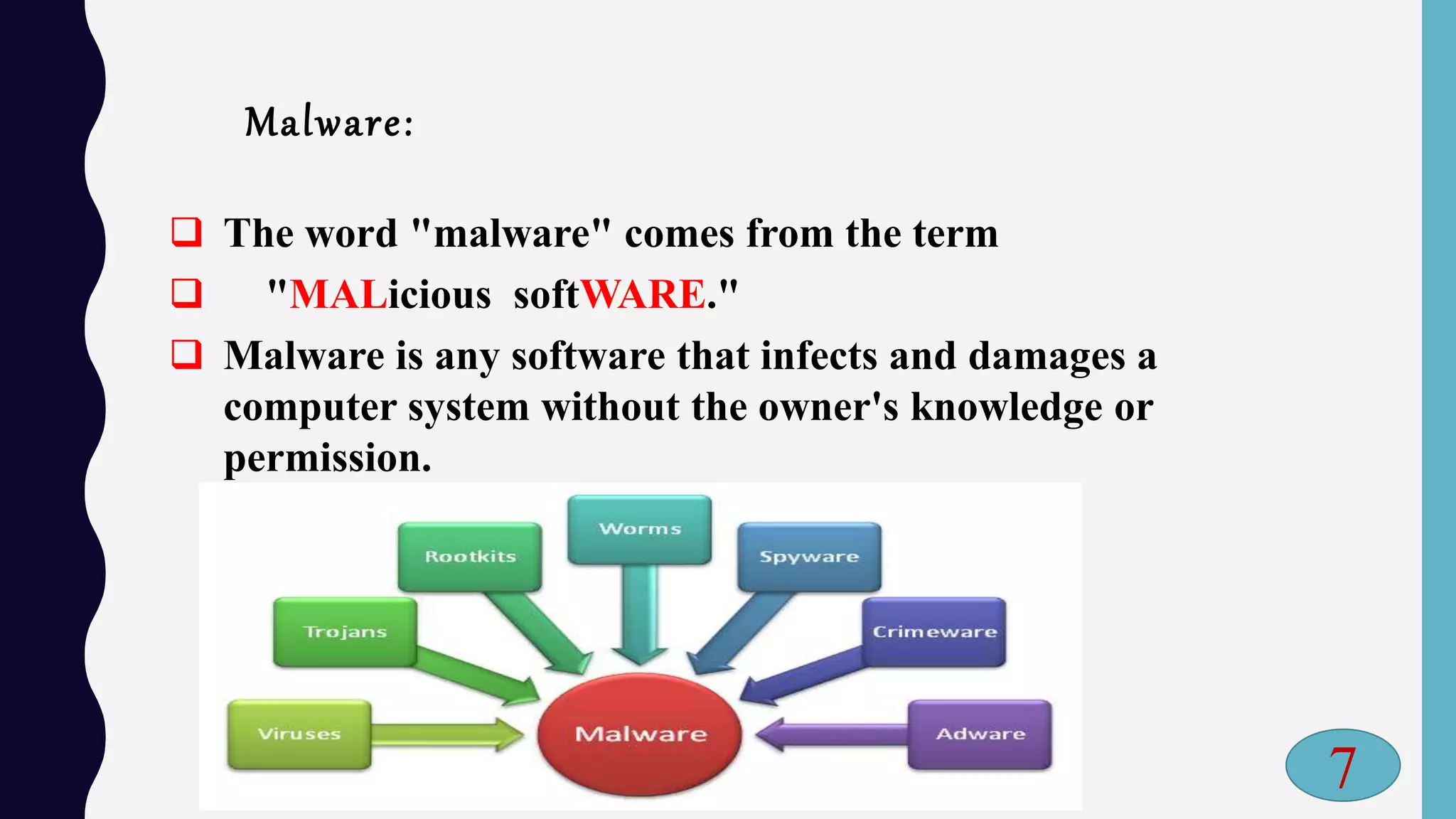
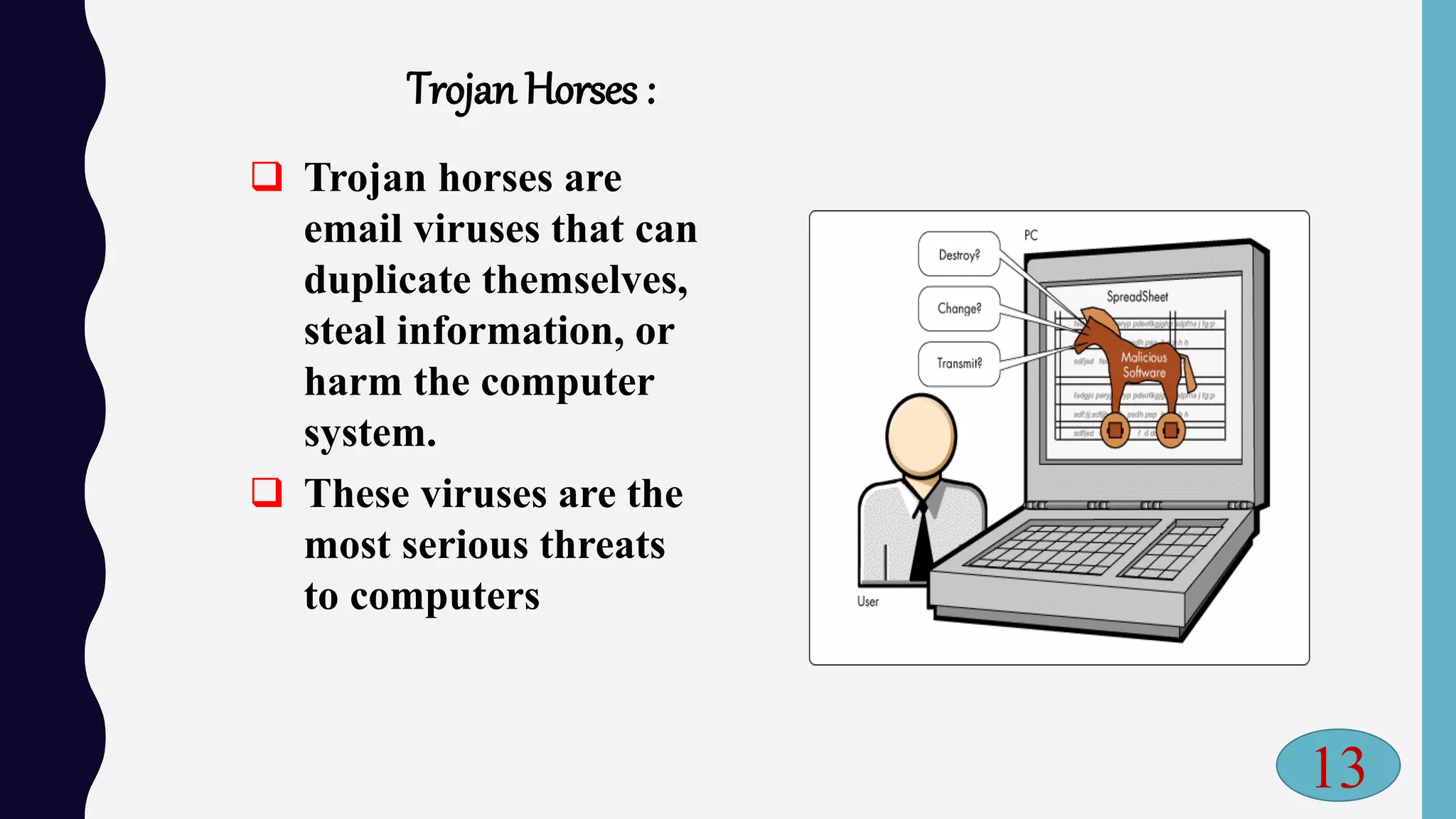
The document discusses the importance of cyber security in protecting online information amidst rising internet threats, including viruses, hackers, and malware. It emphasizes the need for security measures such as antivirus software, strong passwords, and firewalls to safeguard systems from various cyber threats. Furthermore, it outlines the definitions of cyber crime, types of hackers, and preventive strategies against hacking.