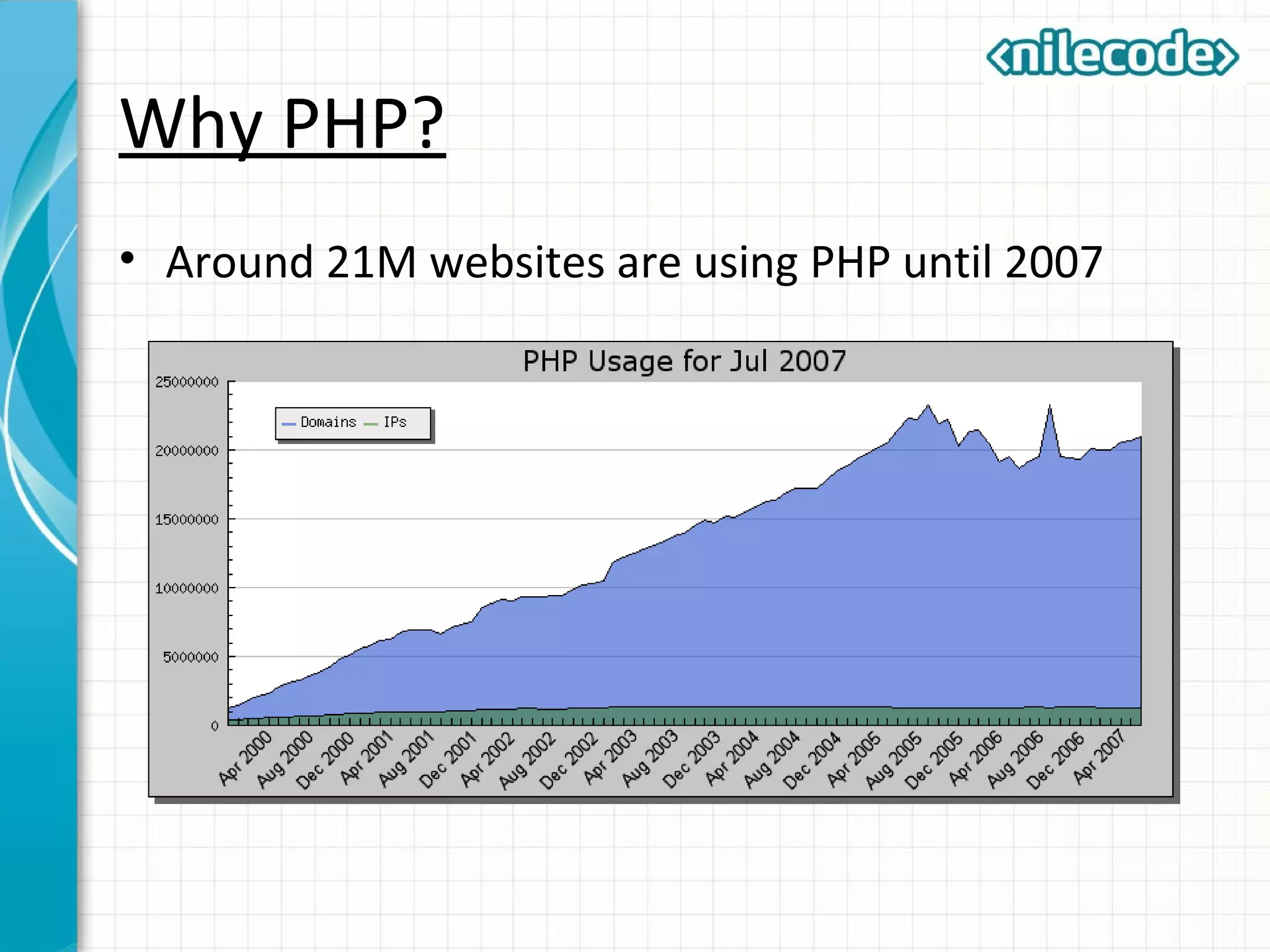
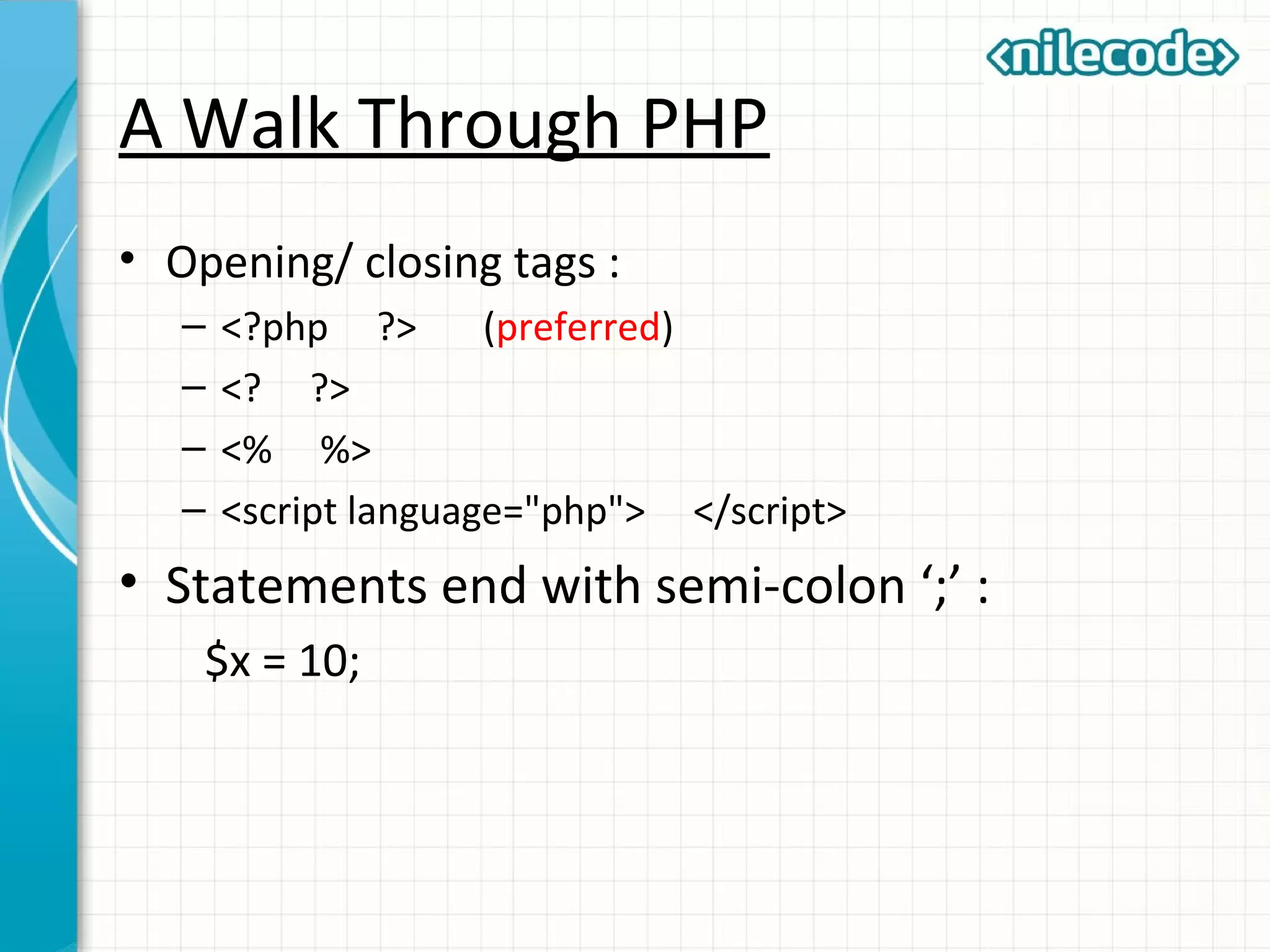
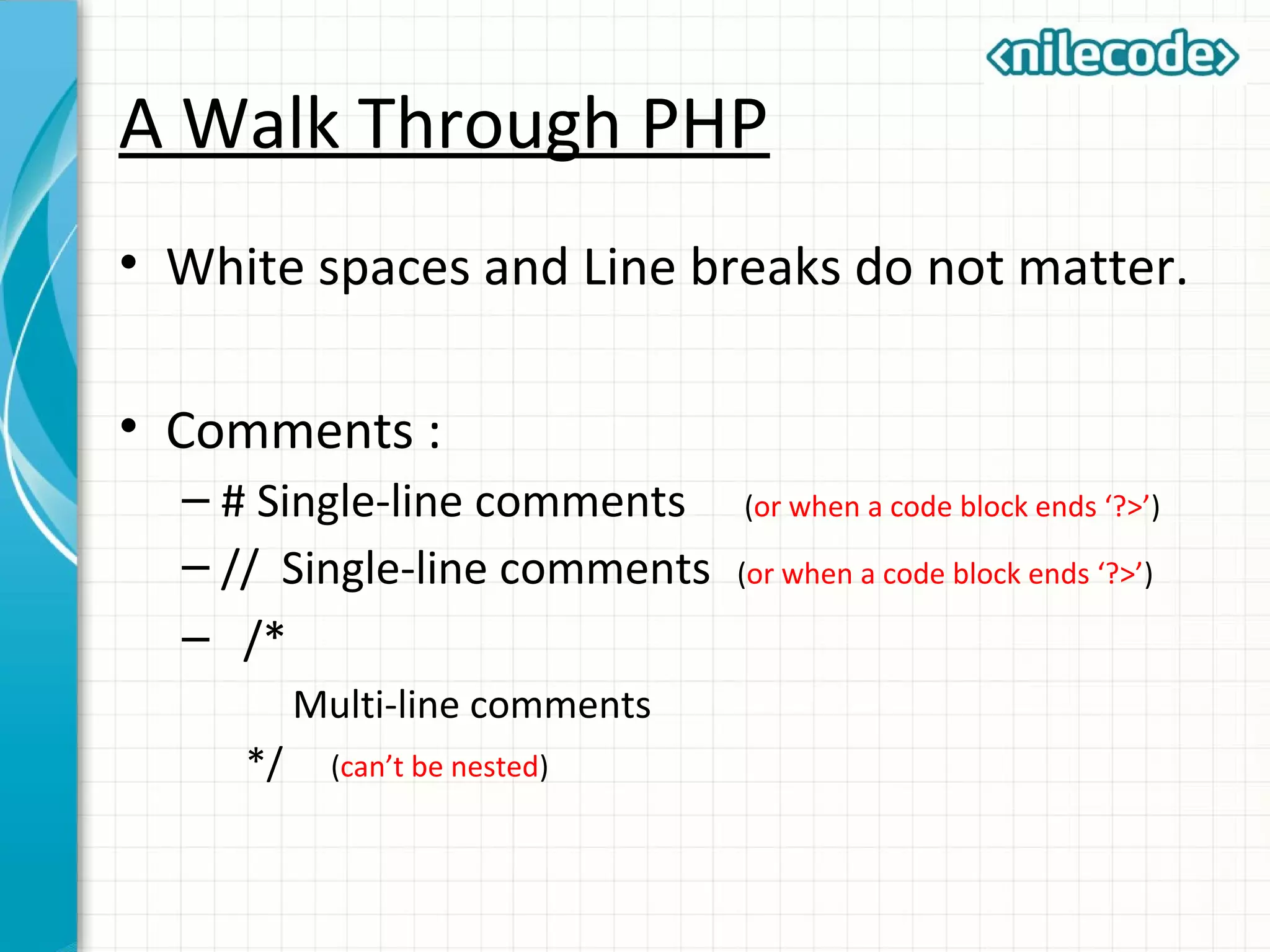
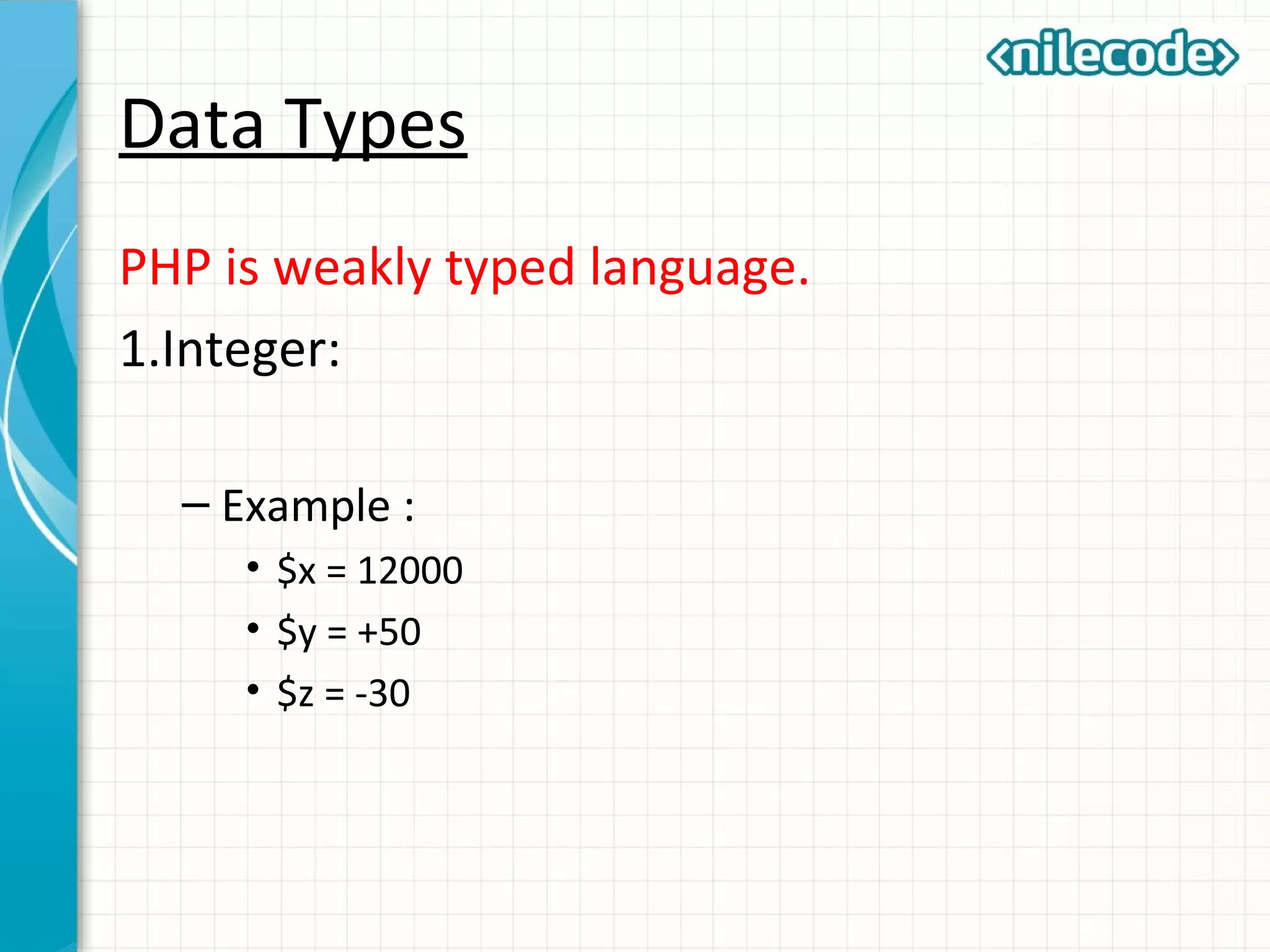
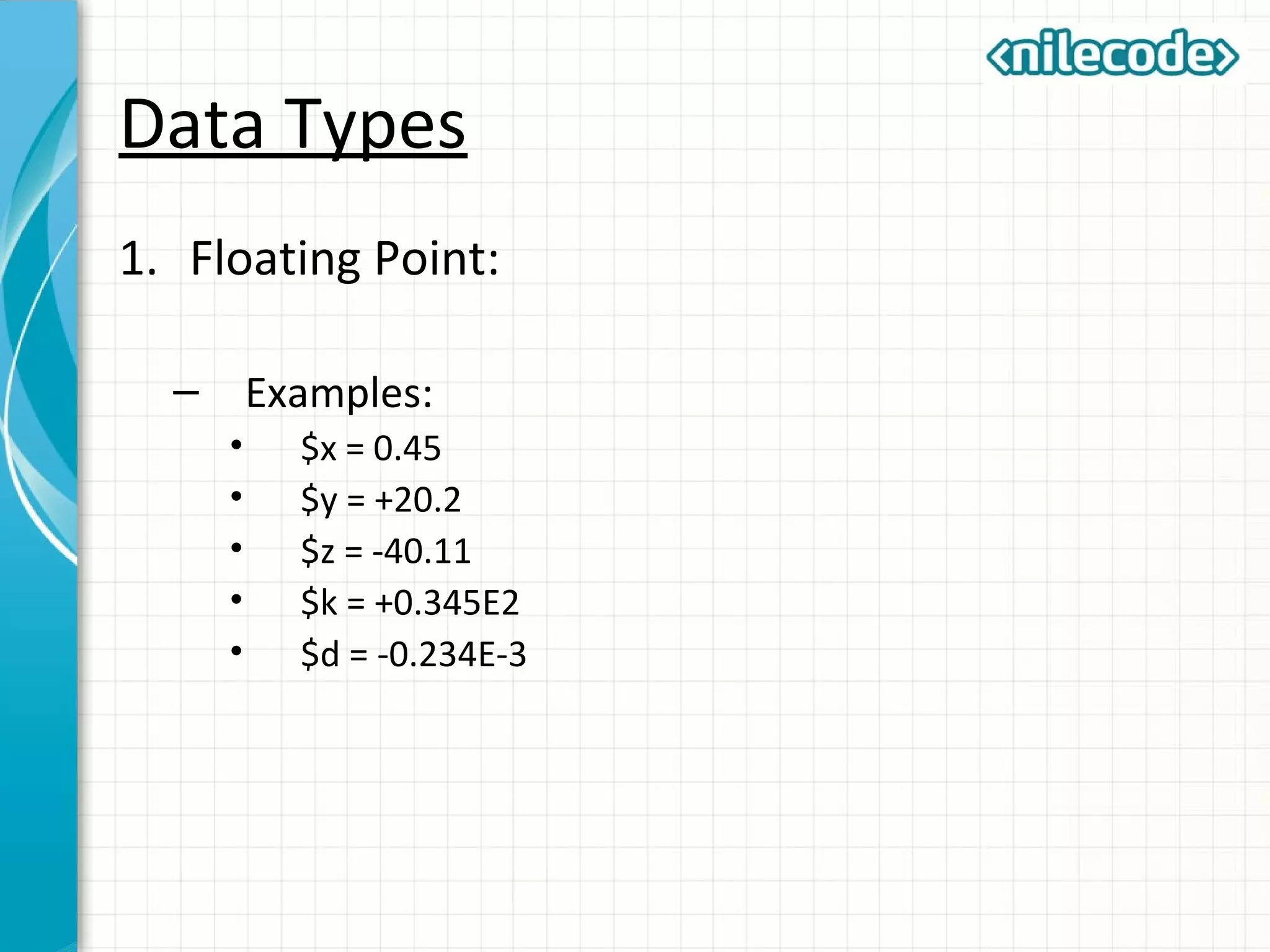
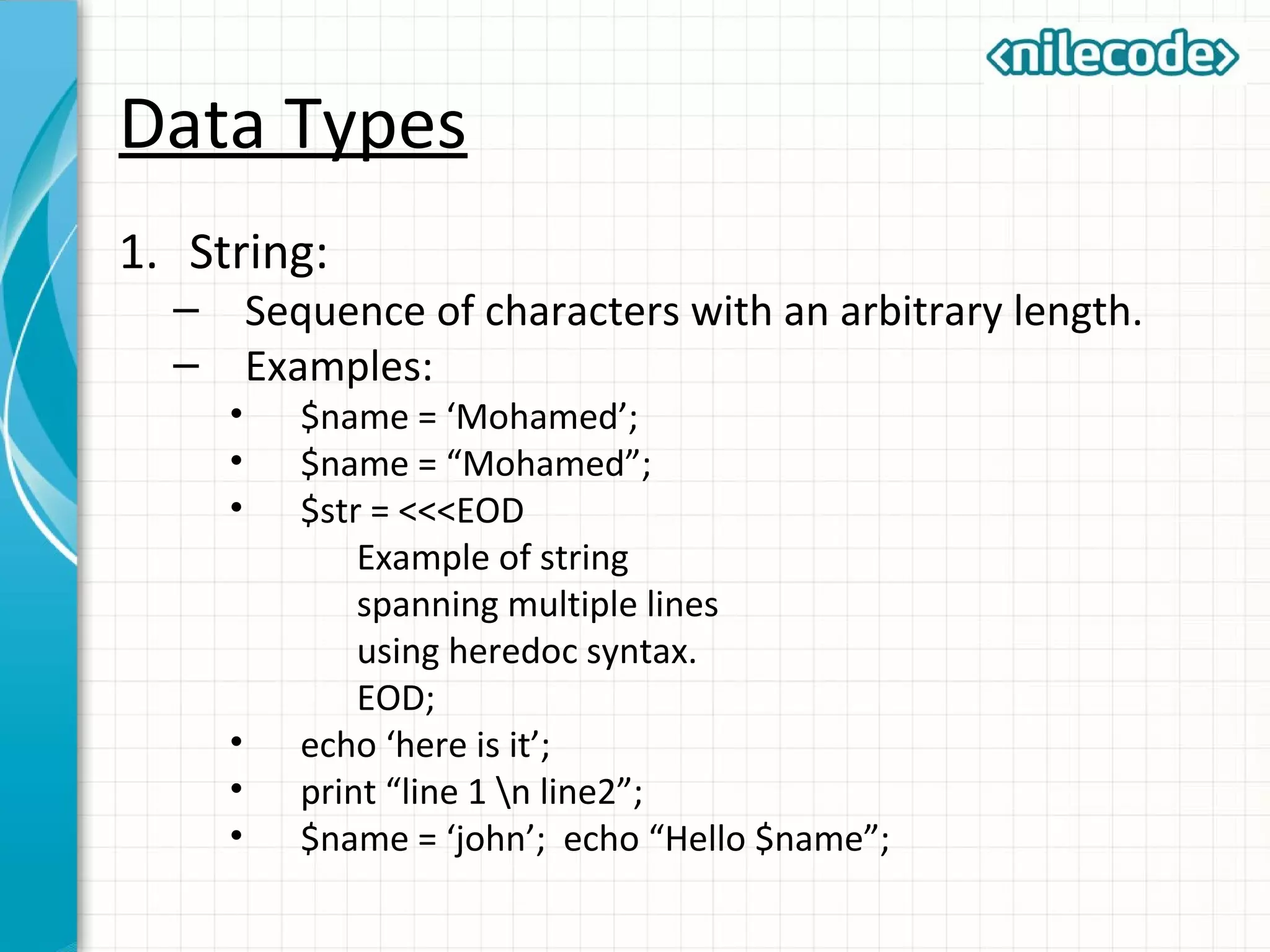
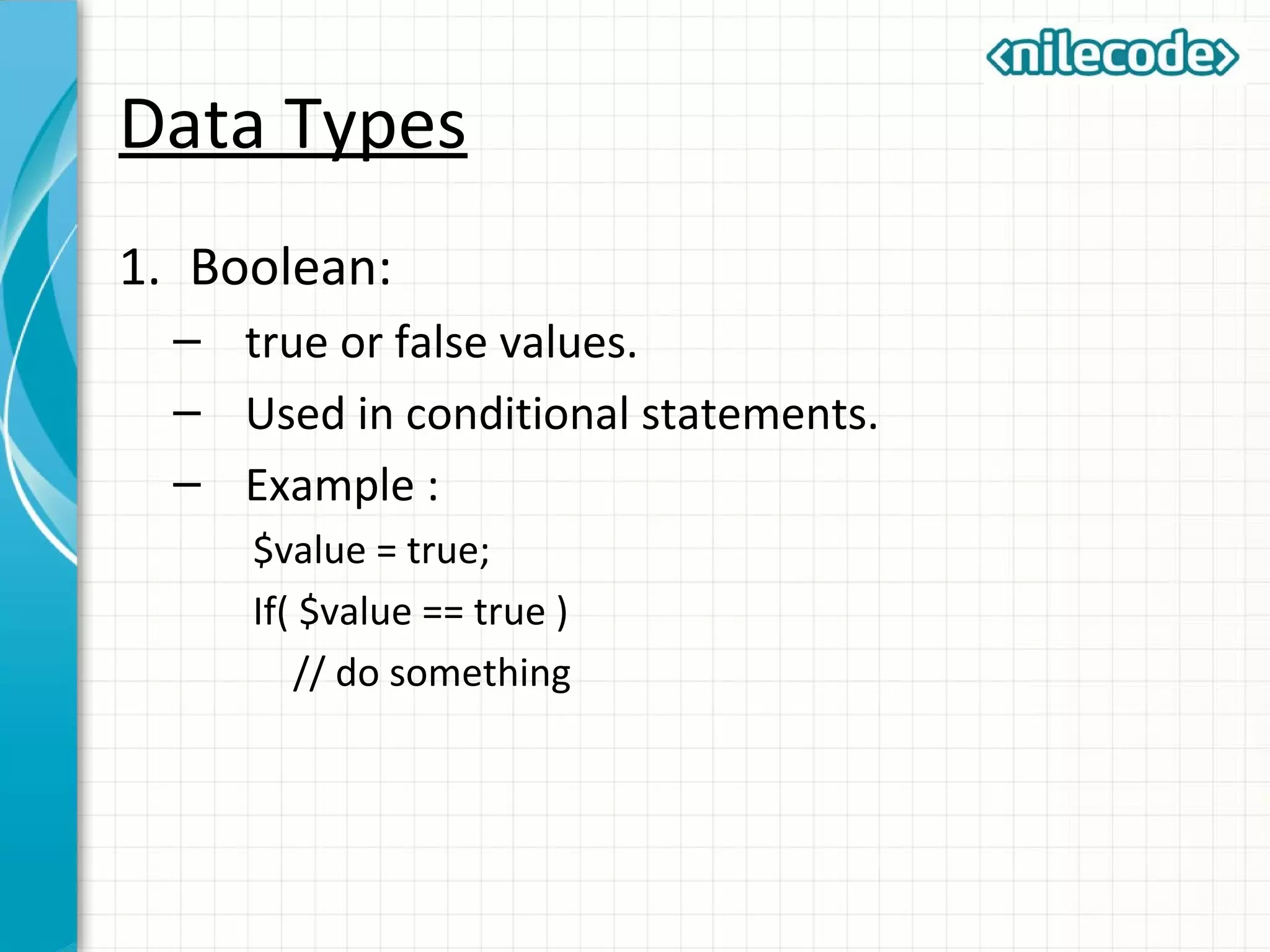
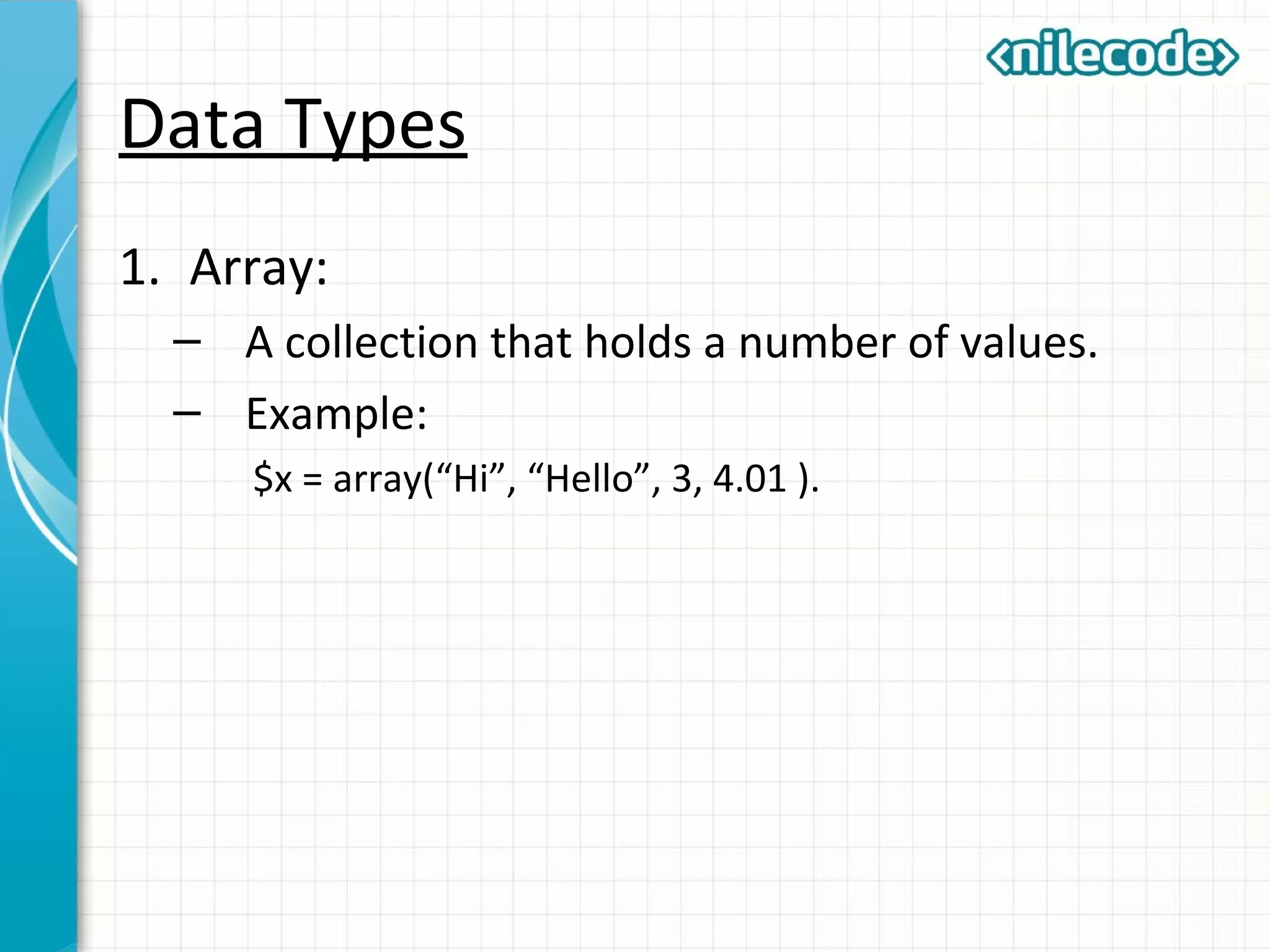
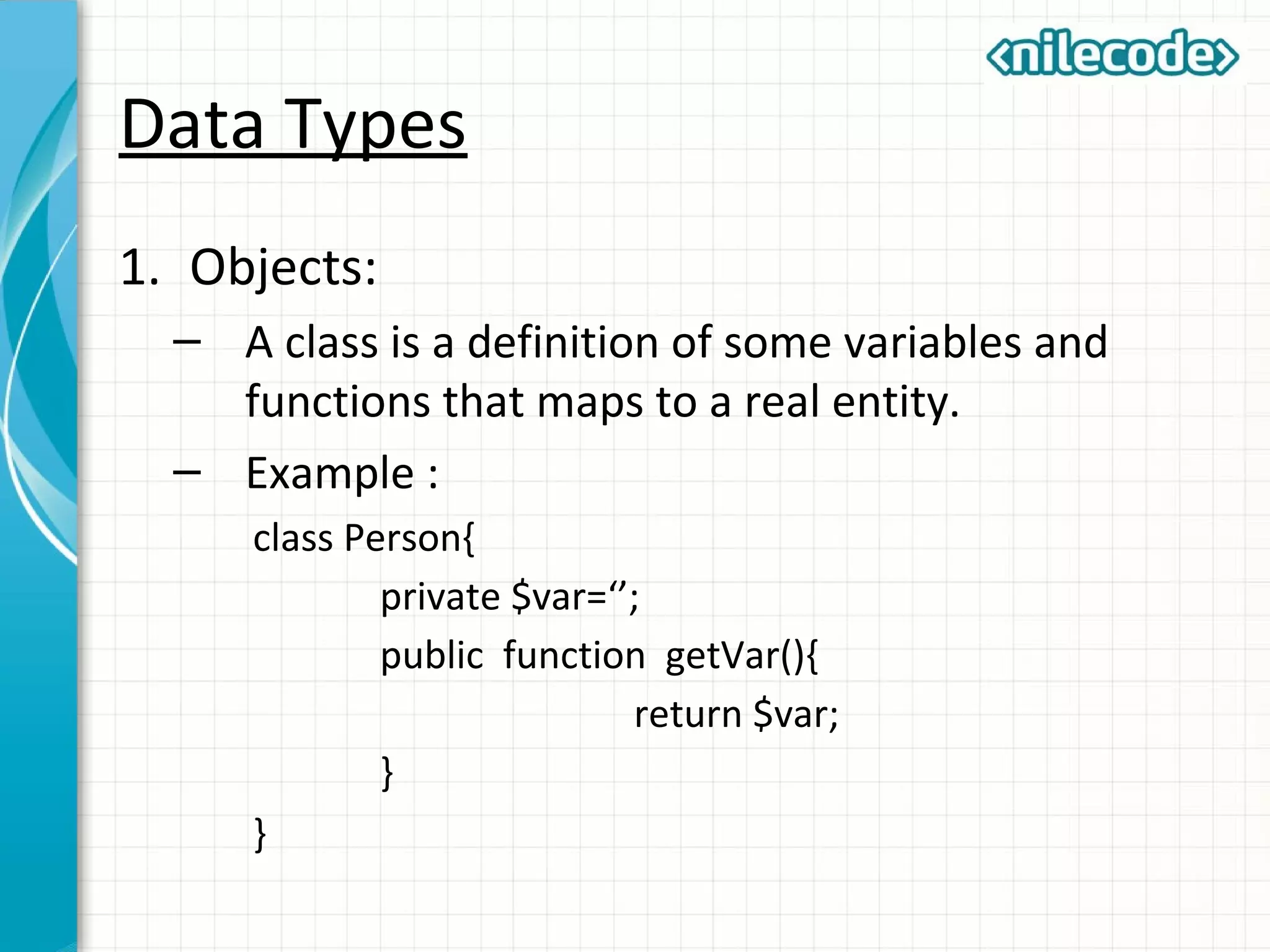
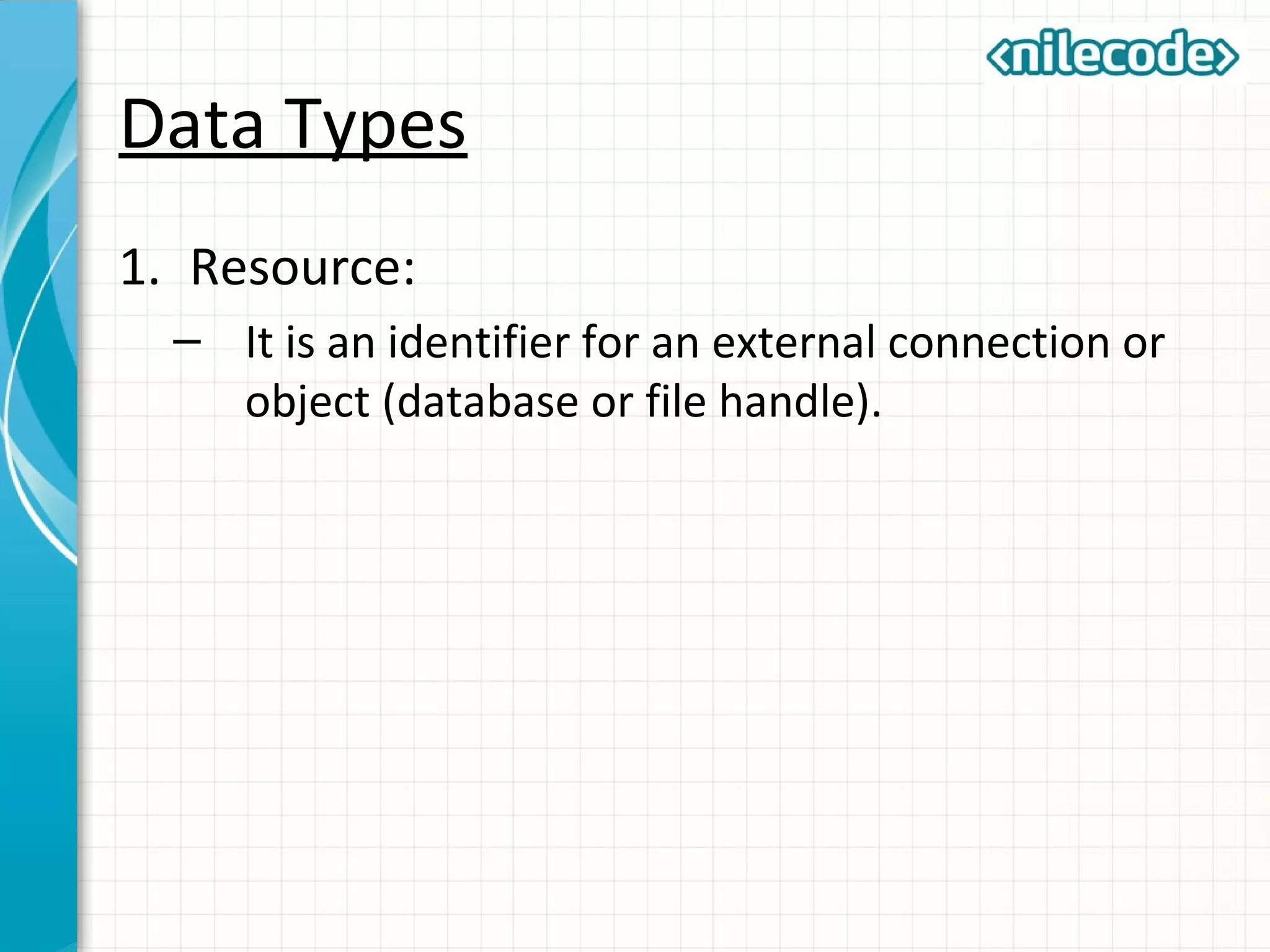
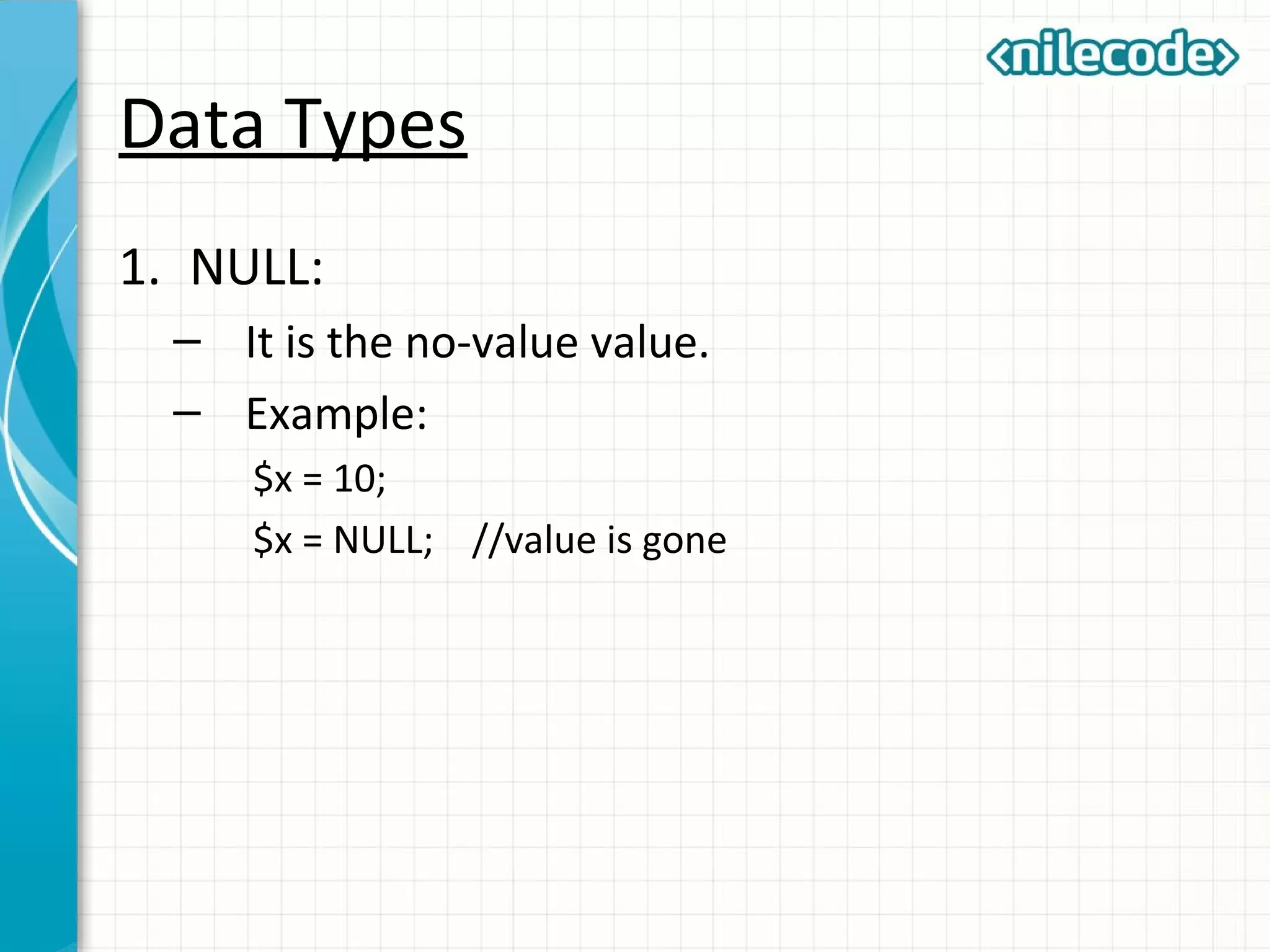
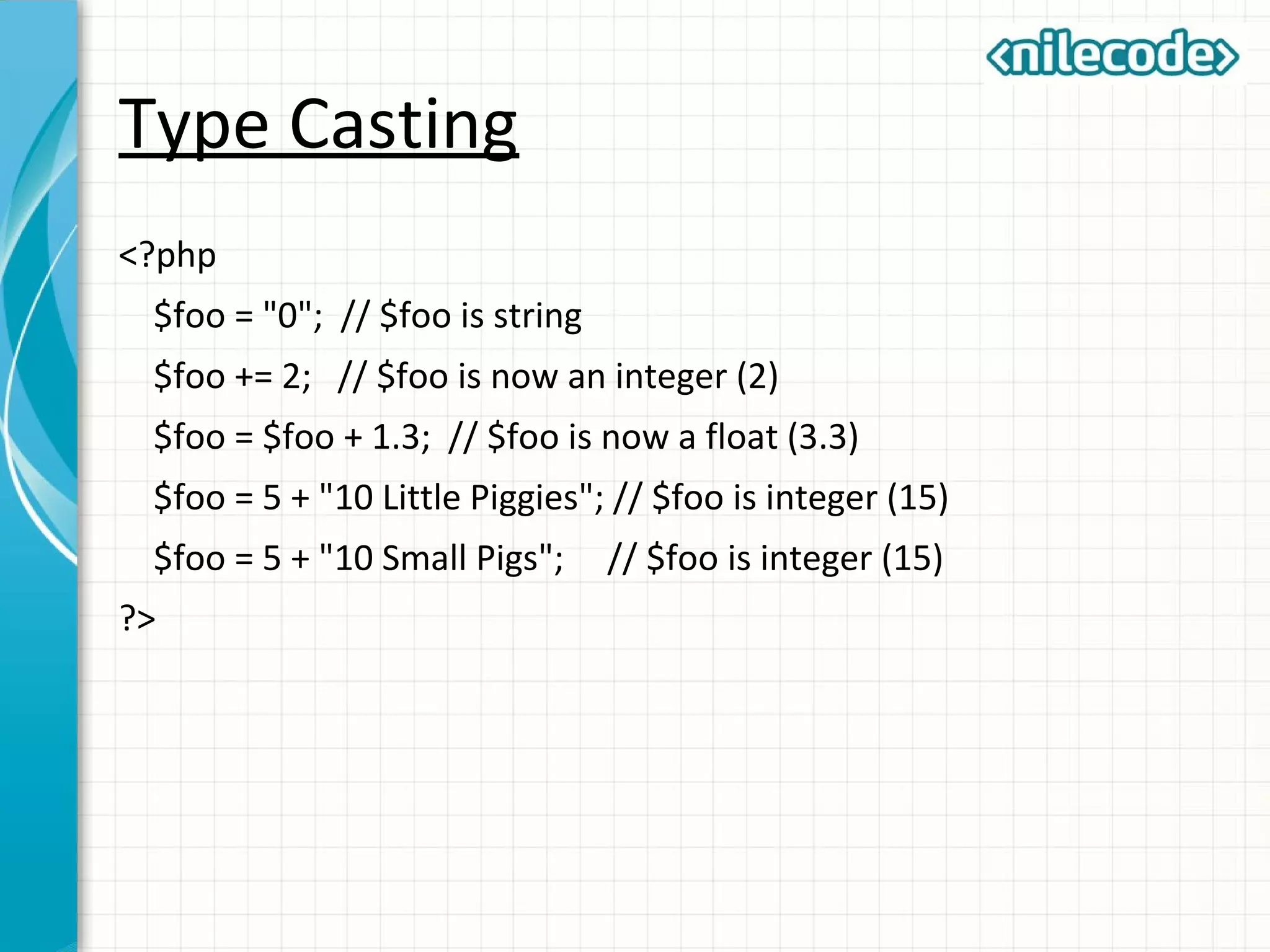
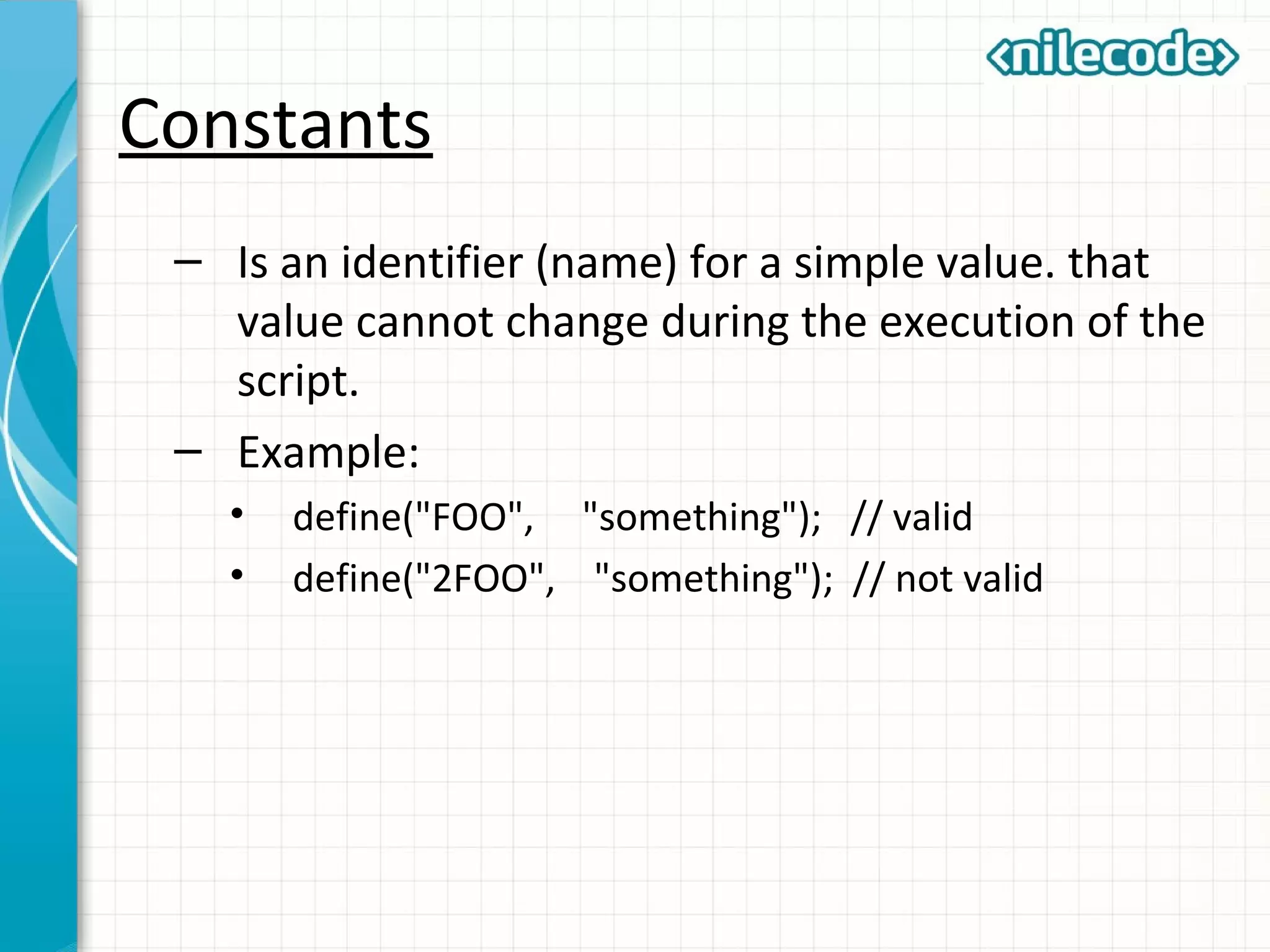
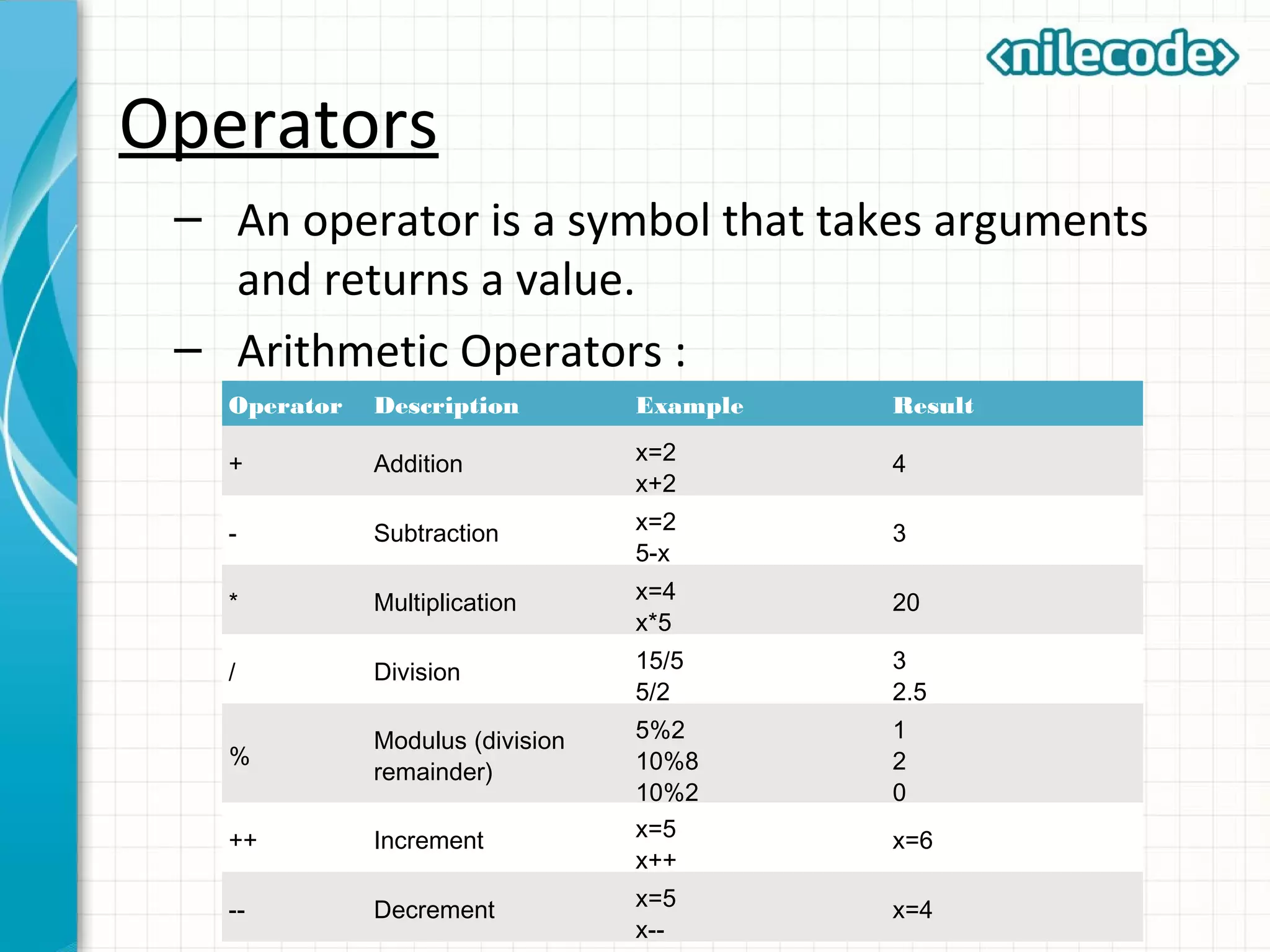
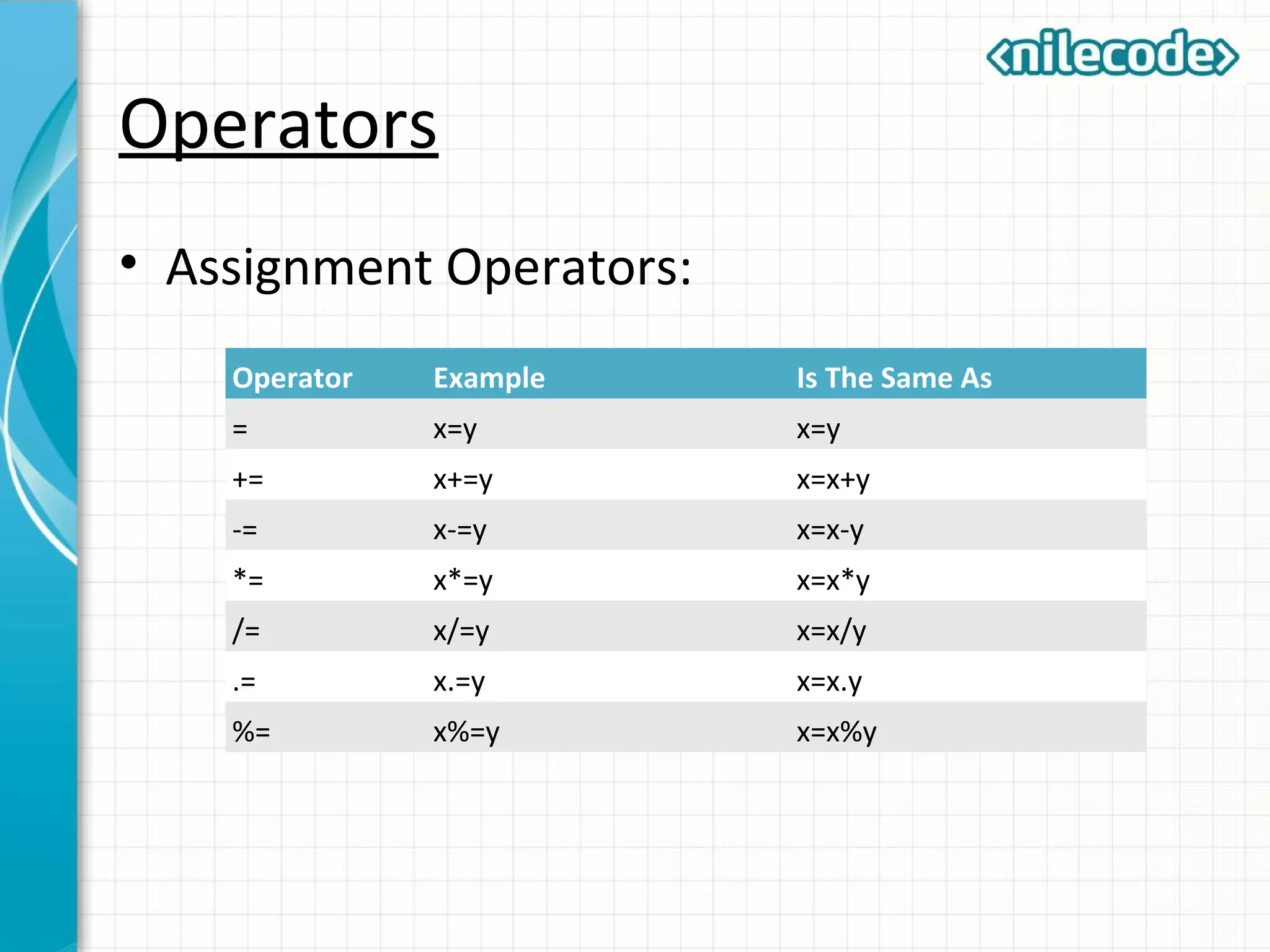
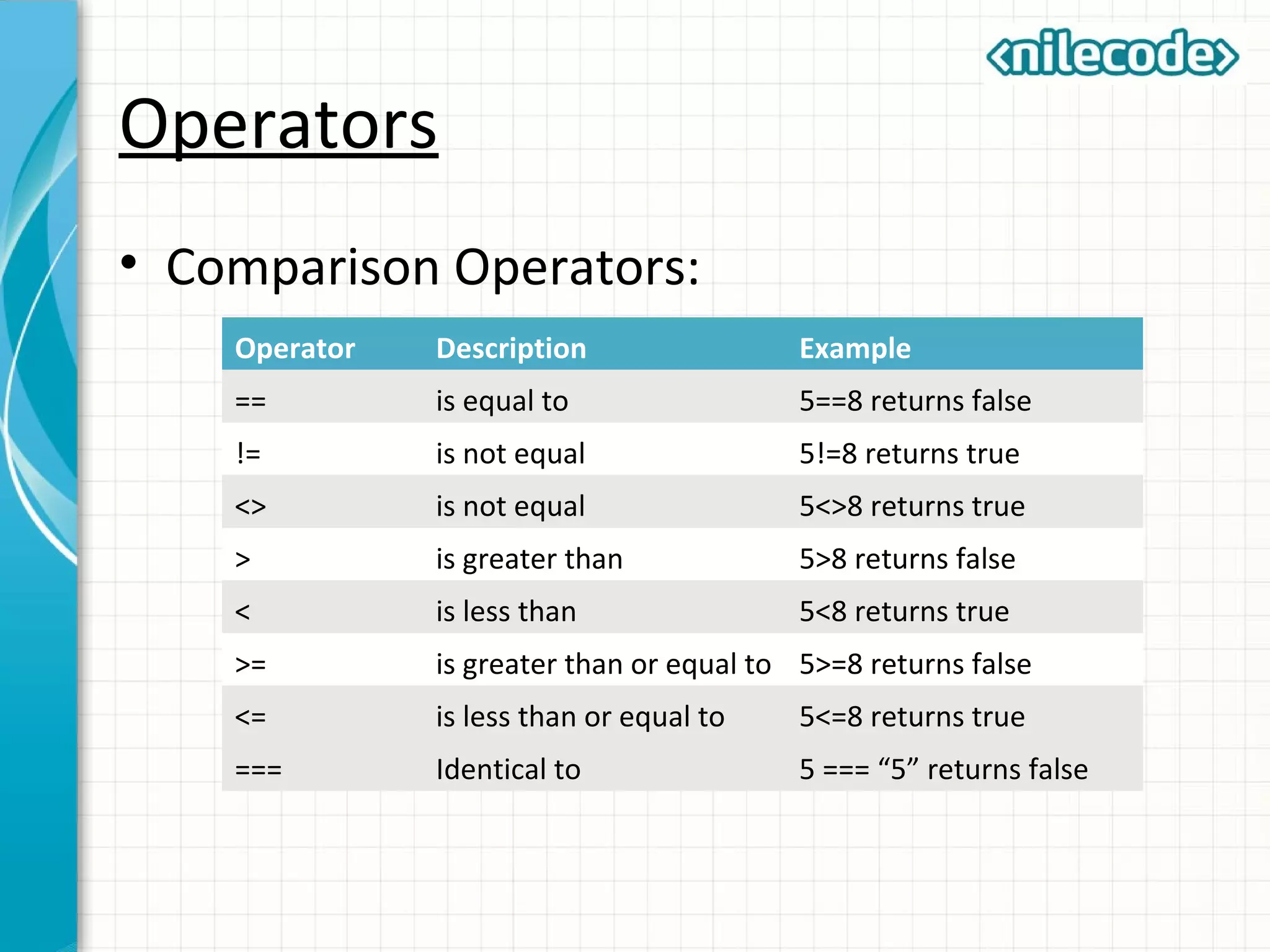
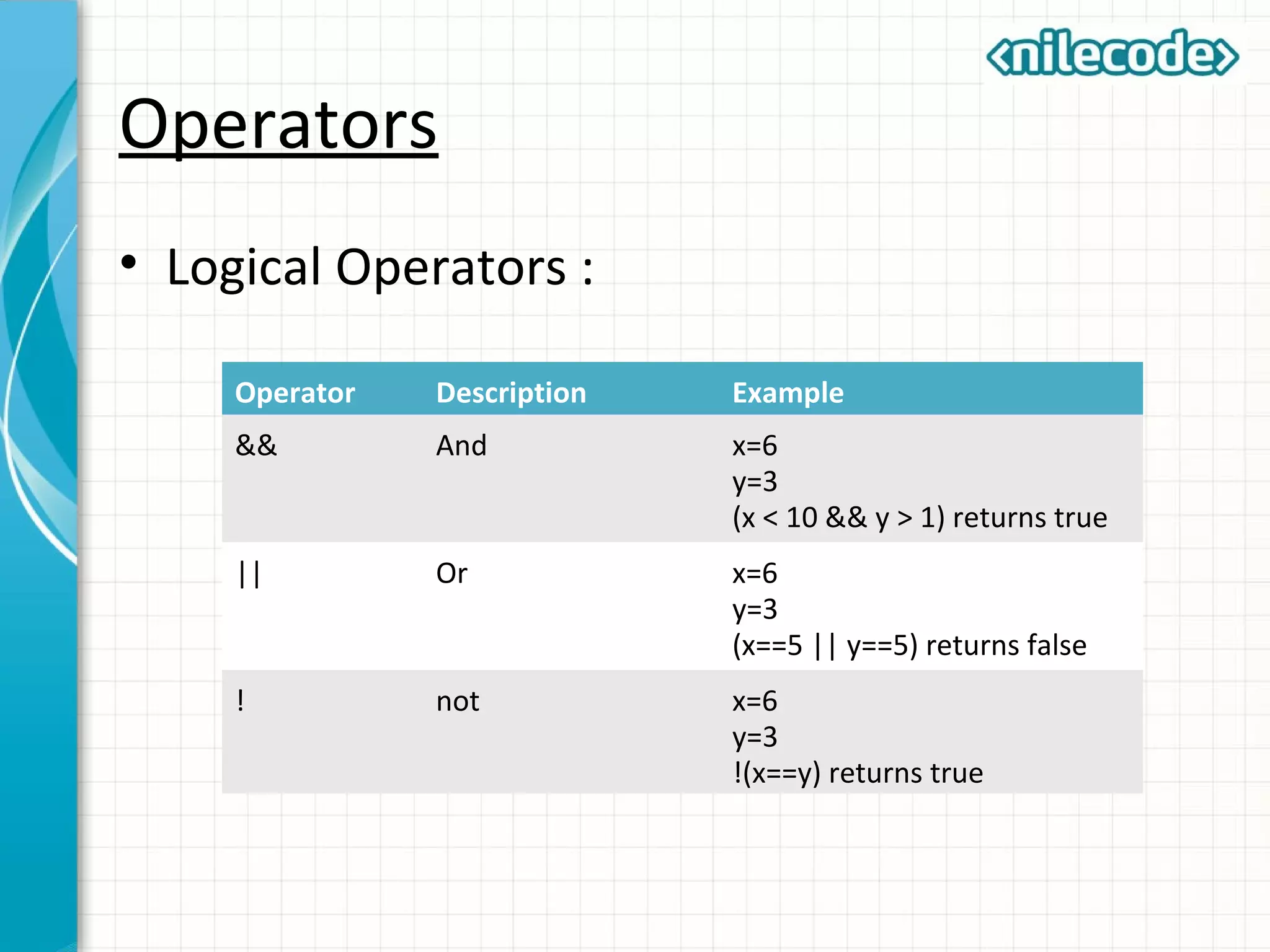
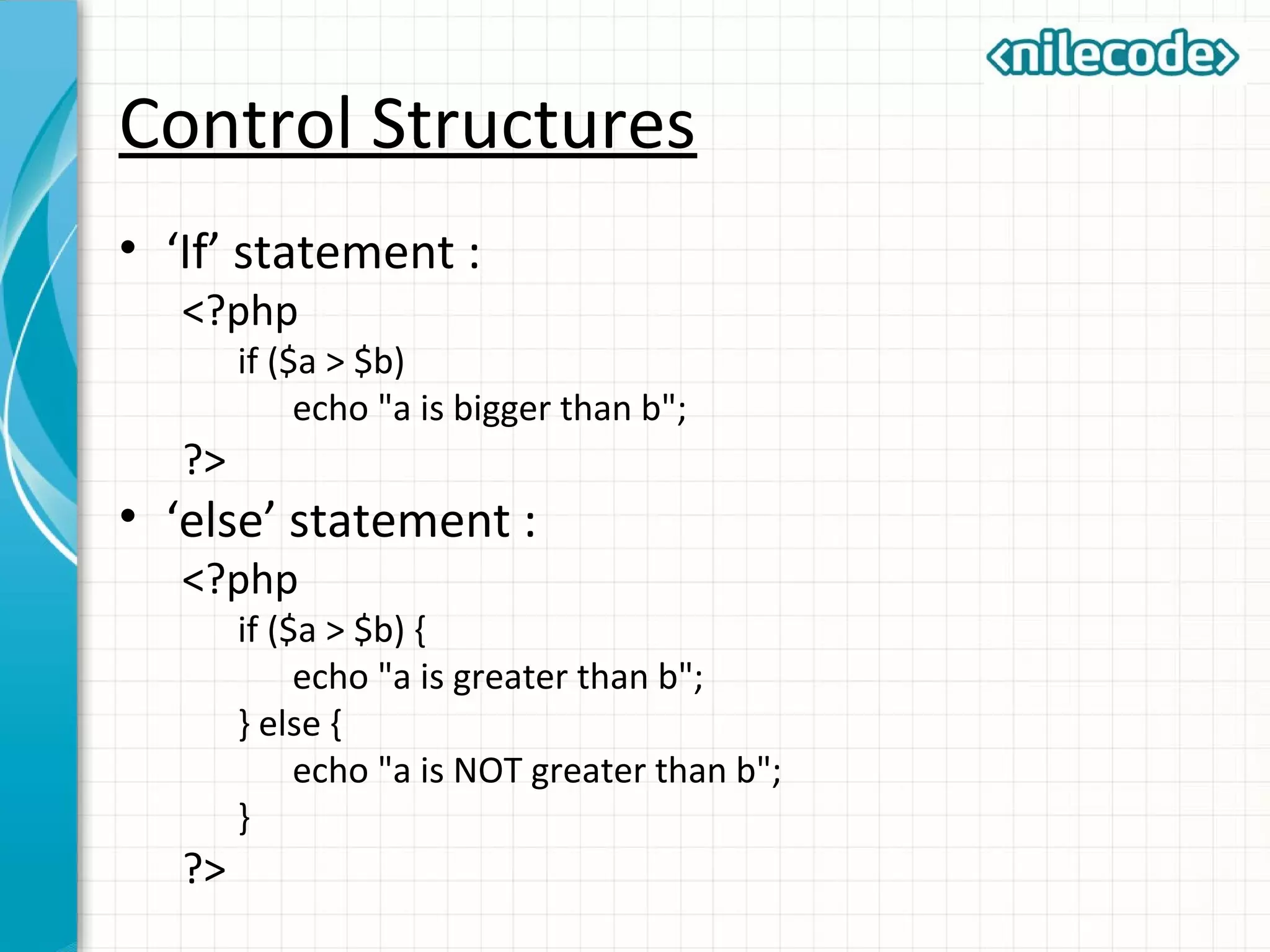
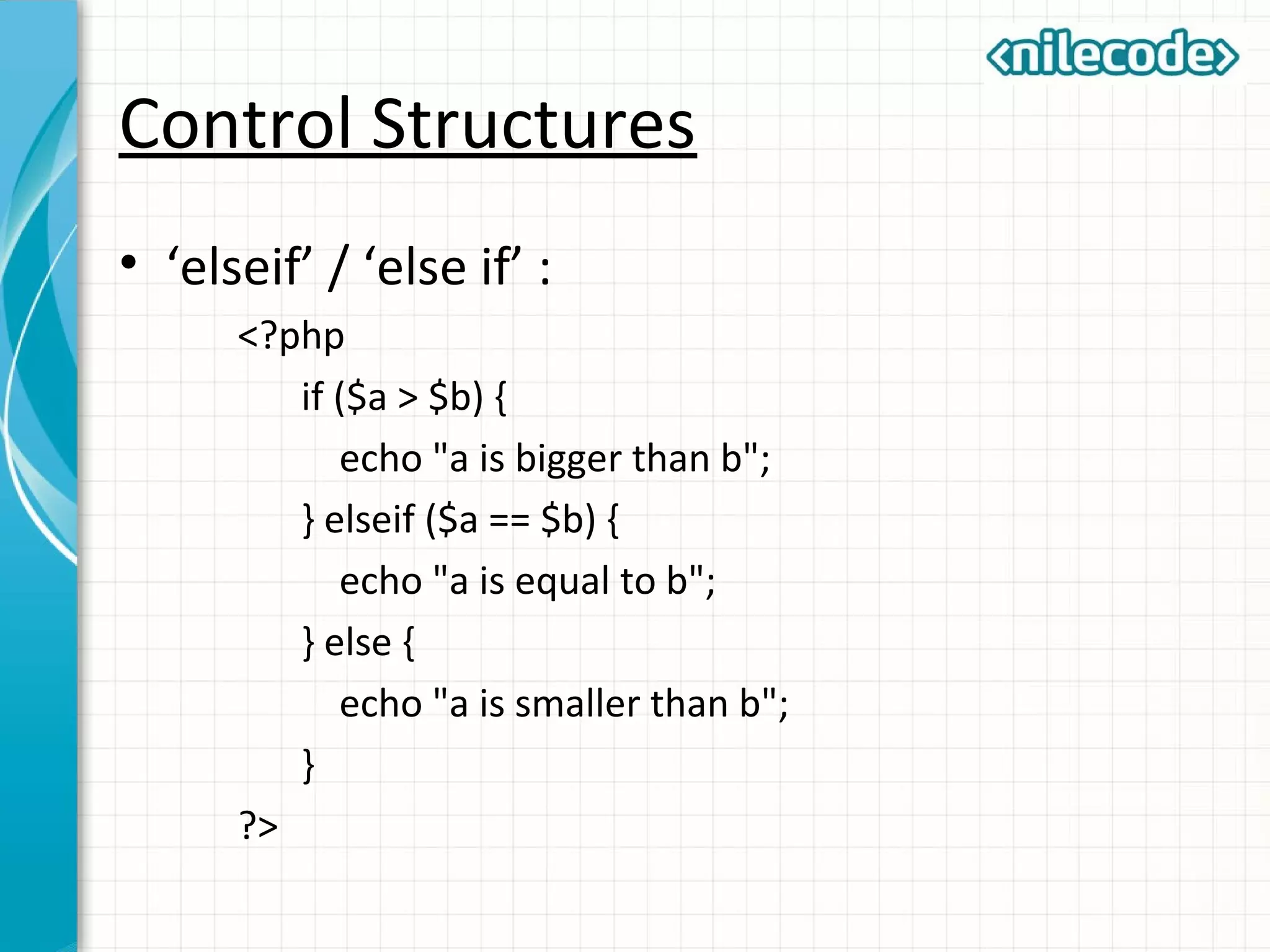
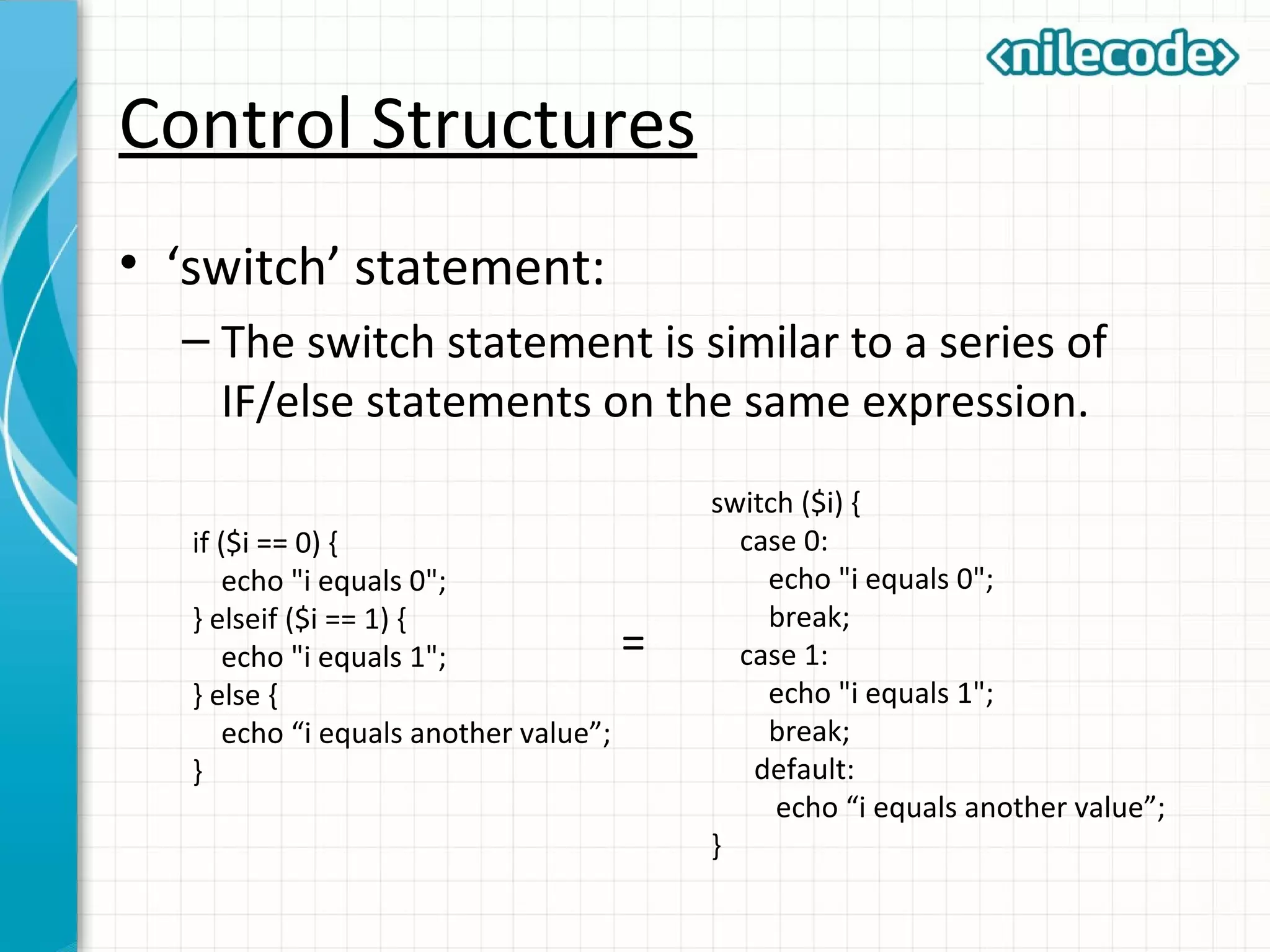
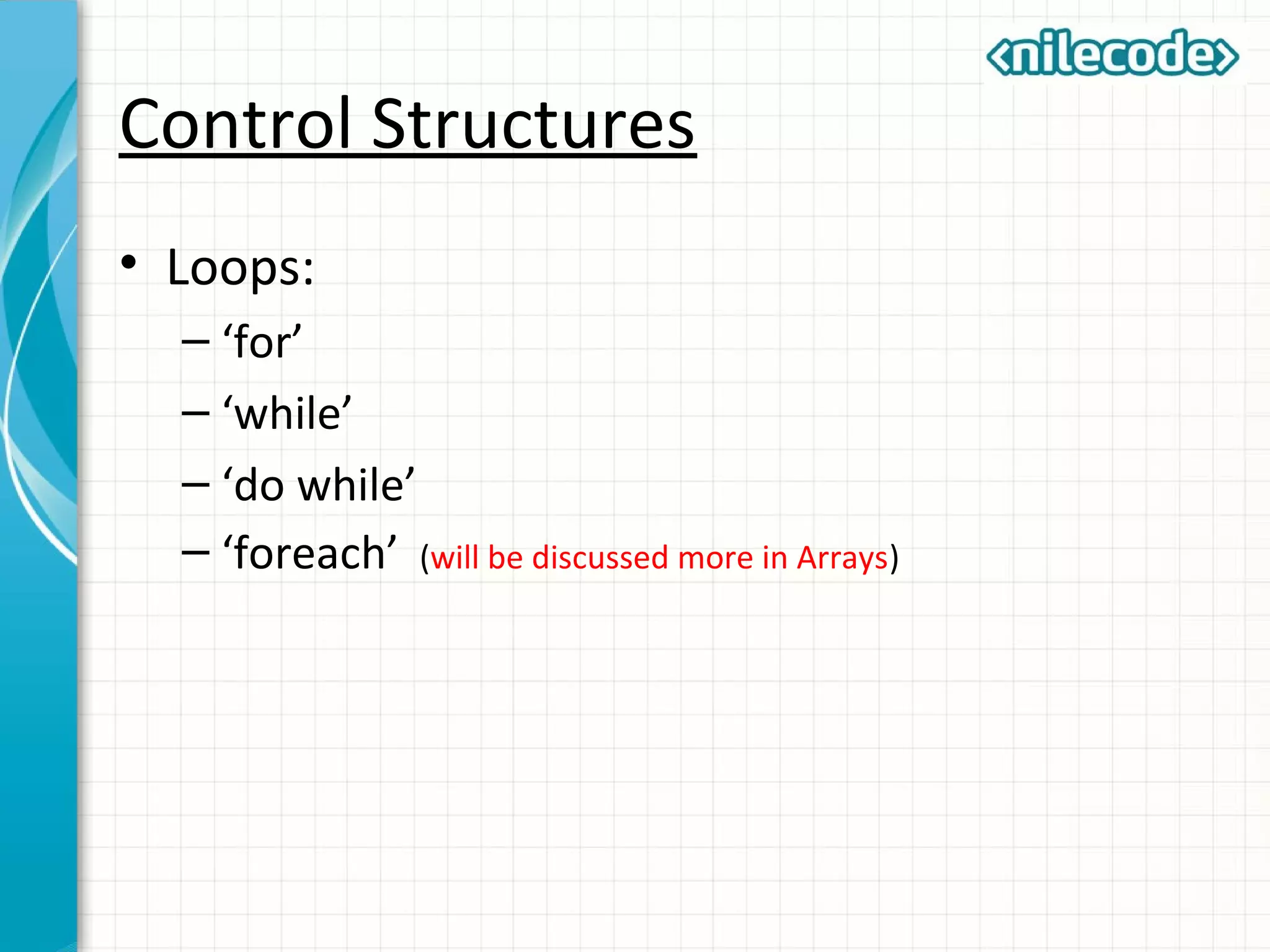
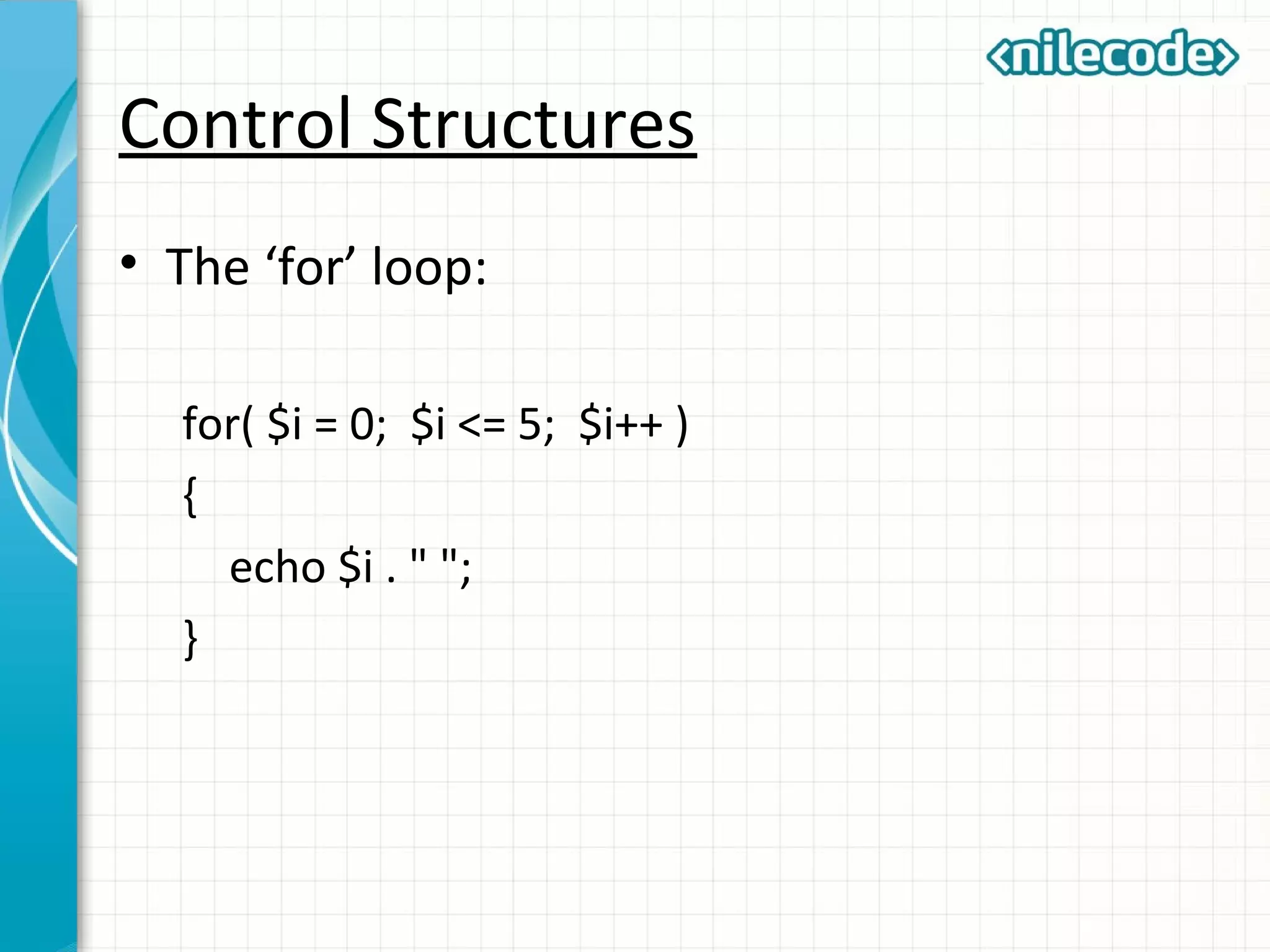
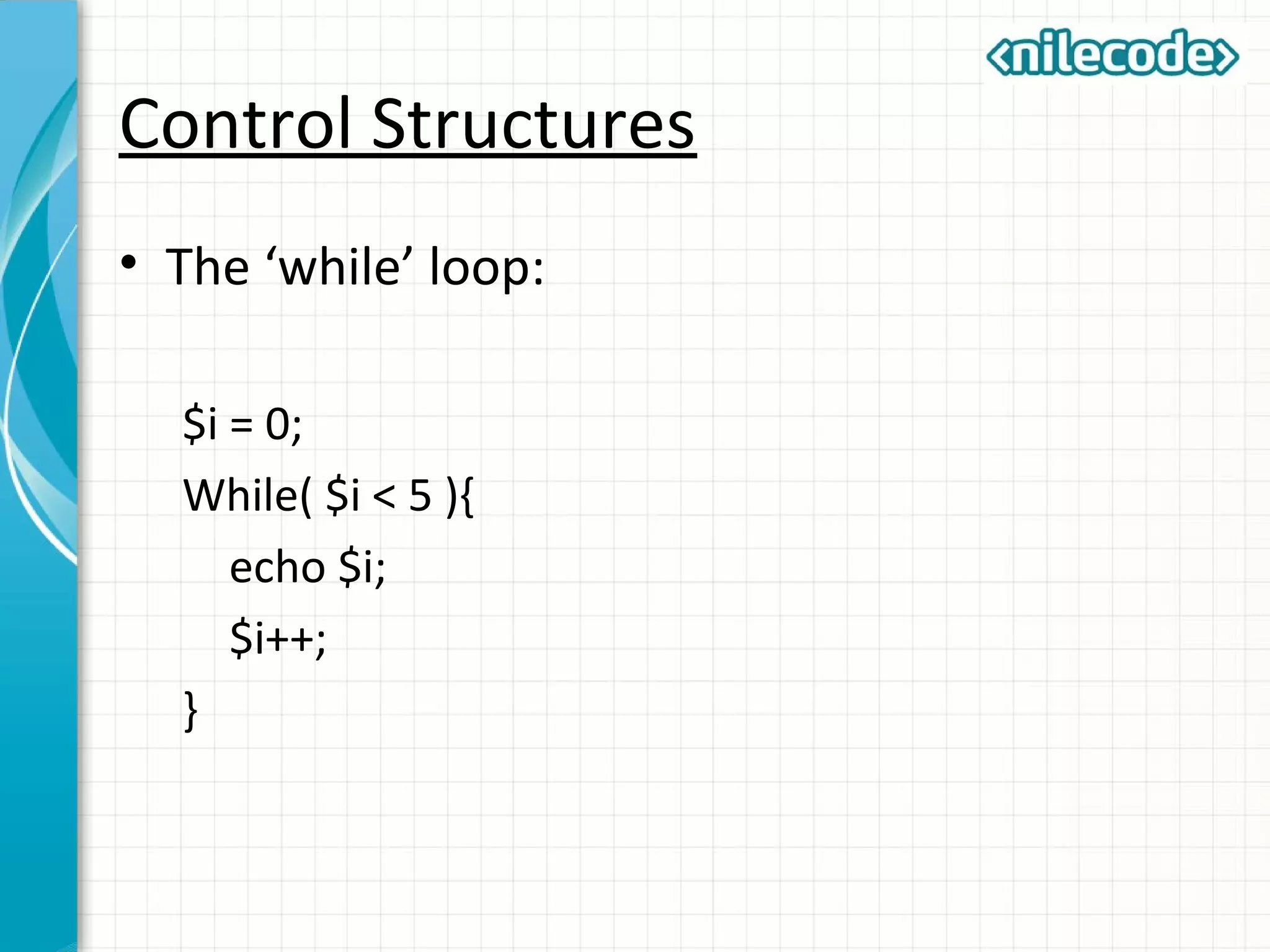
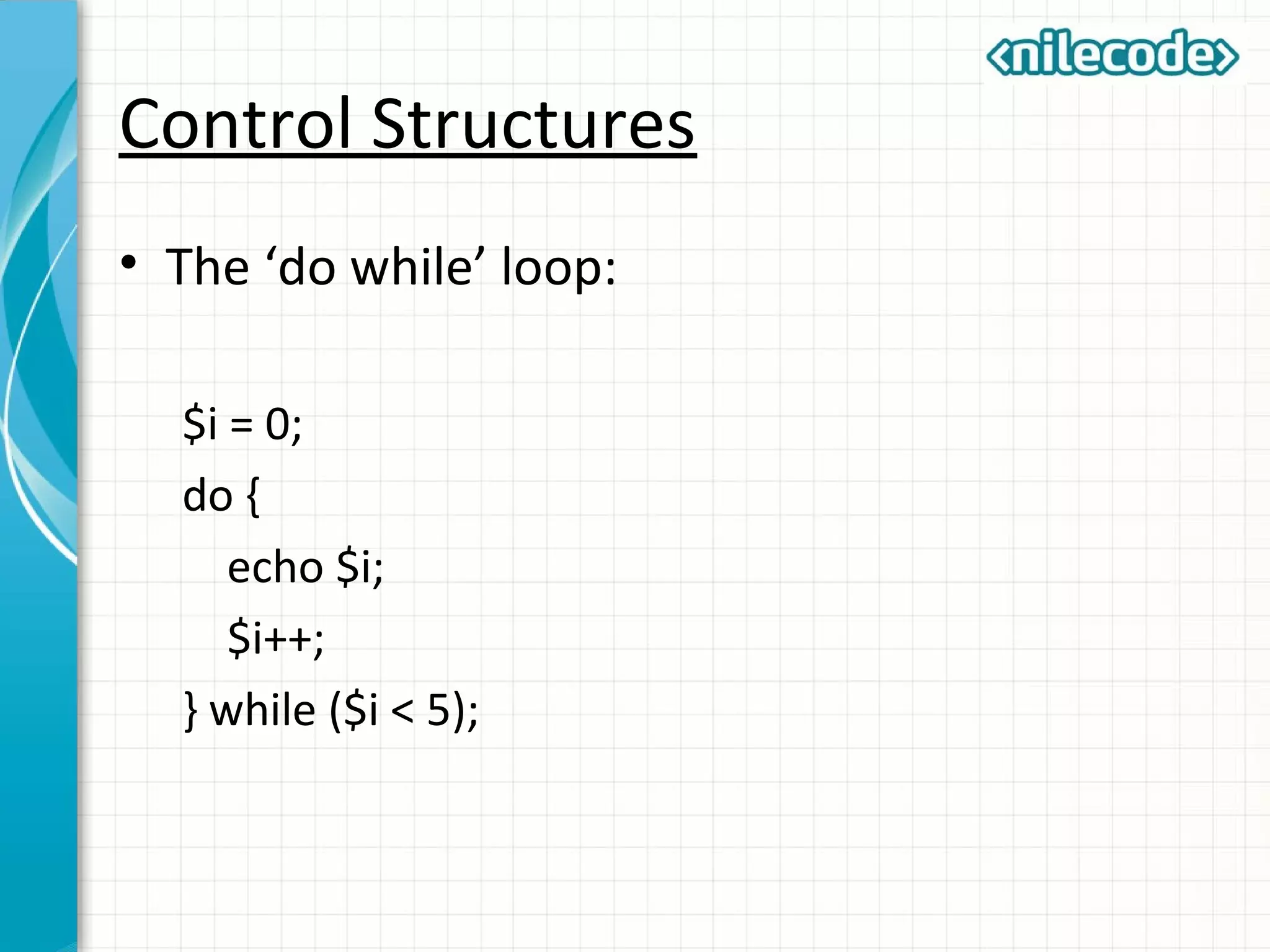
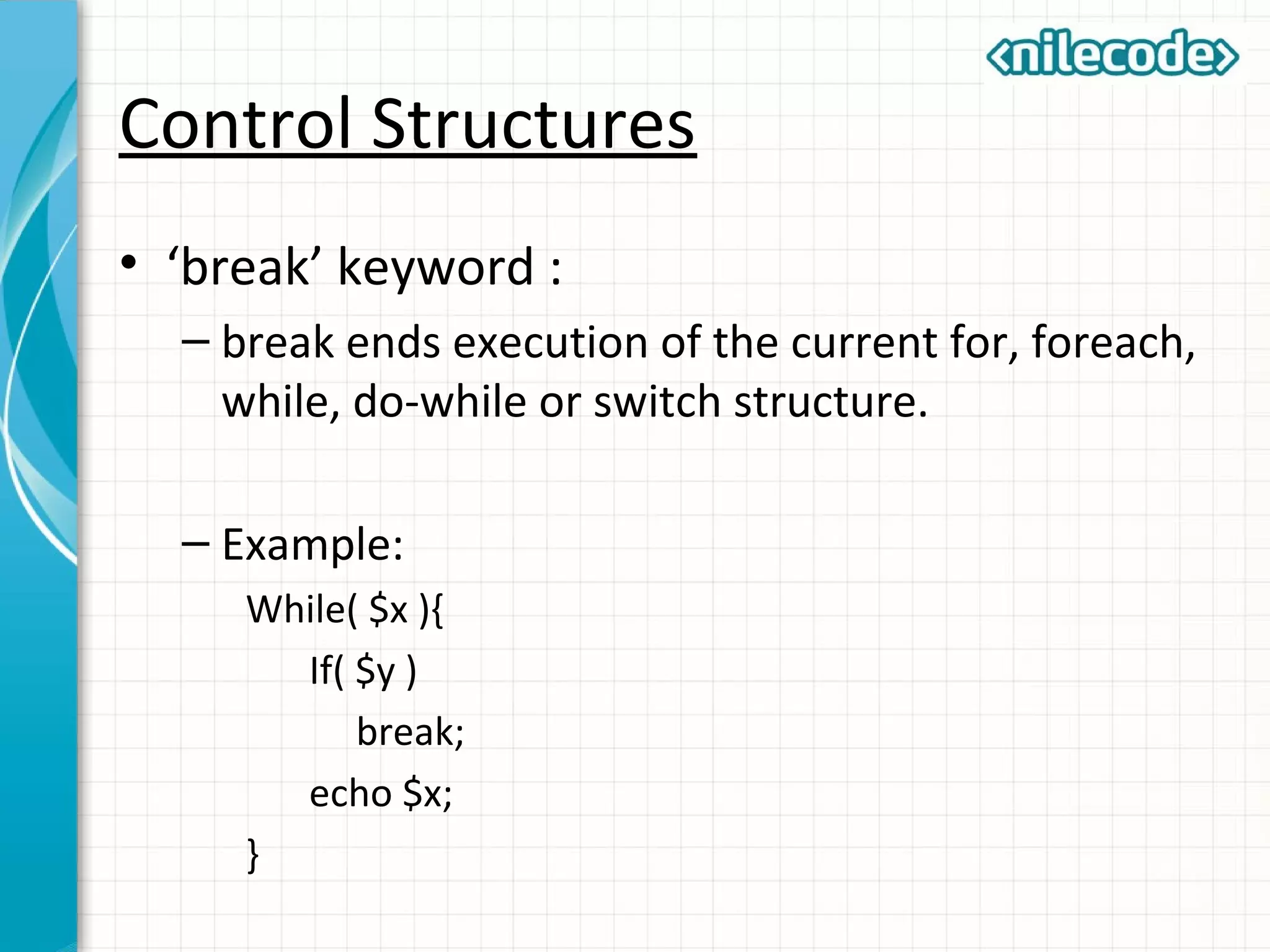
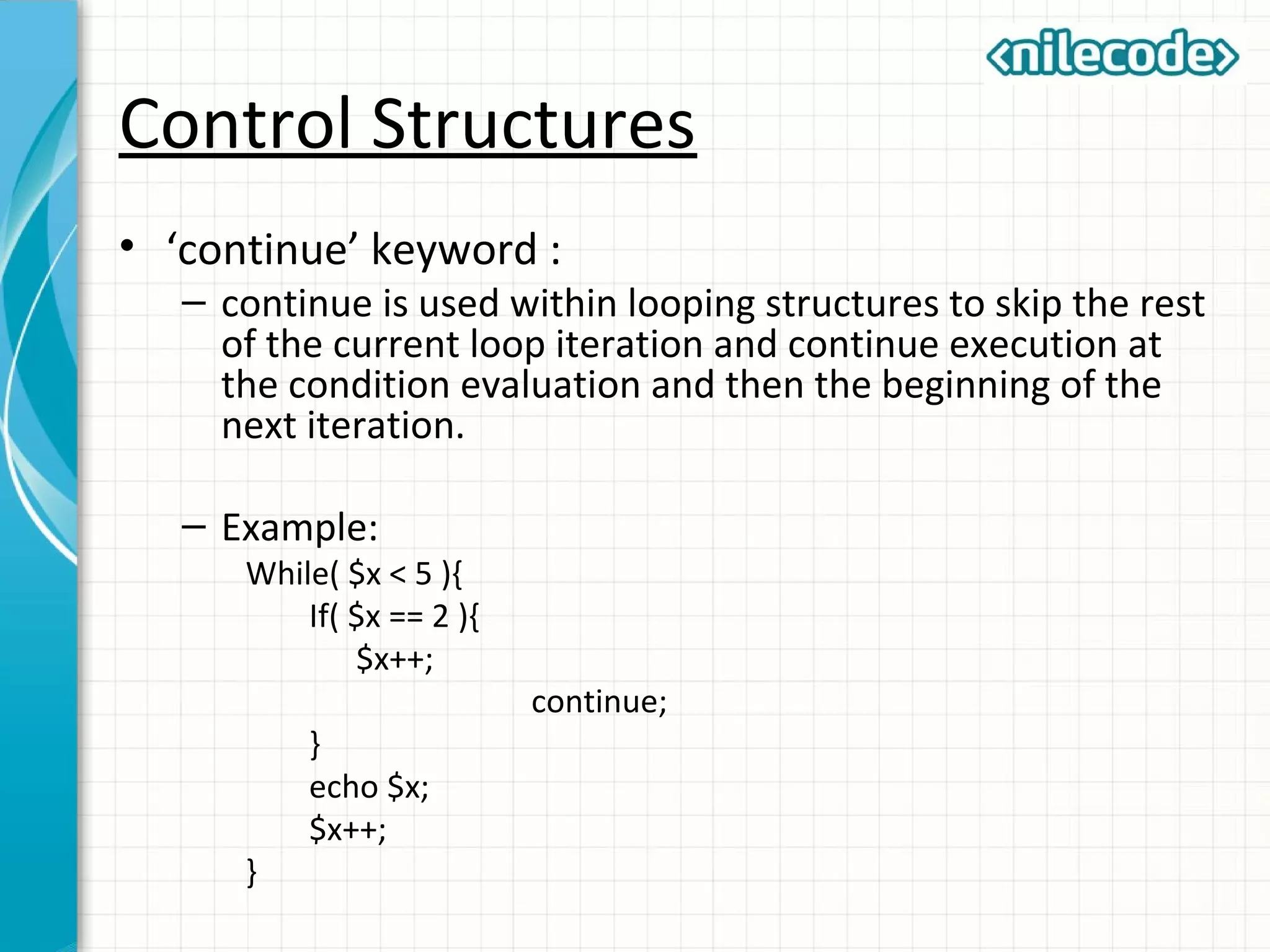
This document provides an introduction to PHP by outlining its key topics and features. It explains that PHP can be used for server-side web development, command-line scripting, and client-side GUI applications. The document then walks through variables, data types, operators, control structures, and loops in PHP. It provides examples to illustrate PHP syntax and best practices.