The document contains 10 programs written in C programming language to perform various 2D and 3D graphics operations like drawing lines, rectangles, circles, ellipses, torus, scaling, rotating, shearing and reflecting objects. Program 1-5 demonstrate drawing basic shapes like line, rectangle, circle and ellipse. Program 6 draws a 3D torus using OpenGL. Program 7-9 demonstrate transformations like scaling, rotating and shearing of objects. Program 10 shows reflection of an object about x-axis, y-axis and origin.








![9
const GLfloat light_ambient[] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
const GLfloat light_diffuse[] = { 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f };
const GLfloat light_specular[] = { 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f };
const GLfloat light_position[] = { 2.0f, 5.0f, 5.0f, 0.0f };
const GLfloat mat_ambient[] = { 0.7f, 0.7f, 0.7f, 1.0f };
const GLfloat mat_diffuse[] = { 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f, 1.0f };
const GLfloat mat_specular[] = { 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f };
const GLfloat high_shininess[] = { 100.0f };
/* Program entry point */
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitWindowSize(640,480);
glutInitWindowPosition(10,10);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_DEPTH);
glutCreateWindow("Programming Techniques - 3D Torus");
glutReshapeFunc(resize);
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glClearColor(1,1,1,1);
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
glCullFace(GL_BACK);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0);
glEnable(GL_NORMALIZE);
glEnable(GL_COLOR_MATERIAL);
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_AMBIENT, light_ambient);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_DIFFUSE, light_diffuse);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_SPECULAR, light_specular);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position);
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_AMBIENT, mat_ambient);
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_DIFFUSE, mat_diffuse);
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_SPECULAR, mat_specular);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-9-2048.jpg)




![14
OUTPUT:
Program 9
WRITE A C PROGRAM TO SHEAR AN OBJECT ABOUT X-SHEAR, Y-SHEAR.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<dos.h>
#include<graphics.h>
int main()
{
int poly[30],a[9][3],b[3][3],c[9][3],poly2[30];
int x=0,y=0,p,i,j,k,xc,yc,ch;
int gd=DETECT,gm;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-14-2048.jpg)
![15
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"C:/TC/BGI");
xc=getmaxx()/2;
yc=getmaxy()/2;
setcolor(1);
setbkcolor(15);
setfillstyle(6,3);
printf("n Enter number of points : ");
scanf("%d",&p);
j=0;
for(i=0;i<p*2;i+=2)
{
printf("n Enter cordinate point x%d and y%d : ",j+1,j+1);
scanf("%d",&poly[i]);
scanf("%d",&poly[i+1]);
j++;
}
poly[p*2]=poly[0];
poly[p*2+1]=poly[1];
for(i=0;i<p*2;i+=2)
{
poly2[i]=xc+poly[i];
poly2[i+1]=yc-poly[i+1];
}
poly2[p*2]=poly2[0];
poly2[p*2+1]=poly2[1];
fillpoly(p+1,poly2);
line(0,yc,xc*2,yc);
line(xc,0,xc,yc*2);
printf("n Shearing of : n 1. x n 2. y n 3. Bothn enter choice : ");
scanf("%d",&ch);
if(ch==1)
{
printf("n Enter x shear value : ");
scanf("%d",&x);
}
if(ch==2)
{
printf("n Enter y shear value : ");
scanf("%d",&y);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-15-2048.jpg)
![16
if(ch==3)
{
printf("n Enter x shear value : ");
scanf("%d",&x);
printf("n Enter y shear value : ");
scanf("%d",&y);
}
j=0;
for(i=0;i<p;i++)
{
a[i][0]=poly[j];
a[i][1]=poly[++j];
a[i][2]=1;
++j;
}
if(ch==1)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[i][j]=0;
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
b[1][0]=x;
}
else if(ch==2)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[i][j]=0;
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=1;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-16-2048.jpg)
![17
b[0][1]=y;
}
else if(ch==3)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[i][j]=0;
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
b[1][0]=x;
b[0][1]=y;
}
for(i=0;i<p;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
c[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
{
c[i][j]=c[i][j]+a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
}
}
printf("nnnnnt After Shearing : ");
for(i=0,j=0;i<p;i++,j+=2)
{
poly[j] =xc+c[i][0];
poly[j+1]=yc-c[i][1];
}
poly[j] =poly[0];
poly[j+1]=poly[1];
setfillstyle(9,2);
fillpoly(p+1,poly);
getch();
closegraph();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-17-2048.jpg)

![19
Program 10
WRITE A PROGRAM TO DEMONSTRATE REFLECTION TRANSFORMATION ABOUT X-
AXIS, Y-AXIS AND ORIGIN.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<dos.h>
#include<graphics.h>
int main()
{
int poly[30],a[9][3],b[3][3],c[9][3],poly2[30];
int x,y,p,i,j,k,xc,yc;
int gd=DETECT,gm;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"C:/TC/BGI");
xc=getmaxx()/2;
yc=getmaxy()/2;
setcolor(1);
setbkcolor(15);
setfillstyle(6,3);
printf("n Enter number of points : ");
scanf("%d",&p);
j=0;
for(i=0;i<p*2;i+=2)
{
printf("n Enter cordinate point x%d and y%d : ",j+1,j+1);
scanf("%d",&poly[i]);
scanf("%d",&poly[i+1]);
j++;
}
poly[p*2]=poly[0];
poly[p*2+1]=poly[1];
for(i=0;i<p*2;i+=2)
{
poly2[i]=xc+poly[i];
poly2[i+1]=yc-poly[i+1];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-19-2048.jpg)
![20
}
poly2[p*2]=poly2[0];
poly2[p*2+1]=poly2[1];
fillpoly(p+1,poly2);
line(0,yc,xc*2,yc);
line(xc,0,xc,yc*2);
printf("n Reflection about : n 1. x axisn 2. y axisn 3. originn enter choice : ");
scanf("%d",&x);
j=0;
for(i=0;i<p;i++)
{
a[i][0]=poly[j];
a[i][1]=poly[++j];
a[i][2]=1;
++j;
}
if(x==1)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[i][j]=0;
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
b[1][1]=-1;
}
else if(x==2)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-20-2048.jpg)
![21
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[i][j]=0;
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
b[0][0]=-1;
}
else if(x==3)
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[i][j]=0;
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=-1;
}
}
}
b[2][2]=1;
}
for(i=0;i<p;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
c[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
{
c[i][j]=c[i][j]+a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
}
}
printf("nnnnnt Reflection : ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-21-2048.jpg)
![22
for(i=0,j=0;i<p;i++,j+=2)
{
poly[j] =xc+c[i][0];
poly[j+1]=yc-c[i][1];
}
poly[j] =poly[0];
poly[j+1]=poly[1];
setfillstyle(9,2);
fillpoly(p+1,poly);
getch();
closegraph();
}
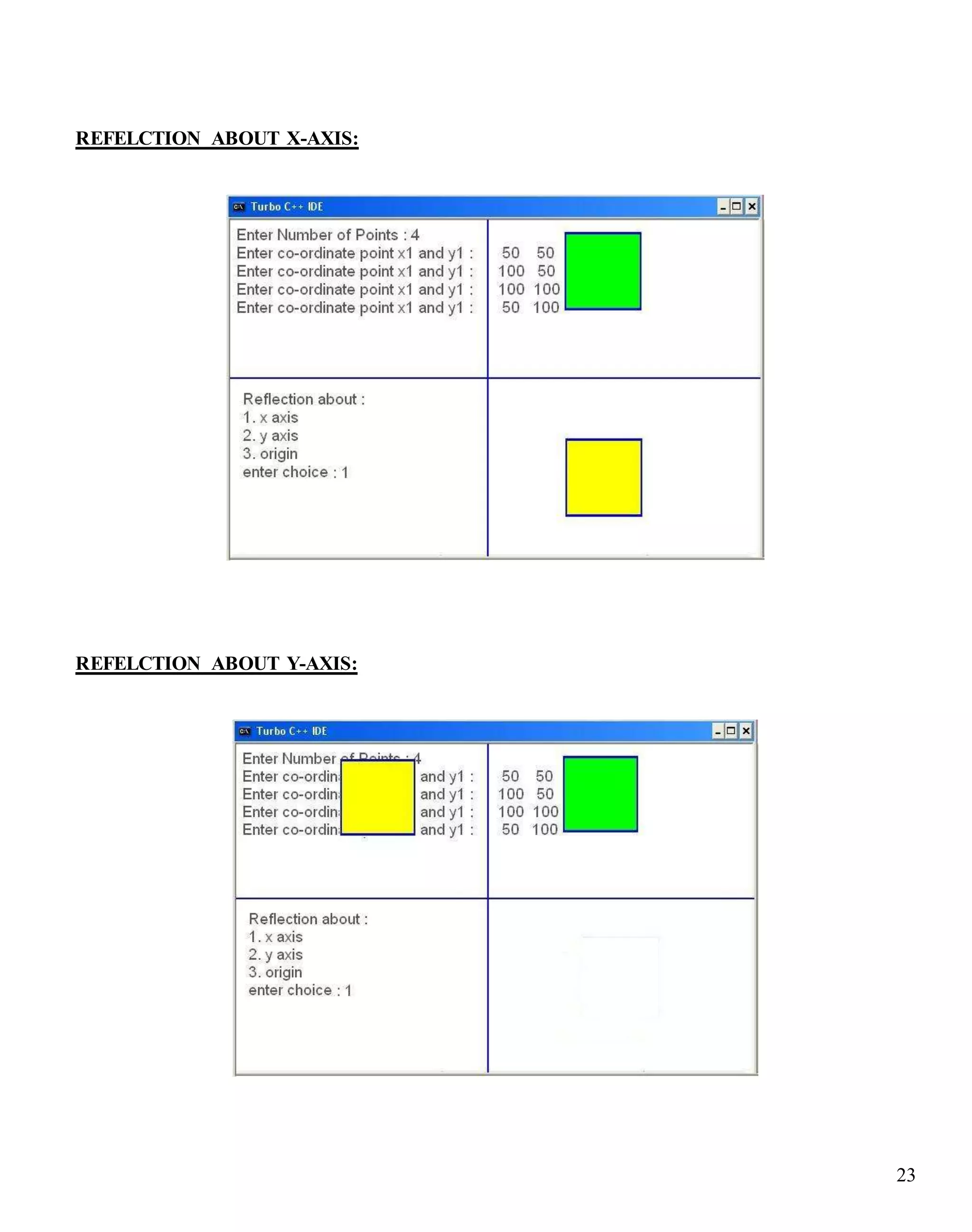
OUTPUT:
REFELCTION ABOUT ORIGIN:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computergraphicslabassignment-160905192356/75/Computer-graphics-lab-assignment-22-2048.jpg)