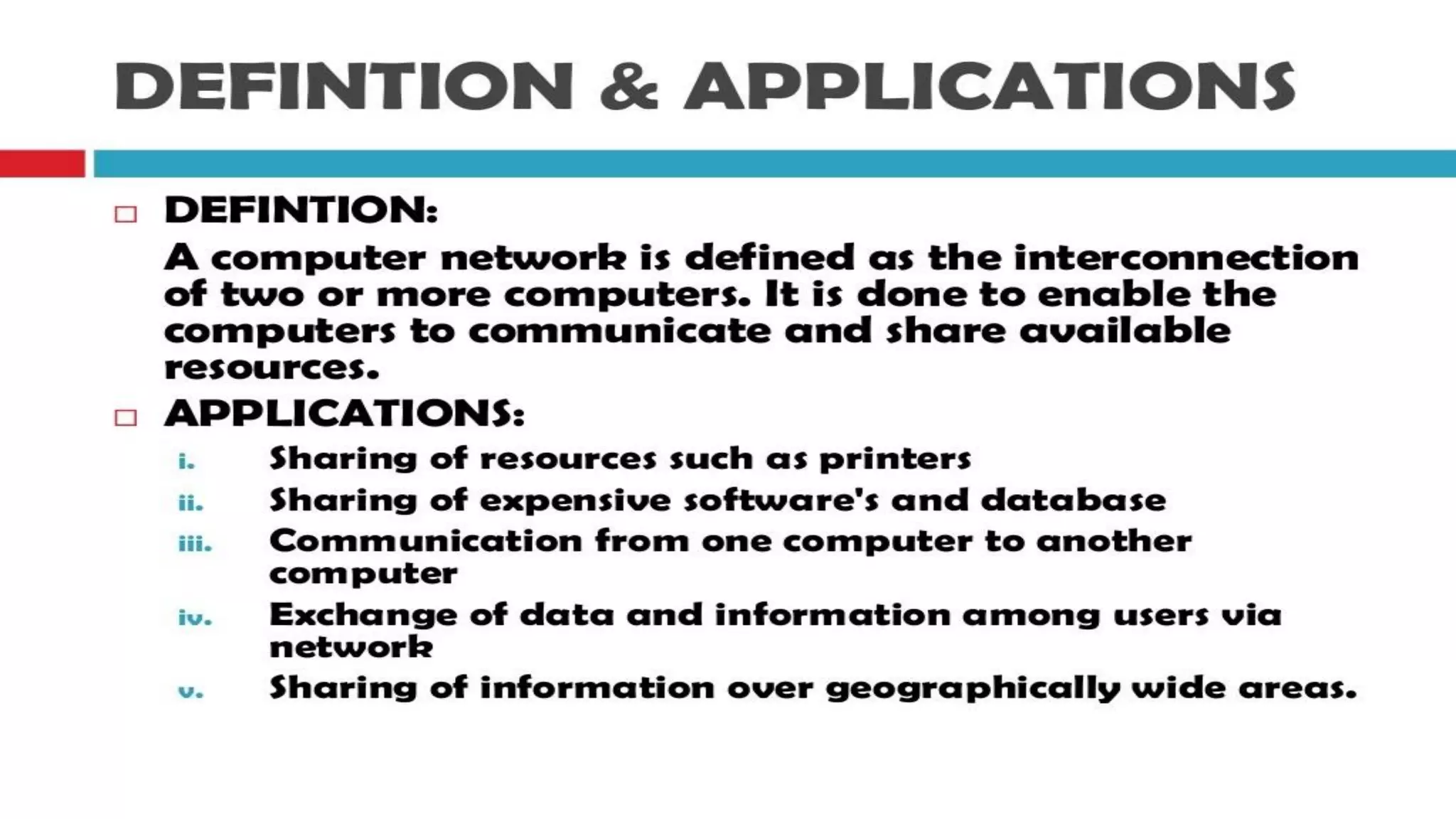
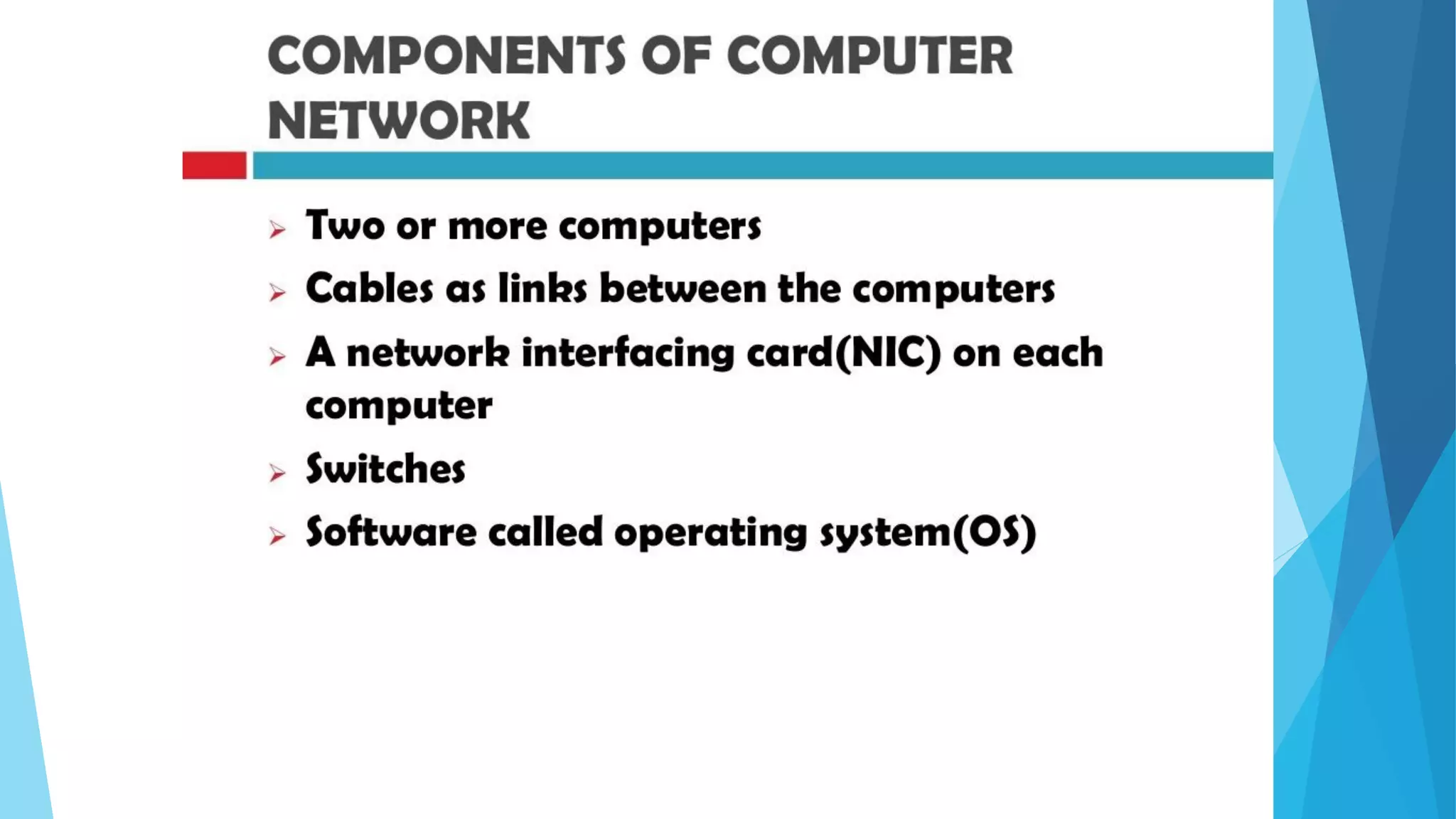
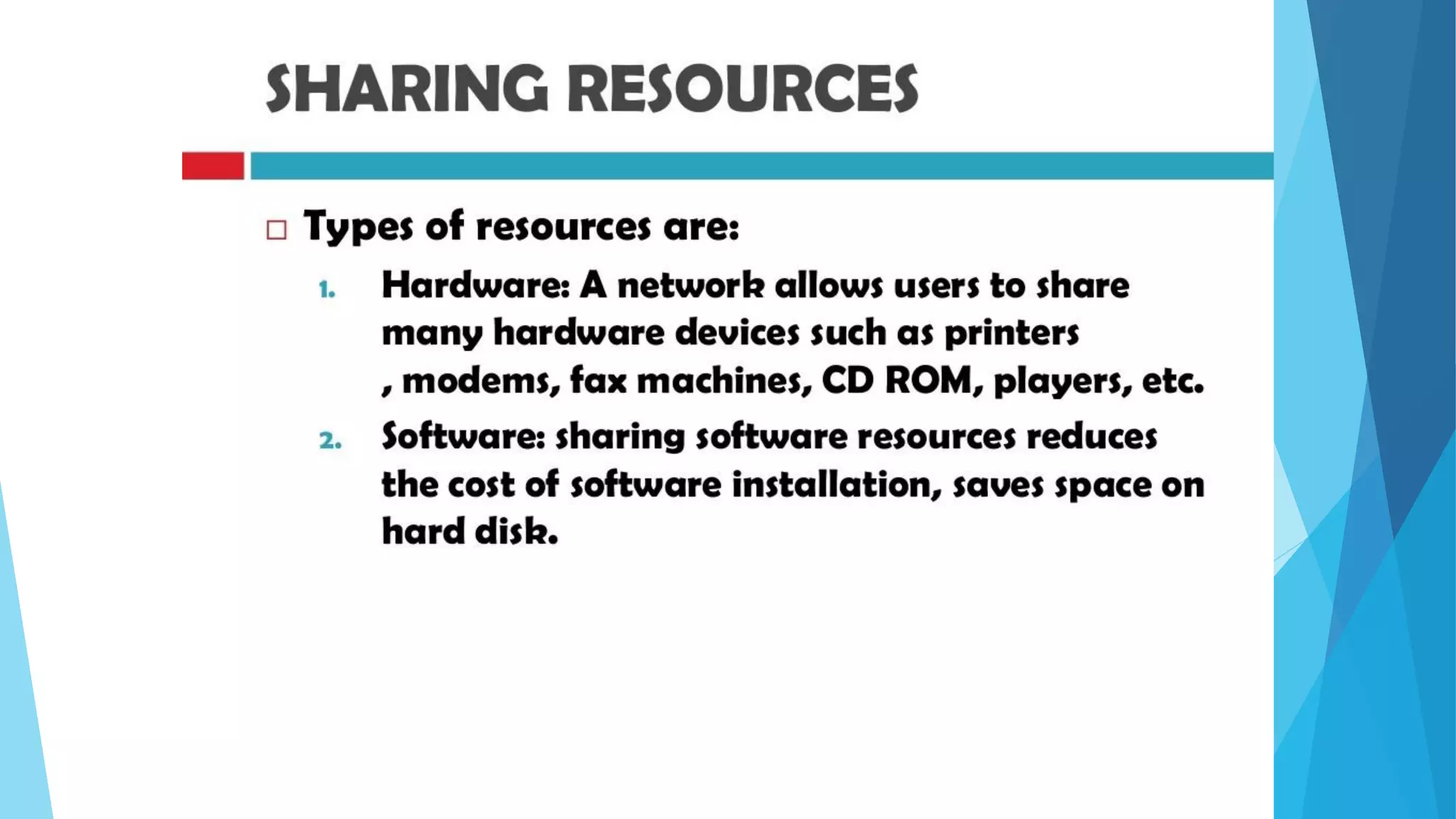
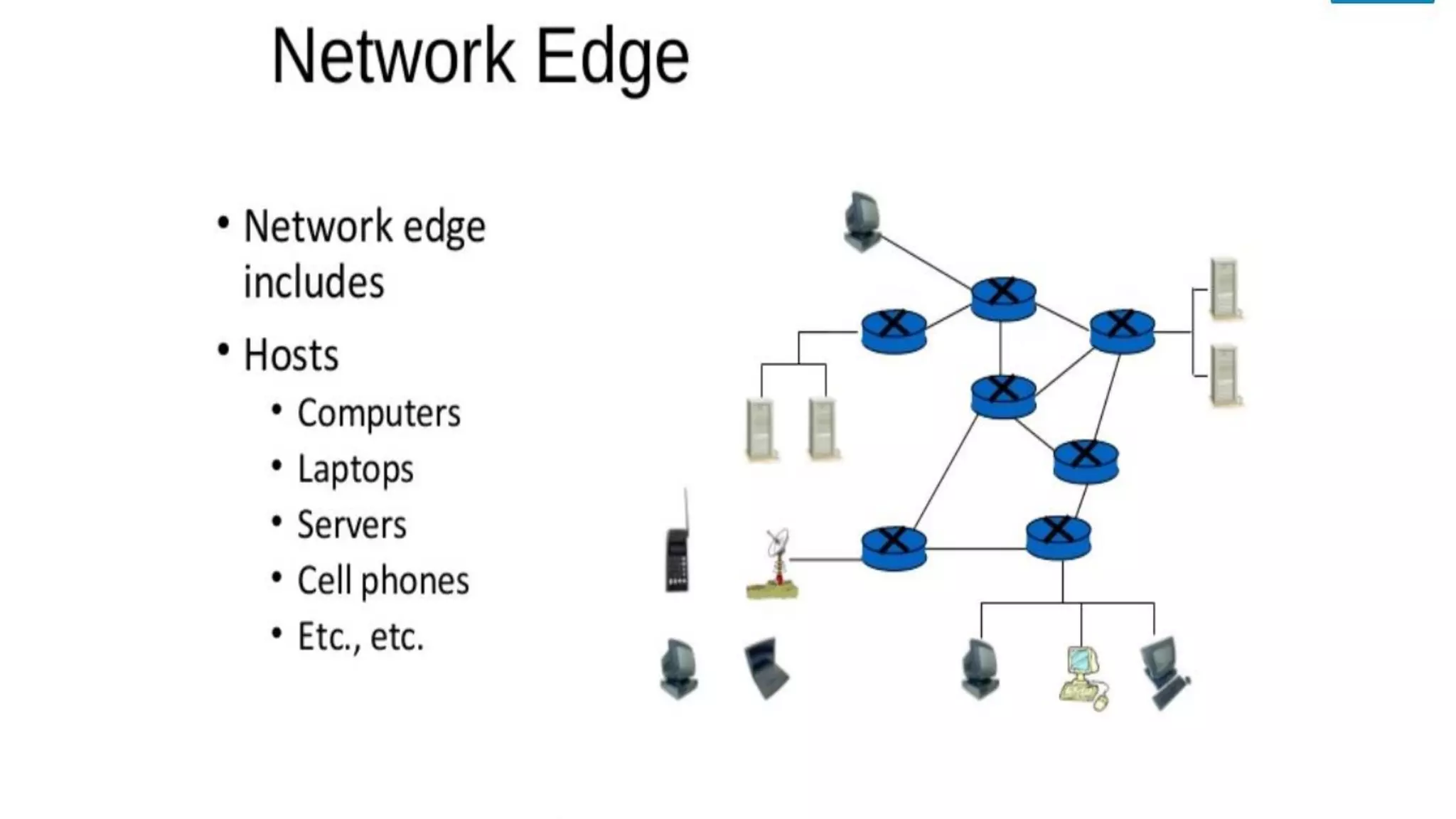
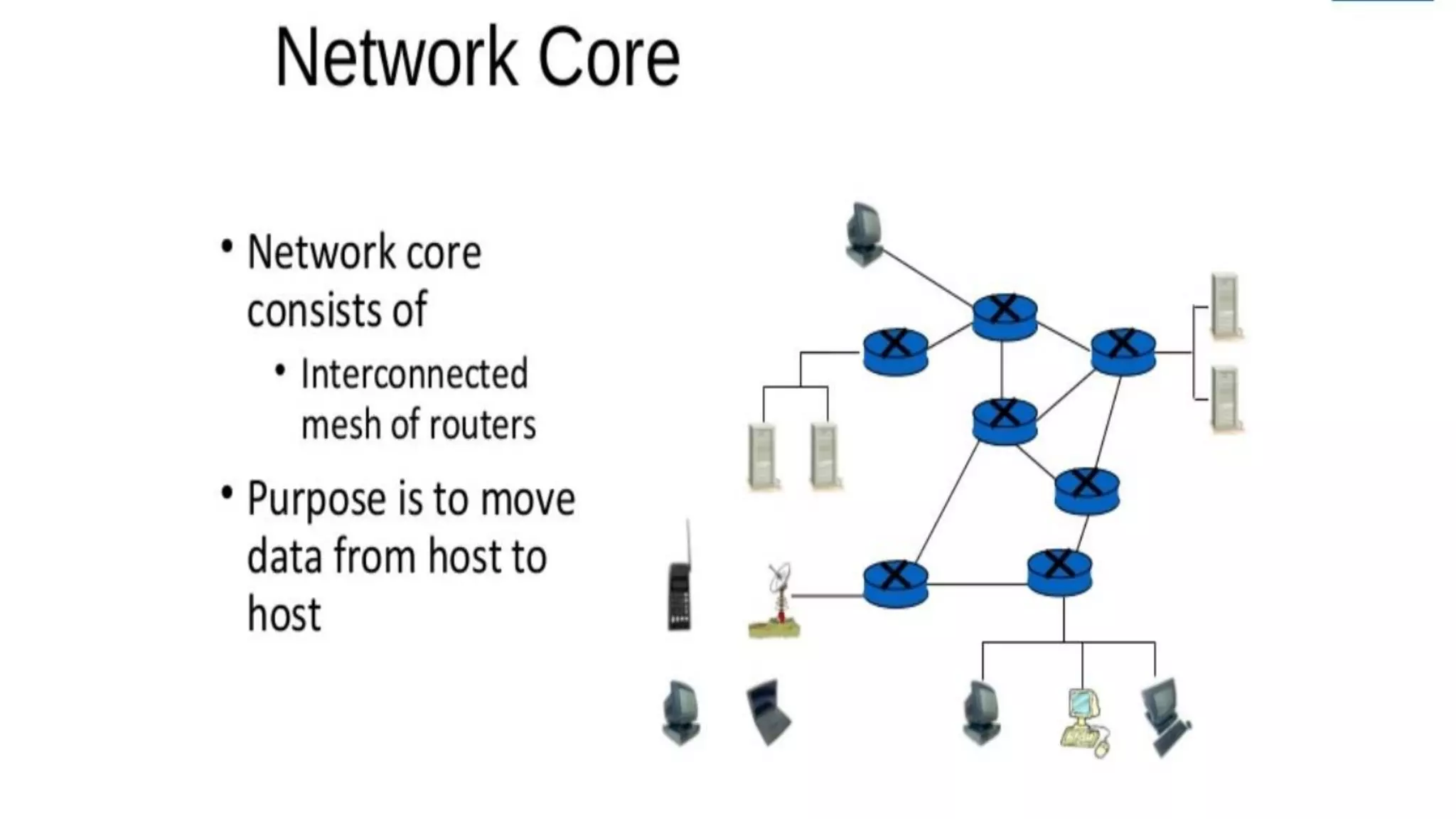
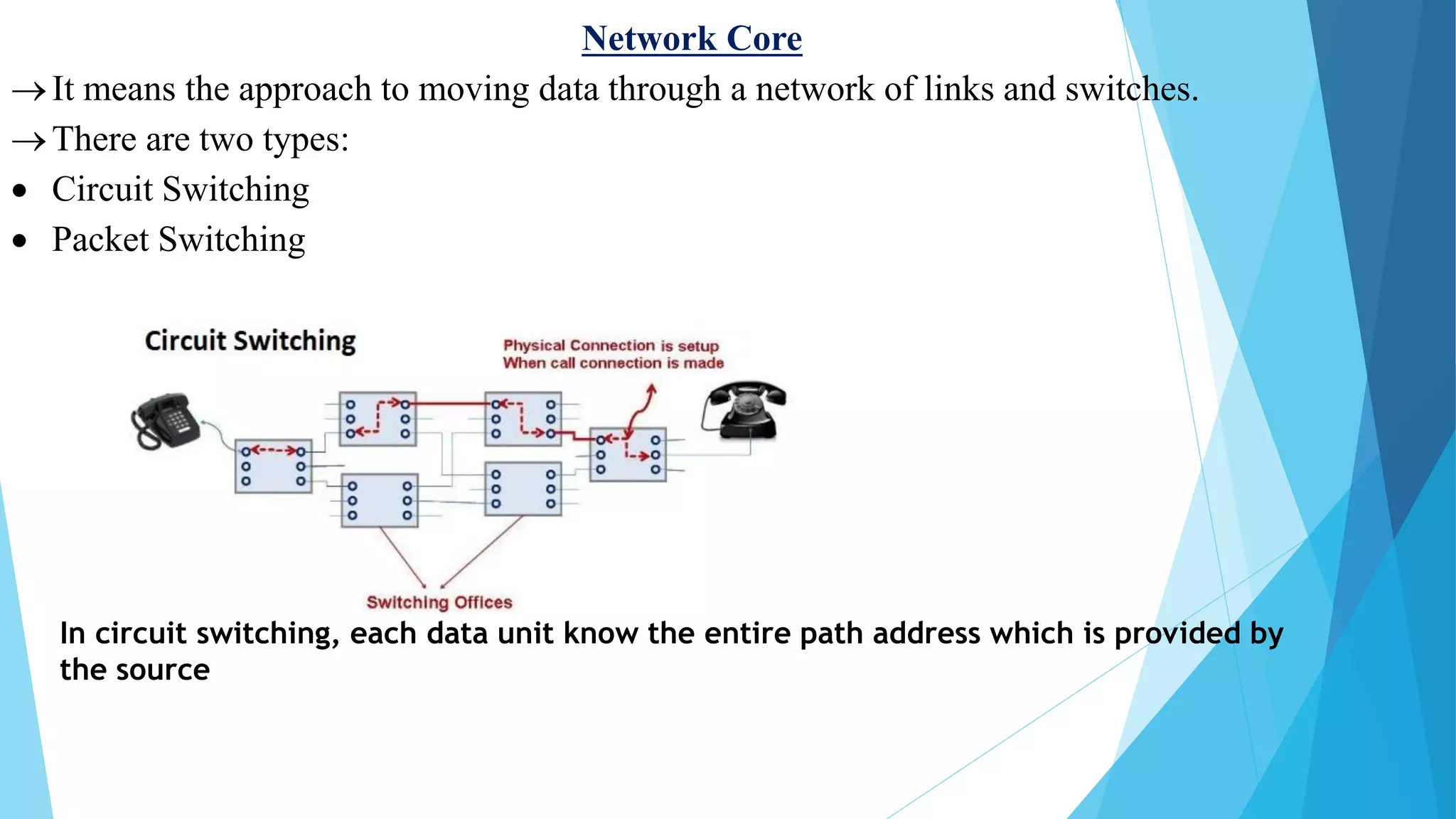
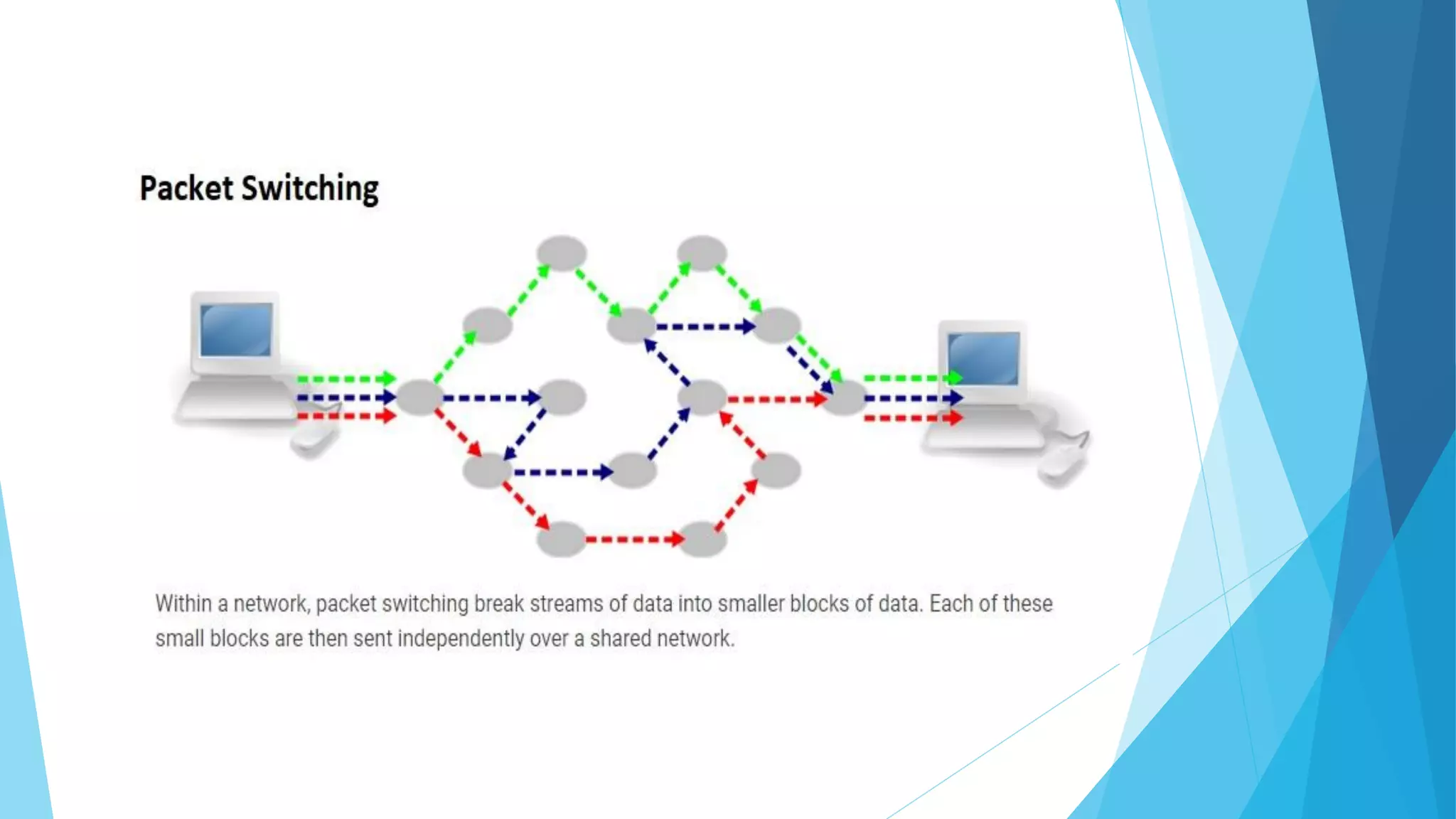
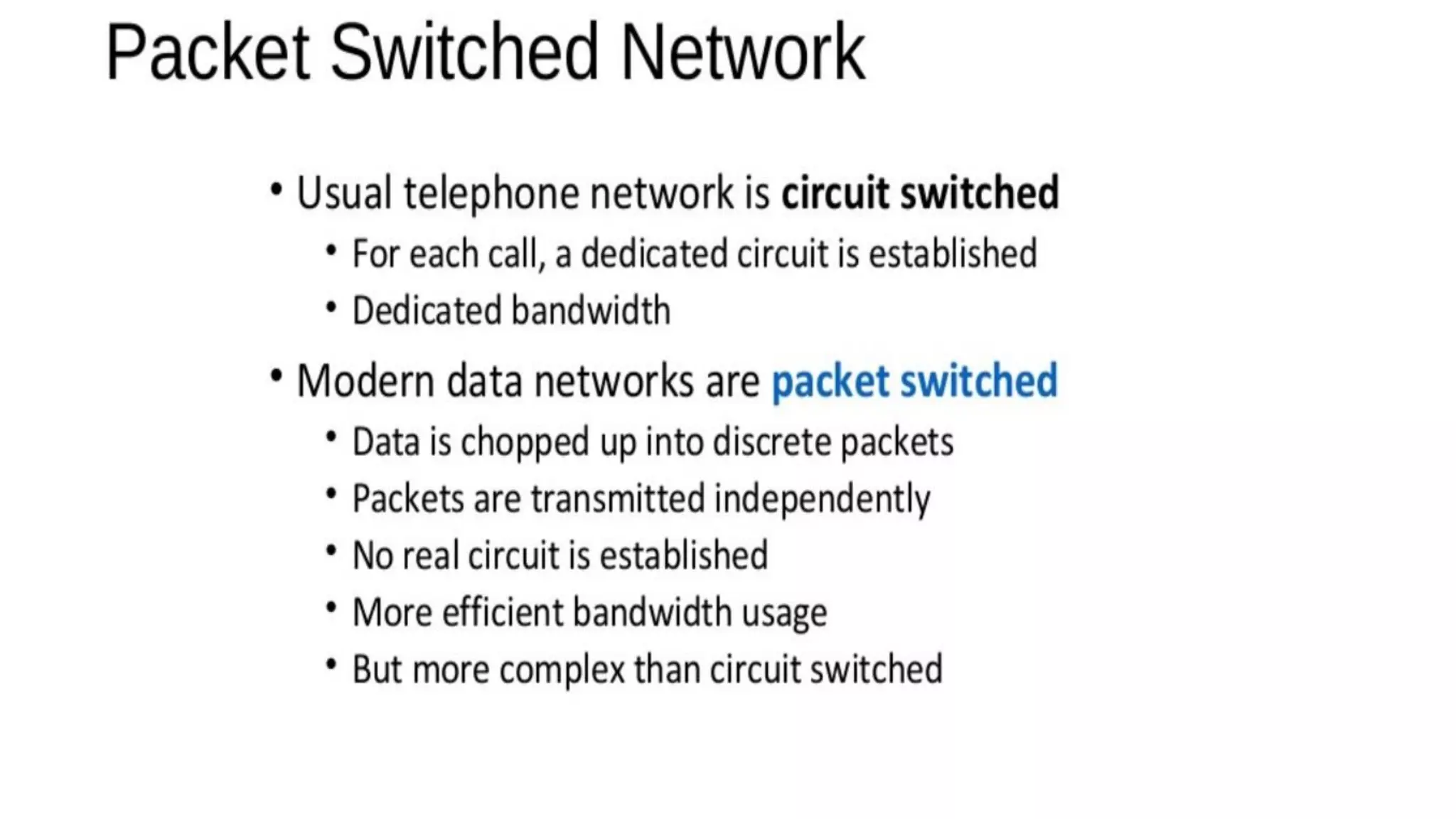
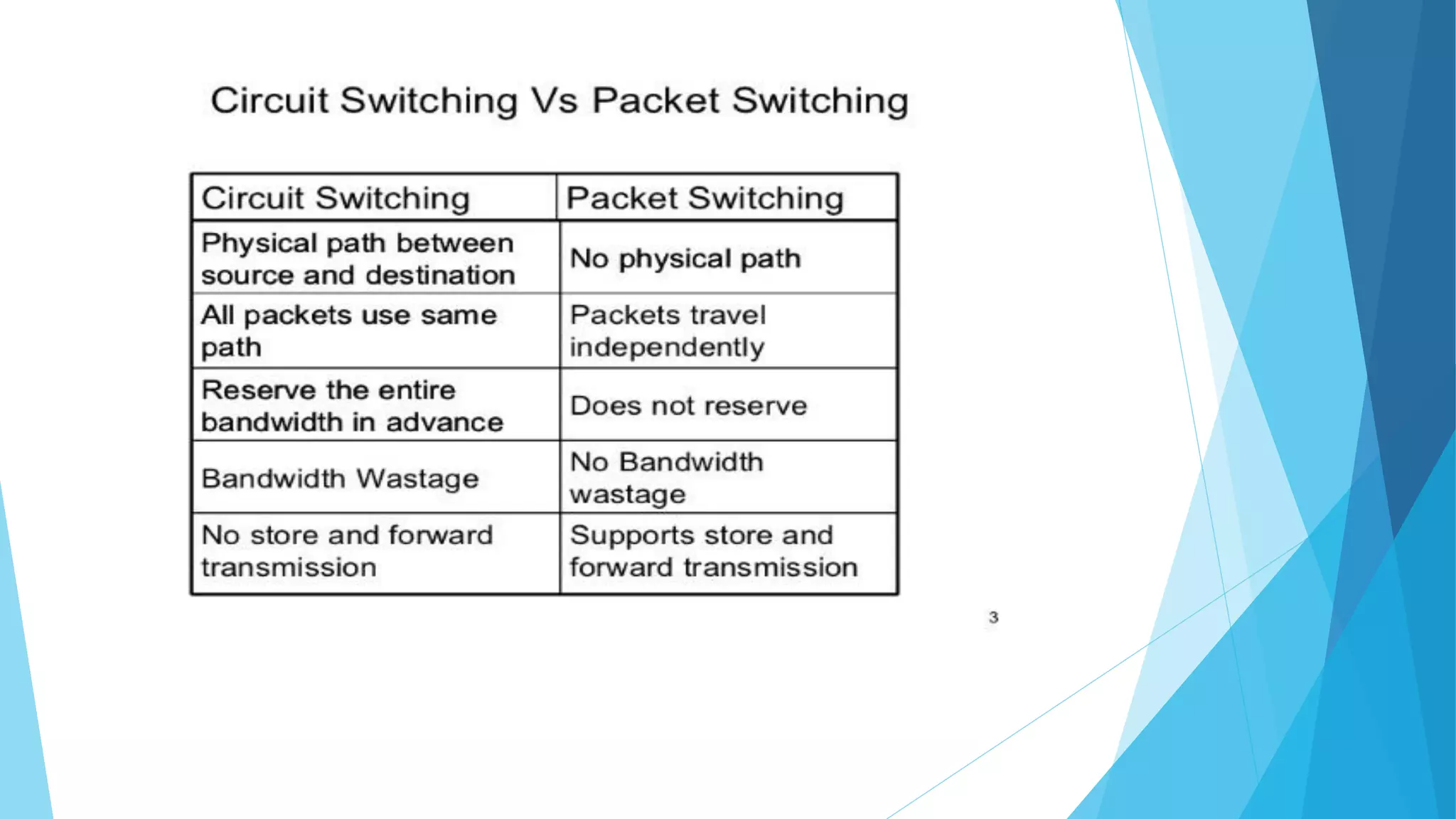
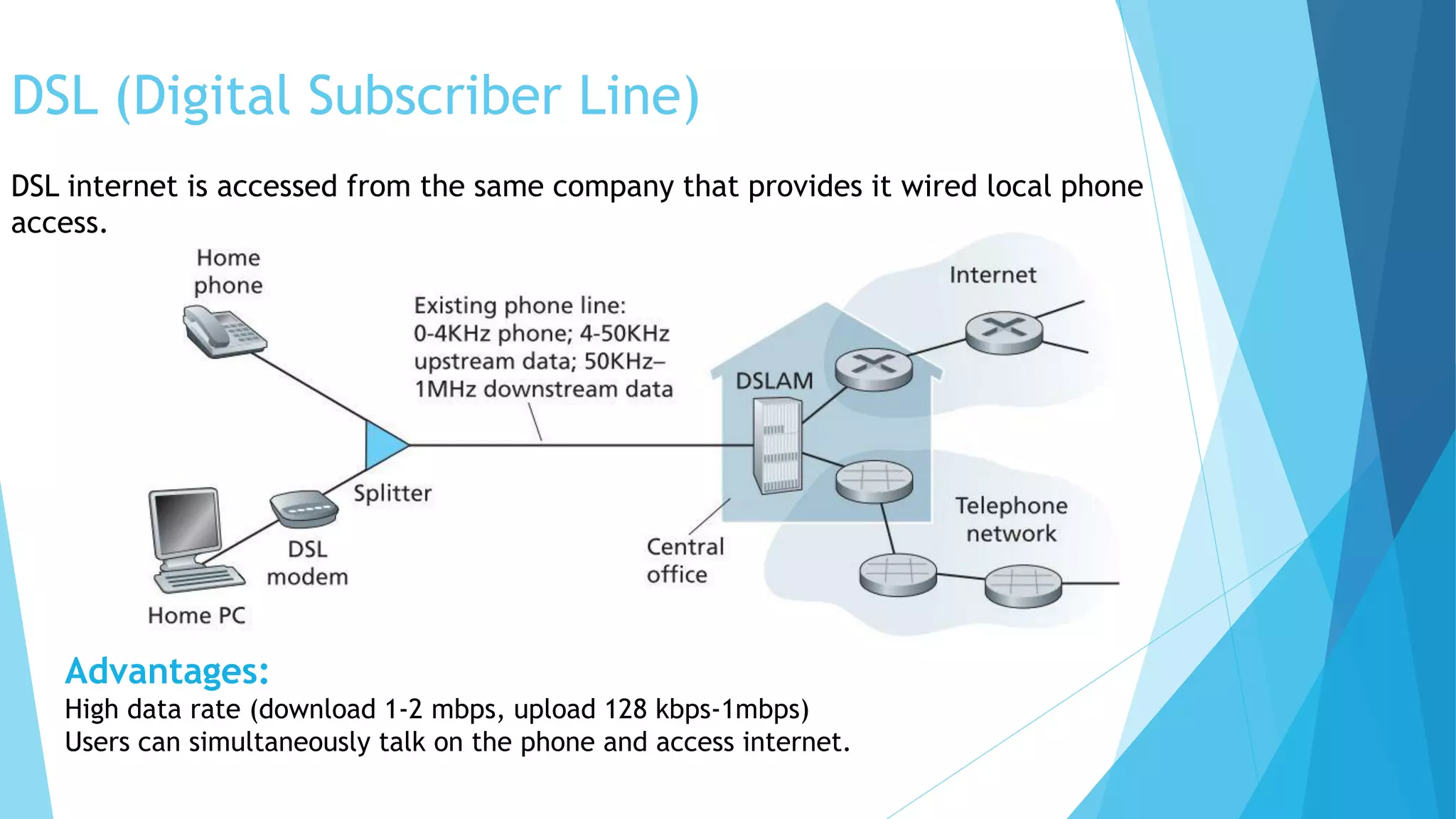
The document discusses computer networks and their components. It describes end systems like clients and servers that run applications. Clients request services from servers. The network core uses either circuit switching or packet switching to move data through links and switches. Packet switched networks can be datagram networks, like the Internet, which forwards packets based on destination address, or virtual circuit networks which use preplanned routes. The document also covers network access technologies like dial-up connections and DSL internet access.