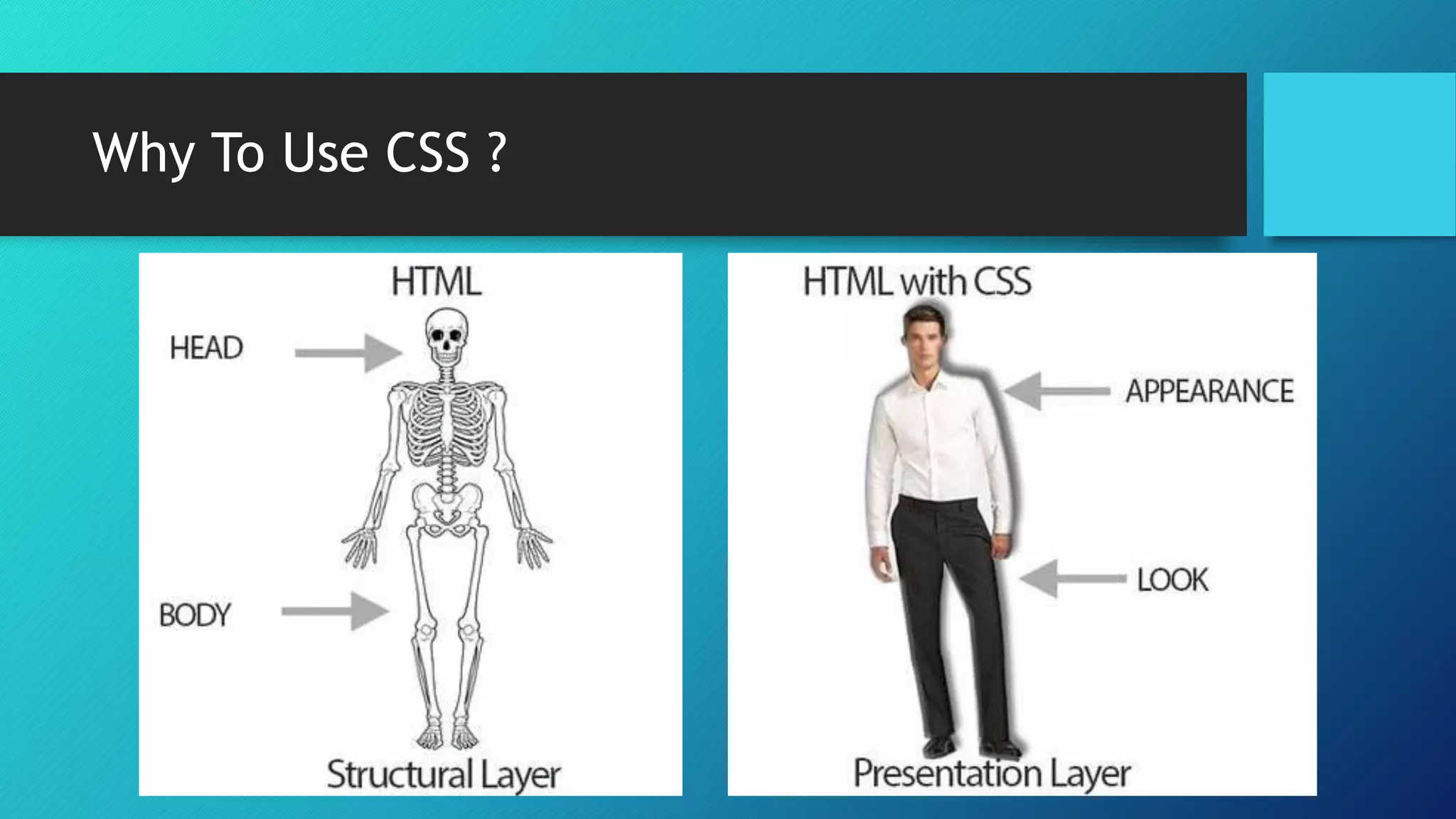
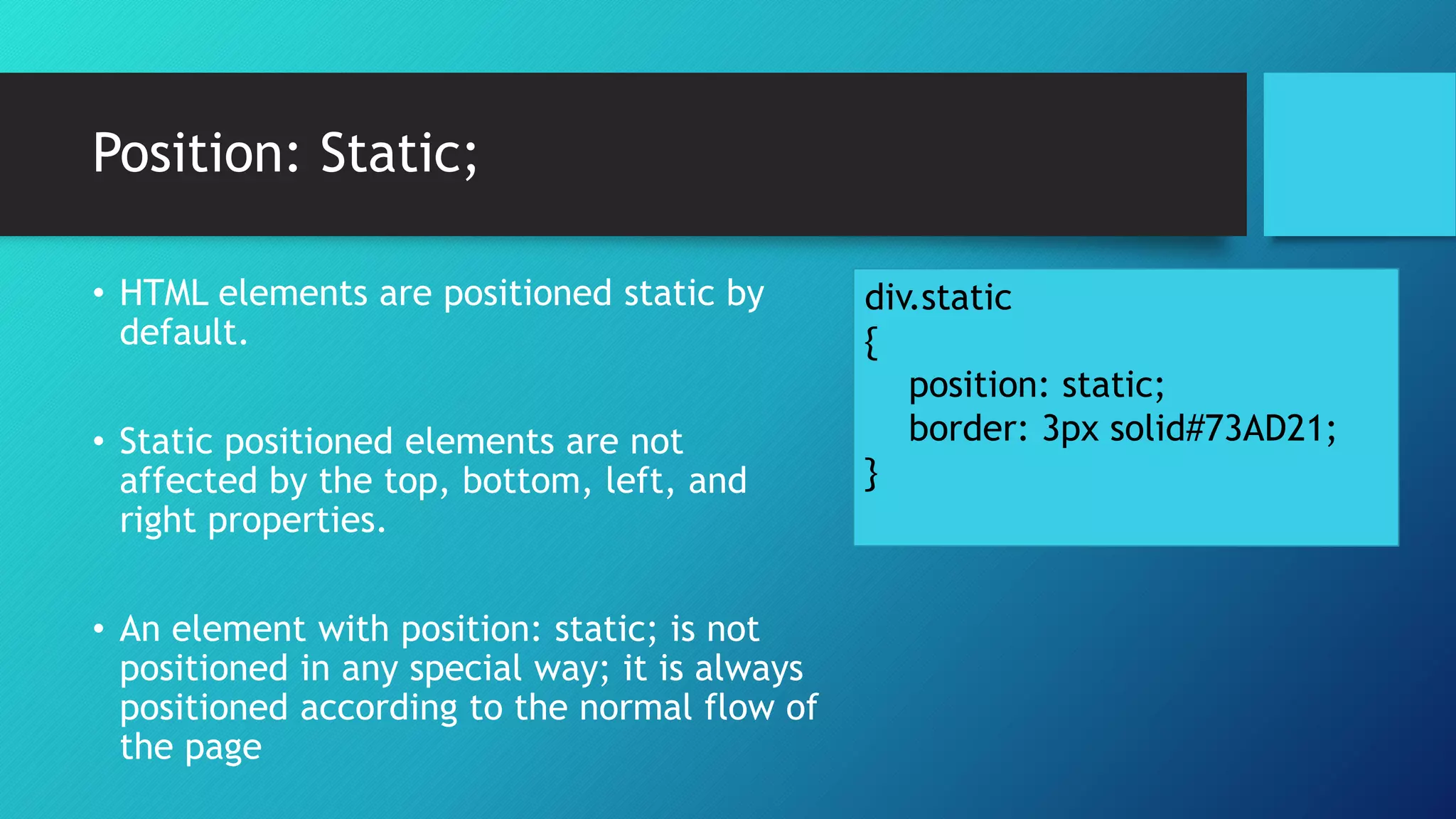
The document provides an overview of CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) and its positioning properties, detailing five different position values: static, relative, fixed, absolute, and sticky. It also introduces CSS3, highlighting its backward compatibility with earlier versions and listing new features such as animations, advanced selectors, and media queries. The document emphasizes the utility of CSS in controlling the layout and design of webpages across various devices.