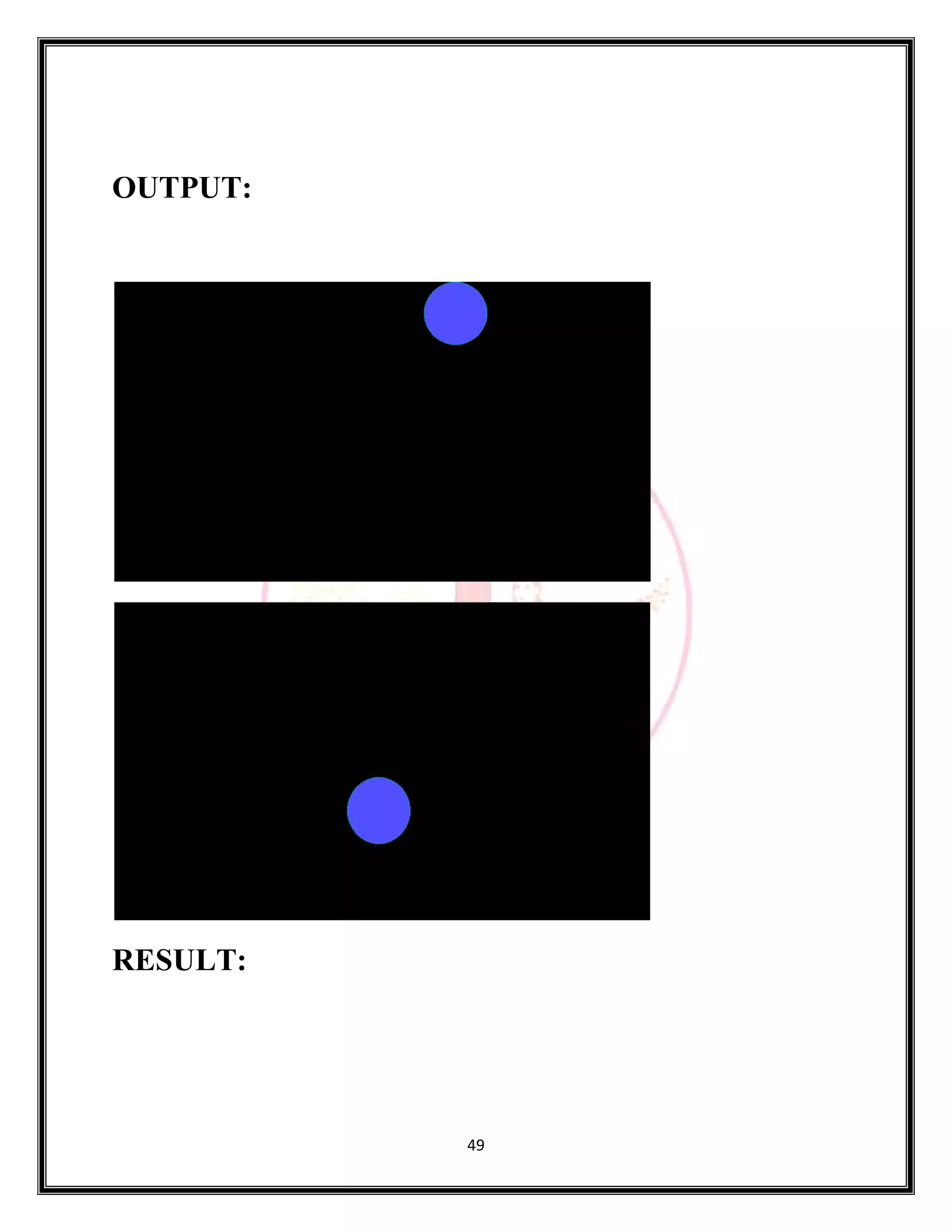
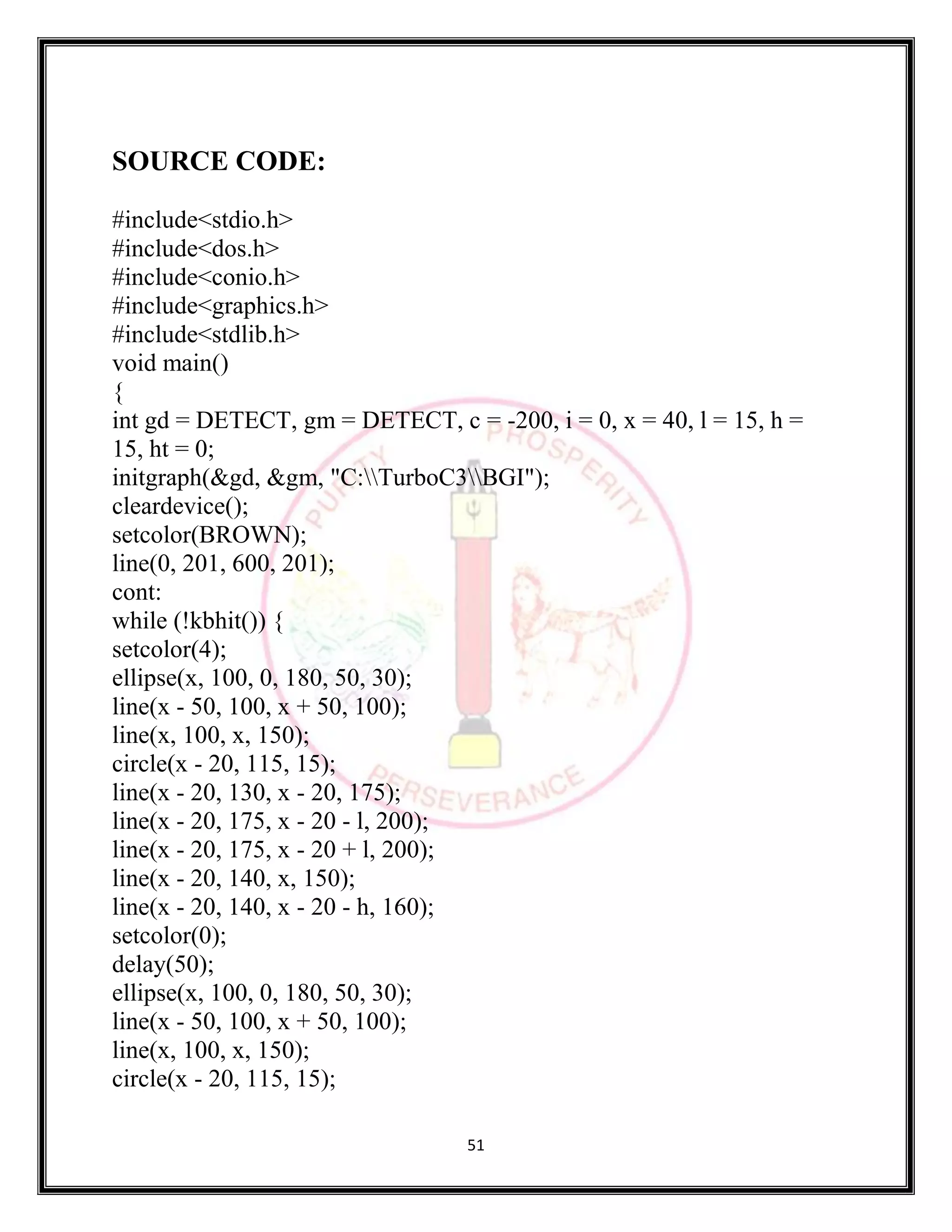
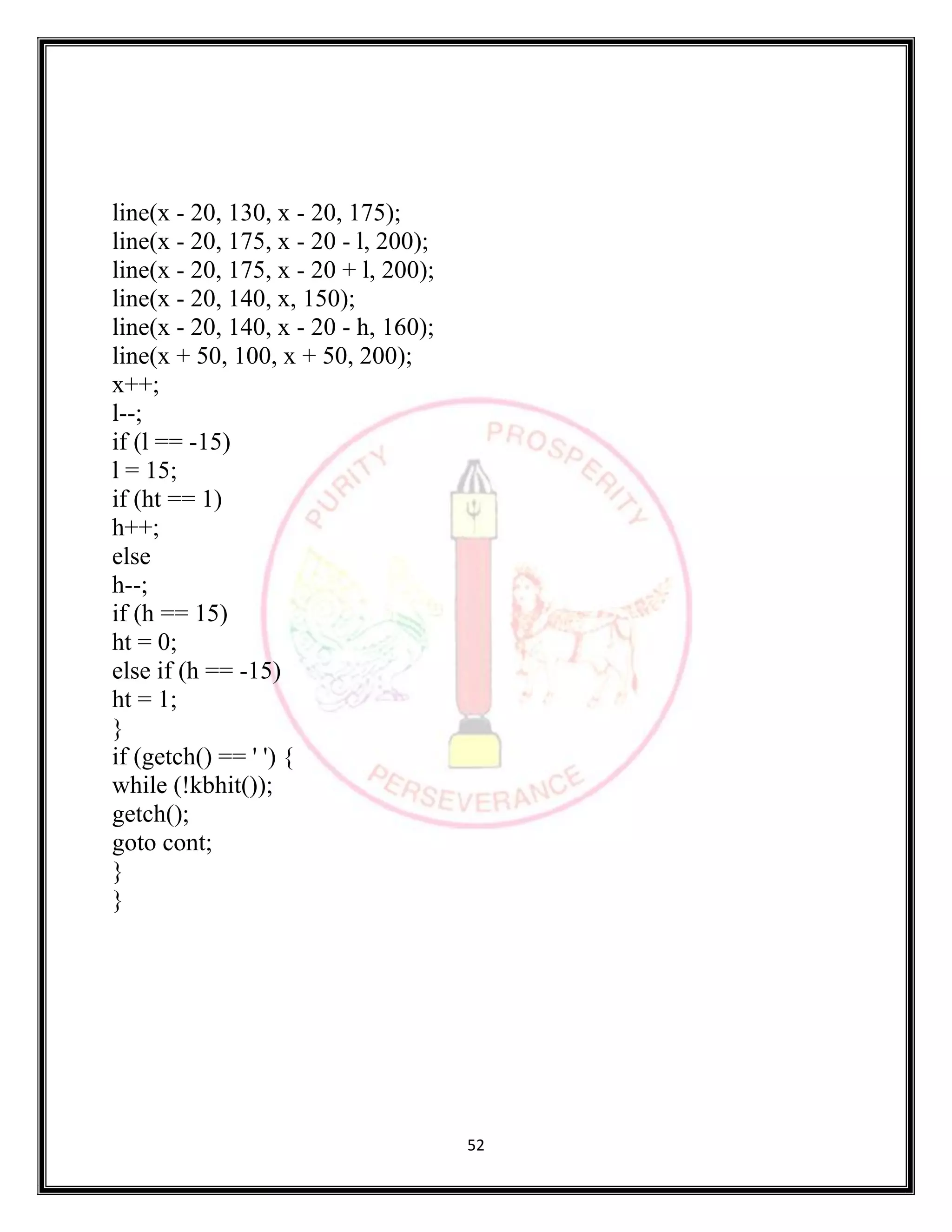
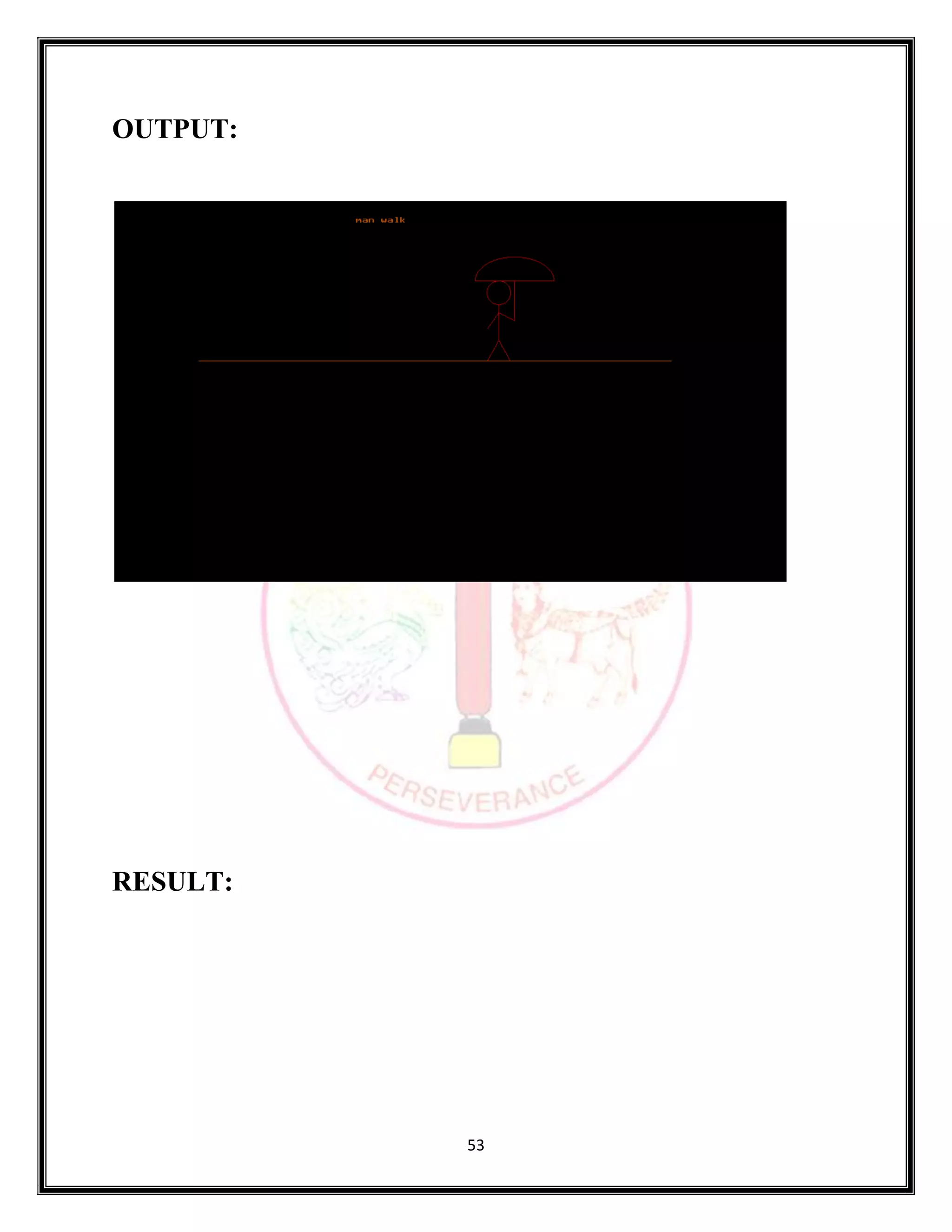
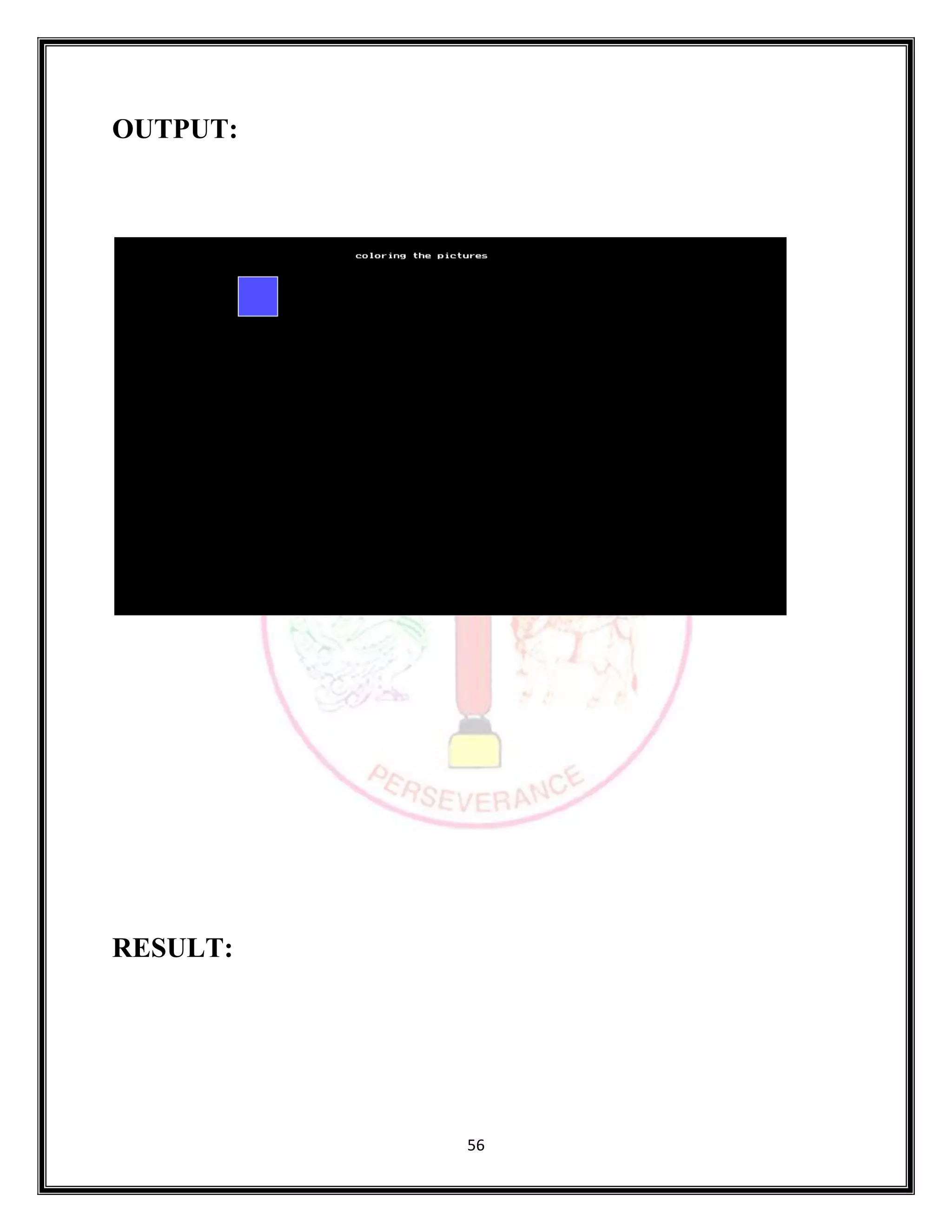
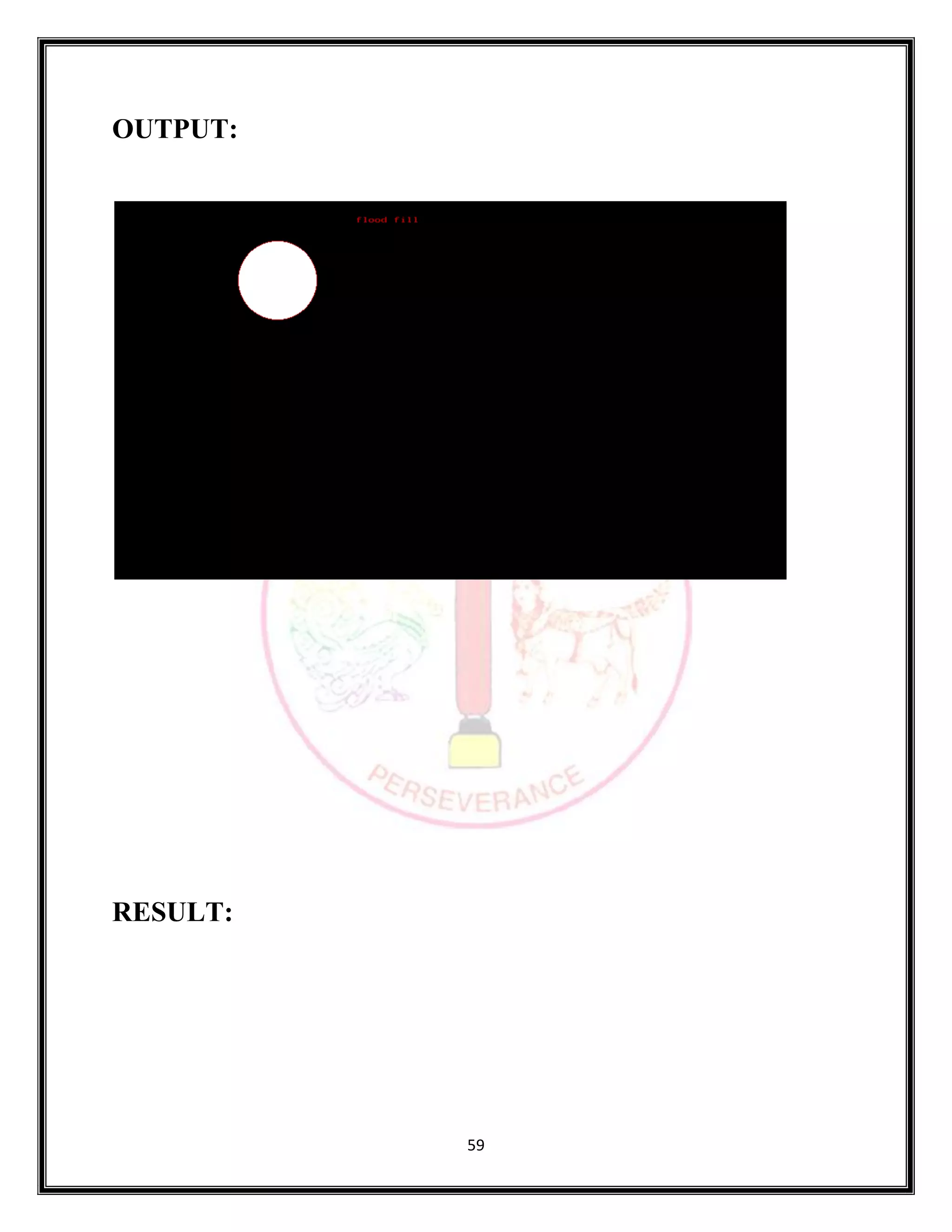
The document provides source code for generating and manipulating computer graphics using various algorithms. It includes algorithms for drawing lines, circles and curves, as well as algorithms for translating, rotating, and scaling two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects. The source code is written in C/C++ and uses graphics libraries to output the results. Various input parameters are taken from the user and output is displayed to demonstrate the algorithms.





























![42
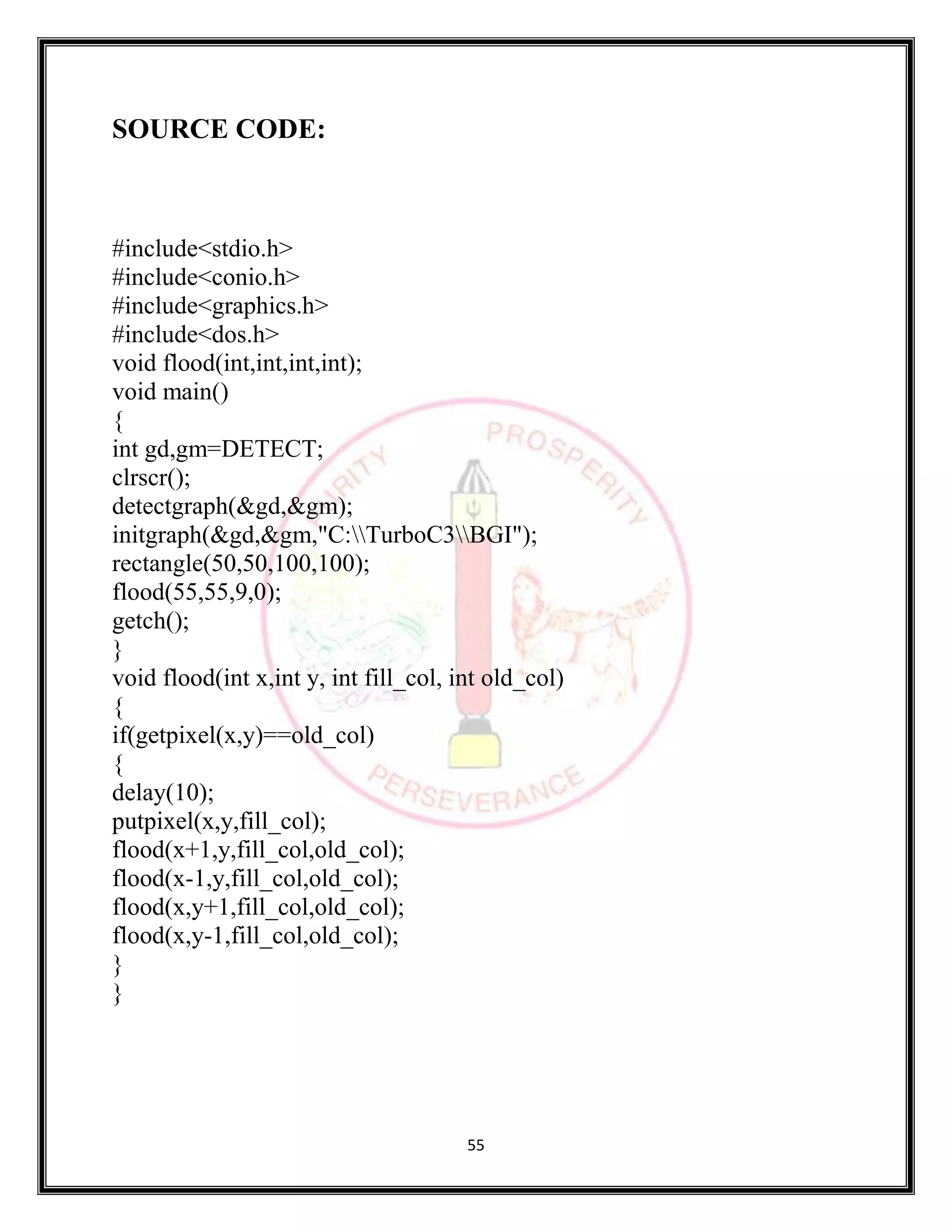
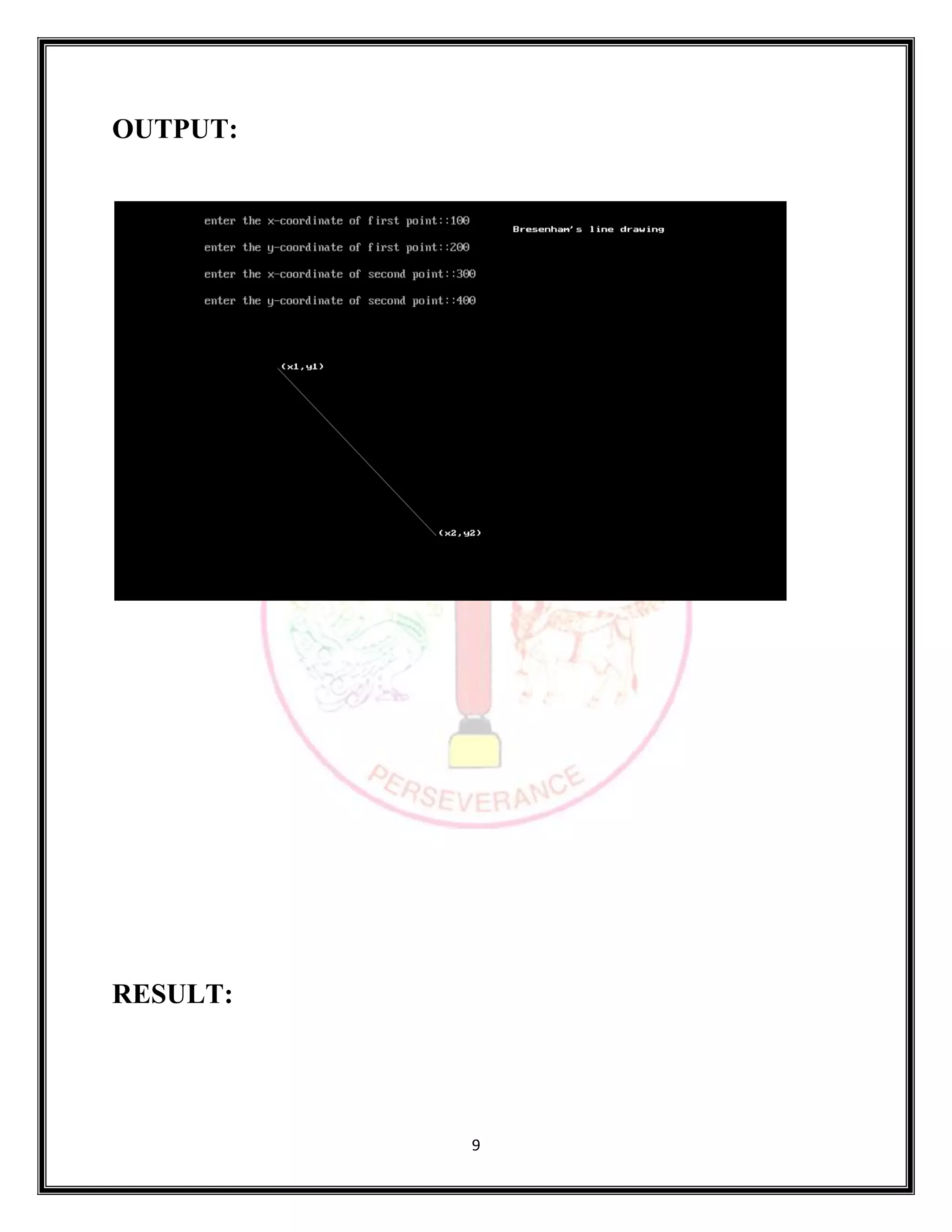
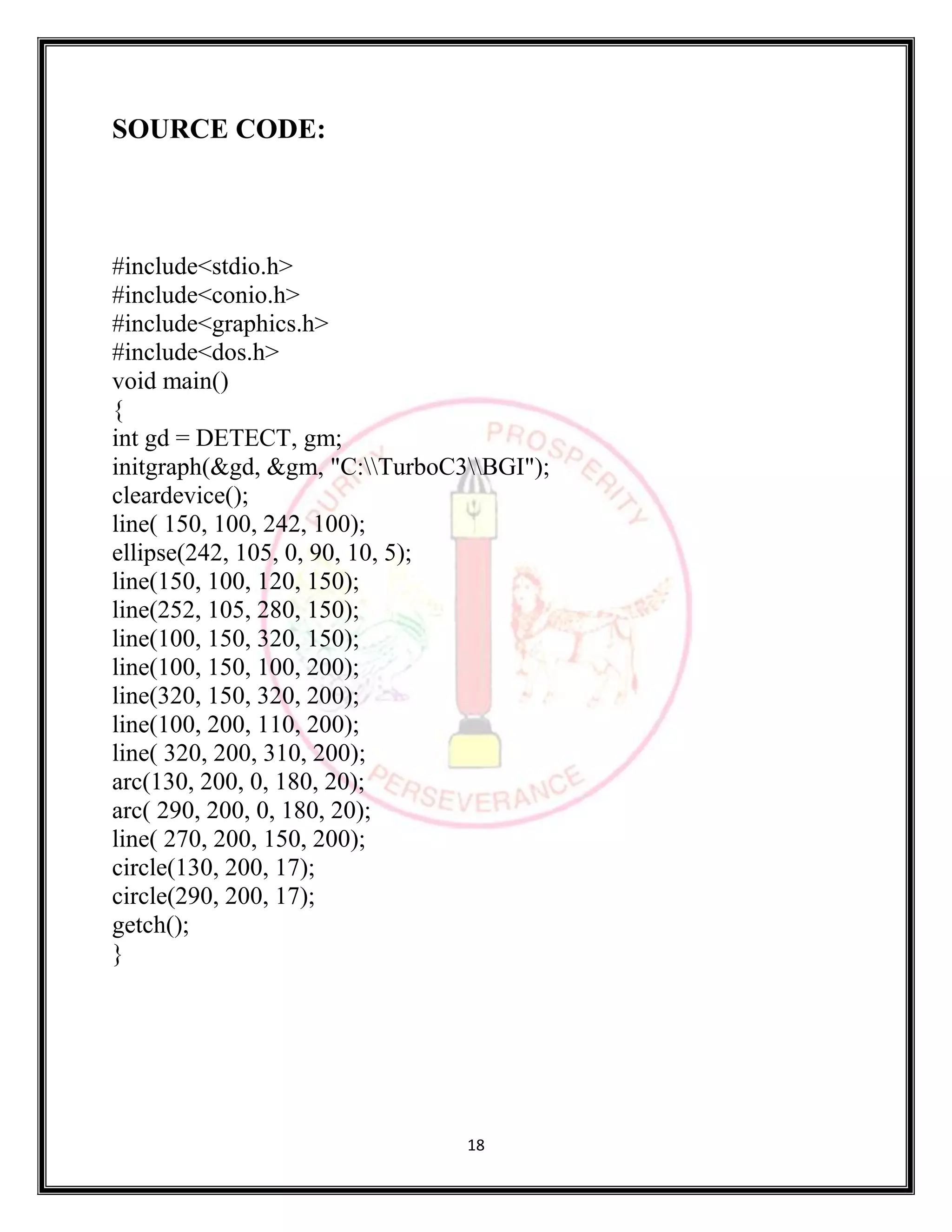
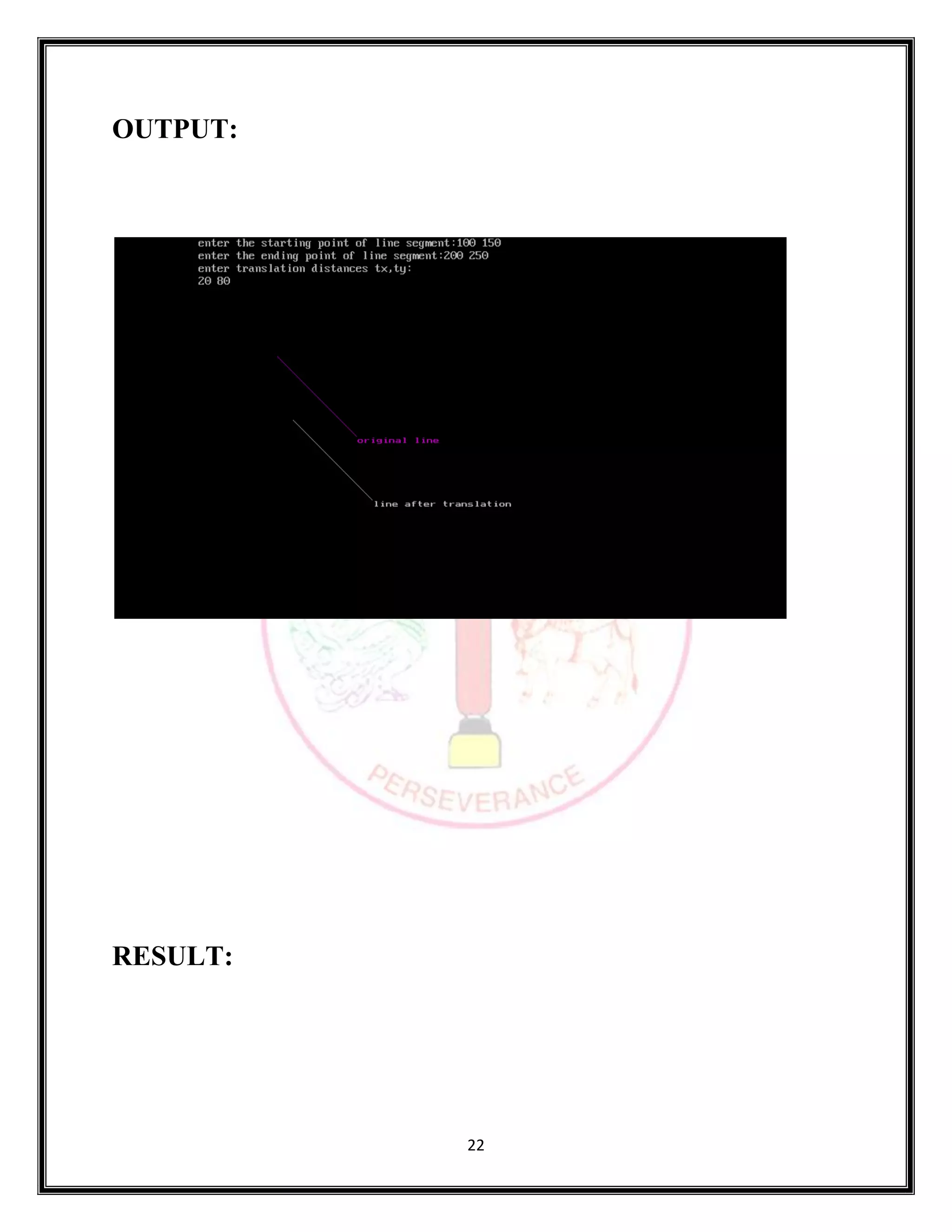
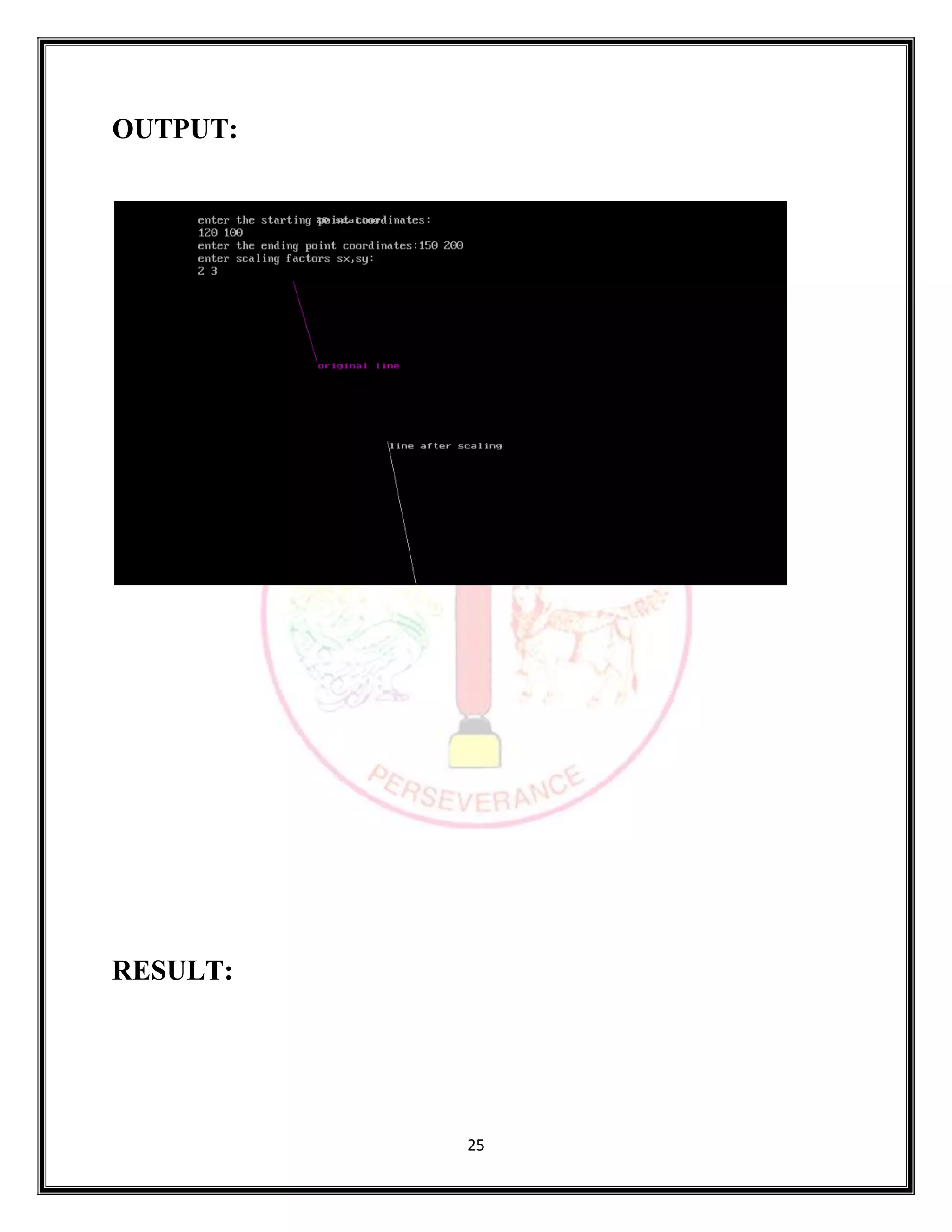
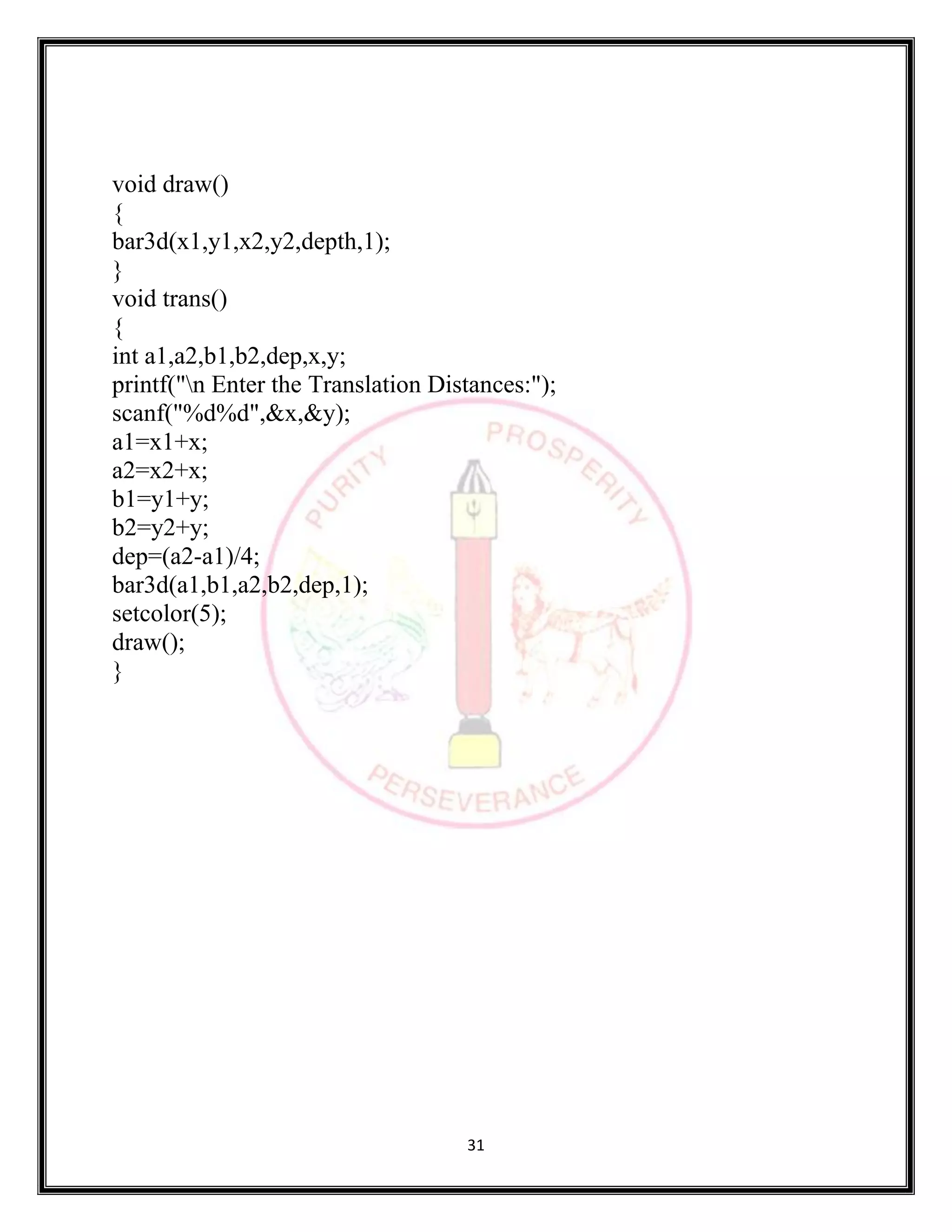
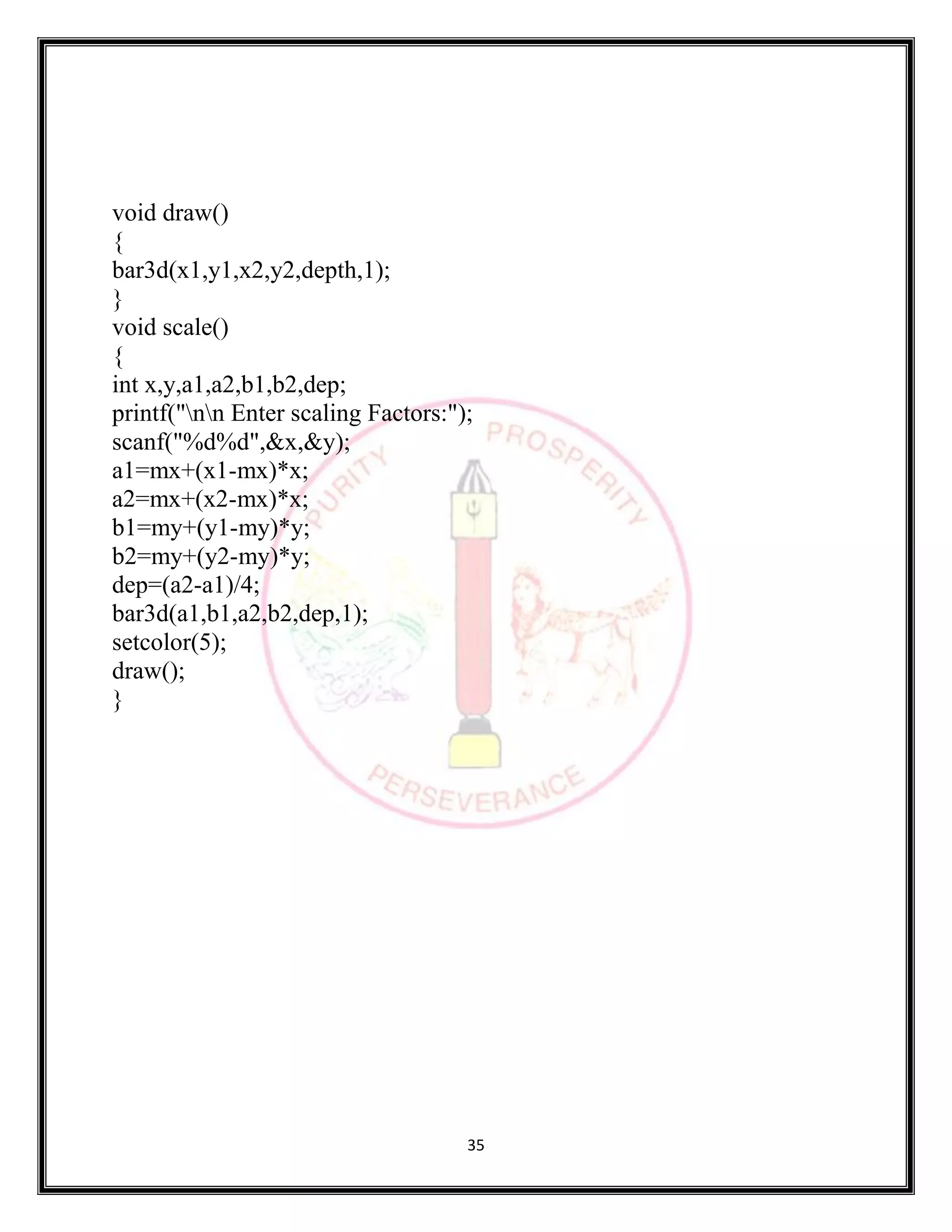
SOURCE CODE:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <math.h>
void bezier (int x[4], int y[4])
{
int gd = DETECT, gm;
int i;
double t;
initgraph (&gd, &gm, "C:TurboC3BGI");
for (t = 0.0; t < 1.0; t += 0.0005)
{
double xt = pow (1-t, 3) * x[0] + 3 * t * pow (1-t, 2) * x[1] +
3 * pow (t, 2) * (1-t) * x[2] + pow (t, 3) * x[3];
double yt = pow (1-t, 3) * y[0] + 3 * t * pow (1-t, 2) * y[1] +
3 * pow (t, 2) * (1-t) * y[2] + pow (t, 3) * y[3];
putpixel (xt, yt, WHITE);
}
for (i=0; i<4; i++)
putpixel (x[i], y[i], YELLOW);
getch();
closegraph();
return;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabmanual-180628095858/75/Computer-graphics-lab-manual-42-2048.jpg)
![43
Void main()
{
int x[4], y[4];
int i;
printf ("Enter the x- and y-coordinates of the four control points.n");
for (i=0; i<4; i++)
scanf ("%d%d", &x[i], &y[i]);
bezier (x, y);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabmanual-180628095858/75/Computer-graphics-lab-manual-43-2048.jpg)