This document discusses machine instructions and how programs are executed at the machine level. It covers number systems, data representation, memory addressing, instruction types, instruction execution, and addressing modes. Binary numbers are used in computers and represented as vectors. Negative numbers can be represented using sign-and-magnitude, one's complement, or two's complement methods. Memory is made up of addresses that store bits, bytes, and words of data. Instructions perform operations like data transfer, arithmetic, and program flow control. Programs are executed through sequential instruction fetch and execution, using techniques like looping and conditional branching. Addressing modes specify how operands are accessed in instructions.



![Big Endian and Little Endian: Consider a 32 bit integer (in hex): 0xabcdef12. It consists of 4
bytes: ab, cd, ef, and 12. Hence this integer will occupy 4 bytes in memory. Say we store it at
memory address starting 1000. There are 24 different orderings possible to store these 4 bytes in
4 locations (1000 - 1003). 2 among these 24 possibilities are very popular. These are called
as little endian and big endian.
INSTRUCTIONS and INSTRUCTION SEQUENCING
A computer must have instruction capable of performing the following operations. They are:
• Data transfer between memory and processor register.
• Arithmetic and logical operations on data.
• Program sequencing and control.
• I/O transfer.
Register Transfer Notation: The possible locations that may be involved during data transfer
are
Memory Location
Processor register
Registers in I/O sub-system.
Location Hardware Binary Address Expression Description
Memory LOC,PLACE,A,VAR2 R1 [LOC] The contents of
memory location LOC
are transferred to the
processor register R1.
Processor R0,R1, R2…Rn [R3] [R1]+[R2] Add the contents of
register R1 &R2 and
the result of the
operation is stored into
register R3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-180429022149/75/COMPUTER-ORGANIZATION-NOTES-Unit-2-6-2048.jpg)
![Assembly Language Notation:
Assembly Language
Format
Description
Move LOC,R1 Transfers the contents of memory location LOC
to the processor register R1.
Add R1,R2,R3 Add the contents of register R1 & R2 and stores
their sum into register R3.
Basic Instruction Type:
Instruction Type Syntax Expression Description
Three Address Operation
Source1,Source2,Destination
Add A,B,C C←[A]+[B]
Two Address Operation
Source,Destination
Add A,B B←[A]+[B]
One Address Operation Operand Add B Content of B
added with
the content of
the
accumulator
INSTRUCTION EXECUTION and STRAIGHT LINE SEQUENCING
Instruction Execution: There are 2 phases for executing an instruction. They are,
• Instruction Fetch
• Instruction Execution
Instruction Fetch:
The instruction is fetched from the memory location whose address is in PC. This is then placed
in IR.
Instruction Execution:
Instruction in IR is examined and decoded to determine which operation is to be performed.
Program execution Steps:
To begin executing a program, the address of first instruction must be placed in PC.
The processor control circuits use the information in the PC to fetch & execute instructions one
at a time in the order of increasing order.
This is called Straight line sequencing. During the execution of each instruction, the PC is
incremented by 4 to point to the address of next instruction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-180429022149/75/COMPUTER-ORGANIZATION-NOTES-Unit-2-7-2048.jpg)
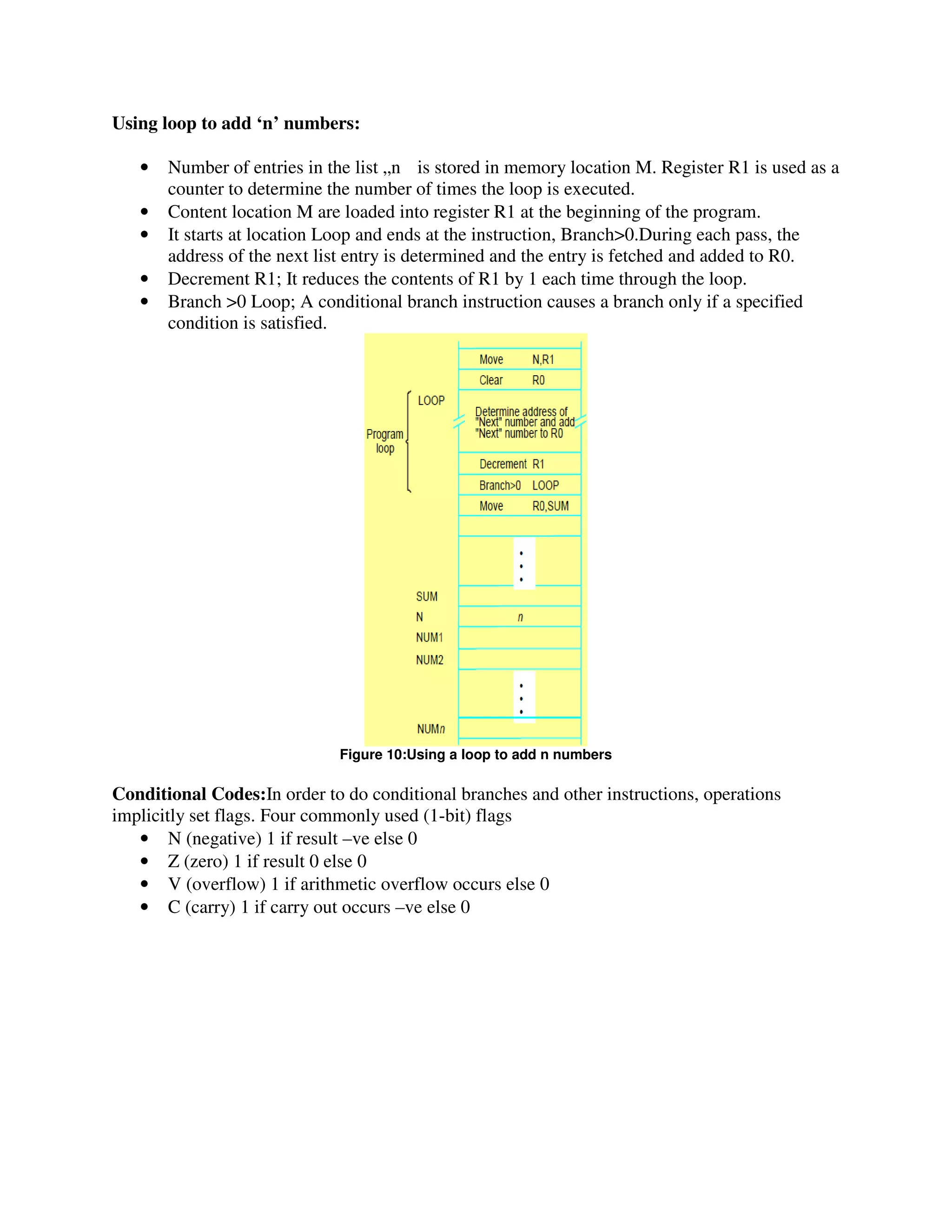
![Figure 8:A program for C [A]+ [B]
Branching: The Address of the memory locations containing the n numbers are symbolically given
as NUM1, NUM2…..NUMn.
Separate Add instruction is used to add each number to the contents of register R0.
After all the numbers have been added, the result is placed in memory location SUM.
Figure 9:A straight line program for adding n numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-180429022149/75/COMPUTER-ORGANIZATION-NOTES-Unit-2-8-2048.jpg)

![Immediate Addressing Mode: The operand is specified in the instruction itself .
Move 200immediate, R0
Move #200, R0
Direct Addressing Mode: Operand resides in Memory and its address is given explicitly in the
address field of an instruction.
Move P, R0
Move R0, S
Add Q, R0
Register Addressing Mode: name of the register (address code of a specific general purpose
register) appears in the address field of an instruction i.e.
Move B, R1
Indexing and Arrays:
Index Mode:
The effective address of an operand is generated by adding a constant value to the contents of a
register. The constant value uses either special purpose or general purpose register.
X (RI)
where X – denotes the constant value contained in the instruction
Ri – name of the register involved.
The Effective Address of the operand EA=X + [Ri]
The index register R1 contains the address of a new location and the value of X defines an offset
(also called a displacement).
To find operand first go to Reg R1 (using address)-read the content from R1 i.e. 1000
Add the content 1000 with offset 20 to get the result. Here the constant X refers to the new
address and the contents of index register that defines the offset to the operand.
The sum of two values is given explicitly in the instruction and the other is stored in register.
Add 20(R1), R2 (or) EA=>1000+20=1020
Relative Addressing: It is same as index mode. The difference is, instead of general purpose
register, here we can use program counter (PC).
Relative Mode:
The Effective Address is determined by the Index mode using the PC in place of the general
purpose register.
This mode can be used to access the data operand. But it’s most common use is to specify the
target address in branch instruction. Eg. Branch>0 Loop
It causes the program execution to go to the branch target location. It is identified by the name
loop if the branch condition is satisfied.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-180429022149/75/COMPUTER-ORGANIZATION-NOTES-Unit-2-11-2048.jpg)