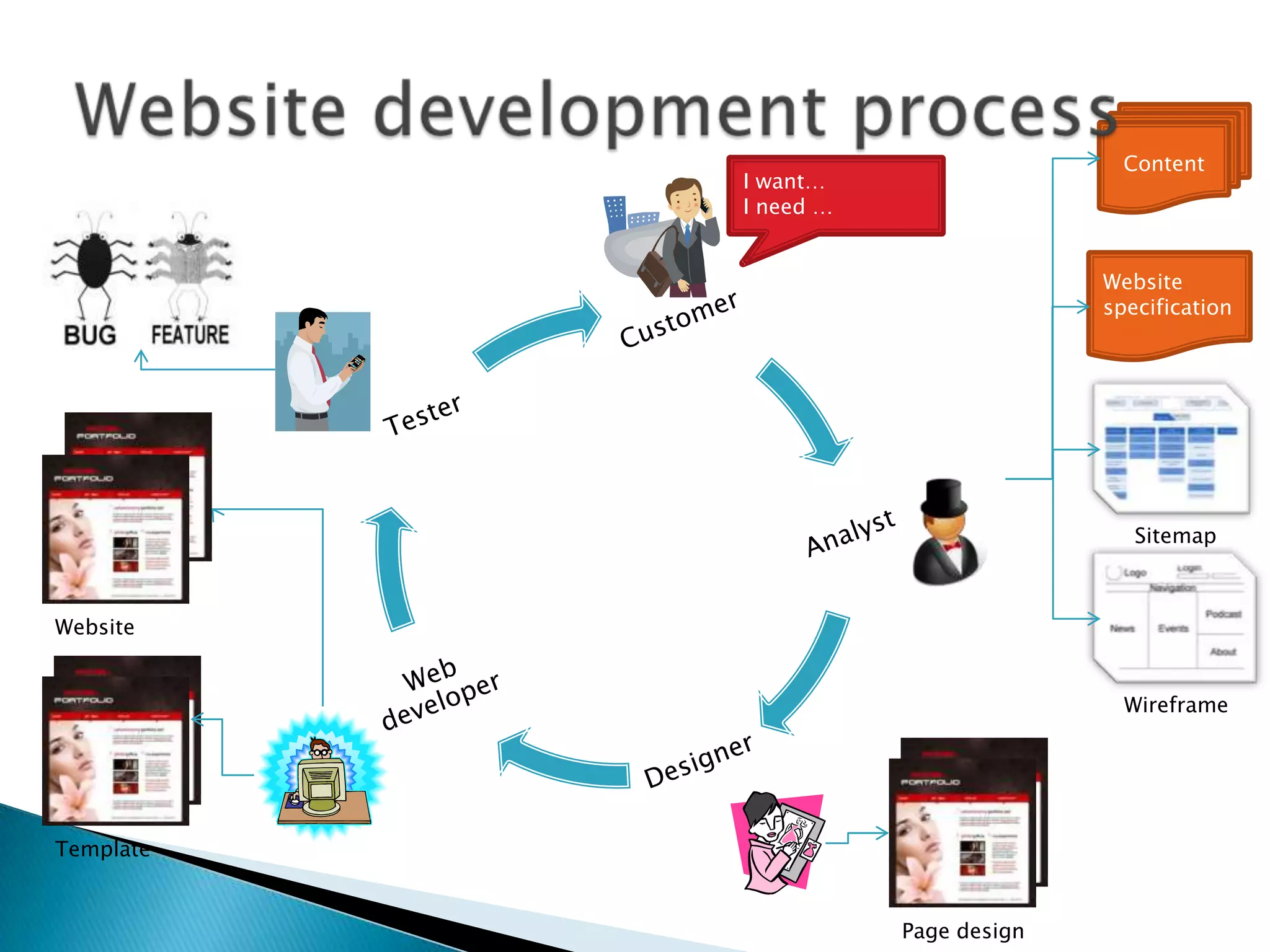
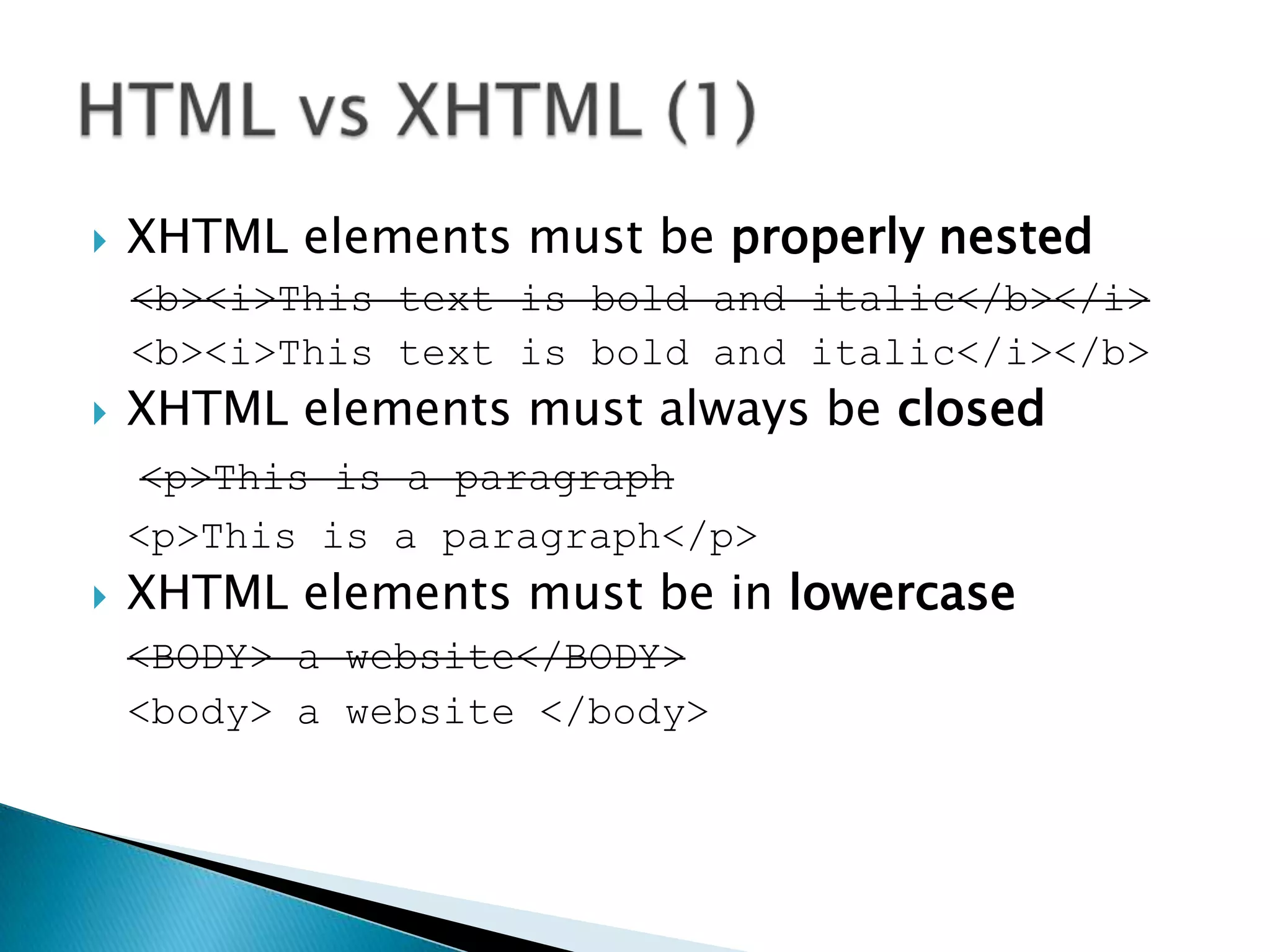
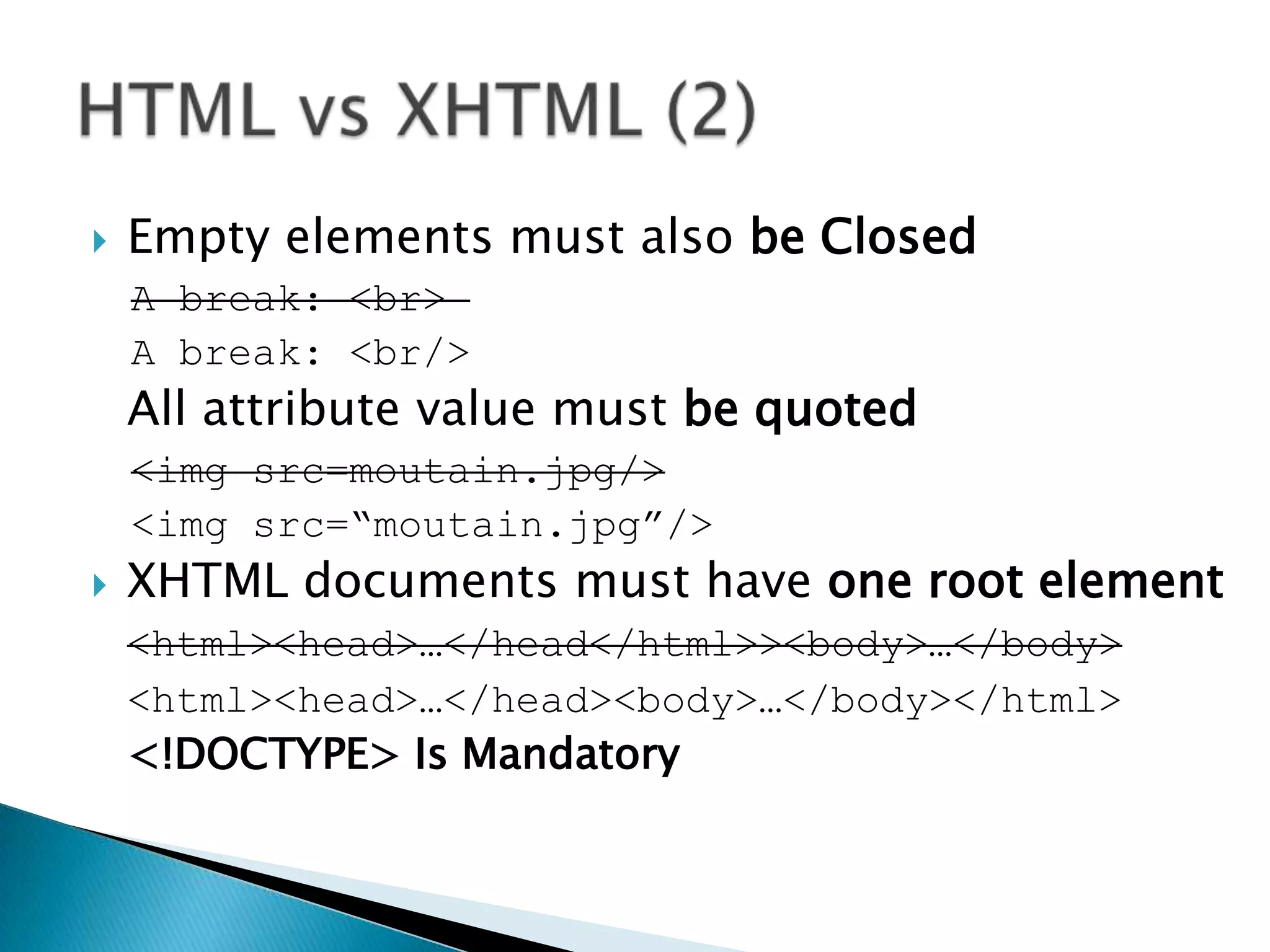
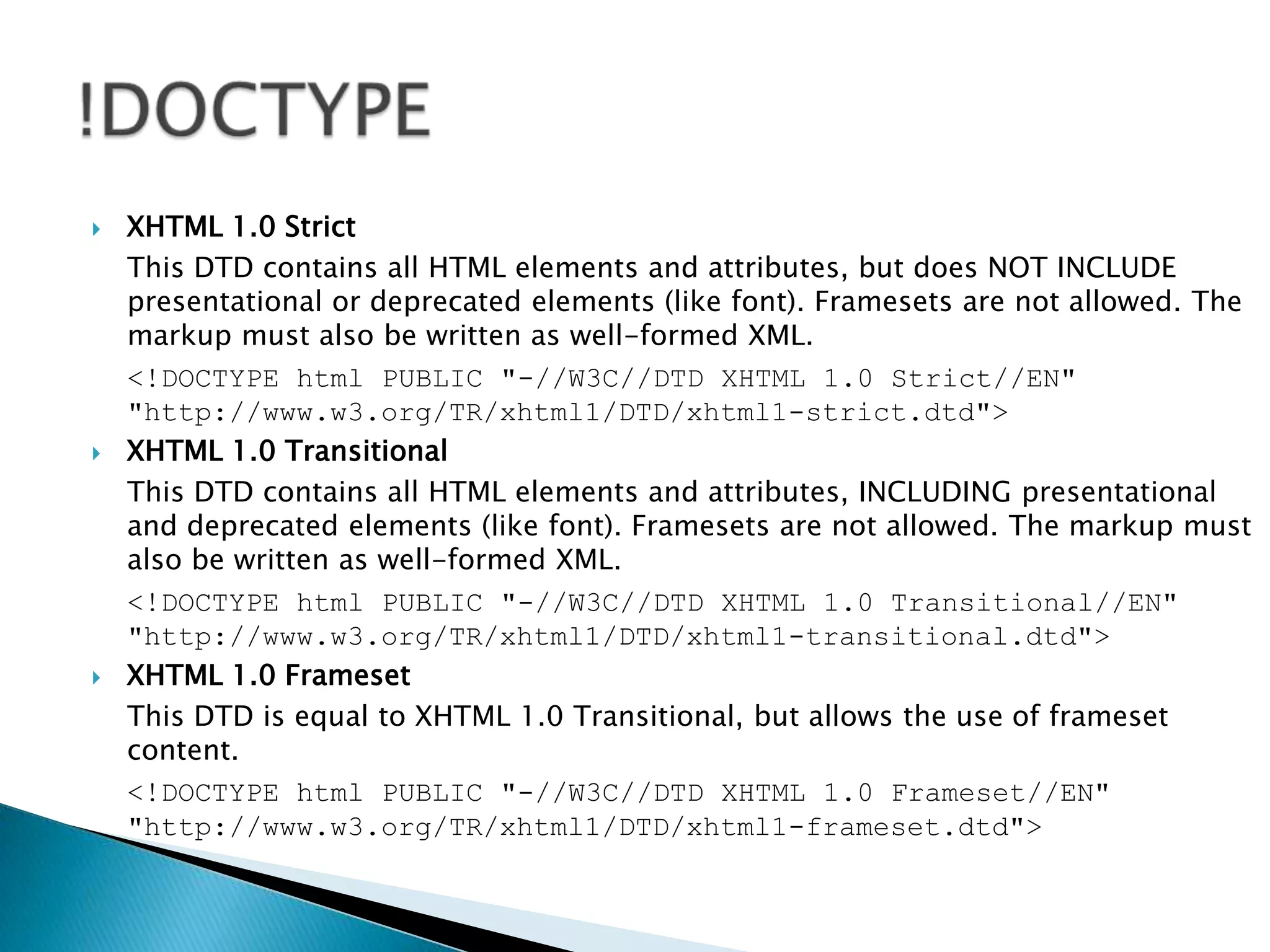
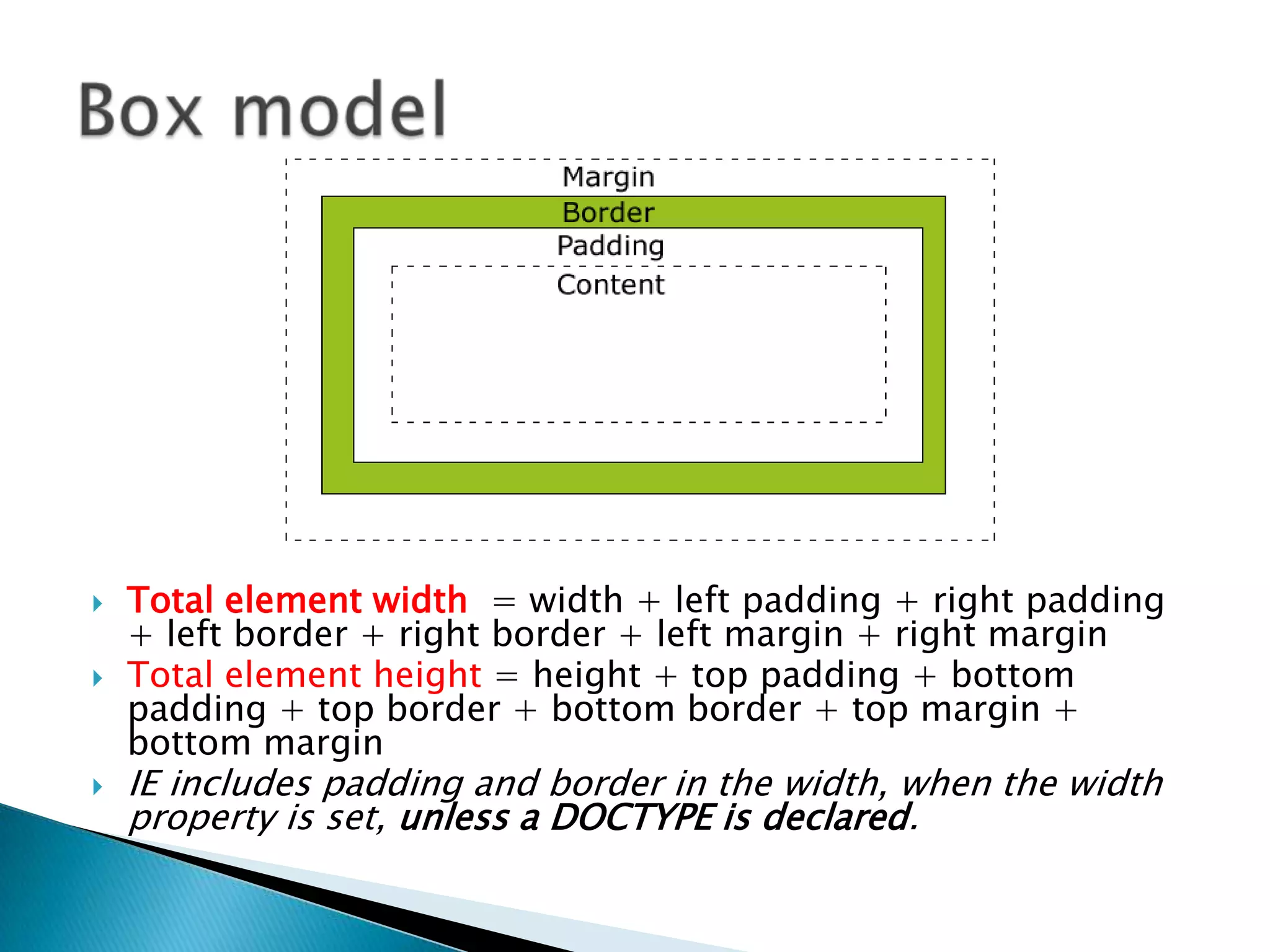
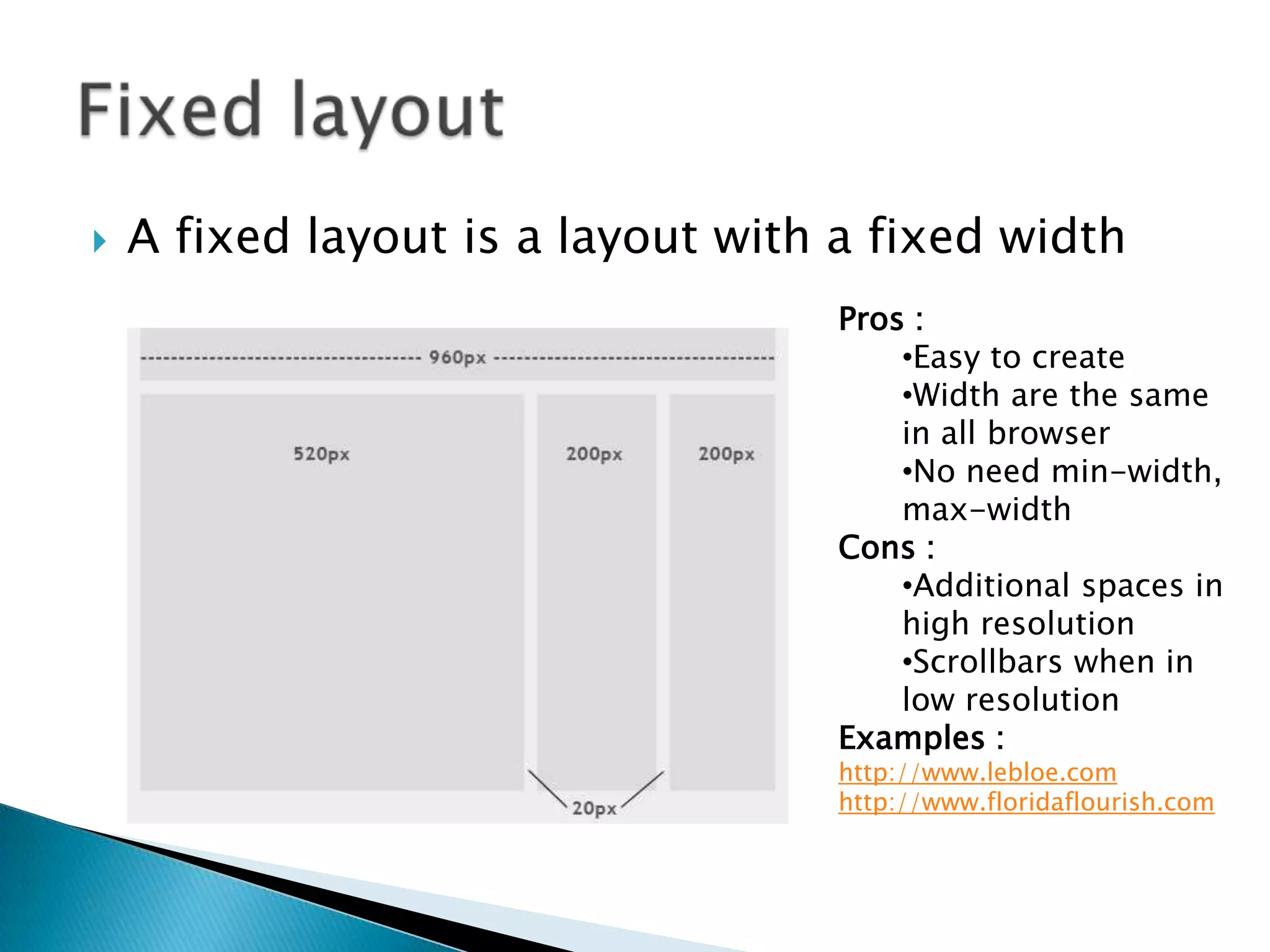
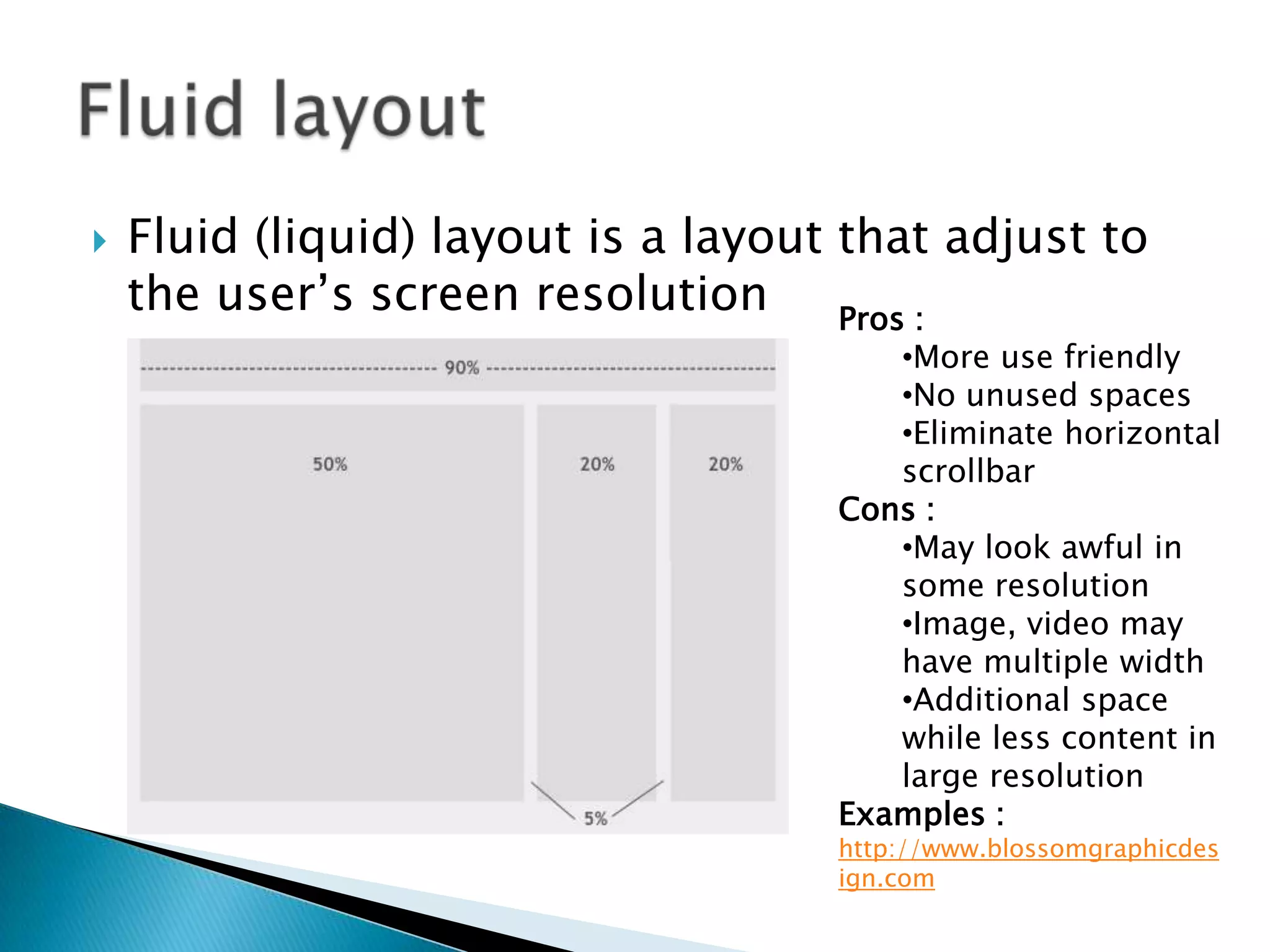
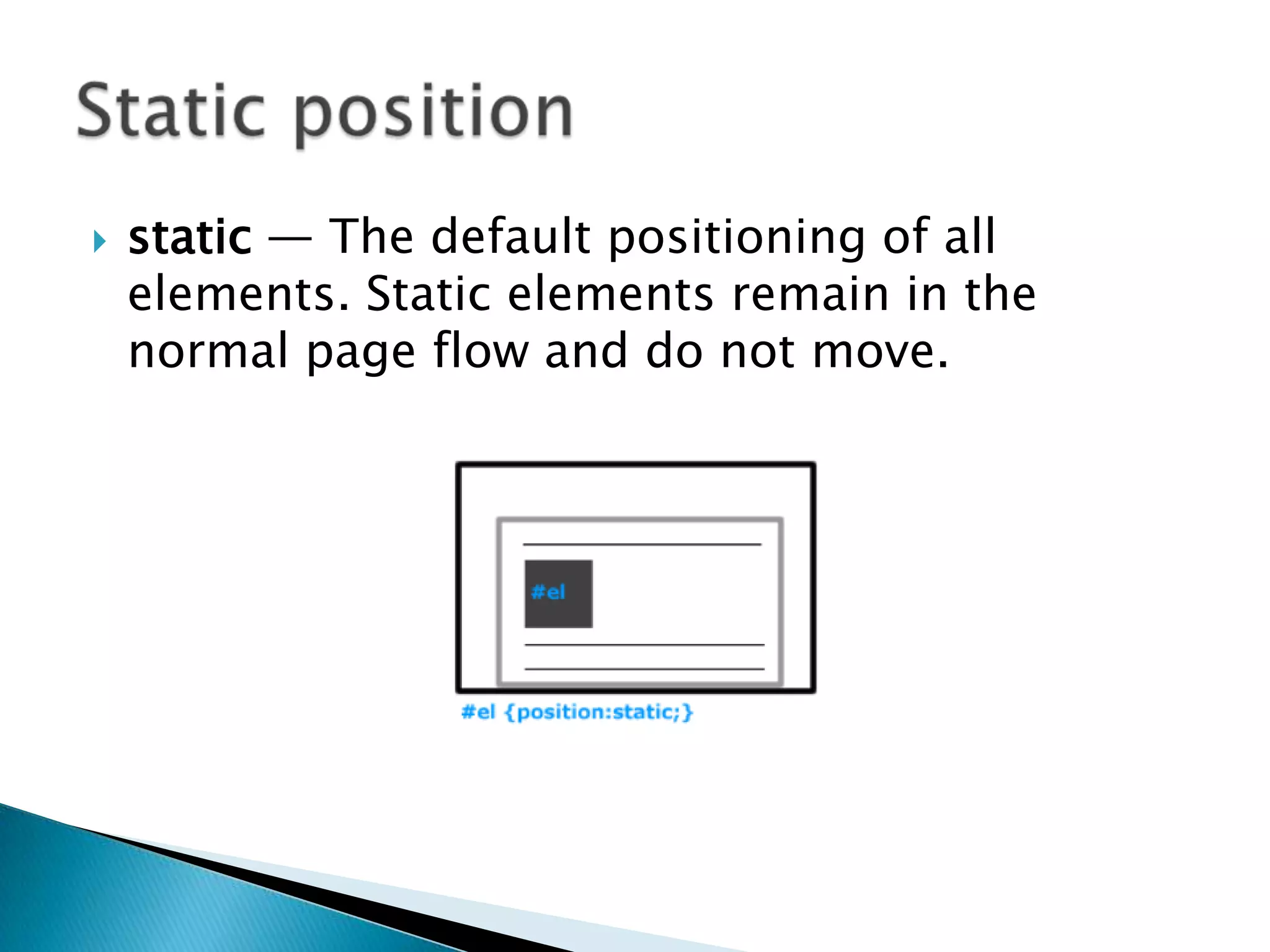
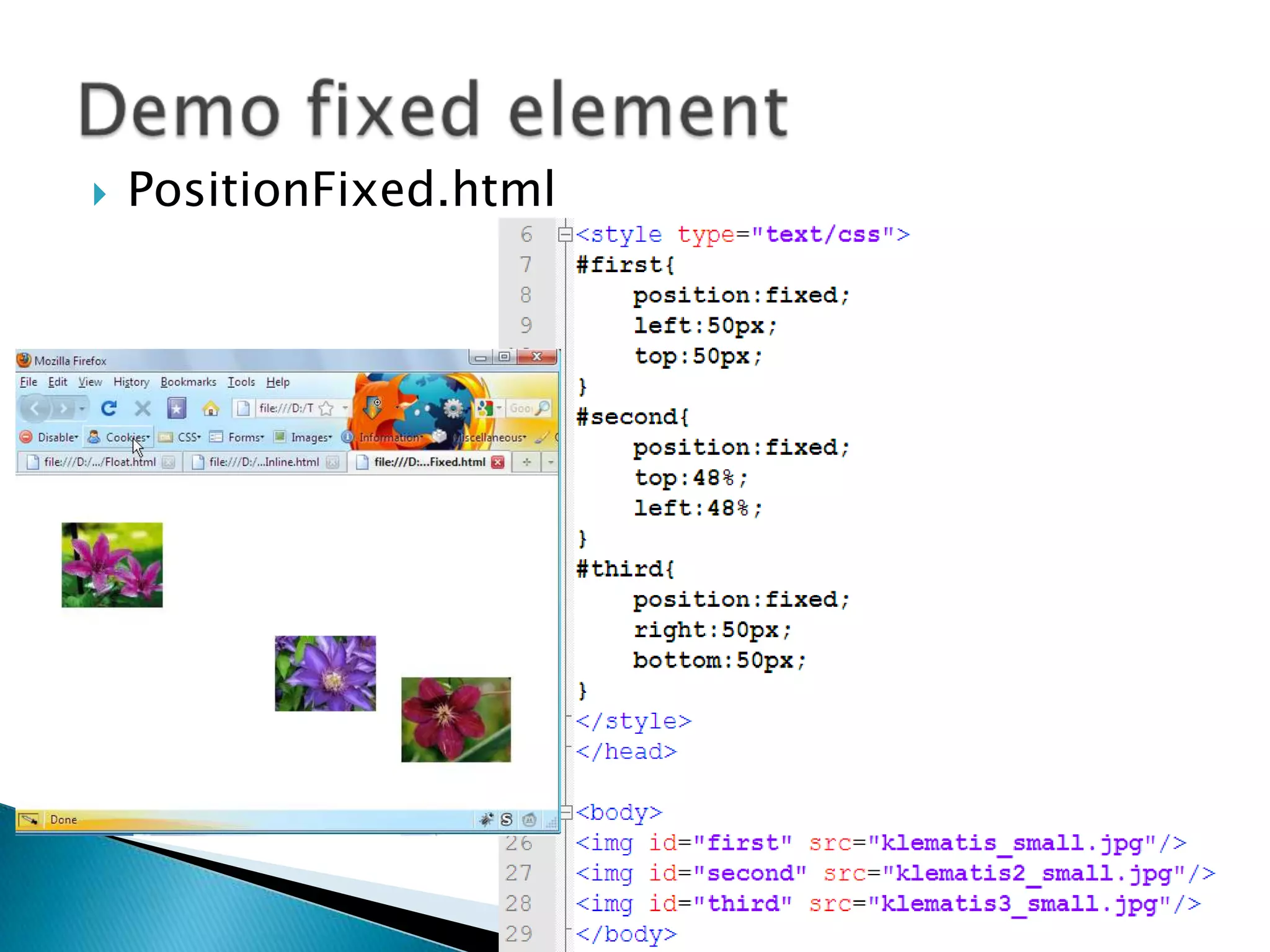
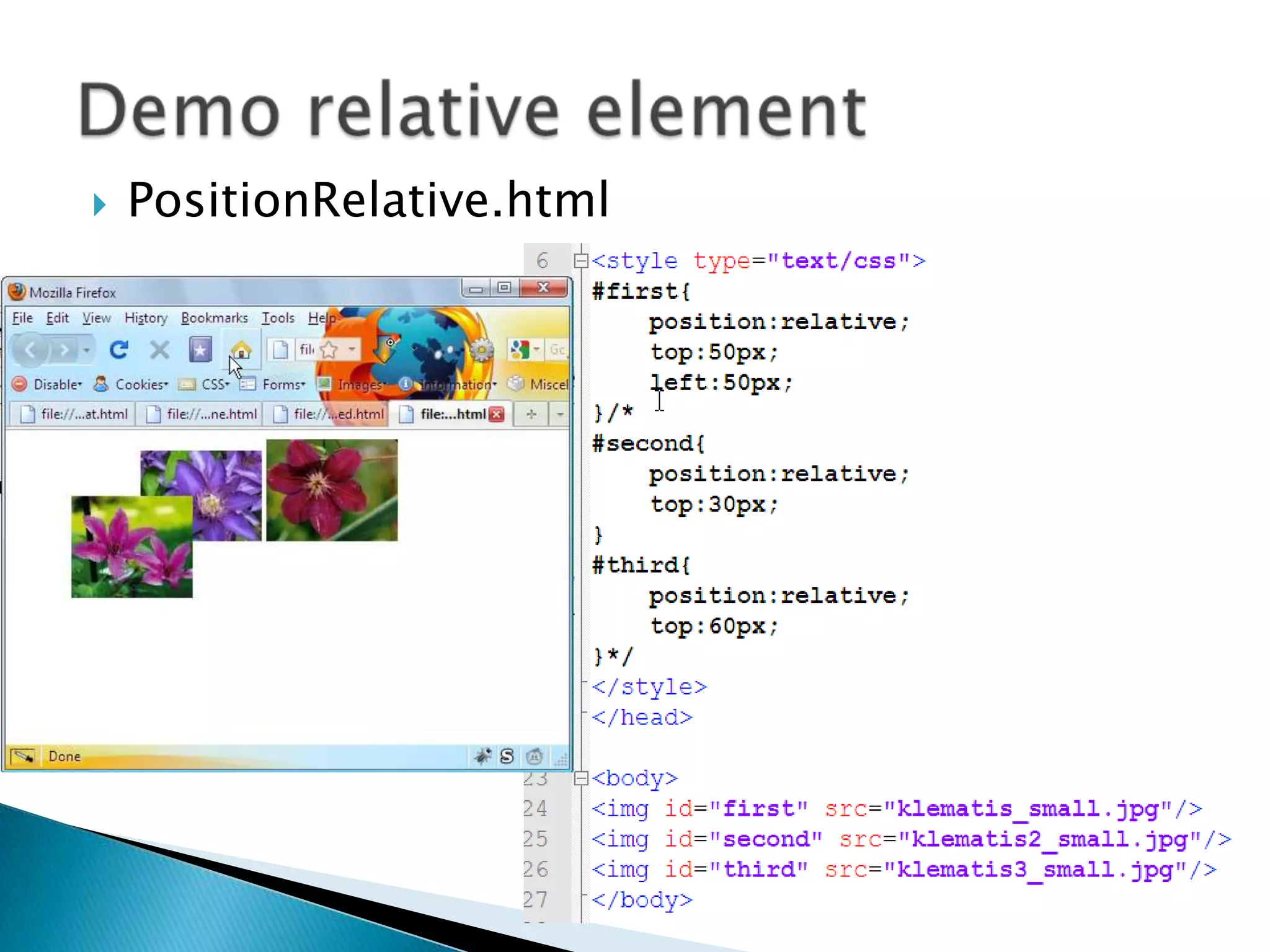
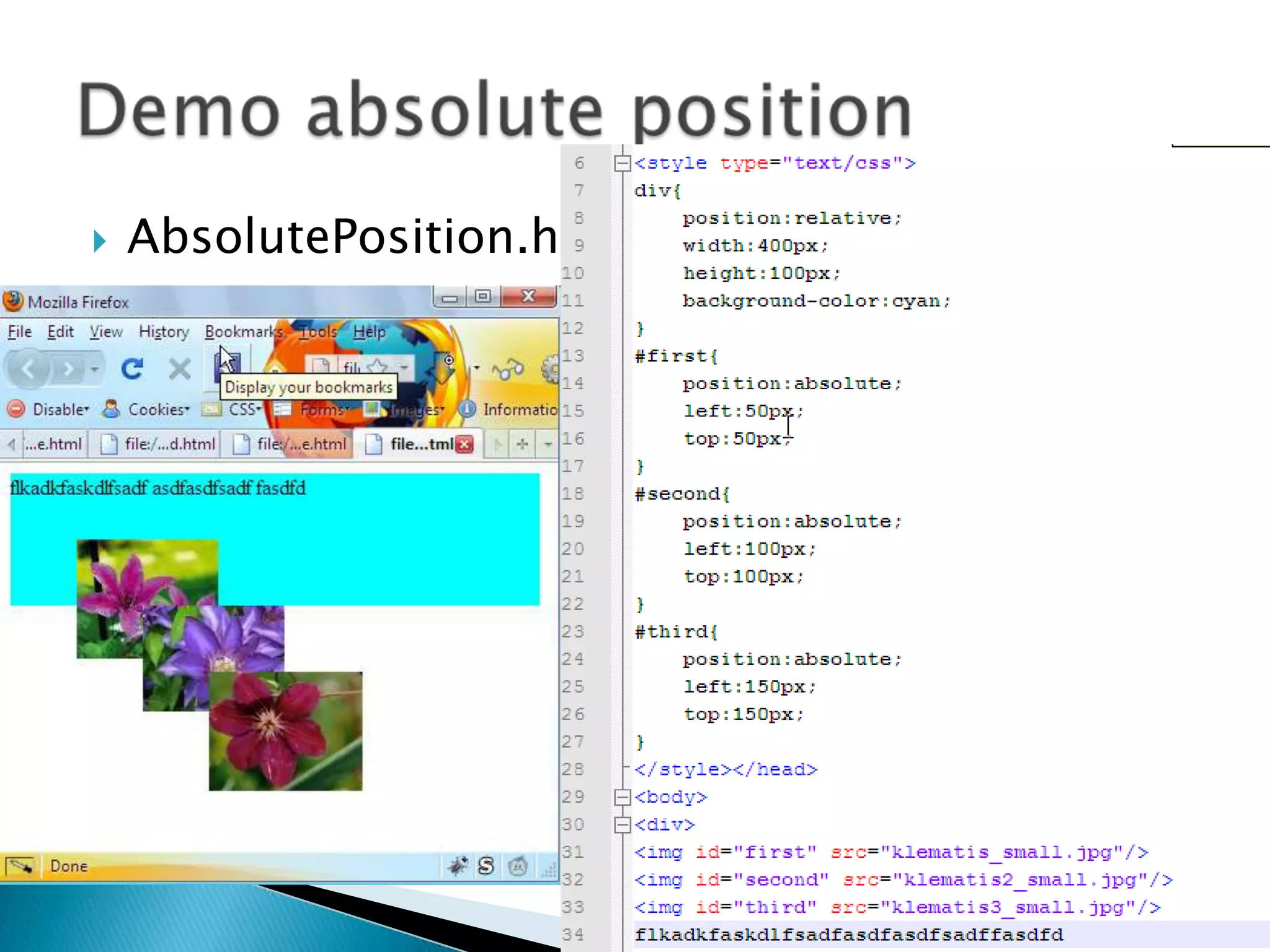
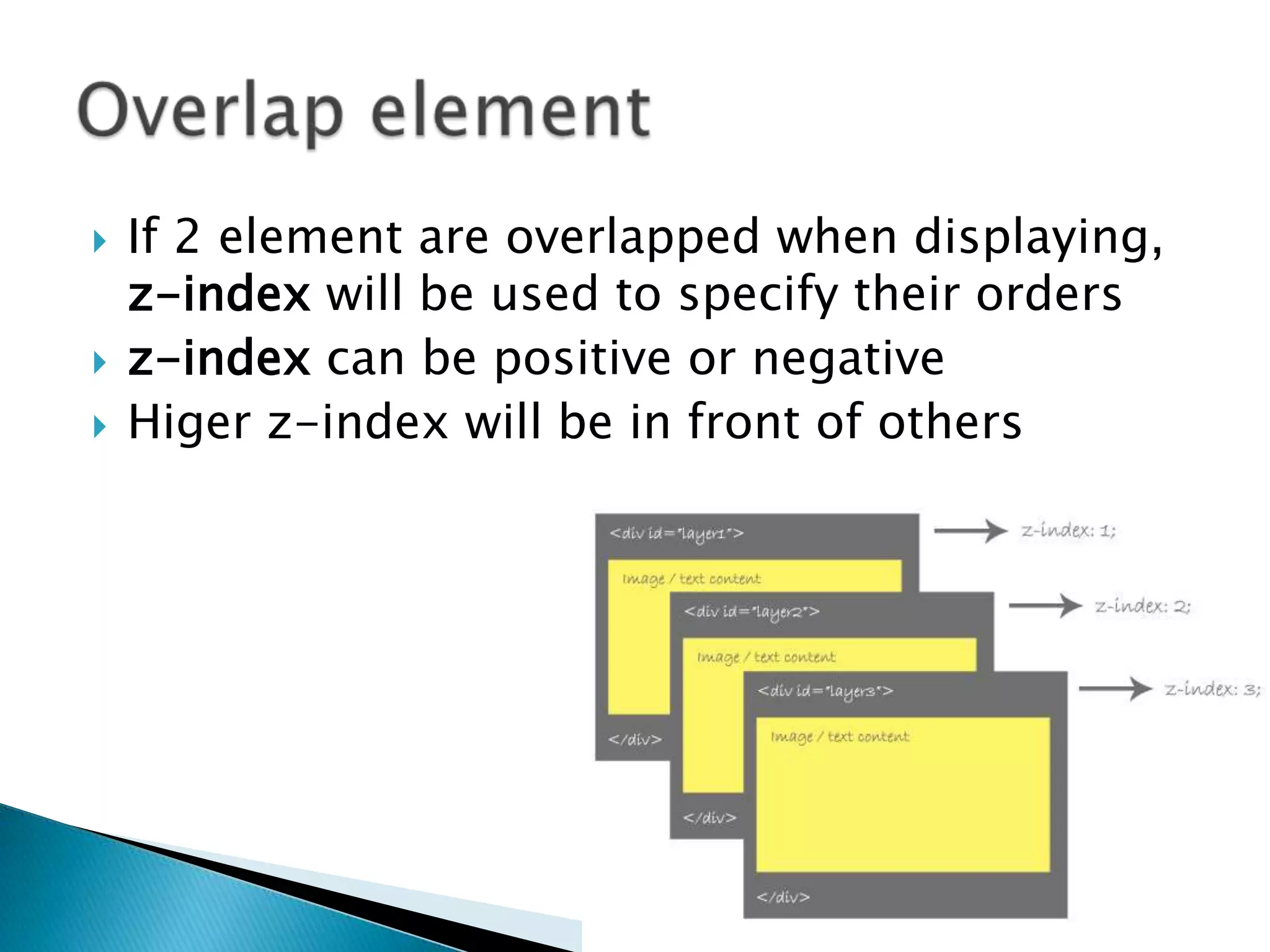
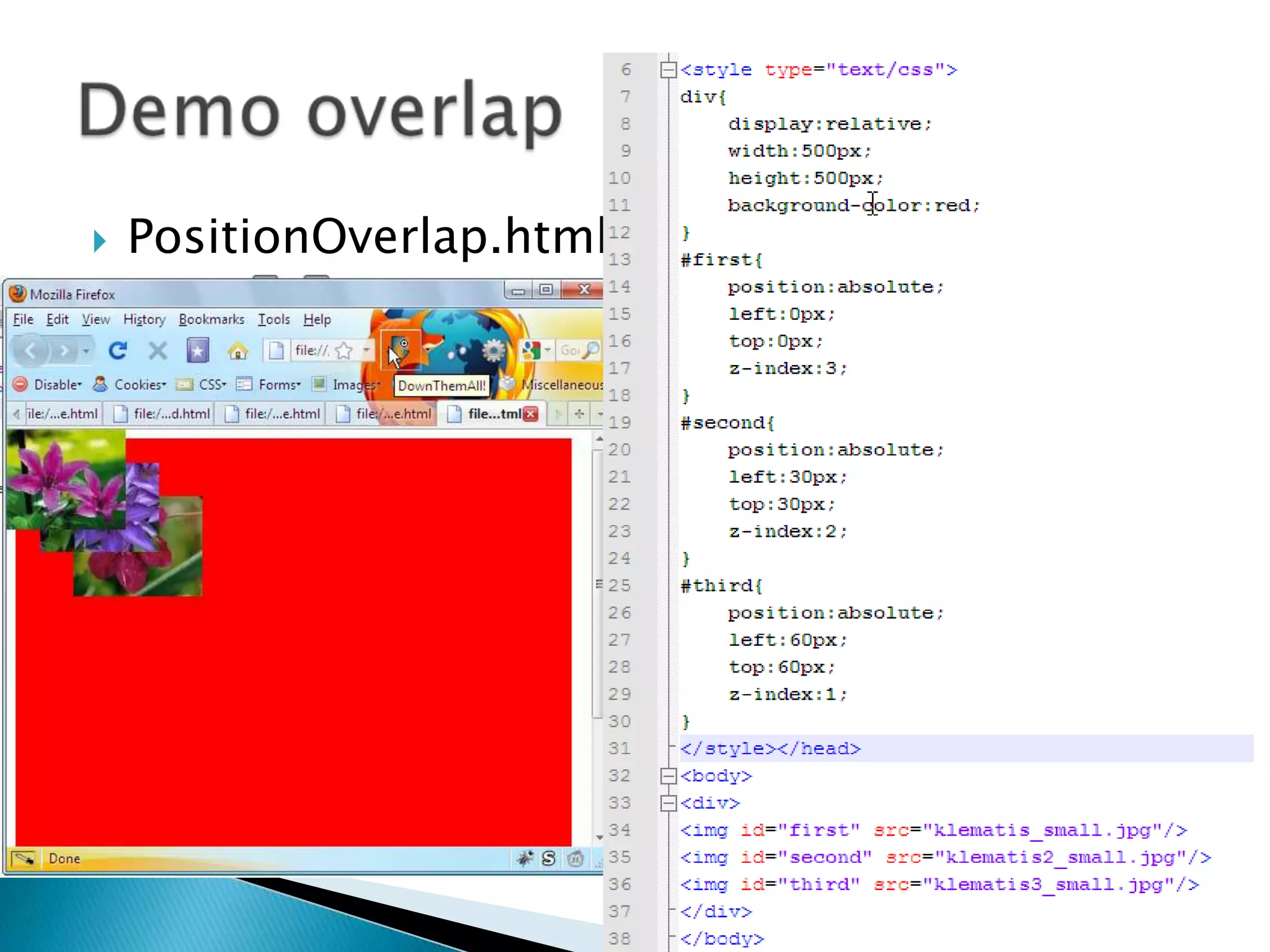
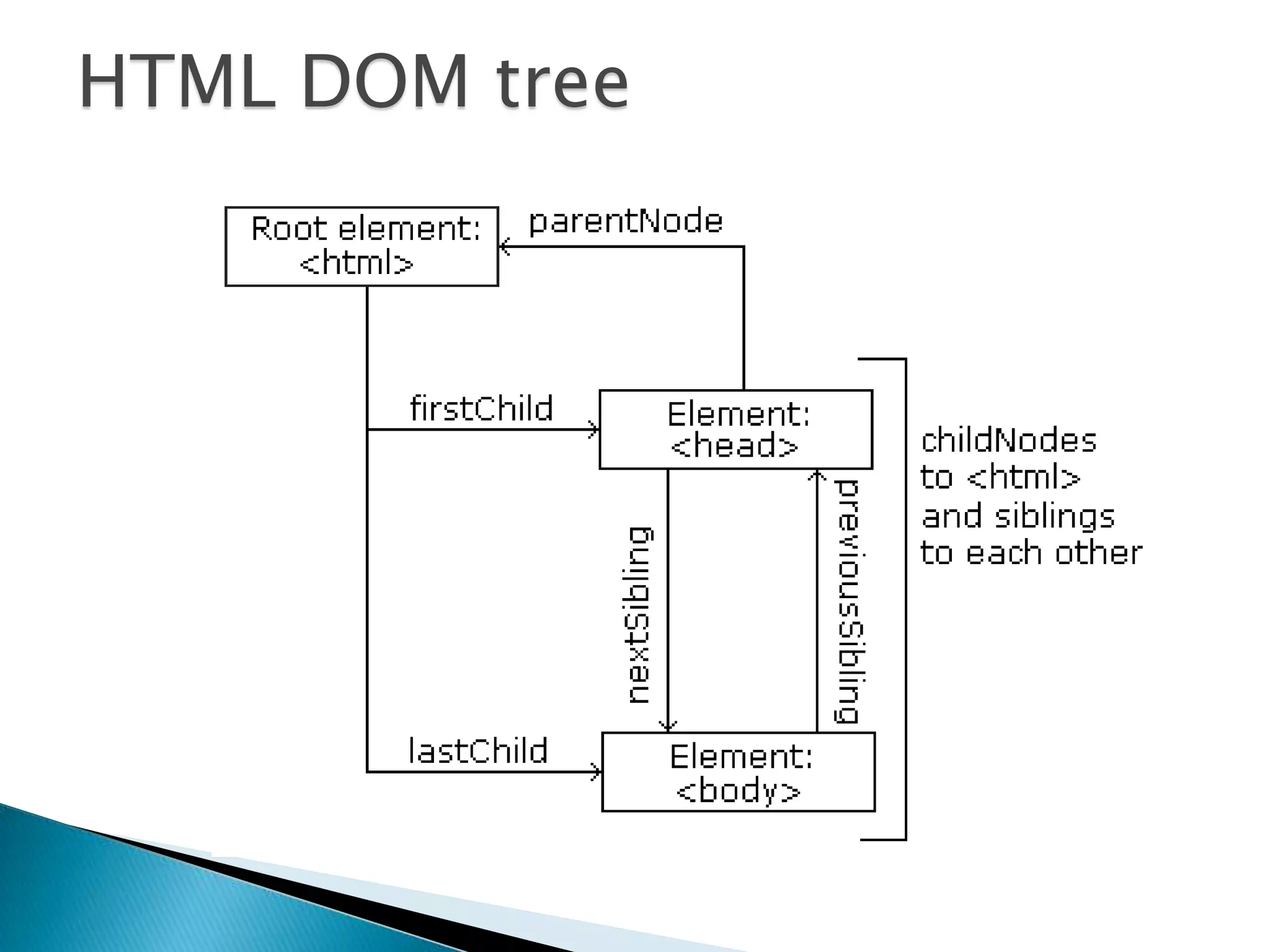
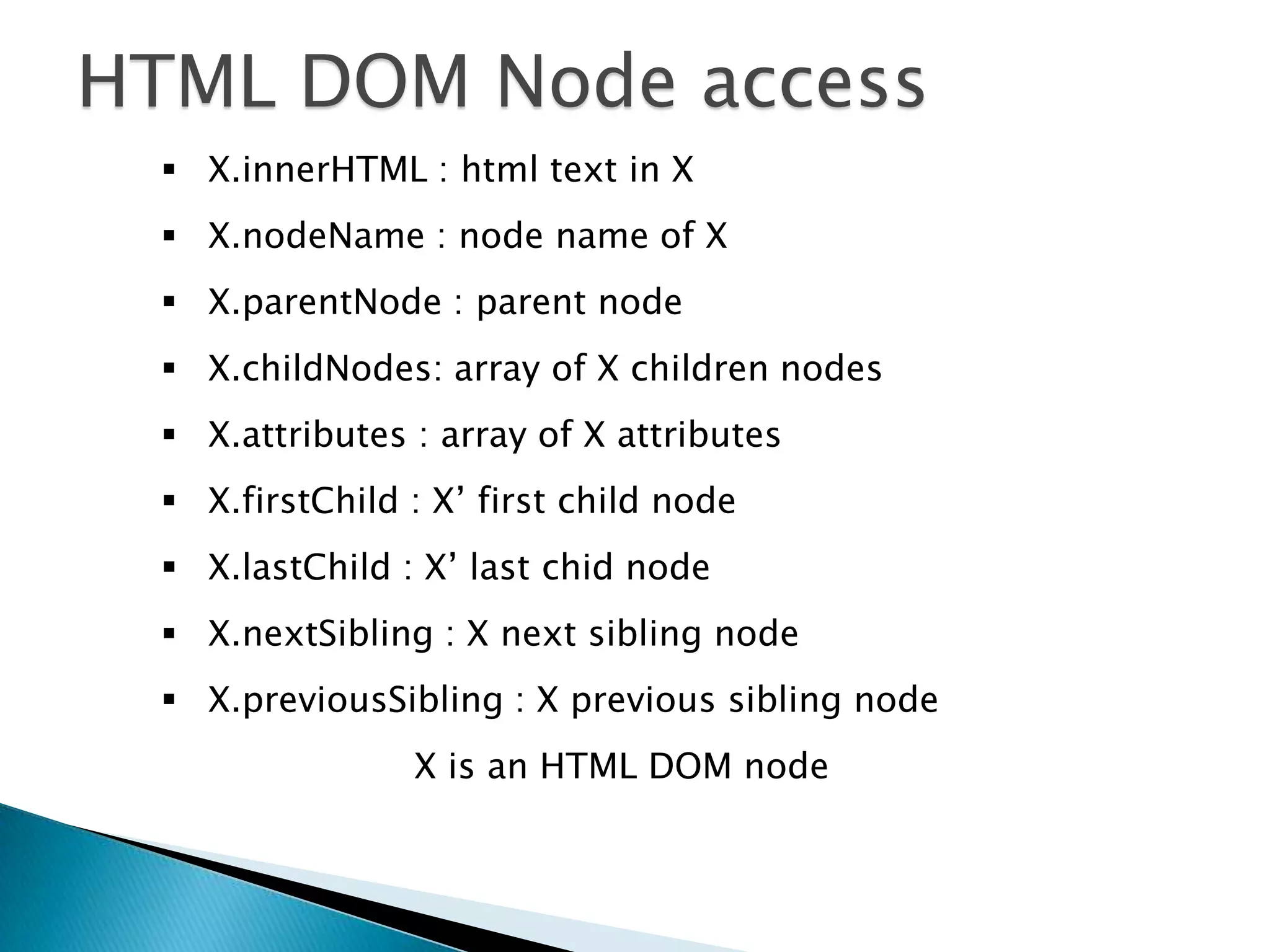
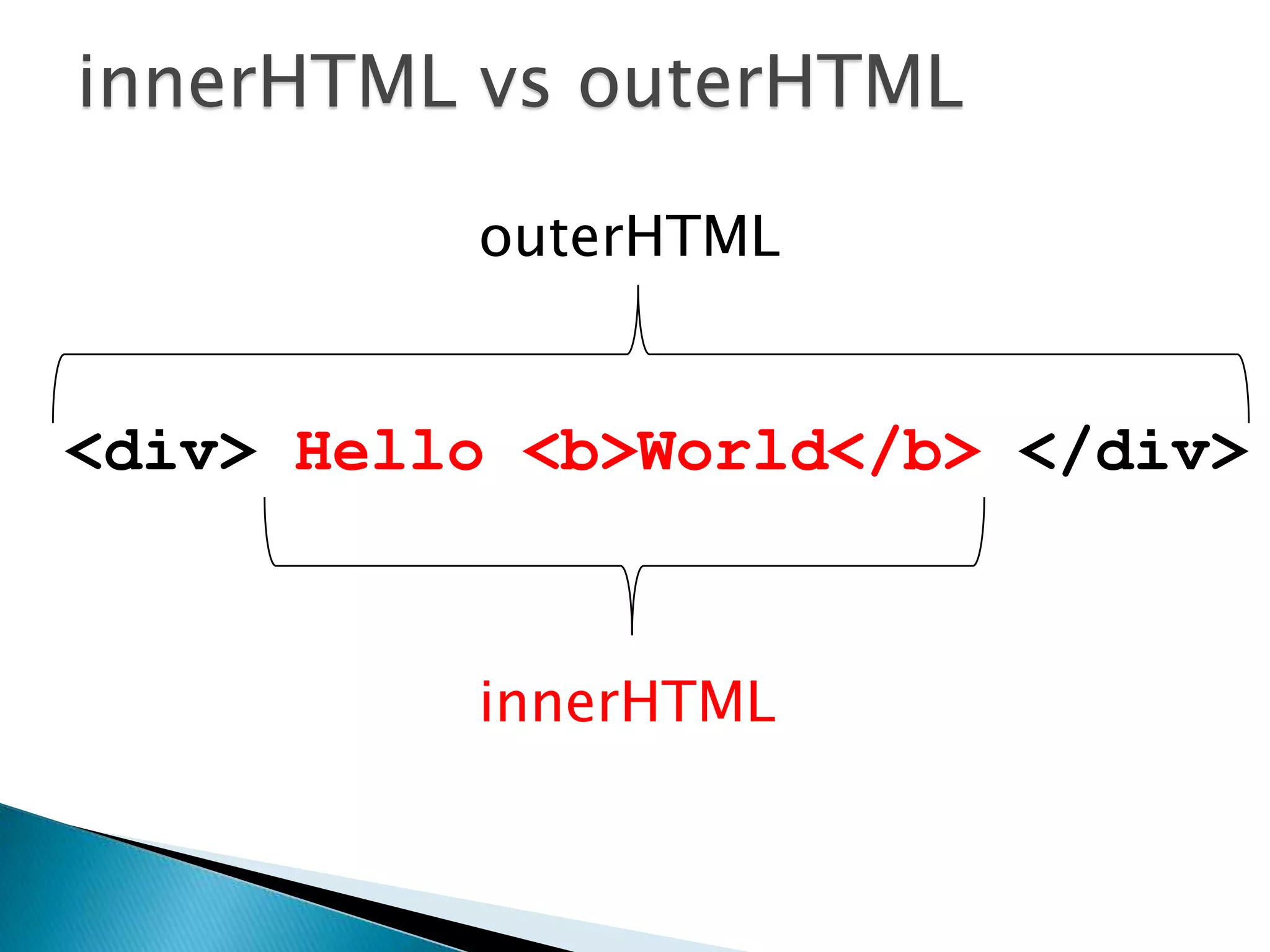
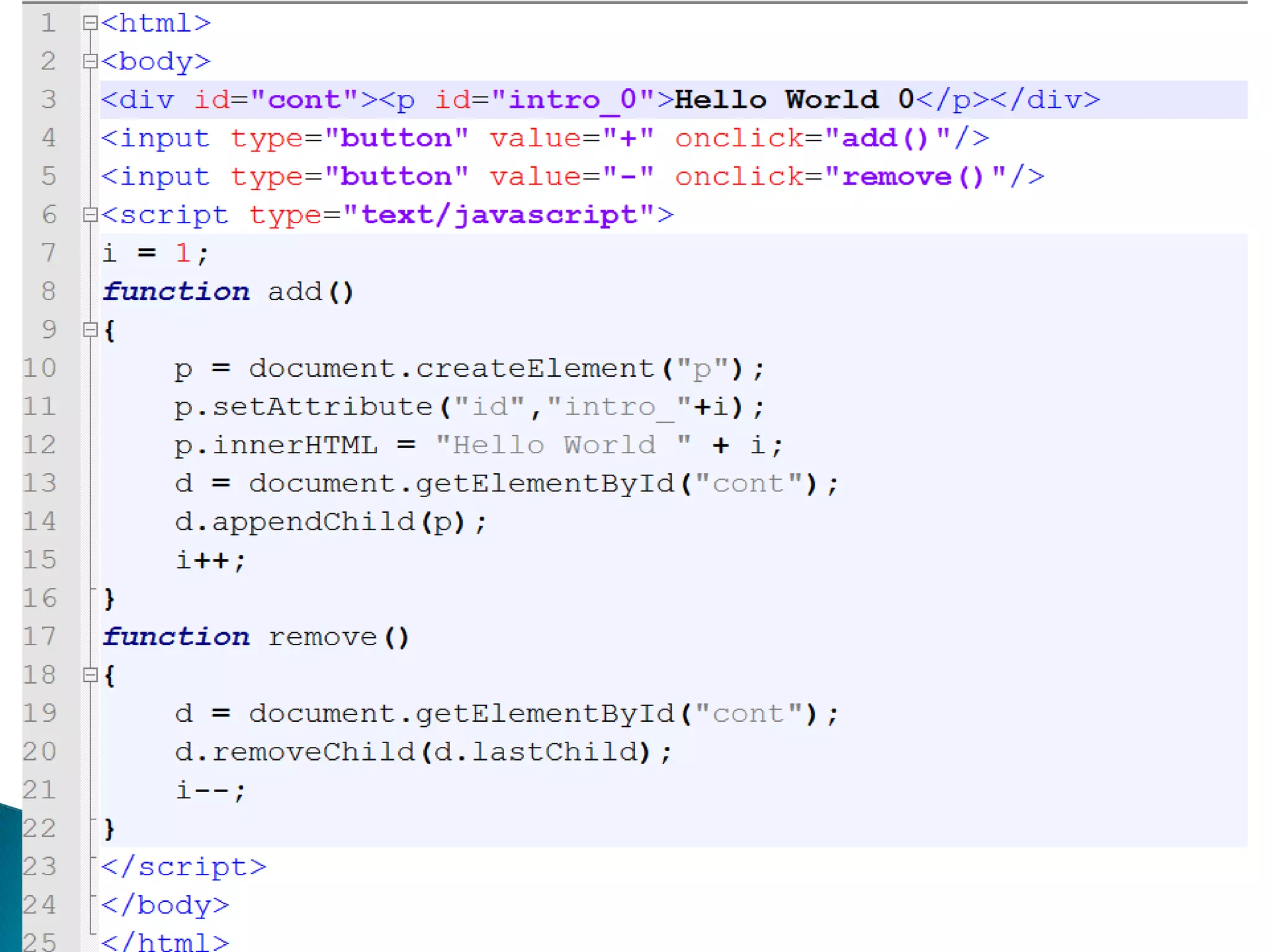
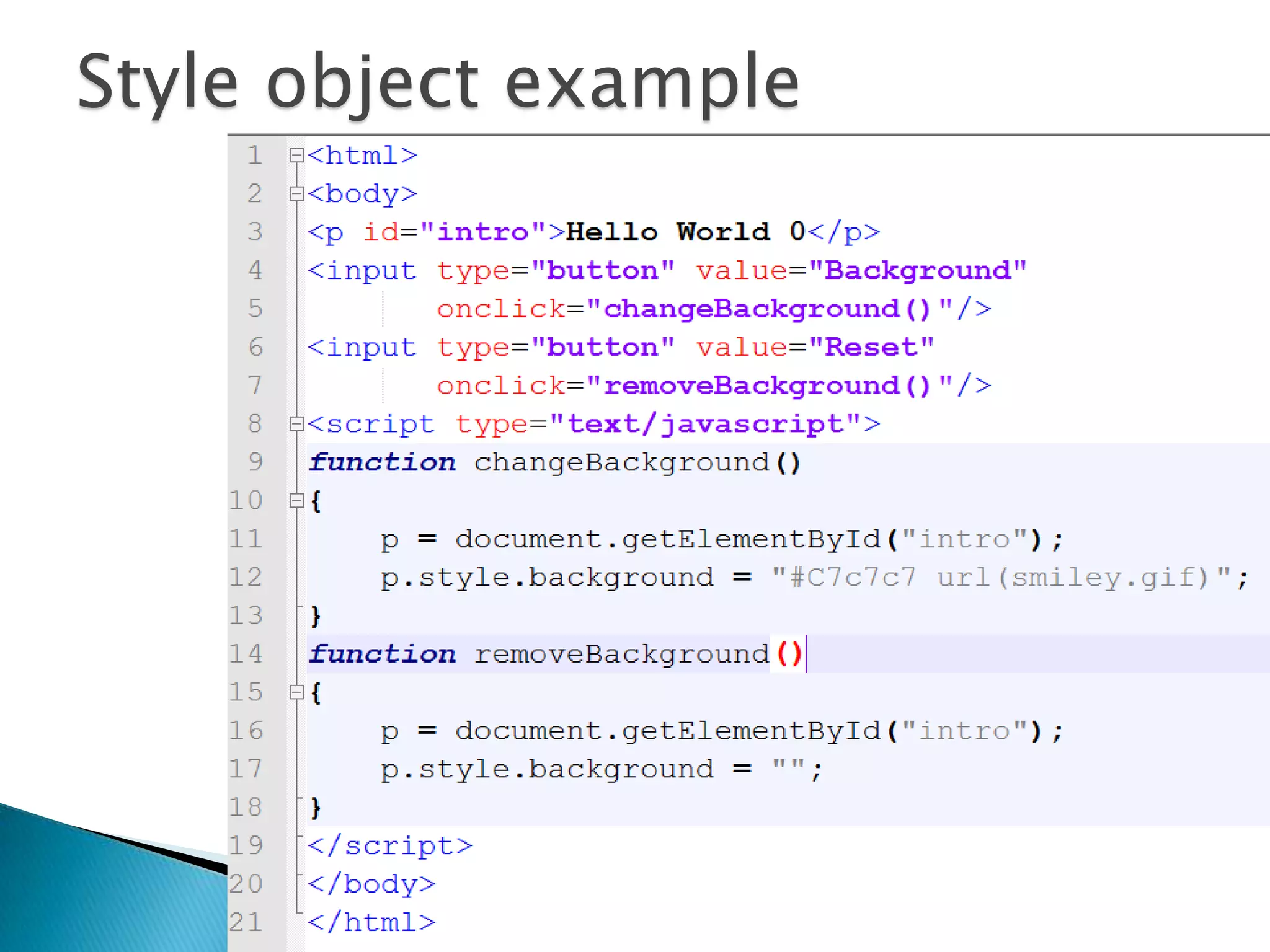
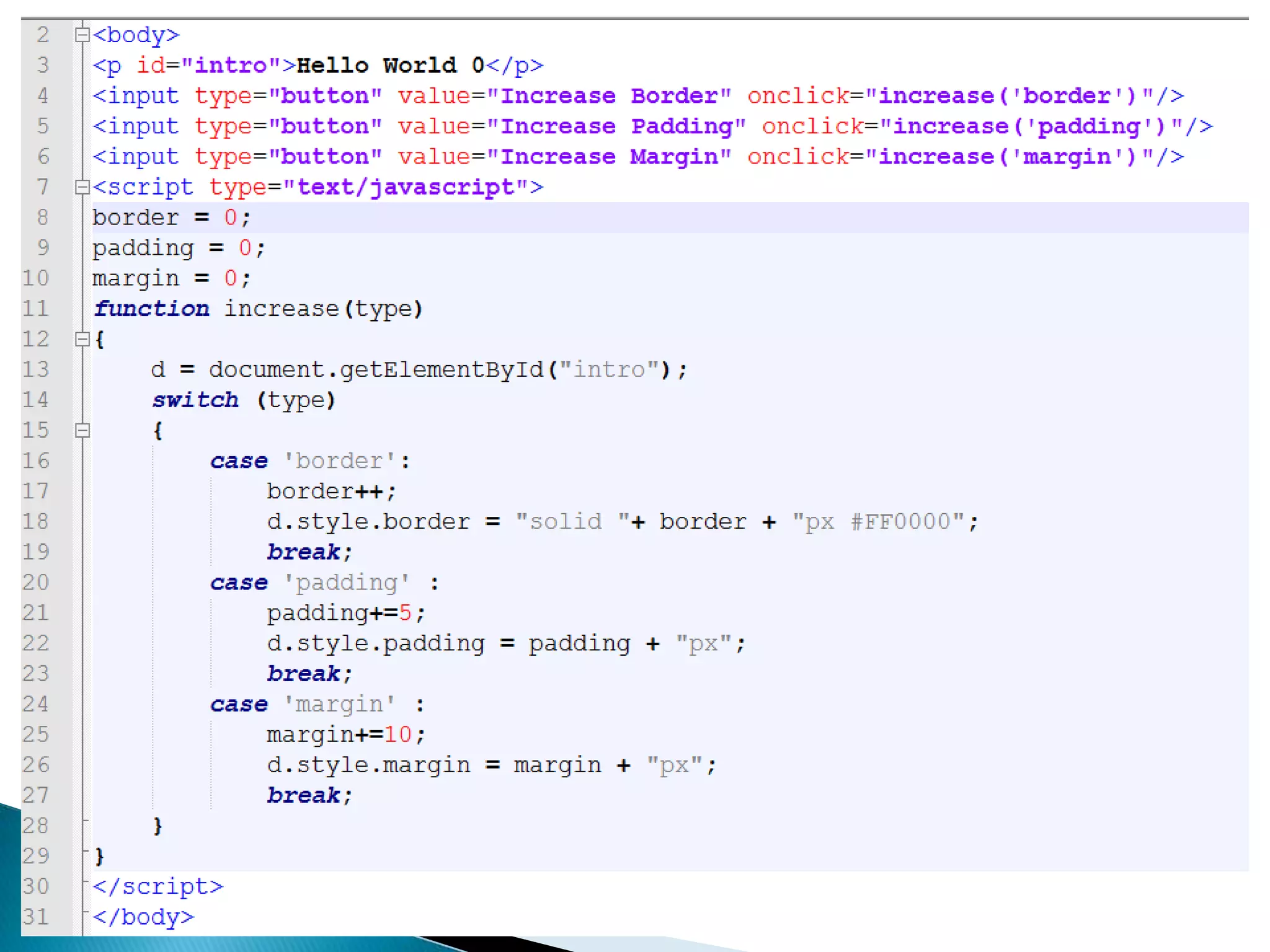
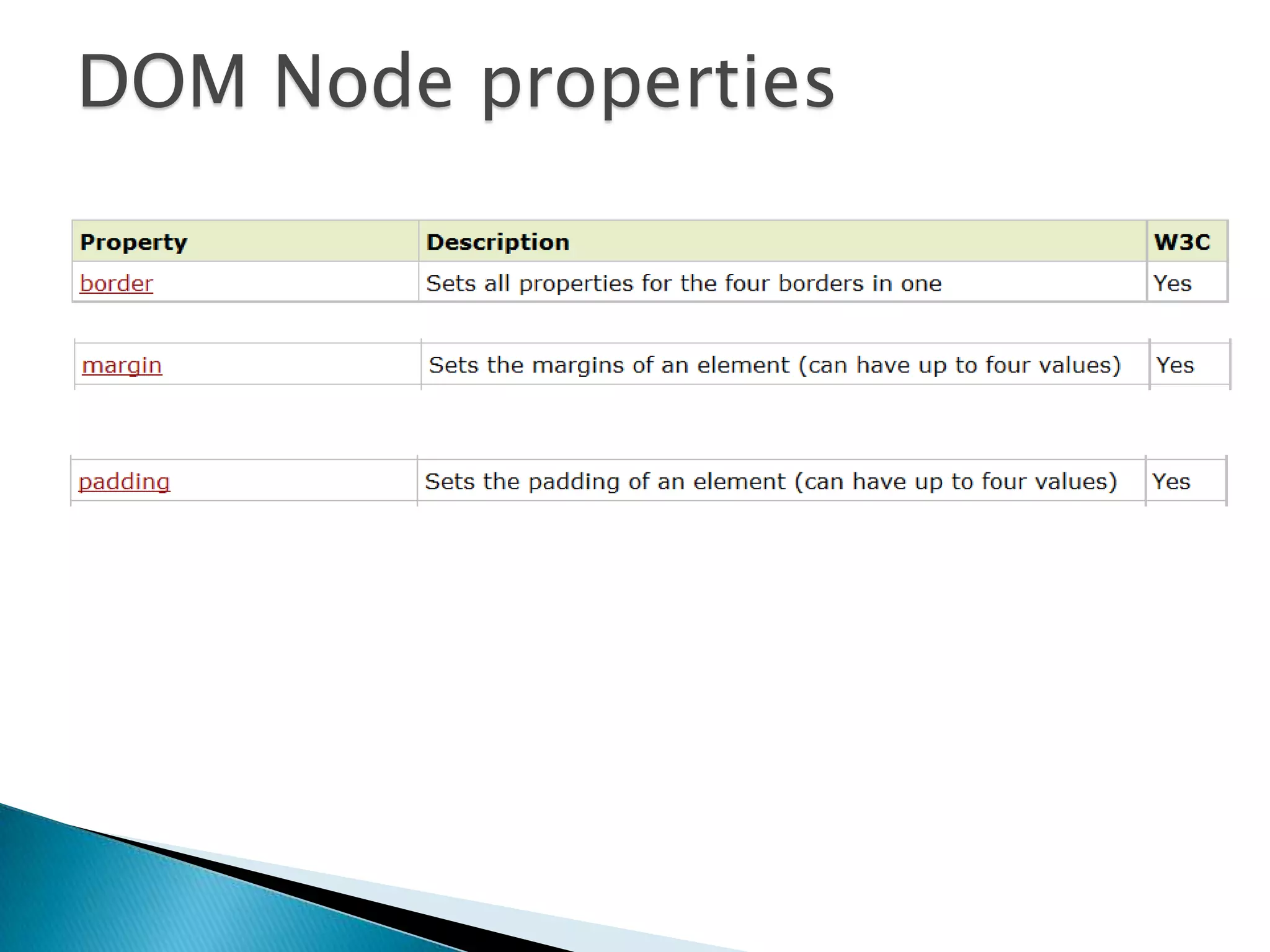
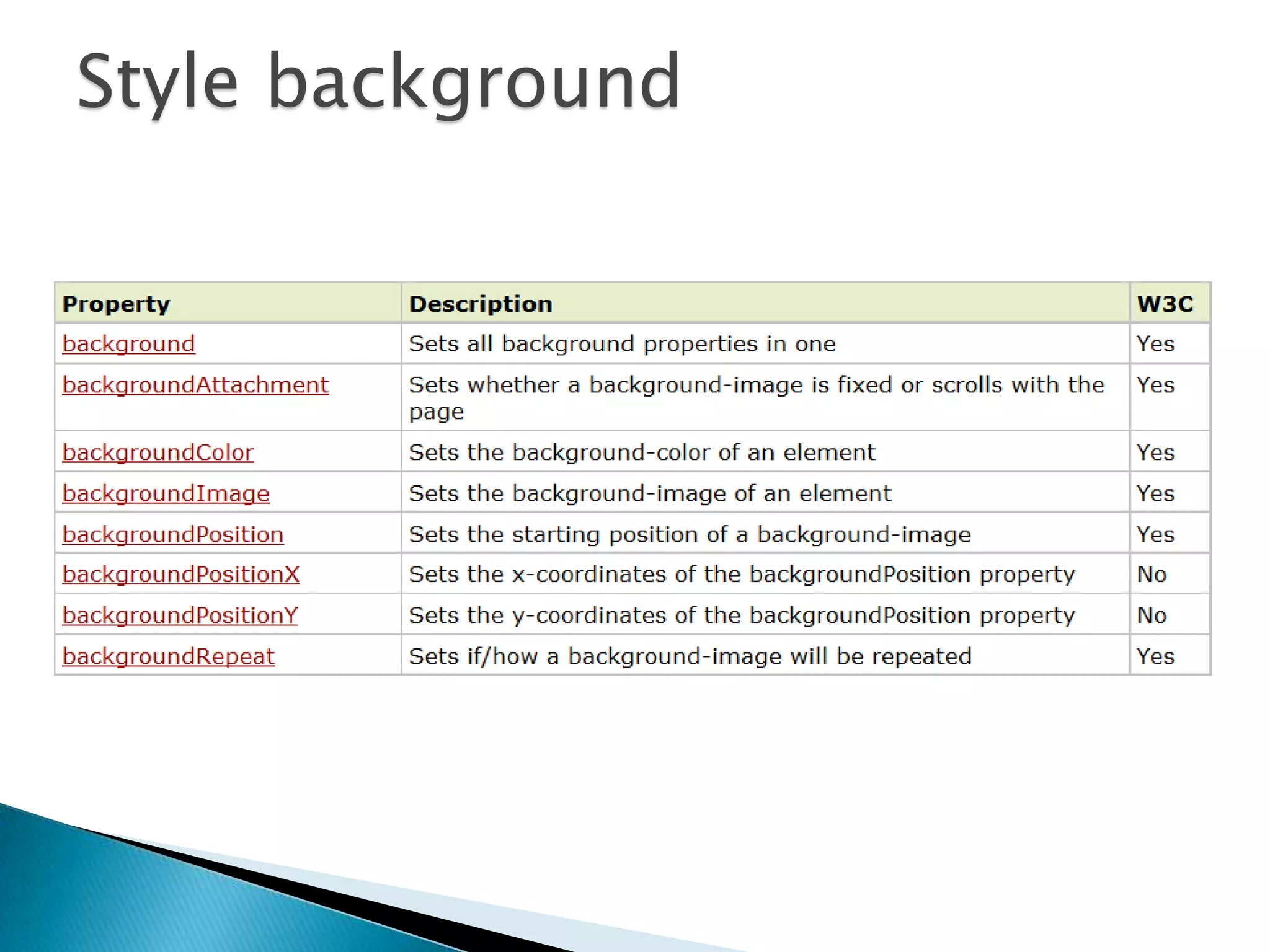
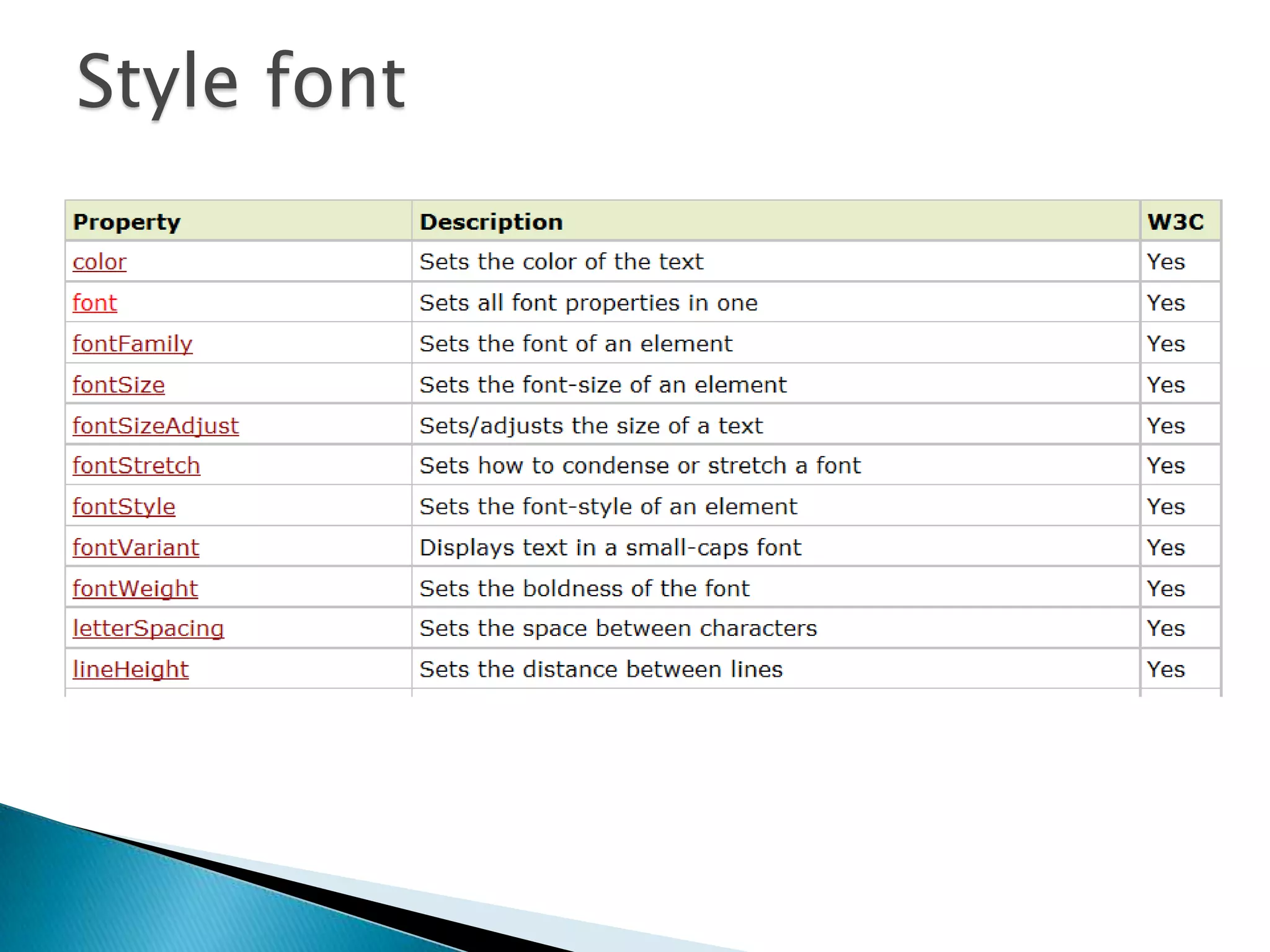
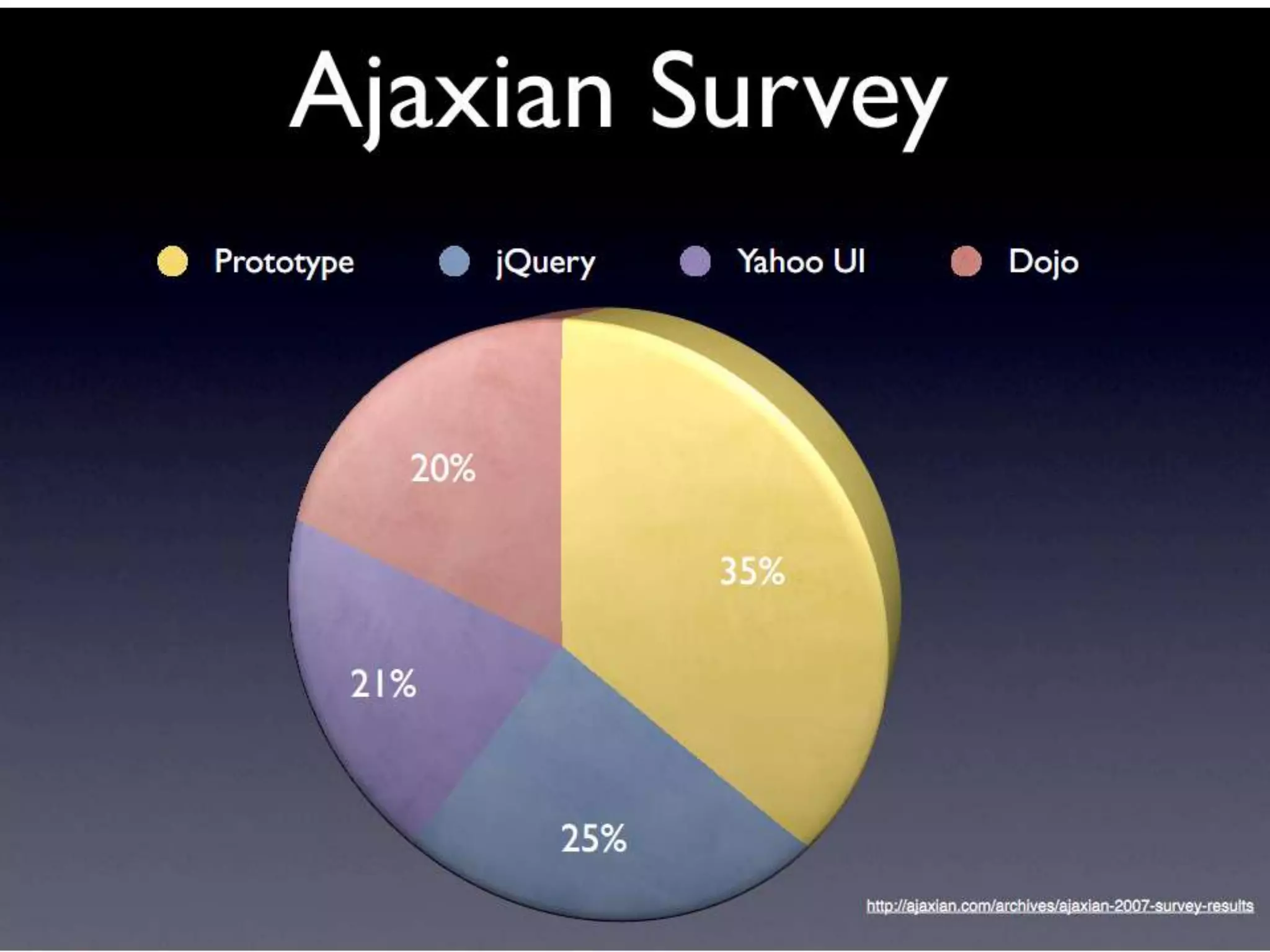
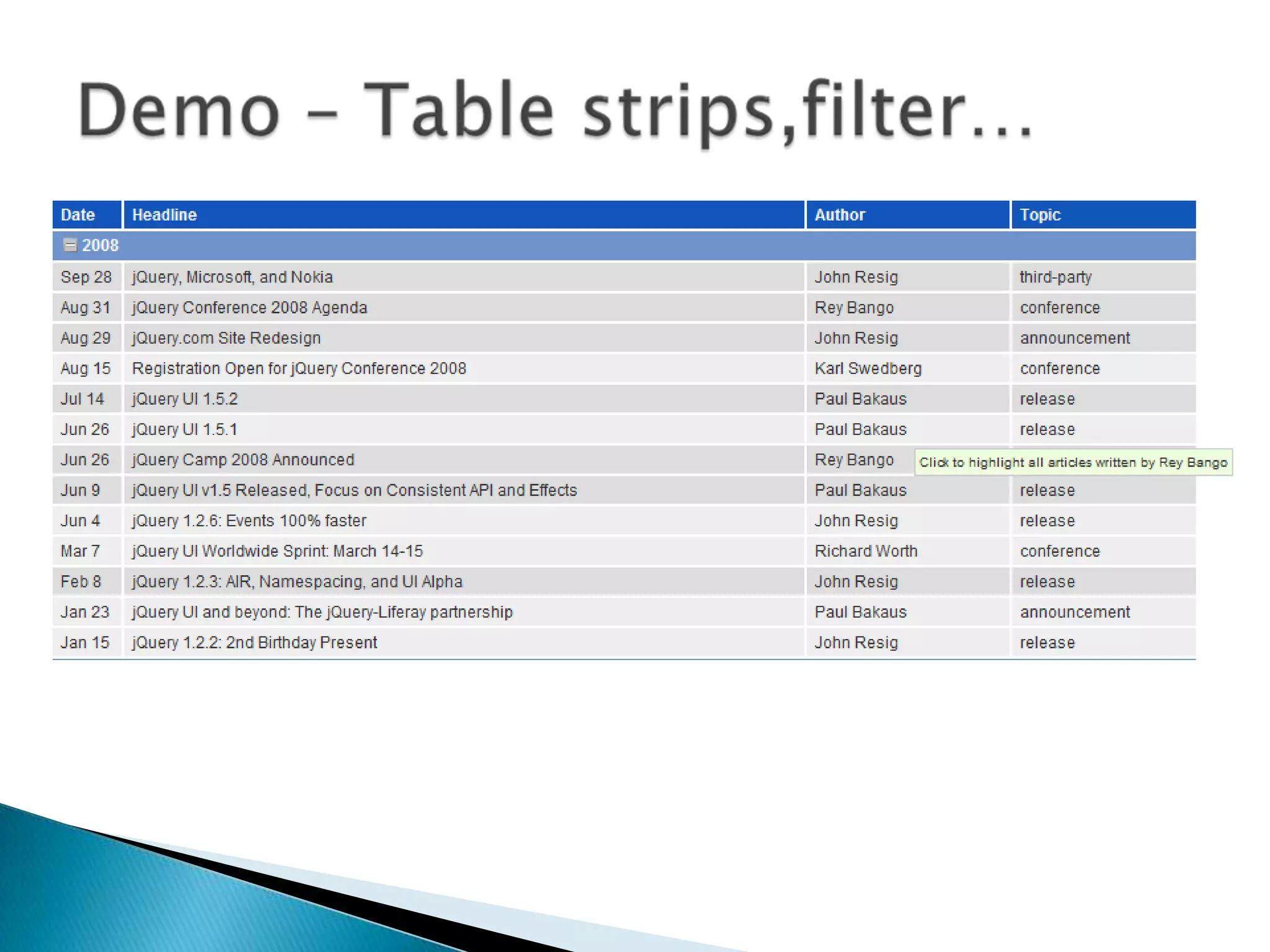
The document discusses various topics related to web development including XHTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It provides definitions and explanations of XHTML, CSS, JavaScript, and the differences between HTML and XHTML. It also covers common issues with supporting older browsers like IE6 and strategies for overcoming those issues such as using frameworks to simplify tasks like DOM manipulation and event handling.