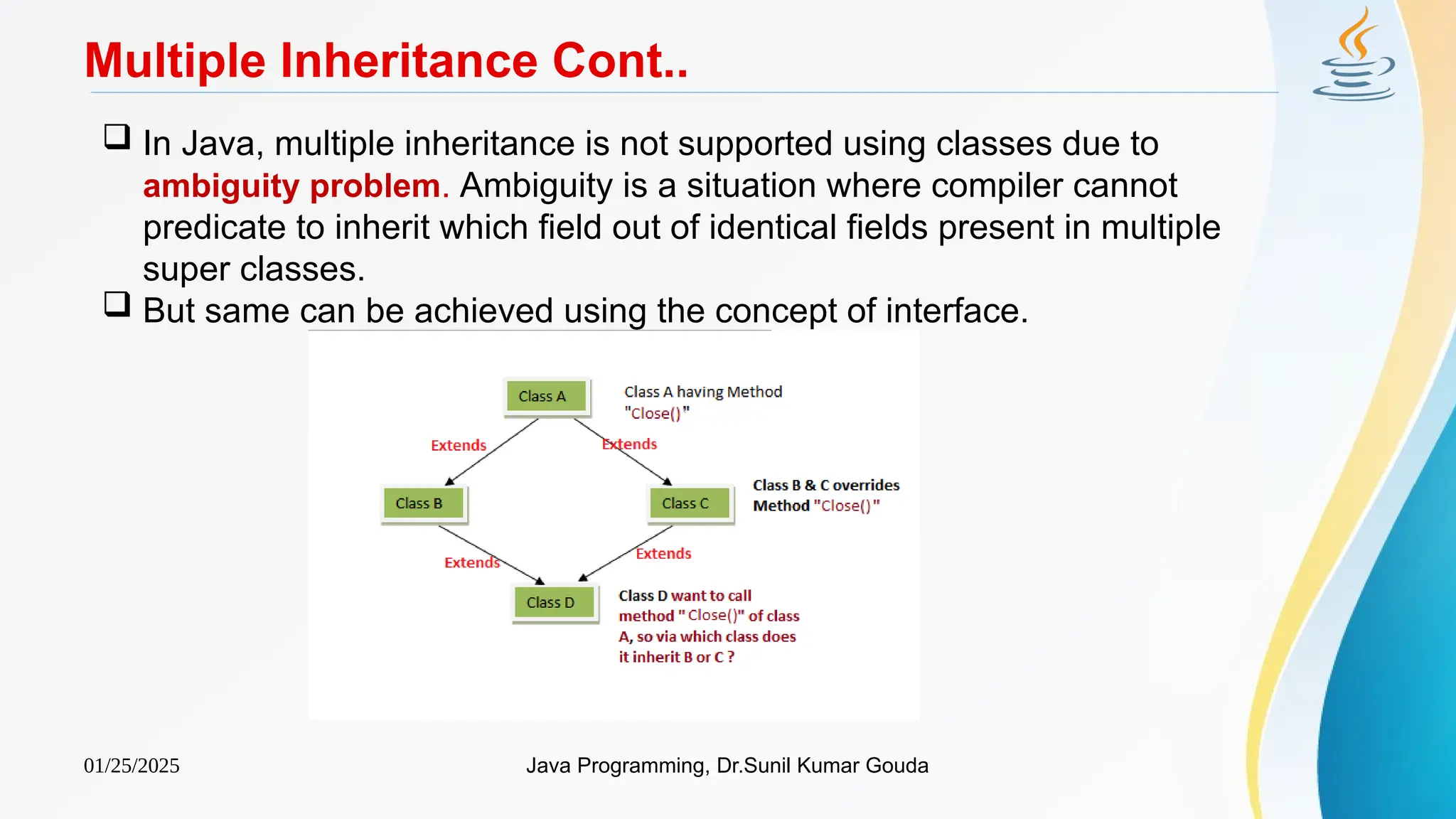
Invoking default constructor of the super class
class A
{
A()
{
System.out.println("Inside A's
constructor.");
}
}
class B extends A
{
B()
{
System.out.println("Inside B's
constructor.");
}
}
class C extends B
{
C()
{
System.out.println("Inside C's constructor.");
}
}
class CallingCons
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
C c = new C();
}
}
Output:
Inside A’s constructor.
Inside B’s constructor.
Inside C’s constructor.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5inheritance-250125152833-8126c1af/75/Ch5Inheritance-pptx-Java-program-Java-file-17-2048.jpg)
![01/25/2025 Java Programming, Dr.Sunil Kumar Gouda
Invoking parameterized constructor of the super class
class Rect
{
int length, breadth;
Rect (int l, int b)
{
length=l;
breadth=b;
}
}
class Cuboid extends Rect
{
double height;
Cuboid (int l, int b, int h)
{
super(l, b);
height=h;
}
void volume()
{
System.out.println (length*breadth*height);
}
}
class Vol
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cuboid v=new Cuboid(1, 2, 3);
v.volume();
}
}
Output:
6.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch5inheritance-250125152833-8126c1af/75/Ch5Inheritance-pptx-Java-program-Java-file-18-2048.jpg)
