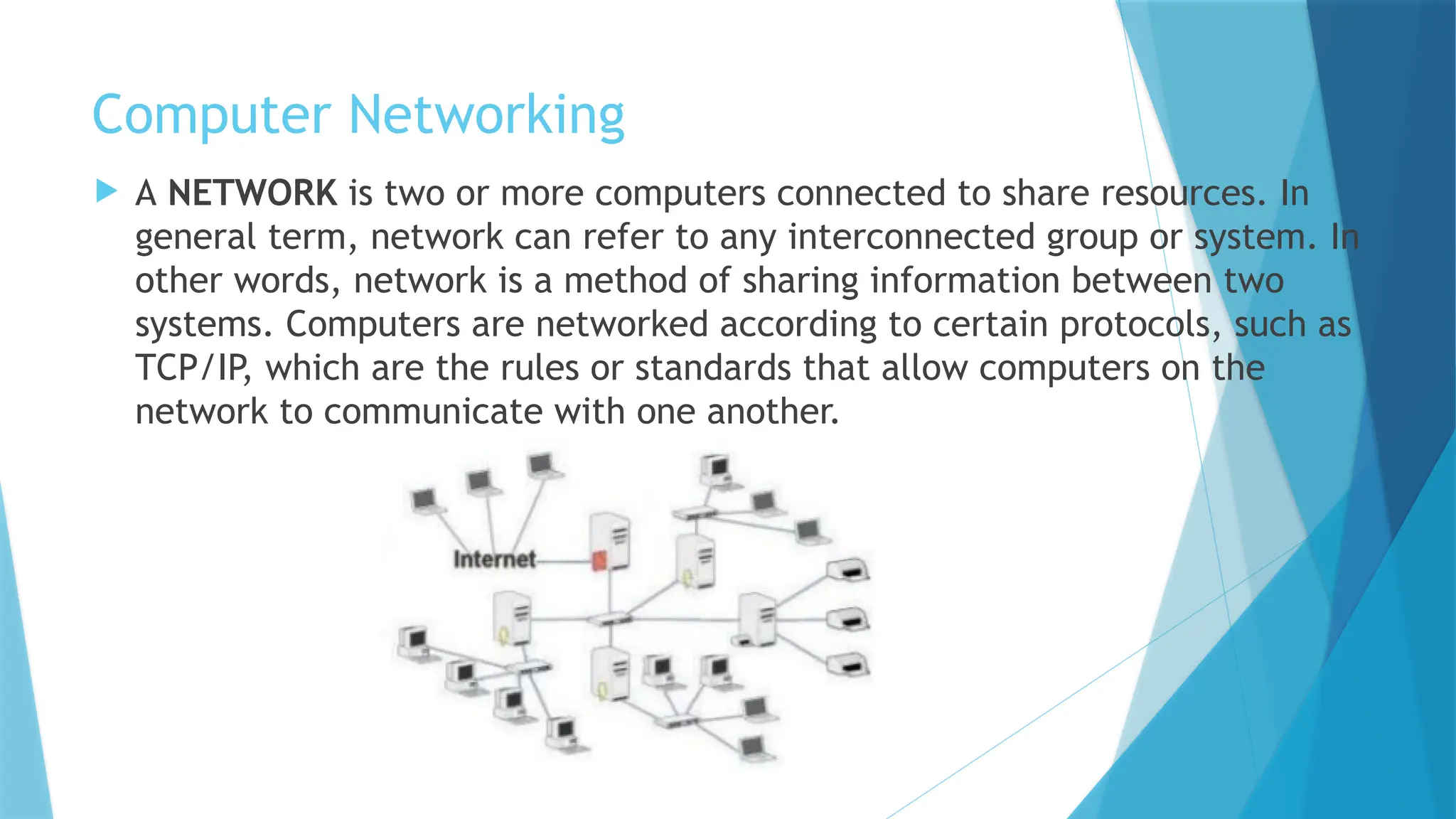
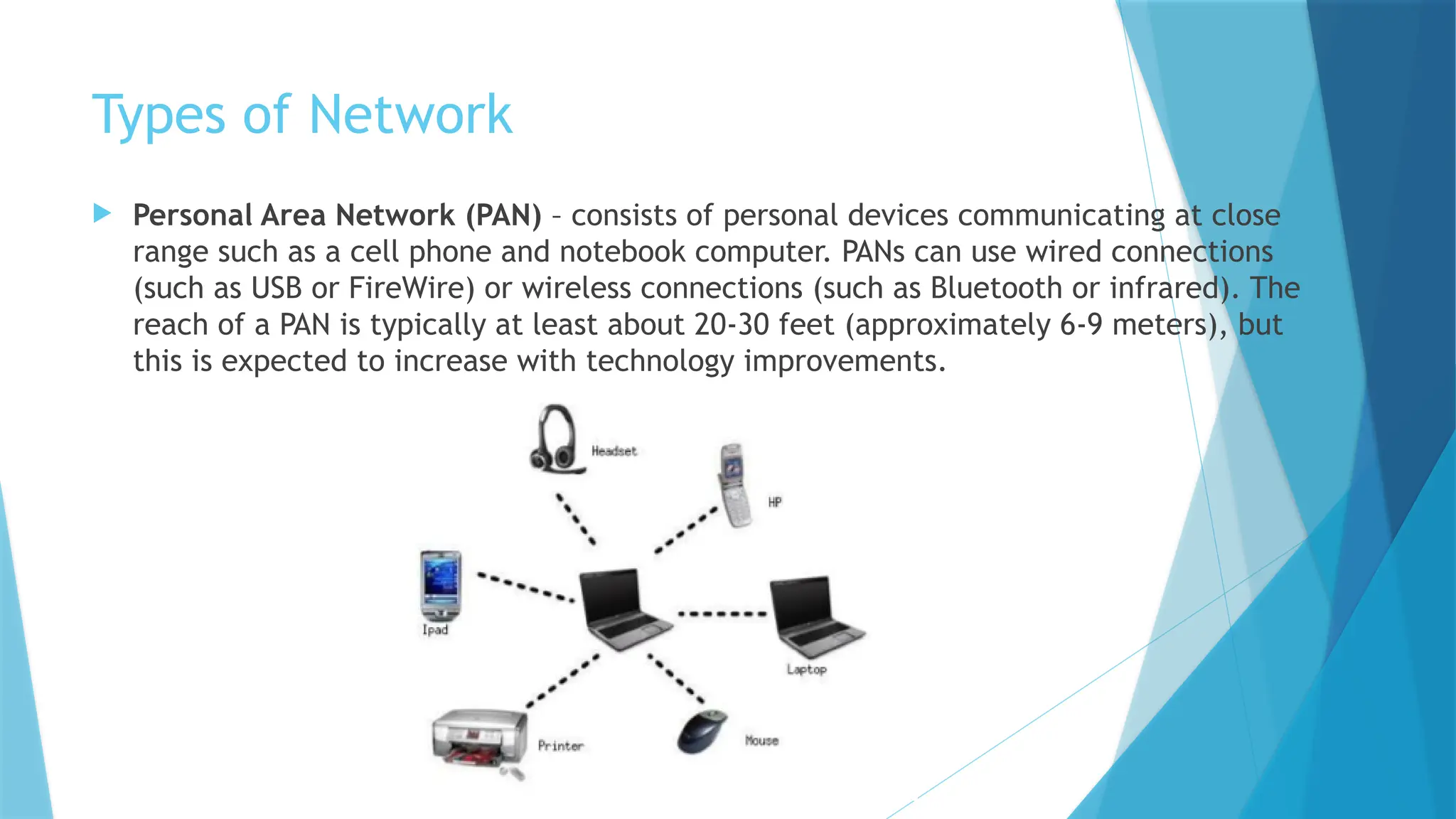
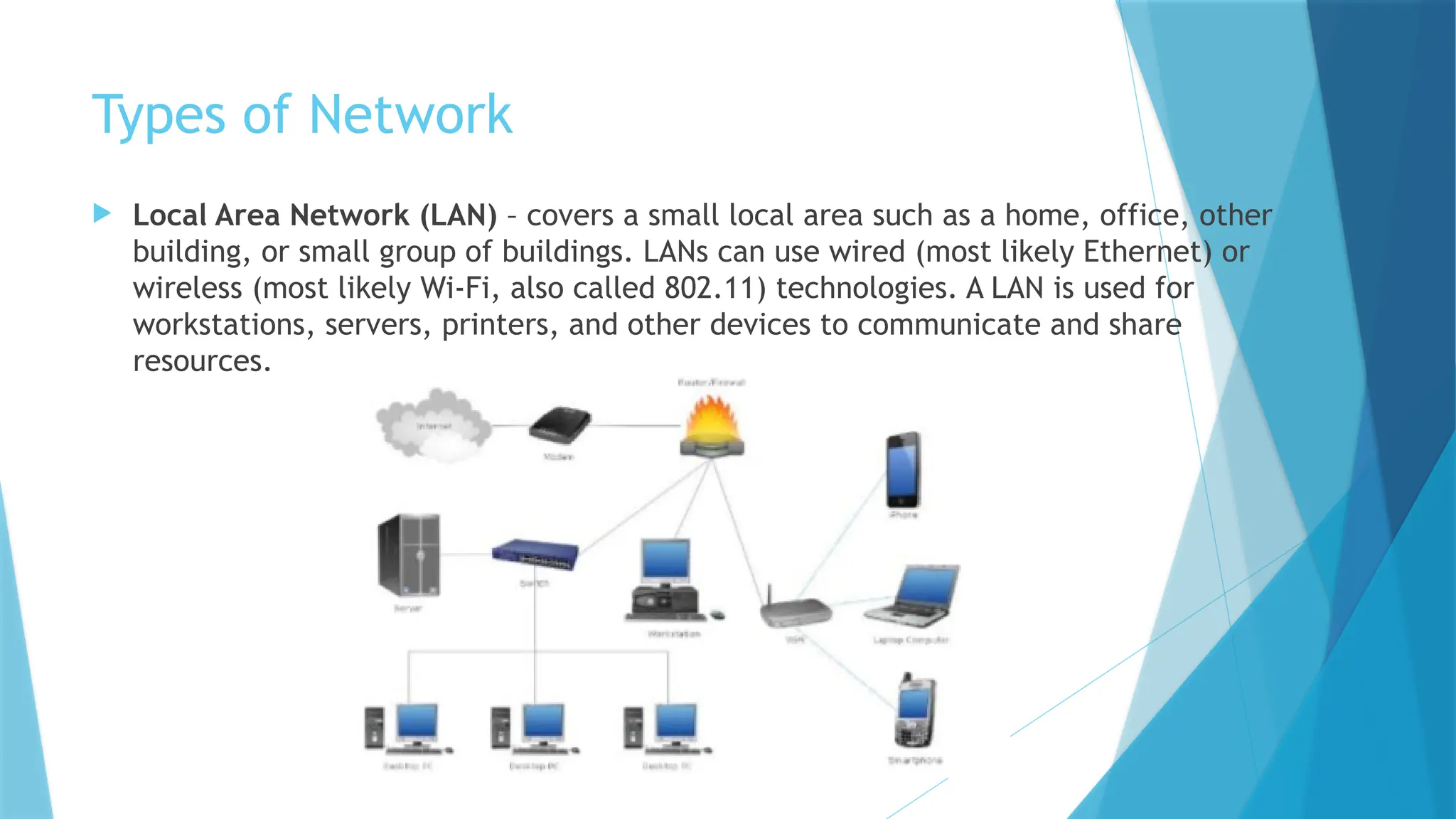
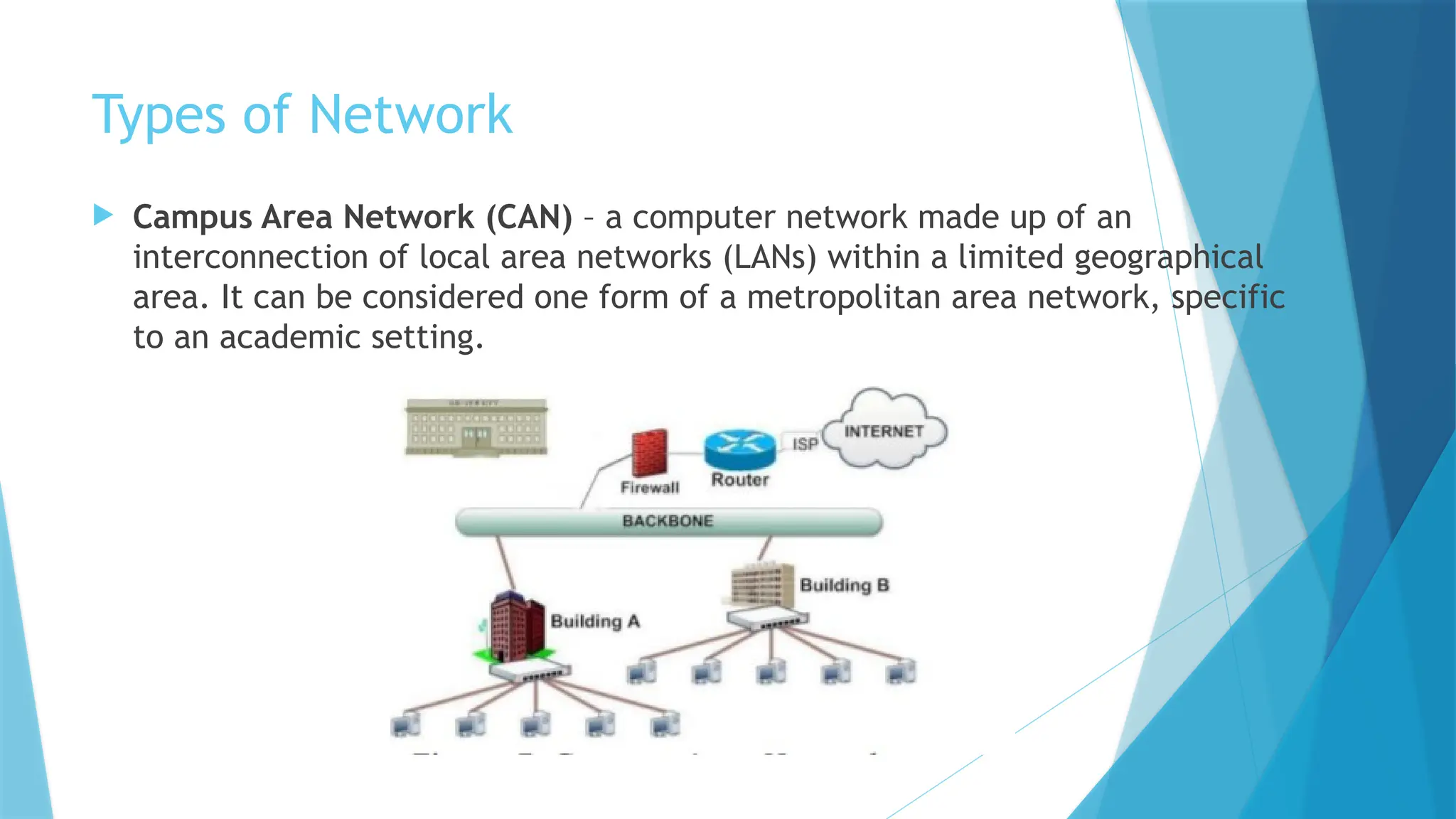
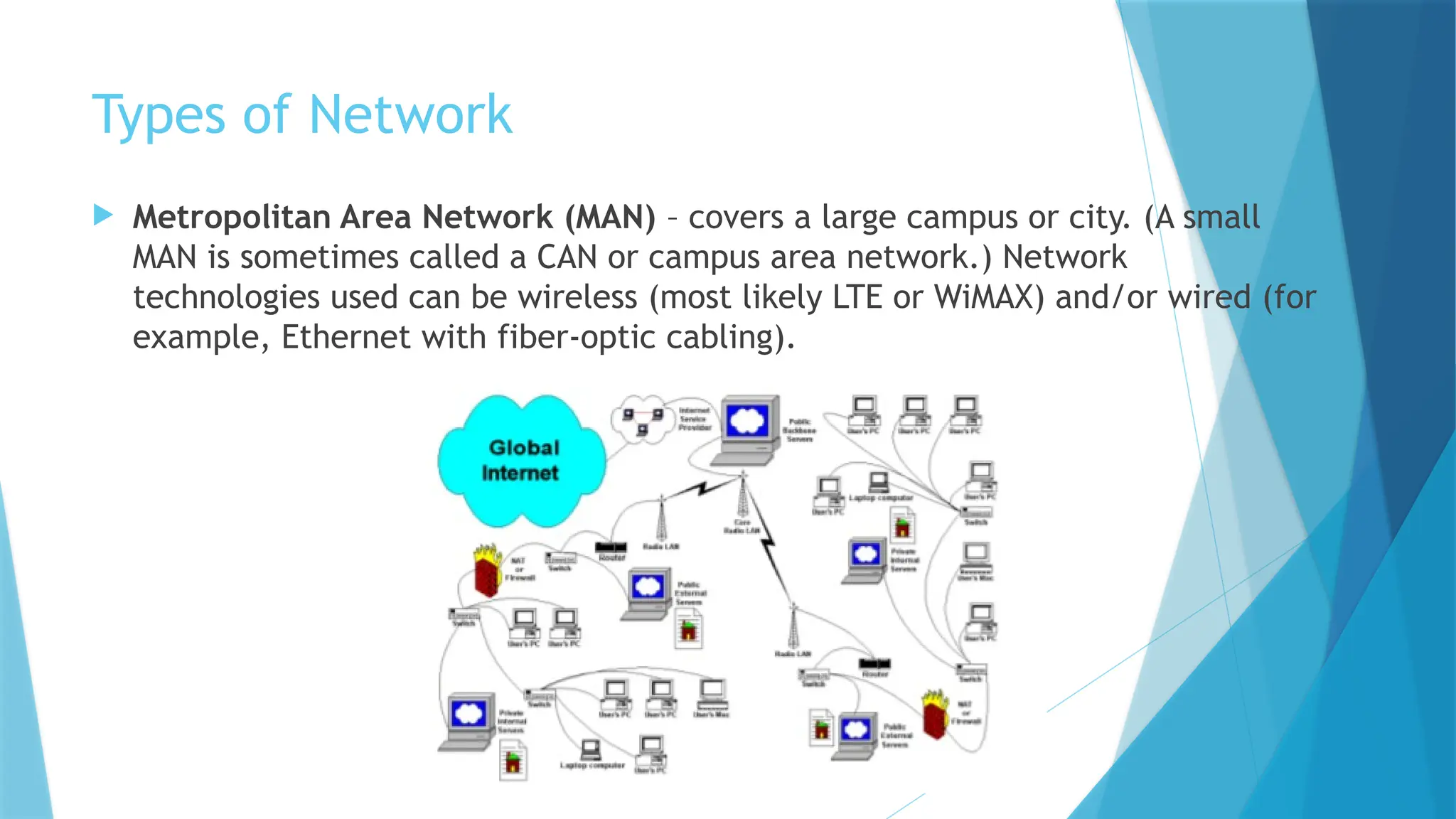
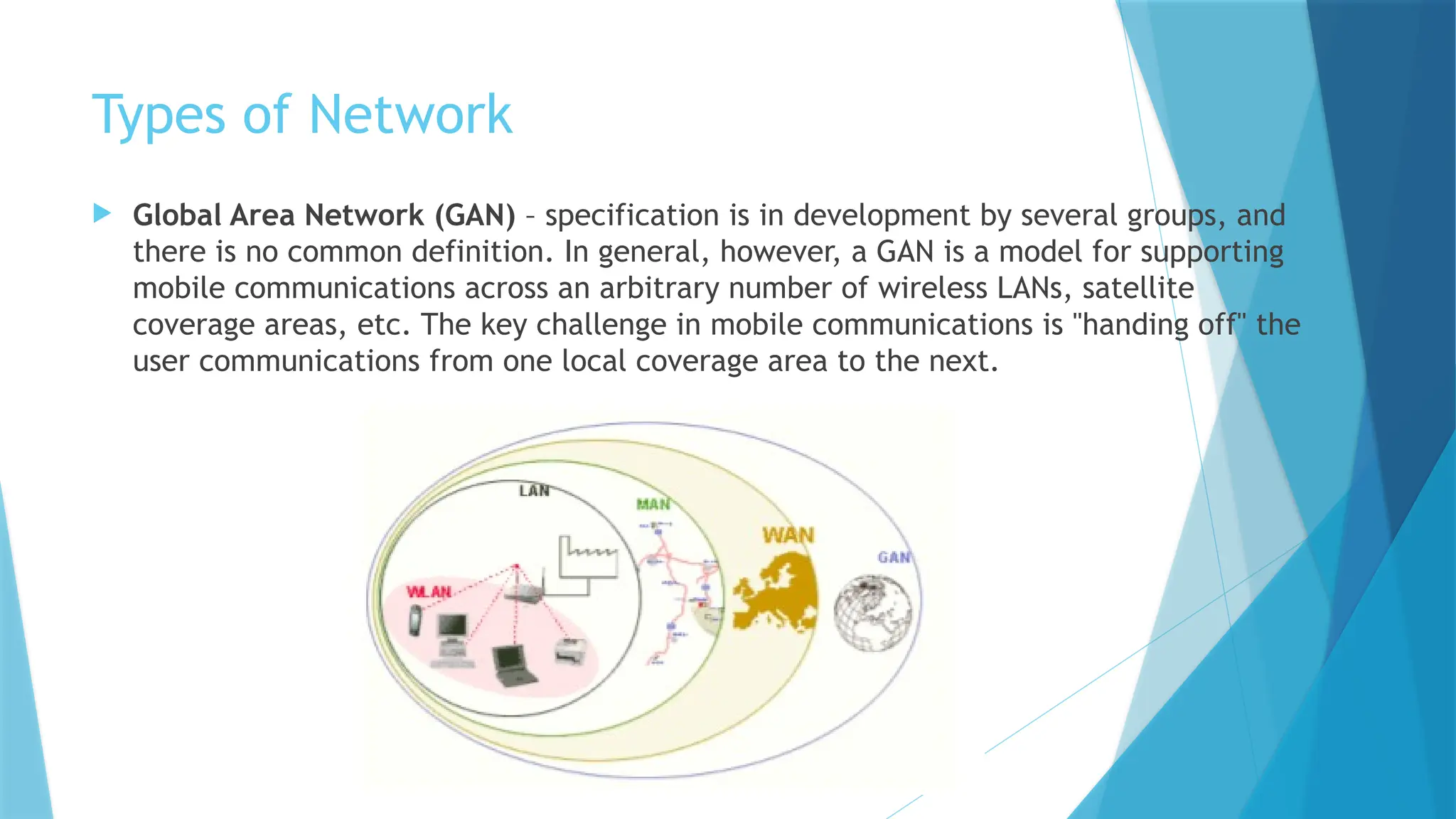
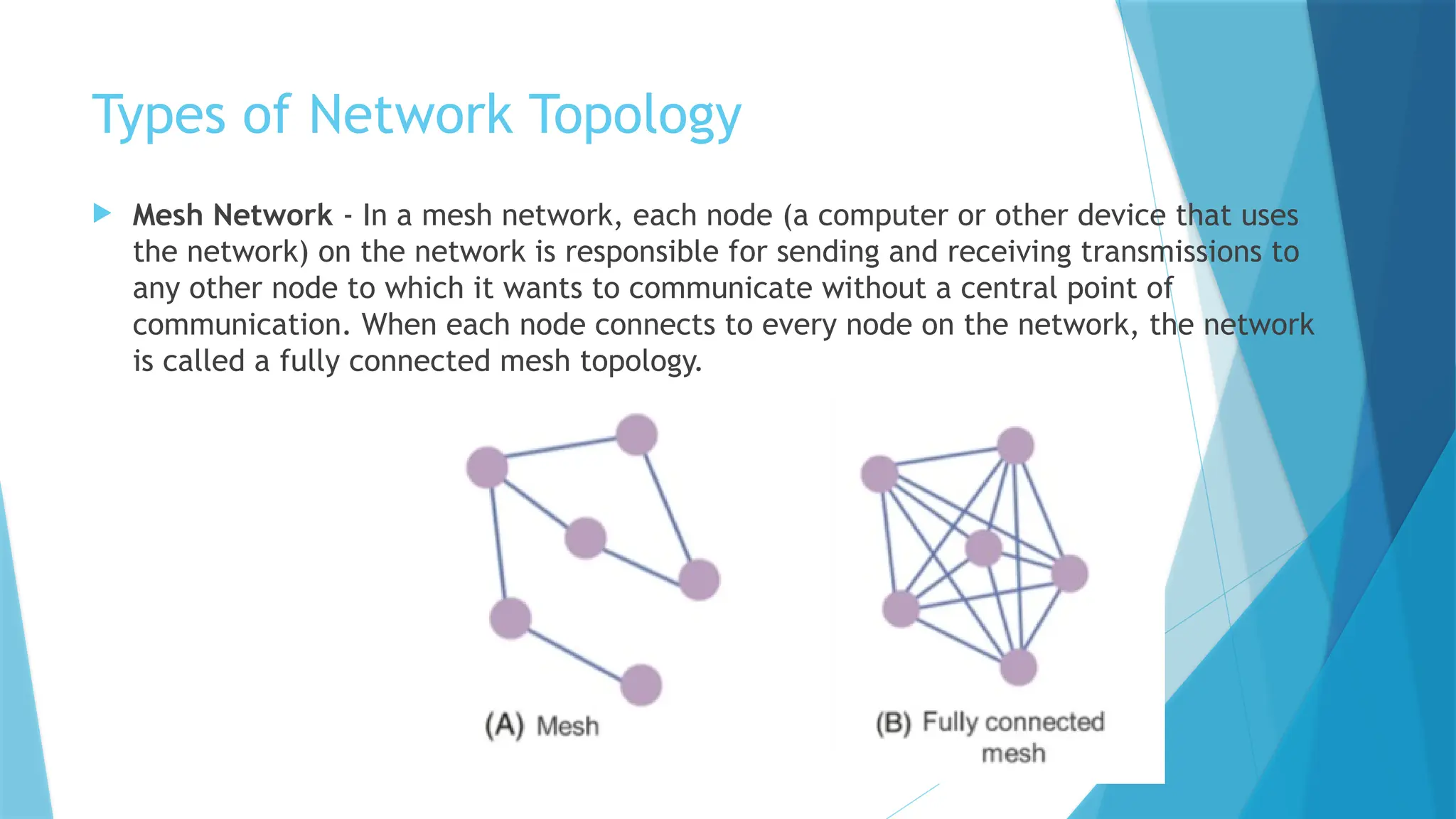
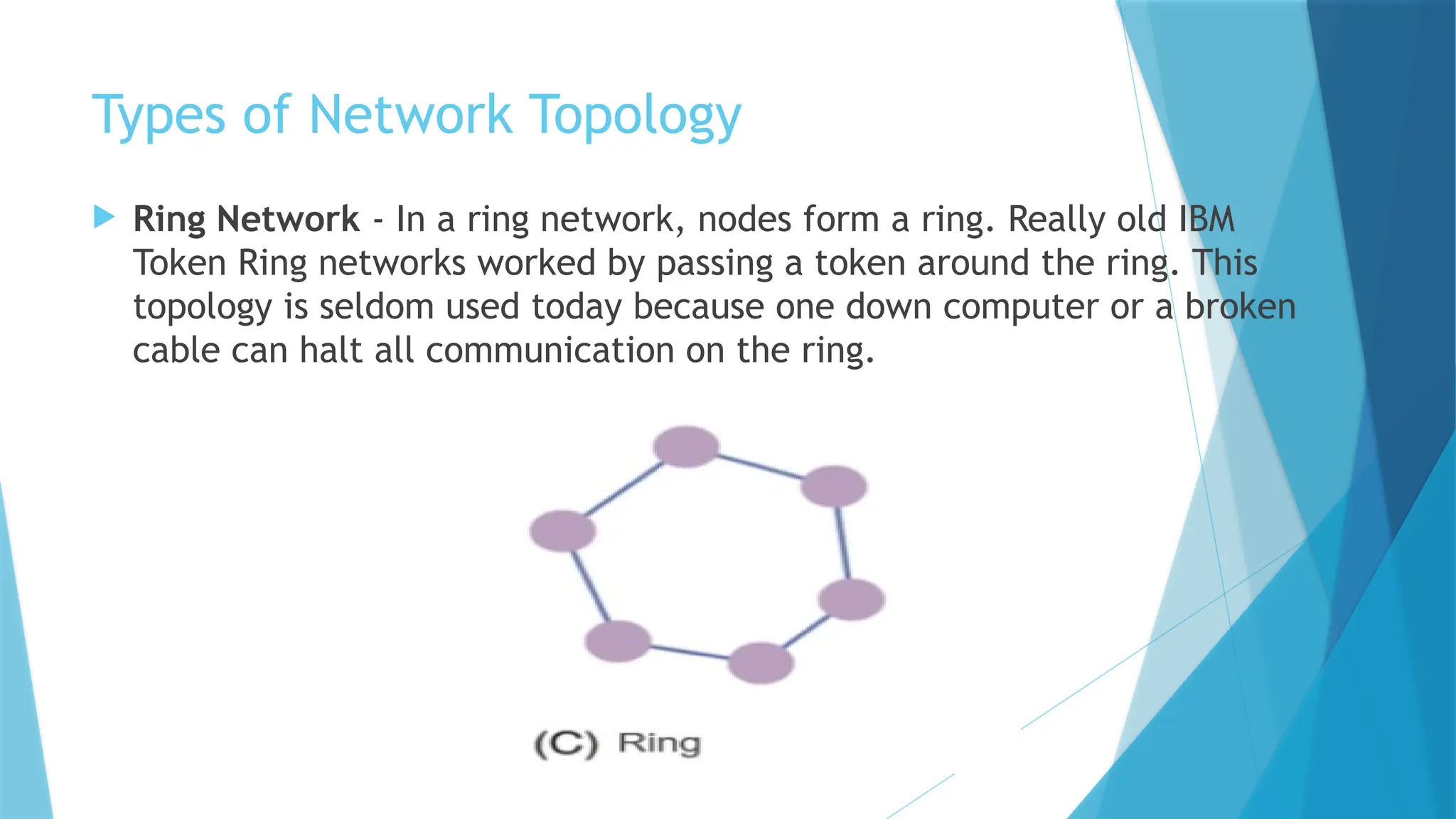
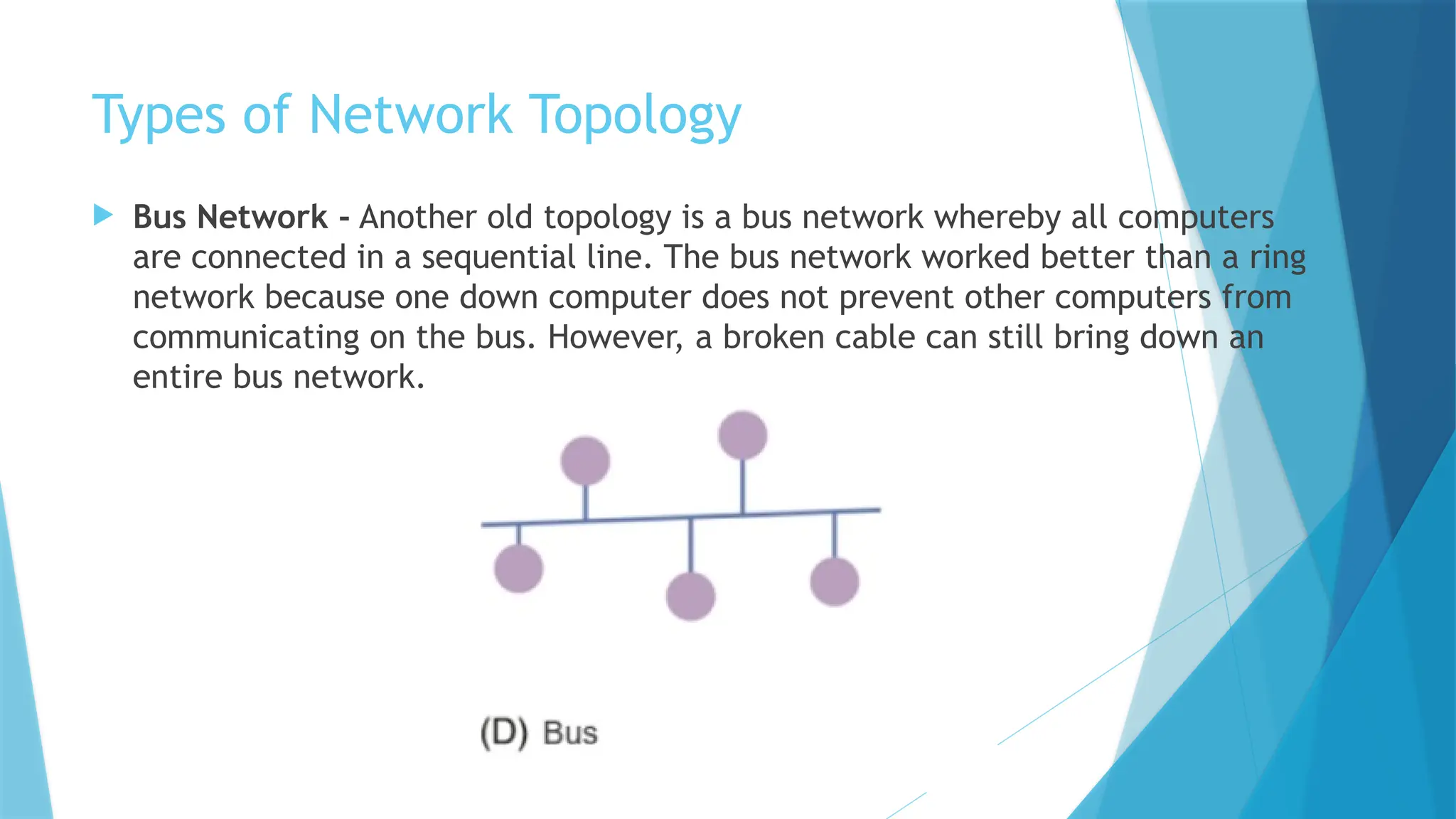
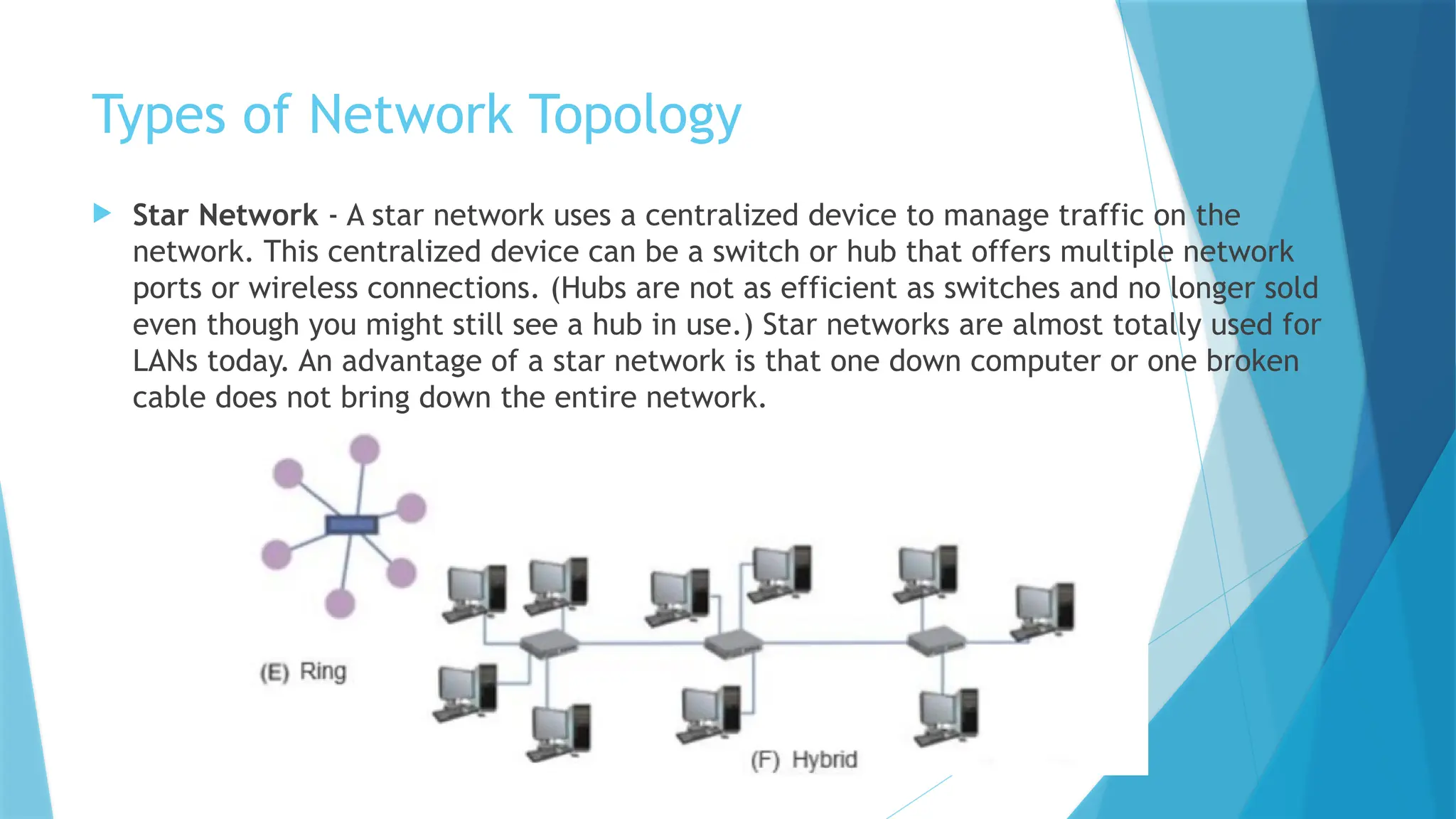
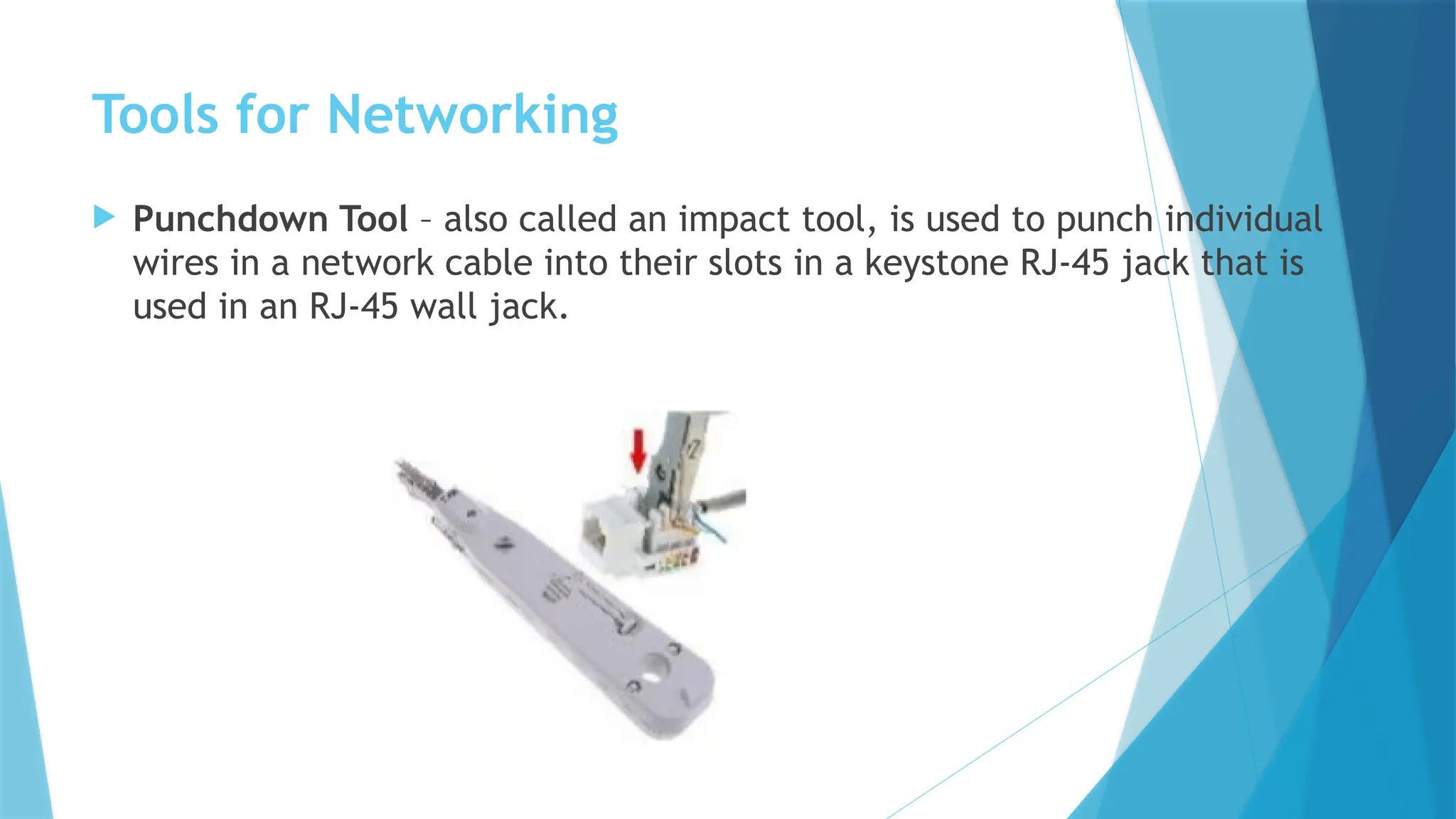
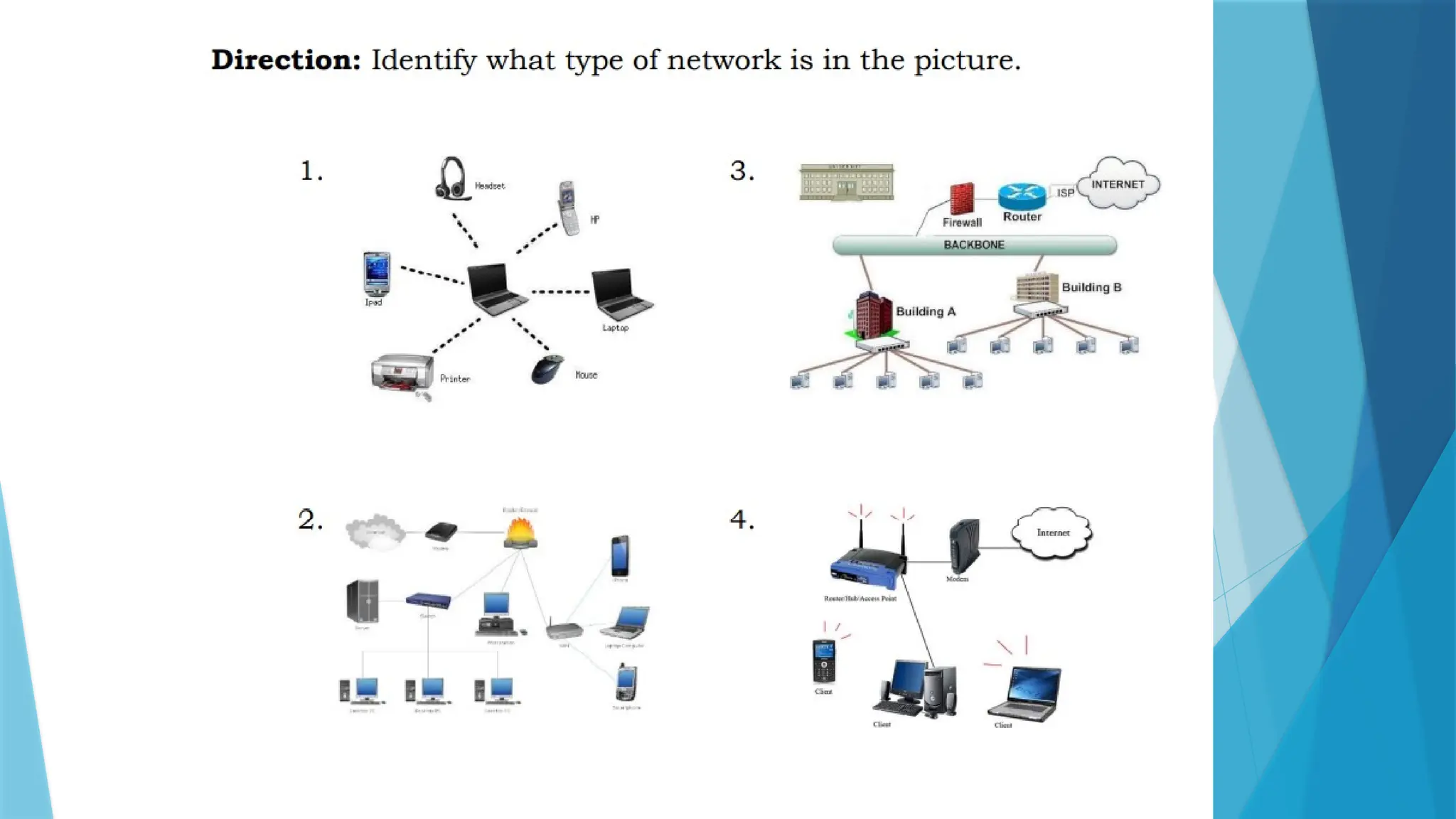
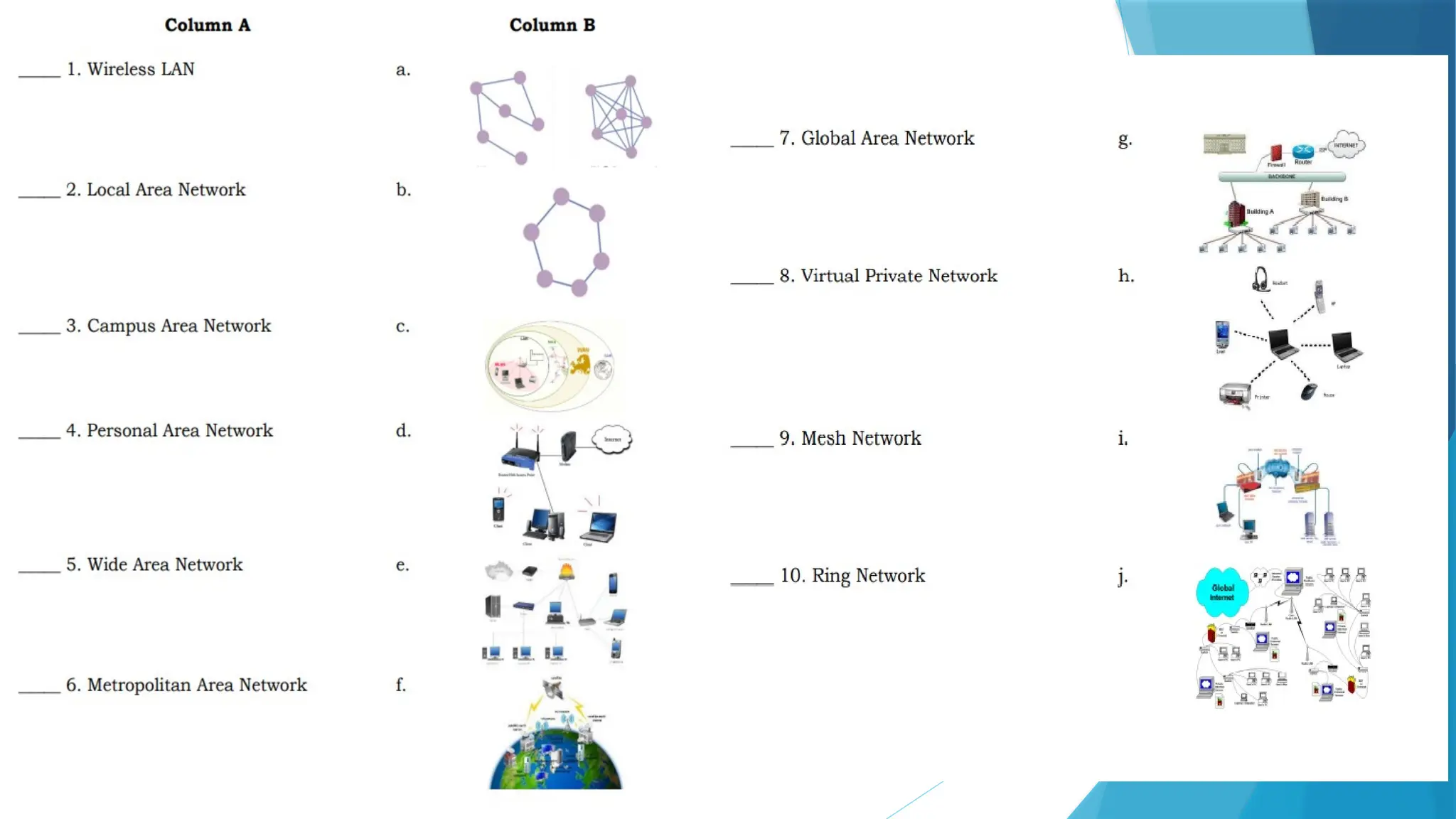
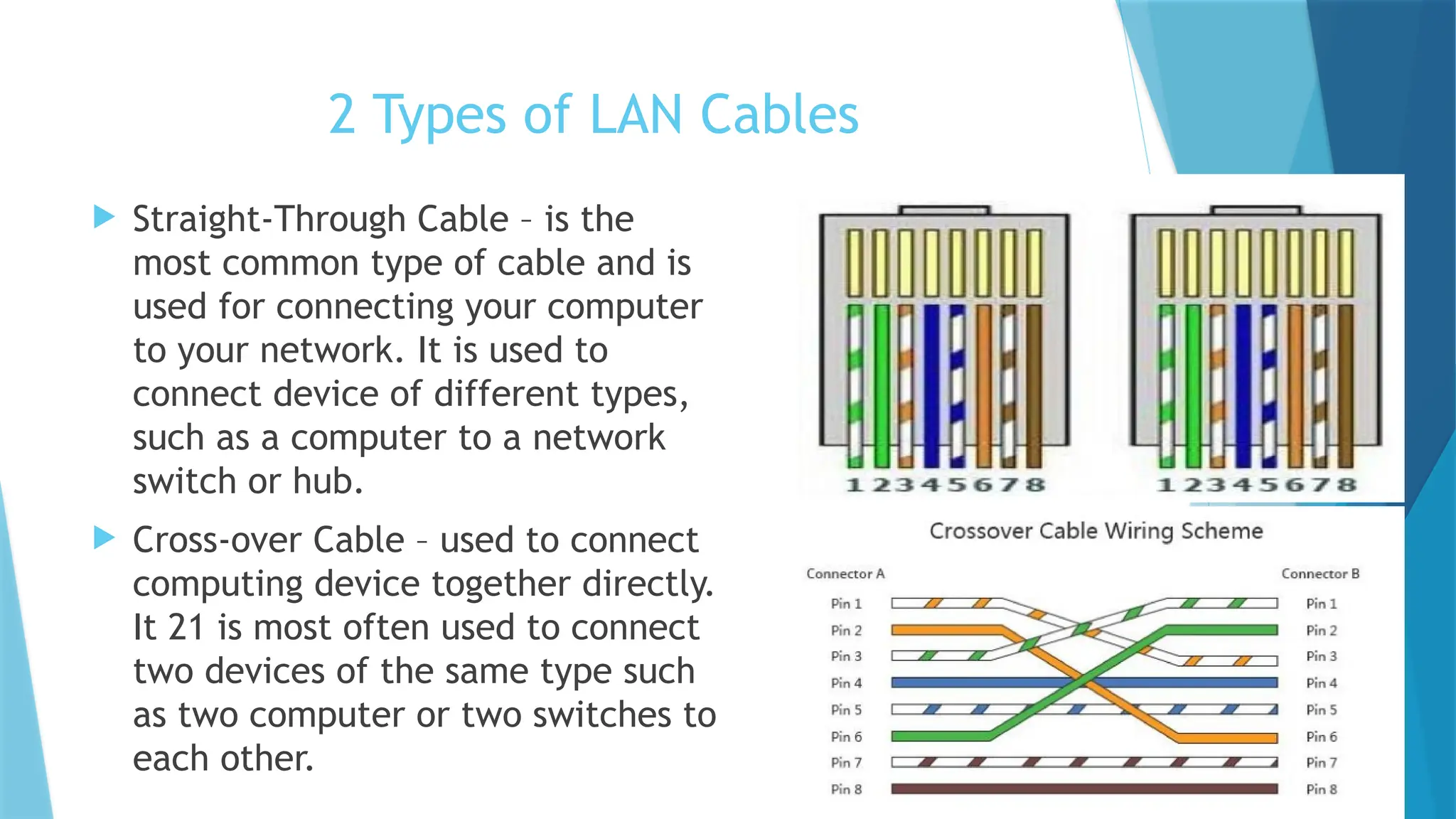
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer networks, including their definitions, types (such as LAN, WAN, and VPN), and topologies (like star, bus, and mesh). It discusses tools used in networking, such as LAN testers and crimping tools, as well as materials for LAN cabling, including UTP cables and routers. Additionally, it outlines the advantages and disadvantages of networking, such as file sharing and security issues.