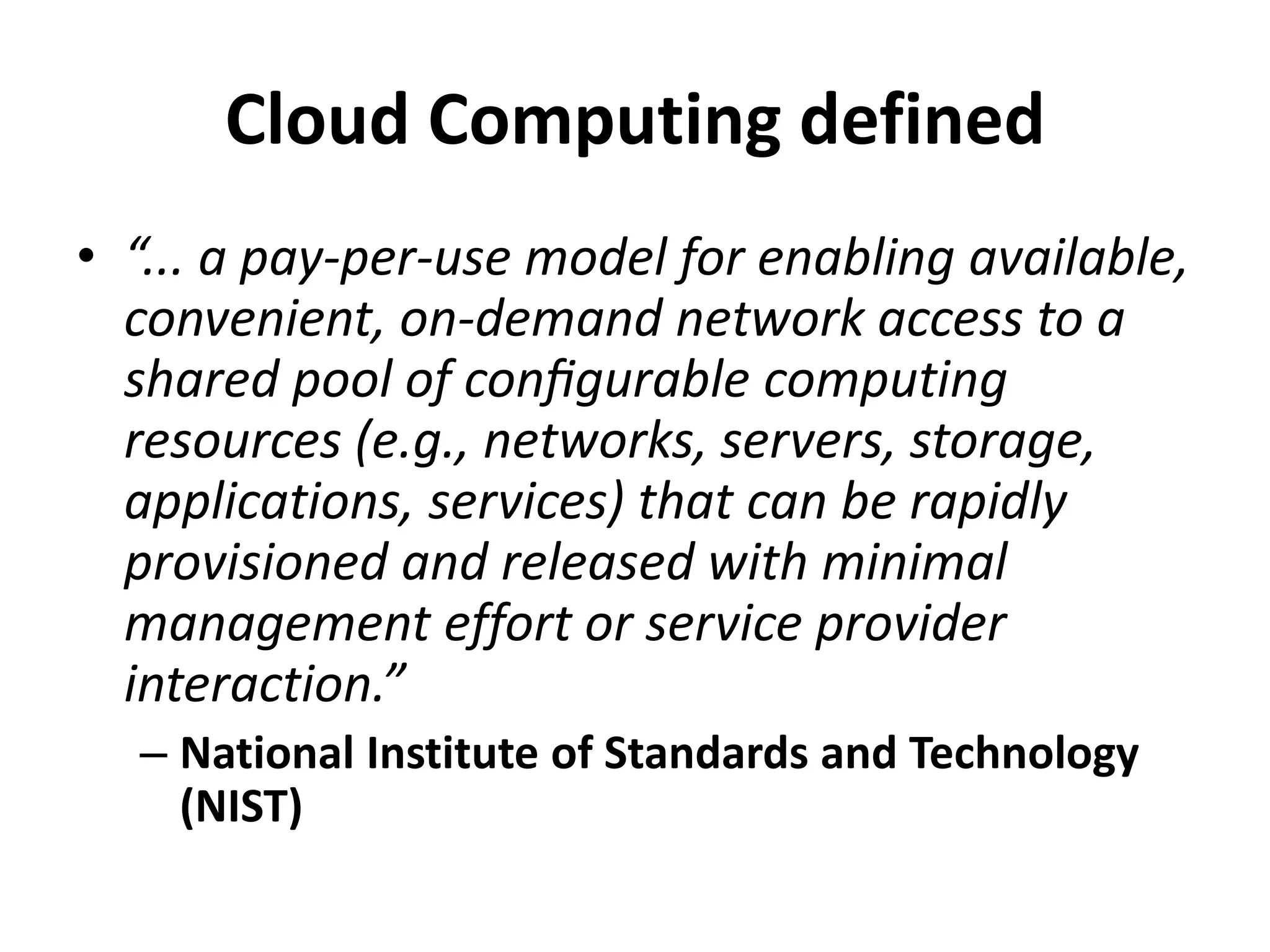
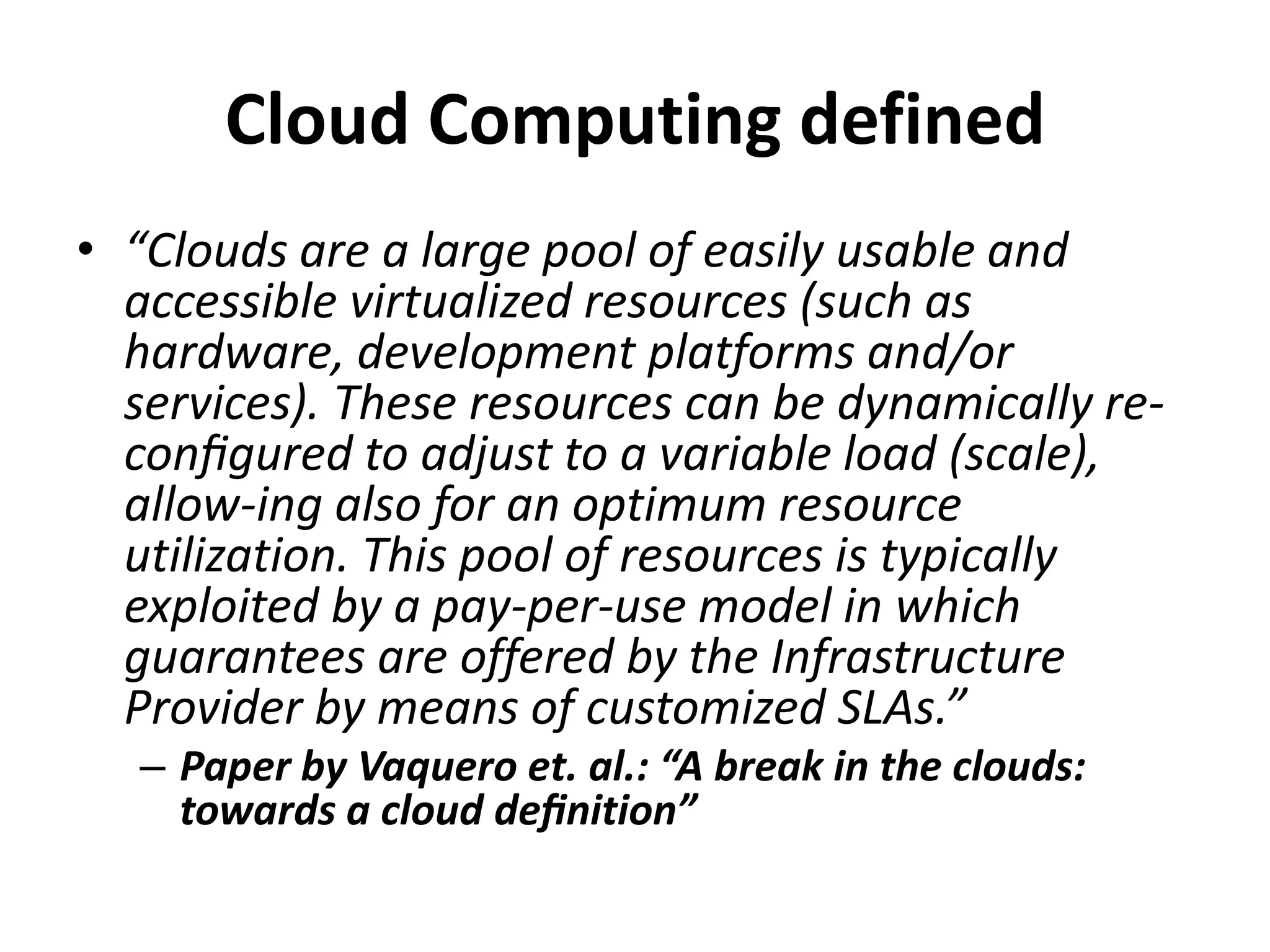
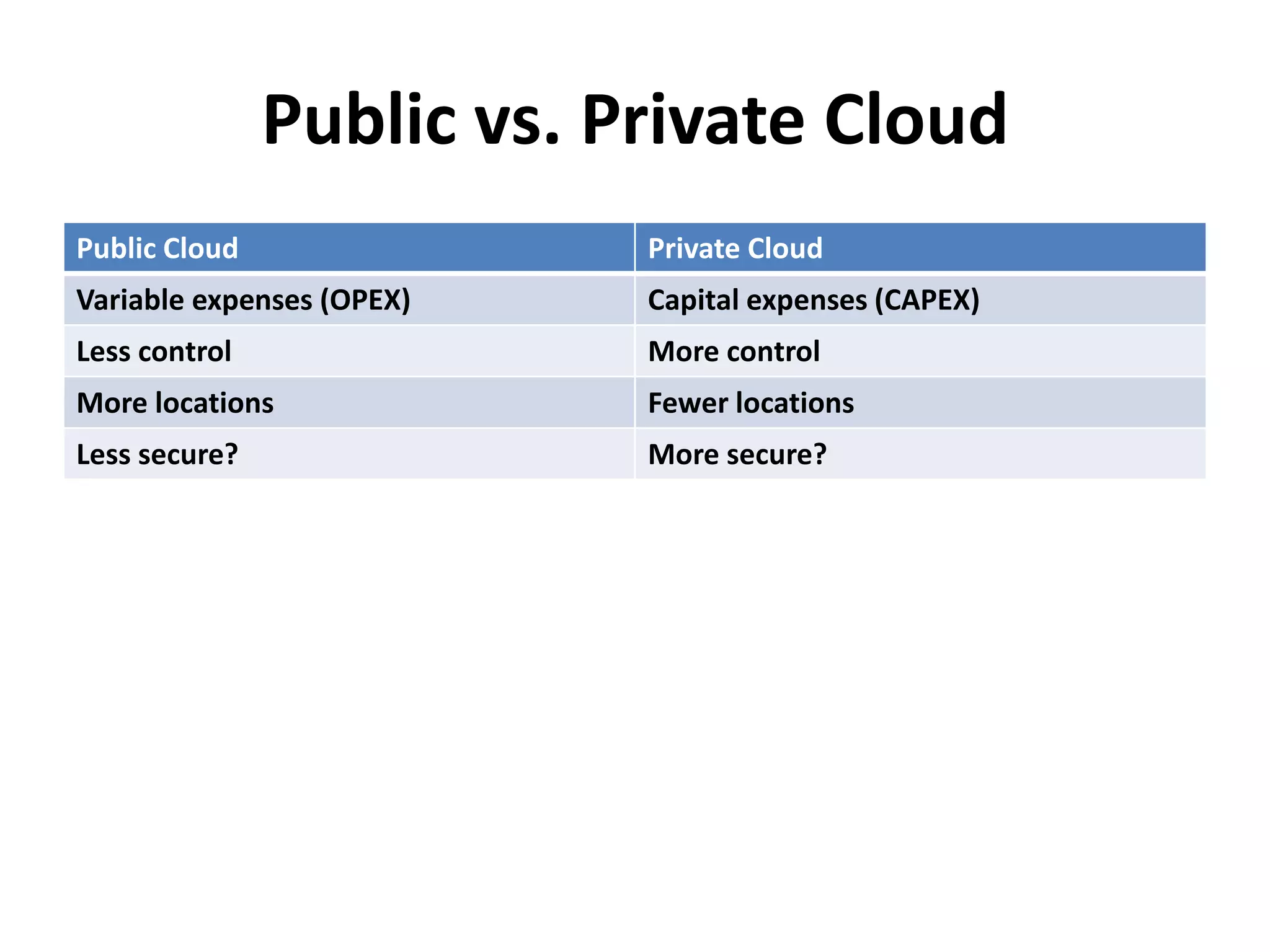
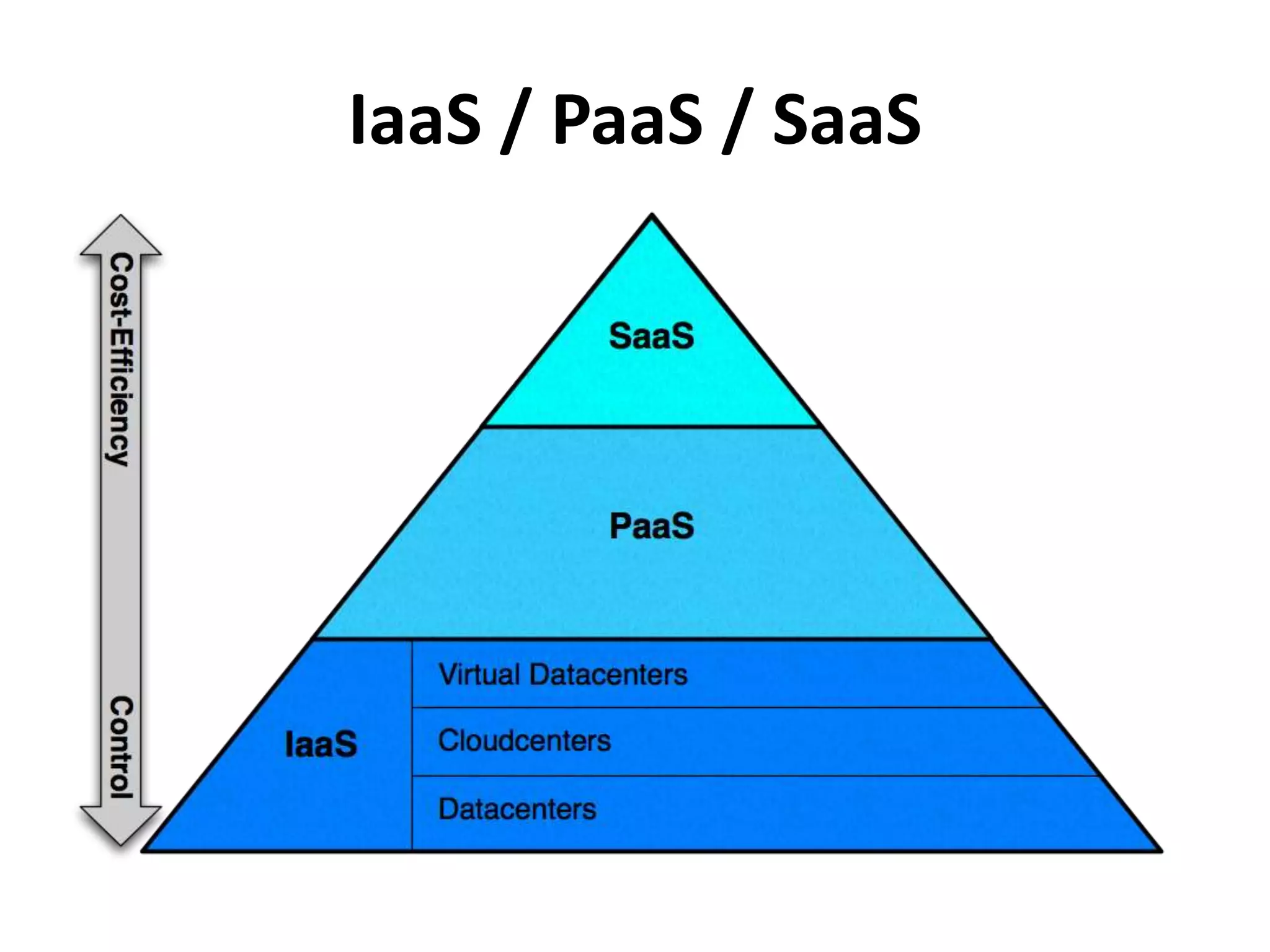
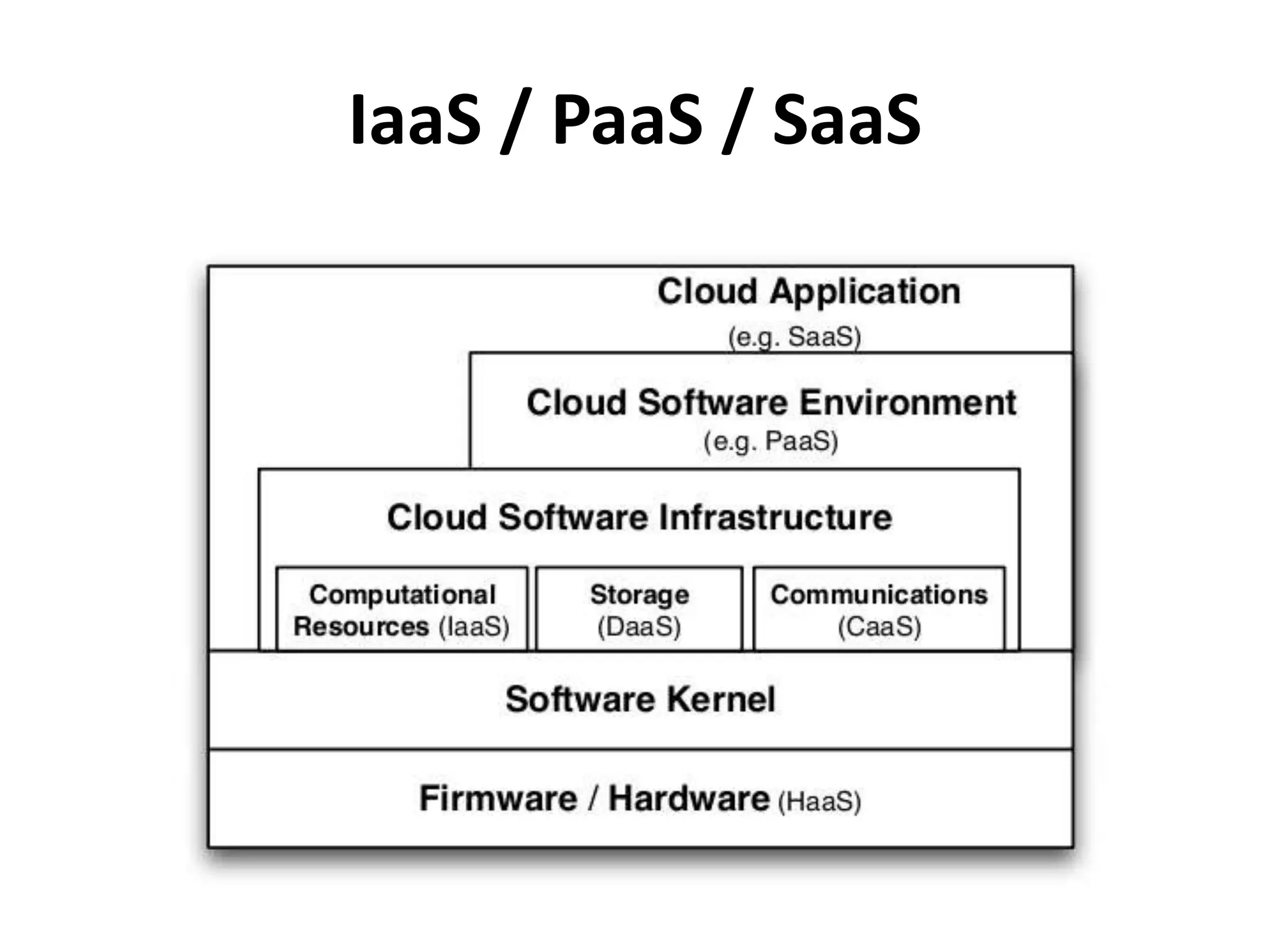
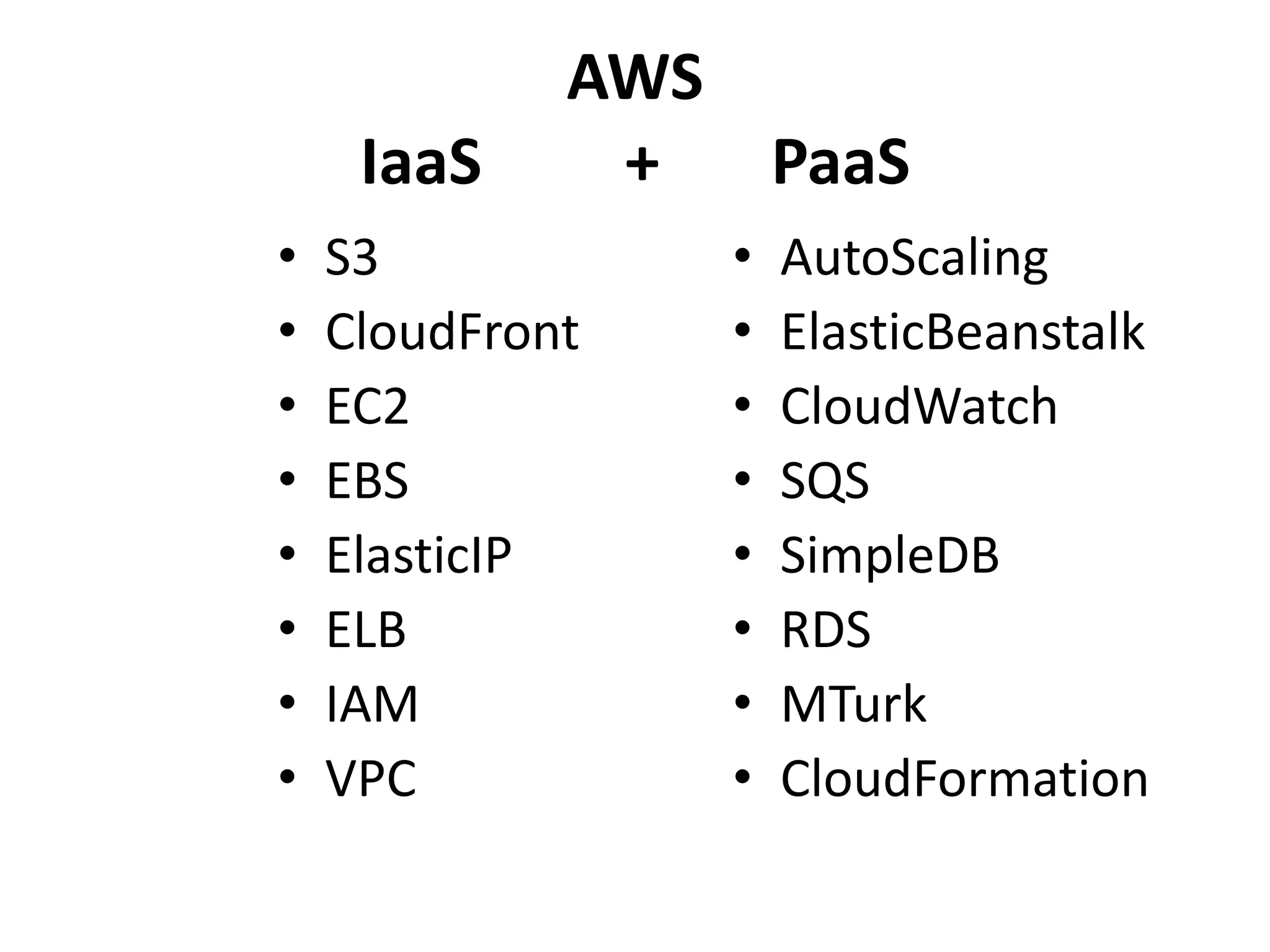
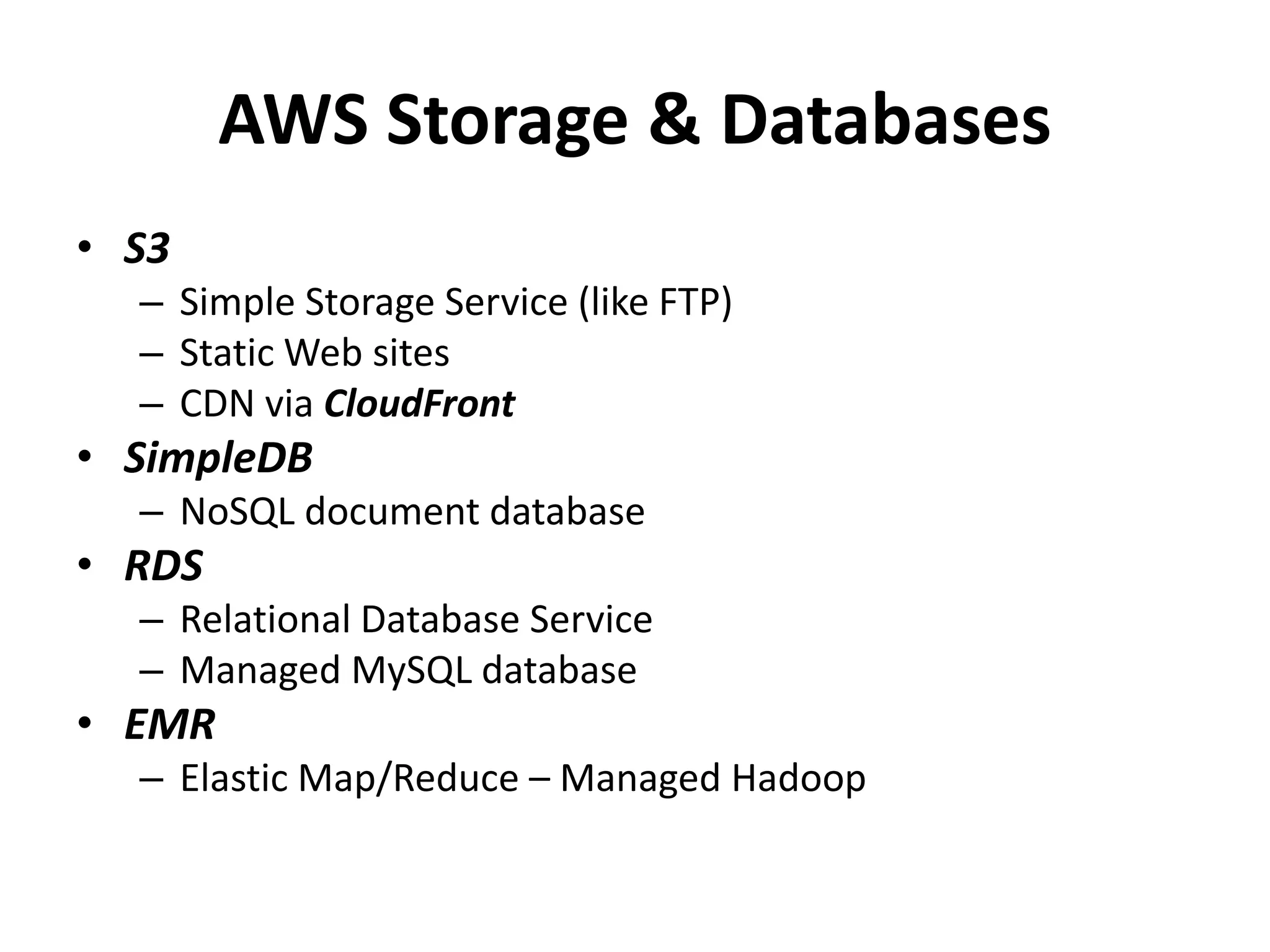
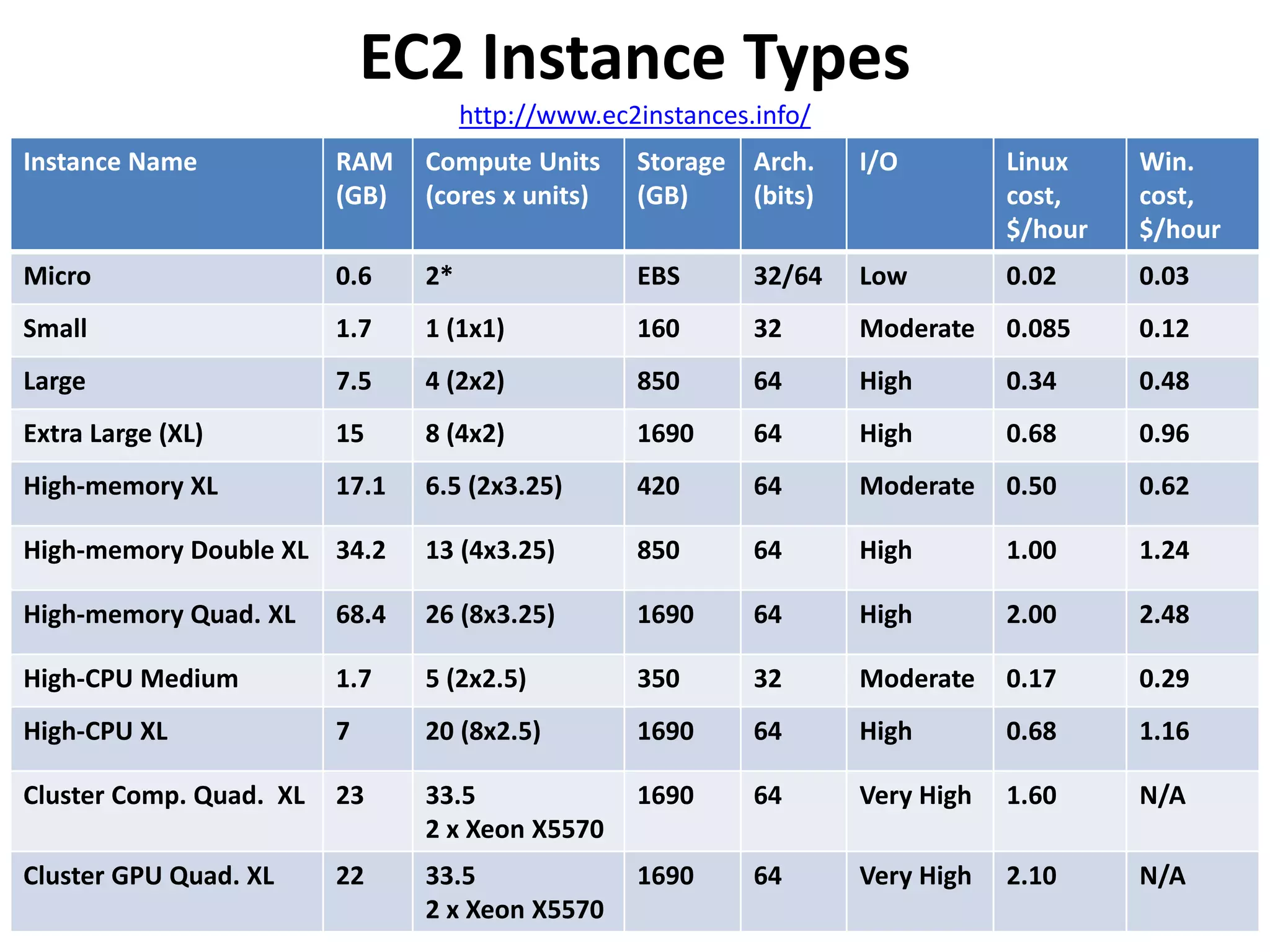
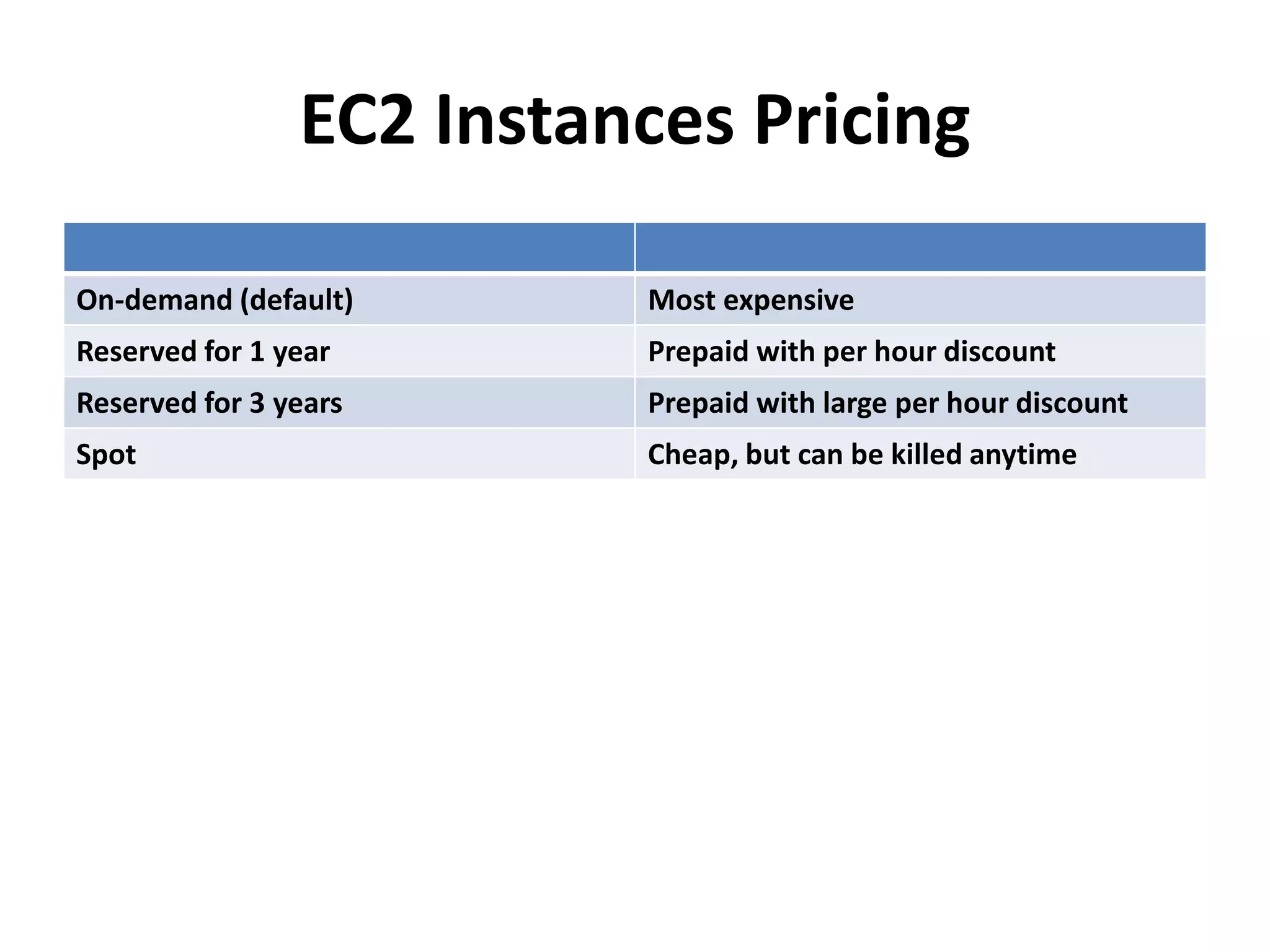
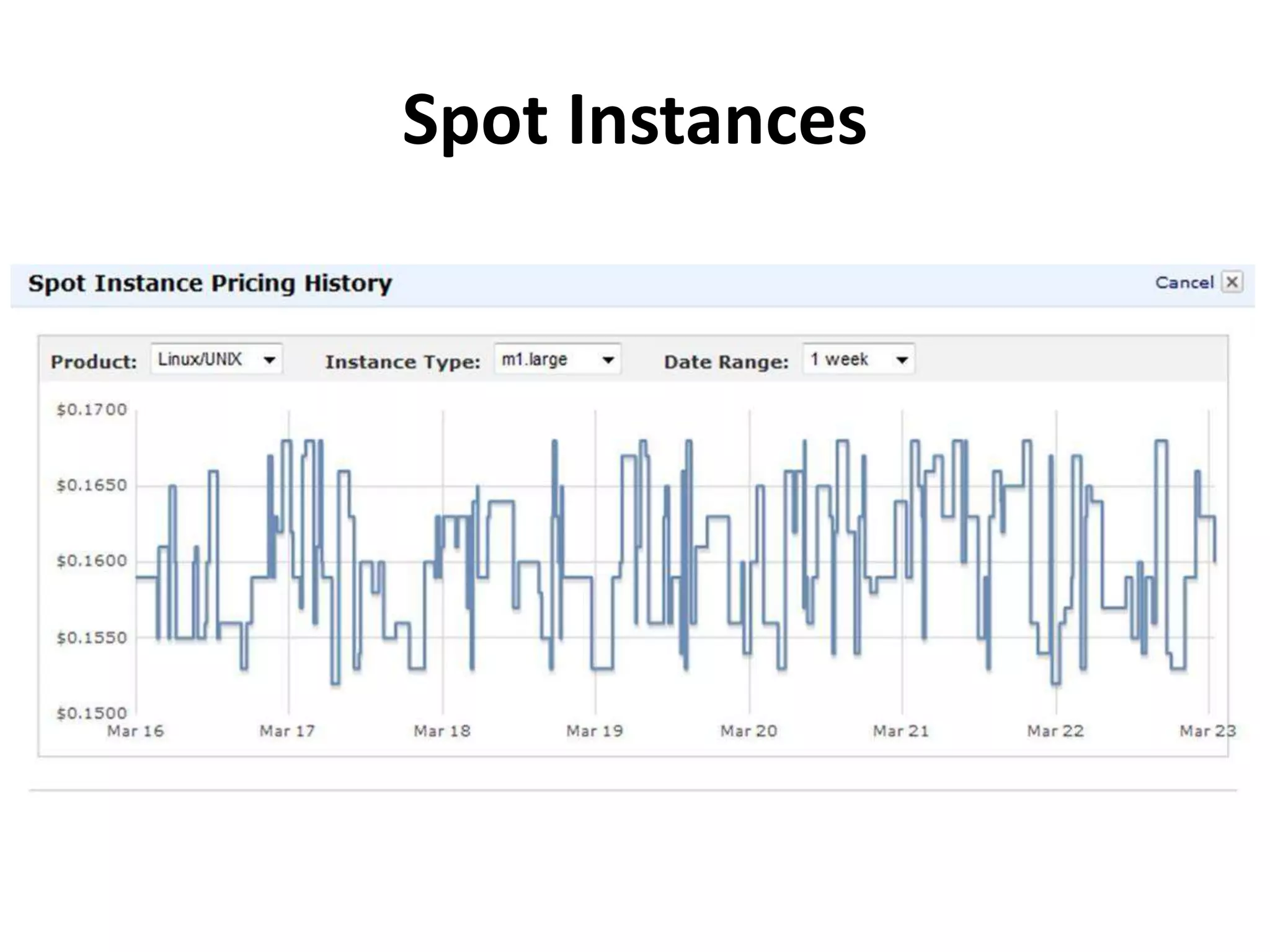
This document discusses cloud computing and Amazon Web Services (AWS). It defines cloud computing and outlines its history and types including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). It describes the characteristics of public and private clouds. It provides examples of popular IaaS and PaaS vendors including AWS and describes key AWS services like EC2, S3, RDS, and more. It also outlines AWS pricing models including on-demand, reserved, and spot instances as well as the AWS free tier for new customers.