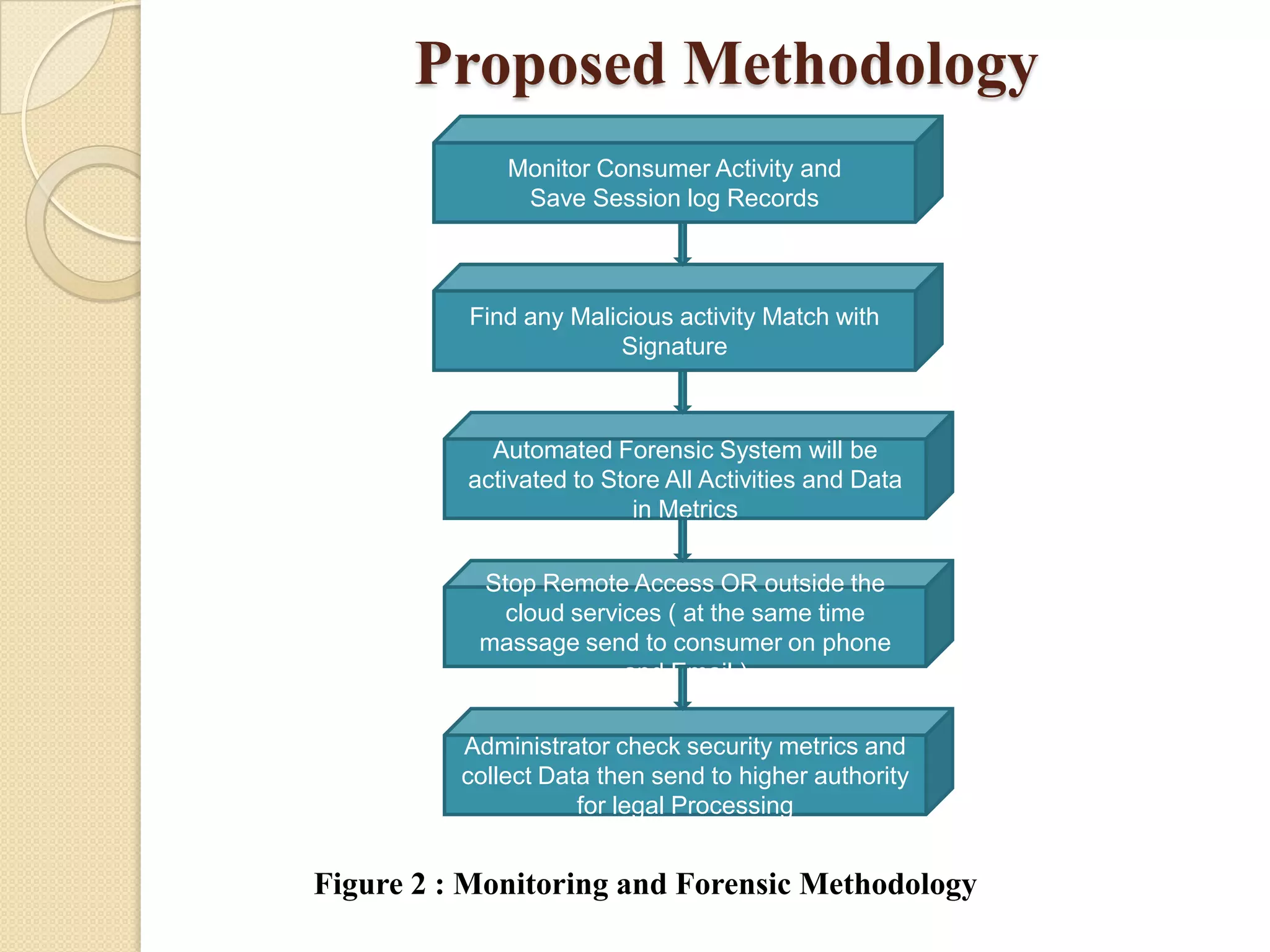
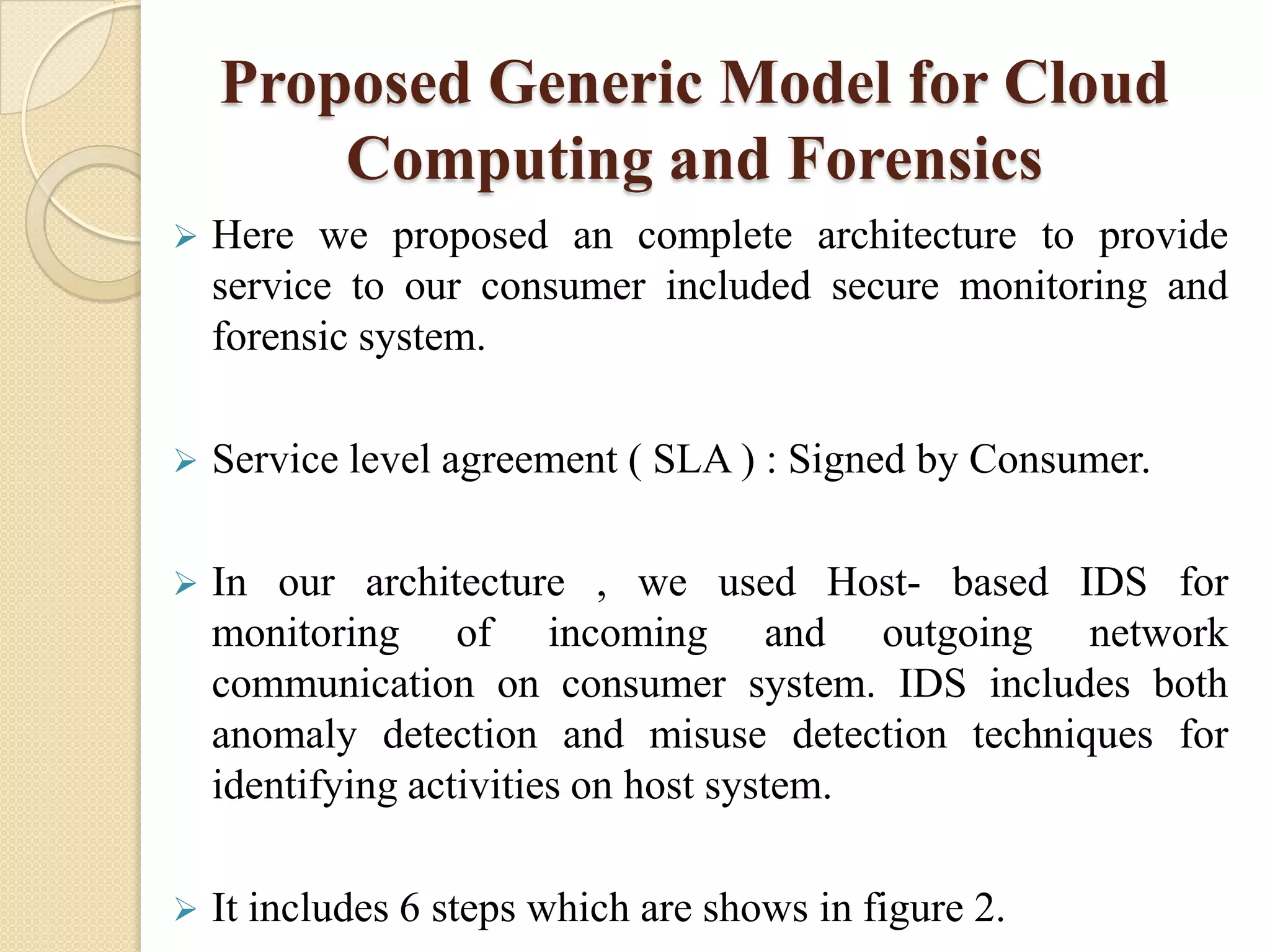
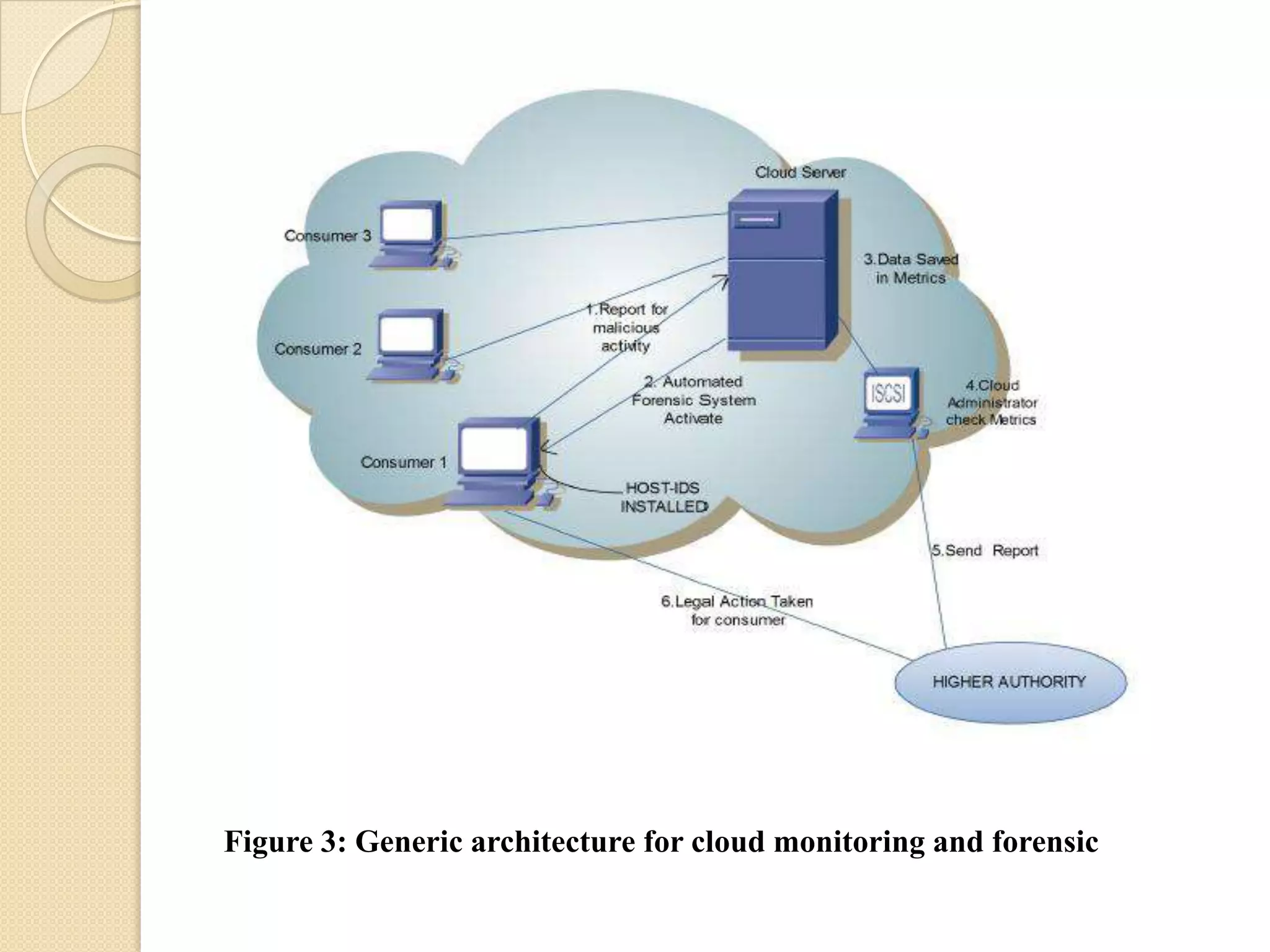
This document presents a methodology for cloud monitoring and forensics using security metrics. It discusses previous research on cloud security issues and architectural services. The proposed methodology monitors consumer activity, detects malicious activity using signatures, and activates an automated forensic system to store activity metrics. When malicious activity is detected, remote access is stopped and administrators are notified to collect data for legal processing. A generic architecture is proposed that uses host-based intrusion detection for monitoring network communications and a six-step process for cloud monitoring and forensics.





![References
[1] Cary Landis and Dan Blacharski,“Cloud Computing
Made Easy” , Version 0.3.
[2] G. Stoneburner, “Underlying Technical Models for
Information Technology Security,” National Institute of
Standards and Technology, 2001
[3] G. McGraw, Software Security: Addison-Wesley,2006
[4] Google App Engine, http://appengine.google.com
[5]Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud(EC2),
http://www.amazon.com/ec2
[6]Gary C. Kessler, “Anti-Forensic and the Digital
Investigator” Champlain College Burlington, VT , USA
Edith Cowan University, Mount Lawley, WA, Australia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudmonitoringandforensicusingsecuritymetrics-13459190187104-phpapp01-120825134218-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Monitoring-And-Forensic-Using-Security-Metrics-12-2048.jpg)
![[7] CSA cloud Security Alliance, top Threats to cloud
Computing V1.0, 2010
[8] Shaftab Ahmad and M. yahin Akhtar Raja, “Tackling
Cloud Security Issues And Forensic Model”, IEEE 2010
[9] Jennifer Bayuk, “Cloud Security Metrics”, 6th
International Conference on System of Systems
Engineering, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA –June 27-
30,2011 (IEEE)
[10] D. Zissis and D. Lekkas , “Addressing Cloud
Computing Security issues”, Future Generation Computer
System (2011) Elsevier, doi:10.1016/j.future.2010.12.006
[11] M.Tayor, J. Haggerty, D. Gresty and R. Hegarty,
“Digital evidence in cloud computing systems”, Computer
Law and Security Review 26 (2010)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudmonitoringandforensicusingsecuritymetrics-13459190187104-phpapp01-120825134218-phpapp01/75/Cloud-Monitoring-And-Forensic-Using-Security-Metrics-13-2048.jpg)
