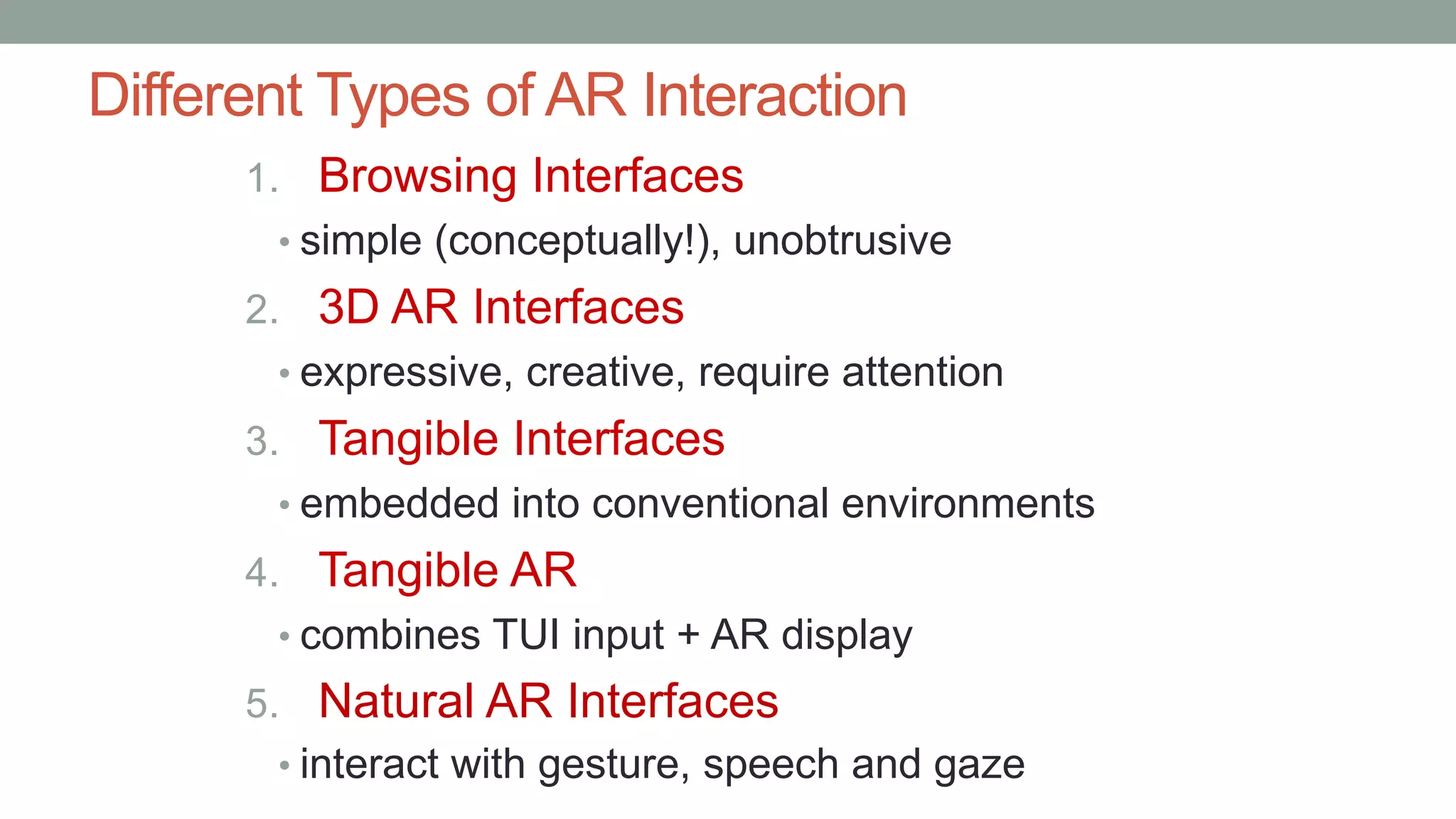
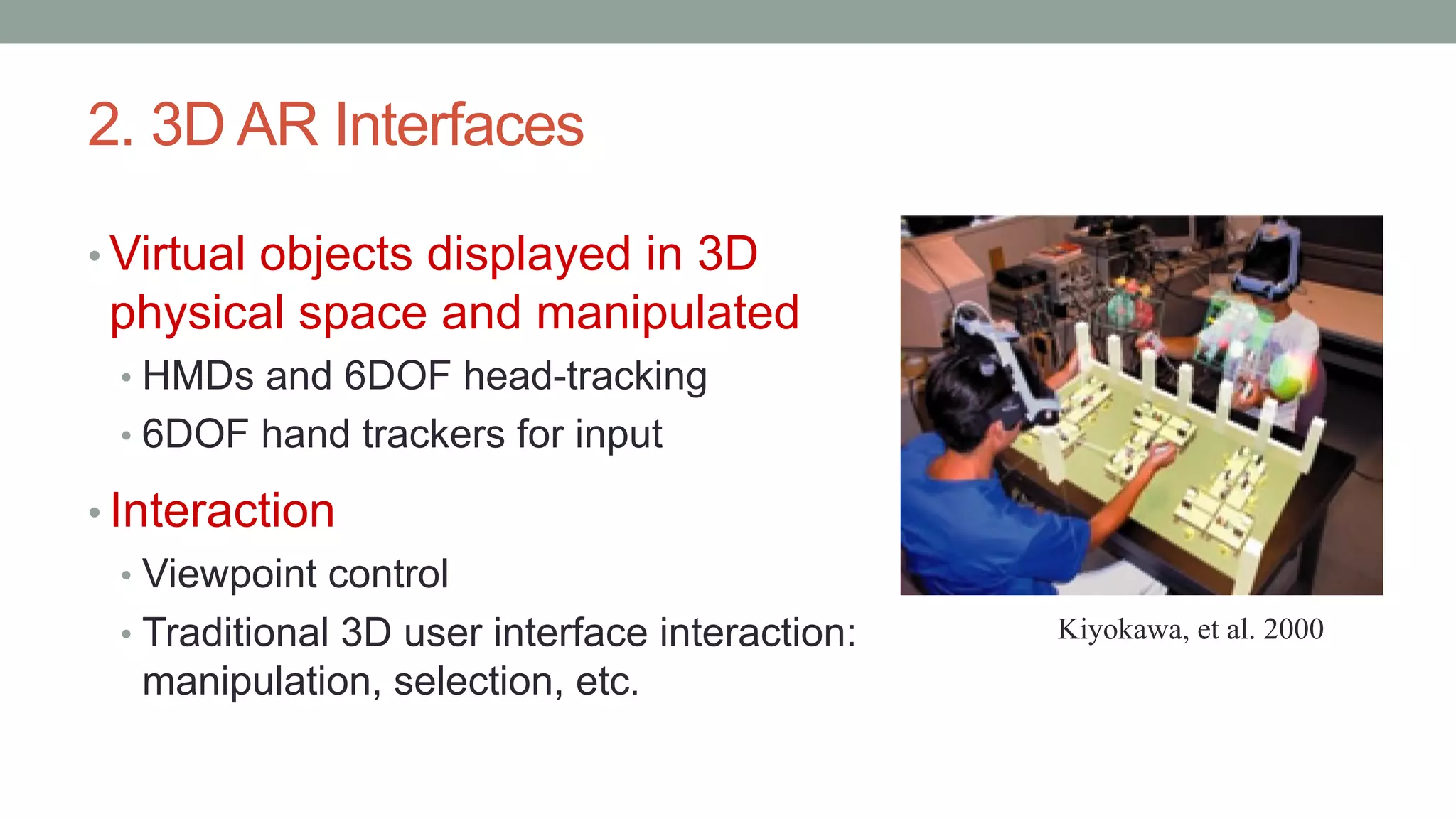
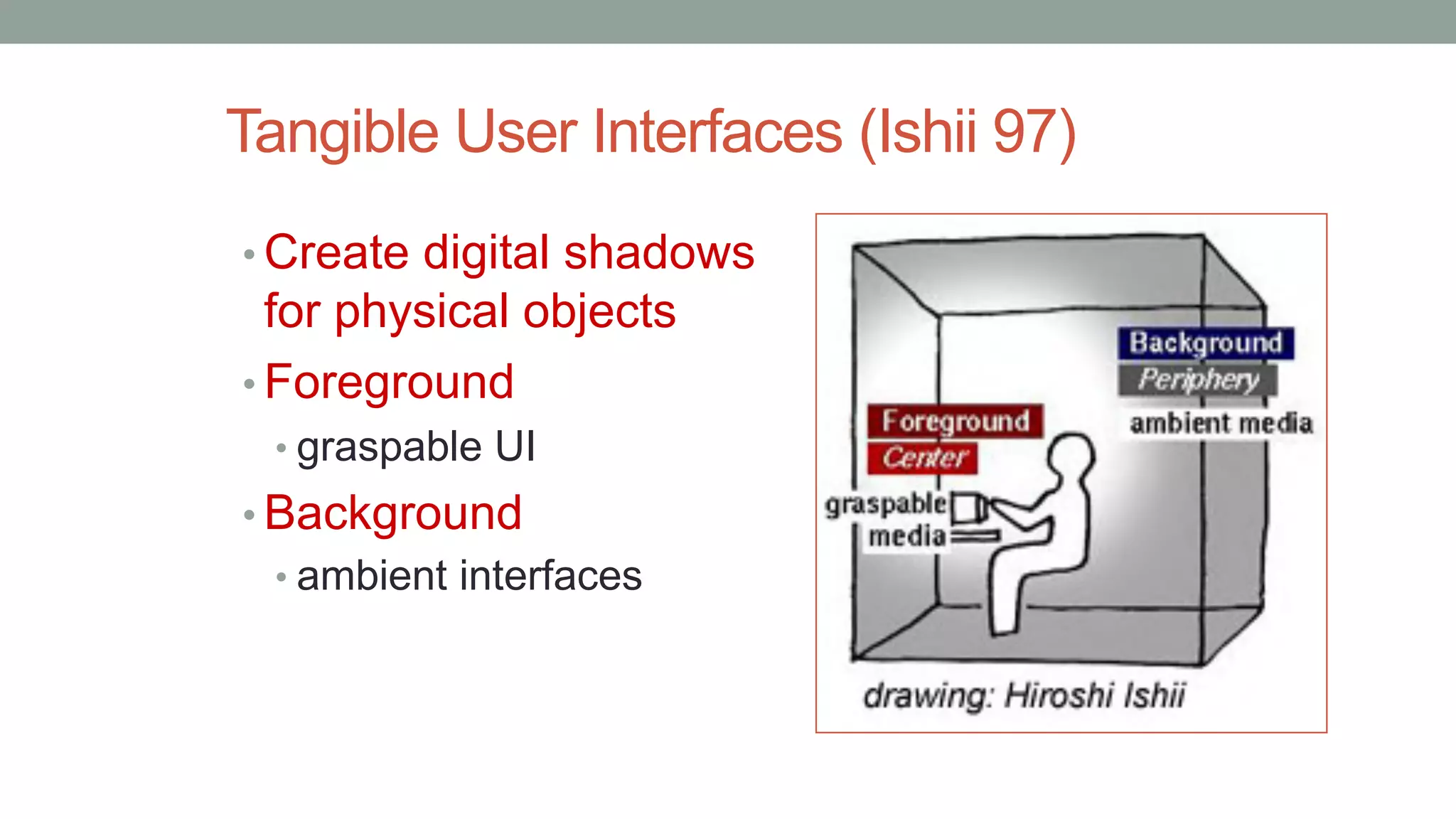
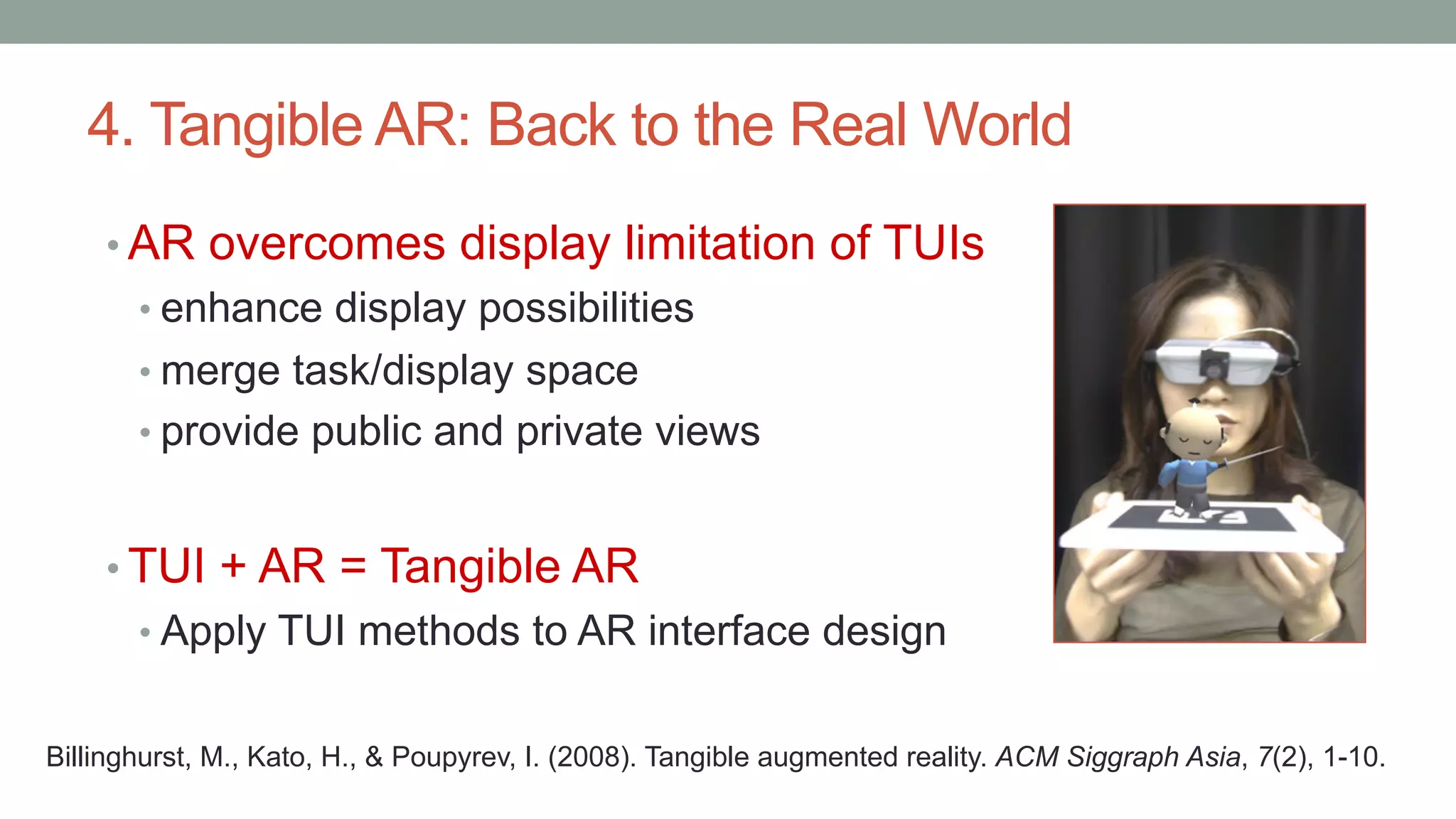
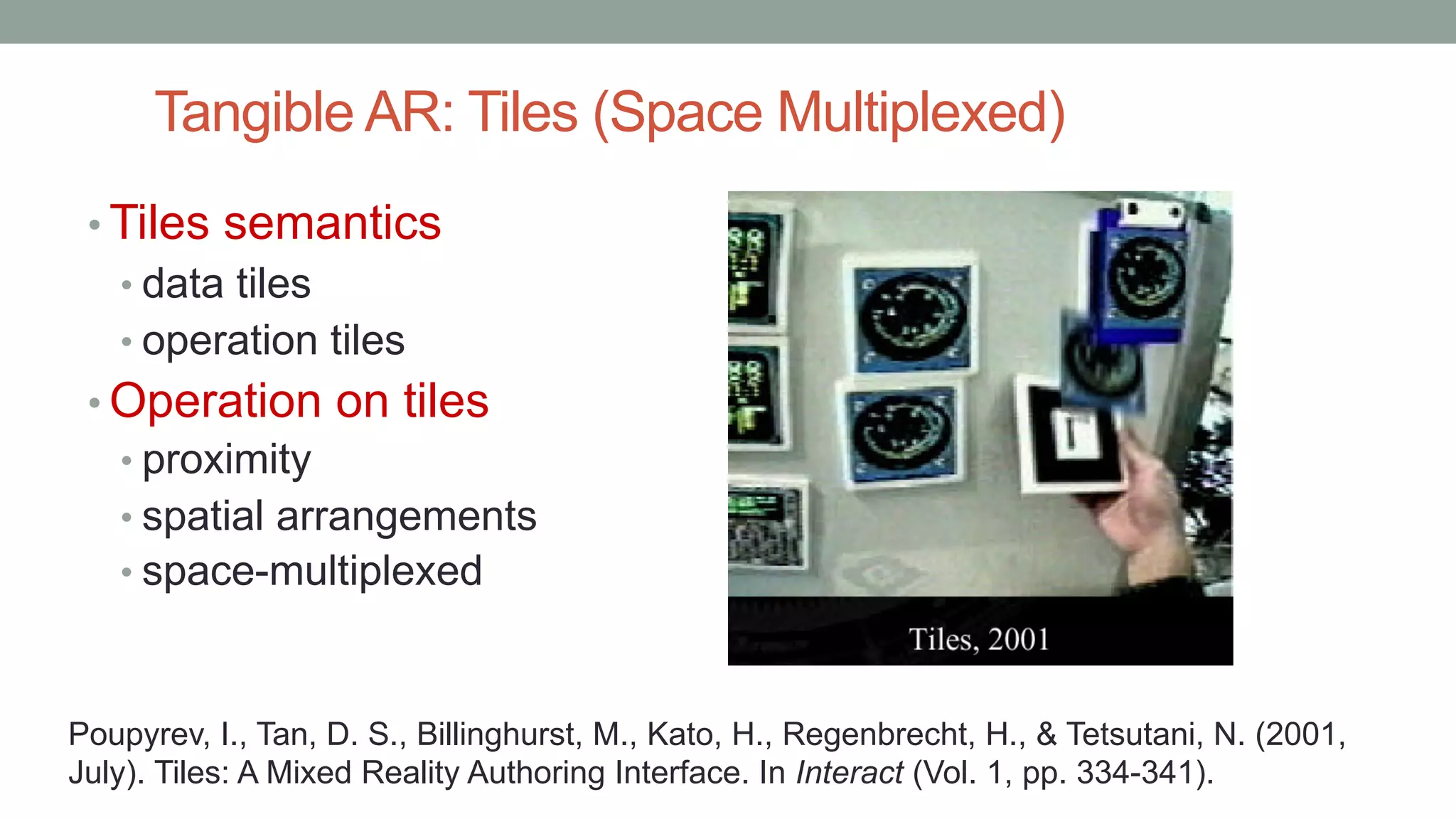
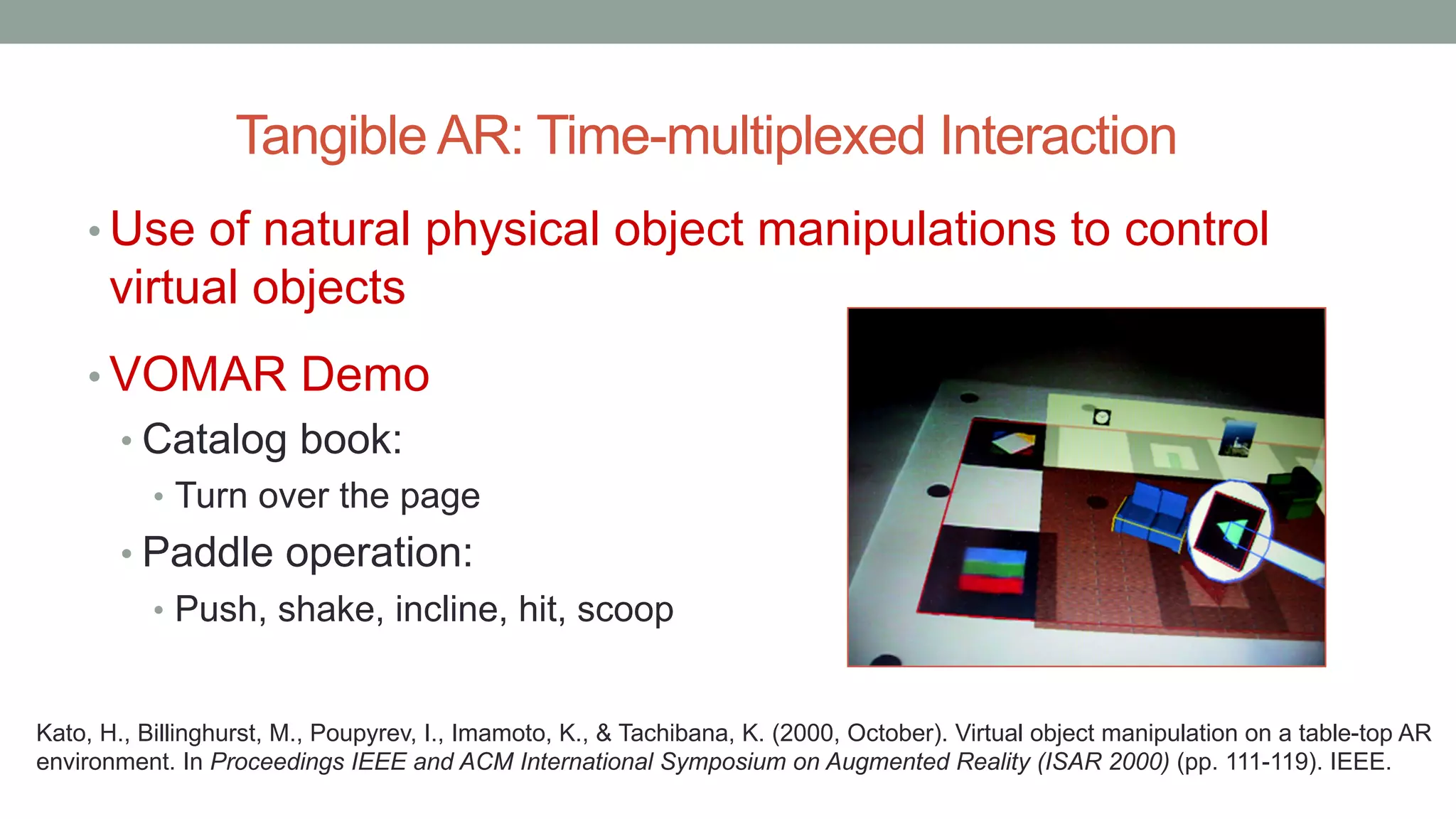
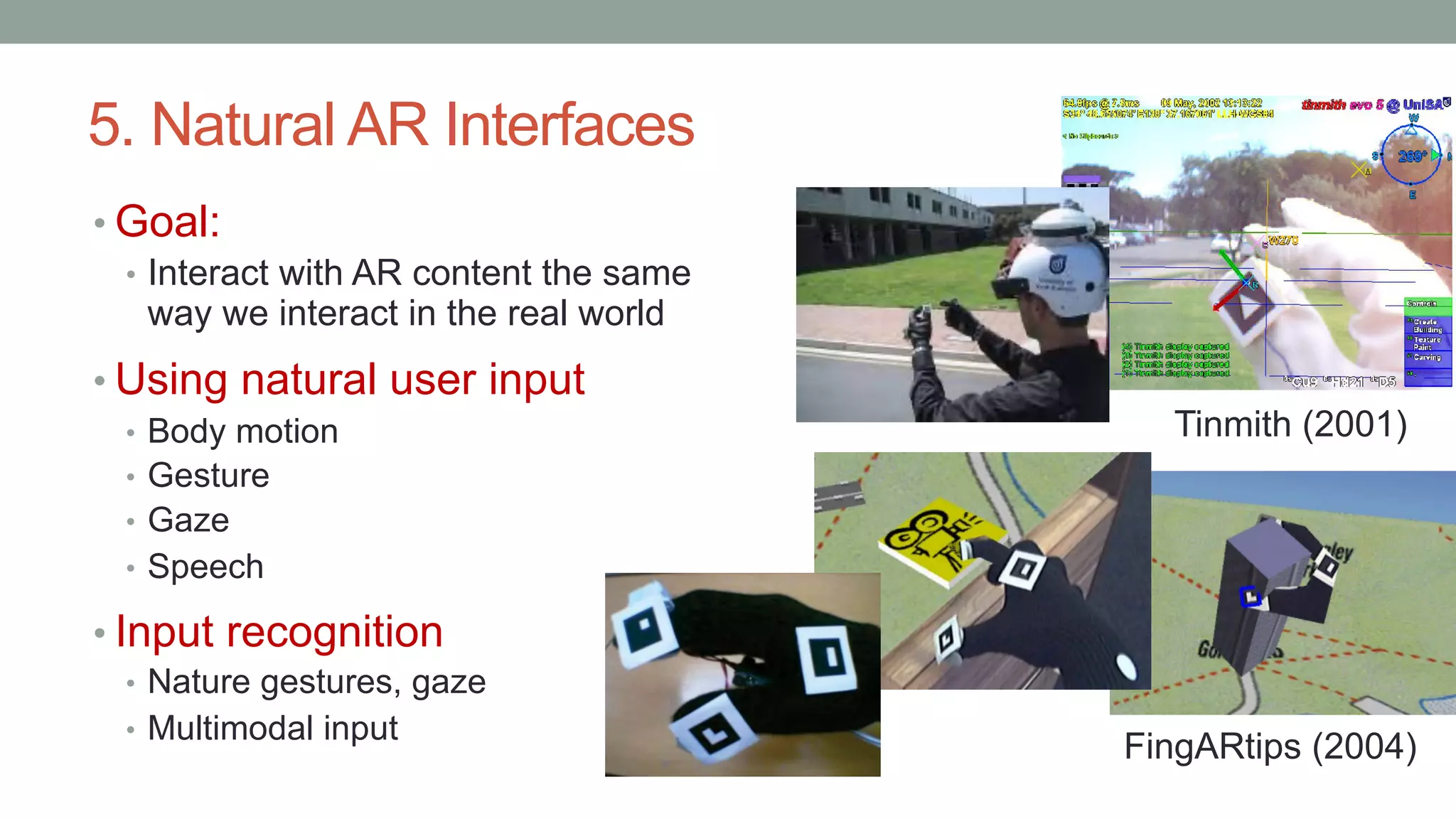
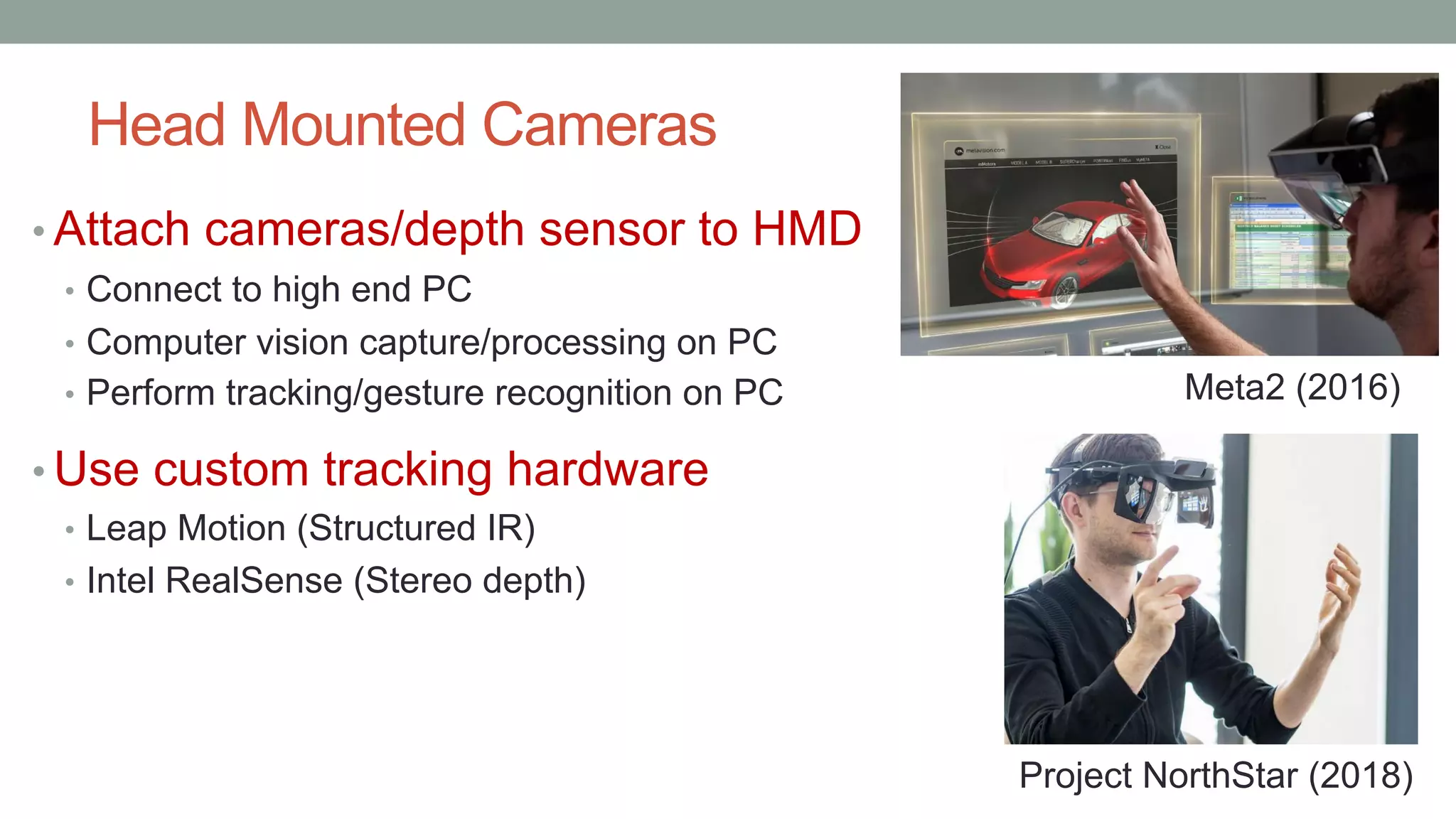
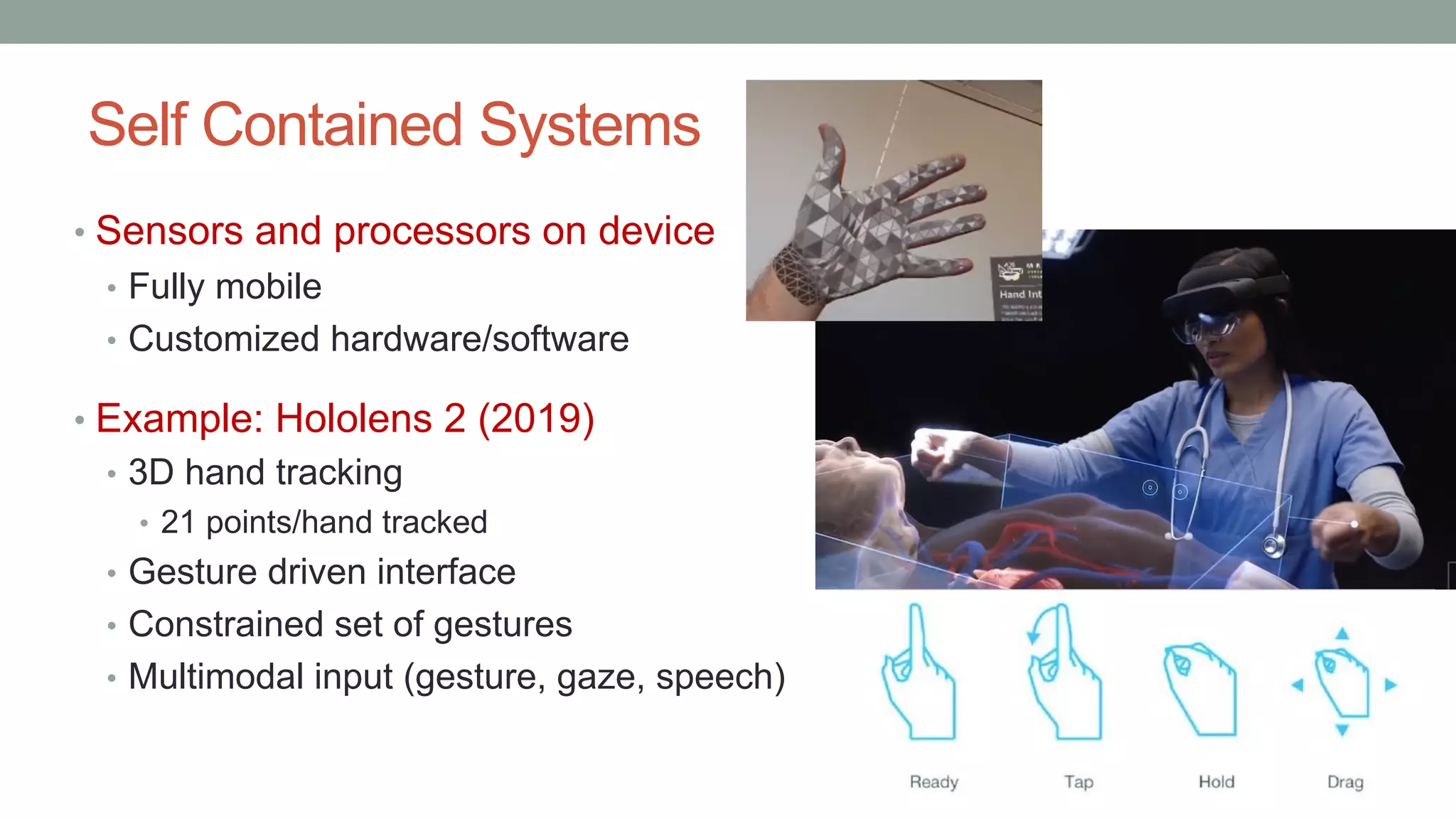
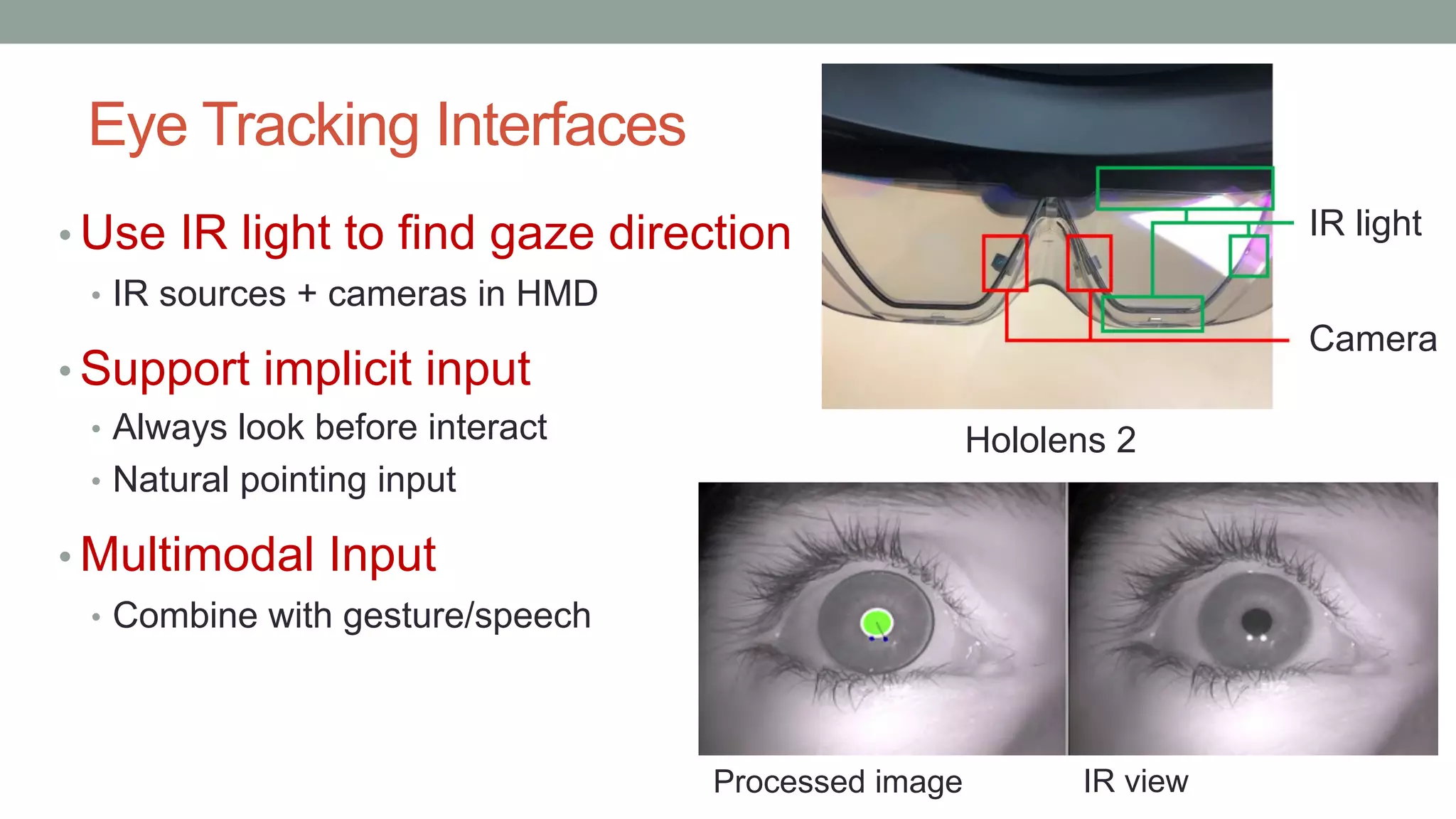
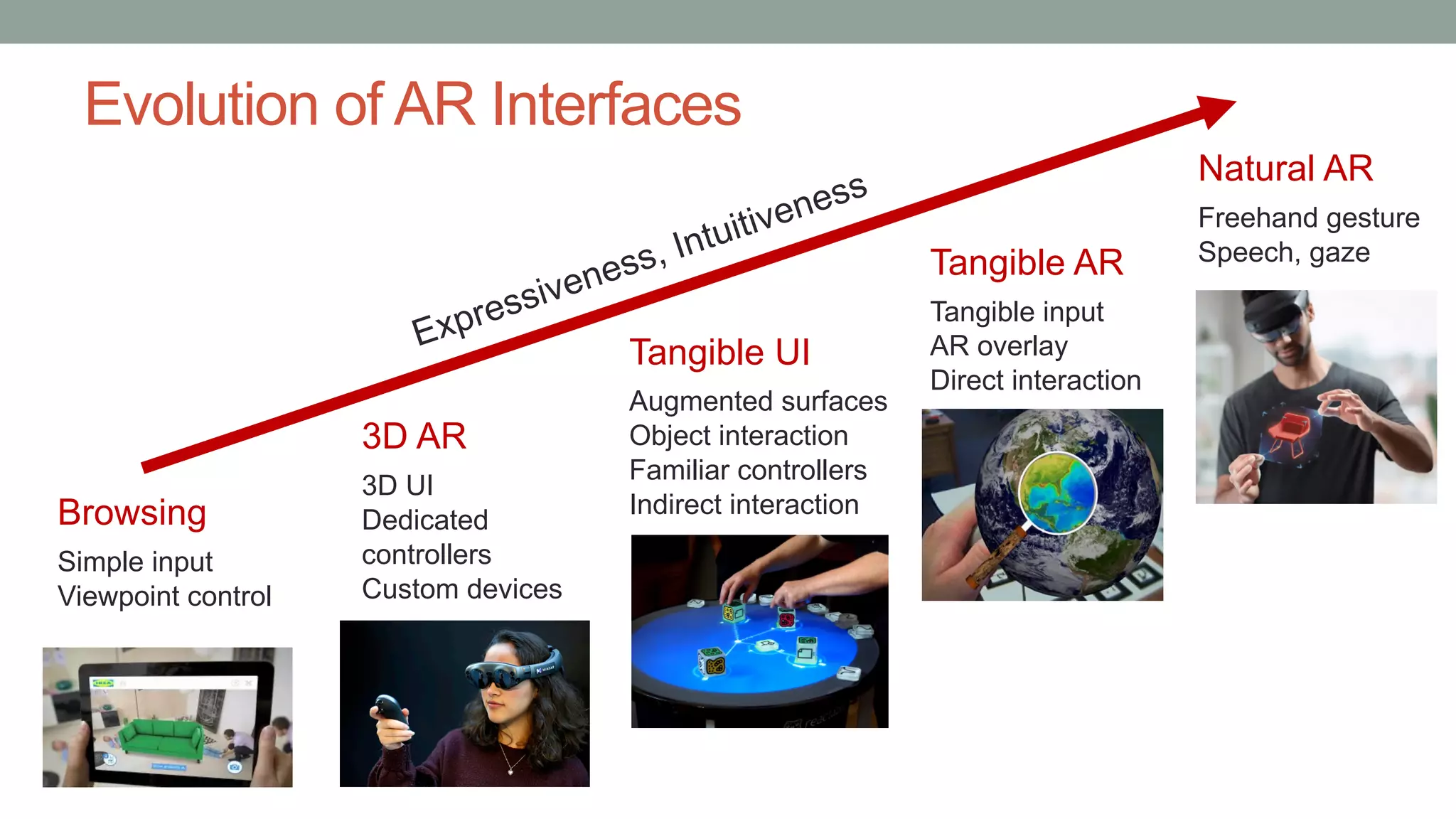
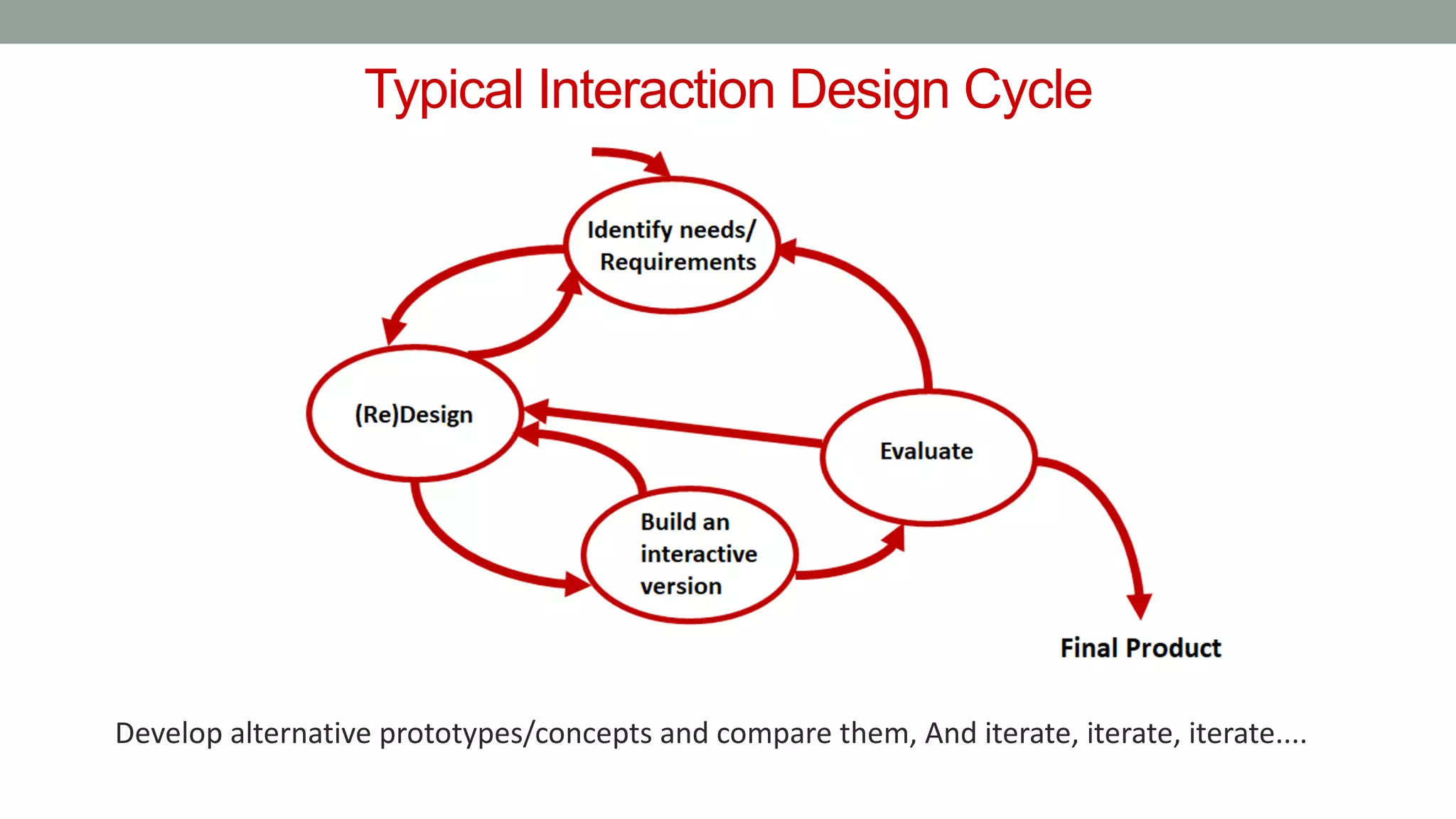
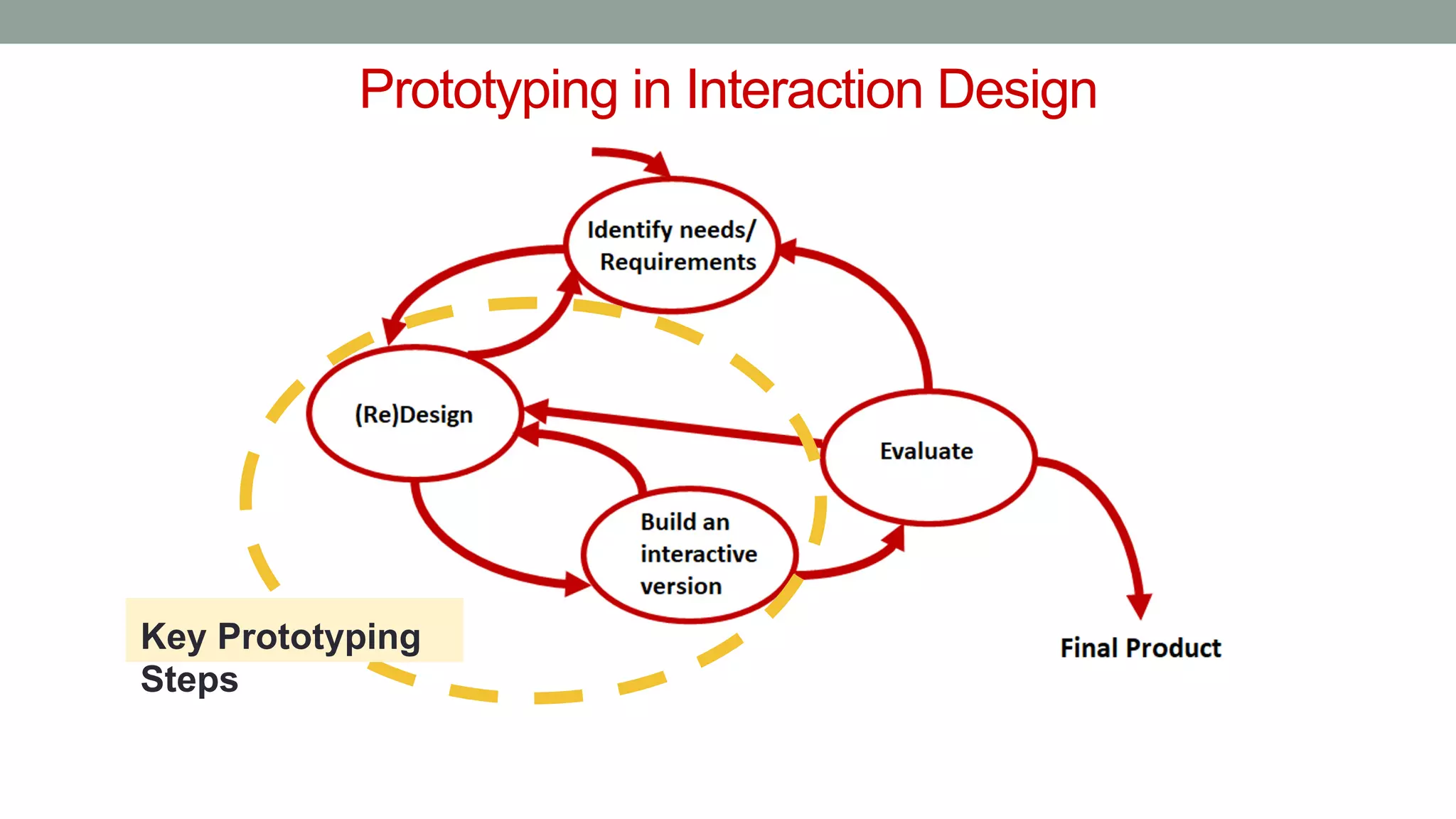
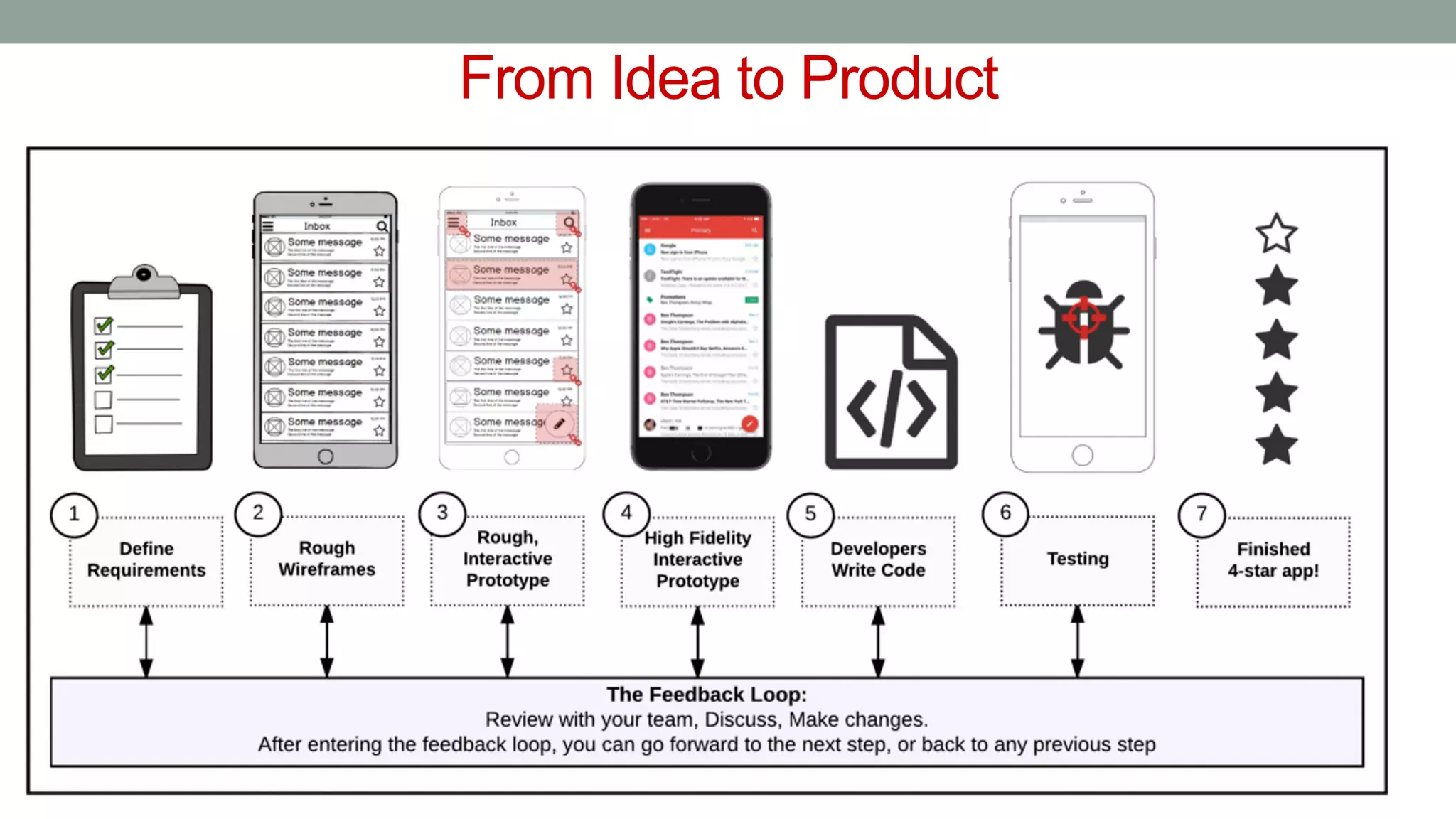
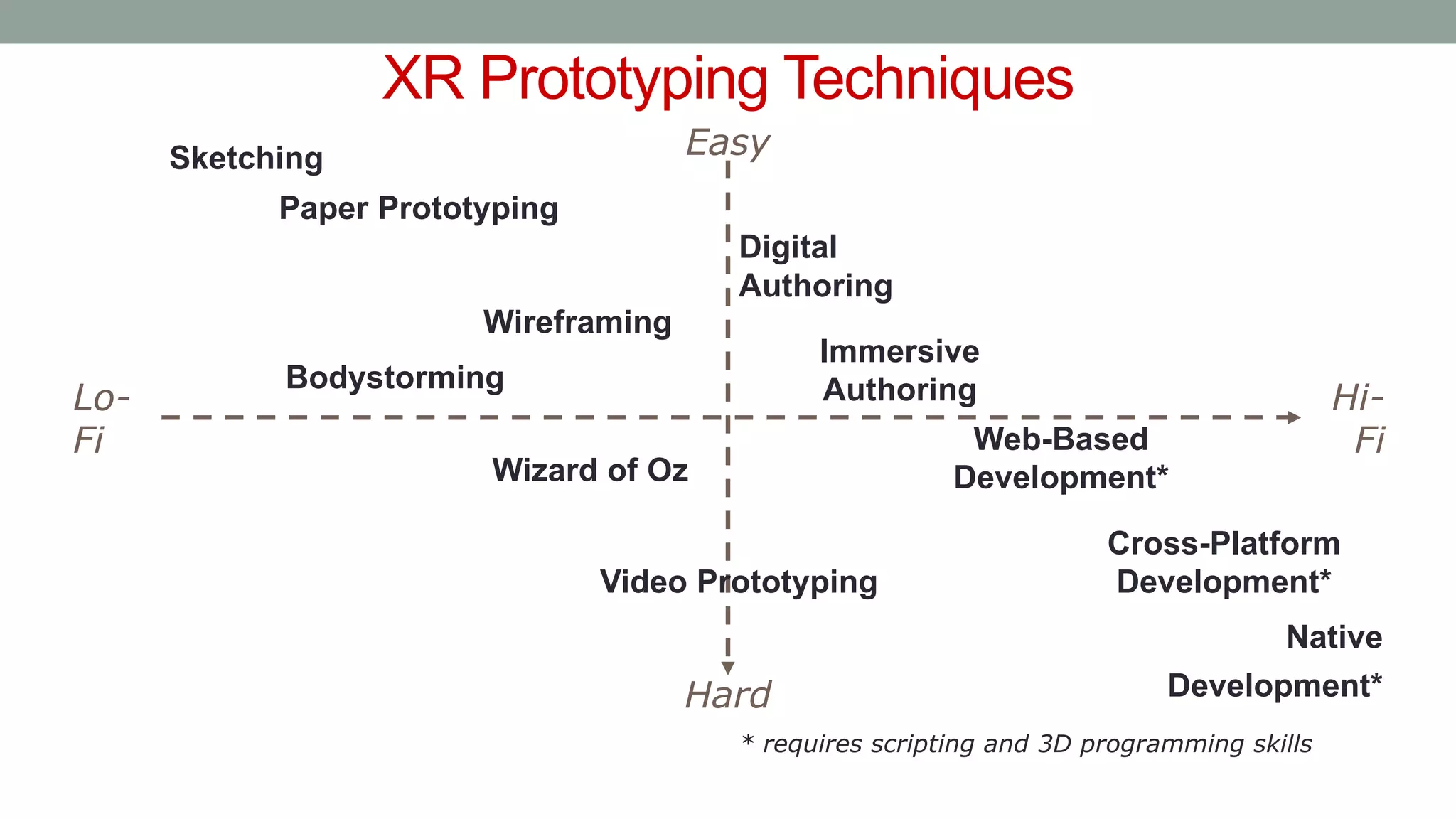
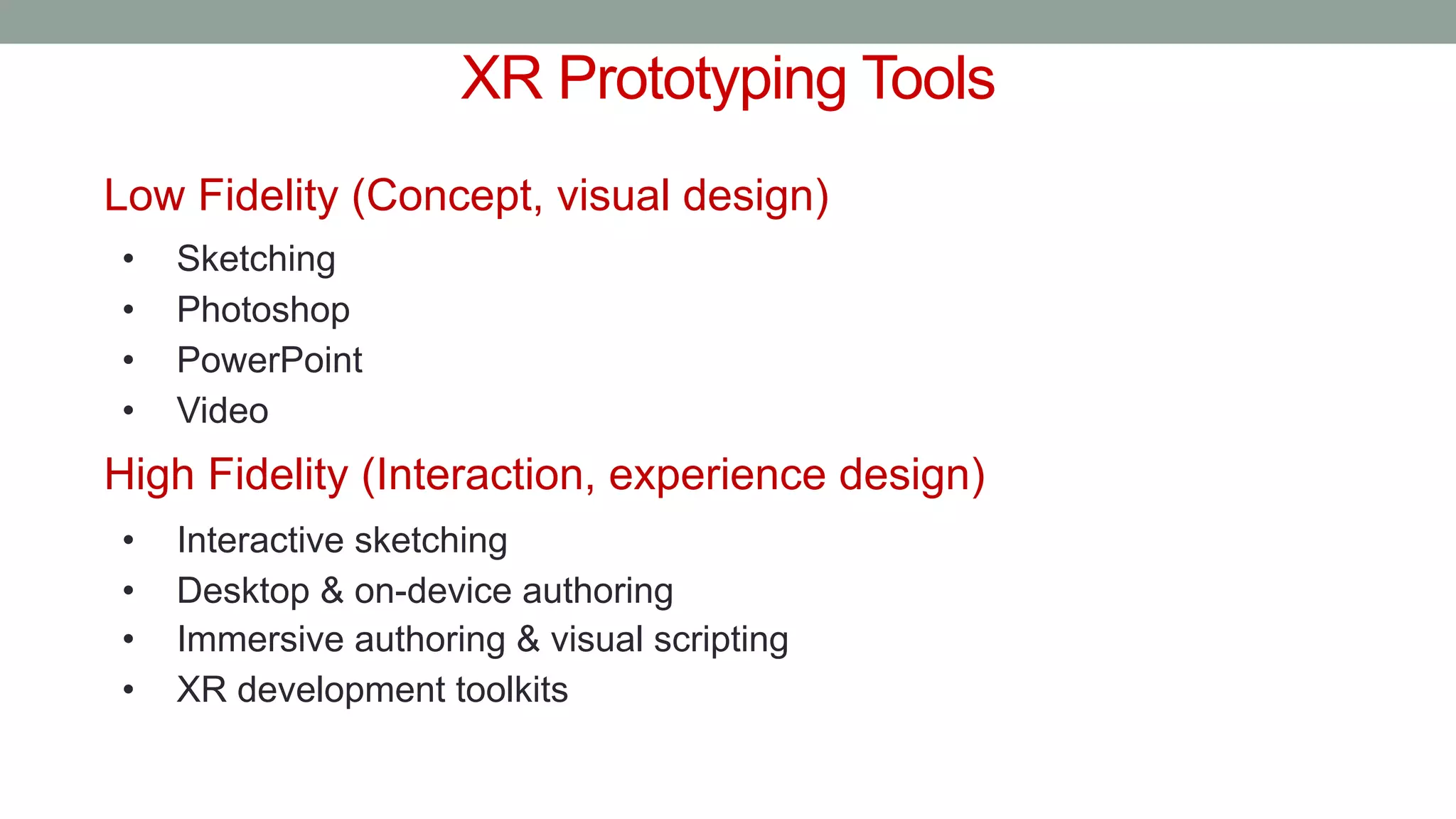
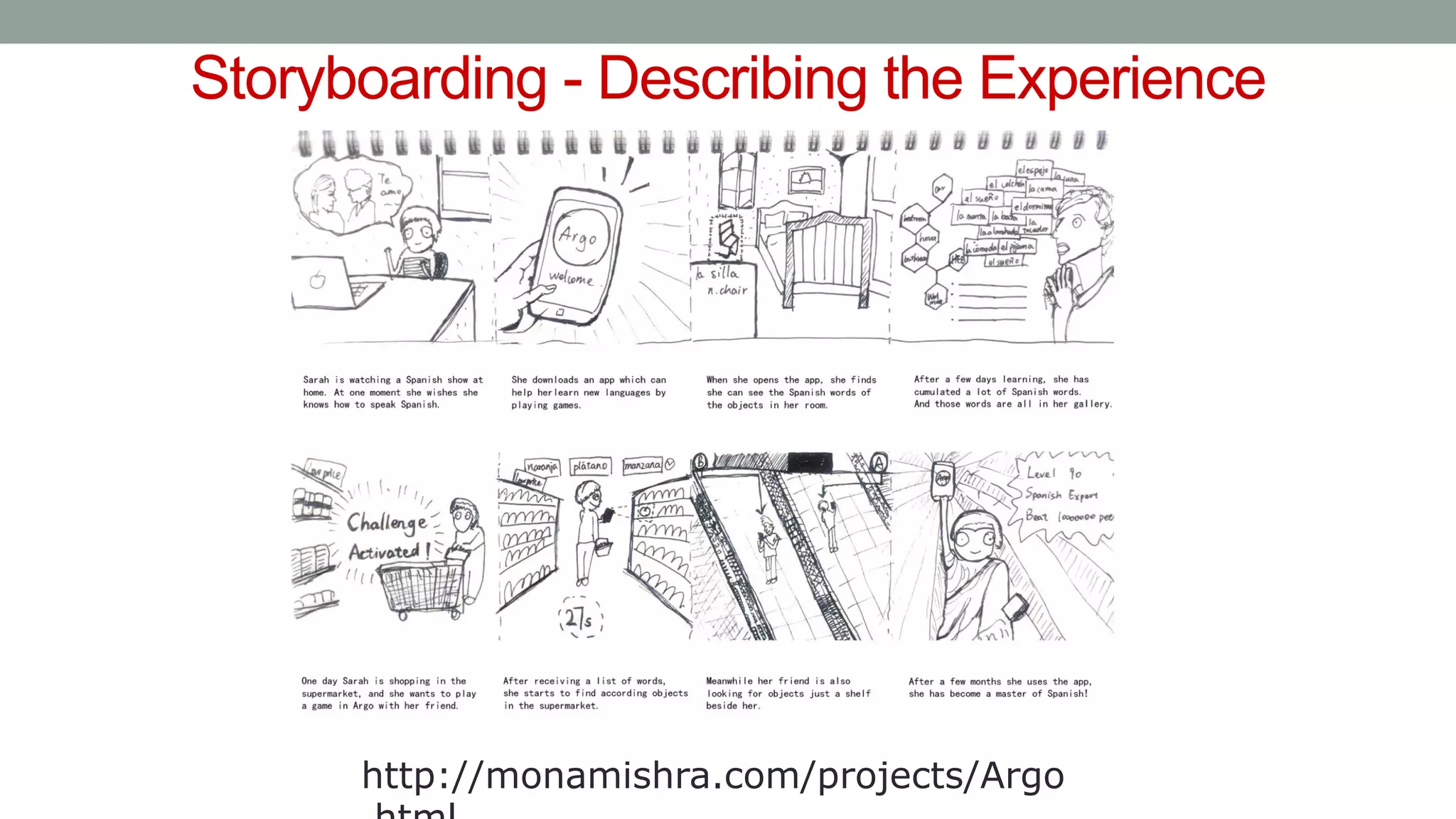
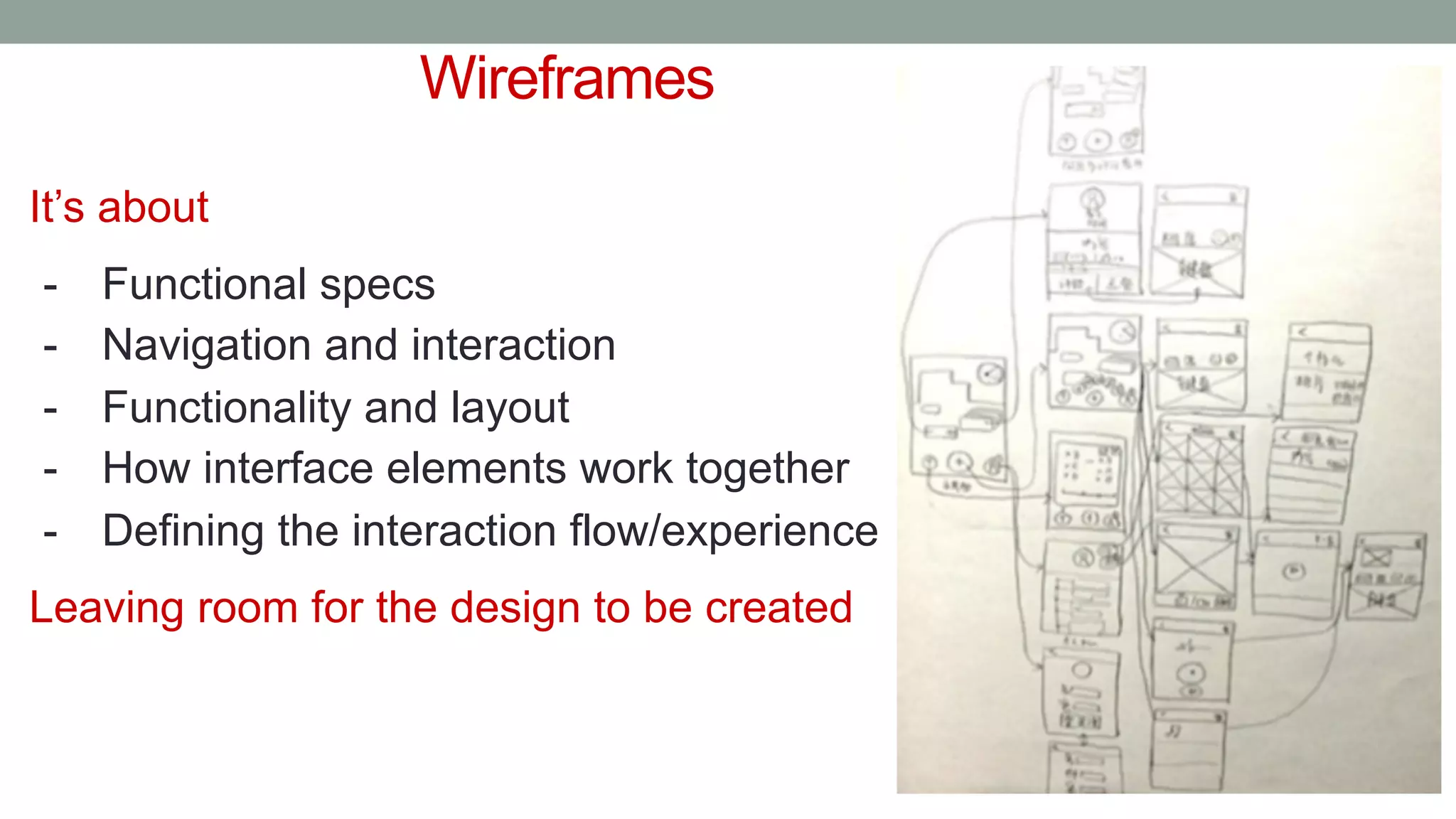
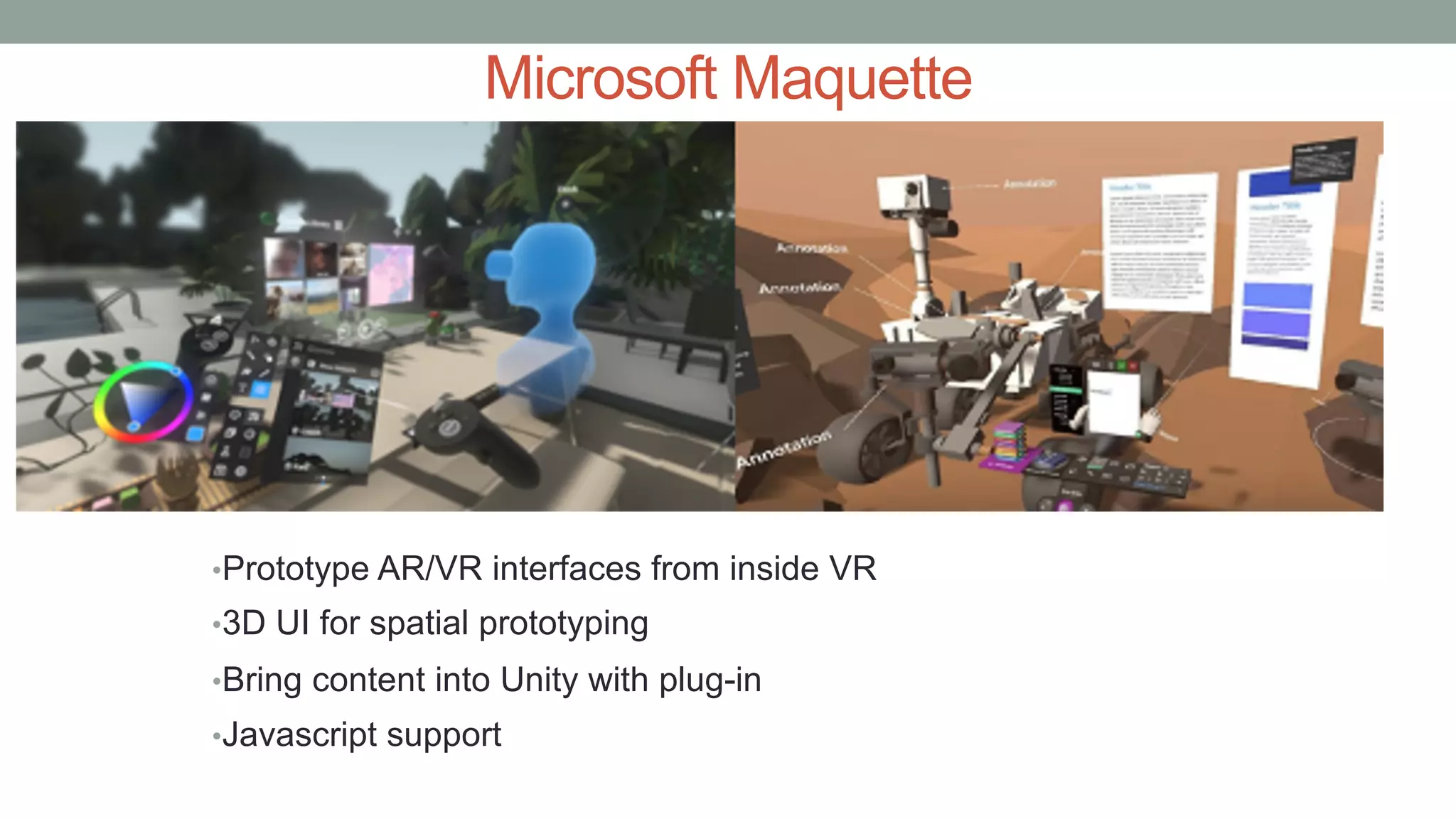
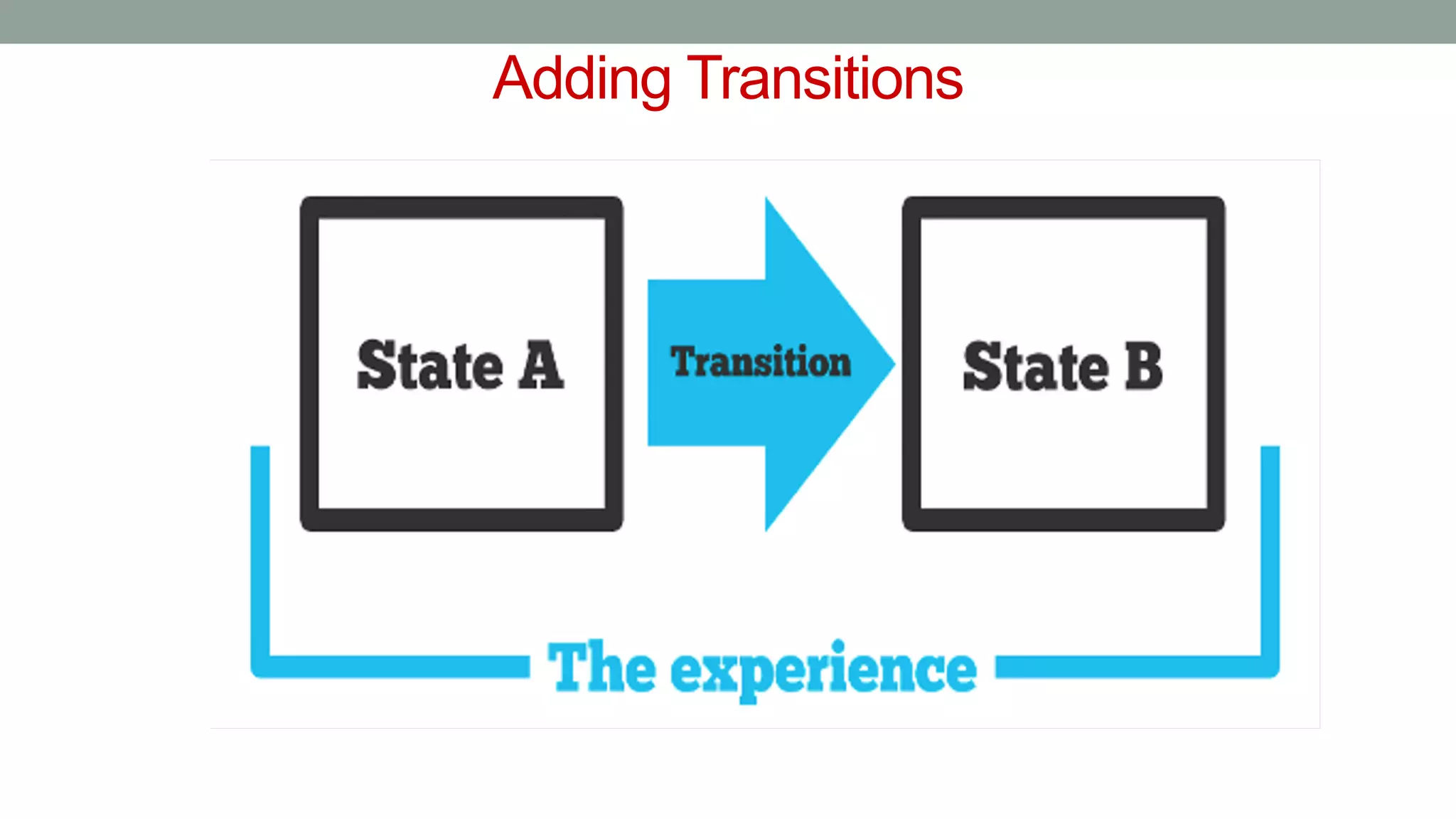
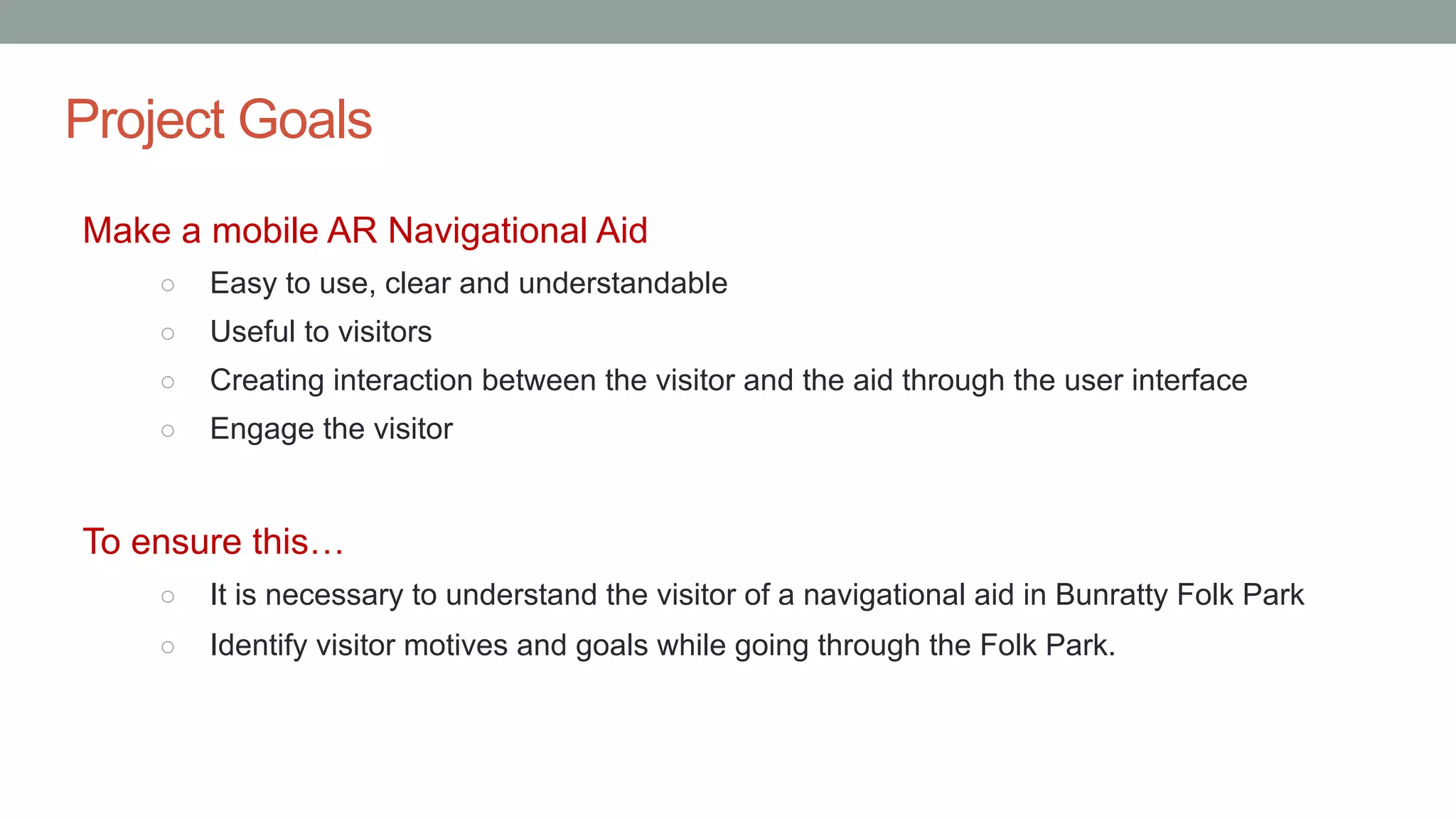
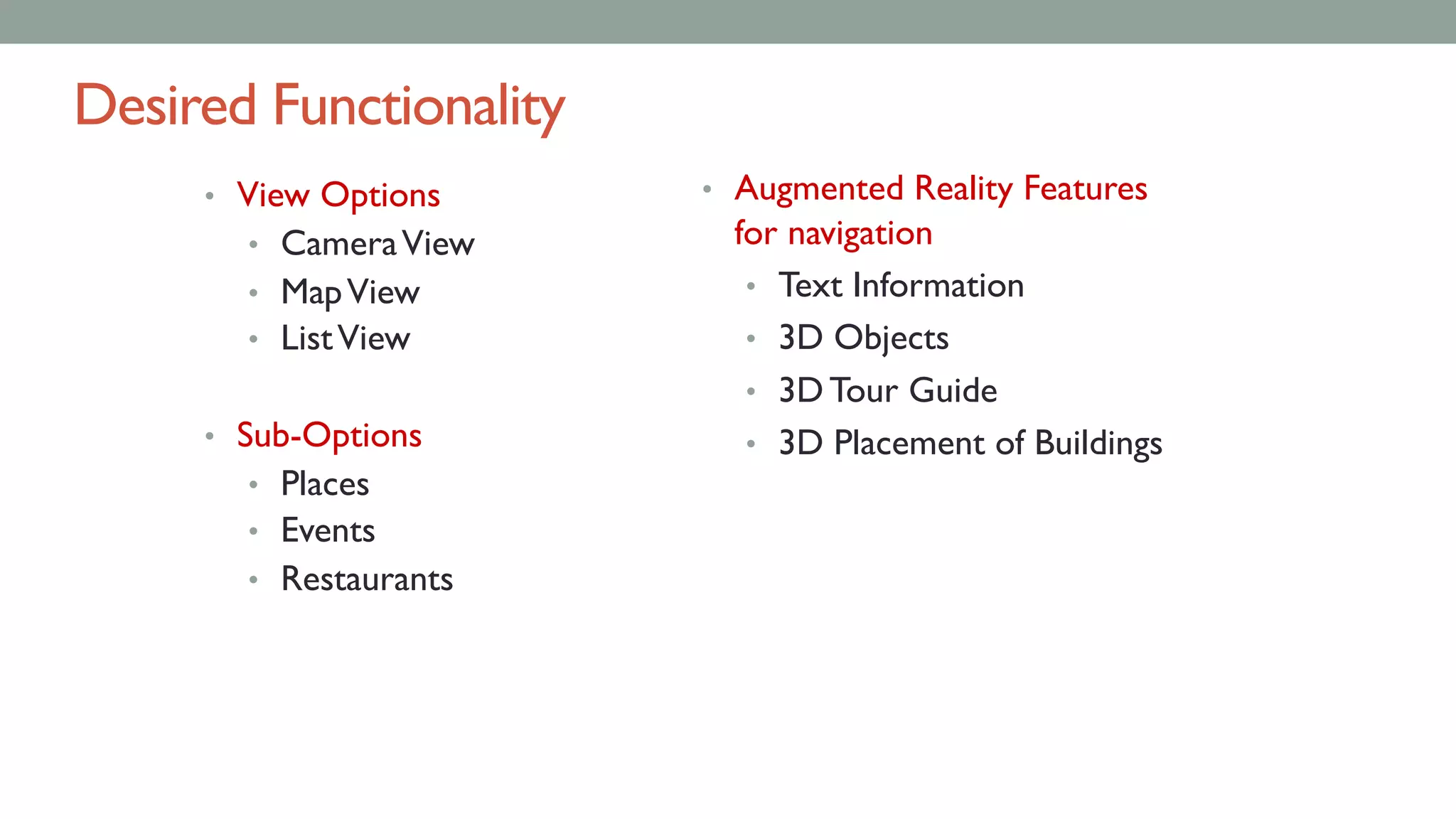
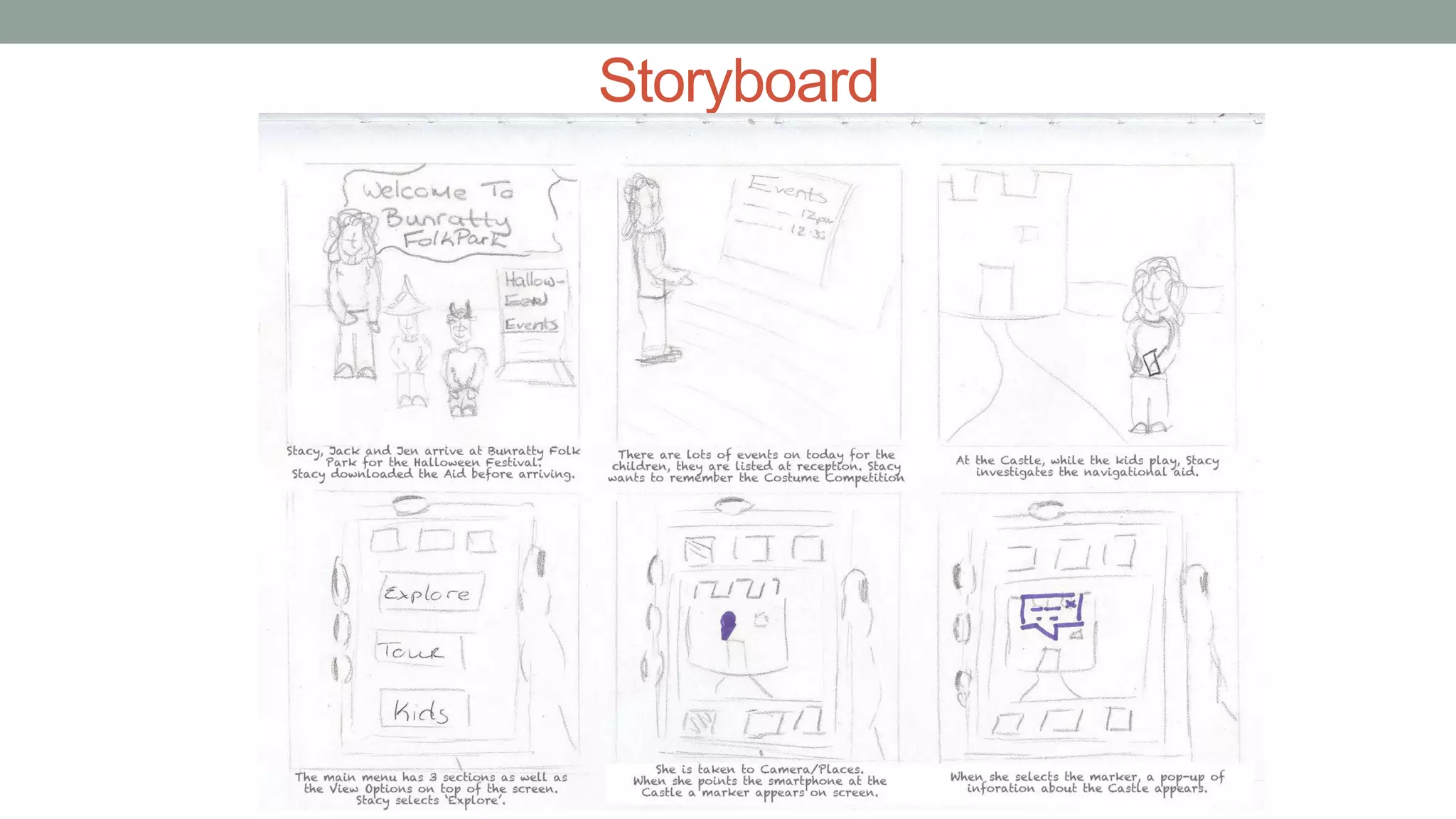
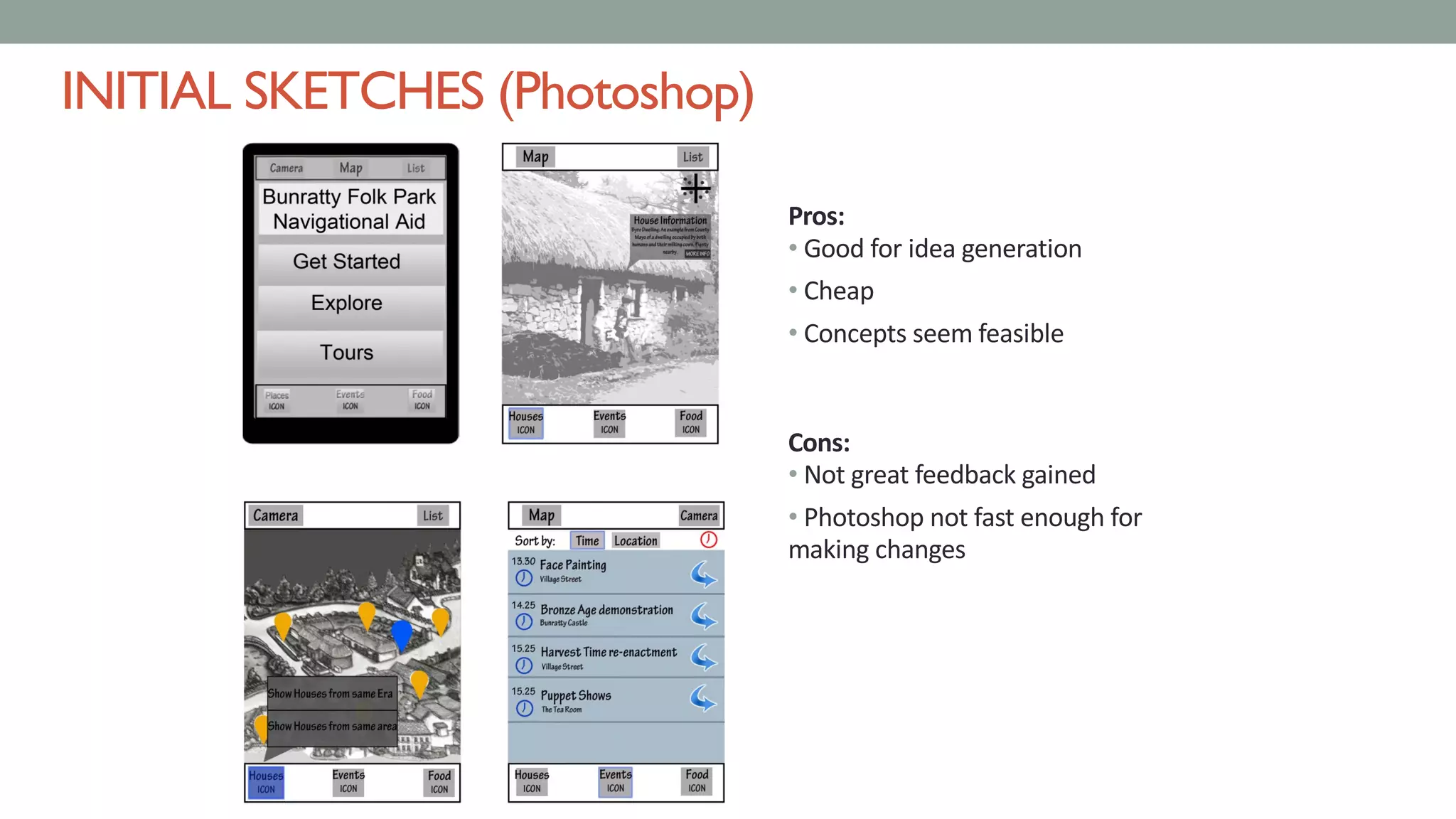
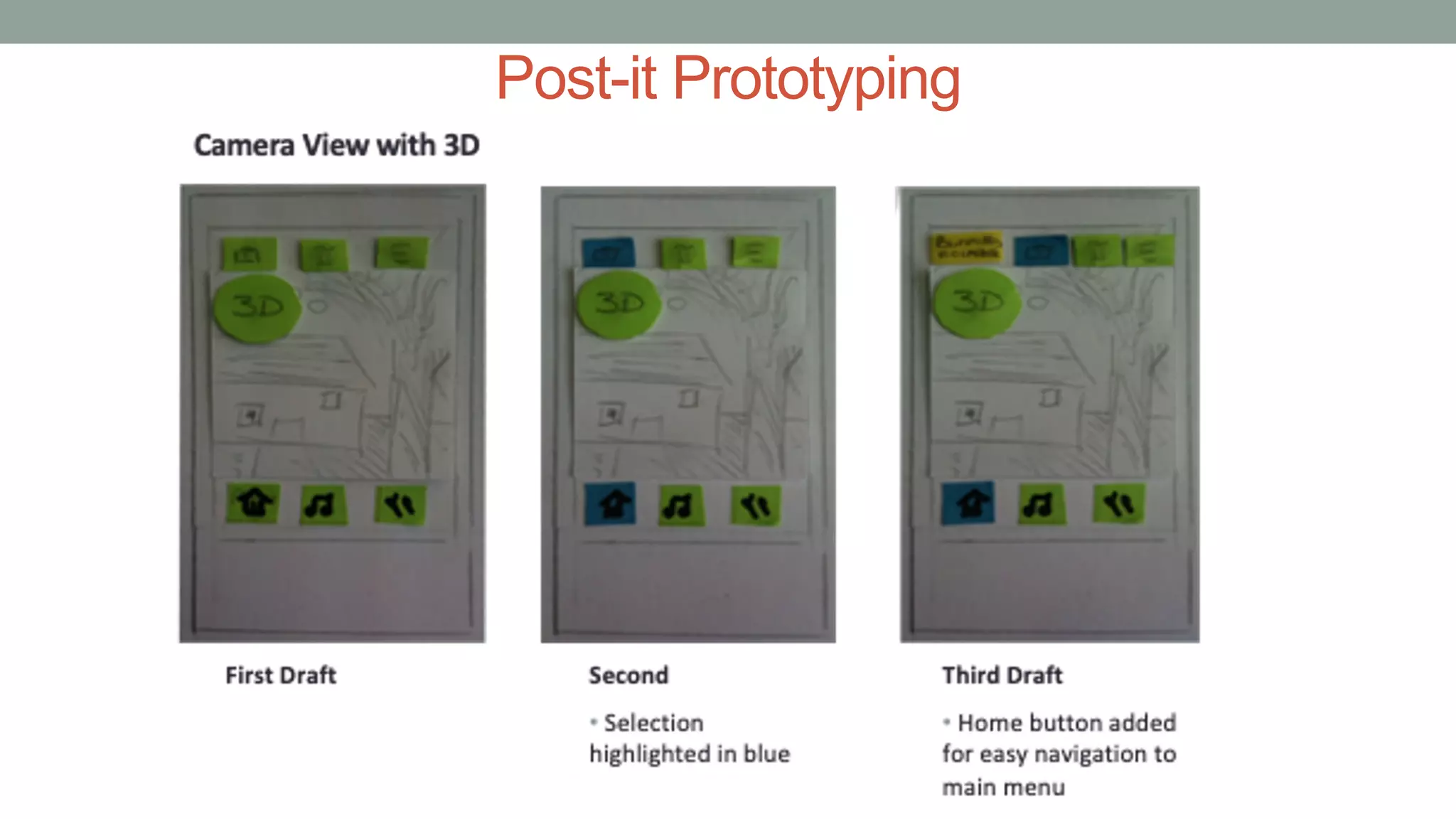
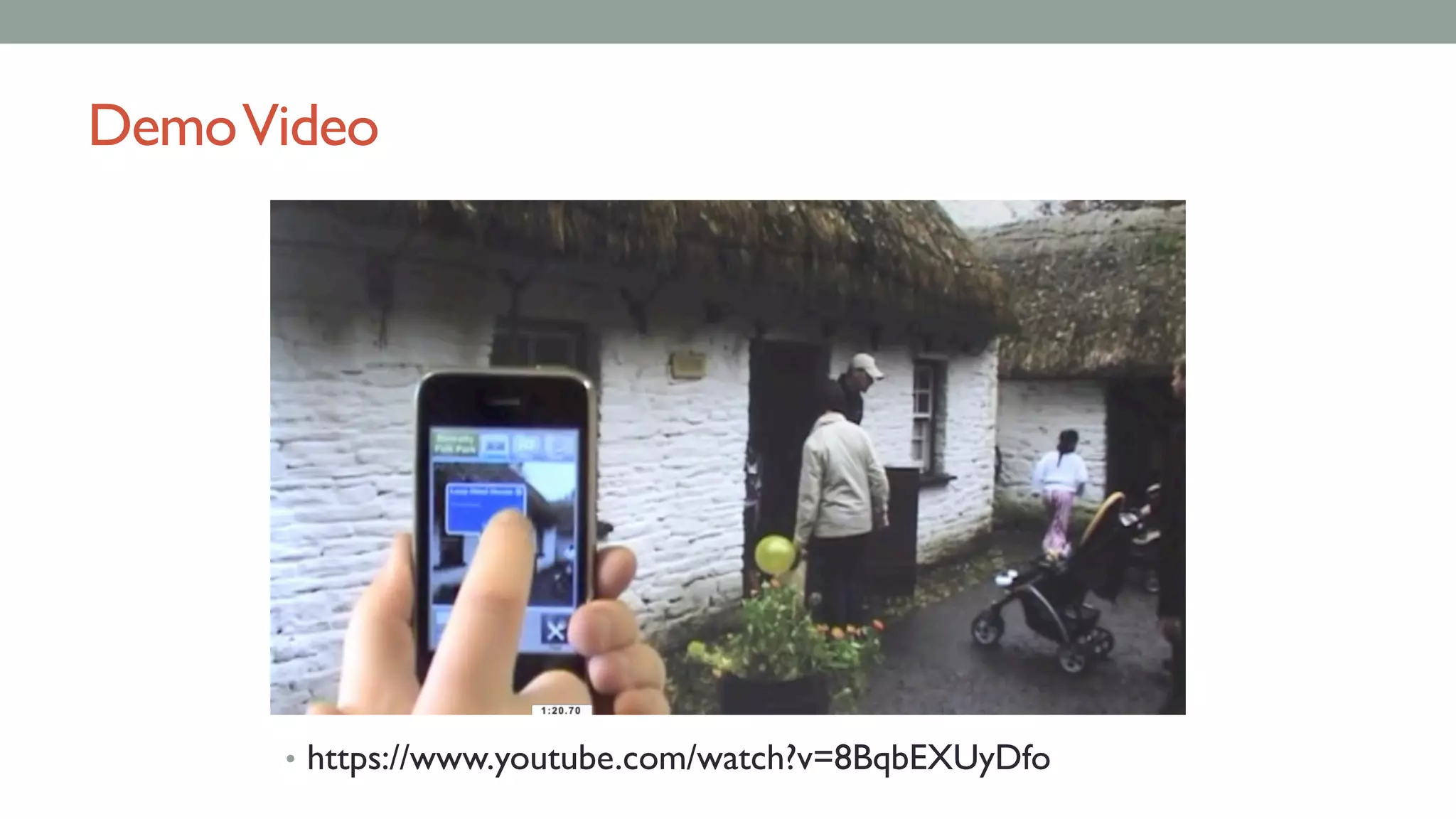
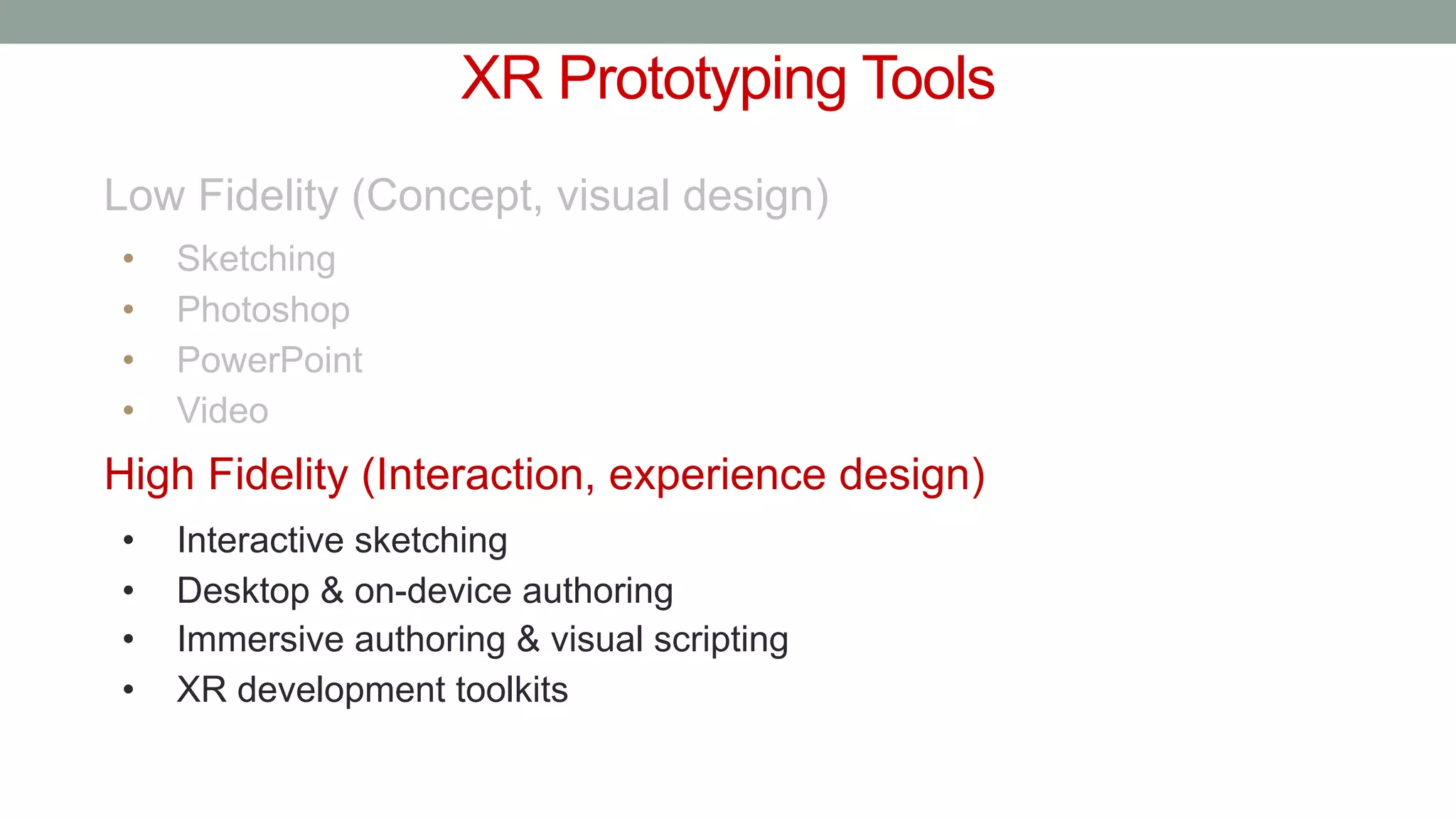
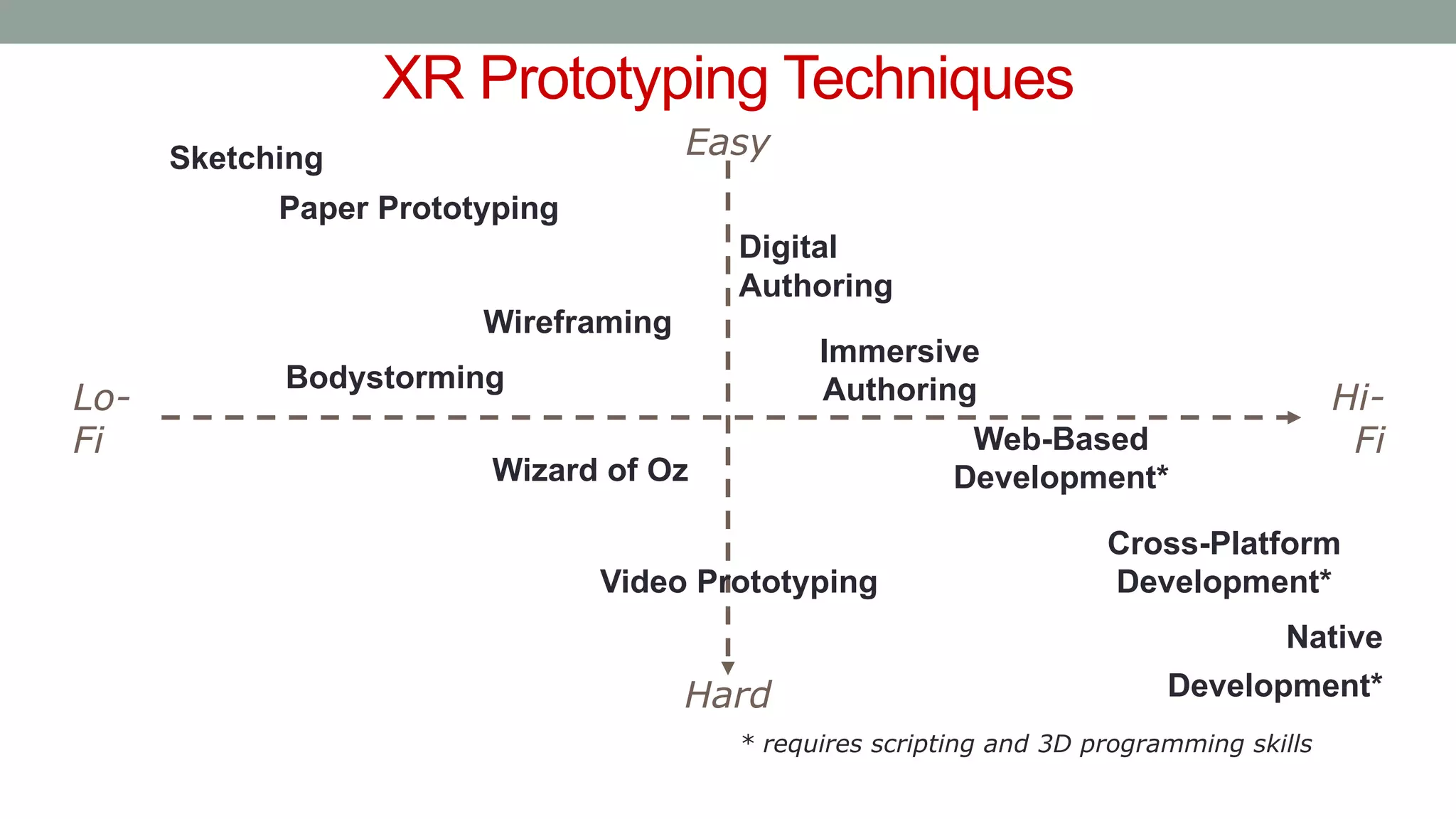
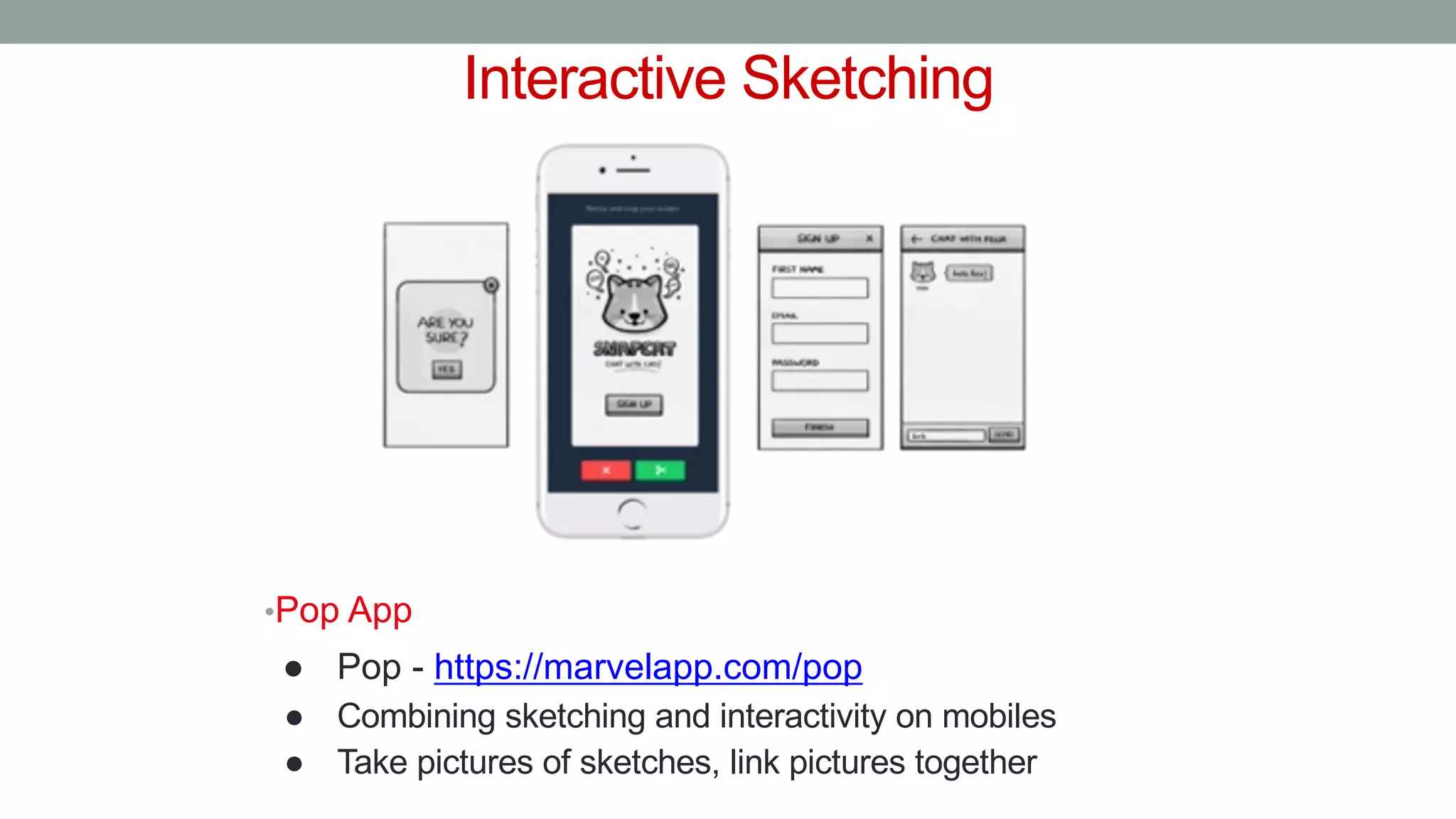
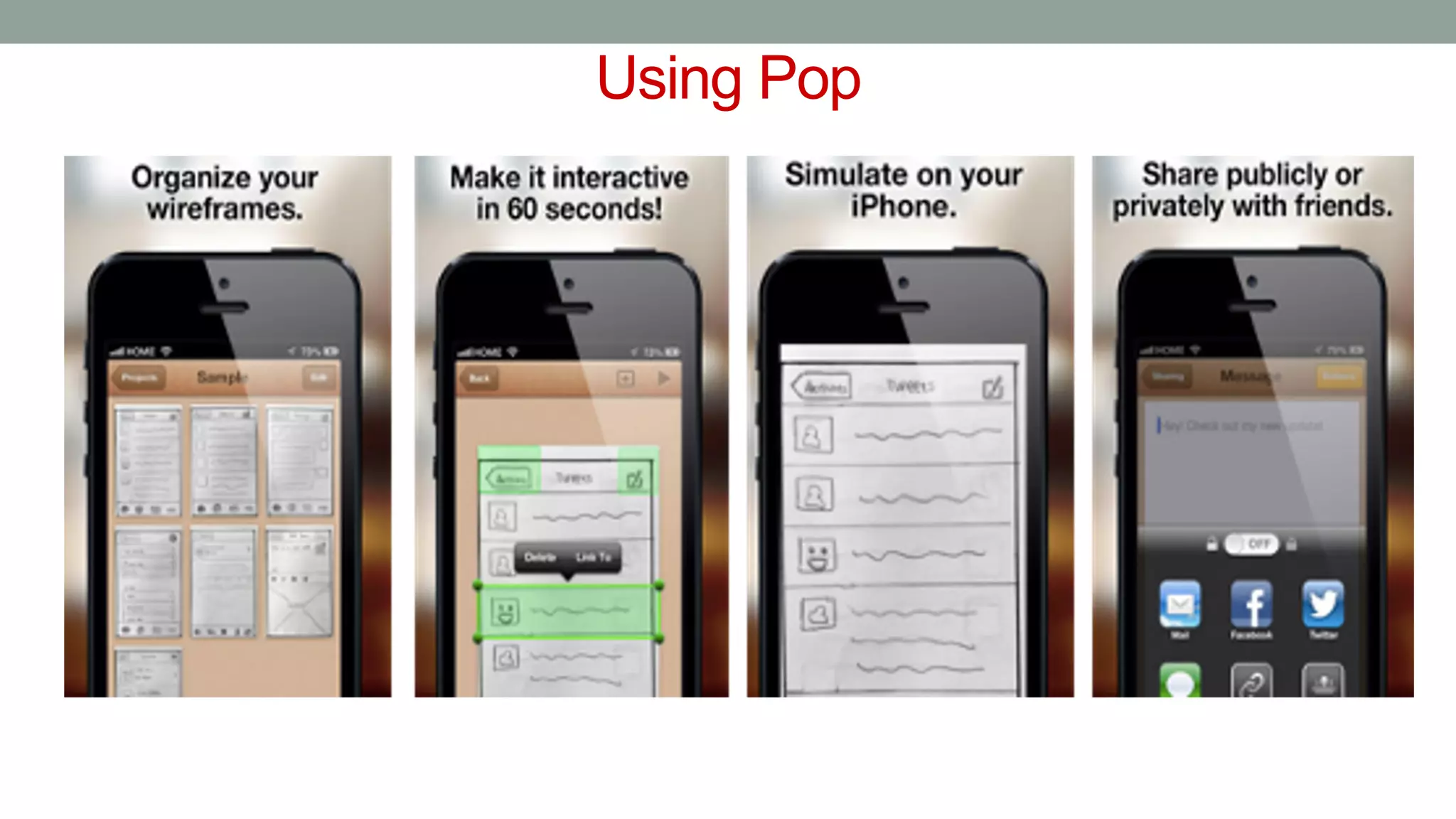
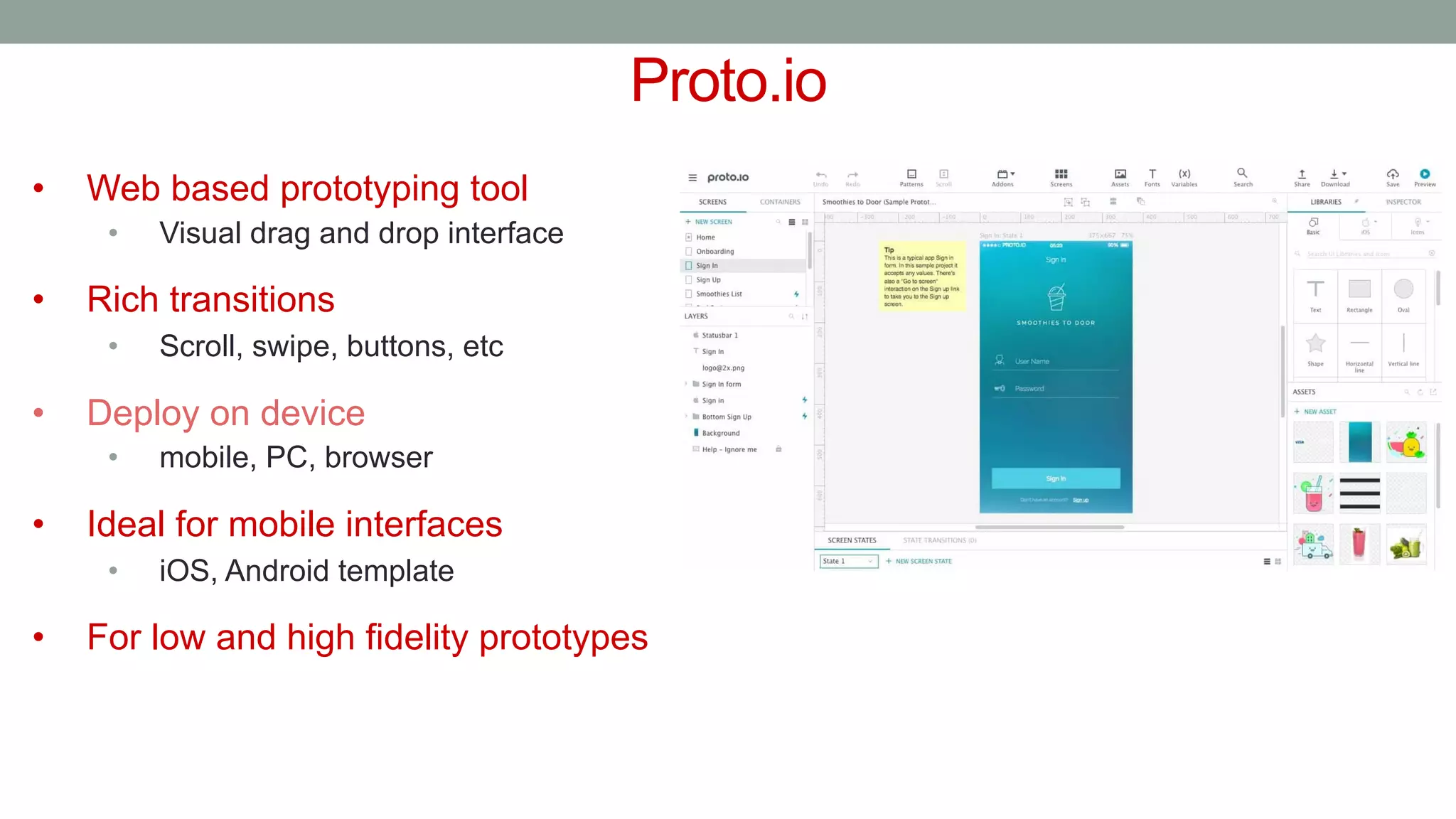
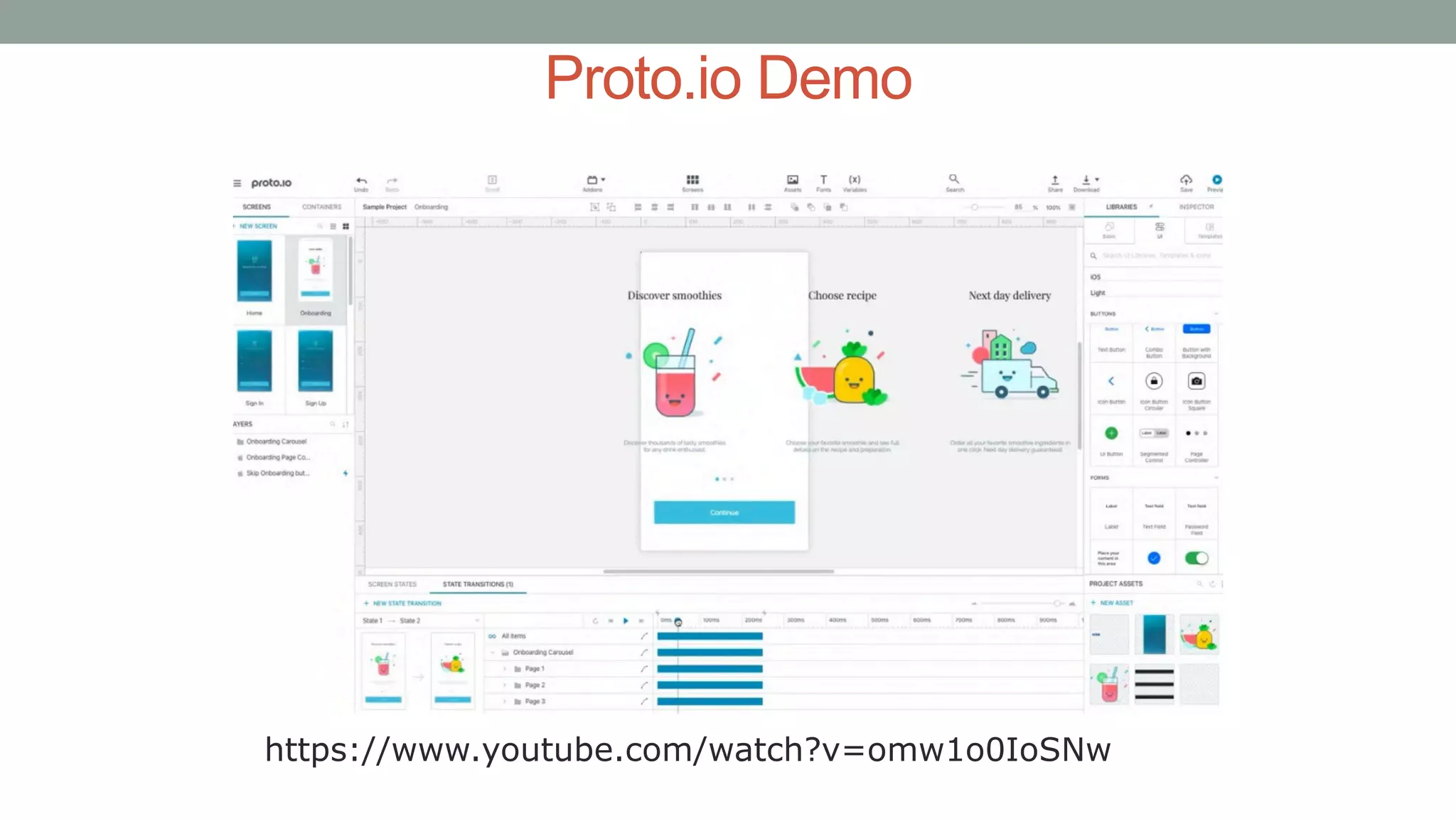
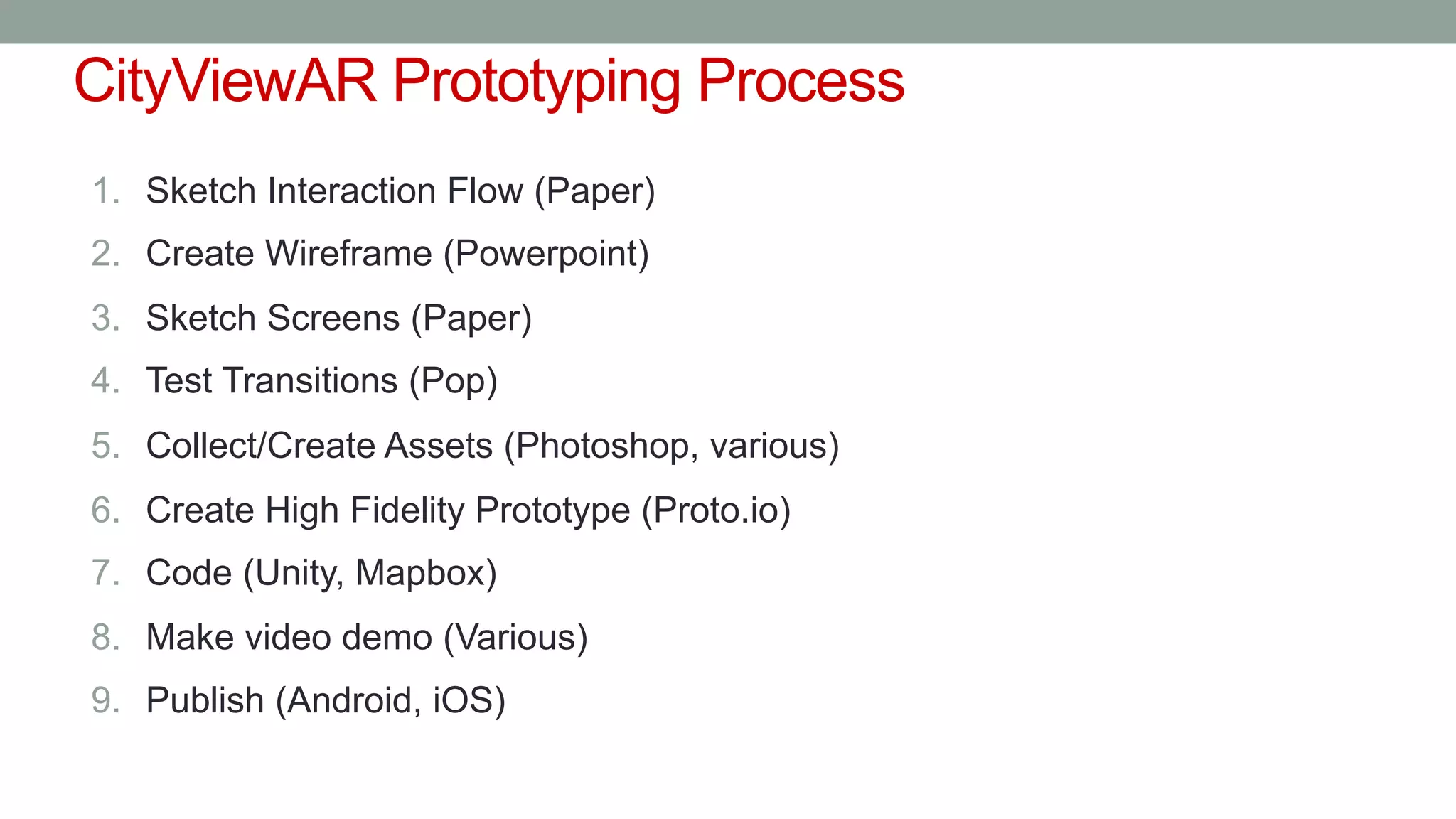
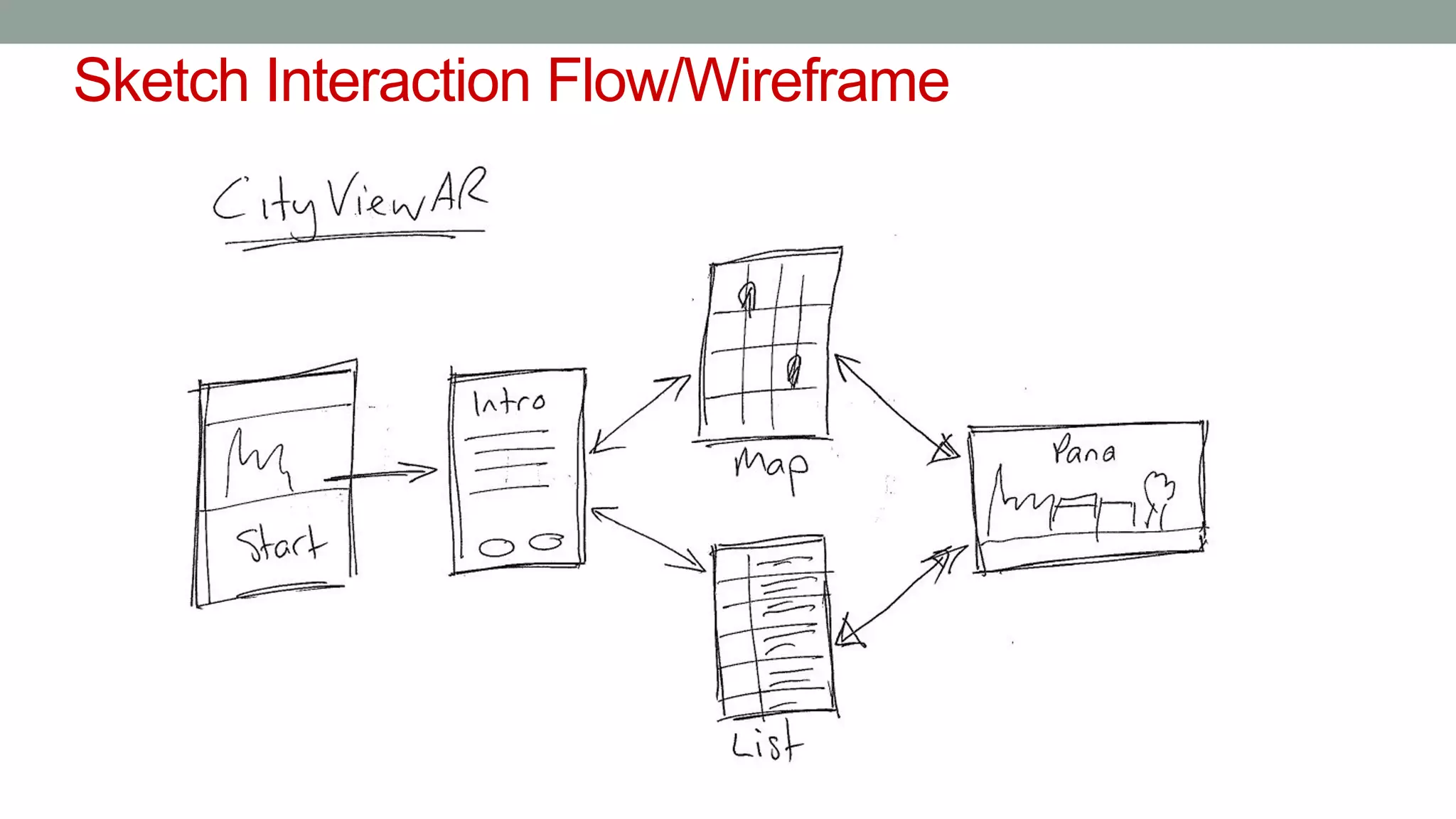
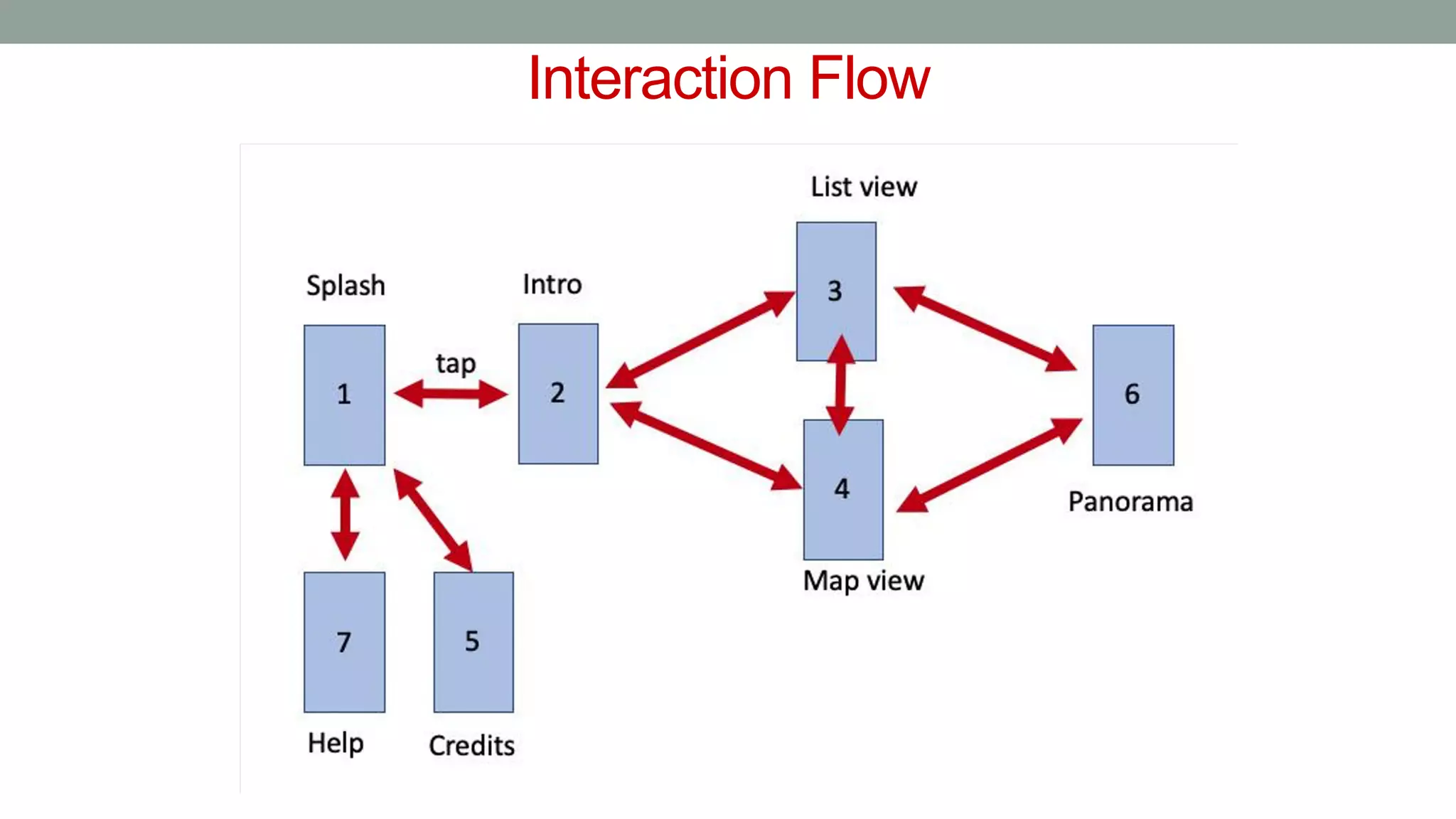
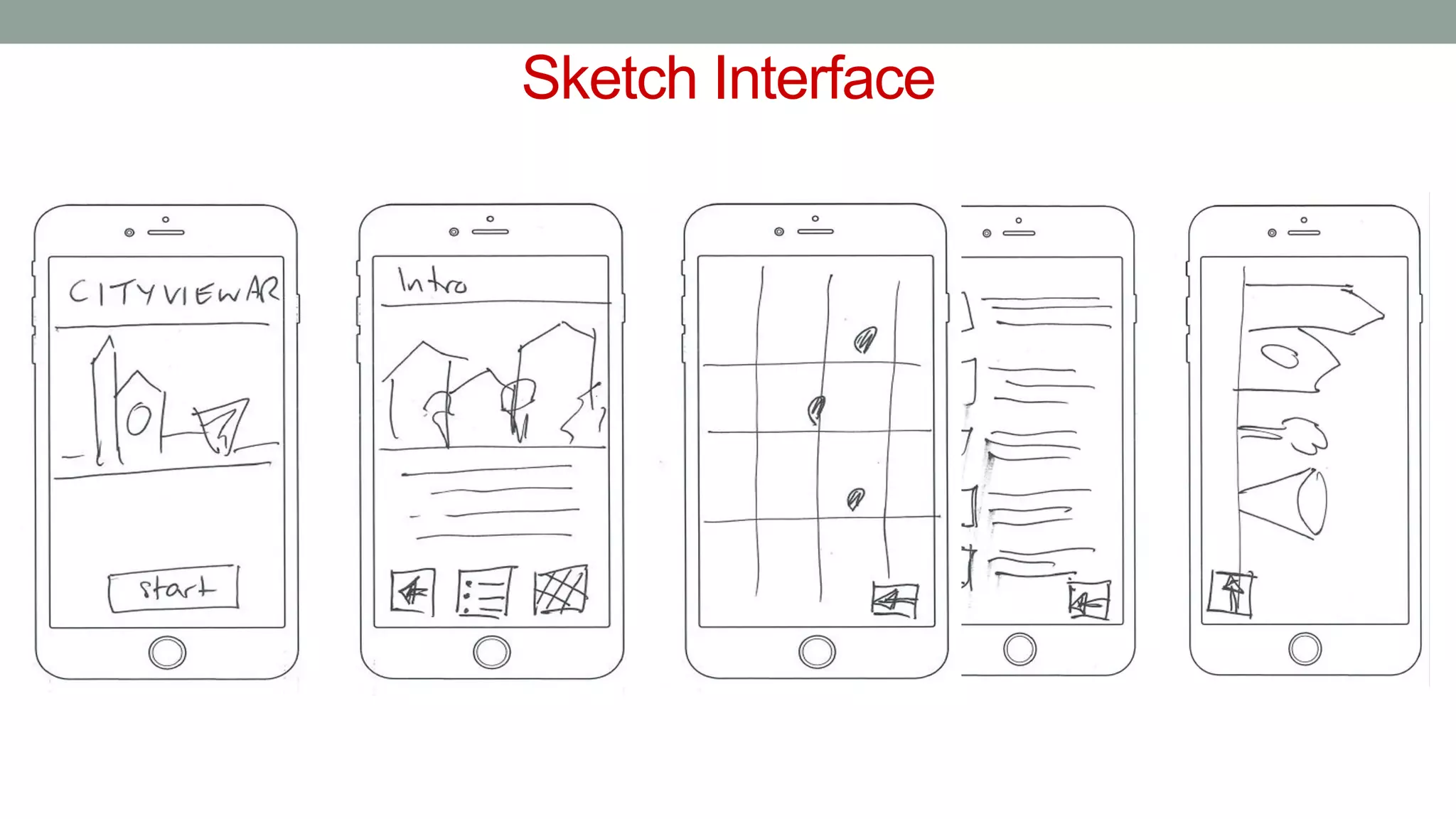
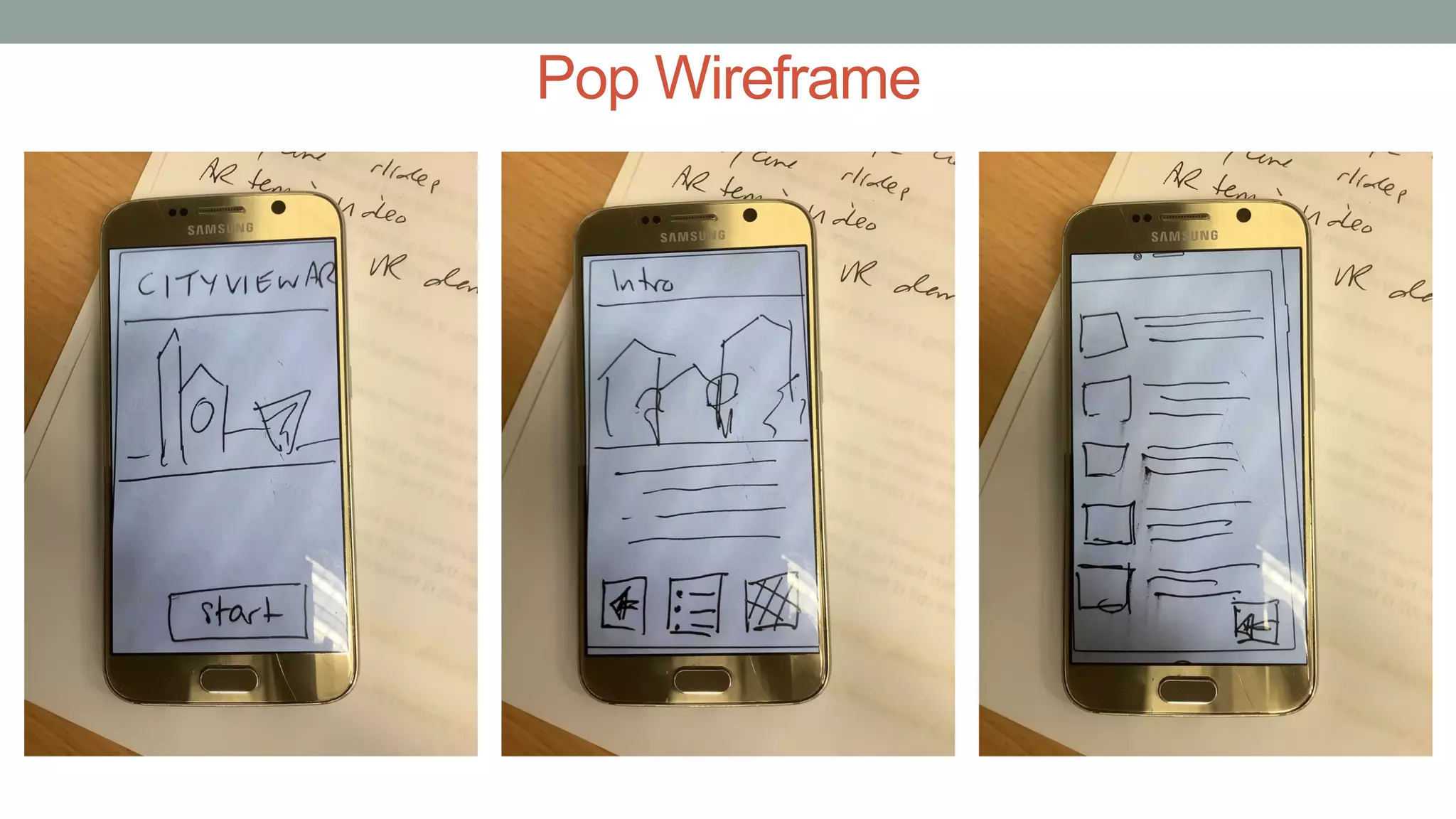
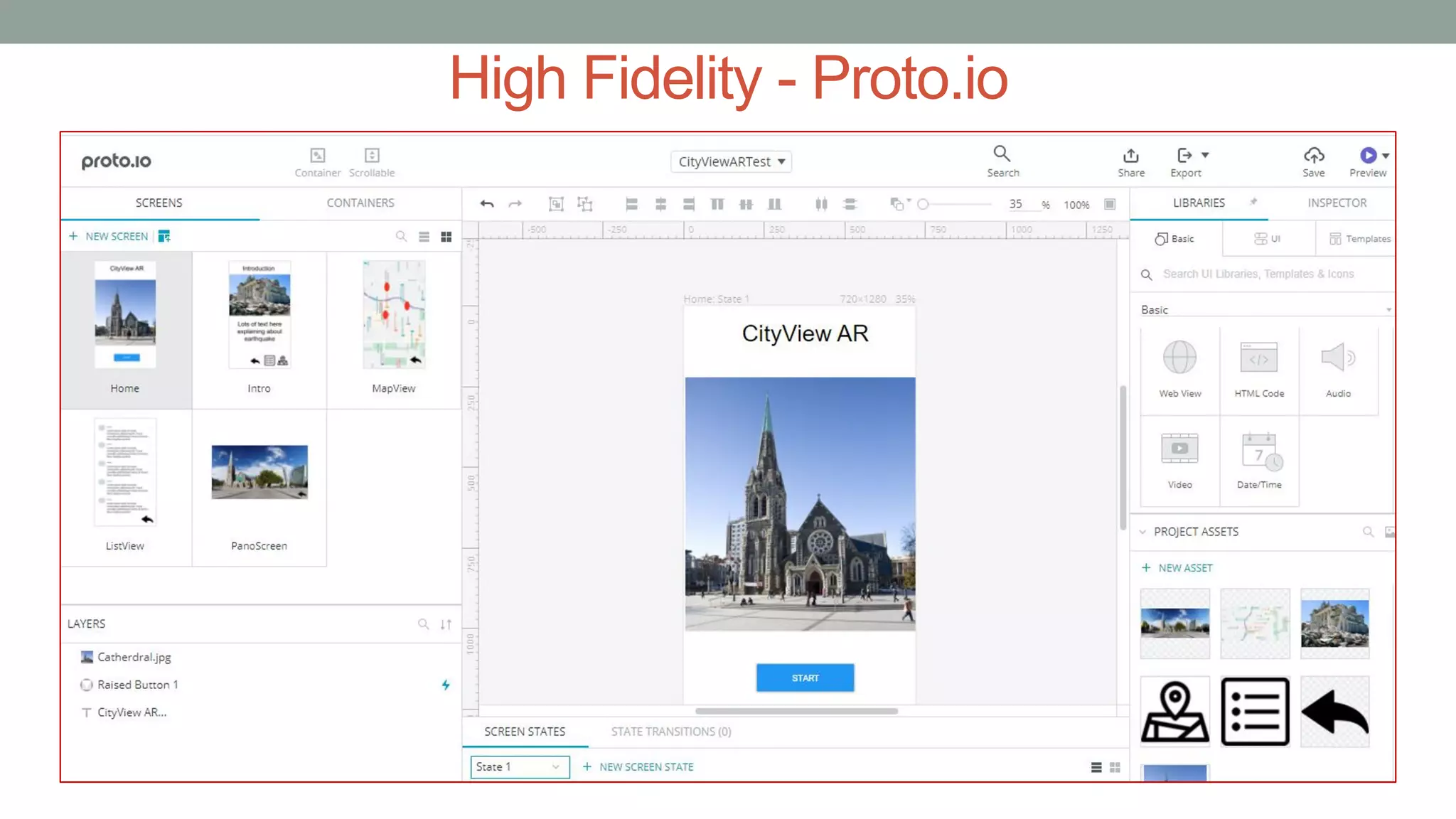
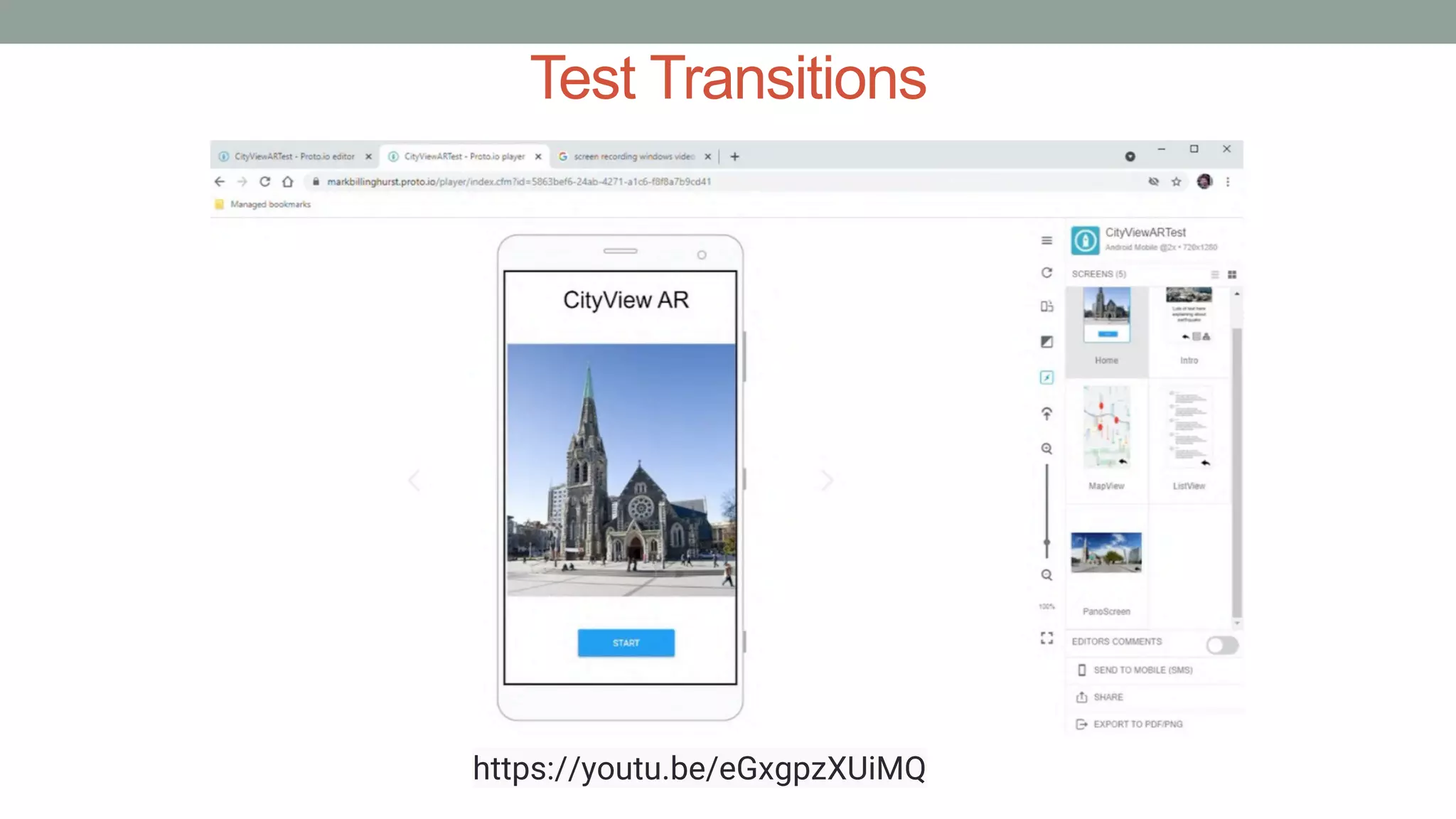
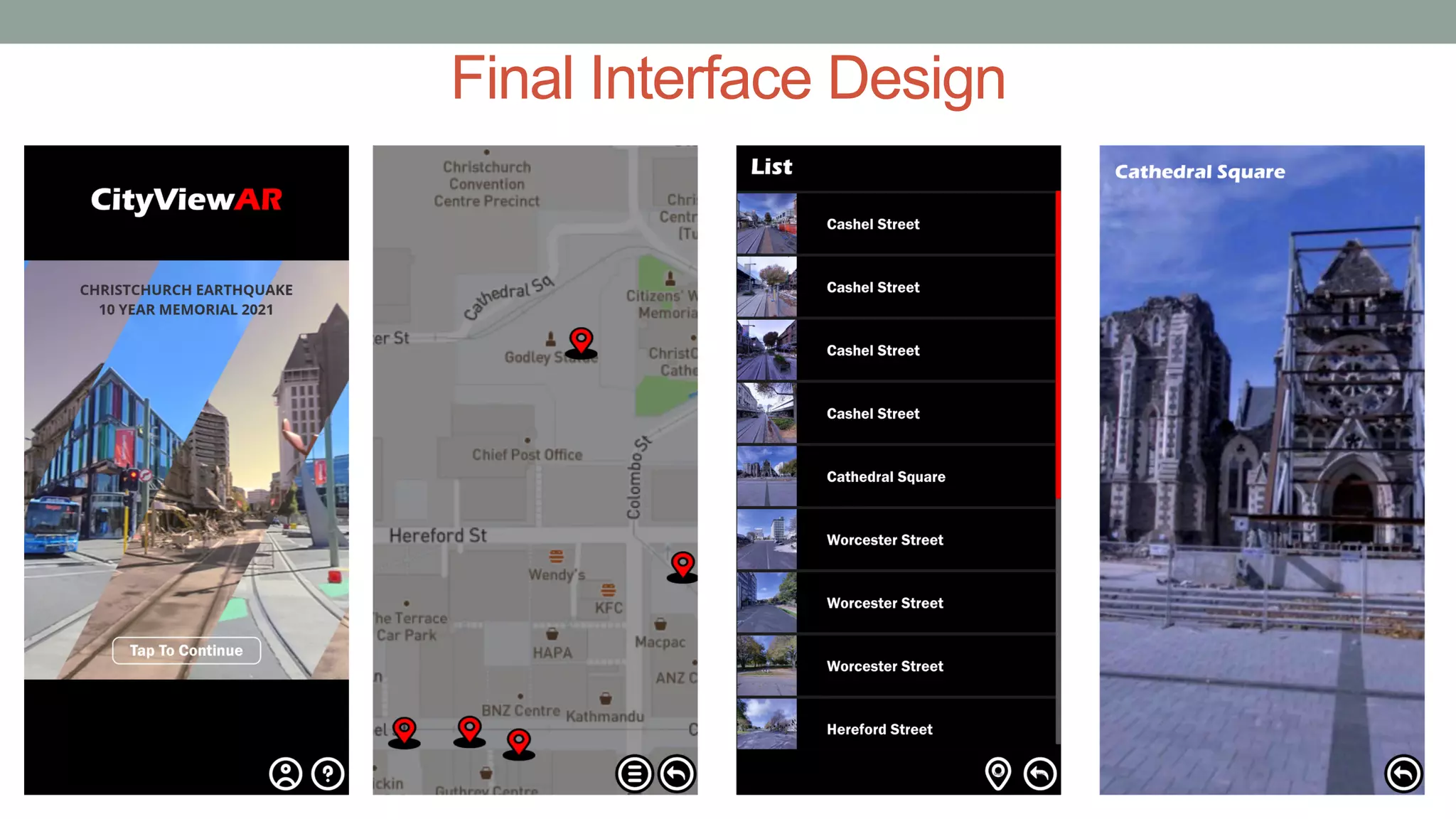
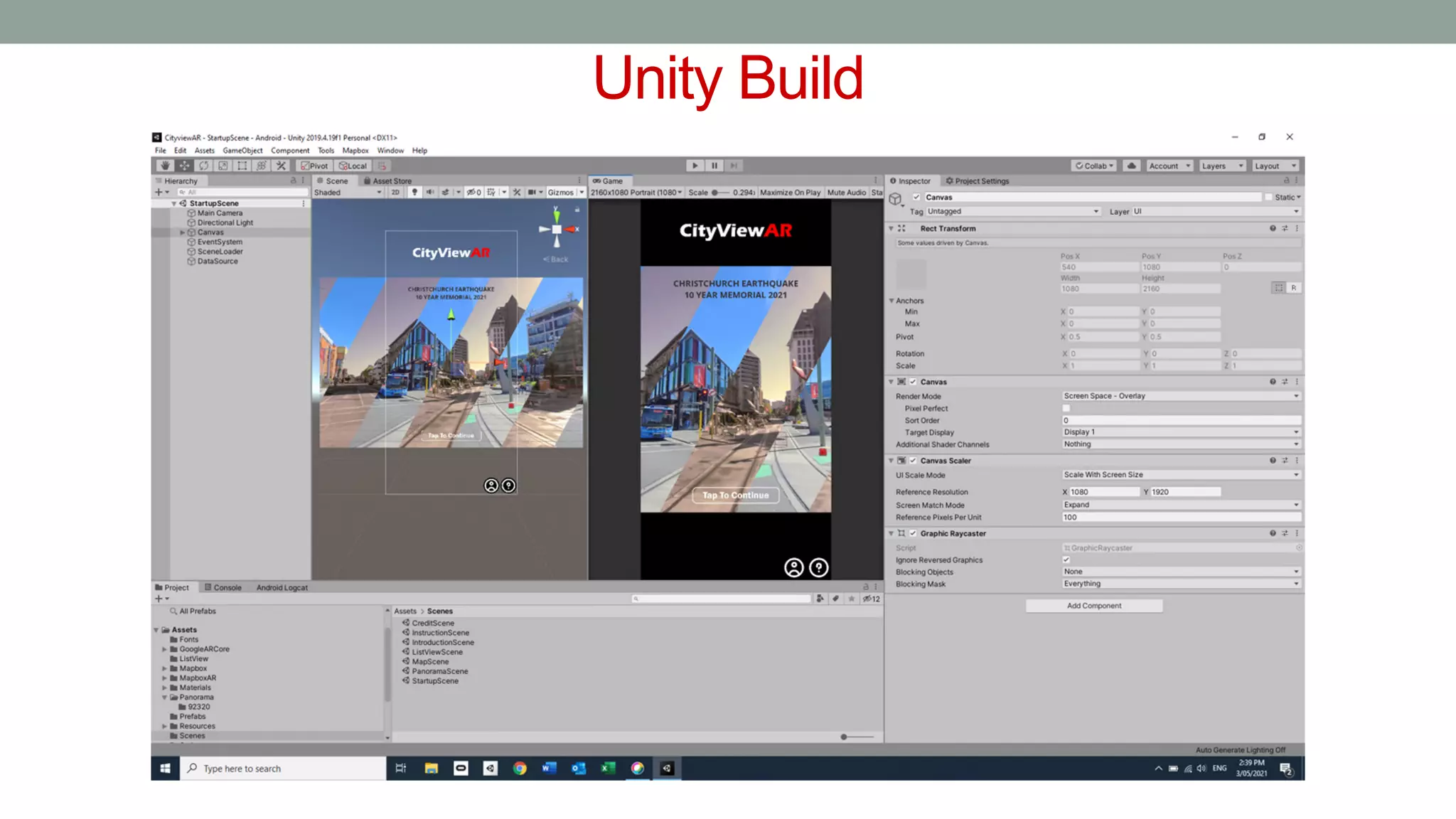
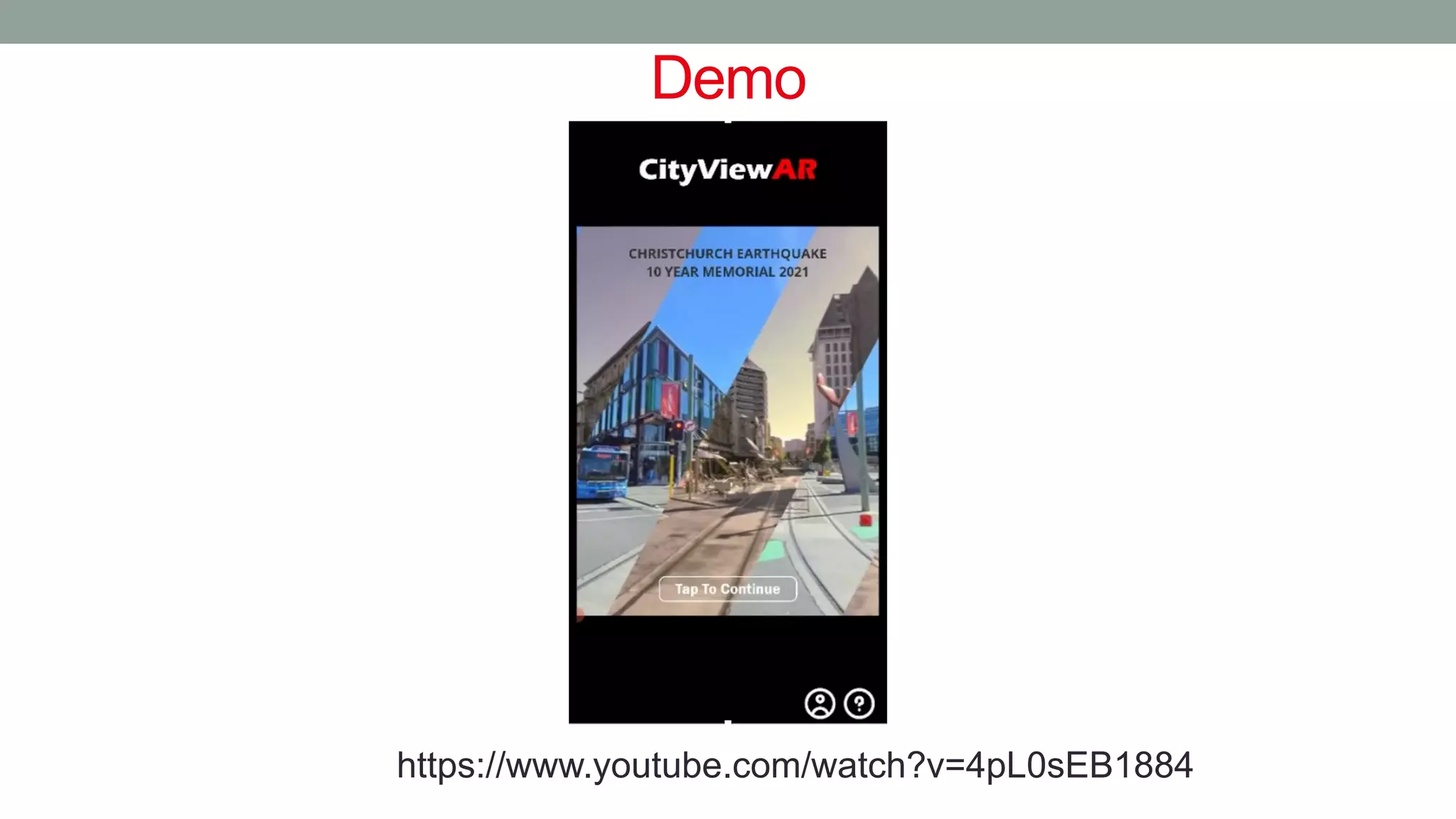
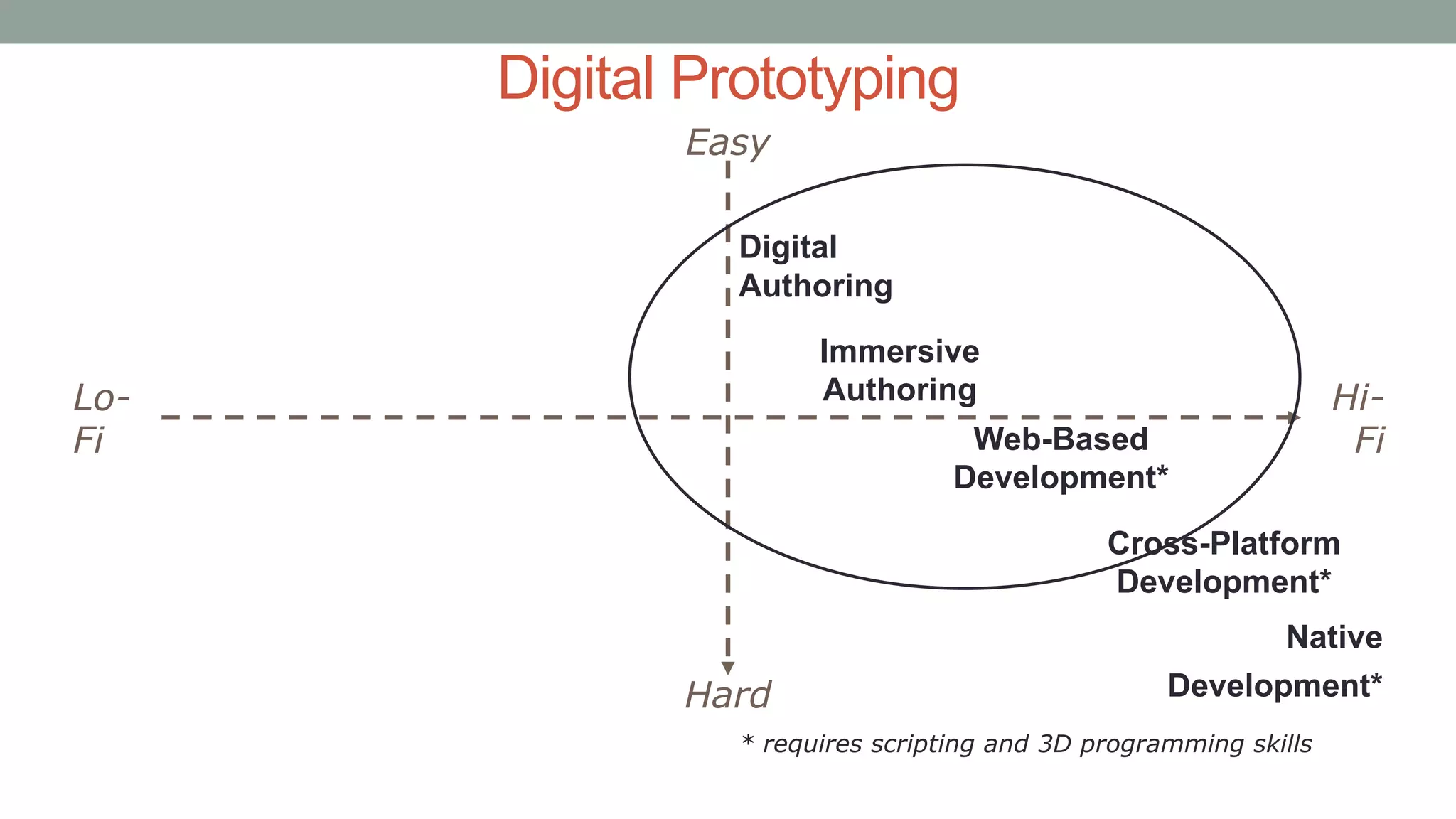
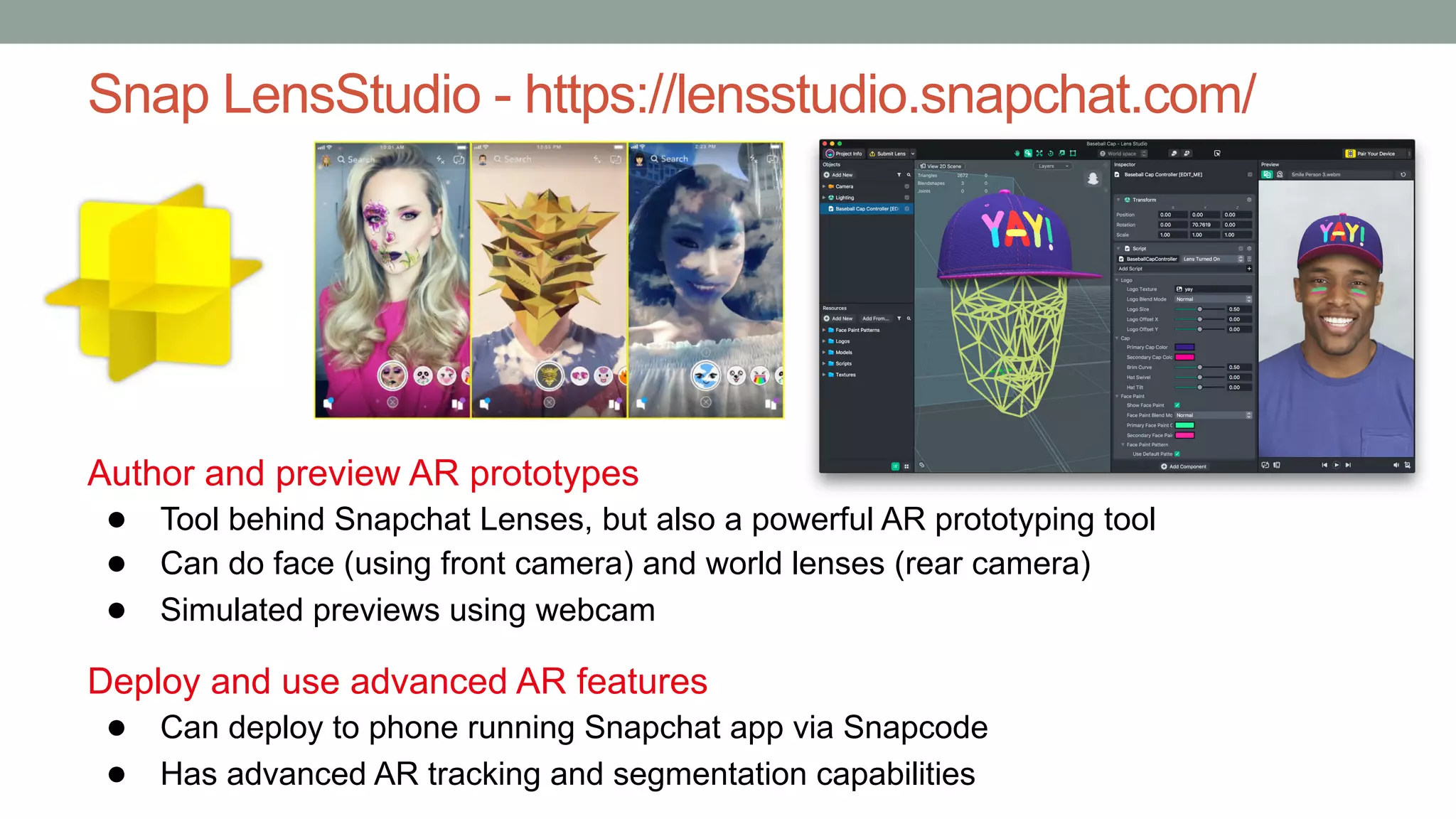
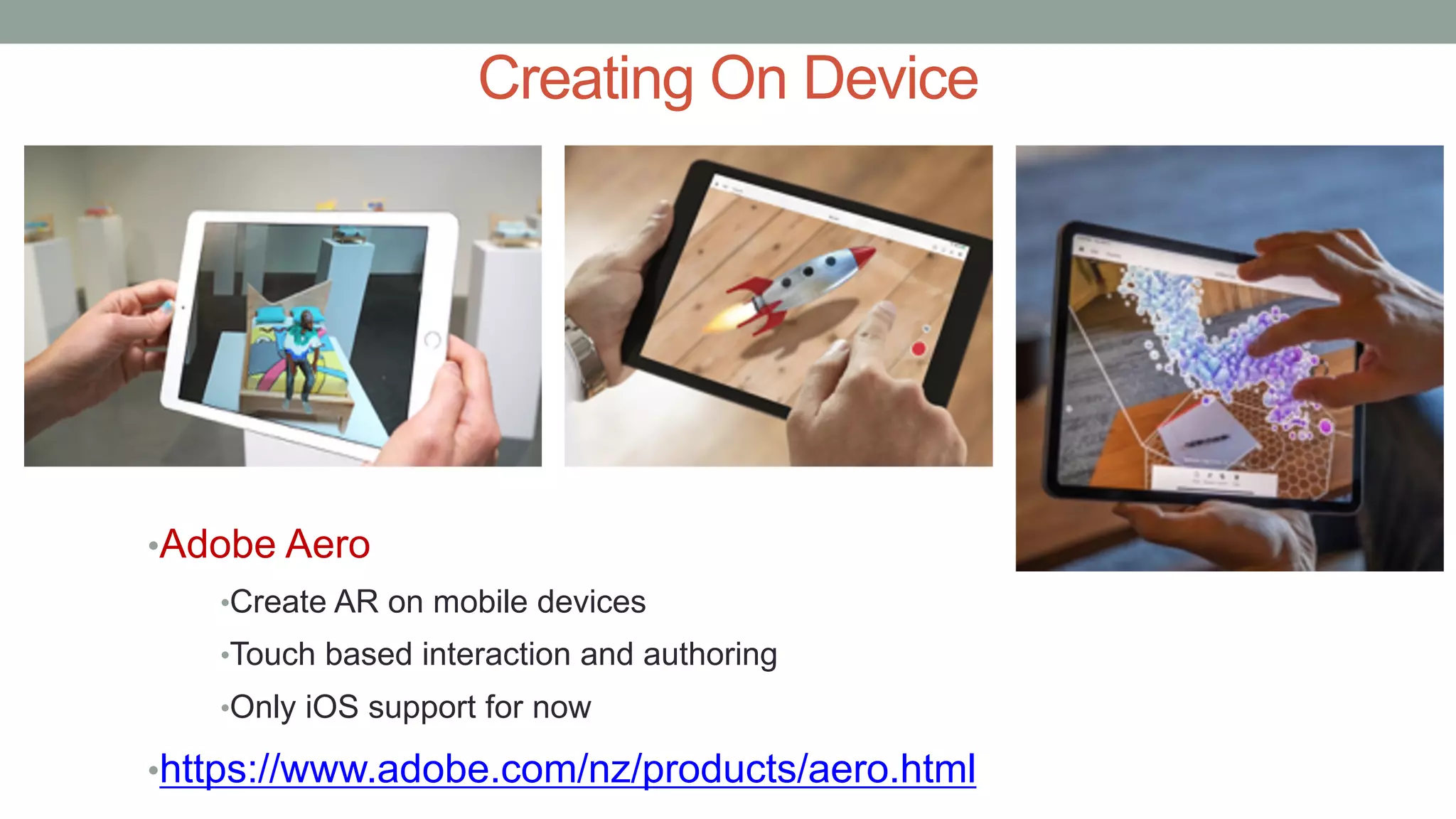
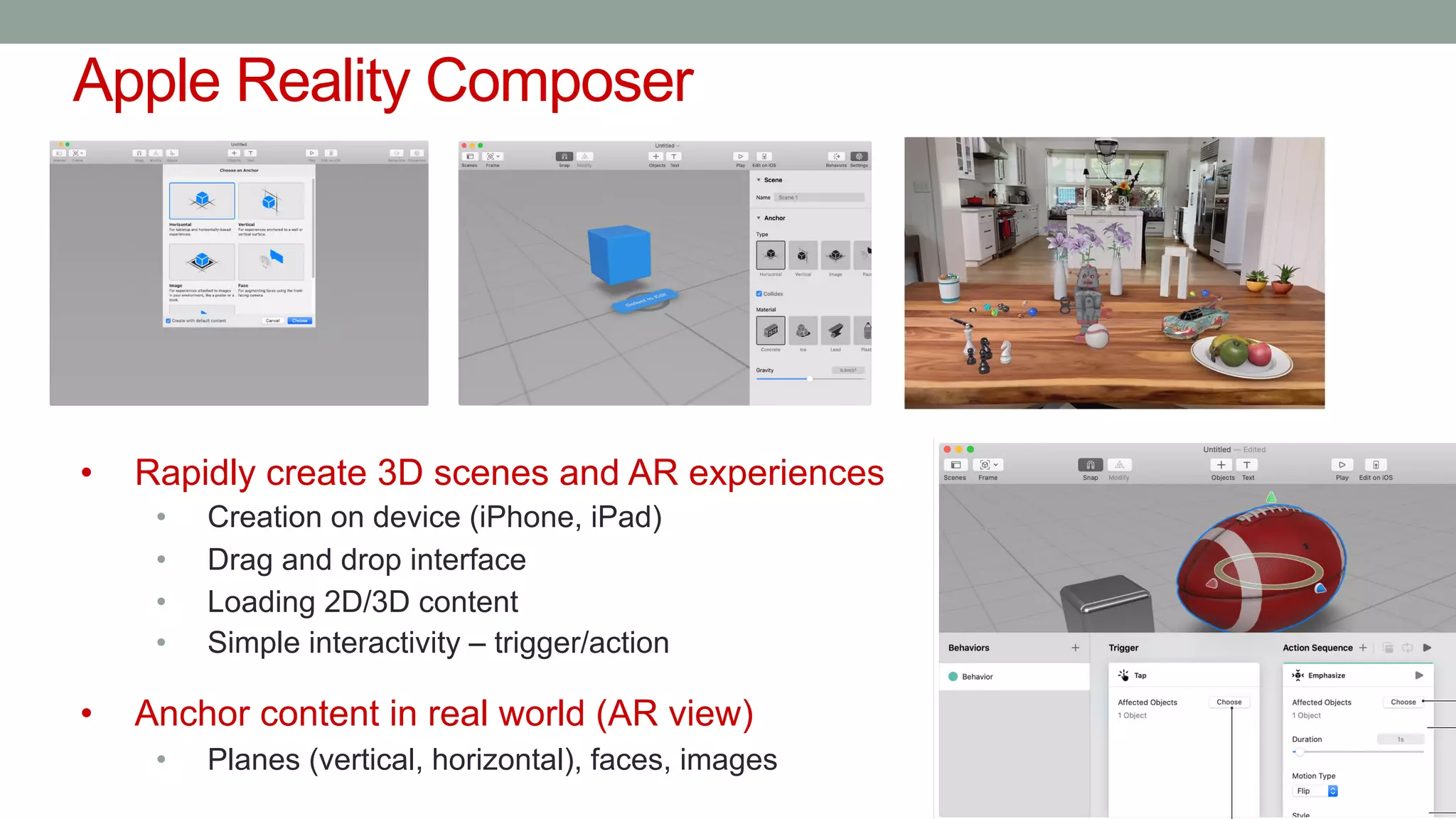
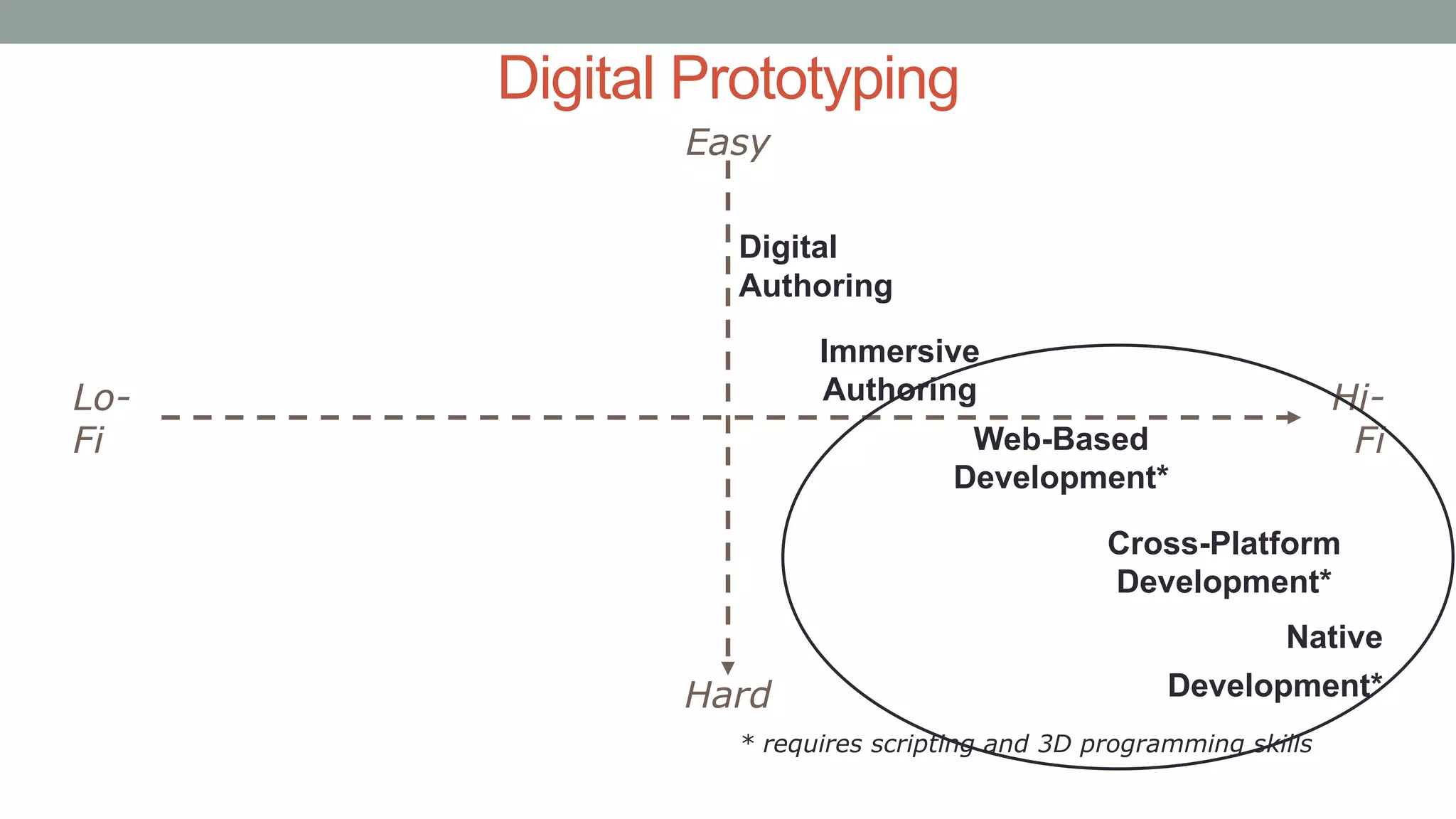
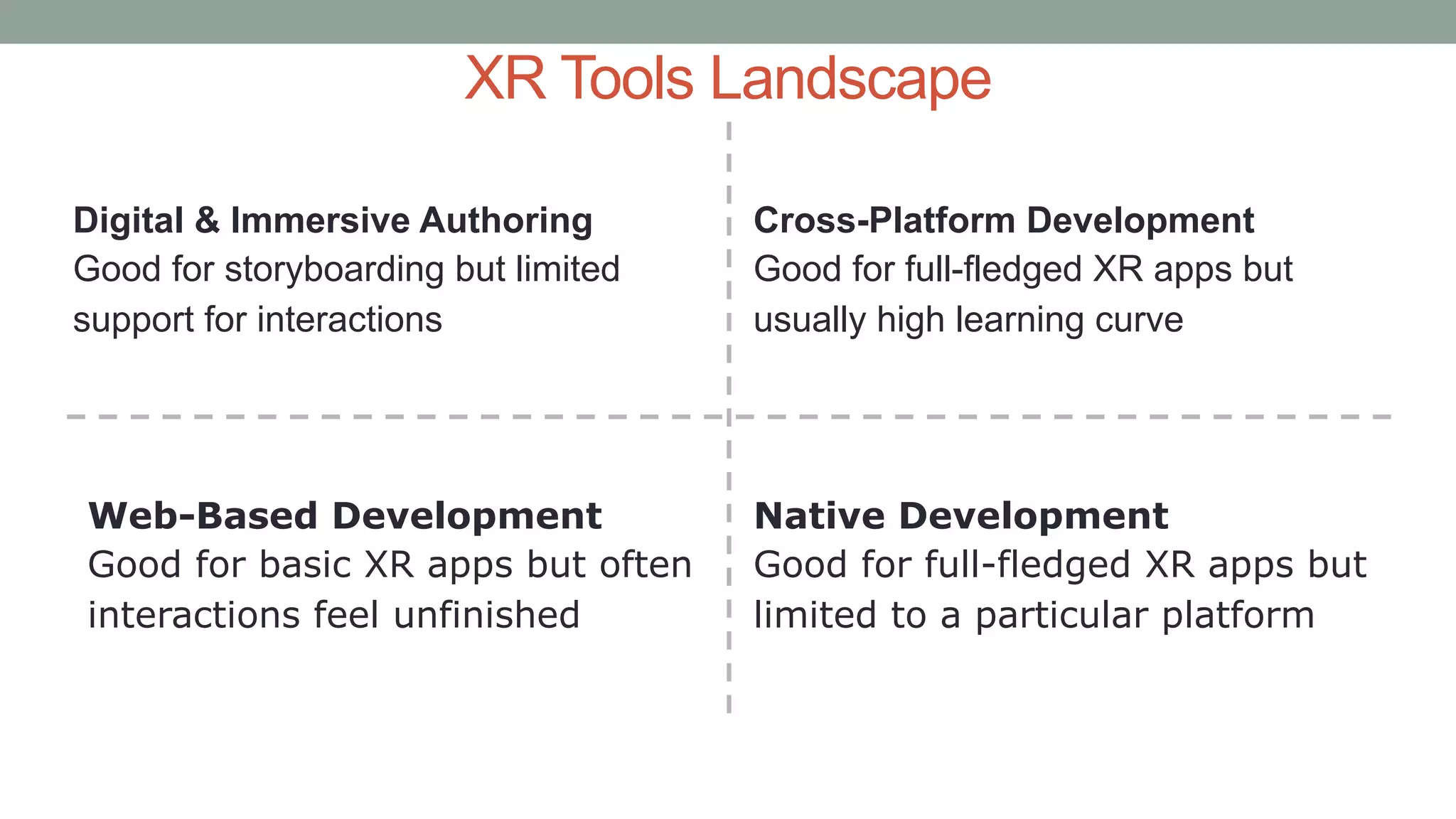
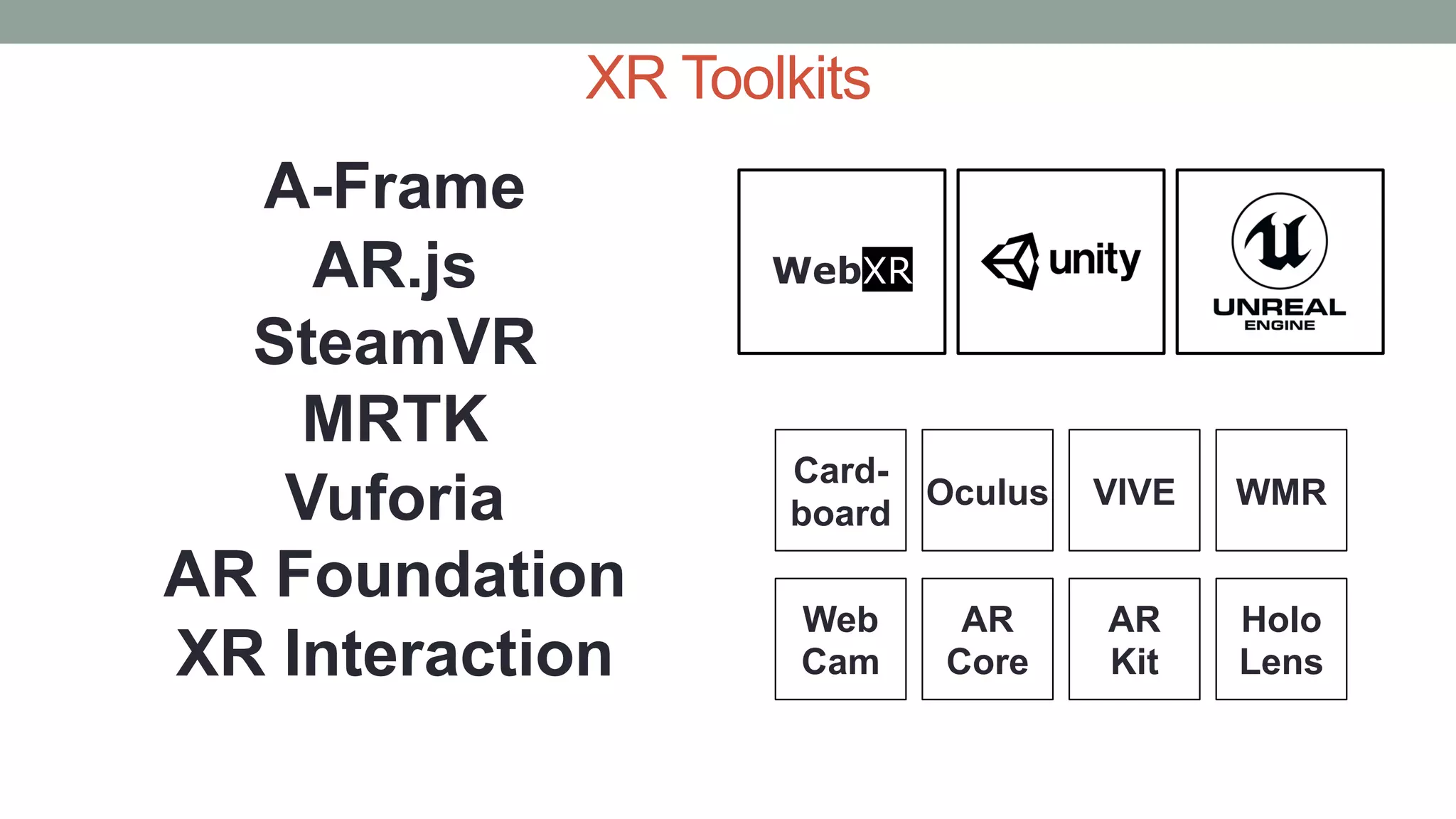
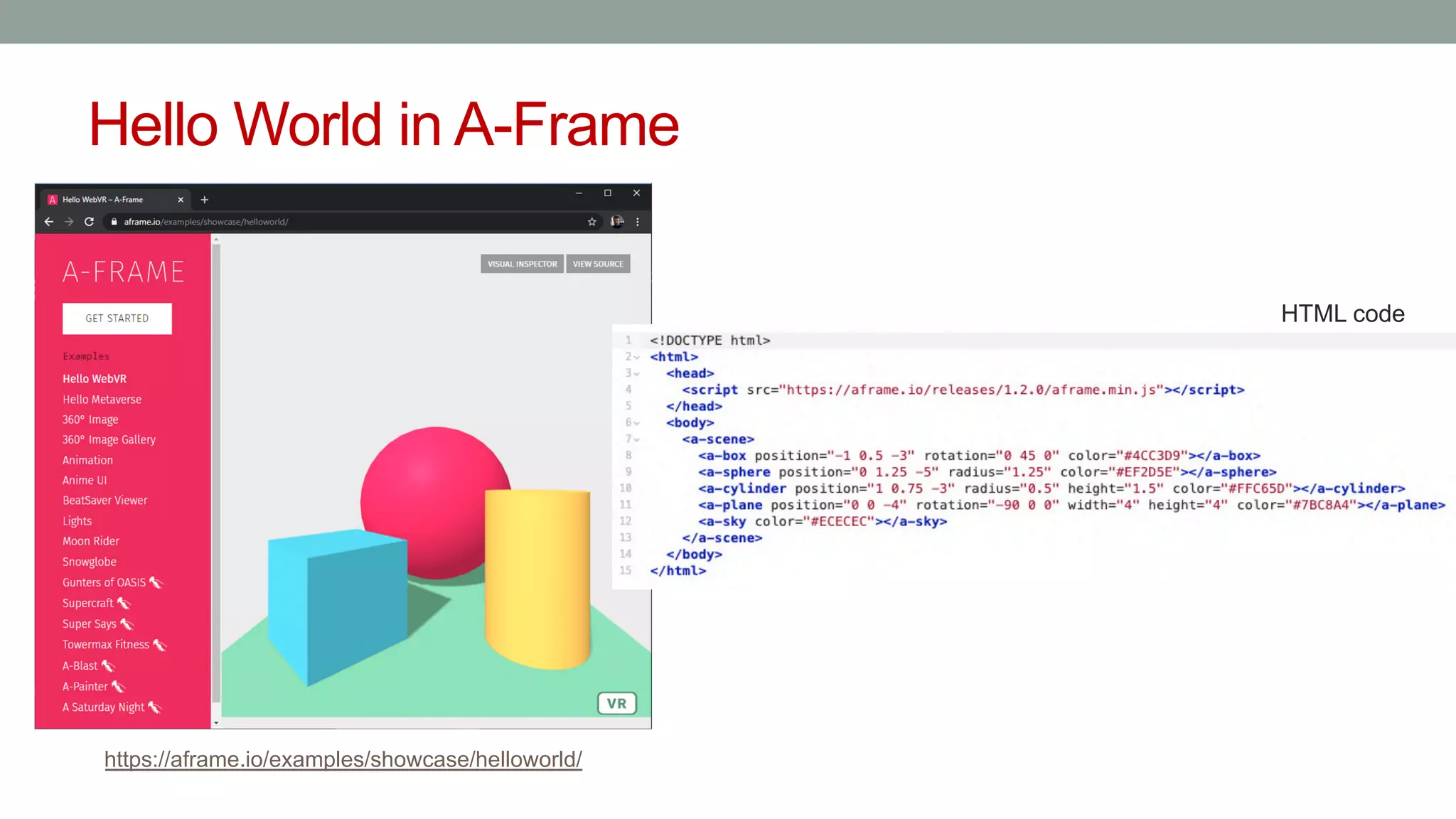
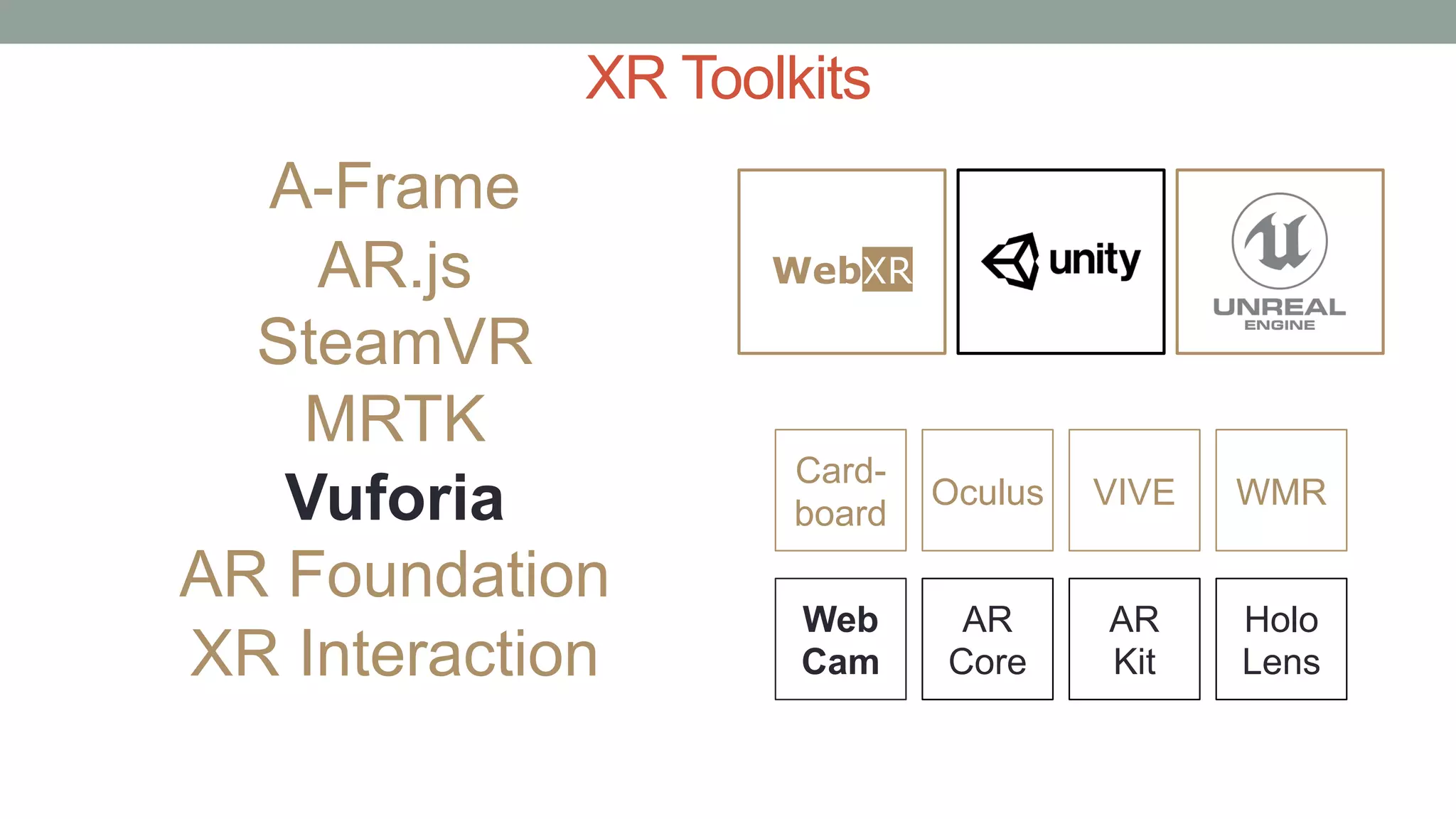
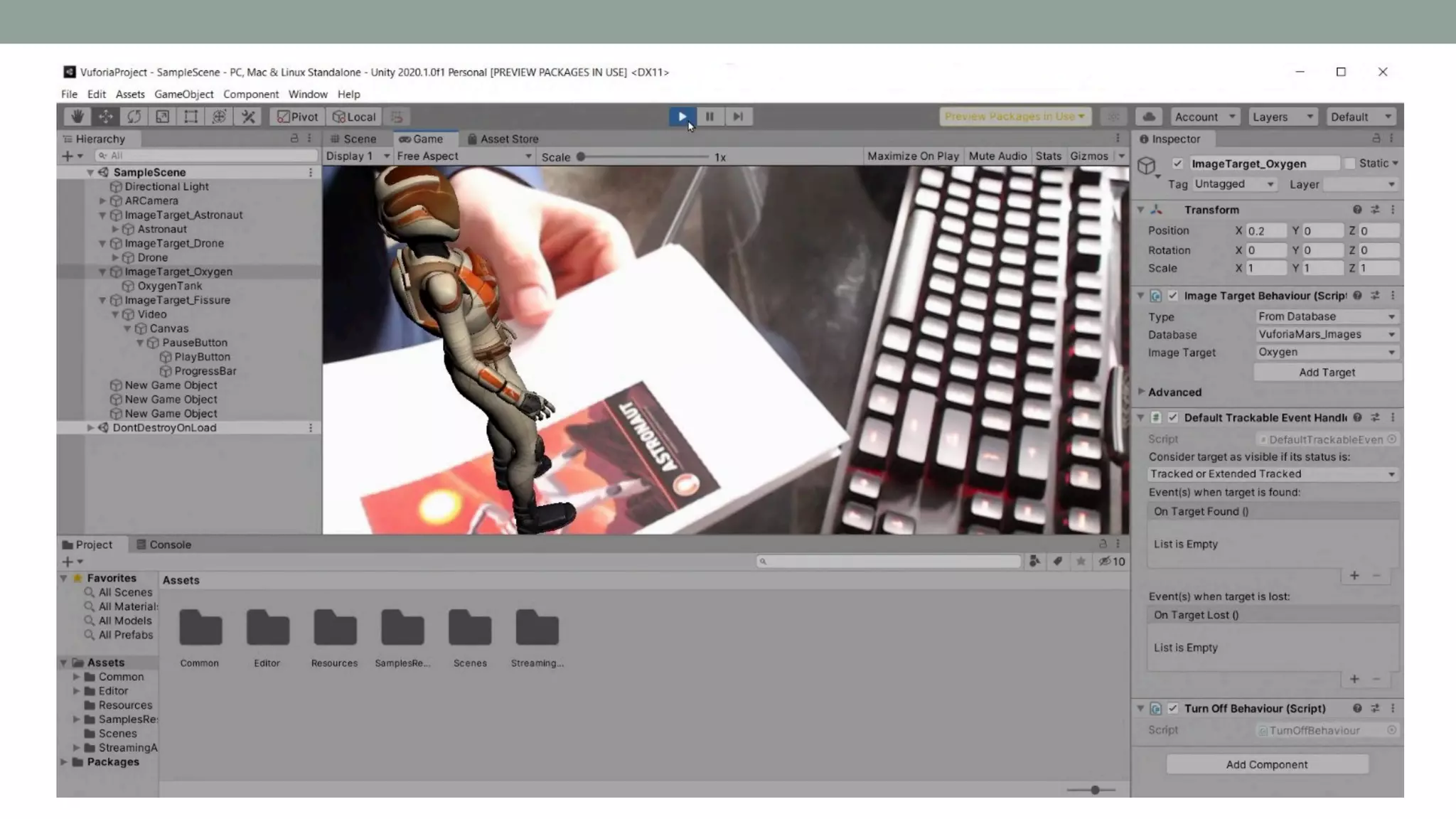
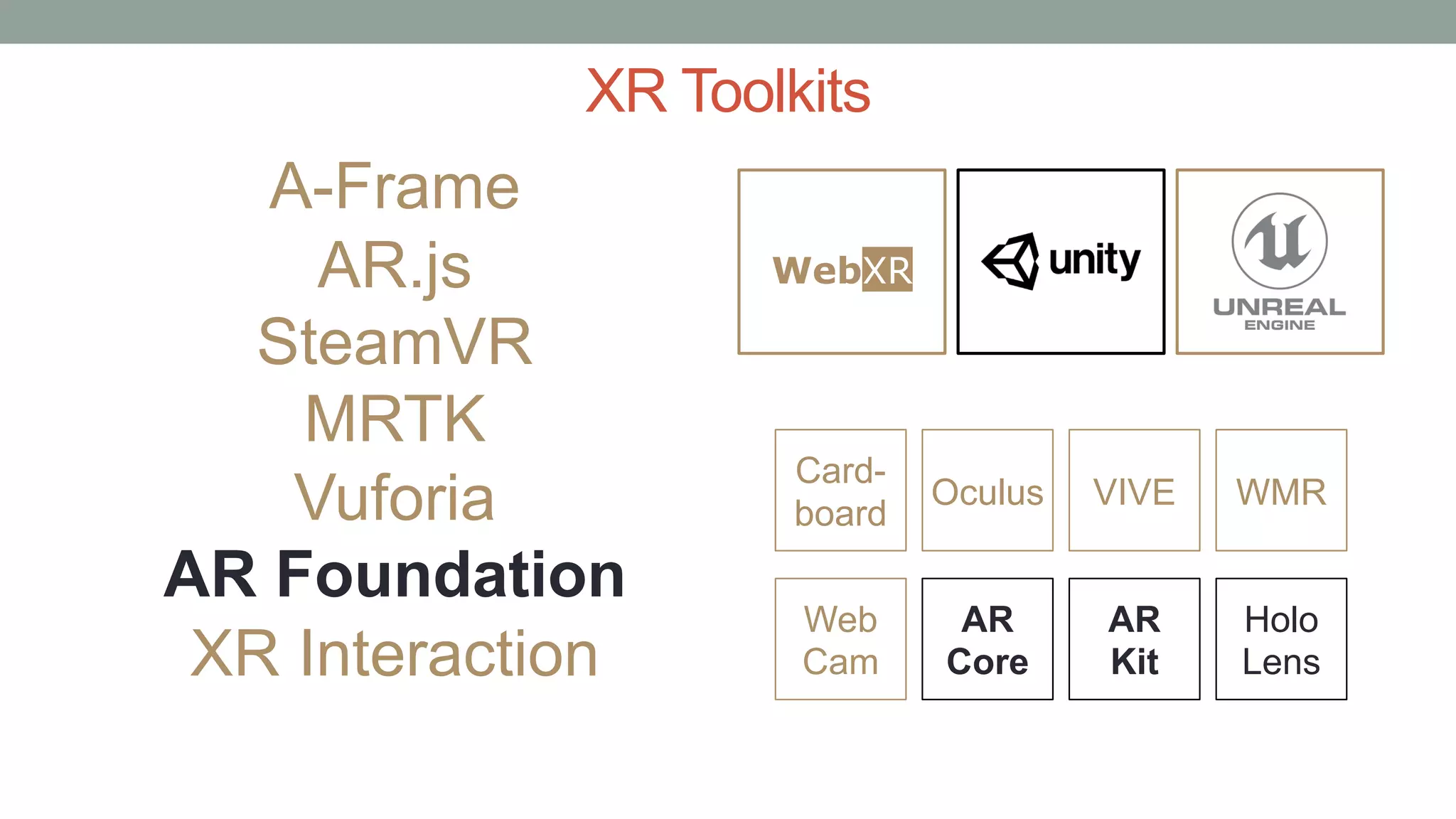
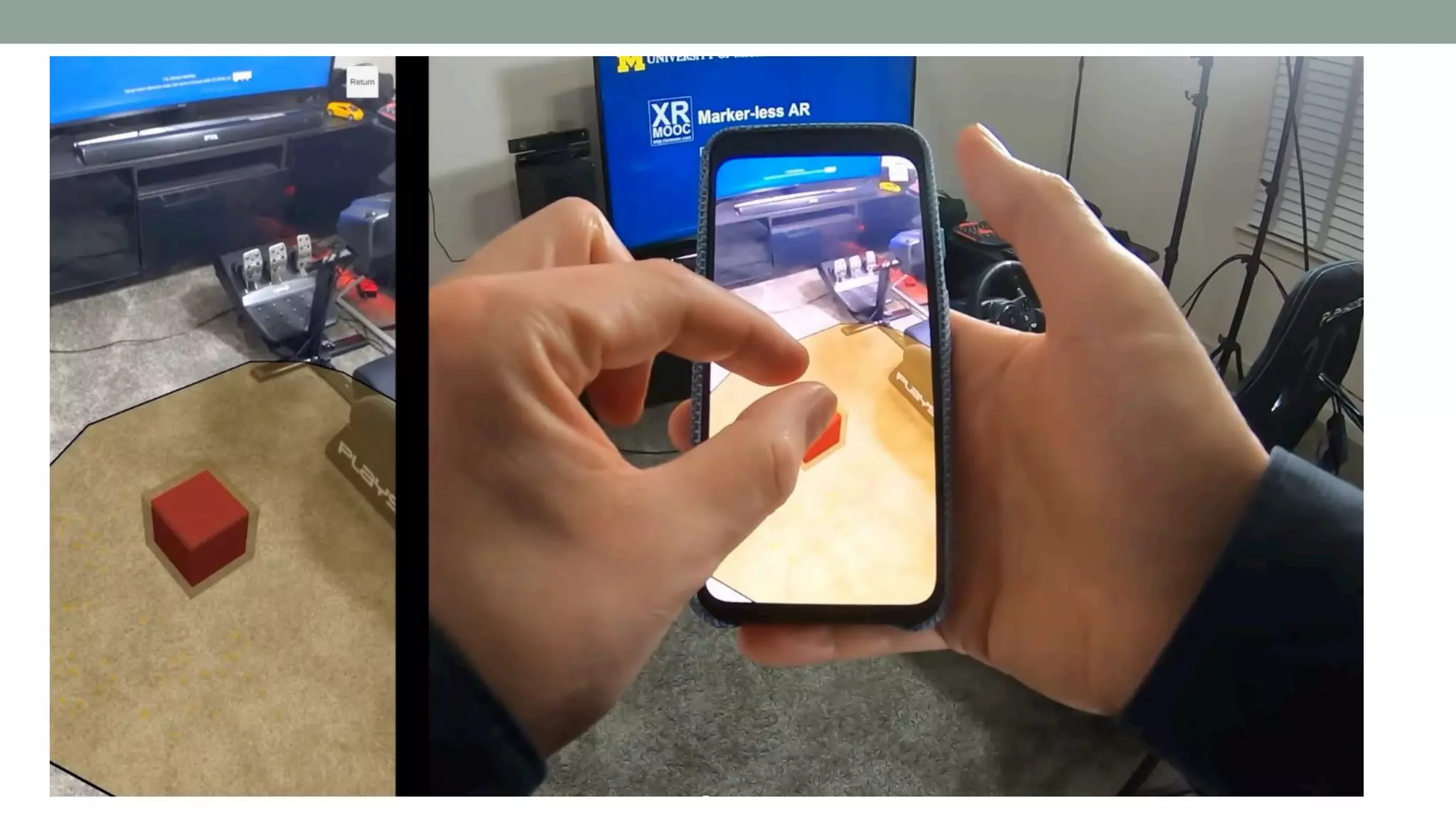
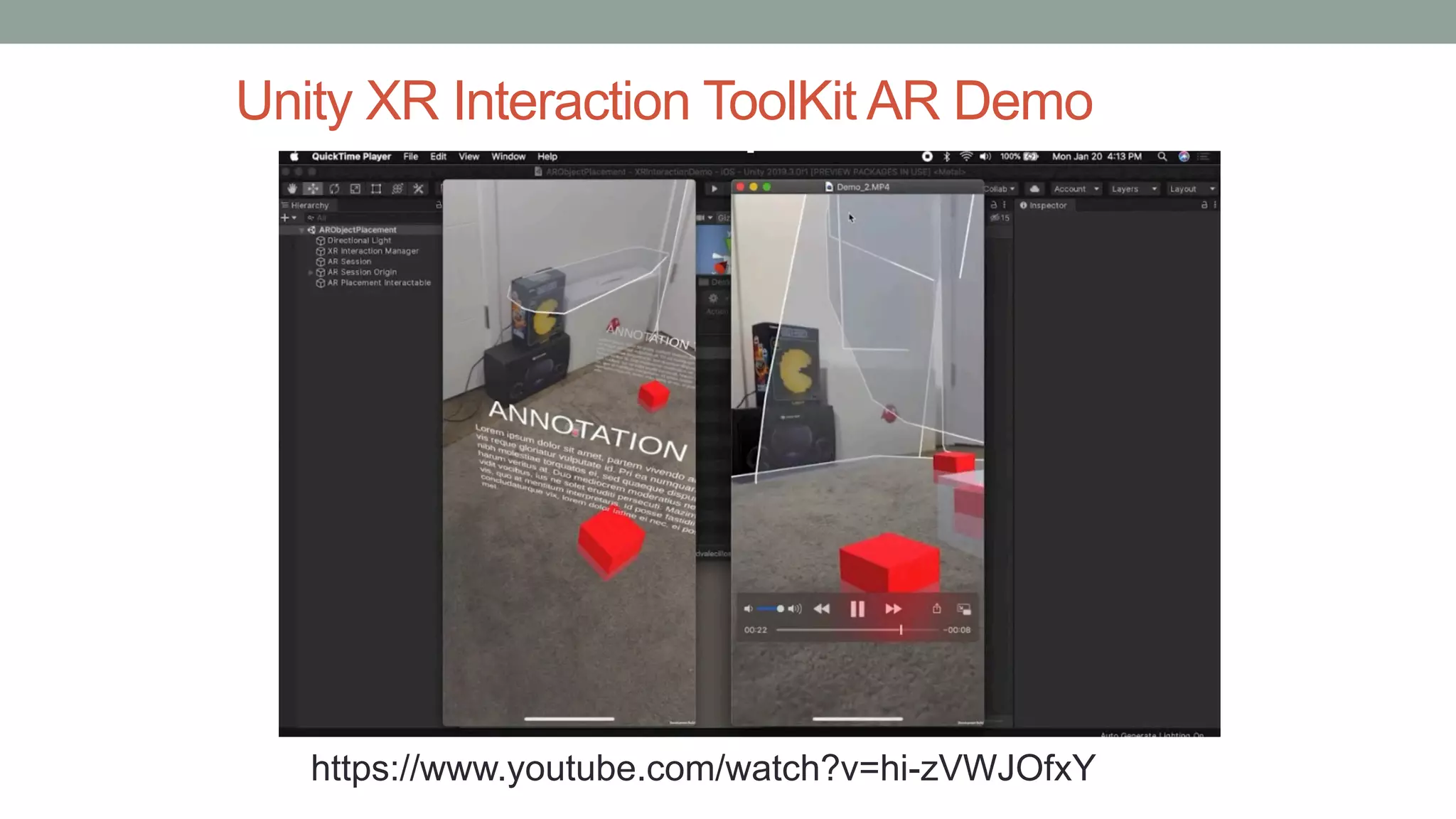
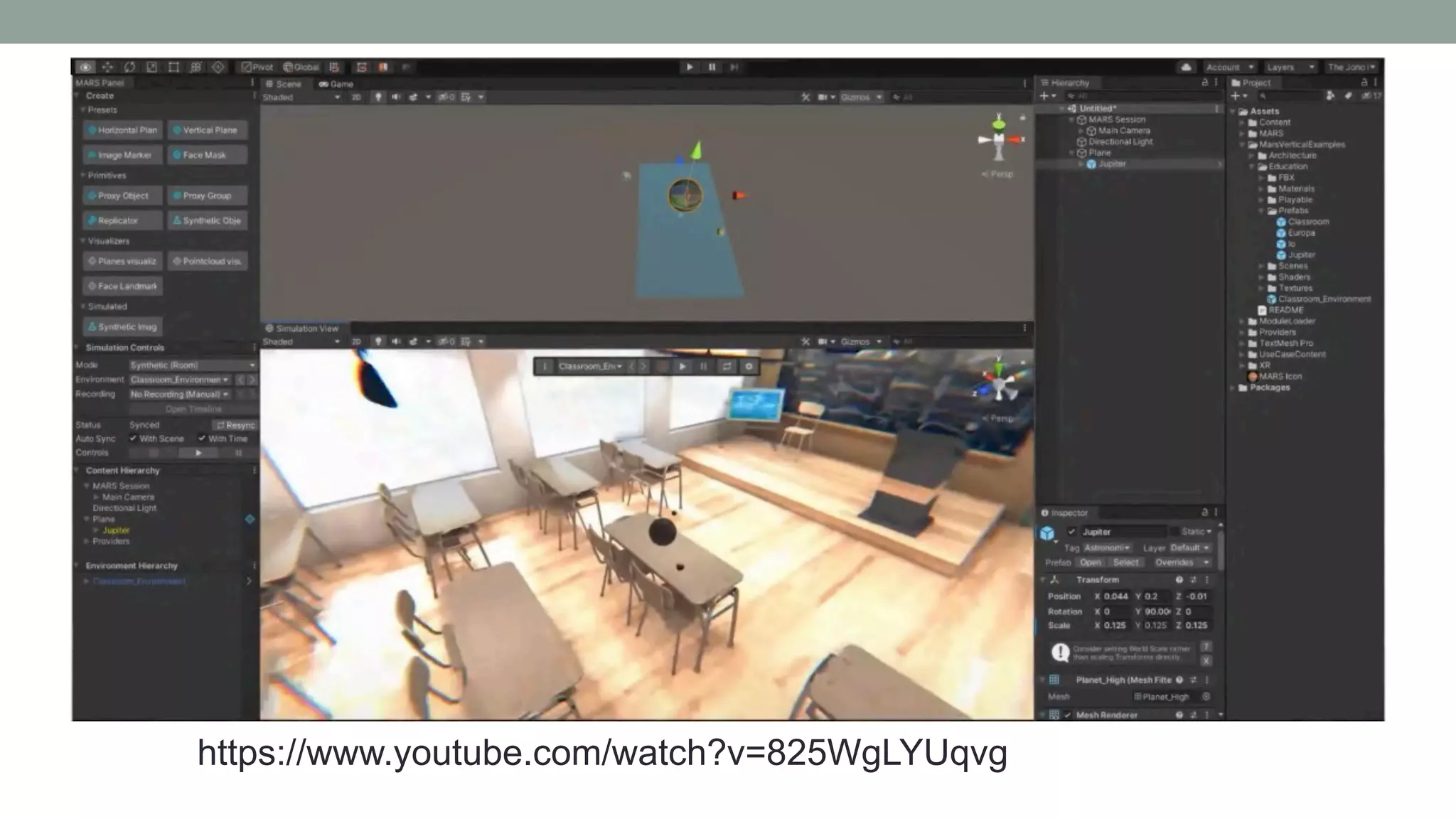
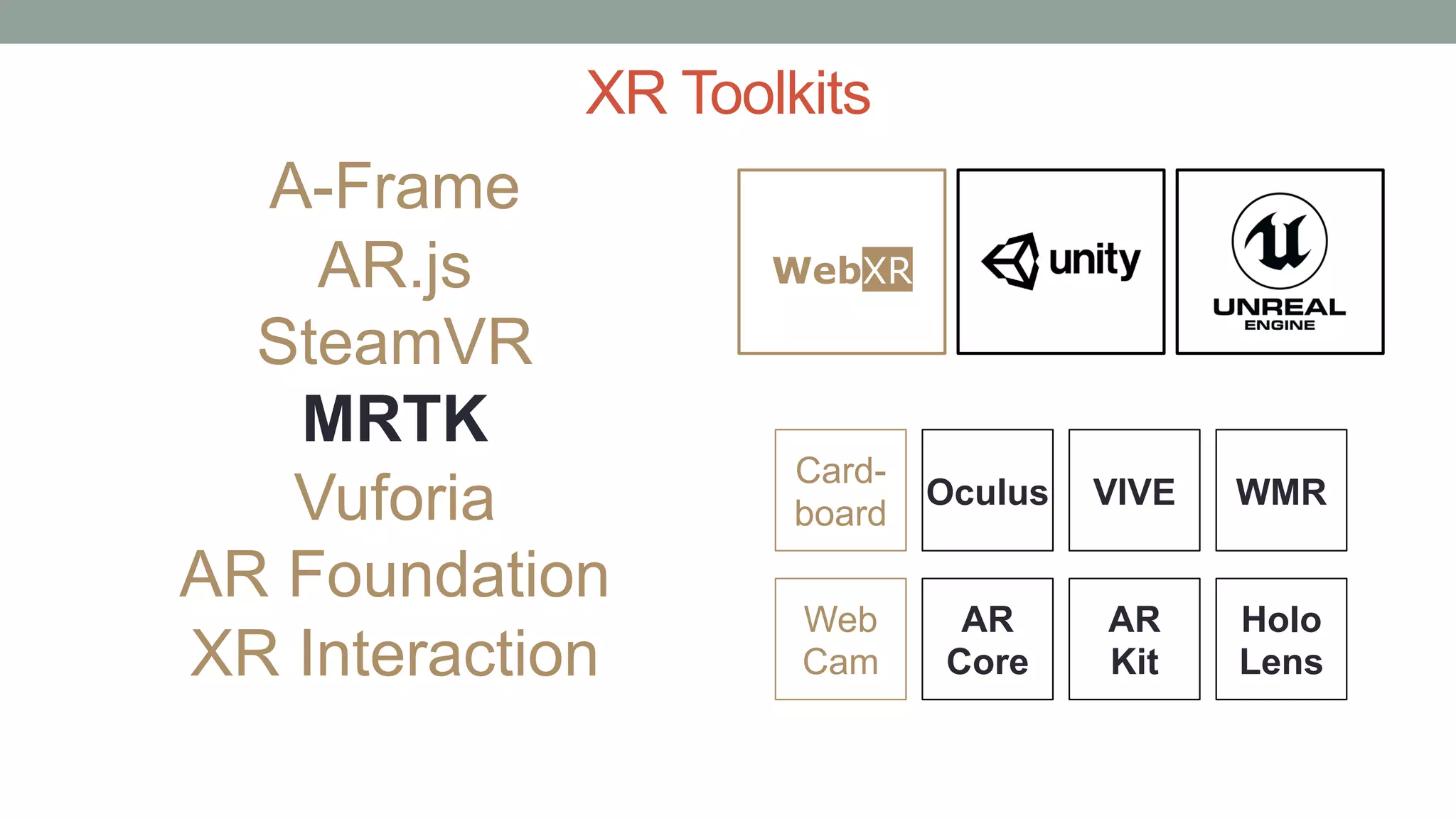
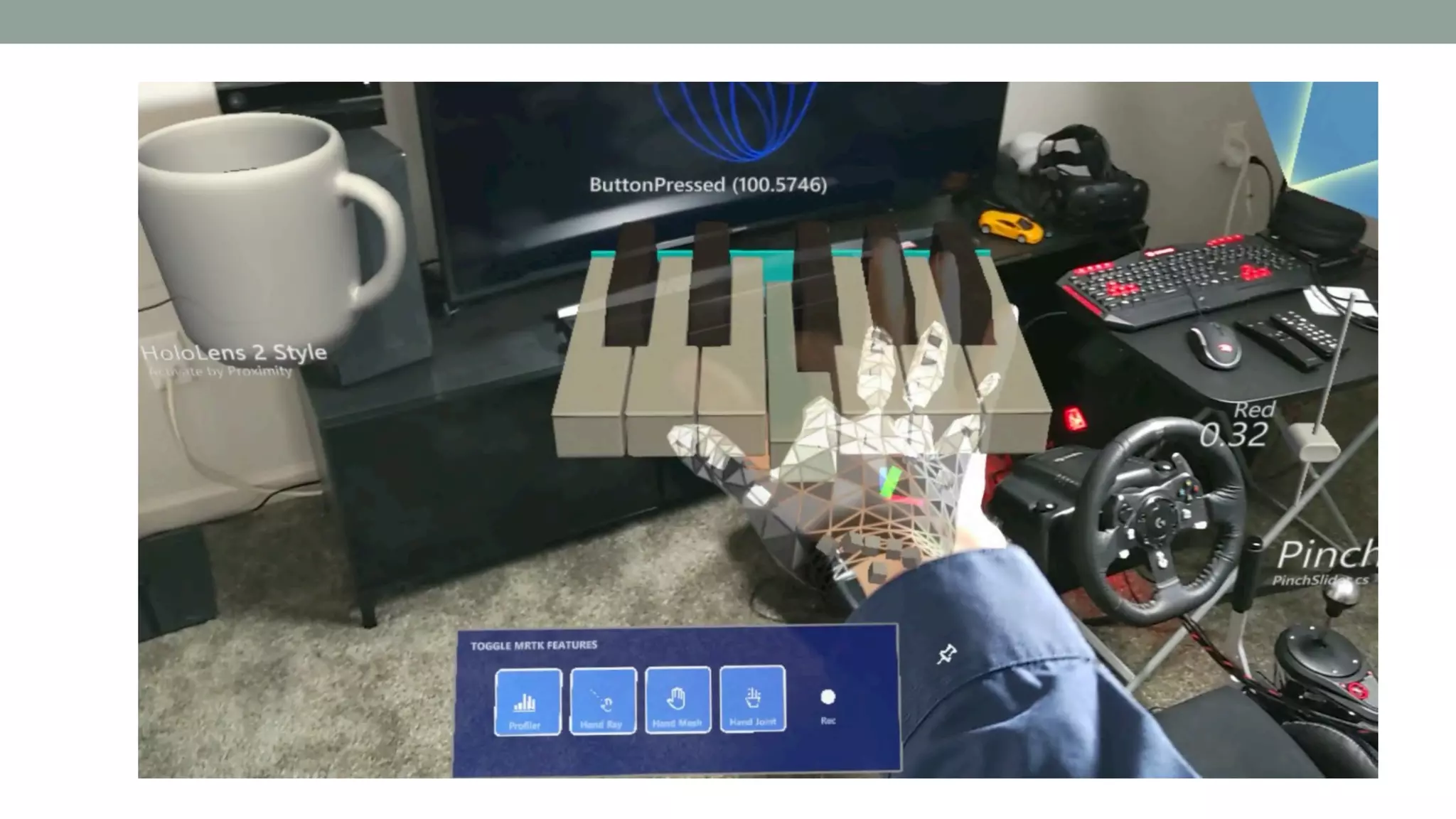
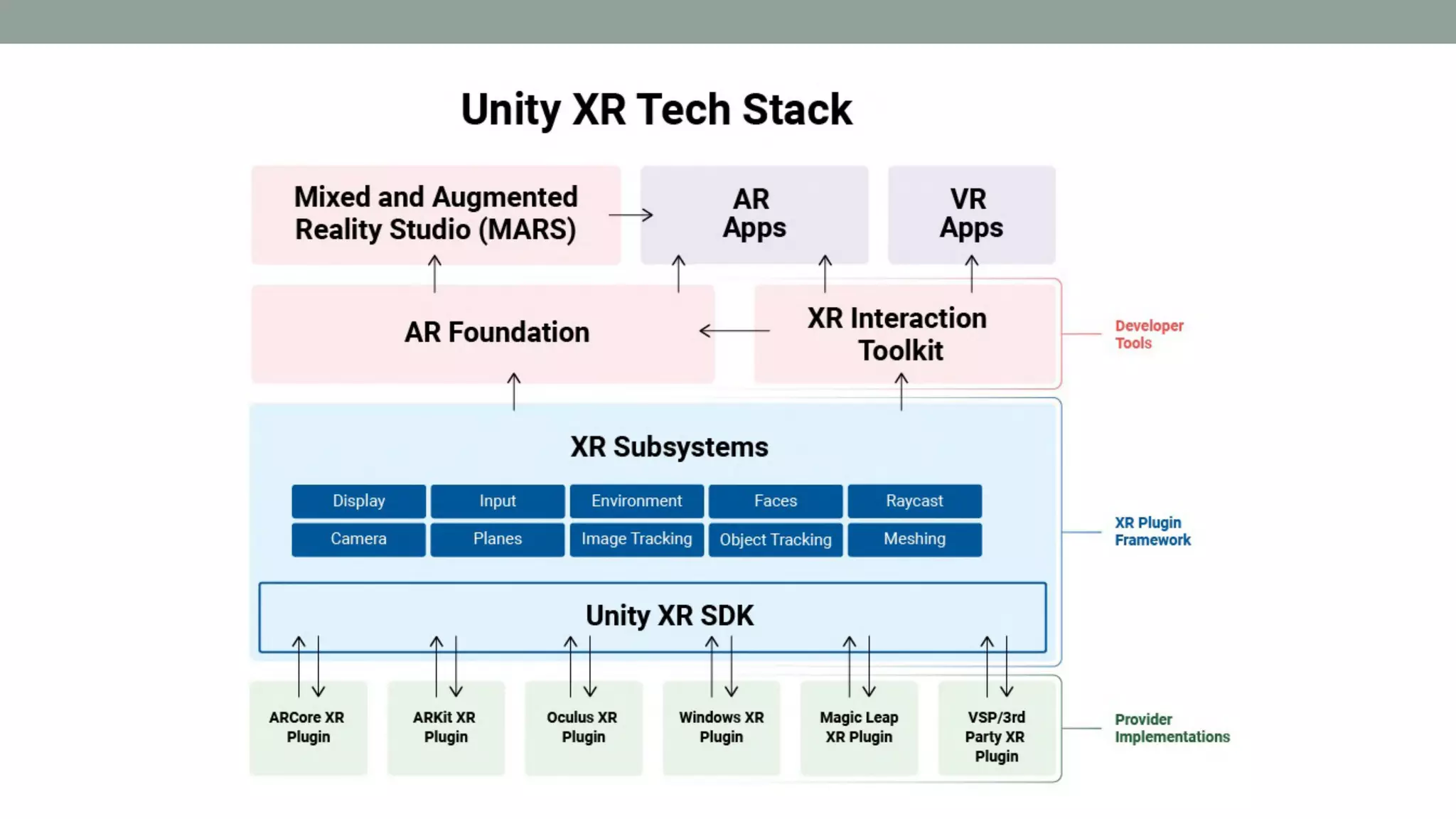
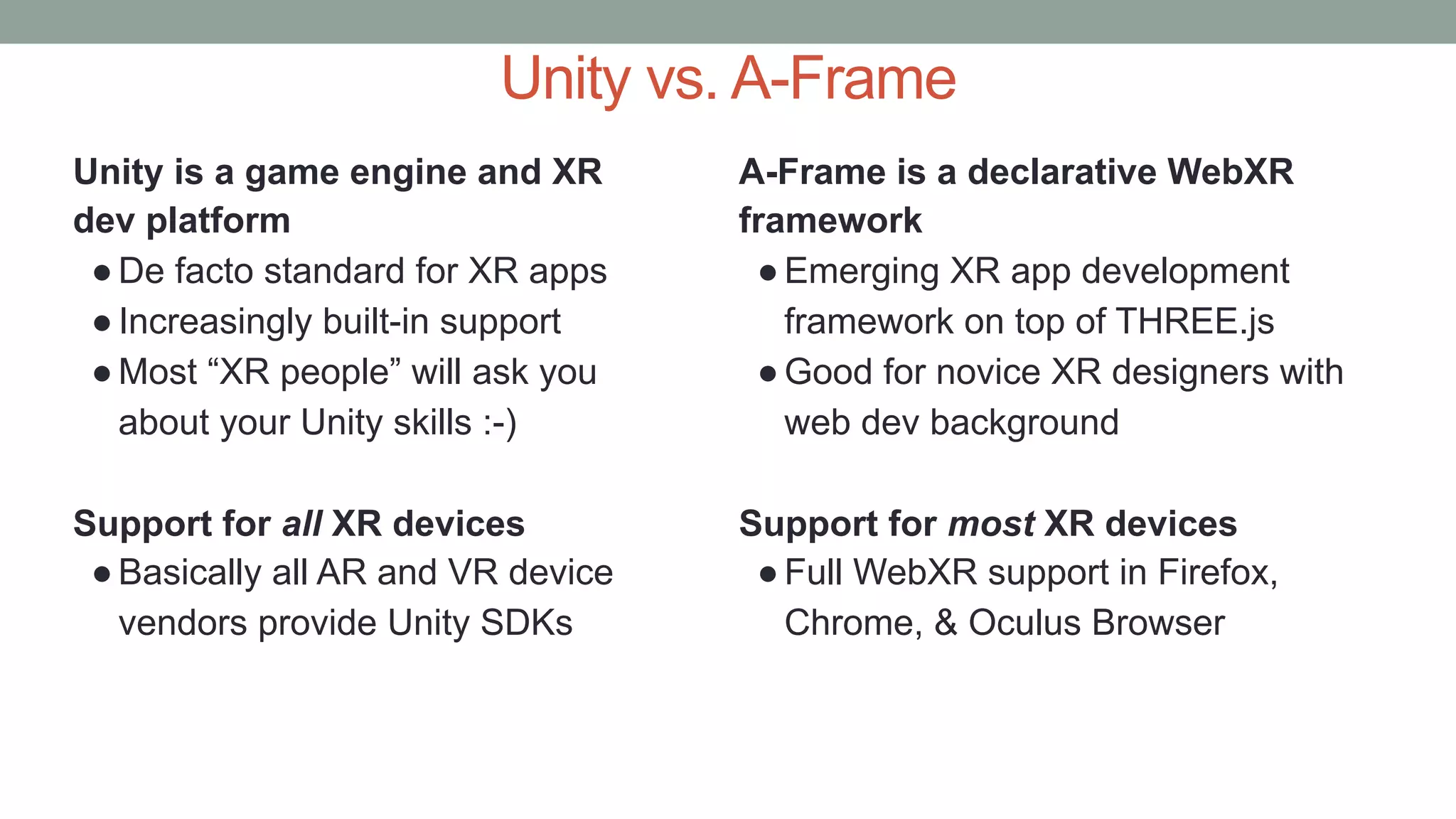
The document discusses various types of augmented reality (AR) interactions, including browsing interfaces, 3D AR, tangible AR, and natural interfaces that facilitate user engagement through gestures, speech, and gaze. It emphasizes the importance of prototyping in interaction design, outlining various high and low fidelity techniques, tools, and processes for developing AR applications. Case studies illustrate the application of AR in navigational aids and immersive experiences, alongside tools for digital authoring and interactive design.