It focuses on aligning QA with modern software development practices through Continuous Testing and Agile methodologies.
🚀 Key topics covered:
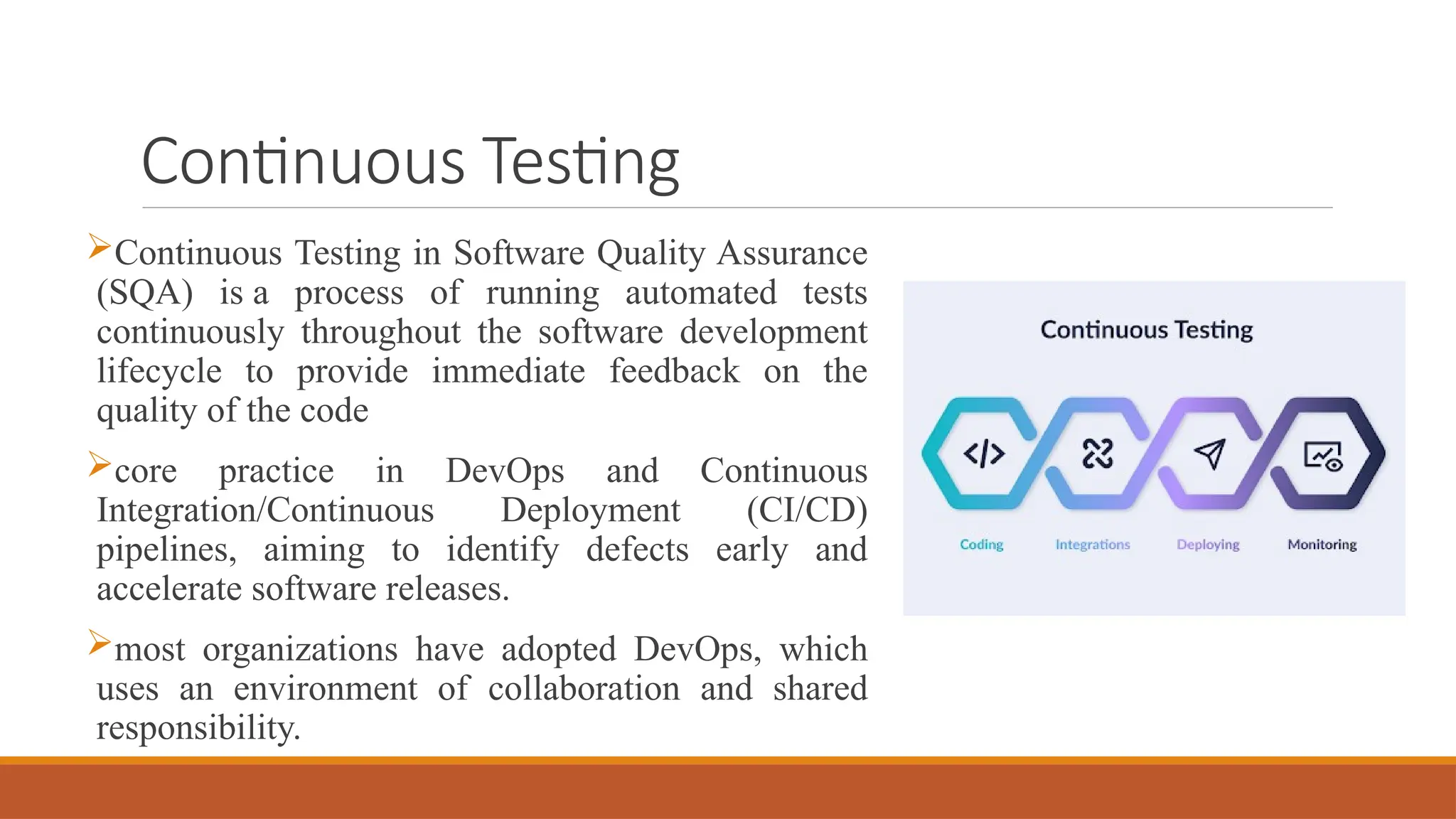
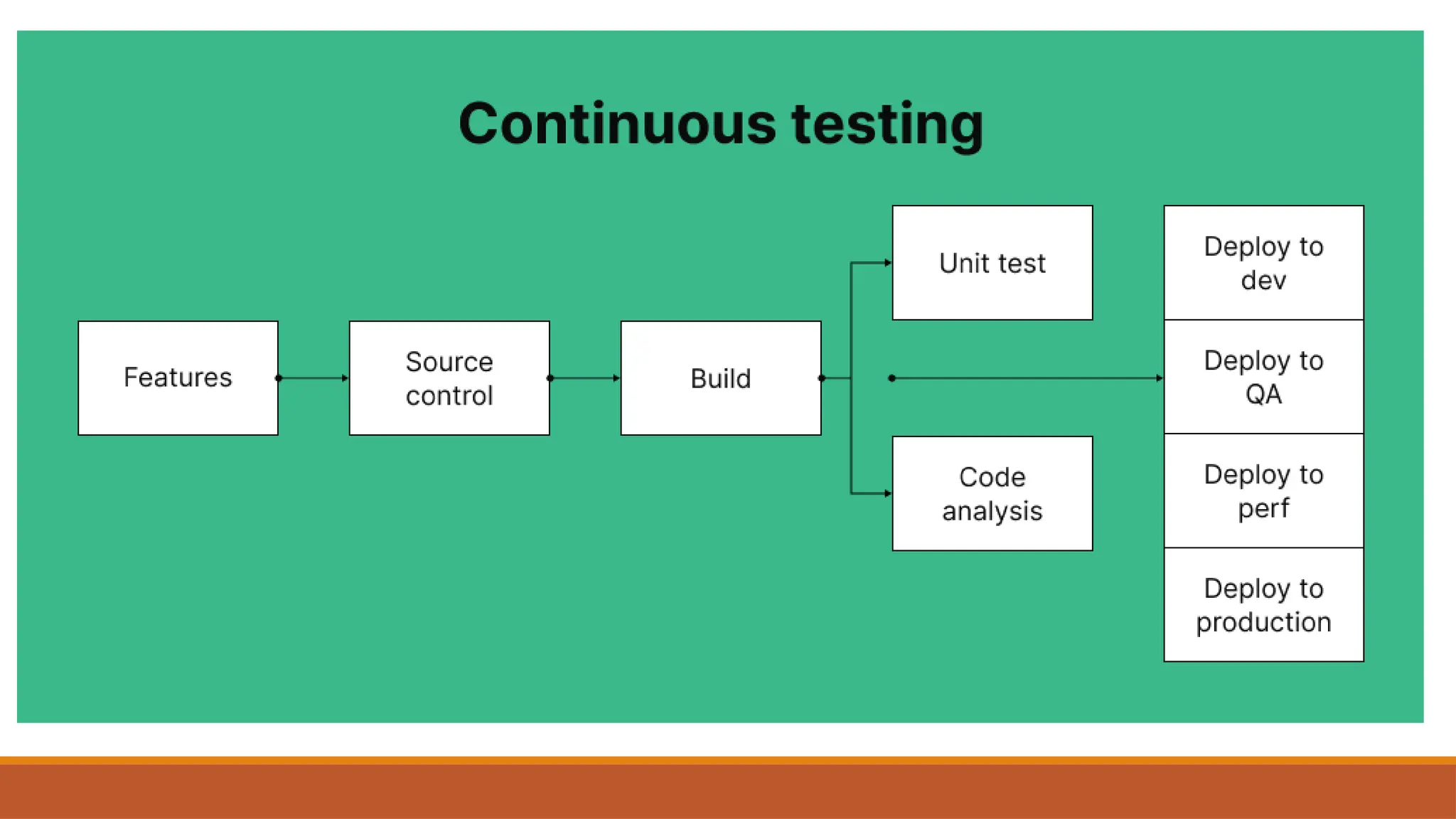
🔄 What is Continuous Testing & Why It Matters
🧩 Key Aspects: Fast Feedback, Risk Reduction, Early Bug Detection
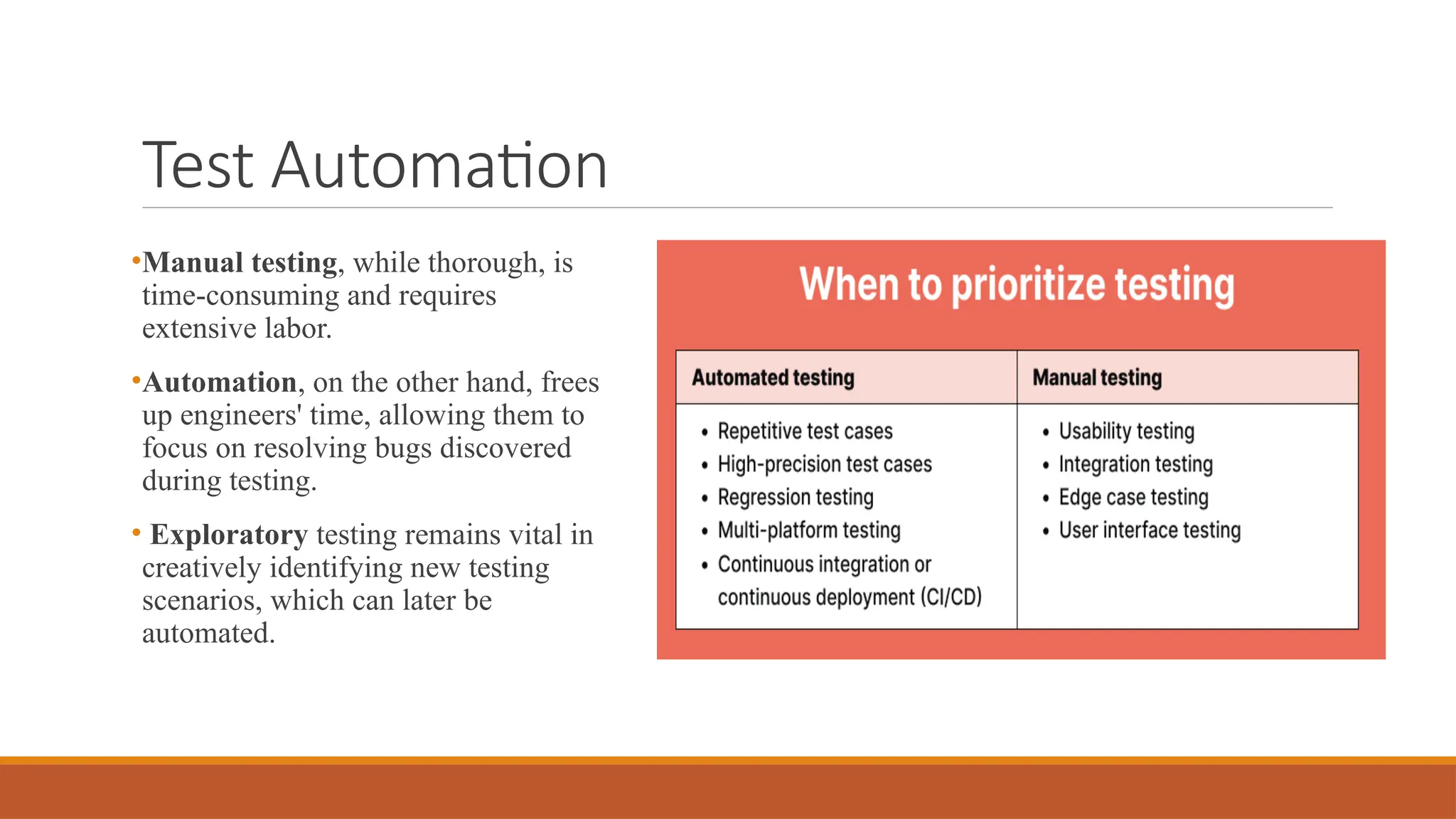
🤖 Role of Test Automation in CI/CD Pipelines
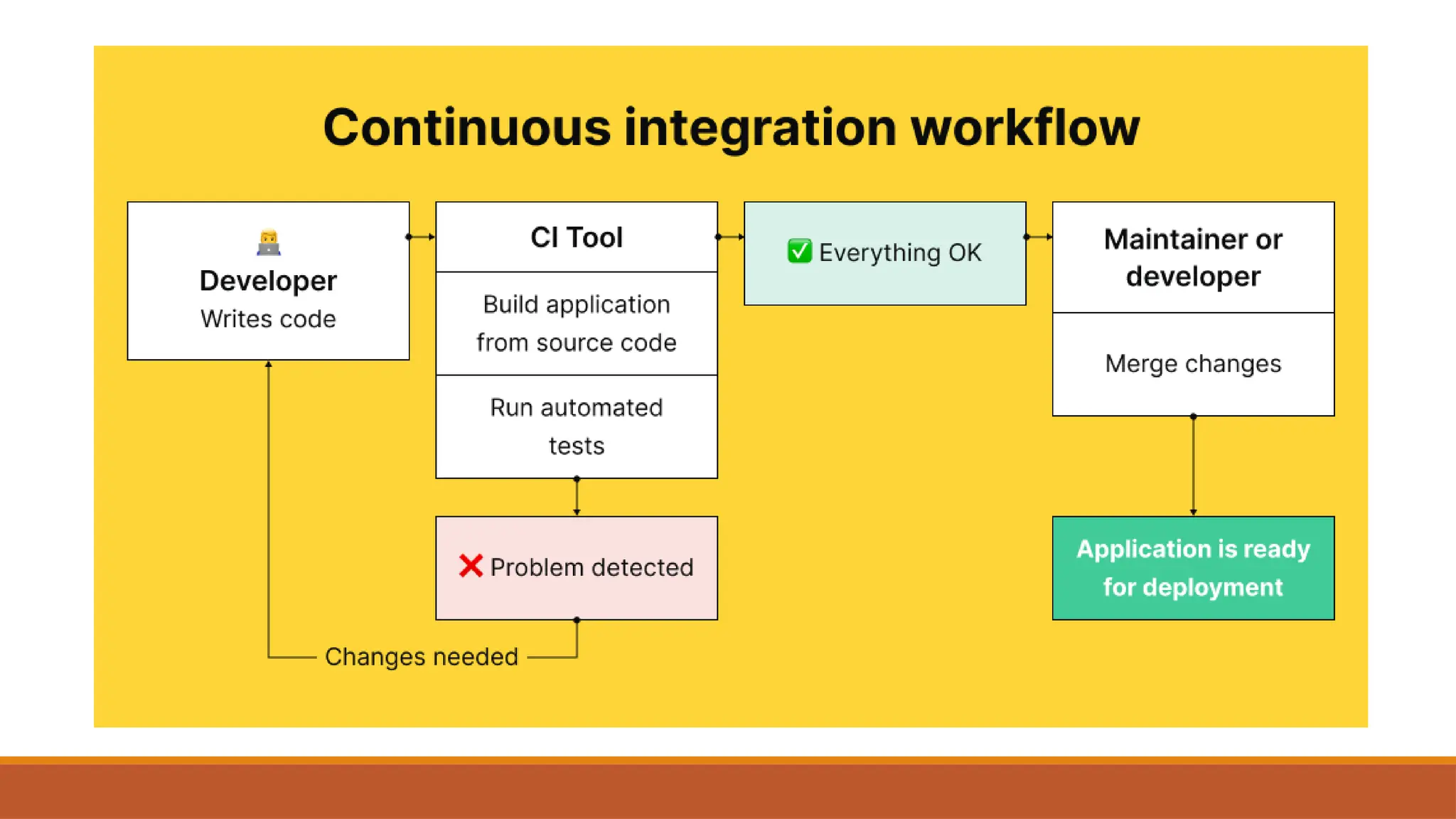
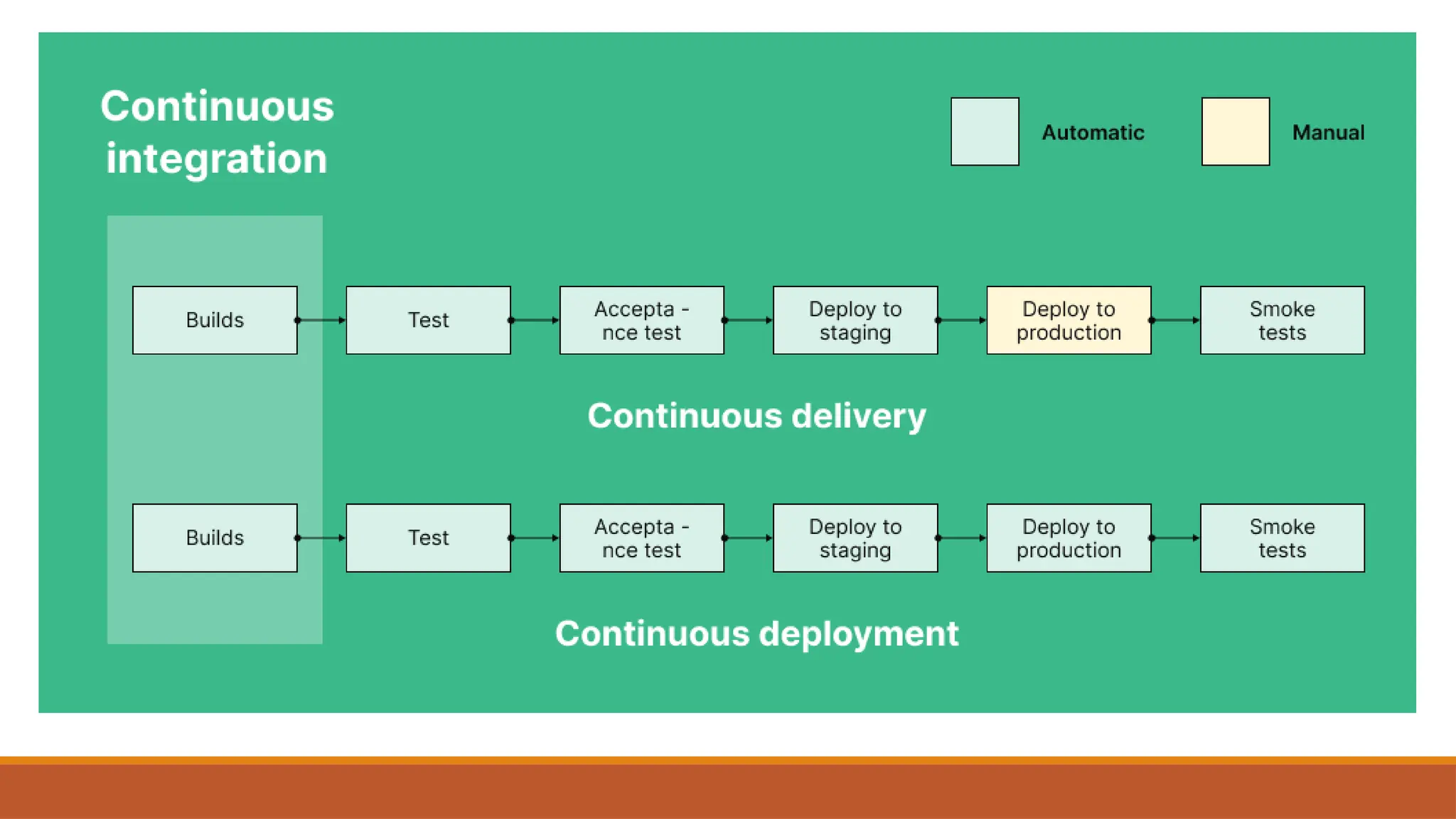
🔧 Integration with Continuous Integration (CI) & Continuous Delivery (CD)
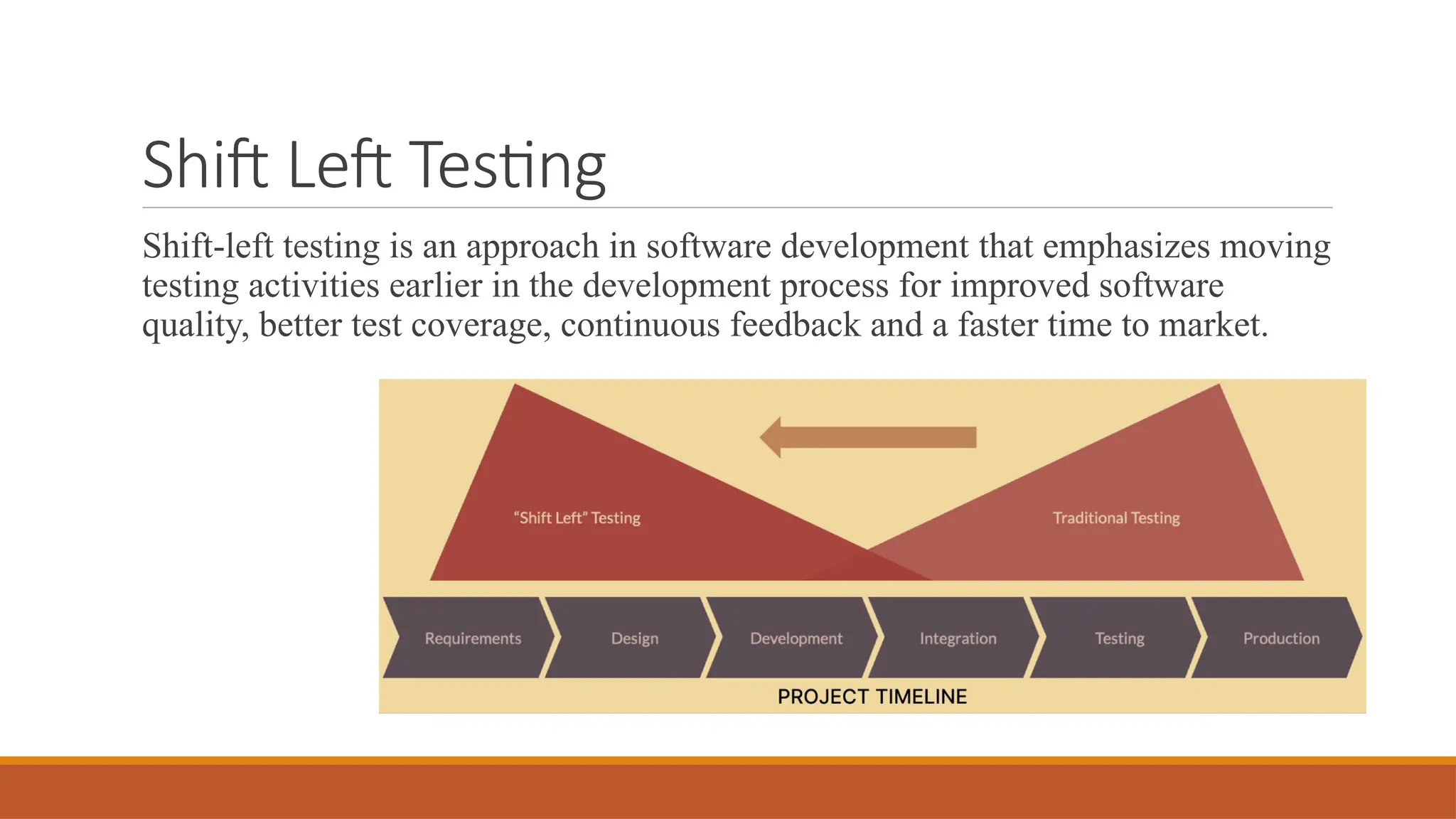
🕒 Shift-Left Testing Approach
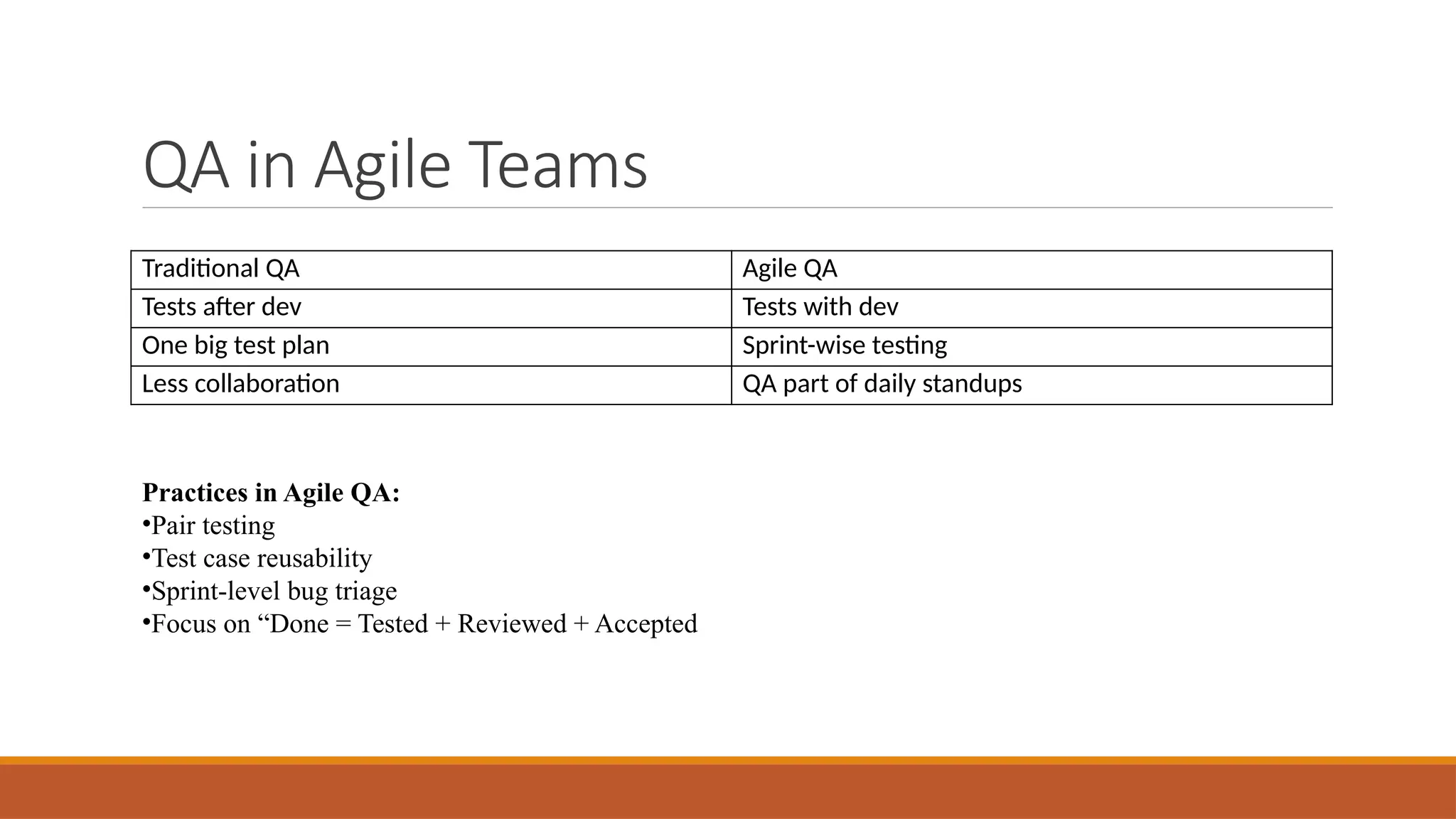
🧠 QA’s Role in Agile Teams
⚠️ Challenges in Agile QA & How to Overcome Them
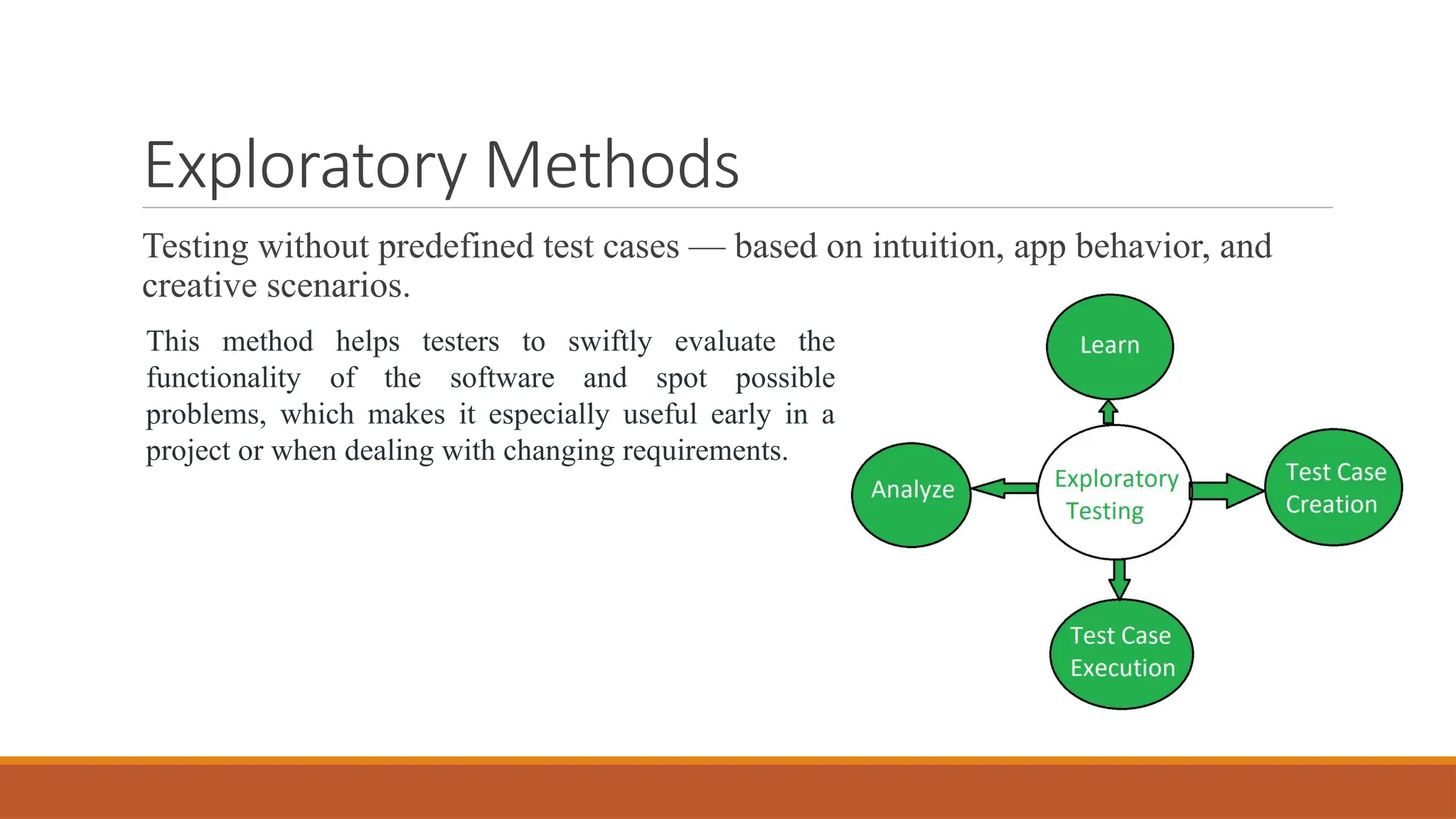
🛠️ Continuous Testing Methodologies & Frameworks
📂 Types of Testing in Agile Environments
✅ Practical Demo to Connect Theory with Real-World Tools
This session is ideal for QA professionals, DevOps engineers, testers, and Agile teams seeking to build a culture of continuous quality.