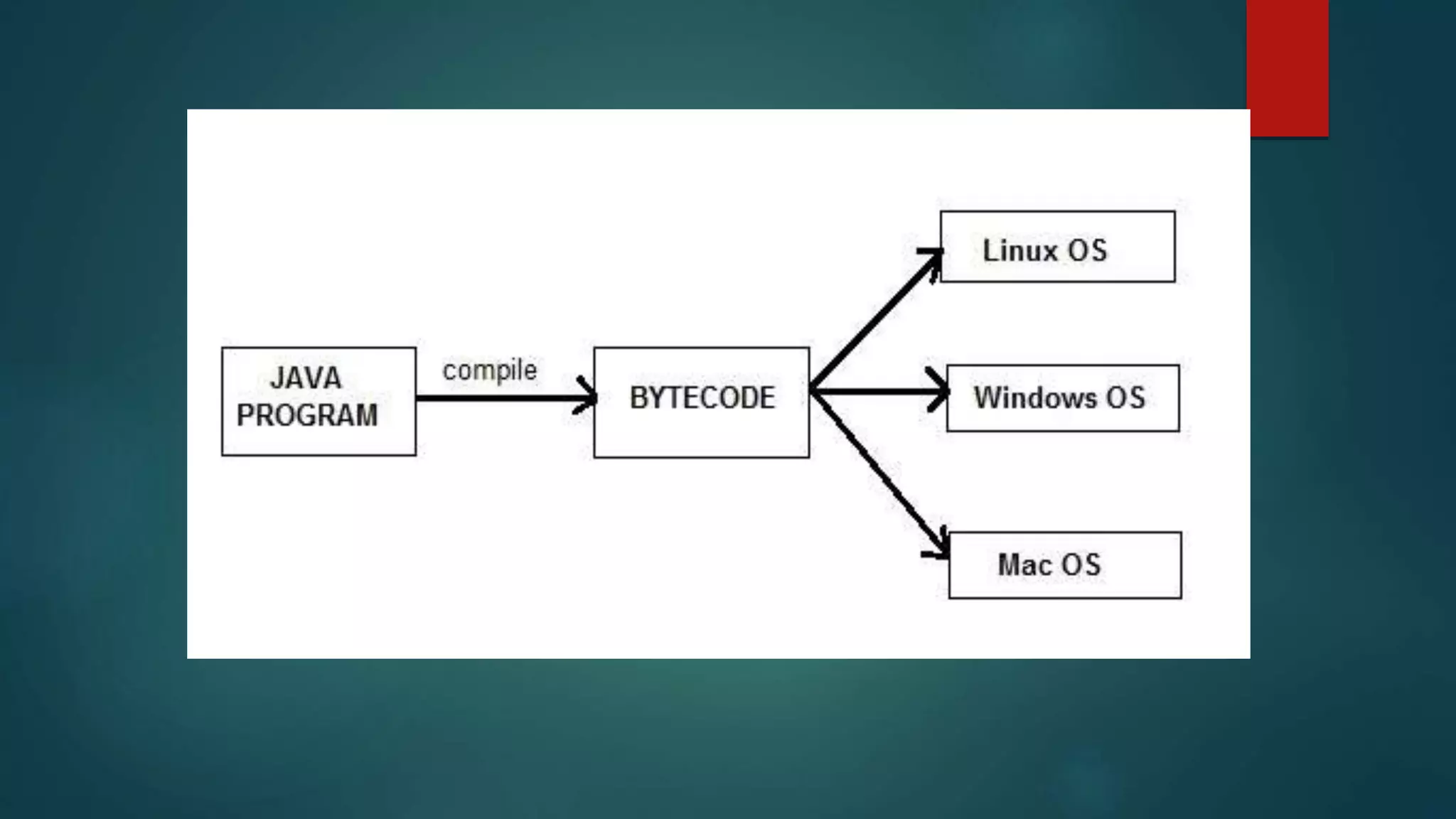
This document provides an introduction to the Java programming language. It discusses the history and creation of Java, its key features such as being platform independent and object oriented, common uses including desktop, web, and mobile applications, and different Java platforms. It also includes a simple "Hello World" Java program example to demonstrate how to write, compile, and run a basic Java program. Finally, it lists the major versions of Java released since 1996.








![SIMPLE PROGRAM
class Simple {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello Java");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-180331205213/75/Corejava-11-2048.jpg)
![ class is a keyword which is used to declare a class in java.
public is an access modifier which represents visibility, it means it is visible to all.
static is a keyword. If we declare any method as static, it is known as static method. The
core advantage of static method is that there is no need to create object to invoke the
static method. The main method is executed by the JVM.
void is the return type. It means it doesn't return any value.
main represents start of the program.
String[] args is used for command line argument.
System.out.println() is used as a print statement.
EXPLAINATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corejava-180331205213/75/Corejava-12-2048.jpg)


