This document provides an overview of PHP web programming concepts including request types, getting parameter values, handling file uploads, cookies, and sessions. The main points are:
- GET and POST requests pass parameters to PHP scripts in different ways, and PHP provides $_GET, $_POST, and $_REQUEST variables to access parameter values.
- $_FILES contains information about uploaded files, including the temporary location on the server.
- Cookies store small amounts of data in the user's browser and can be used to identify returning users. PHP uses setcookie() and $_COOKIE.
- Sessions use a cookie to track users across page loads, storing data on the server indexed by the user's ID cookie value.



![Getting Parameter Values in PHP
When opening it like this :
http://localhost/getit.php?name=john&age=15
The out put should be like this :
array(2) {
["name"]=>
string(4) "john"
["age"]=>
string(2) "15"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-6-2048.jpg)
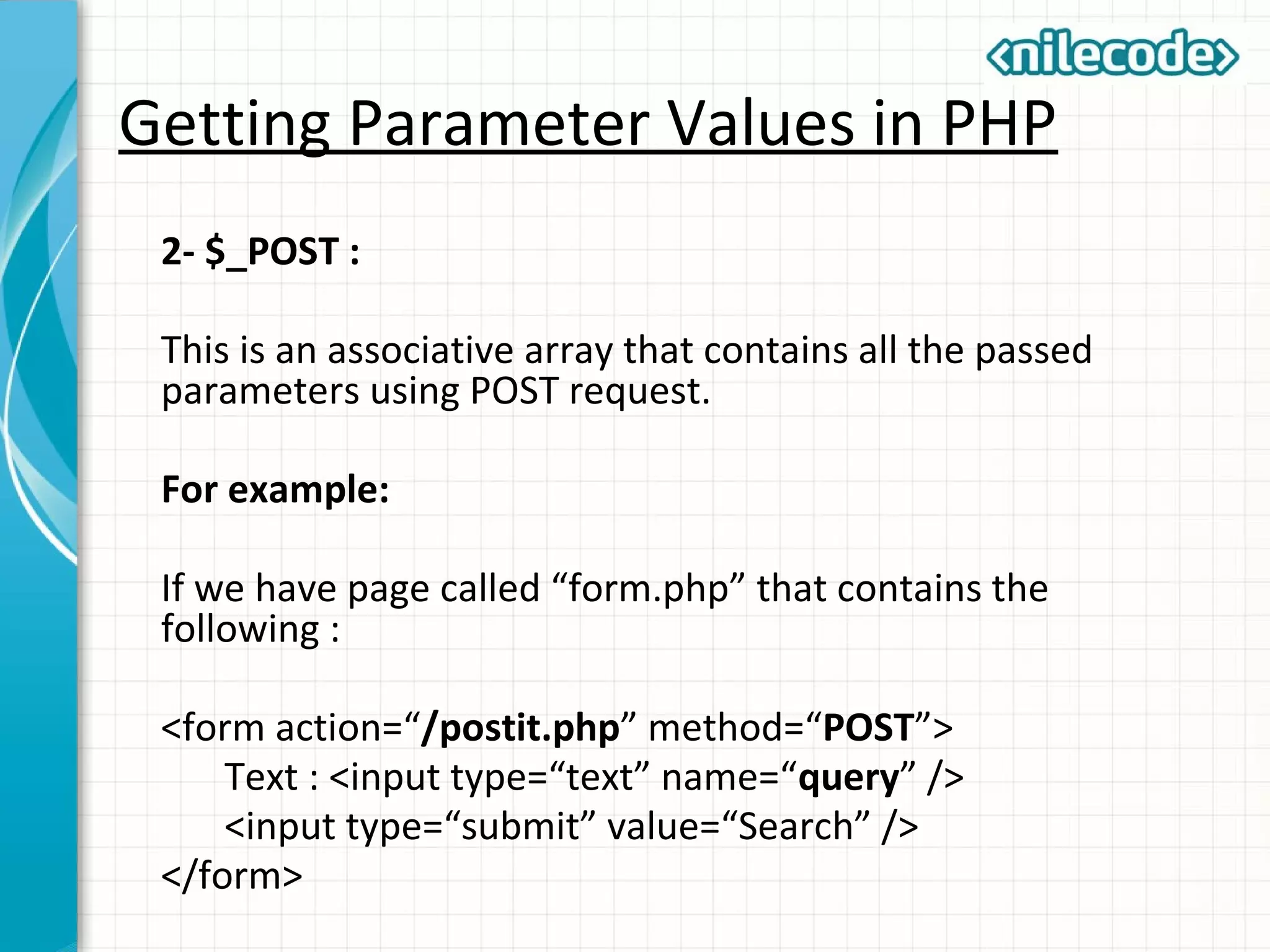
![Getting Parameter Values in PHP
And the script “postit.php” has :
<?php
var_dump($_POST);
?>
Opening that script :
http://localhost/form.php
After opening that and putting a value “Hello” in the text
box and clicking on the search button, you should see :
array(1) {
["query"]=>
string(5) "Hello"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-8-2048.jpg)



![Exercise Solution
1. Script name “greet.php”:
<?php
echo “Hello “ . $_POST[‘name’];
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-12-2048.jpg)

![Handling file uploads
And we have another script named “upload.php” :
<?php
if( is_uploaded_file($_FILES['uploadedfile']['tmp_name']) ){
echo file_get_contents($_FILES['uploadedfile']
['tmp_name']);
}
?>
This script will show the contents of the file once uploaded.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-14-2048.jpg)


![Exercise Solution
The first script is named “doit.php” :
<?php
echo "Your name : ". $_POST['name'] . "<br/>";
echo "Your email: ";
if( preg_match( '/^[w]+@[w]+.[a-z]{2,3}$/i',
$_POST['email']) == 1 )
echo $_POST['email'];
else
echo "Not Valid“;
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-17-2048.jpg)

![Cookies in PHP
PHP provides the function setcookie() and the global
variable $_COOKIE to allow us to deal with cookies.
bool setcookie ( string $name [, string $value [, int $expire =
0 [, string $path [, string $domain [, bool $secure = false [,
bool $httponly = false ]]]]]] )
setcookie() defines a cookie to be sent along with the rest of
the HTTP headers. Like other headers, cookies must be sent
before any output from your script.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-19-2048.jpg)
![Cookies in PHP
The $_COOKIE super global is used to get the cookies set.
Example:
<?php
setcookie(‘name’, ‘mohamed’, time() + 3600 );
?>
In another script on the same domain we can do this :
<?php
echo $_COOKIE[‘name’]; // mohamed
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-20-2048.jpg)
![Sessions
• Session support in PHP consists of a way to preserve
certain data across subsequent accesses.
• This is implemented by creating a cookie with a random
number for the user and associate this data with that id.
• PHP maintains a list of the user ids on the server with
corresponding user data.
Example:
<?php
session_start();
$_SESSION[‘age’] = 20;
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-21-2048.jpg)
![Sessions
Another script on the same domain contains:
<?php
session_start();
echo $_SESSION[‘age’] ; // 20
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-22-2048.jpg)


![Exercise Solution
<?php
session_start();
if( !isset($_SESSION['views']) )
$_SESSION['views'] = 0;
++$_SESSION['views'];
echo "Number of views : " . $_SESSION['views'];
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class6-phpwebprogramming-150930071116-lva1-app6891/75/Class-6-PHP-Web-Programming-25-2048.jpg)


