Downloaded 376 times


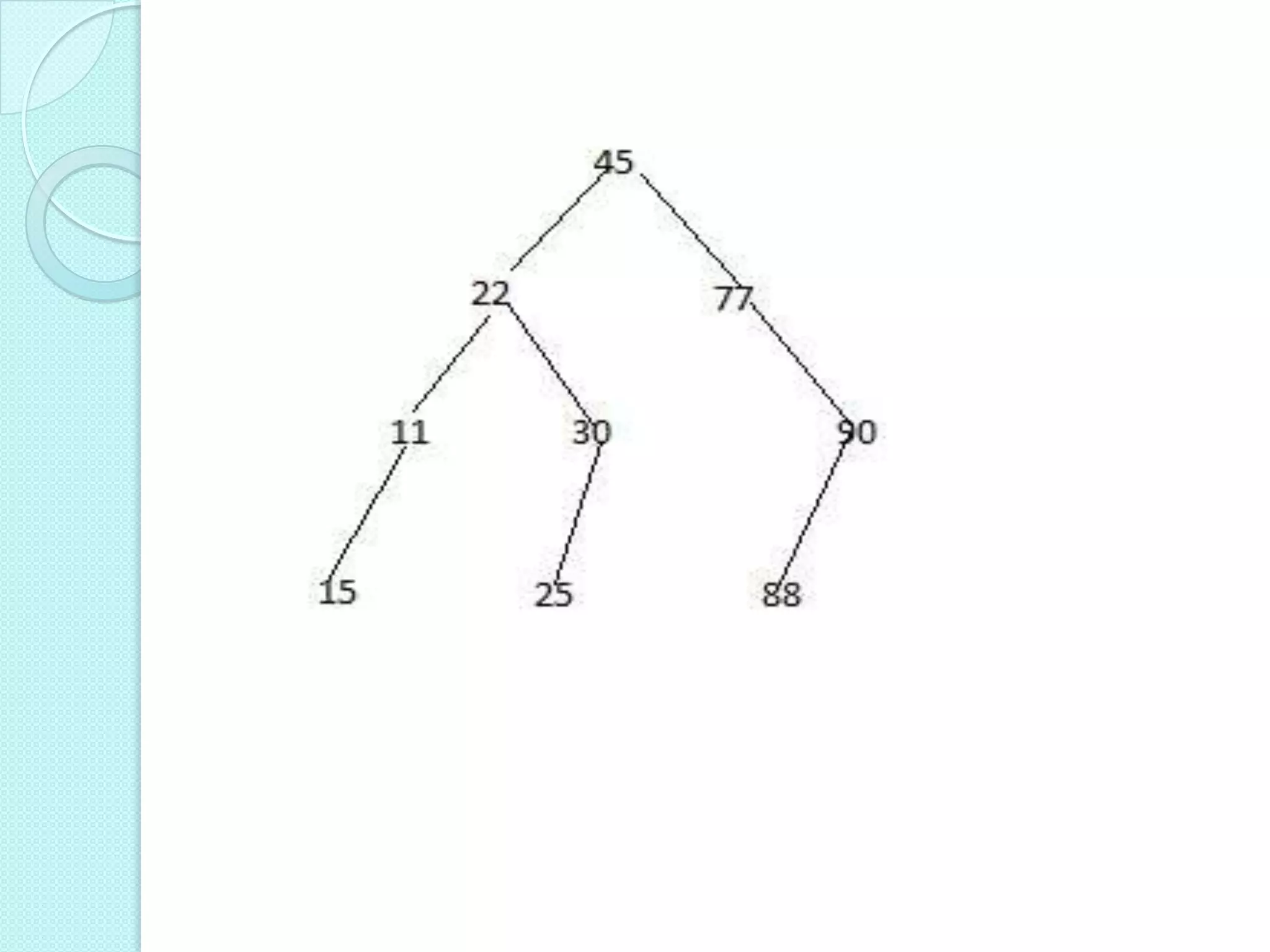
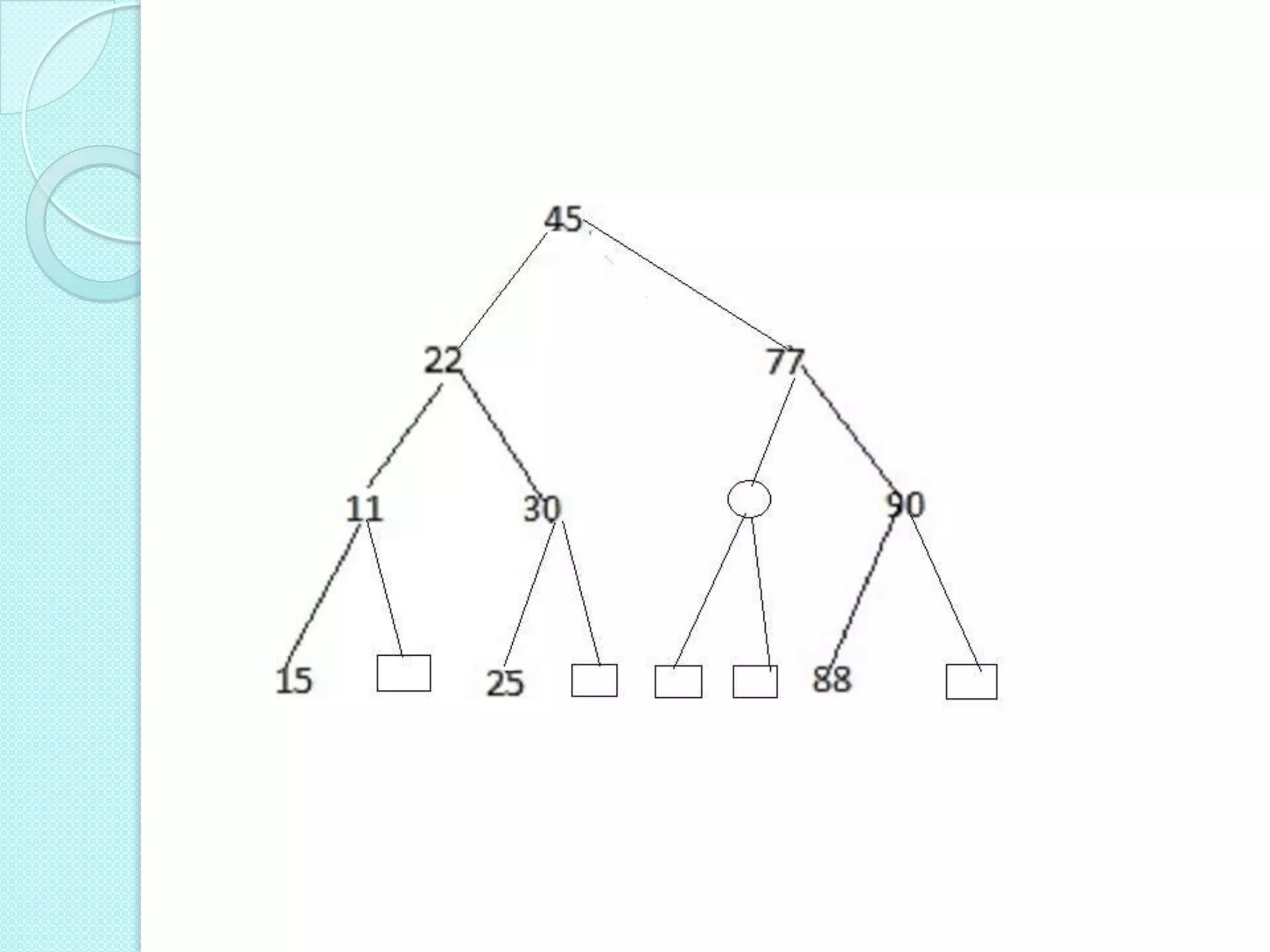
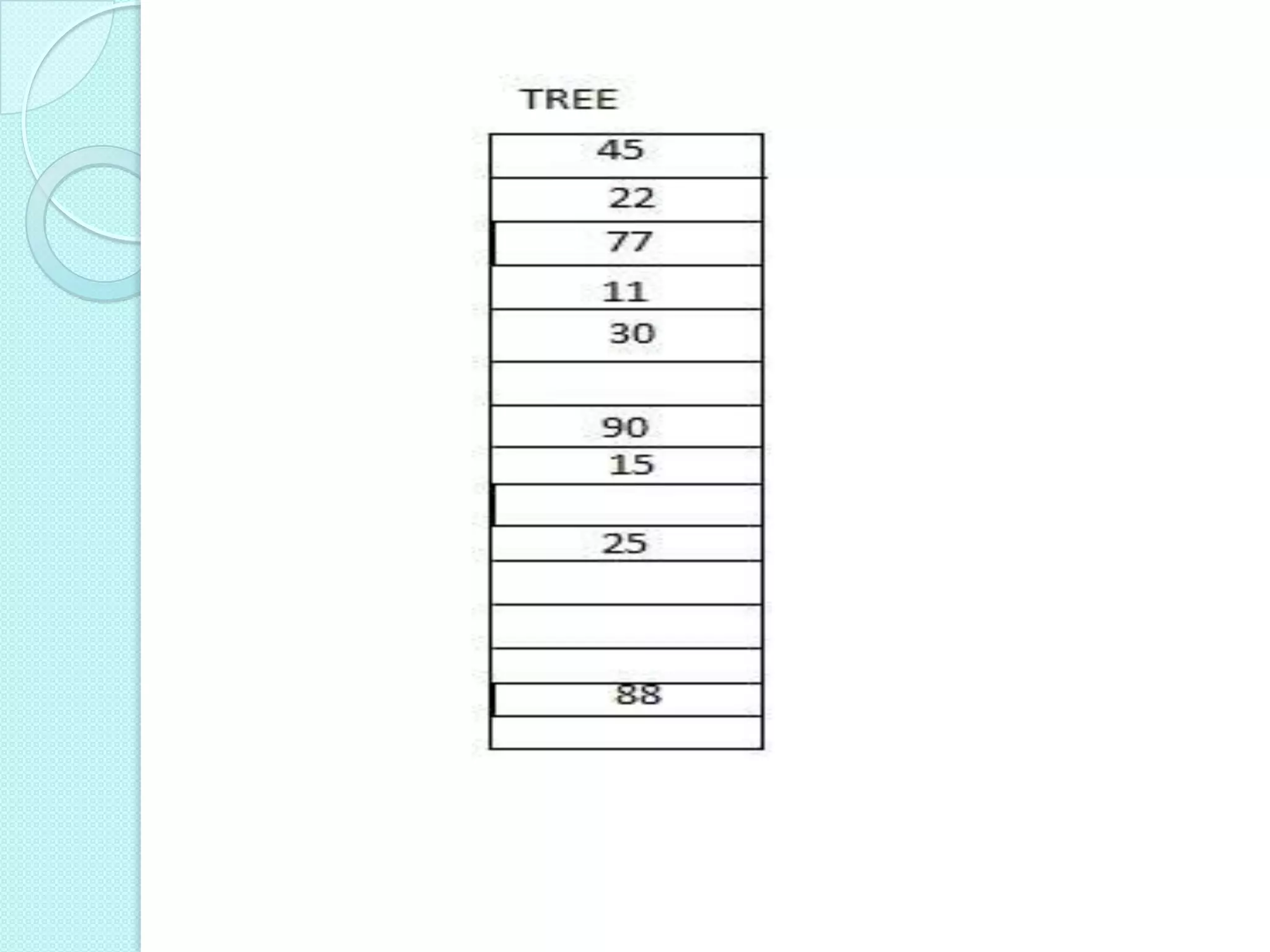
![ The root R is stored in TREE[0].
If a node n occupies TREE[K],
then its left child in TREE[2*K]
& right child TREE [2*K+1].
If TREE[1]=NULL then it is empty
tree.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/representationofbinarytreeinmemory-130215094958-phpapp01/75/Representation-of-binary-tree-in-memory-3-2048.jpg)
![Linked Representation
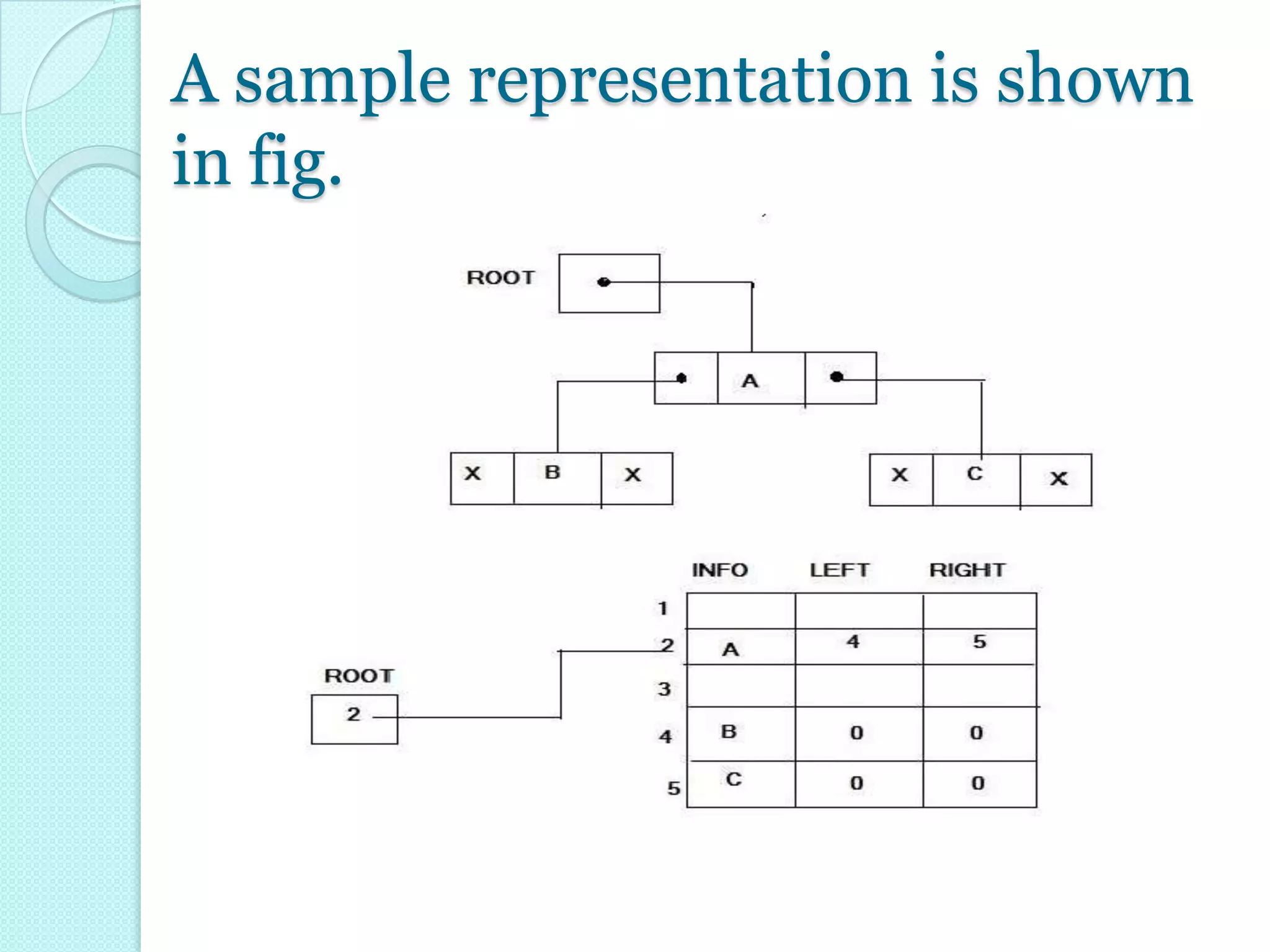
The linked representation uses three parallel
arrays,INFO,LEFT & RIGHT & a pointer variable
ROOT.Each node N of Y will correspond to a location K
such that:
1) INFO[K] contains the data at node N.
2) LEFT[K] contains the location of left child of node N.
3) RIGHT[K] contains the location of right child of node
N.
ROOT will contain location of root R of T.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/representationofbinarytreeinmemory-130215094958-phpapp01/75/Representation-of-binary-tree-in-memory-7-2048.jpg)

There are two ways to represent a binary tree in memory: sequential representation which uses a single linear array to store the tree, and linked representation which uses three parallel arrays (INFO, LEFT, and RIGHT) along with a ROOT pointer to link nodes. The sequential representation stores the root at index 0 of the array and children at calculated indices, while the linked representation stores the data, left child index, and right child index of each node in the parallel arrays.


![ The root R is stored in TREE[0].
If a node n occupies TREE[K],
then its left child in TREE[2*K]
& right child TREE [2*K+1].
If TREE[1]=NULL then it is empty
tree.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/representationofbinarytreeinmemory-130215094958-phpapp01/75/Representation-of-binary-tree-in-memory-3-2048.jpg)



![Linked Representation
The linked representation uses three parallel
arrays,INFO,LEFT & RIGHT & a pointer variable
ROOT.Each node N of Y will correspond to a location K
such that:
1) INFO[K] contains the data at node N.
2) LEFT[K] contains the location of left child of node N.
3) RIGHT[K] contains the location of right child of node
N.
ROOT will contain location of root R of T.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/representationofbinarytreeinmemory-130215094958-phpapp01/75/Representation-of-binary-tree-in-memory-7-2048.jpg)

Explains representation of binary trees in memory through sequential representation using a linear array. Discusses root position and child node indexing in a complete binary tree.
Describes linked representation of binary trees using three arrays for data, left, and right child locations, along with a pointer to the root node, exemplified in a figure.