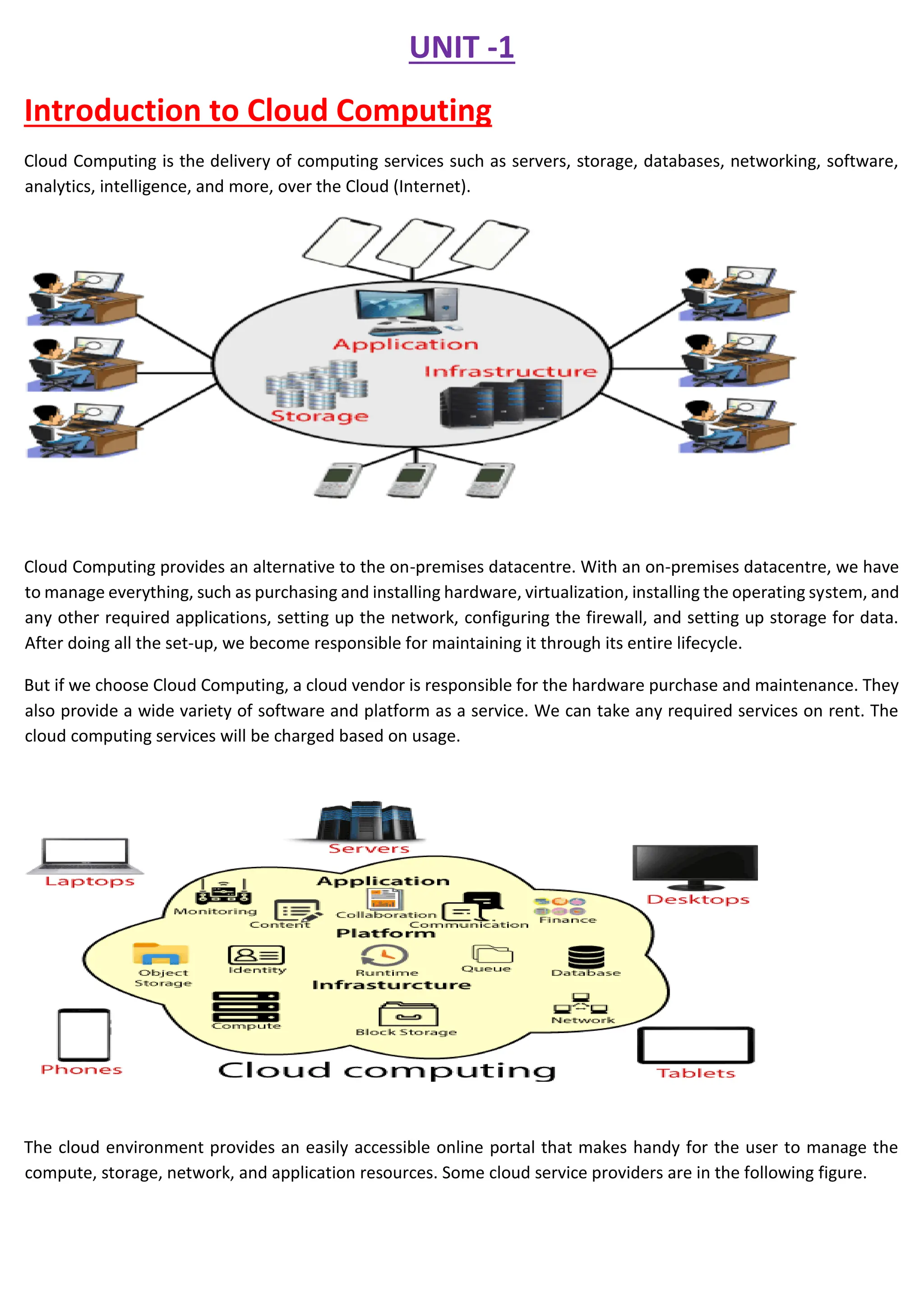
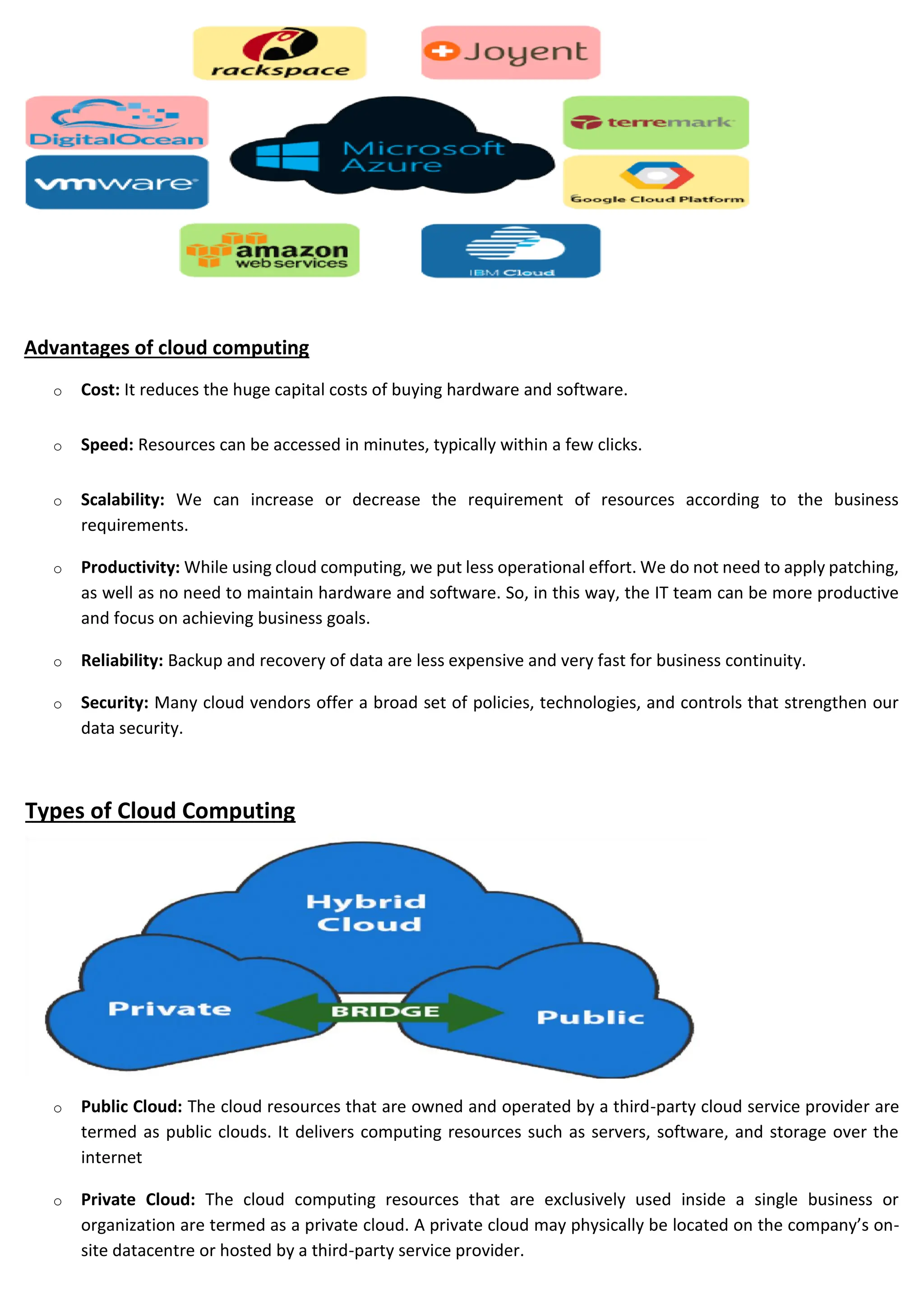
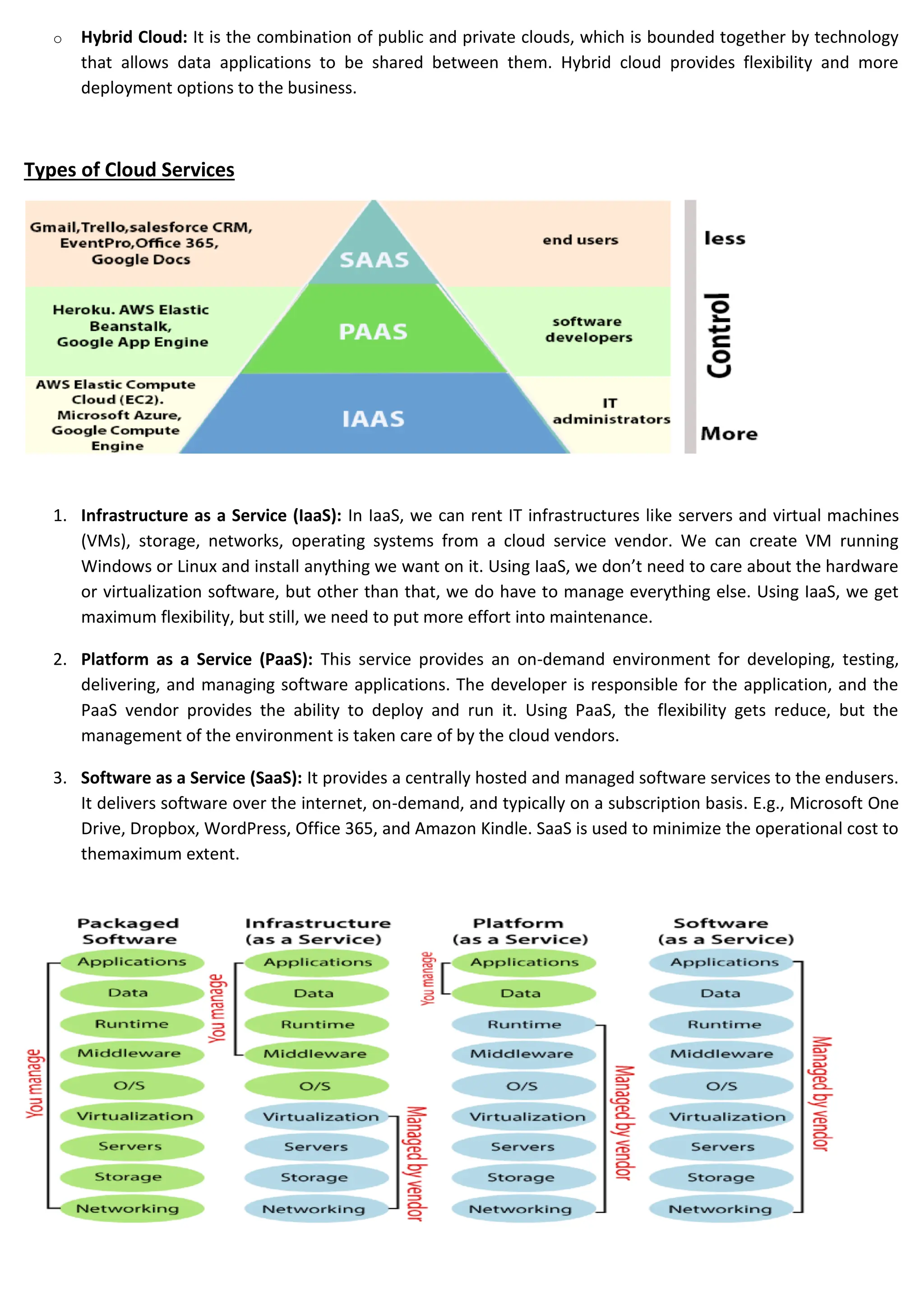
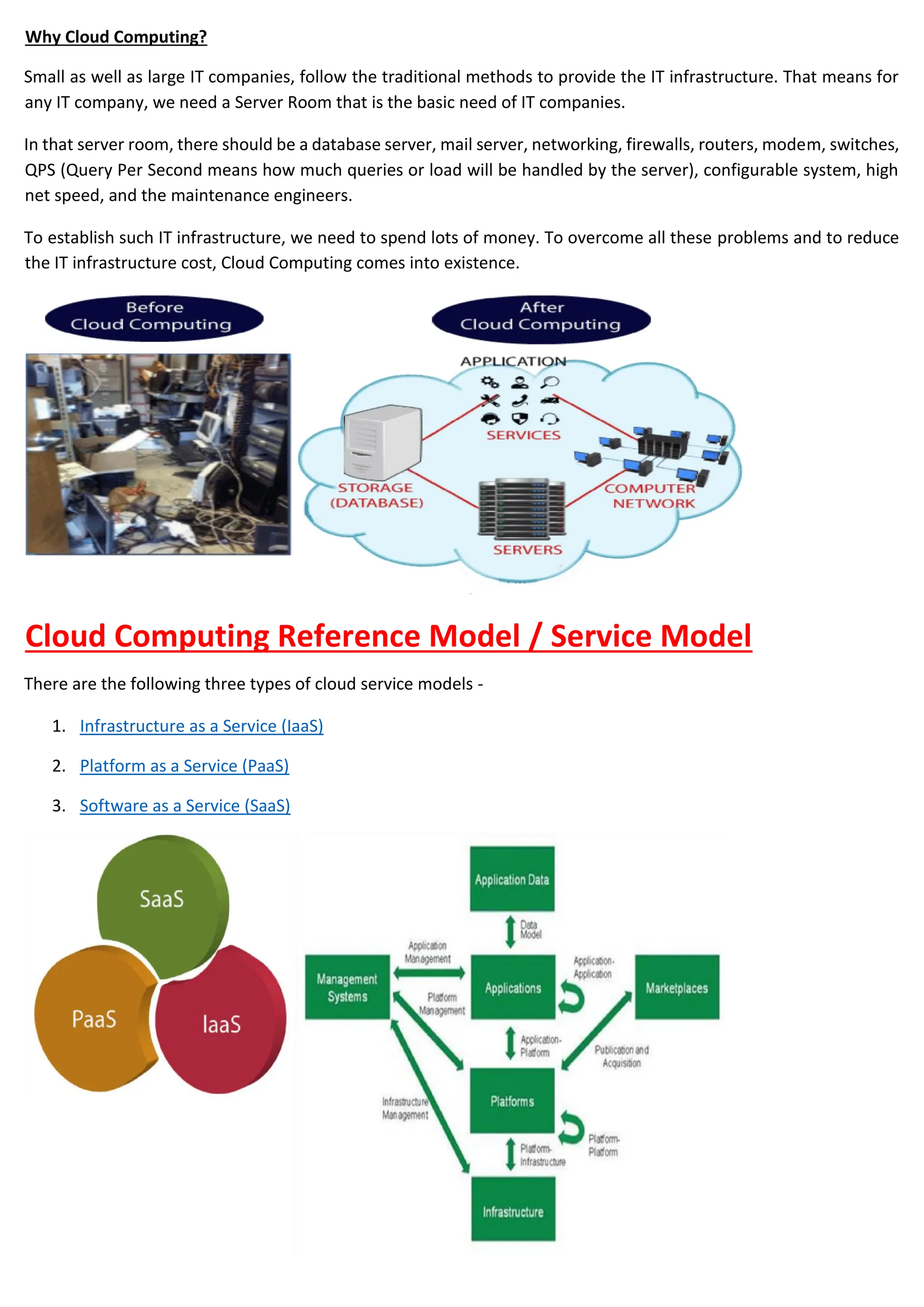
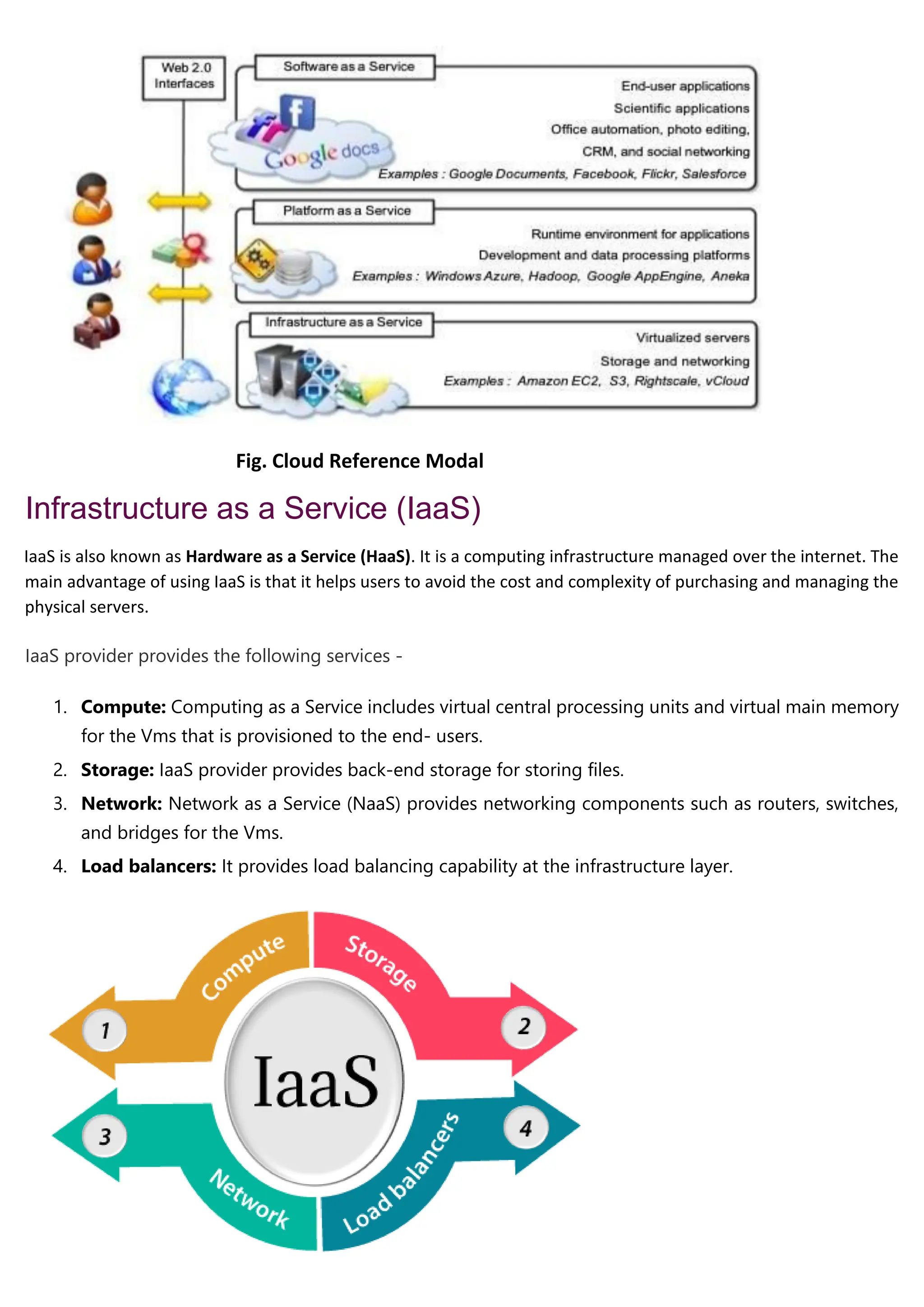
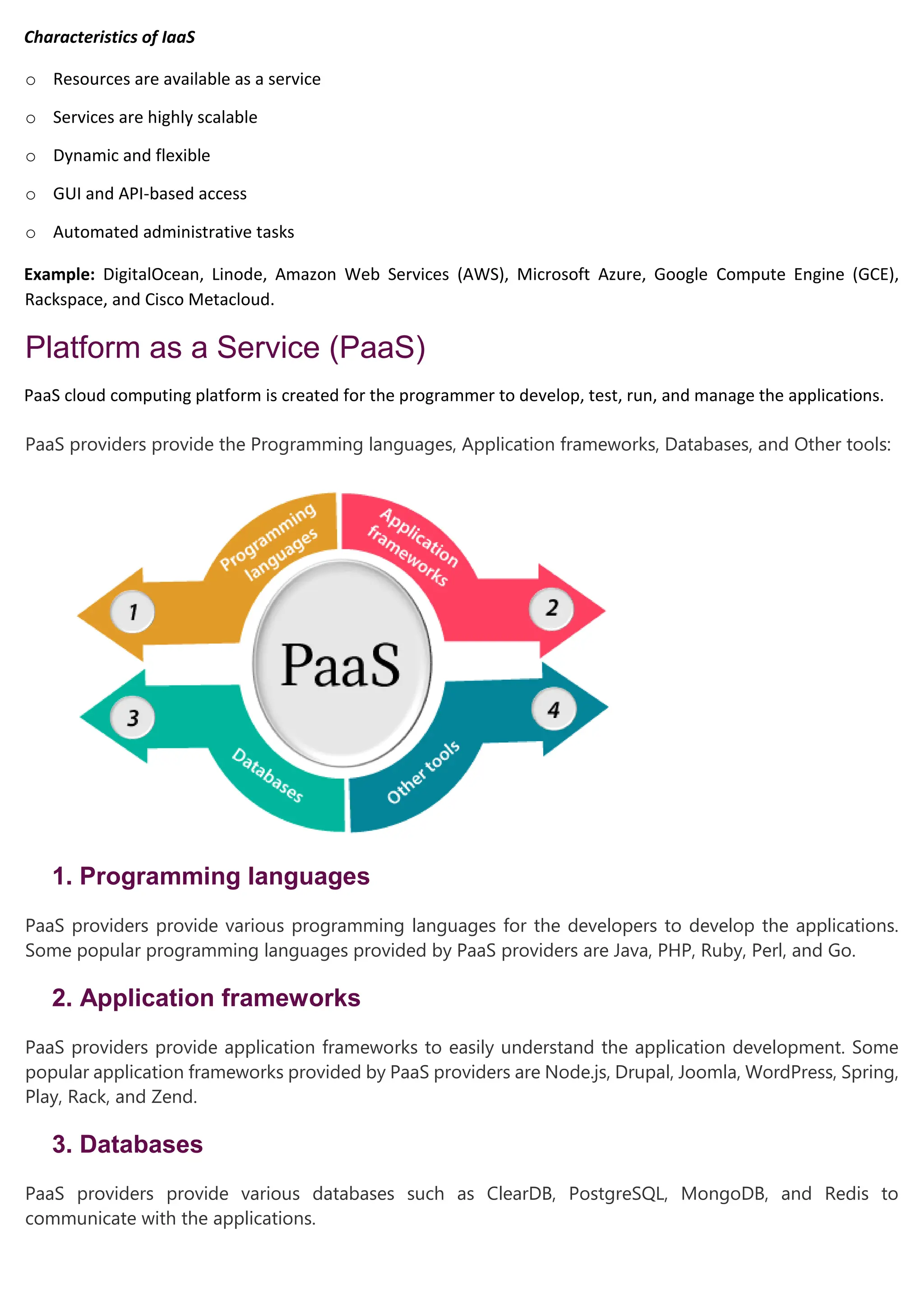
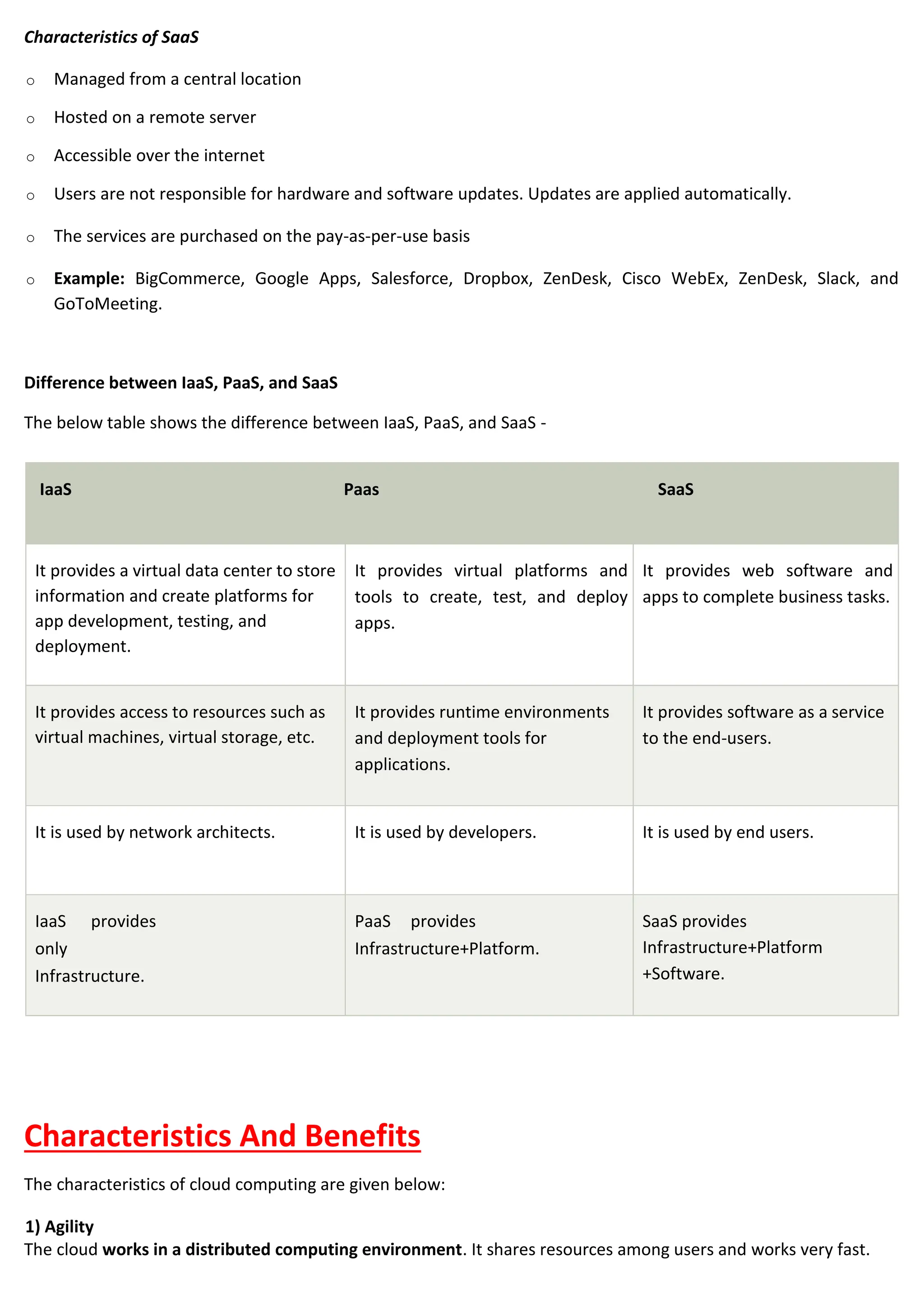
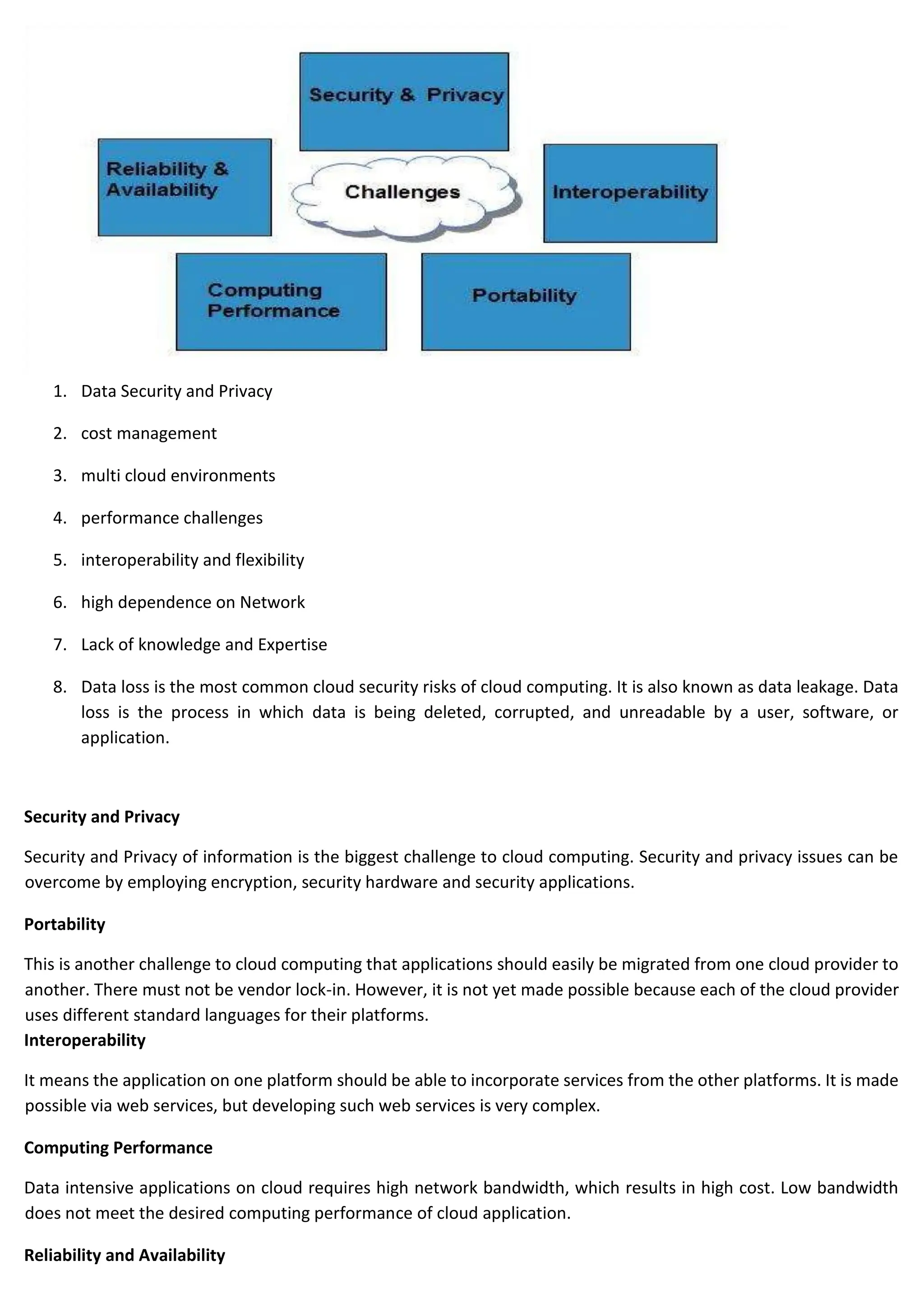
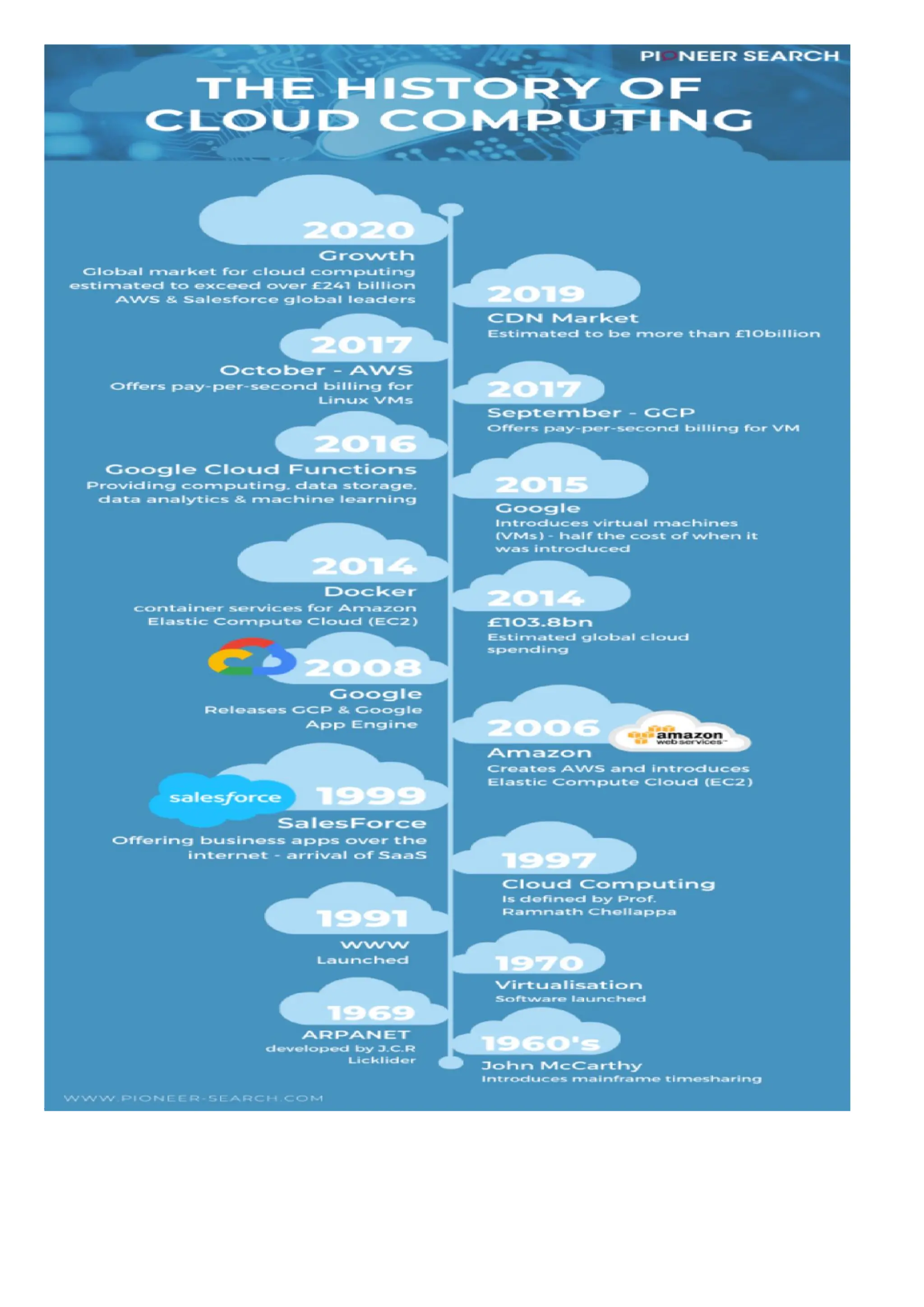
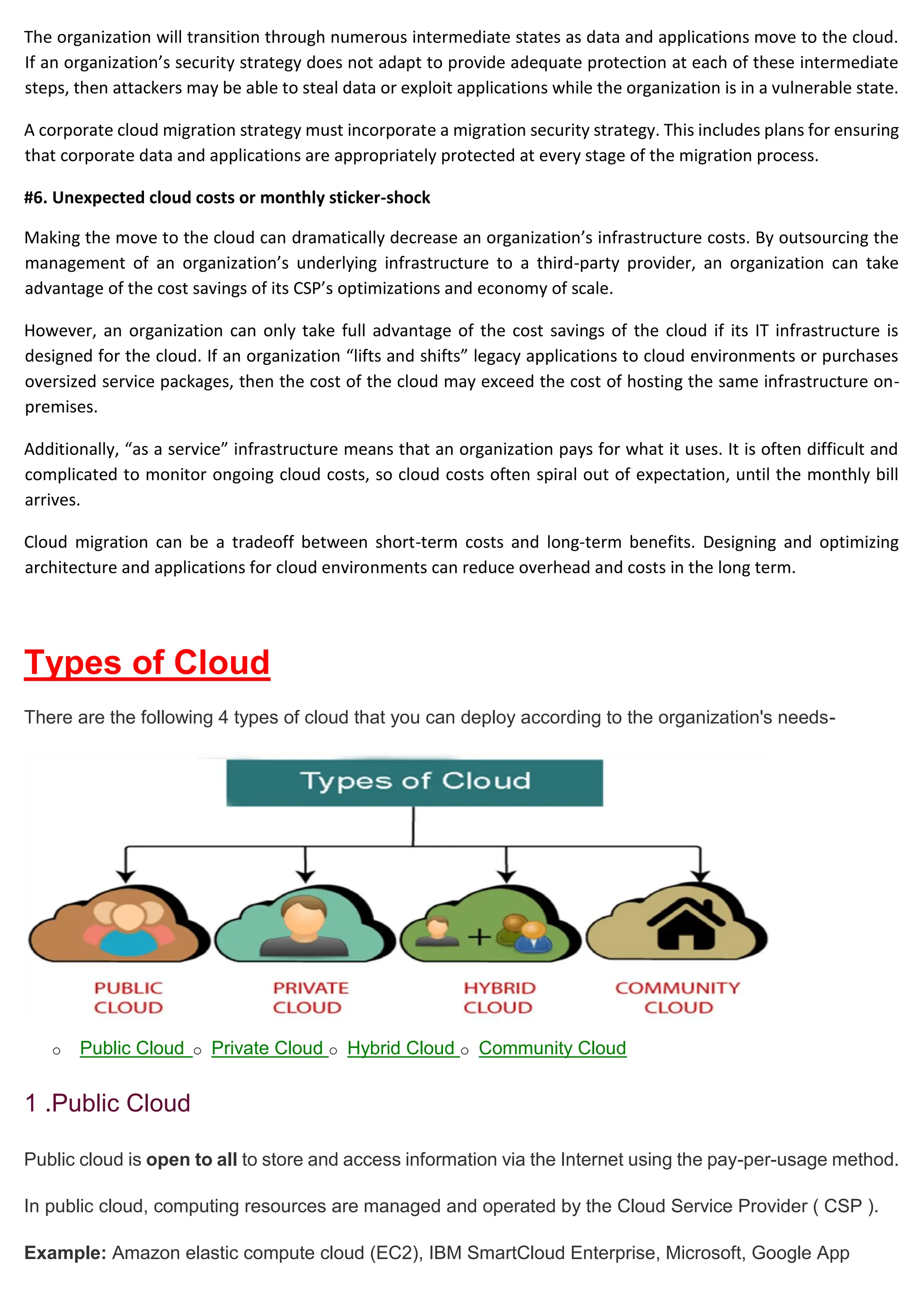
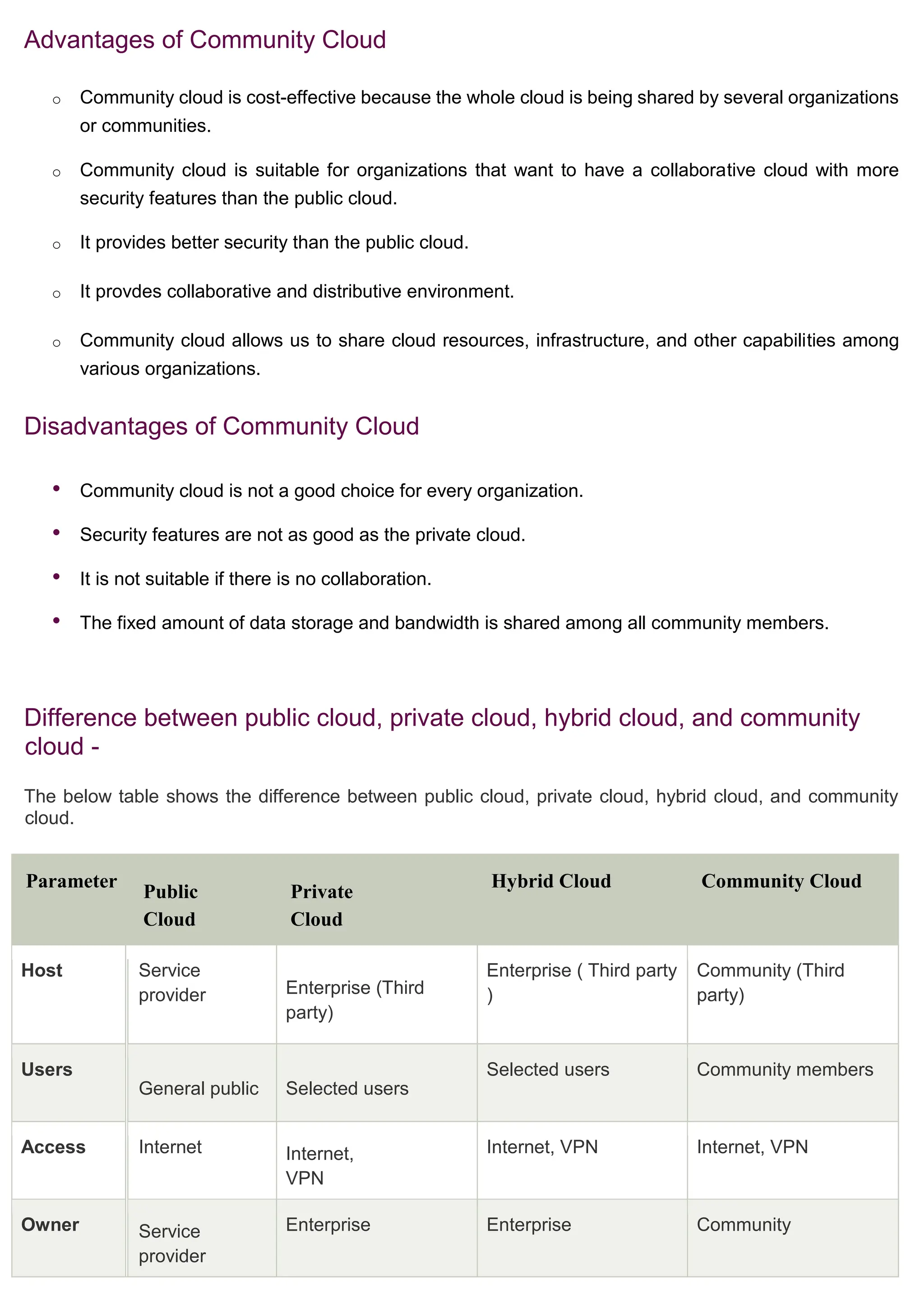
Cloud computing delivers computing services over the internet, enabling organizations to avoid the complexities of on-premises infrastructure, with several service models including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Benefits include cost savings, scalability, and increased productivity, while challenges encompass data security, portability, and performance. The evolution of cloud computing has transformed how companies manage IT resources, providing flexible and efficient solutions to meet business needs.