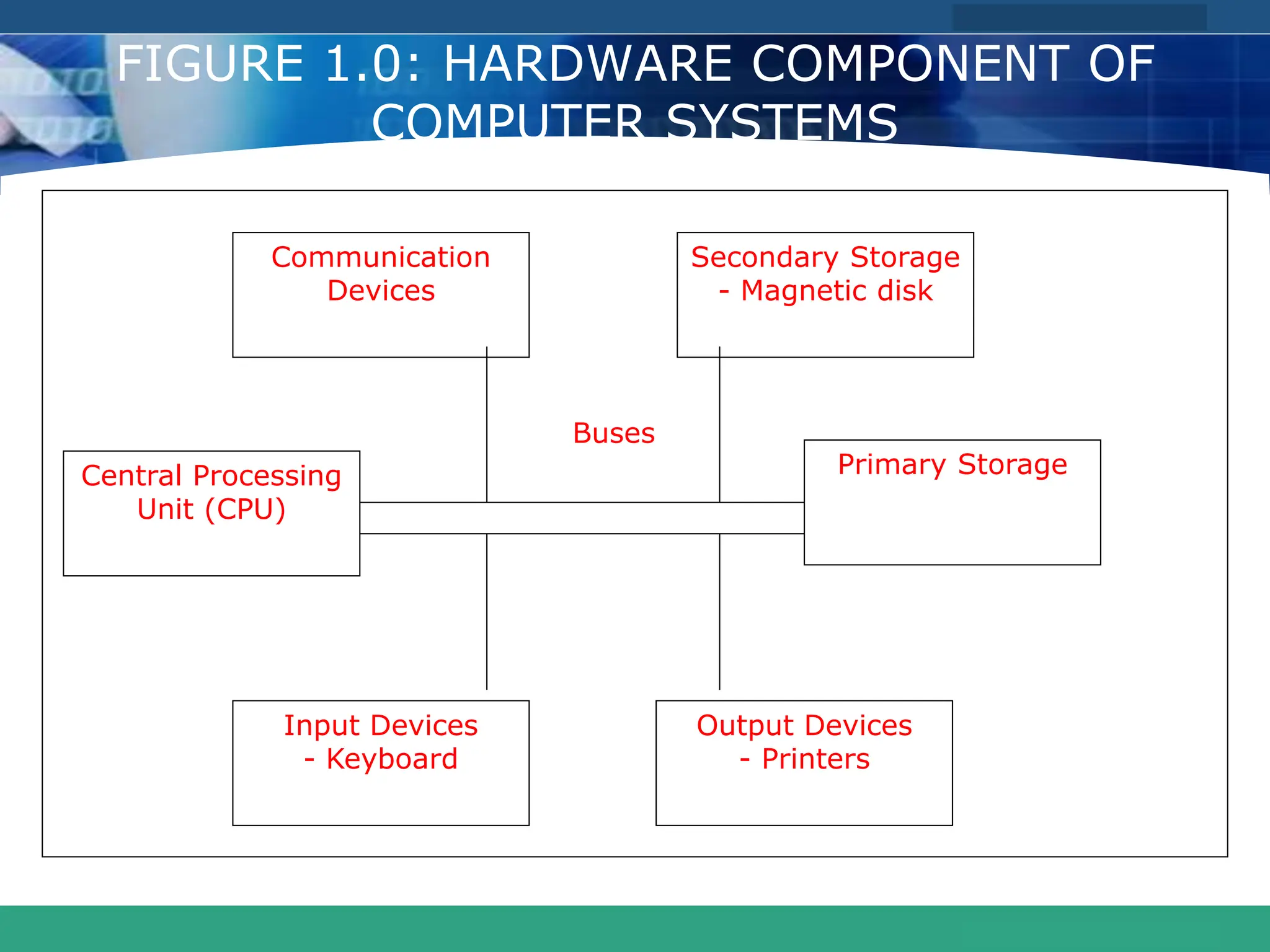
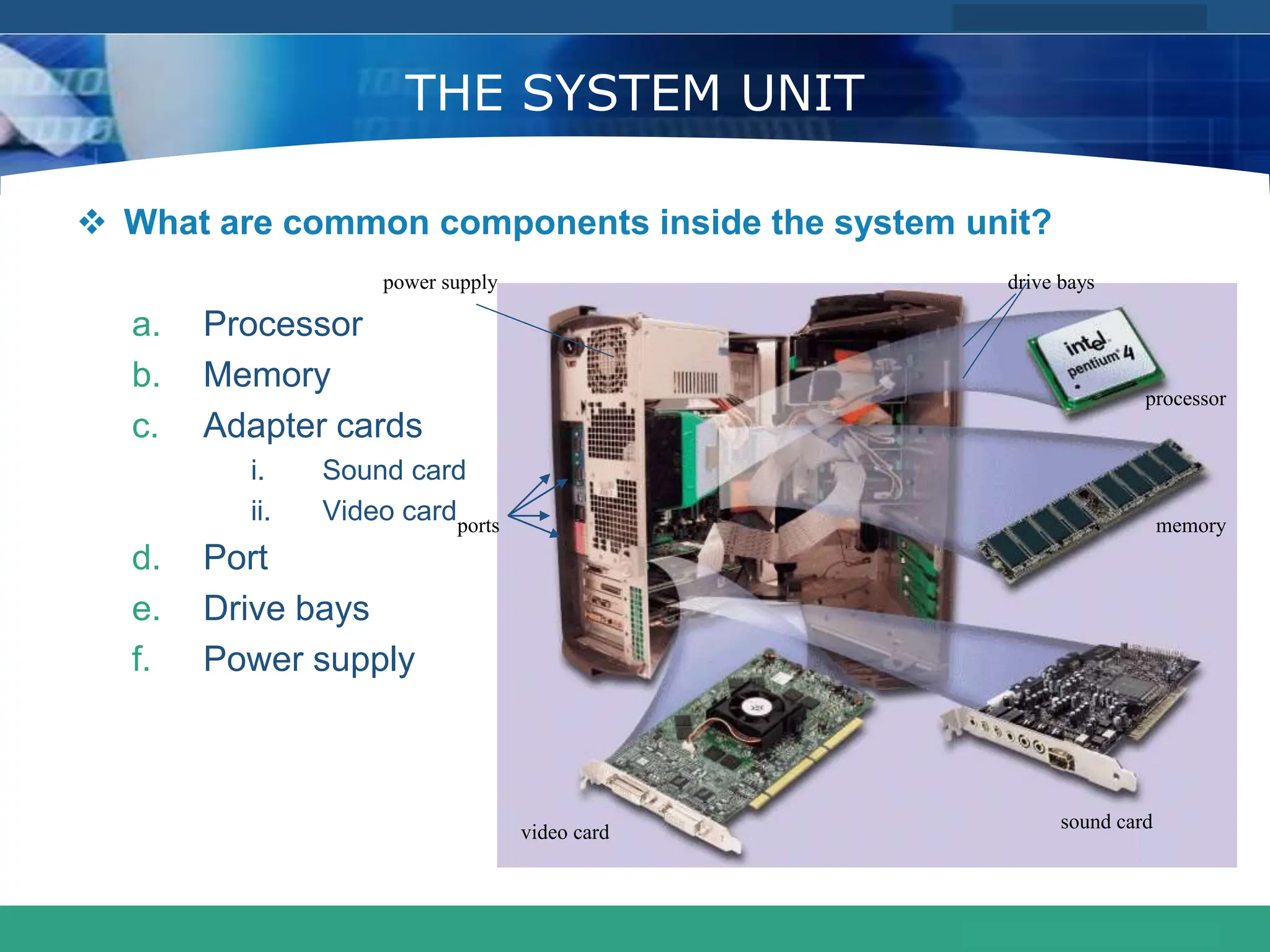
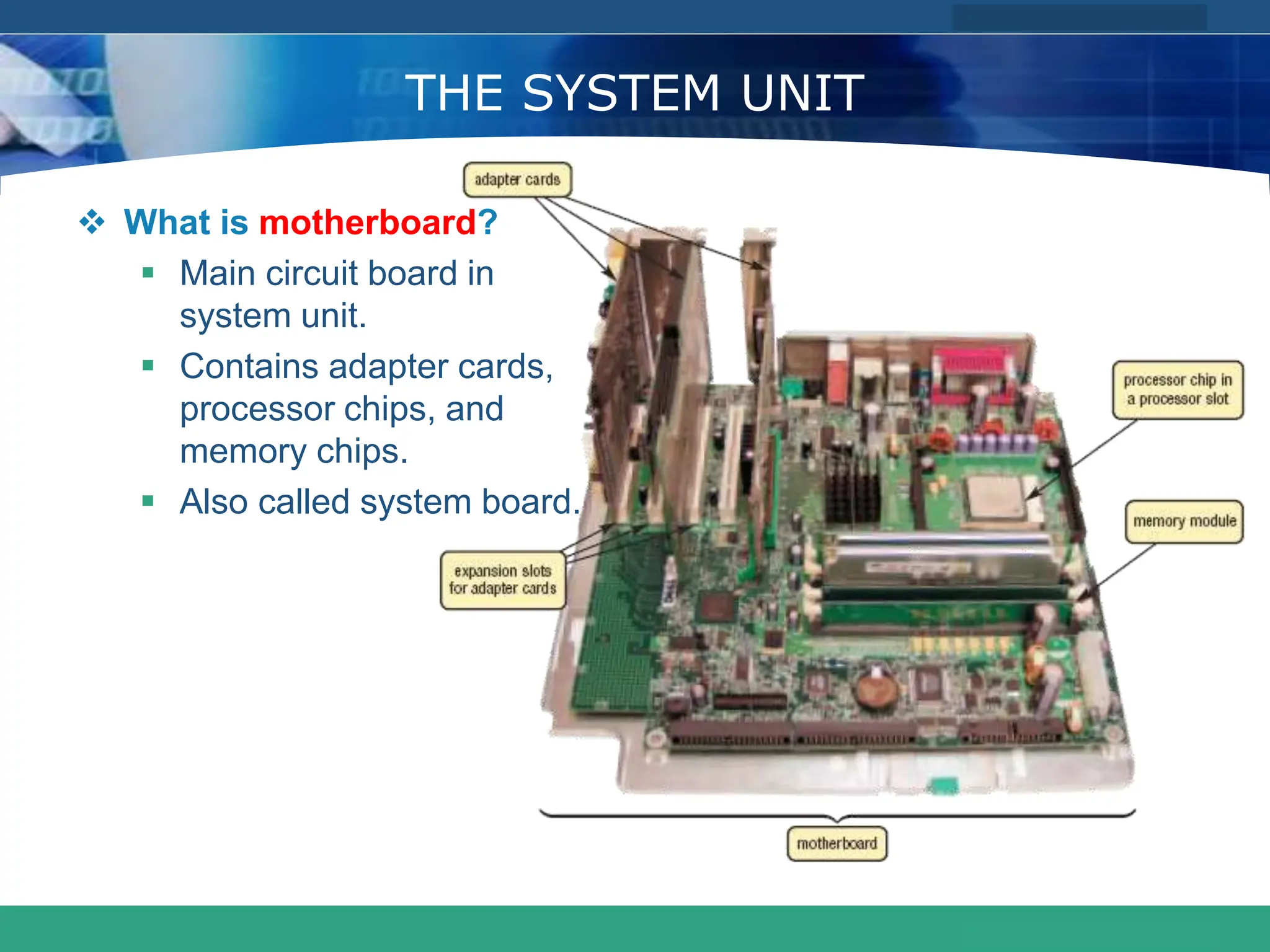
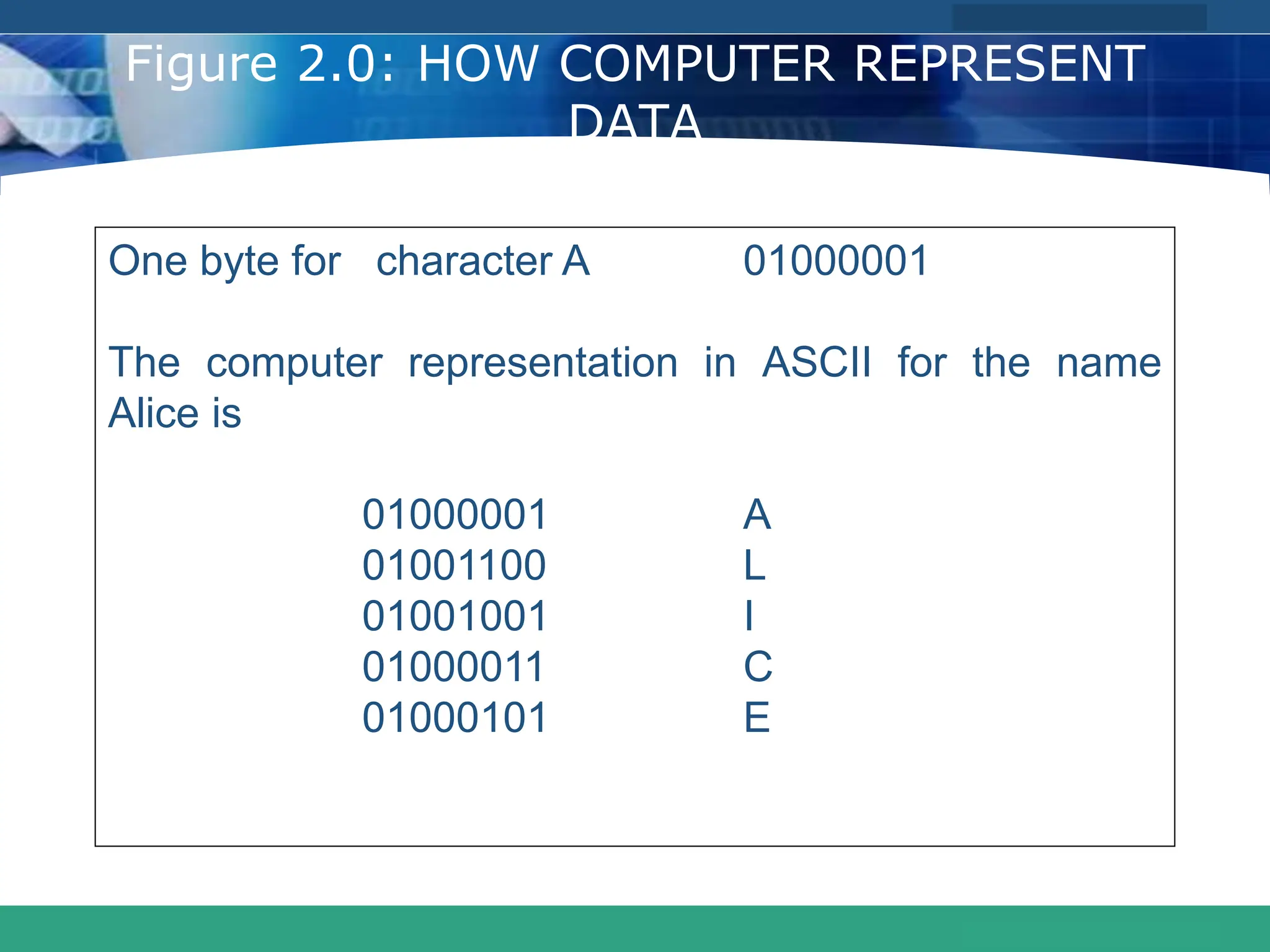
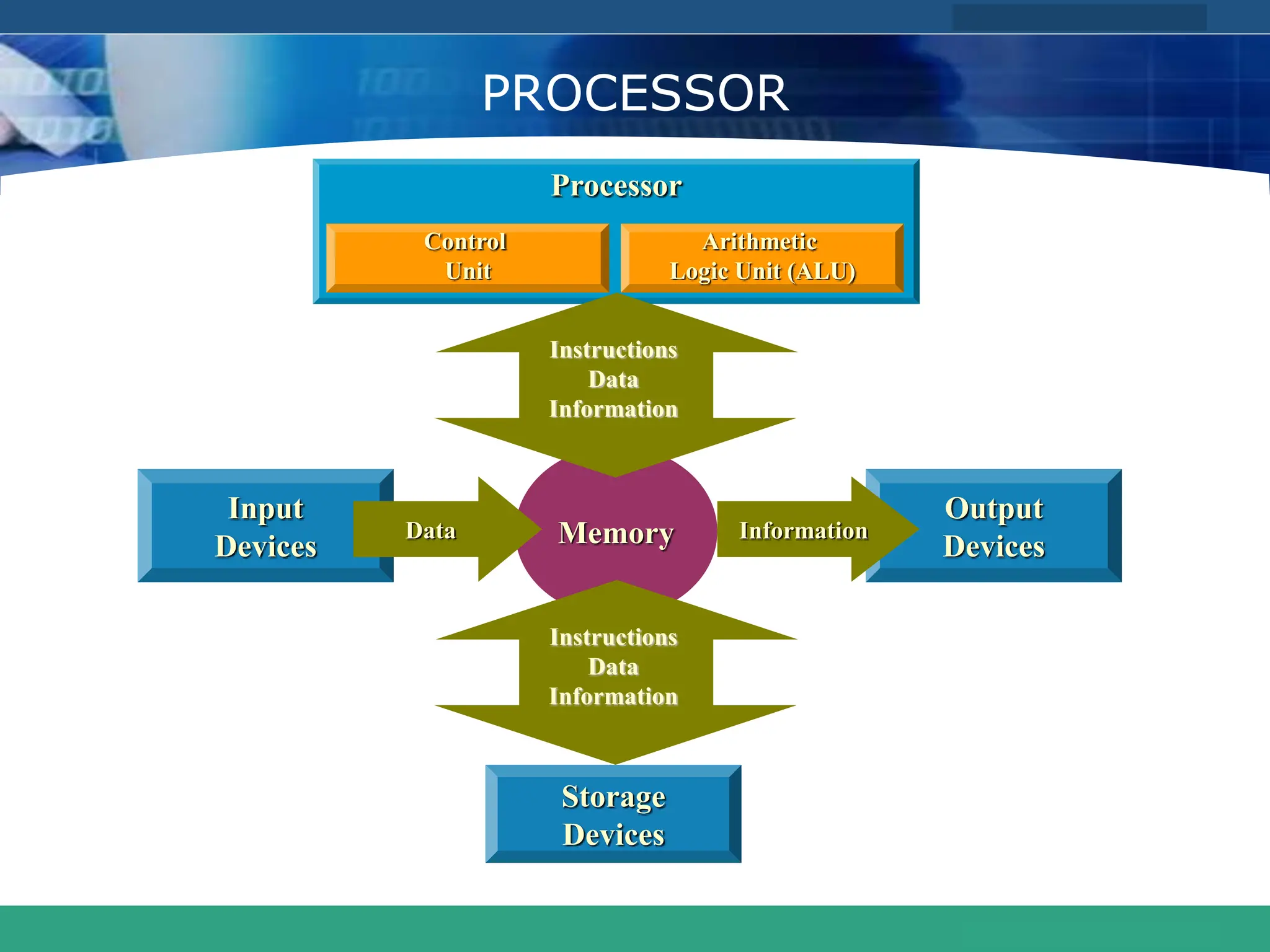
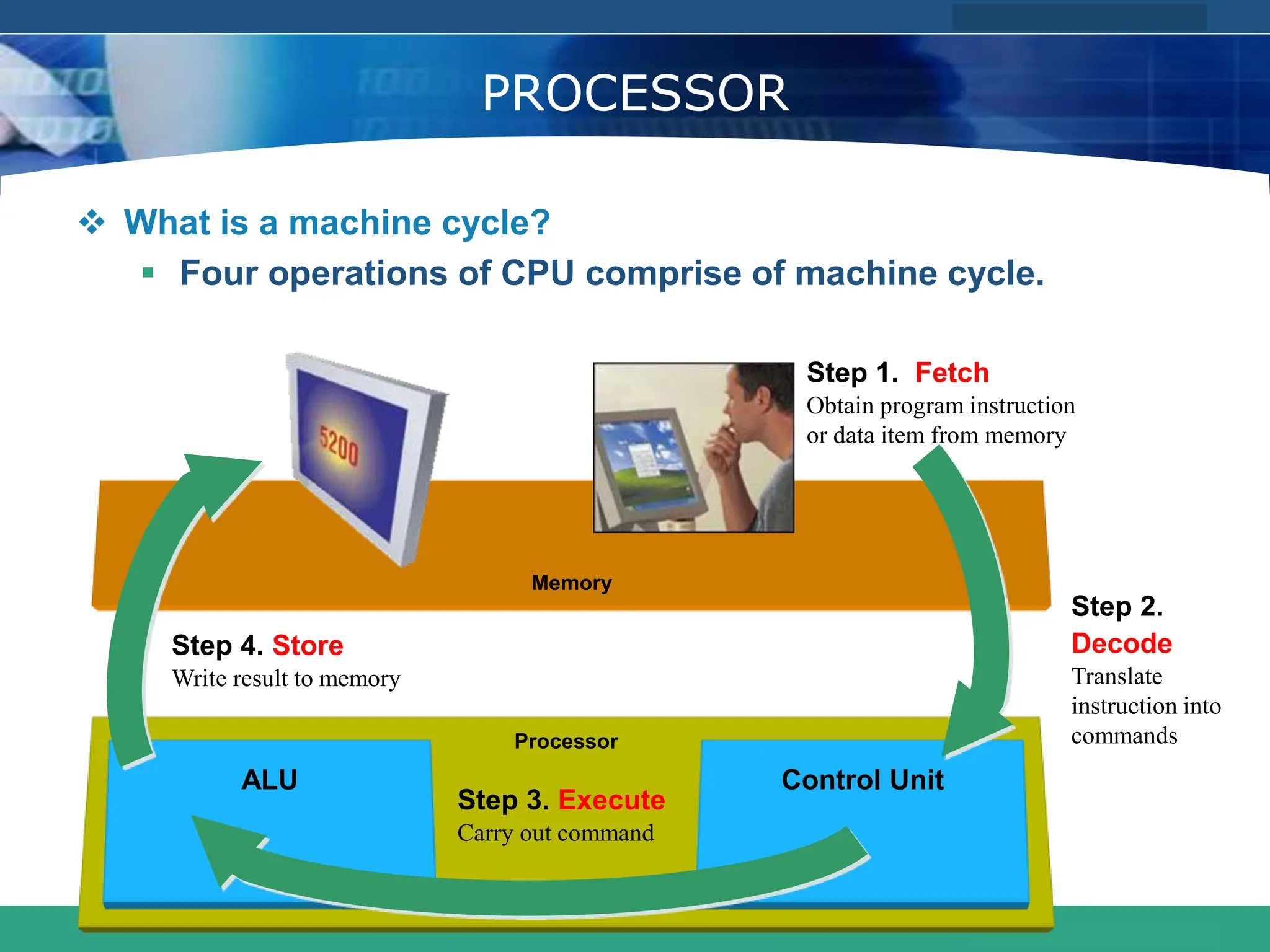
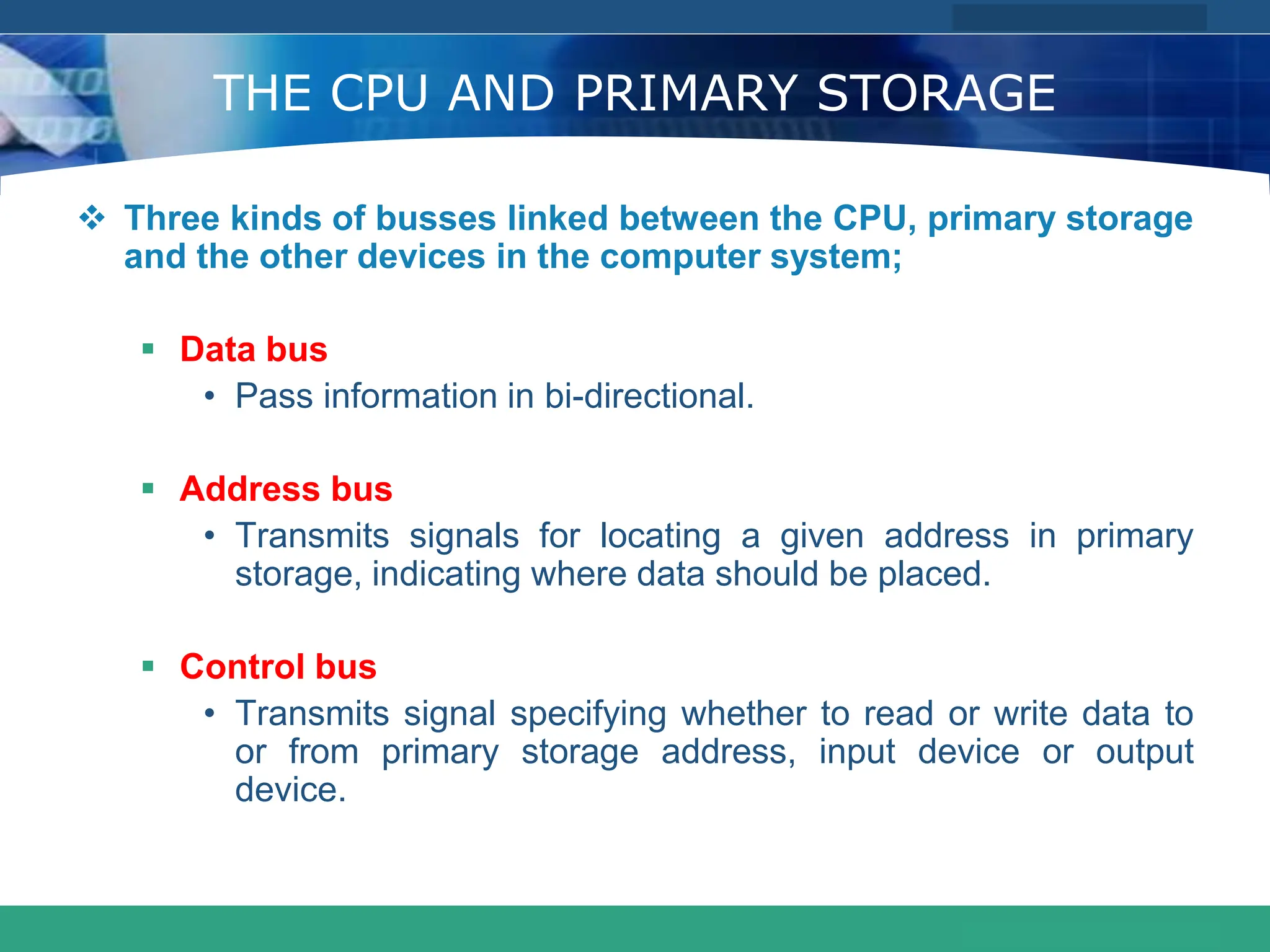
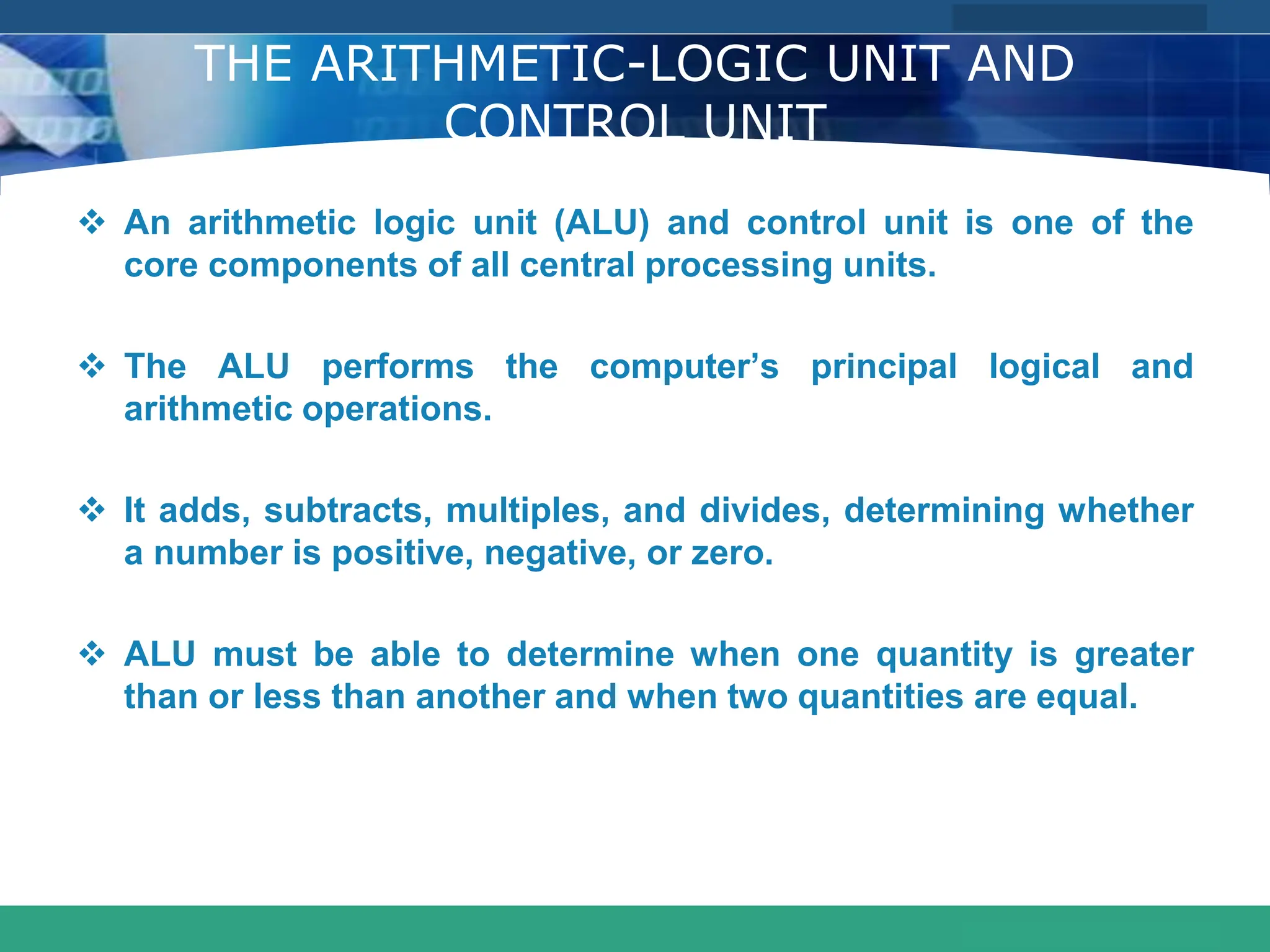
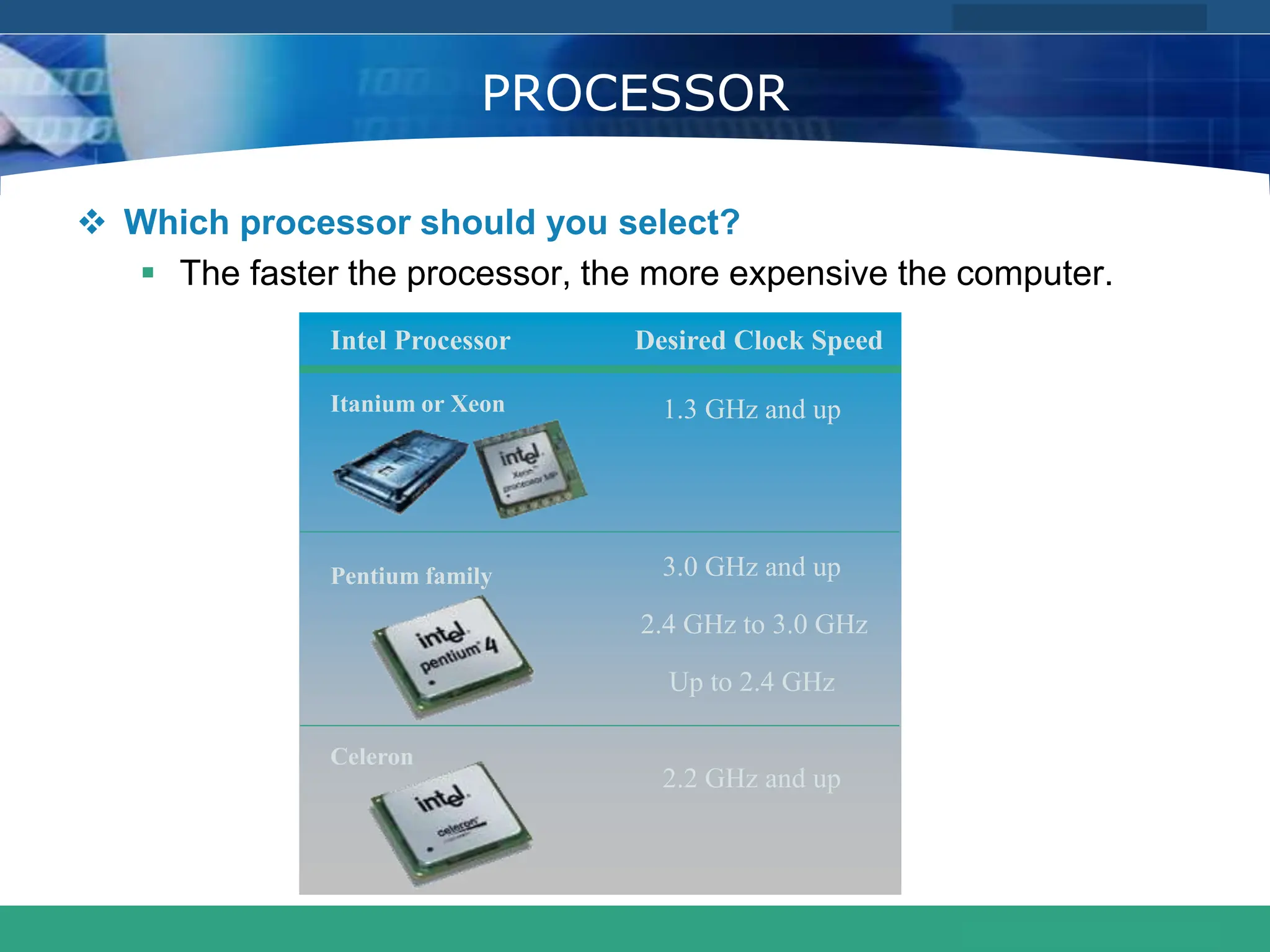
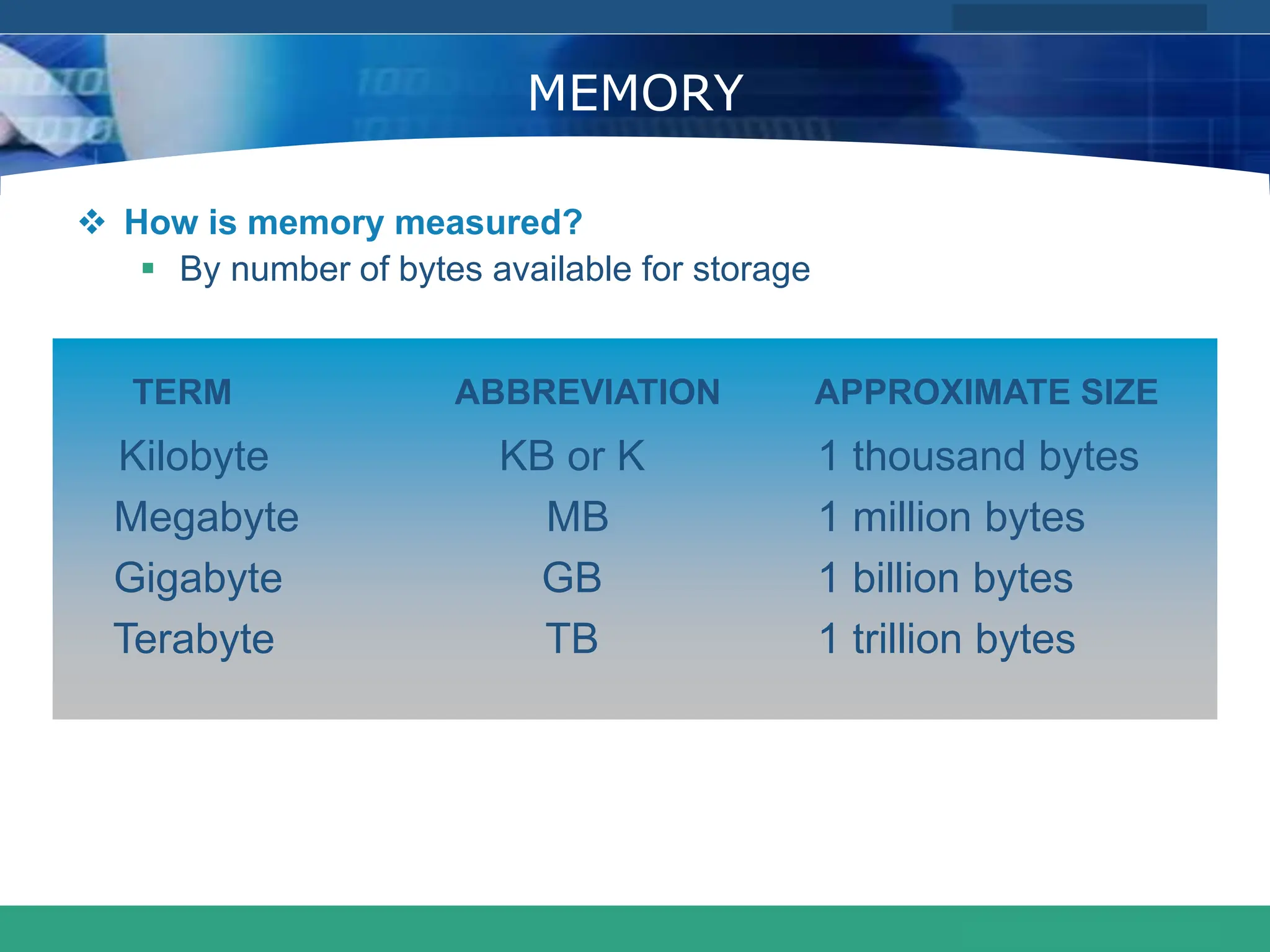
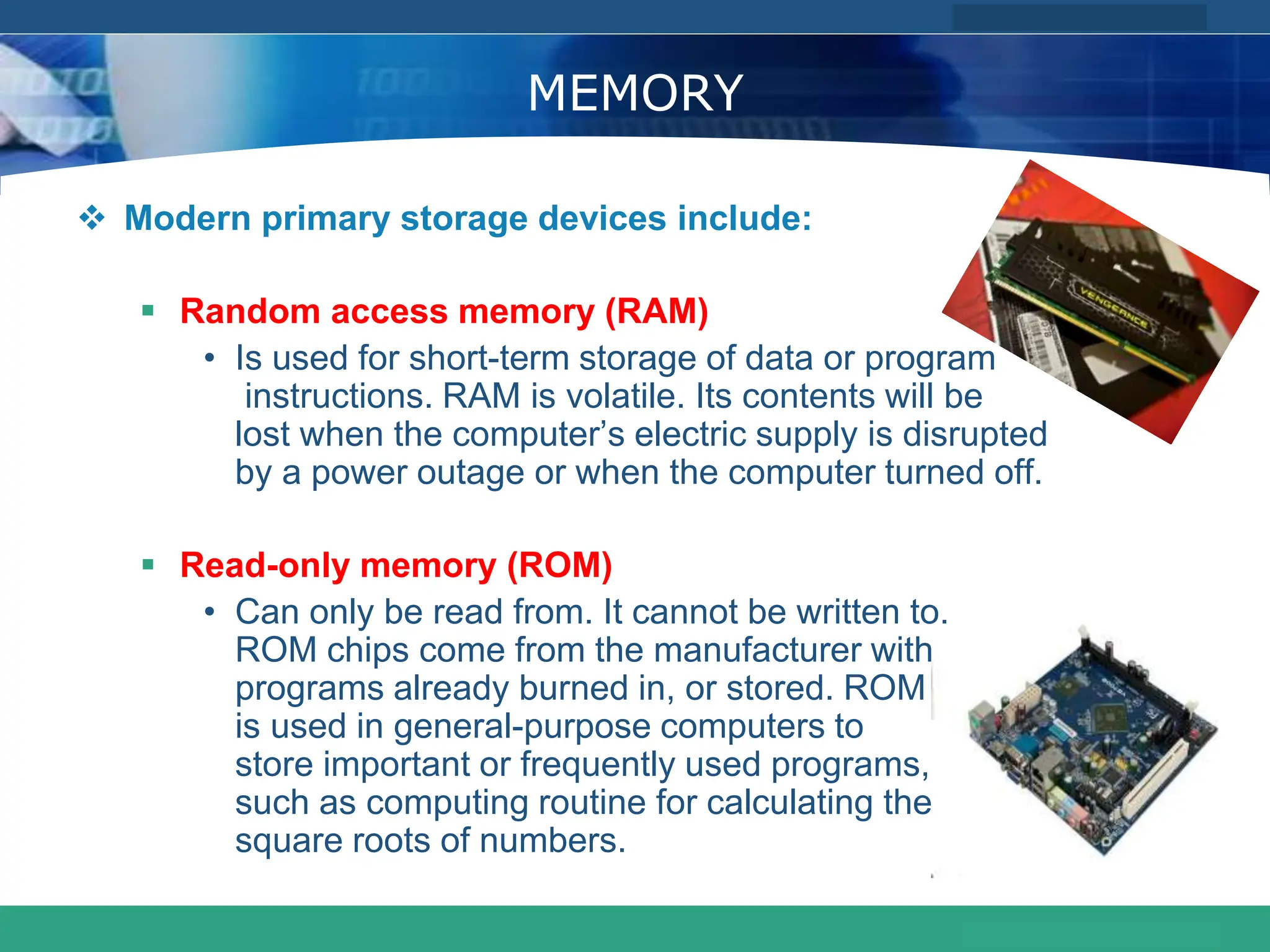
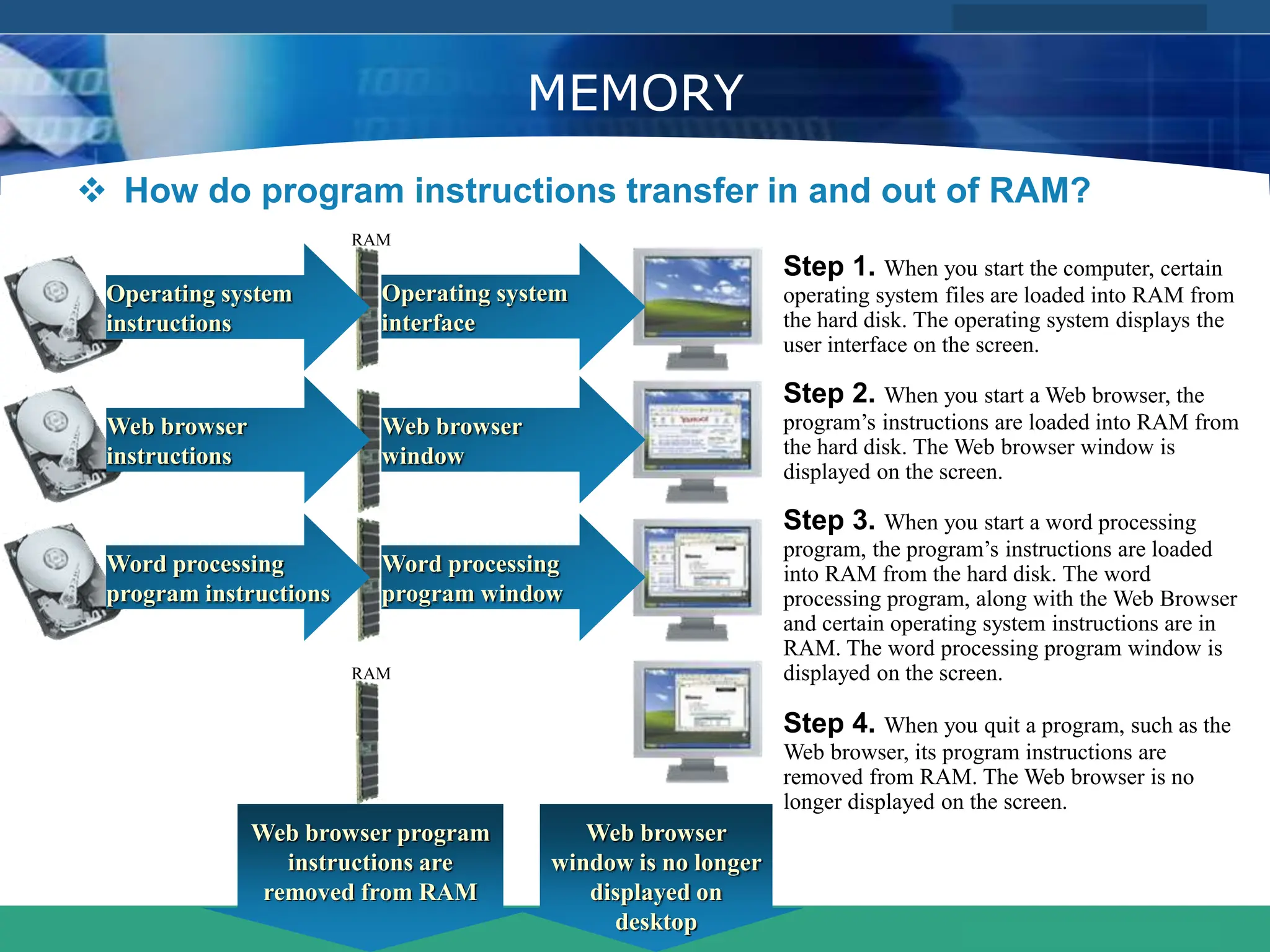
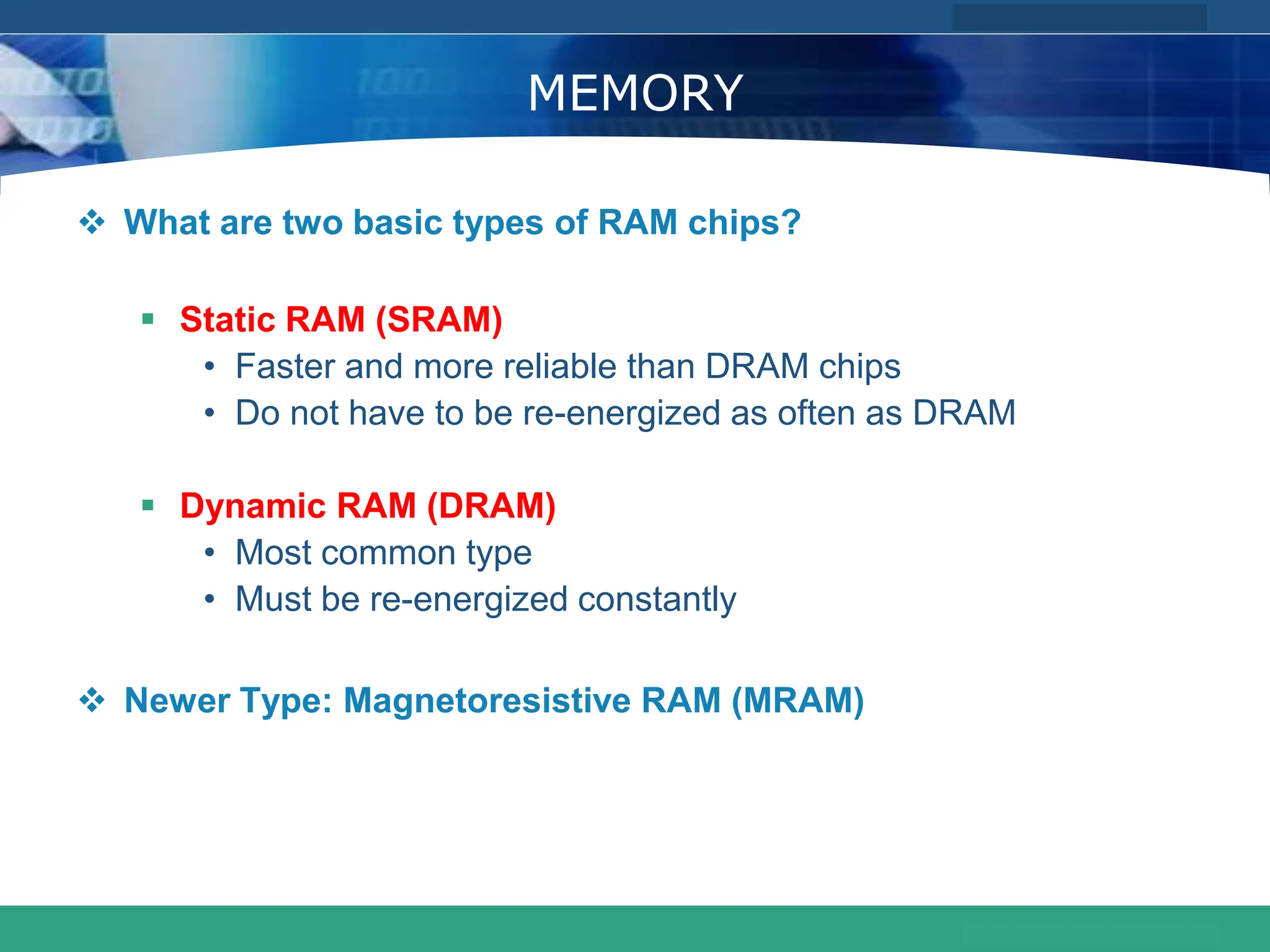
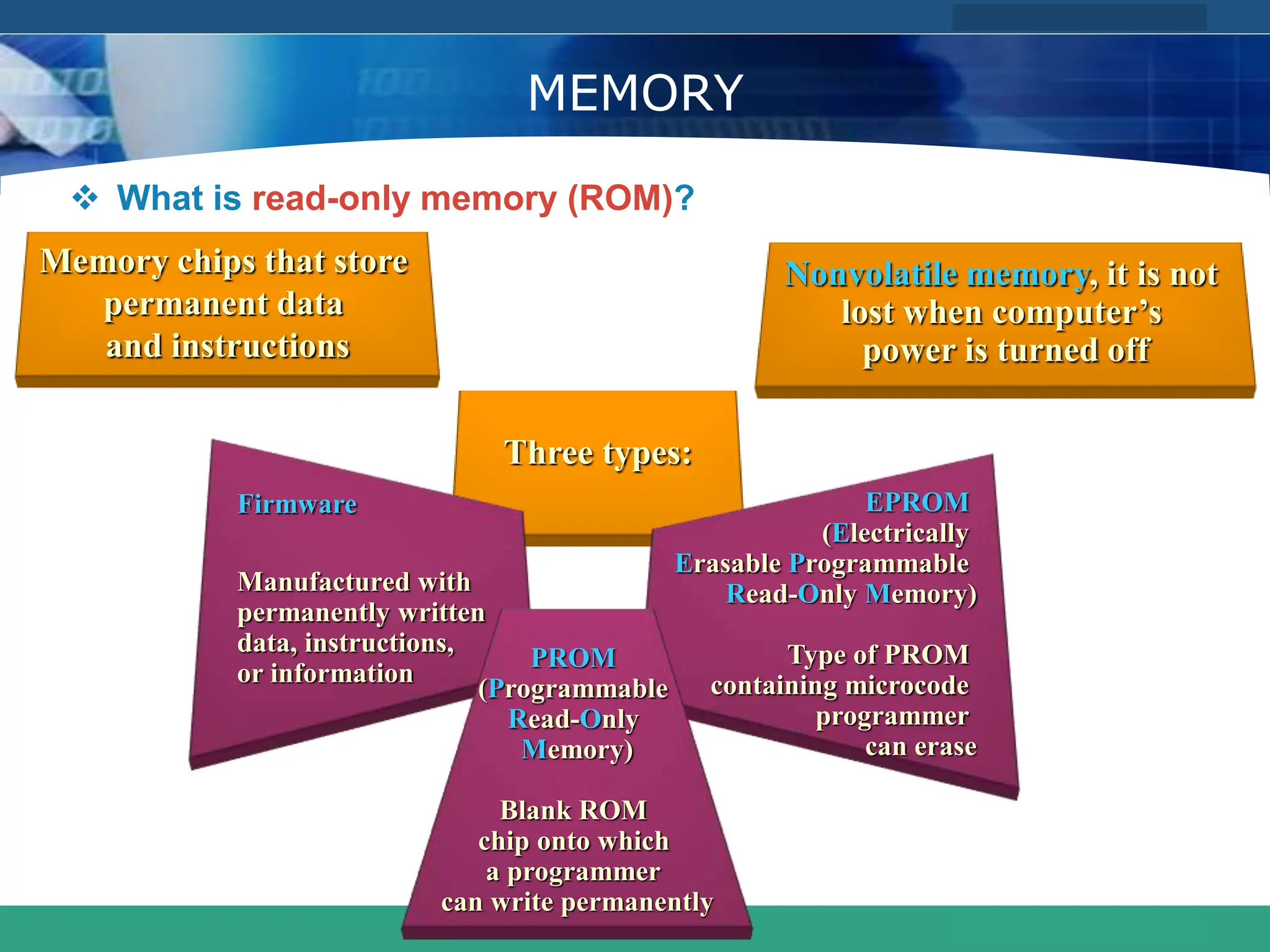
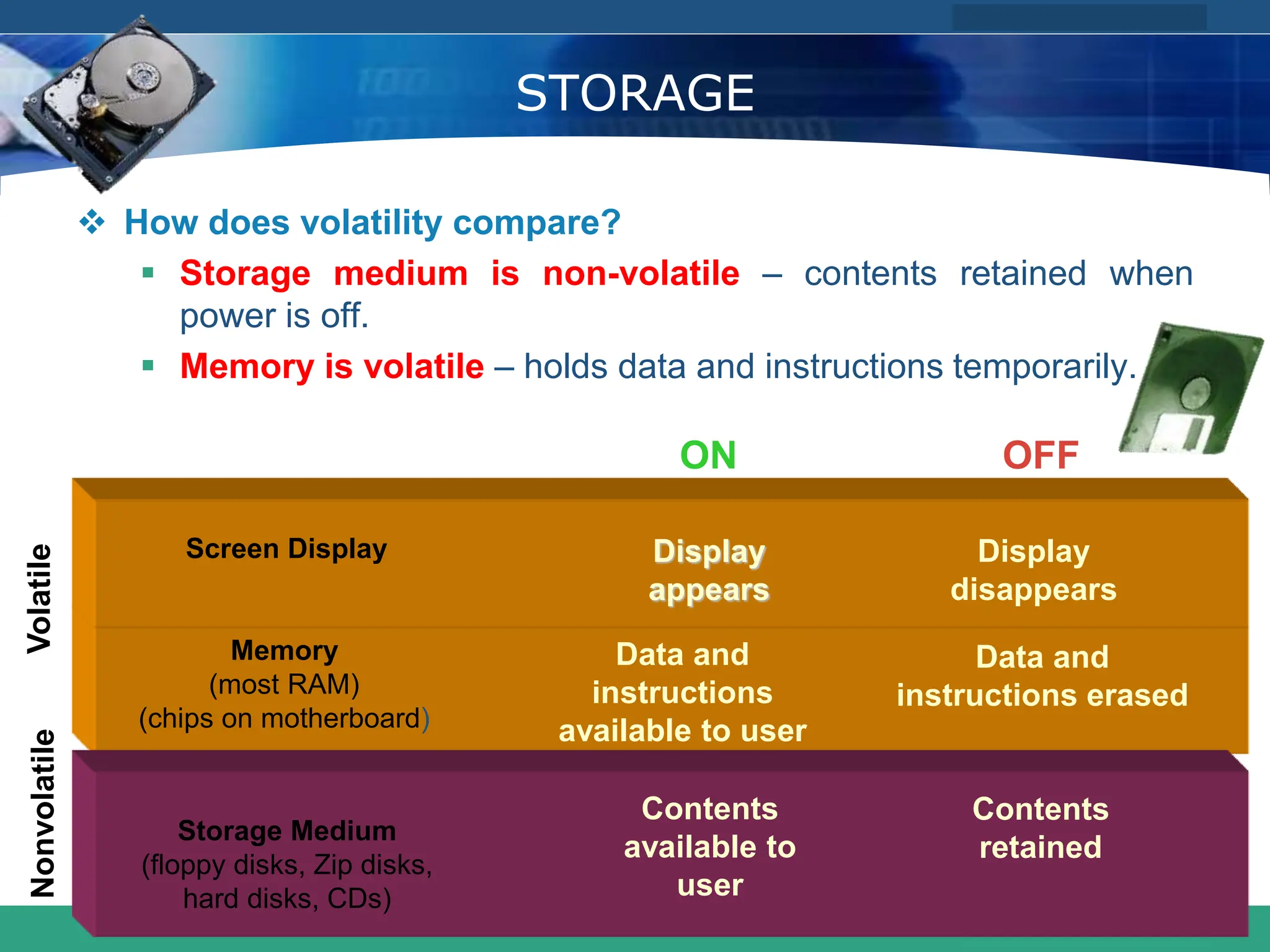
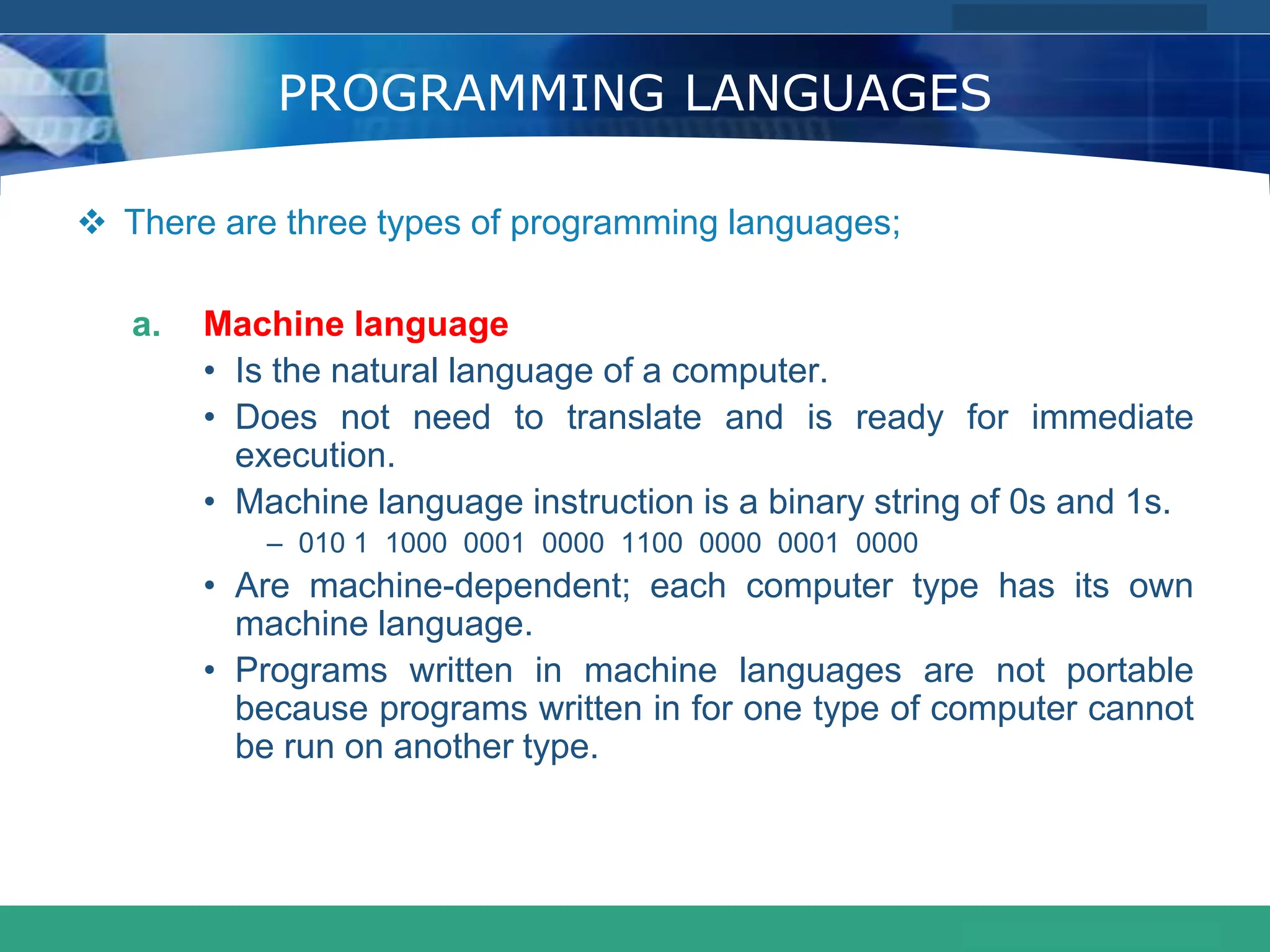
This document provides an introduction to computer systems. It defines the basic components of a computer system including the system unit, storage, input devices, output devices, and communication devices. The system unit contains the central processing unit (CPU), primary storage (RAM), adapter cards, ports, drive bays, and power supply. The CPU manipulates data and controls other parts using control, address, and data buses. Data is represented digitally using binary digits and encoded using ASCII or EBCDIC. Programs and data are stored temporarily in primary storage during processing.