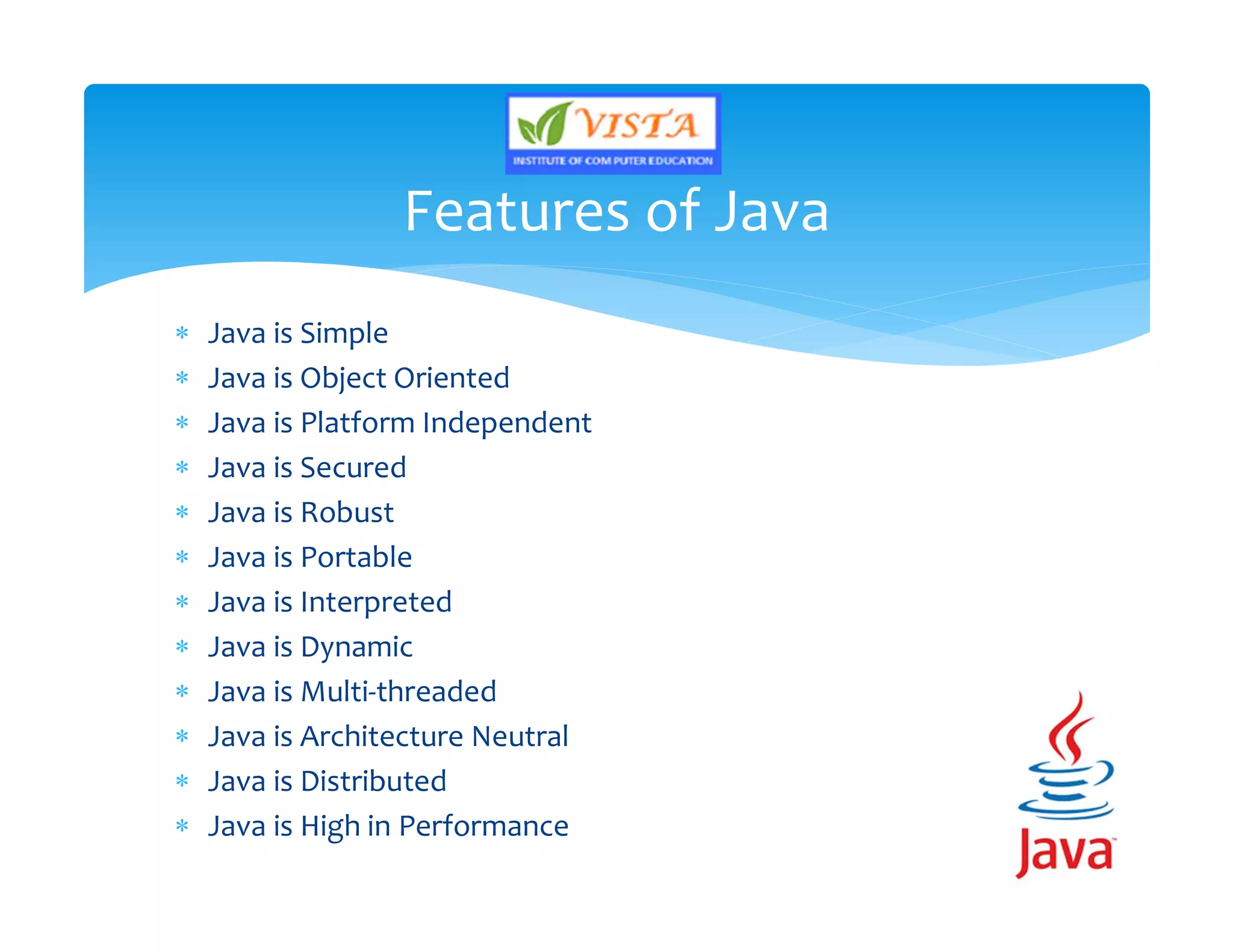
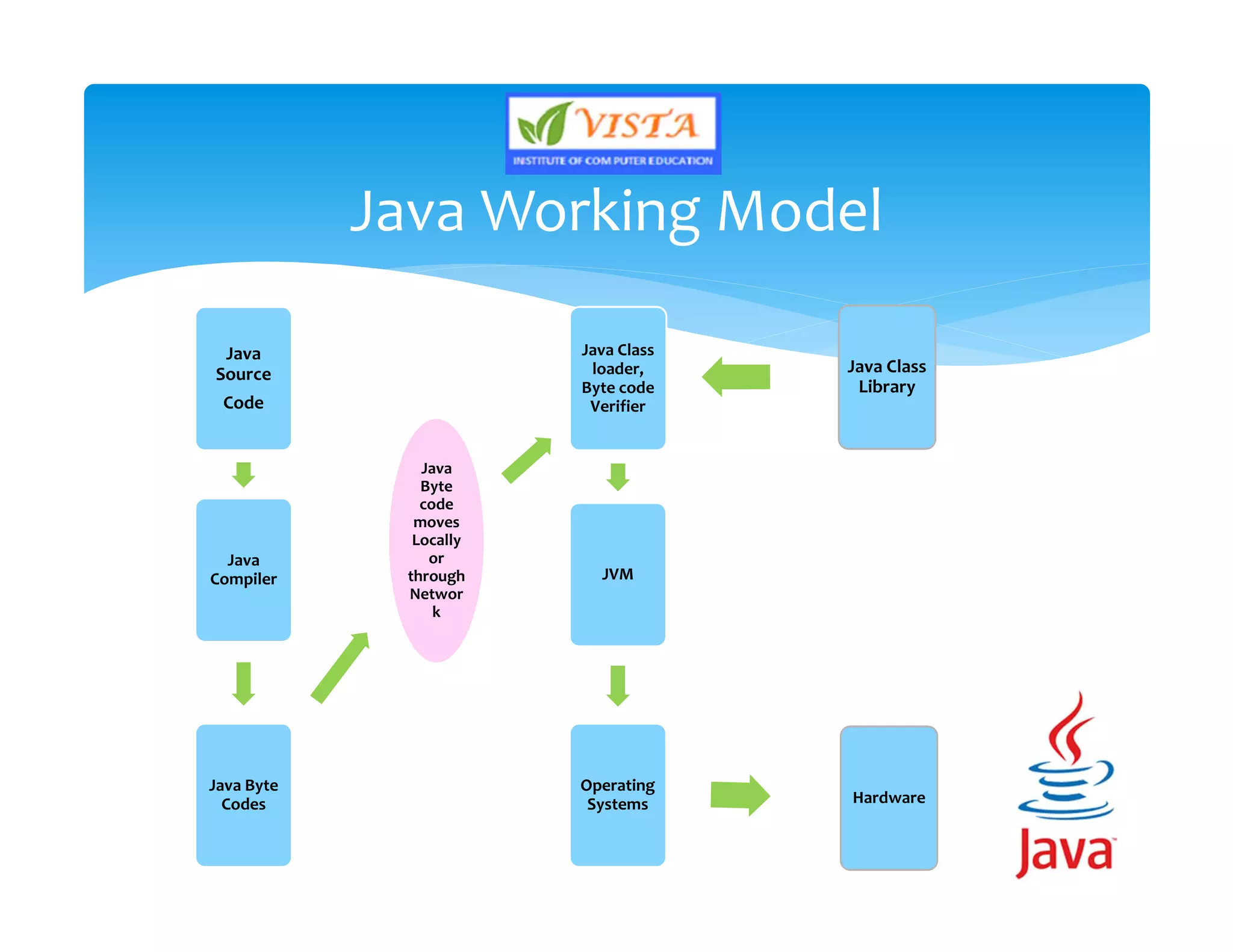
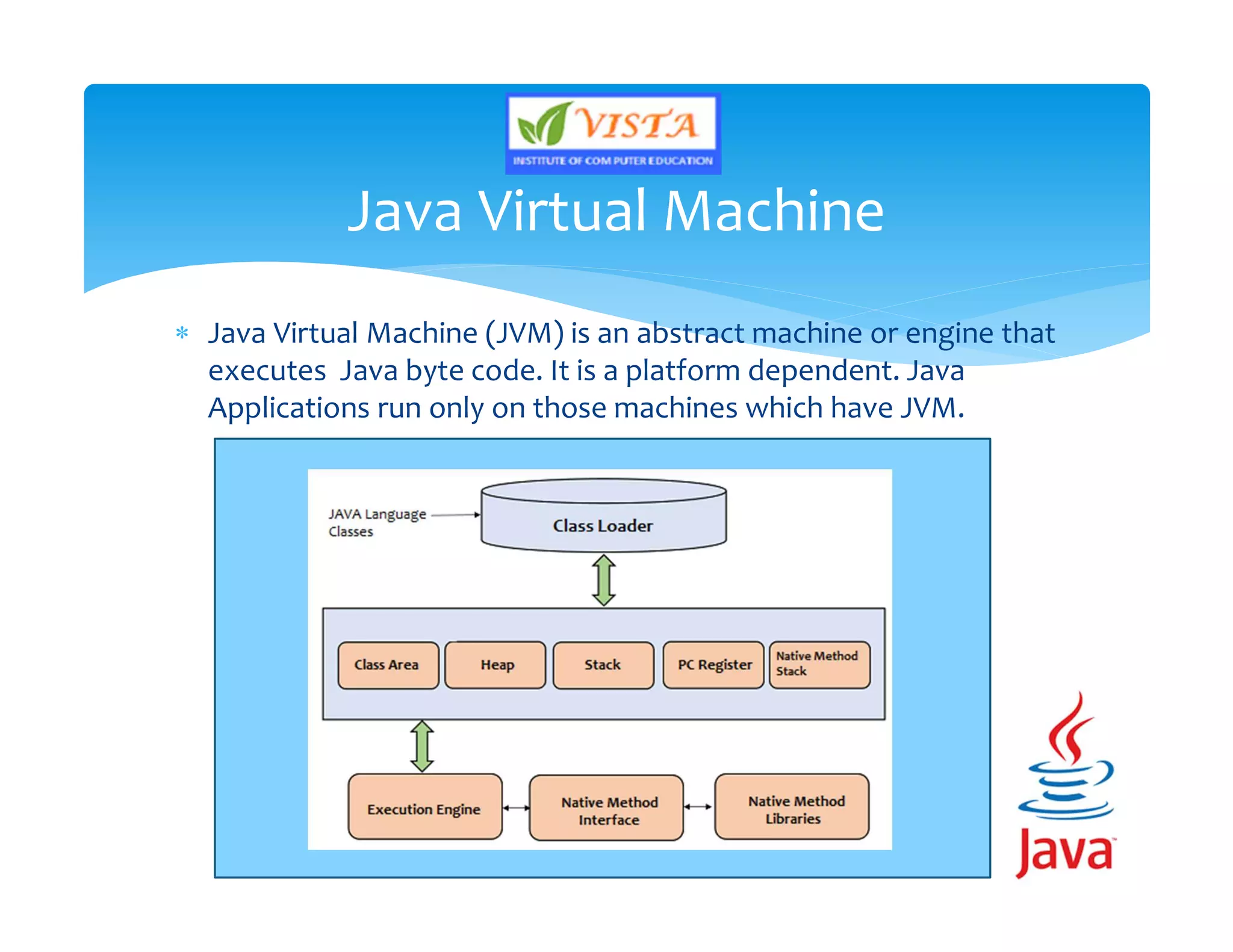
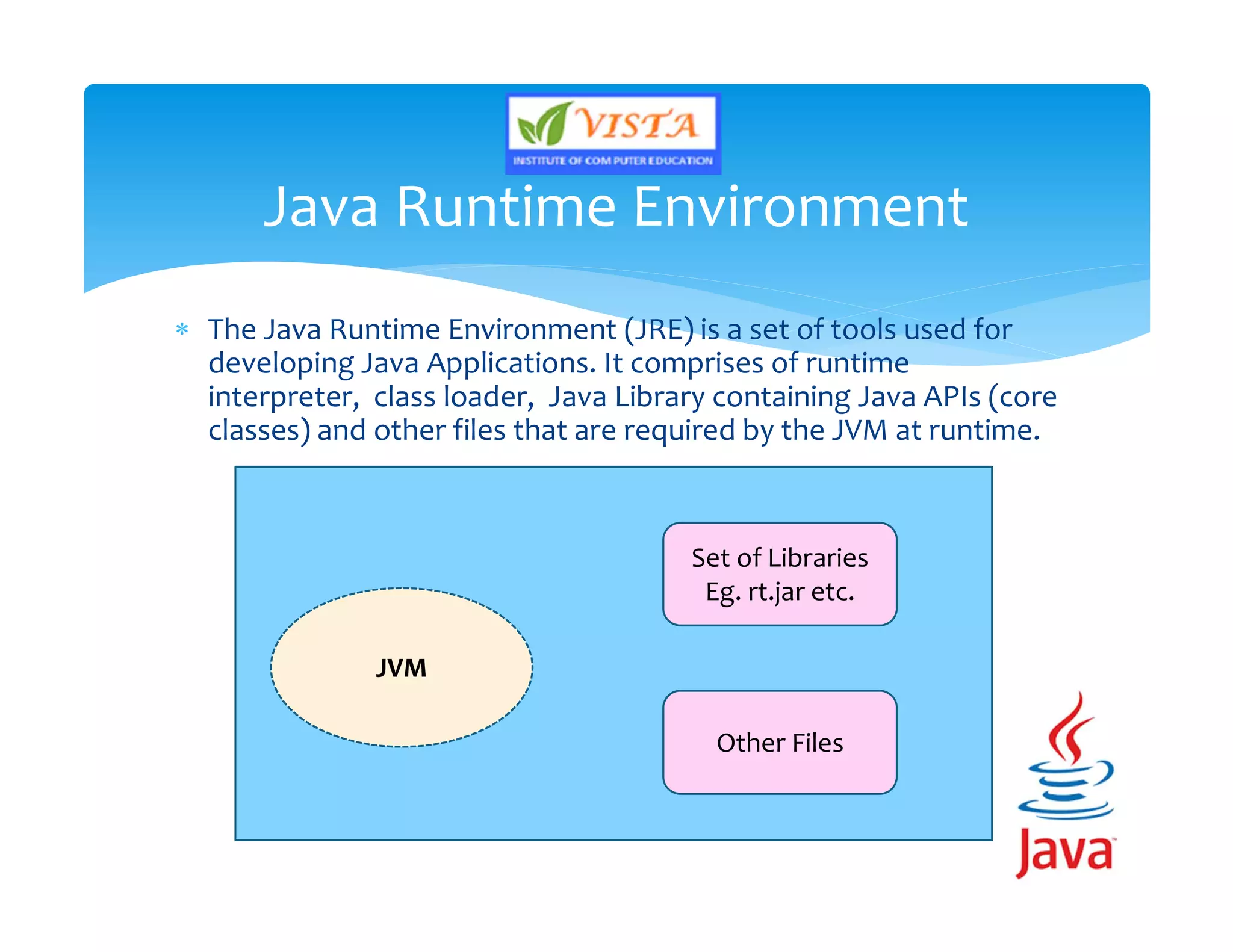
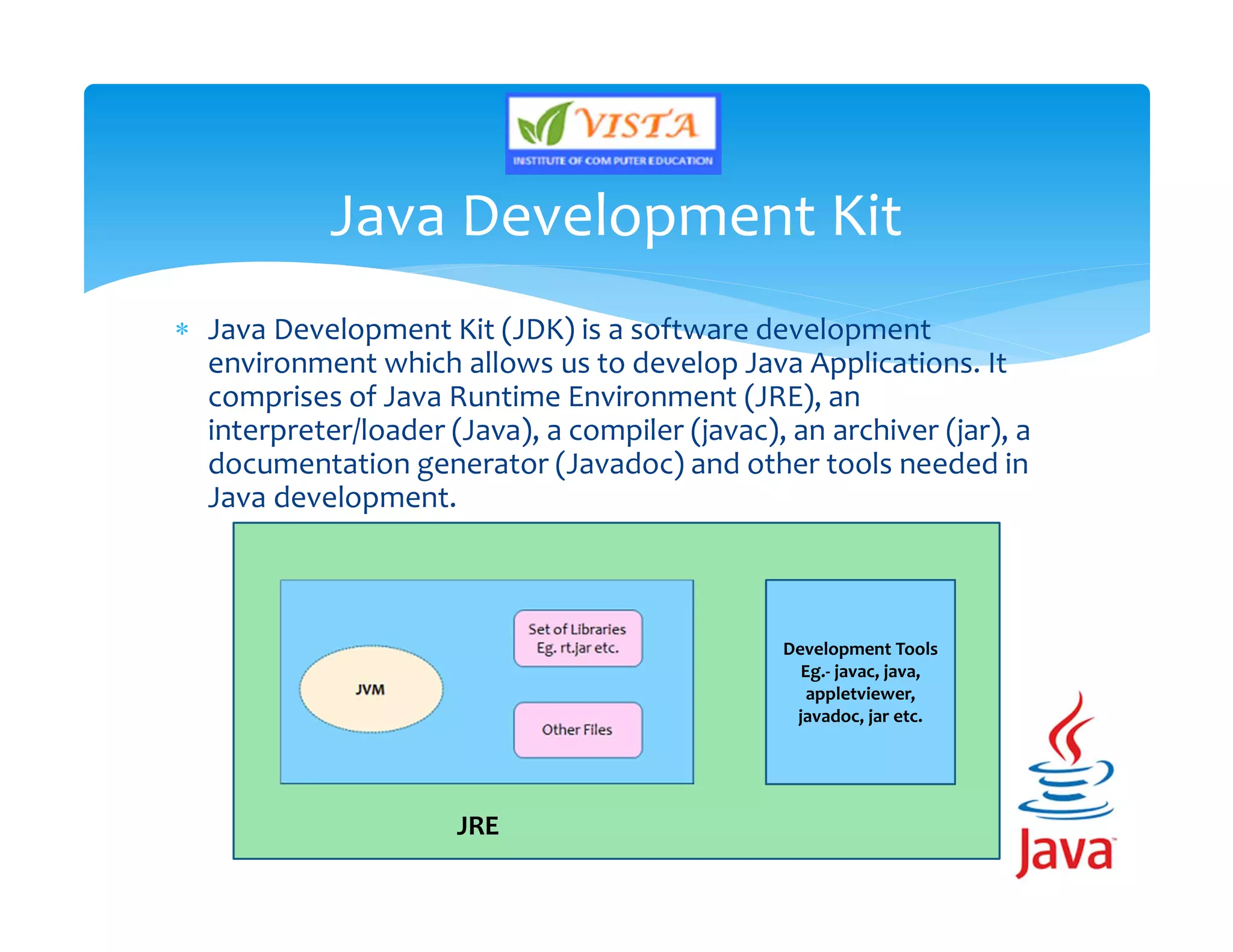
This document provides an overview of the Java programming language. It discusses that Java is an object-oriented language created by James Gosling in 1991. It then lists the major versions of Java and describes some of its key features like being platform independent, secure, robust and portable. The document also provides brief explanations of Java concepts like the Java Virtual Machine, Java Runtime Environment and Java Development Kit.









![ A “Hello Java” program is a simple Java program that outputs
“Hello Java!” on the screen.
Let’s explore the “Hello Java” Program.
class HelloJava
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(“Hello Java!”);
}
}
To Compile:- javac HelloJava.java
To Run:- java HelloJava
“Hello Java” Program](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-ataglance-180715173111/75/Java-At-a-glance-15-2048.jpg)


