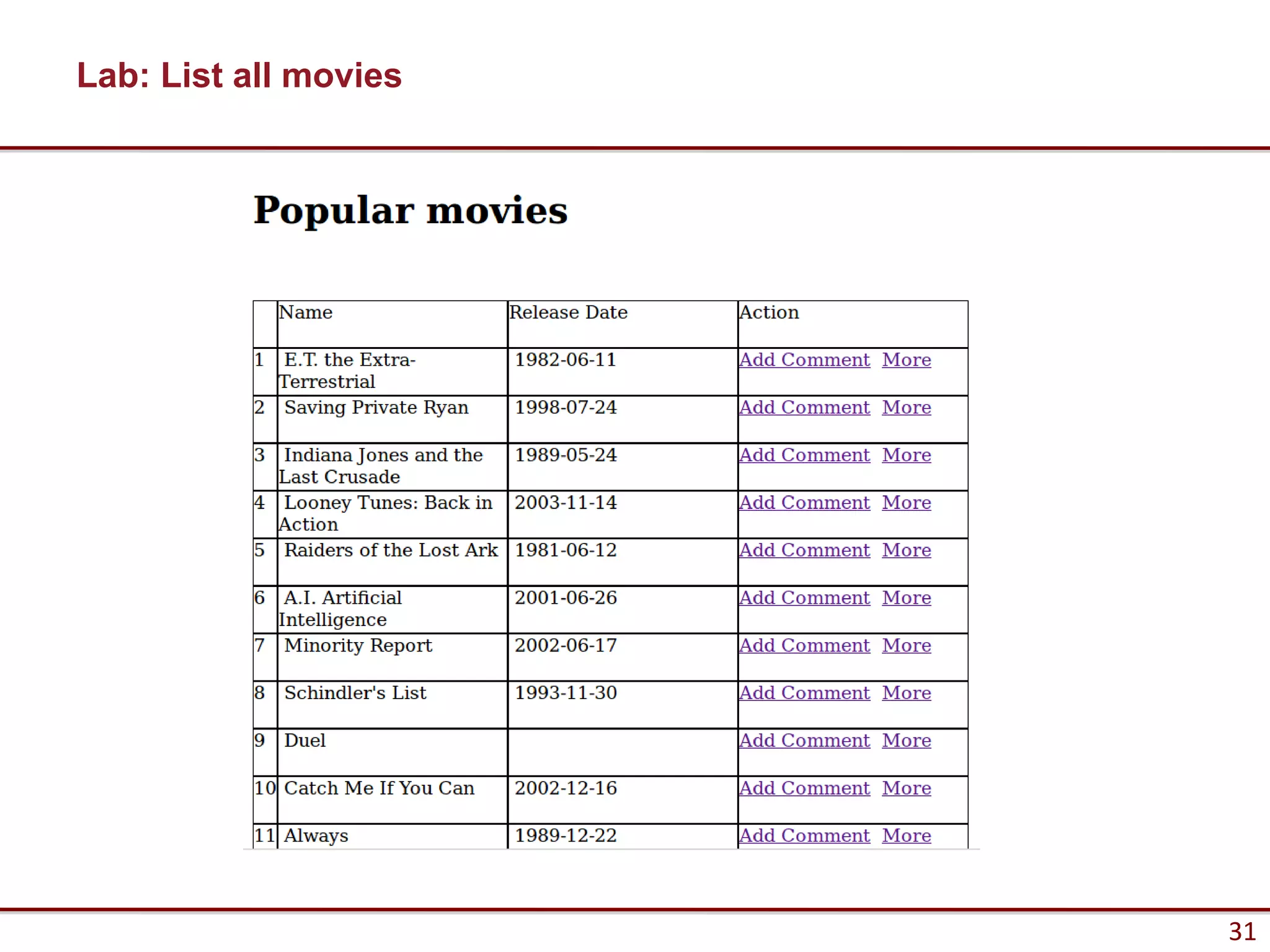
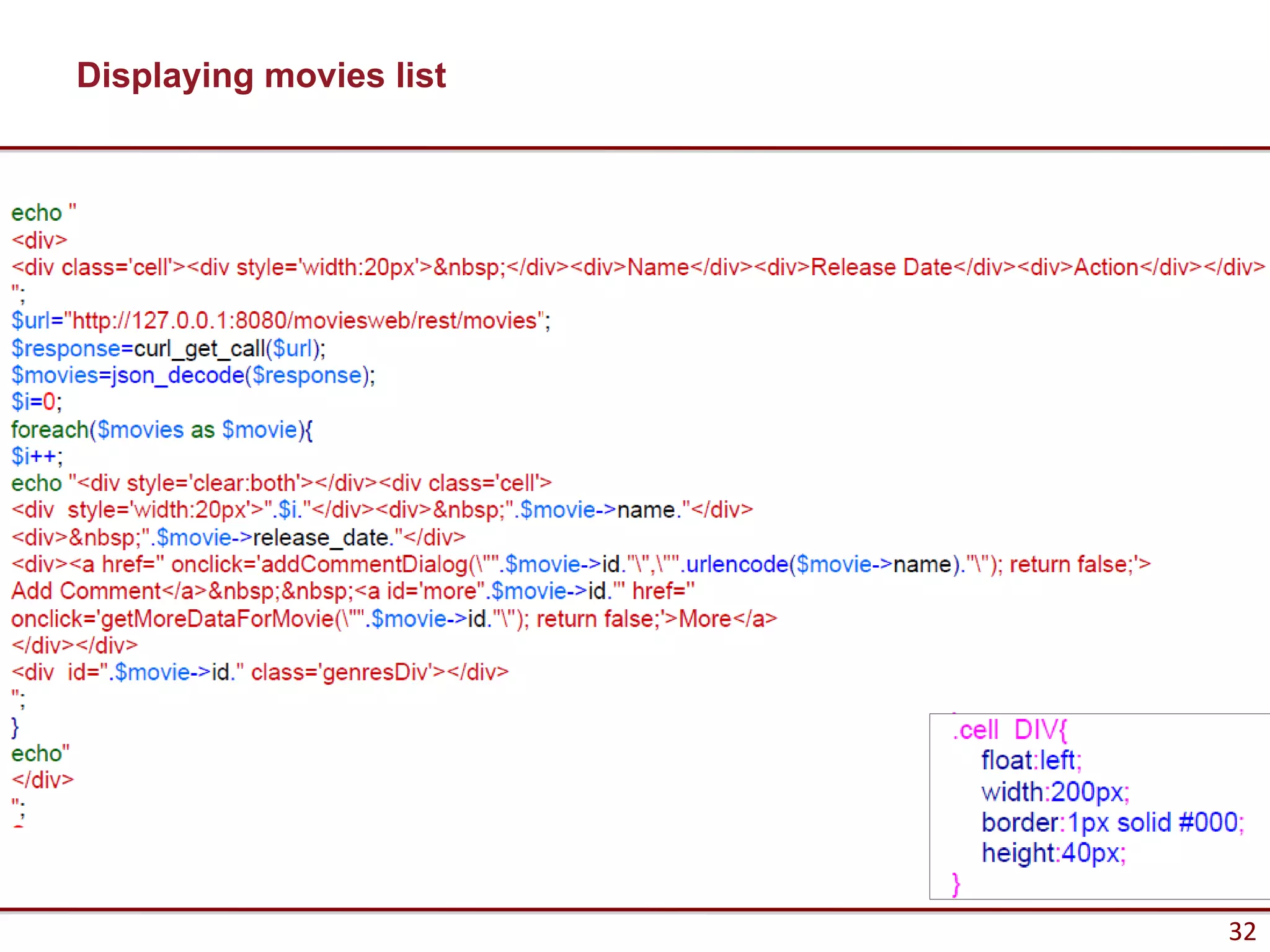
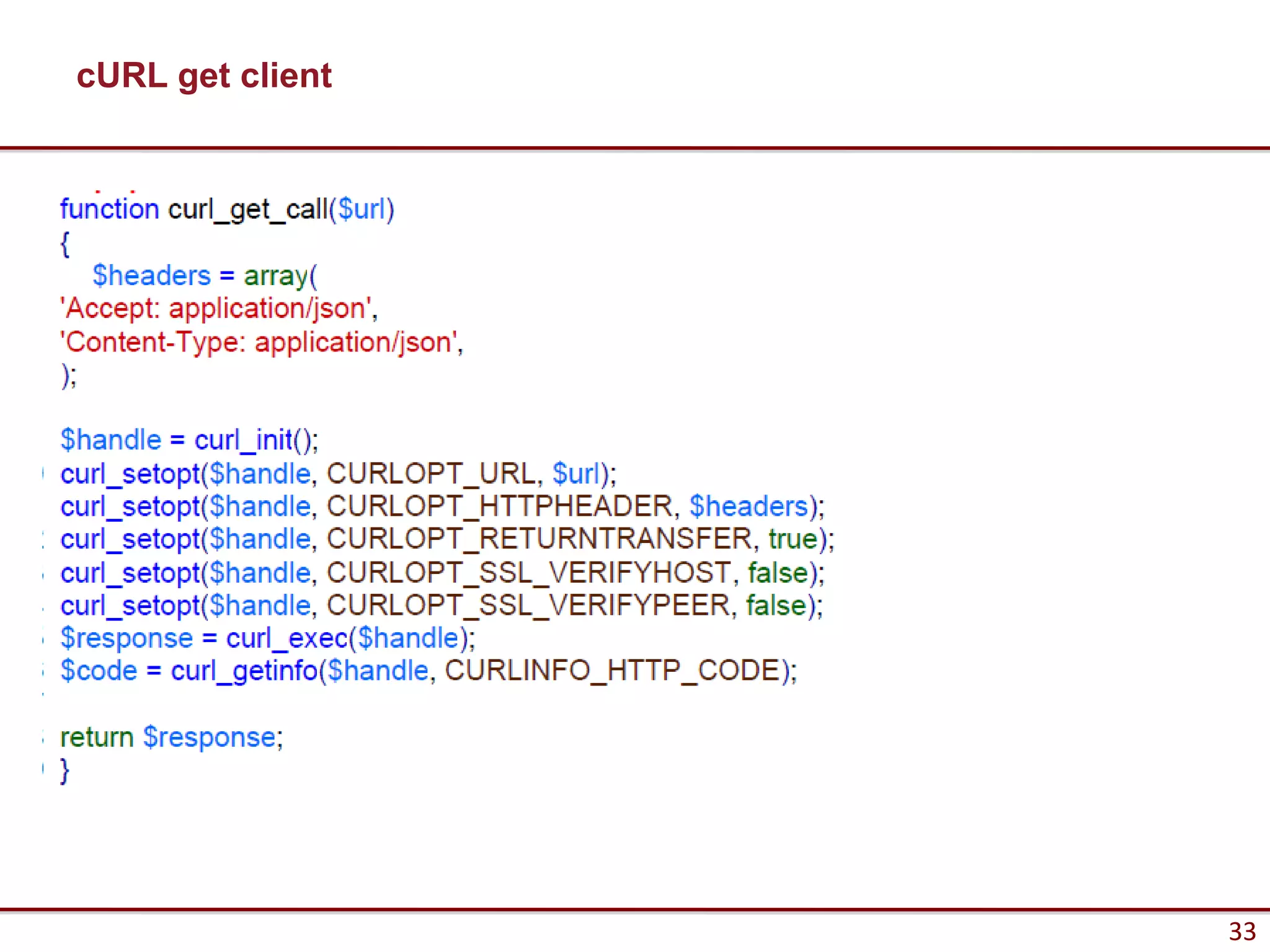
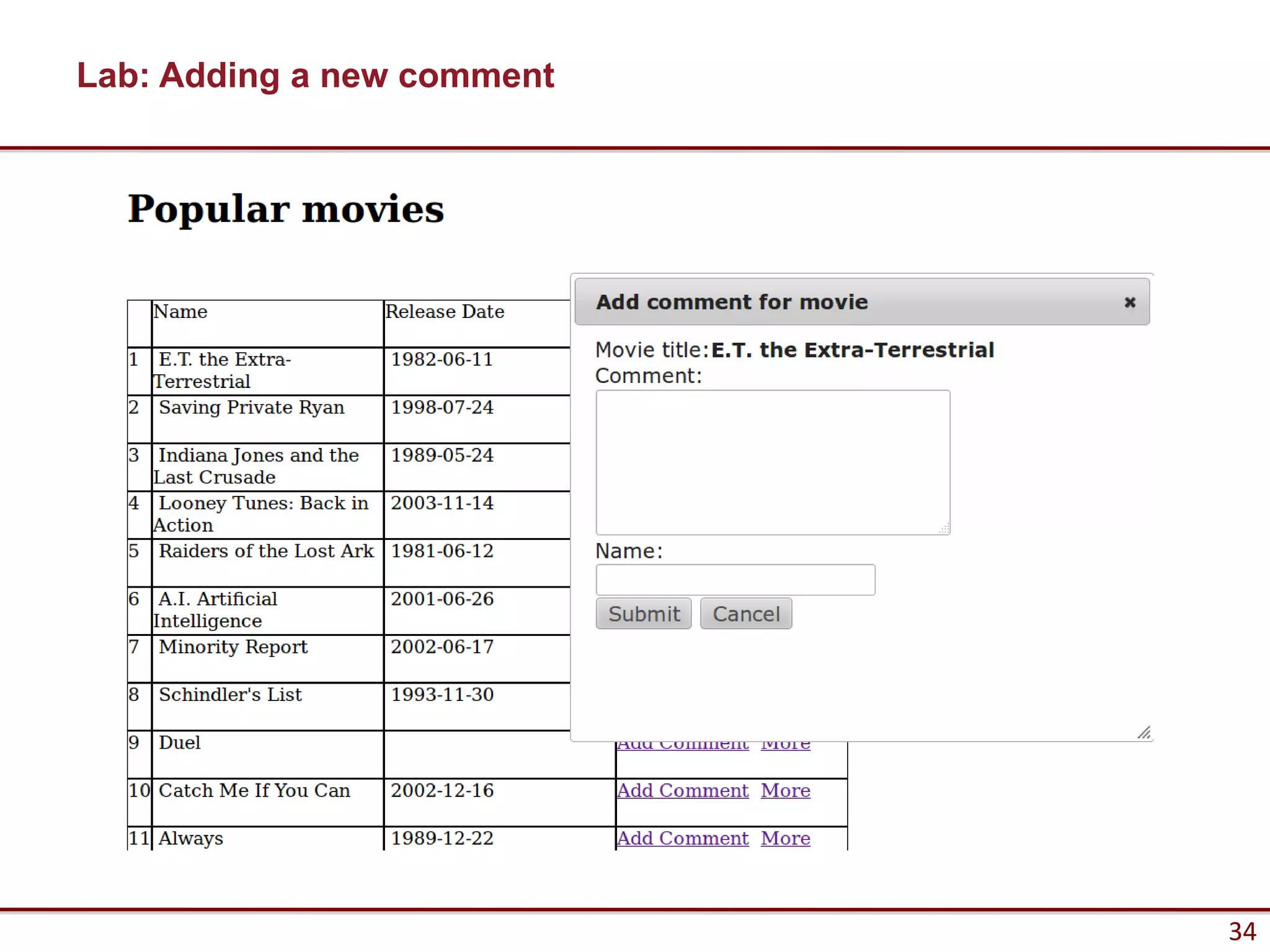
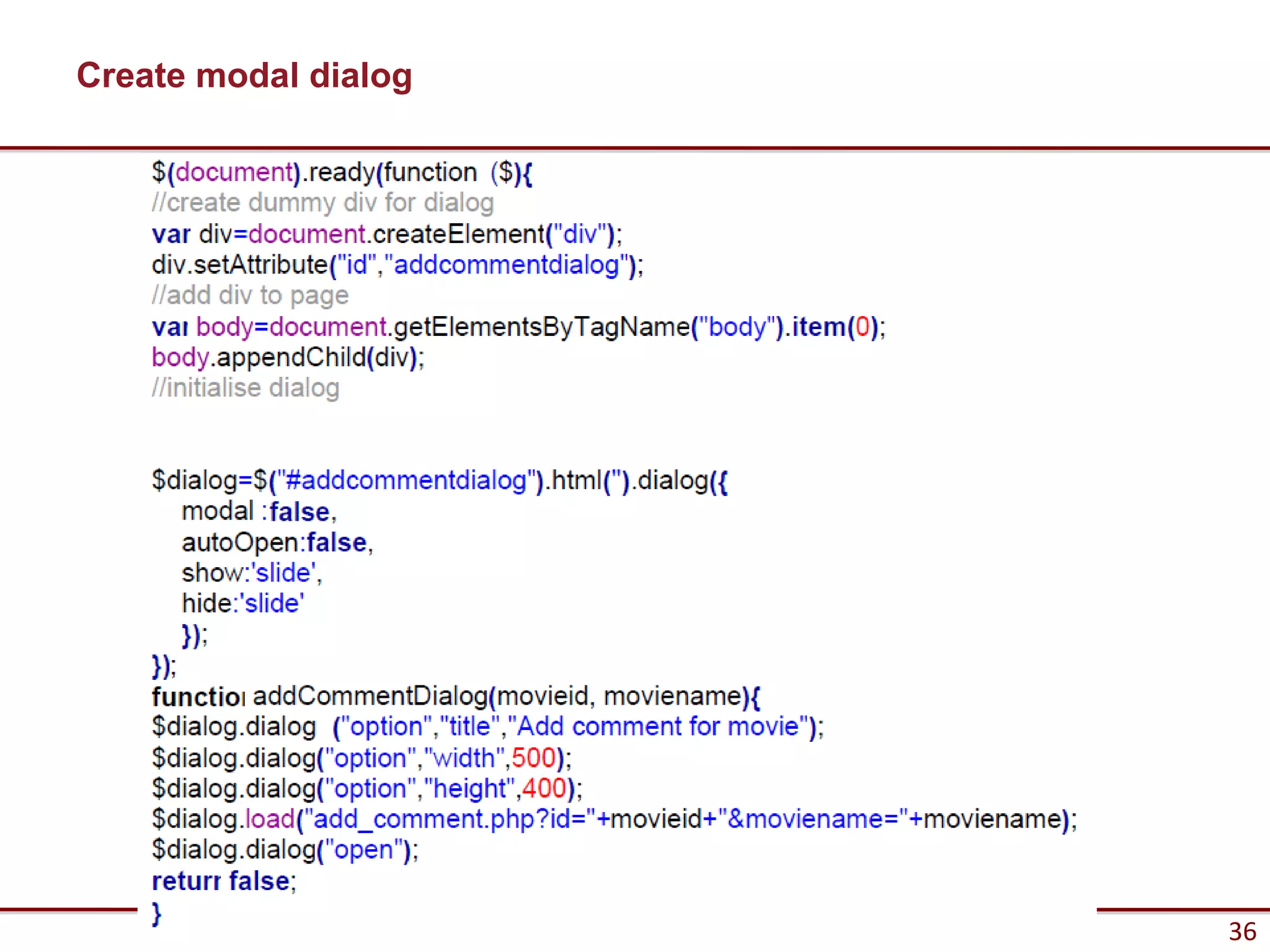
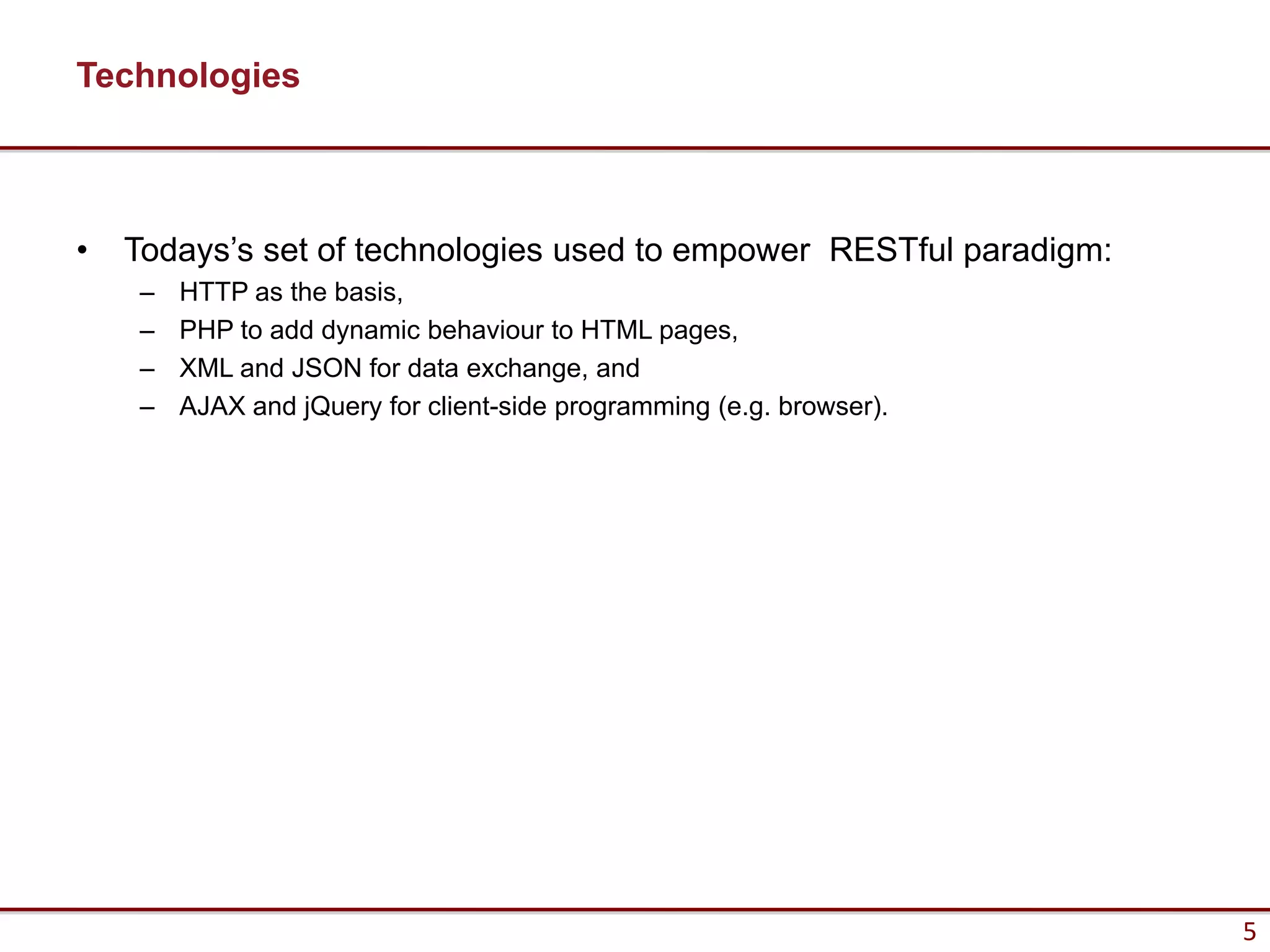
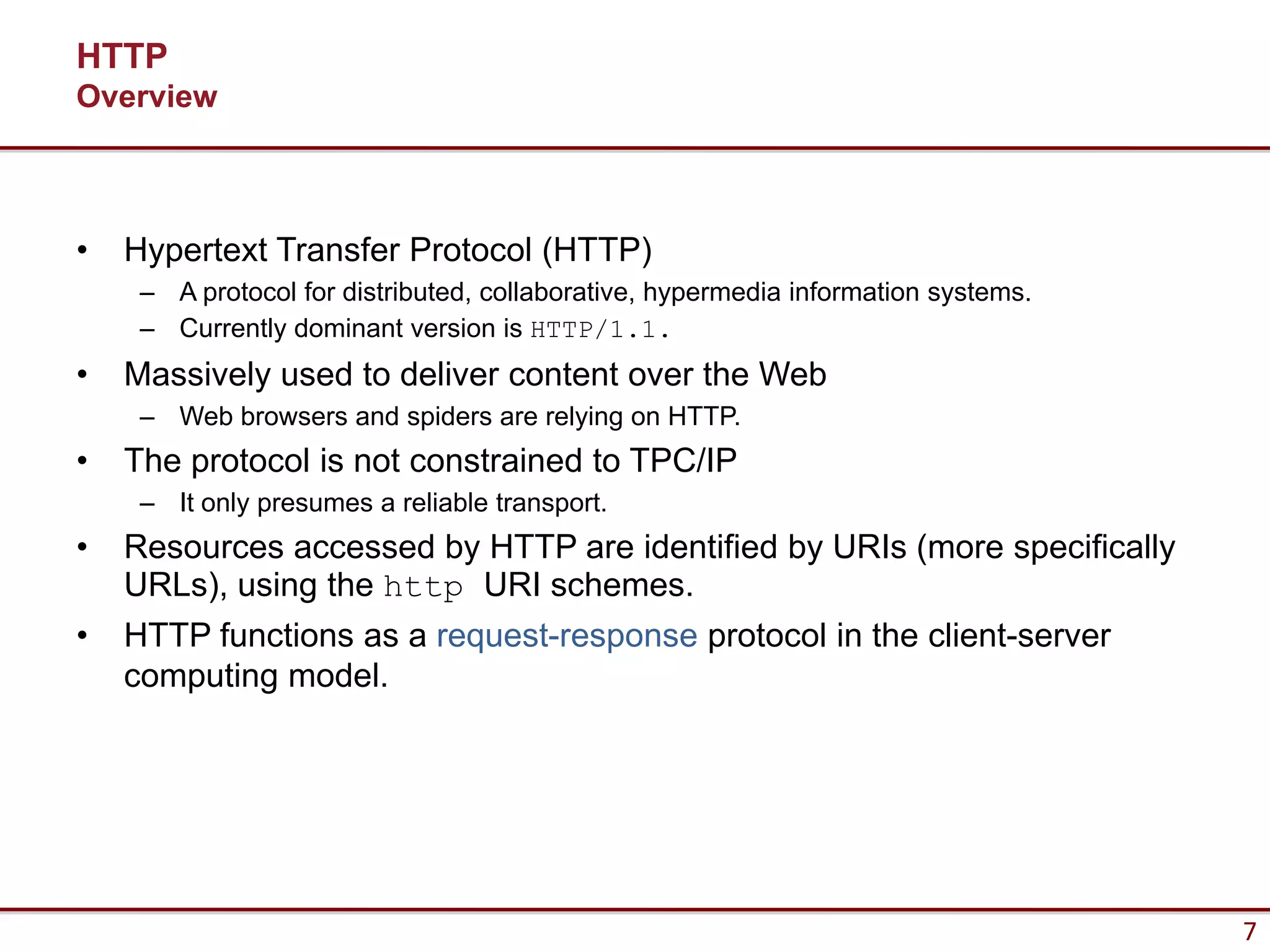
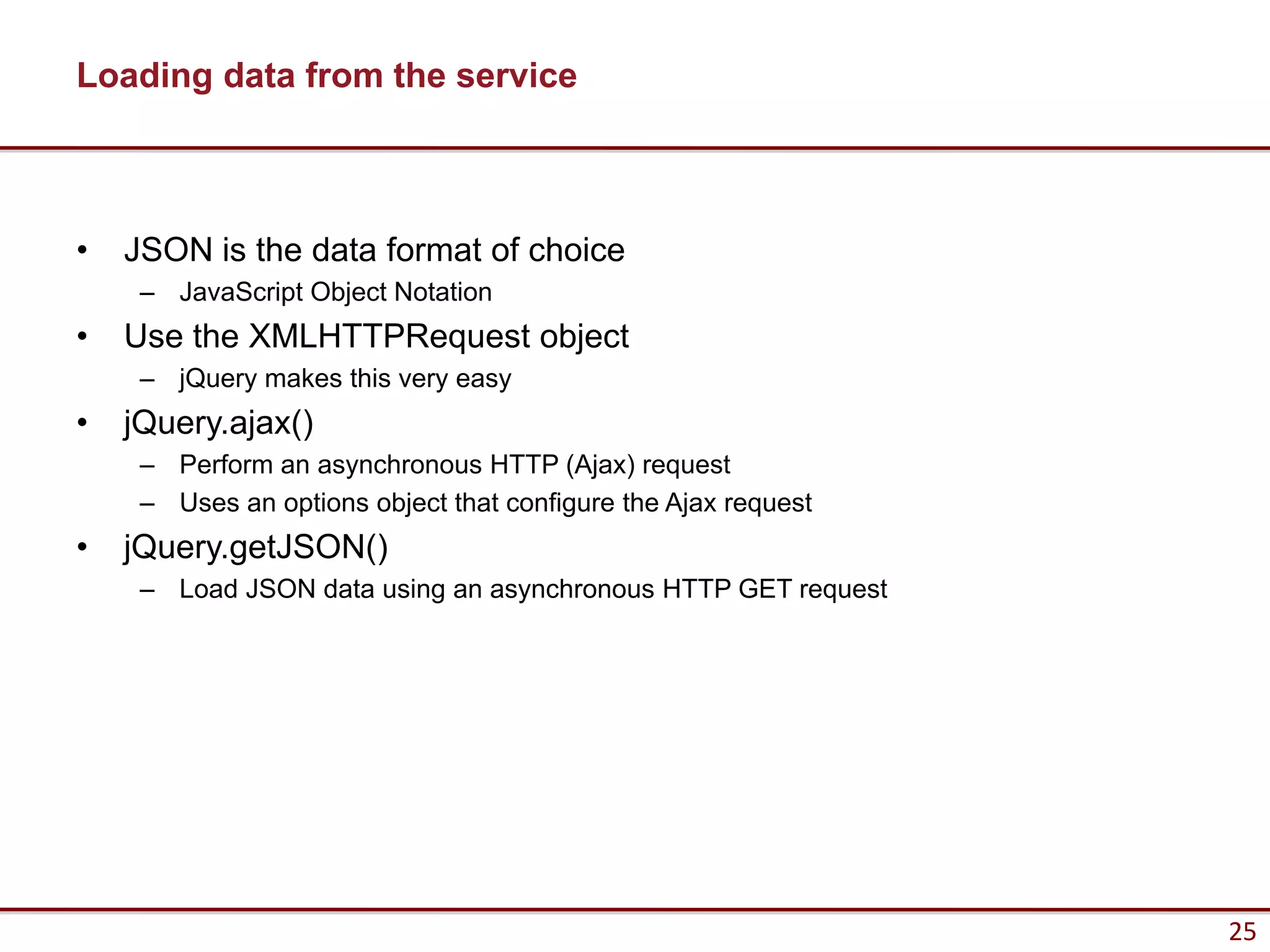
Here are the key steps to load data from a RESTful service using AJAX and jQuery:
1. Make an AJAX GET request to the REST API endpoint using jQuery.ajax() or jQuery.getJSON().
2. Specify the URL, set the data type to "json", and provide a success callback.
3. On success, the JSON response will be passed to the callback function where it can be used to update the UI.
4. Parse the JSON response into a JavaScript object for easy access to the data.
5. Update the HTML using the jQuery DOM manipulation methods like html(), text(), etc.
So in summary - make an AJAX GET, parse the JSON response,






![JSON
Example
{
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Smith",
"age": 25,
"address": {
"streetAddress": "21 2nd Street",
"city": "New York",
"state": "NY",
"postalCode": "10021"
},
"phoneNumbers": [
{ "type": "home", "number": "212 555-1234" },
{ "type": "fax", "number": "646 555-4567" }
],
"newSubscription": false,
"companyName": null
}
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consumingrestfulservicesinphp-120201064749-phpapp02/75/Consuming-RESTful-services-in-PHP-10-2048.jpg)






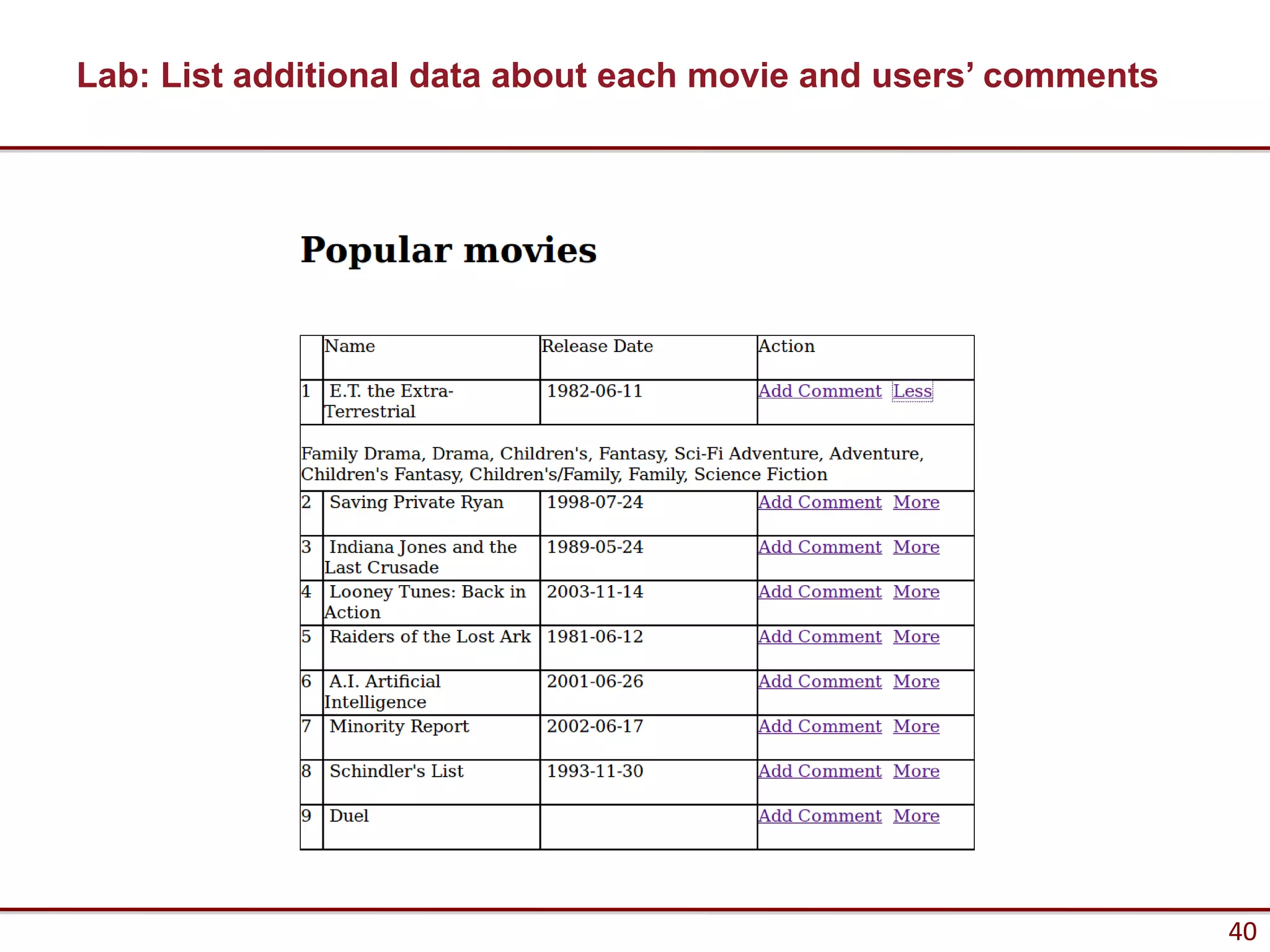
![Simple example
Filling Out Forms
<form method="post" action="form_processing_page.php">
<input type="text" name="name" />
<input type="text" name="color" />
</form>
Processing form
$name = $_POST[‘name'];
$color = $_POST[‘color'];
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consumingrestfulservicesinphp-120201064749-phpapp02/75/Consuming-RESTful-services-in-PHP-20-2048.jpg)


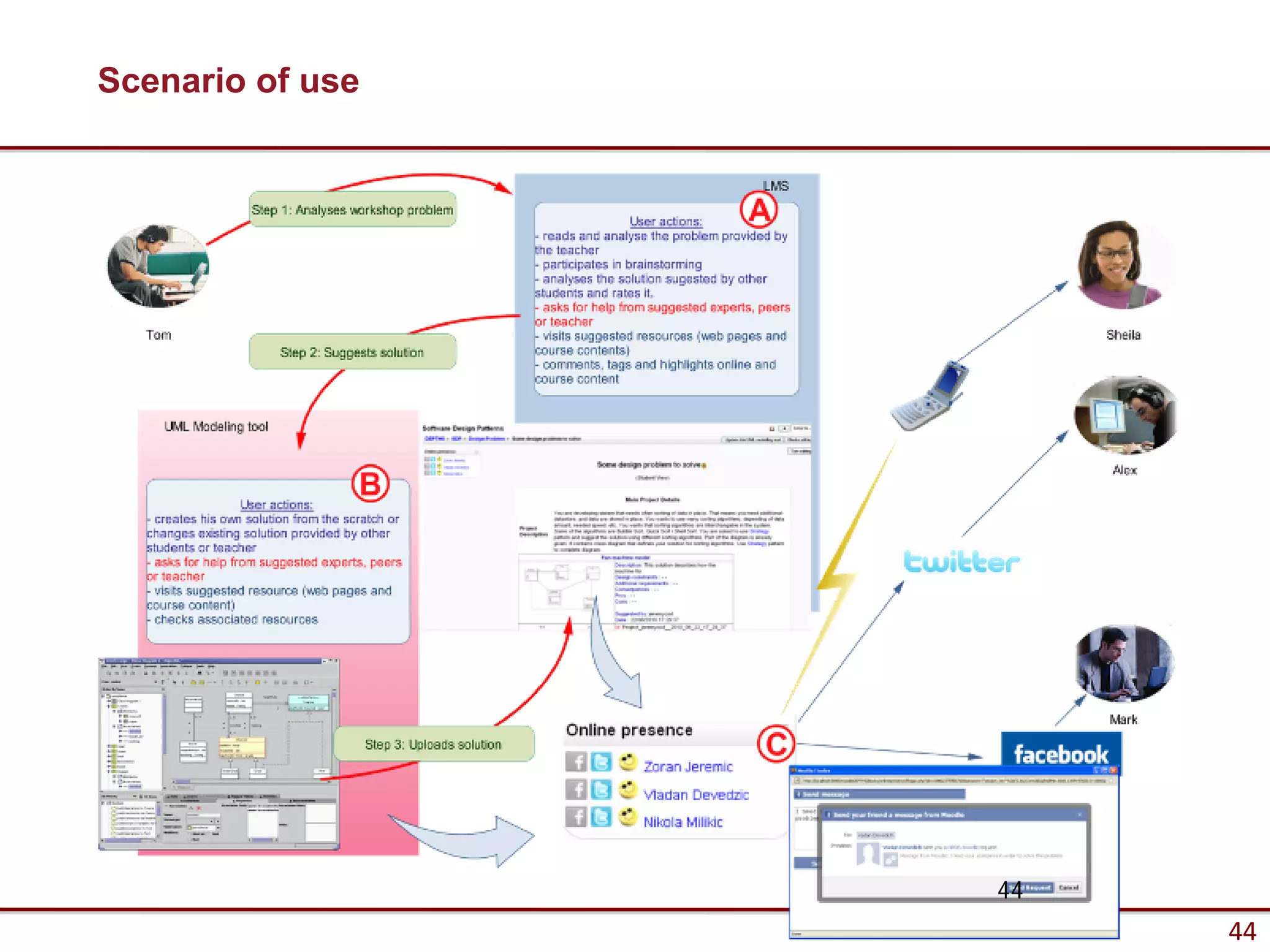
![PHP and JSON
$json = '{"a":1,"b":2,"c":3,"d":4,"e":5}';
var_dump(json_decode($json));
var_dump(json_decode($json, true));
Output: object(stdClass)#1 (5) {
["a"] => int(1)
["b"] => int(2)
["c"] => int(3)
["d"] => int(4)
["e"] => int(5)
}
array(5) {
["a"] => int(1)
["b"] => int(2)
["c"] => int(3)
["d"] => int(4)
["e"] => int(5)
}
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consumingrestfulservicesinphp-120201064749-phpapp02/75/Consuming-RESTful-services-in-PHP-23-2048.jpg)


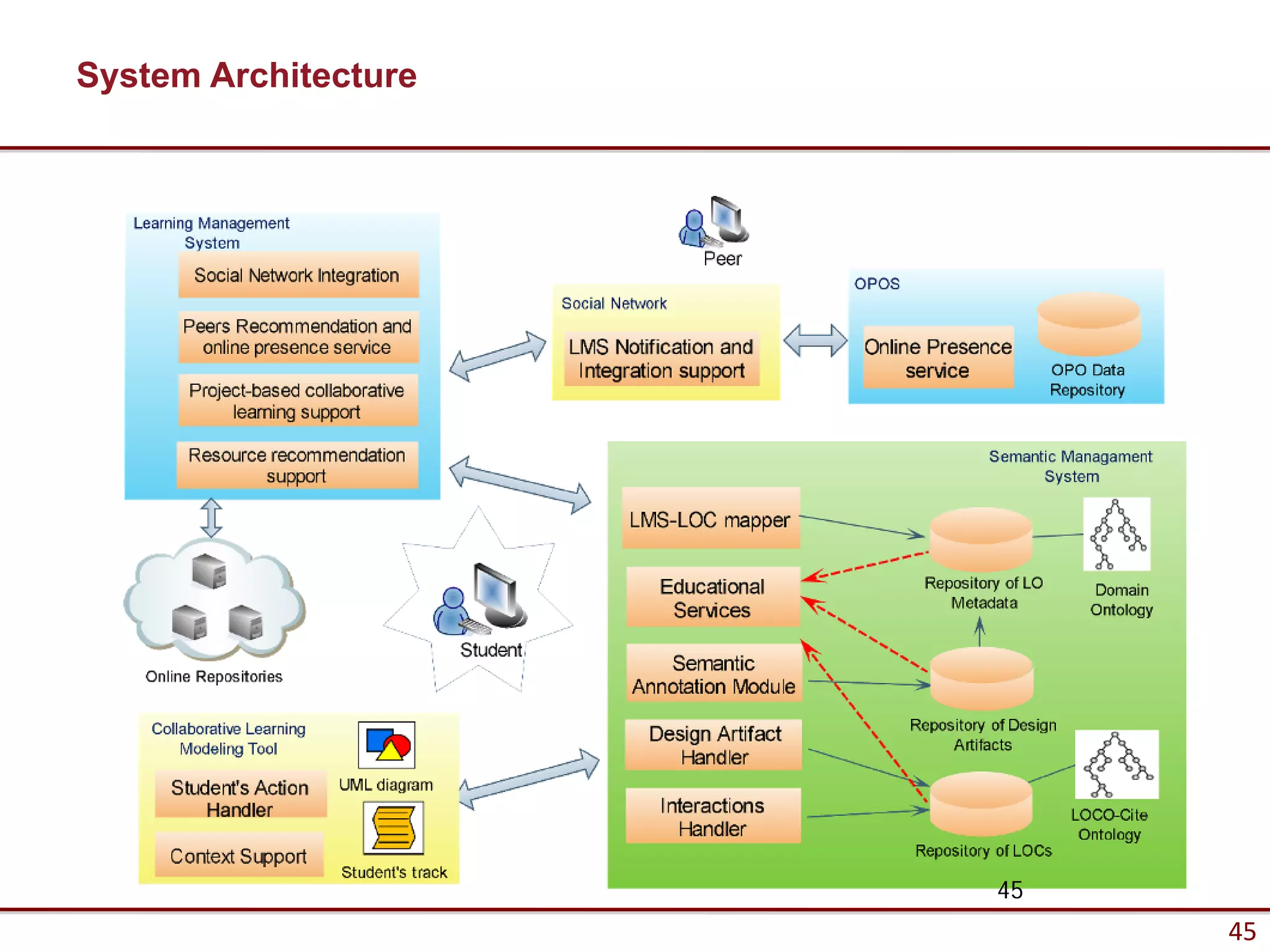
![jQuery client - getJSON()
$.getJSON( url, [data], [callback], [type] )
• url: (String) The URL of the page to load.
• data (Optional): (Map) Key/value pairs that will be sent to the server.
• callback (Optional): (Function) A function to be executed whenever the data is
loaded successfully.
• type (Optional): (String) Type of data to be returned to callback function: “xml”, “html”,
“script”, “json”, “jsonp”, or “text”.
$.getJSON(
"http://some-remote-site",
"{key:value}",
function(data) { alert(data); },
“json");
$.getJSON(
"http://some-remote-site",
function(data) { alert(data); },
);
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/consumingrestfulservicesinphp-120201064749-phpapp02/75/Consuming-RESTful-services-in-PHP-27-2048.jpg)