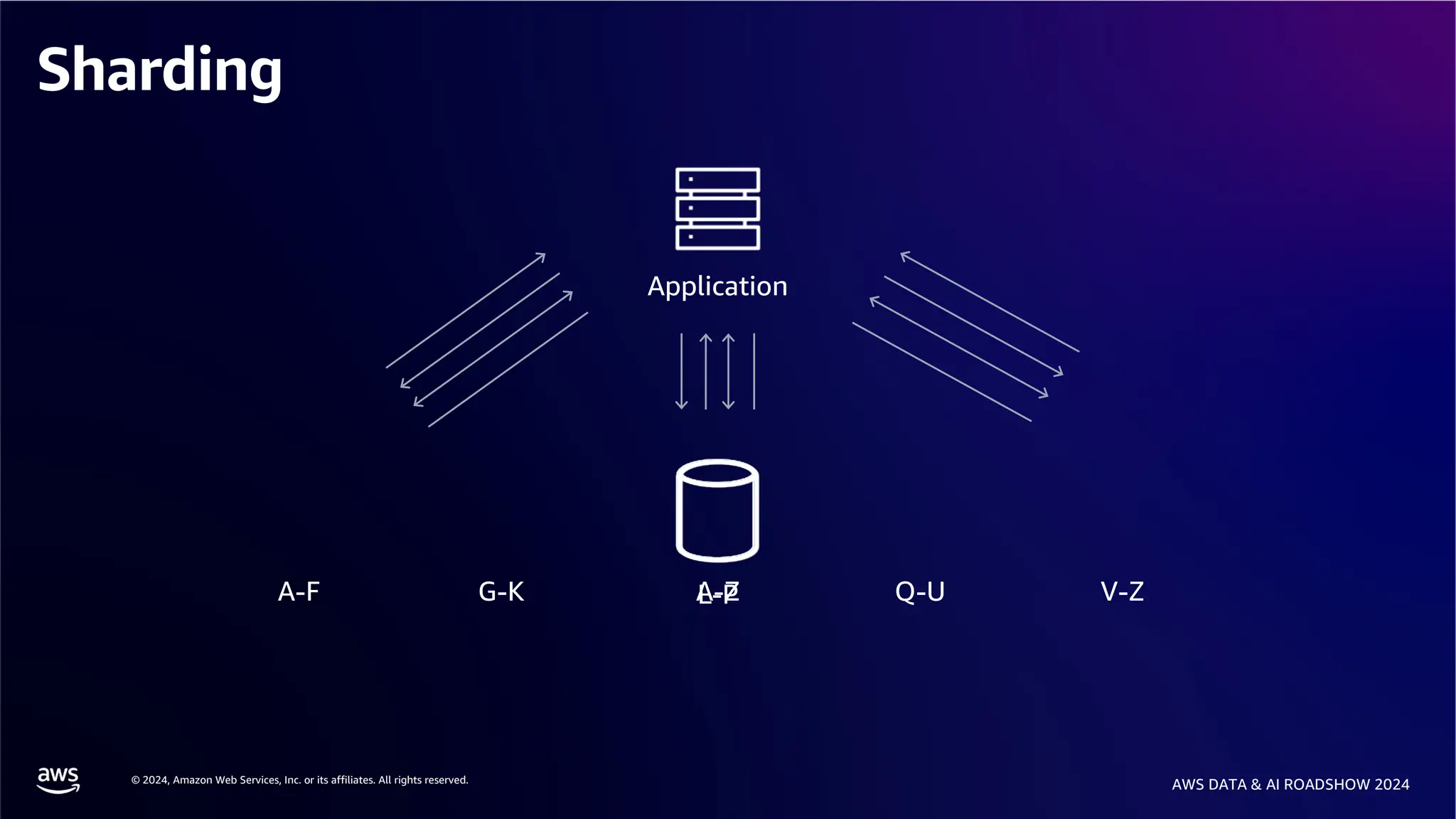
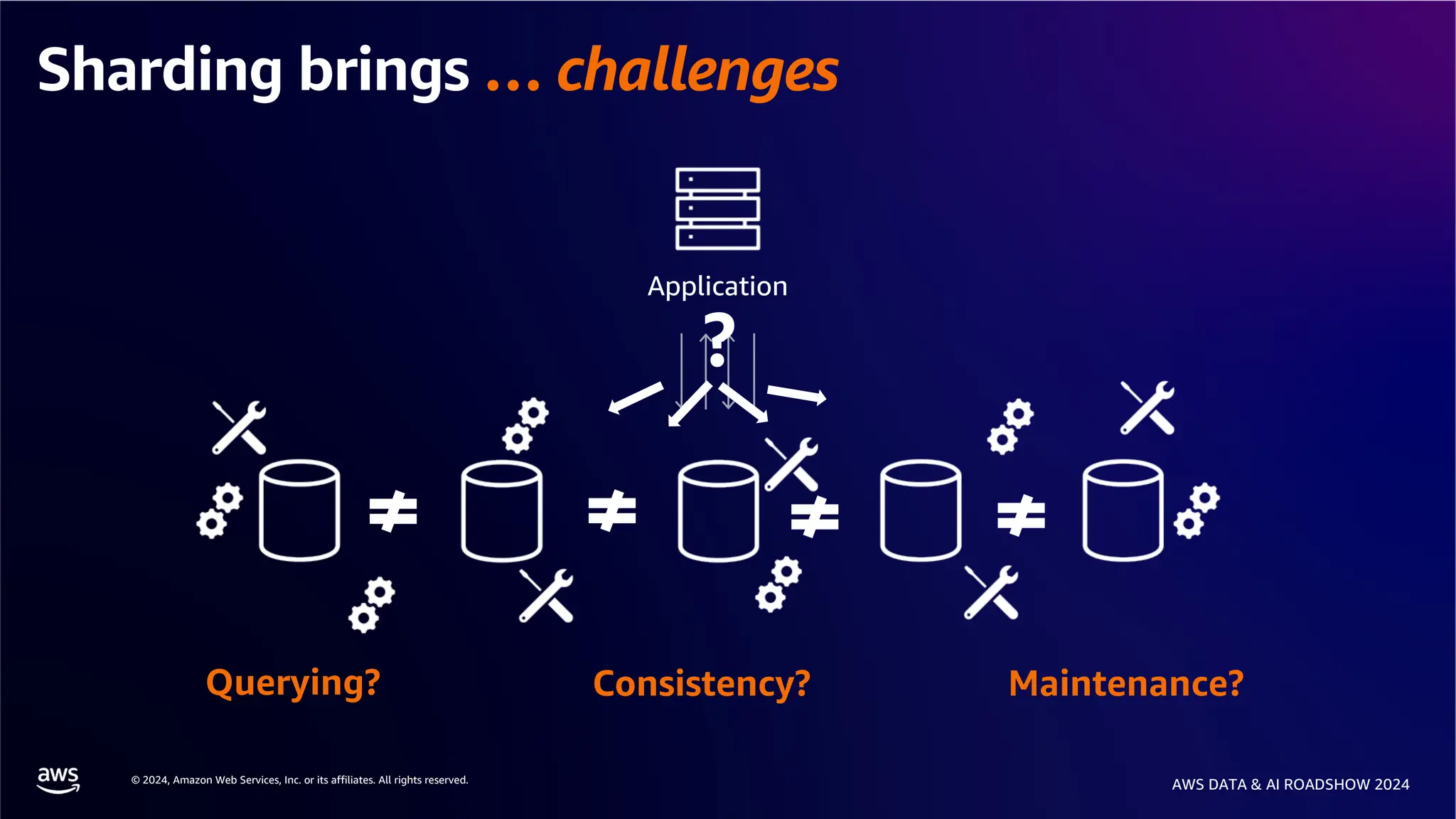
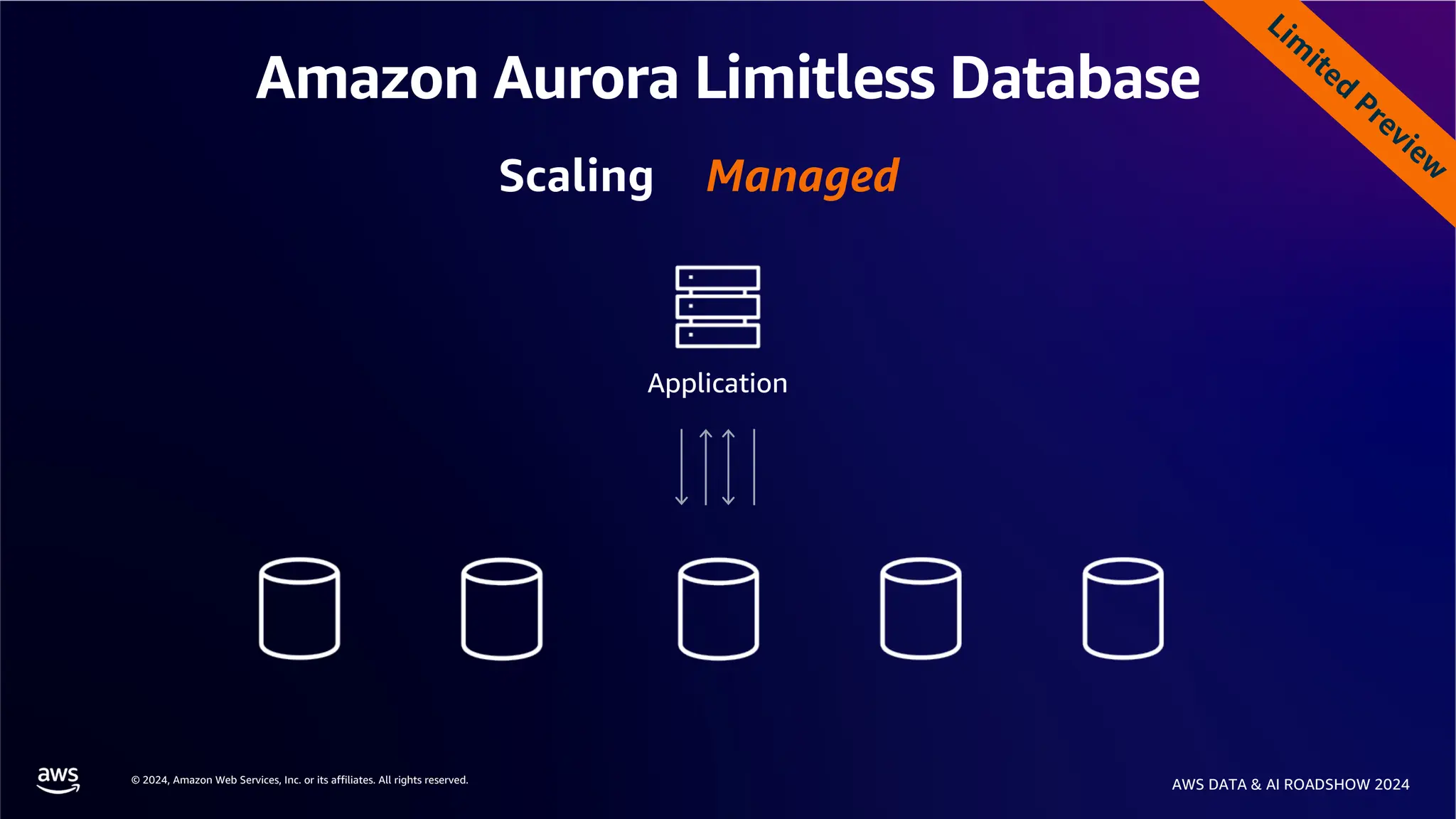
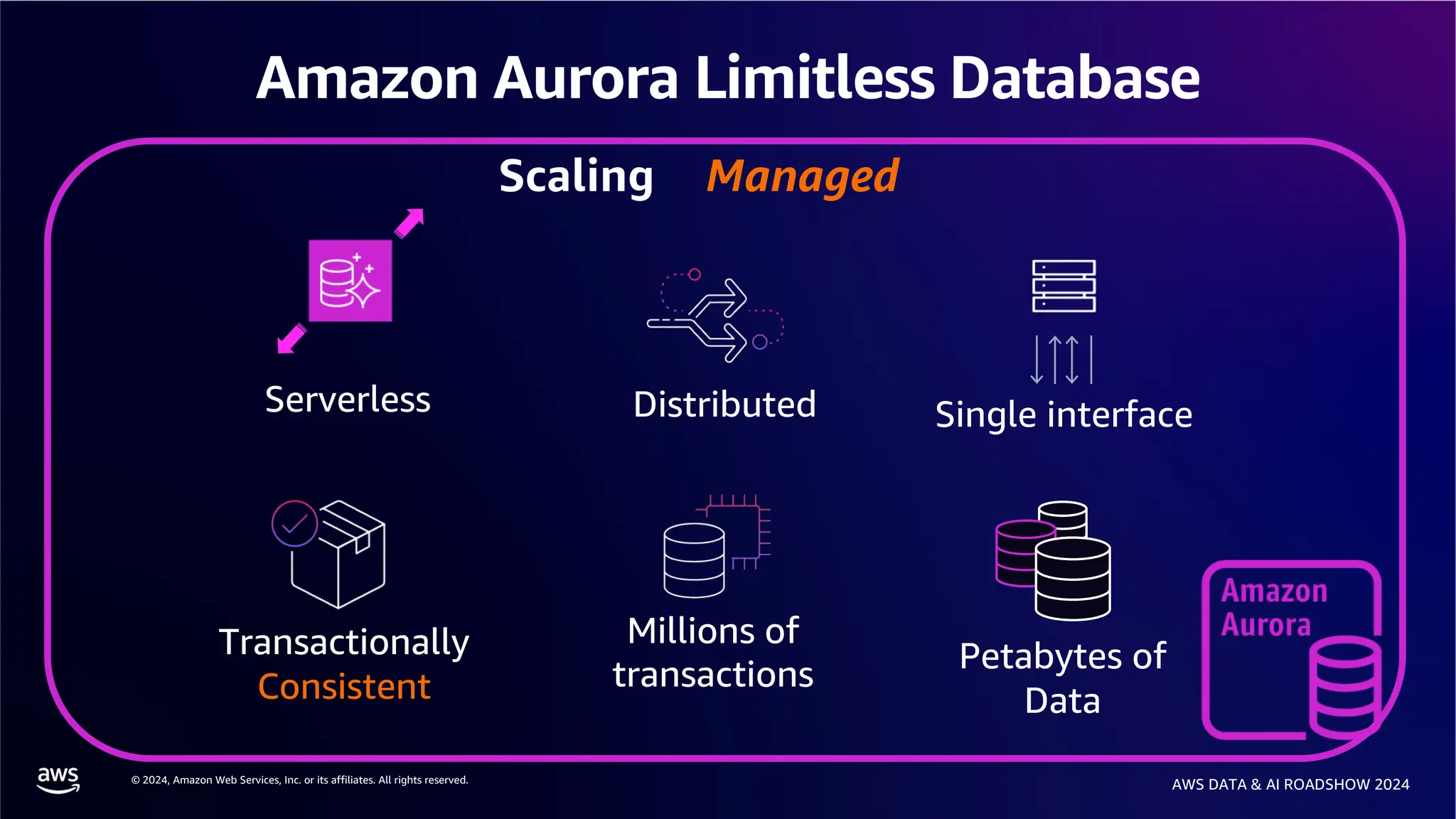
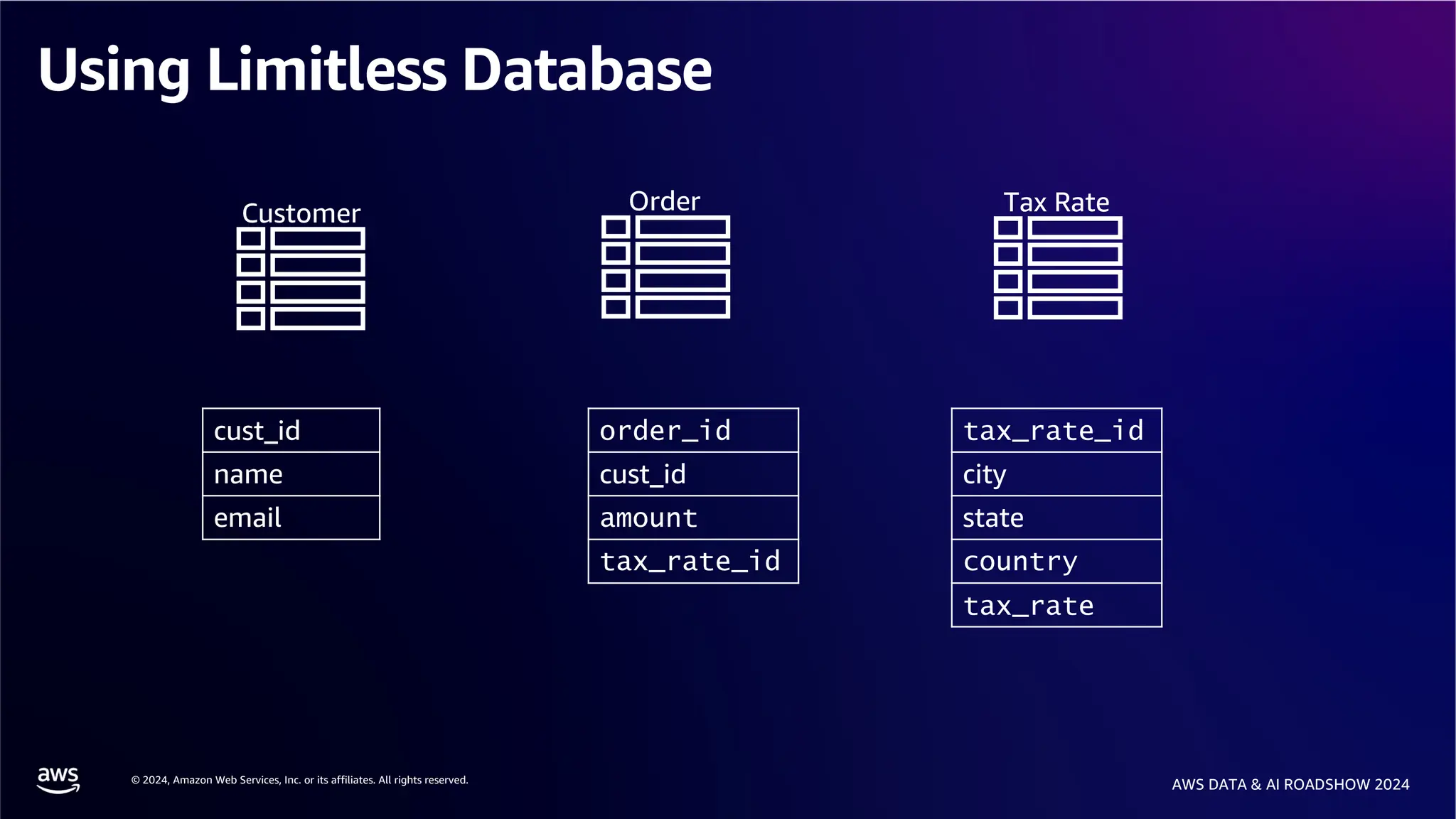
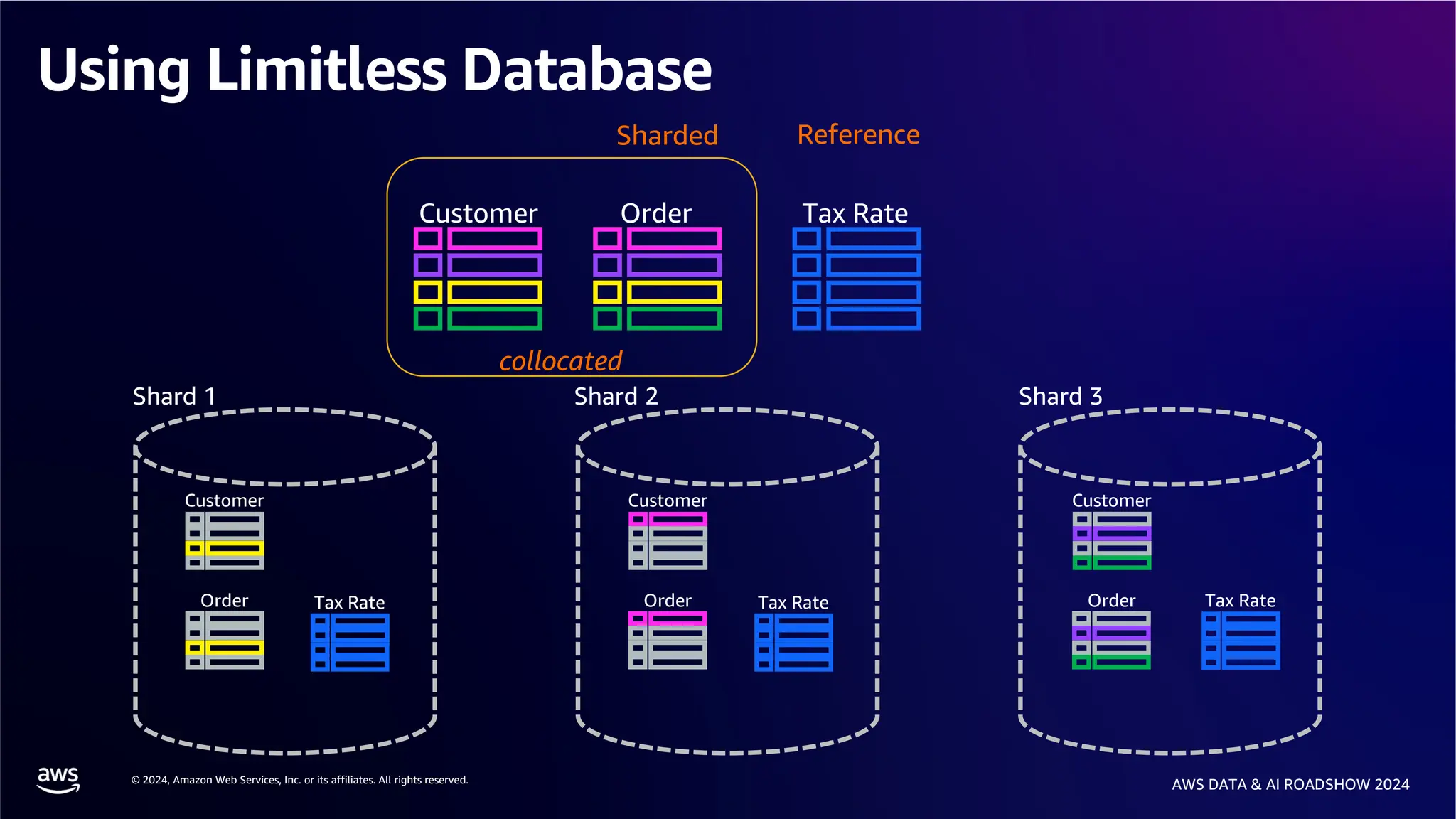
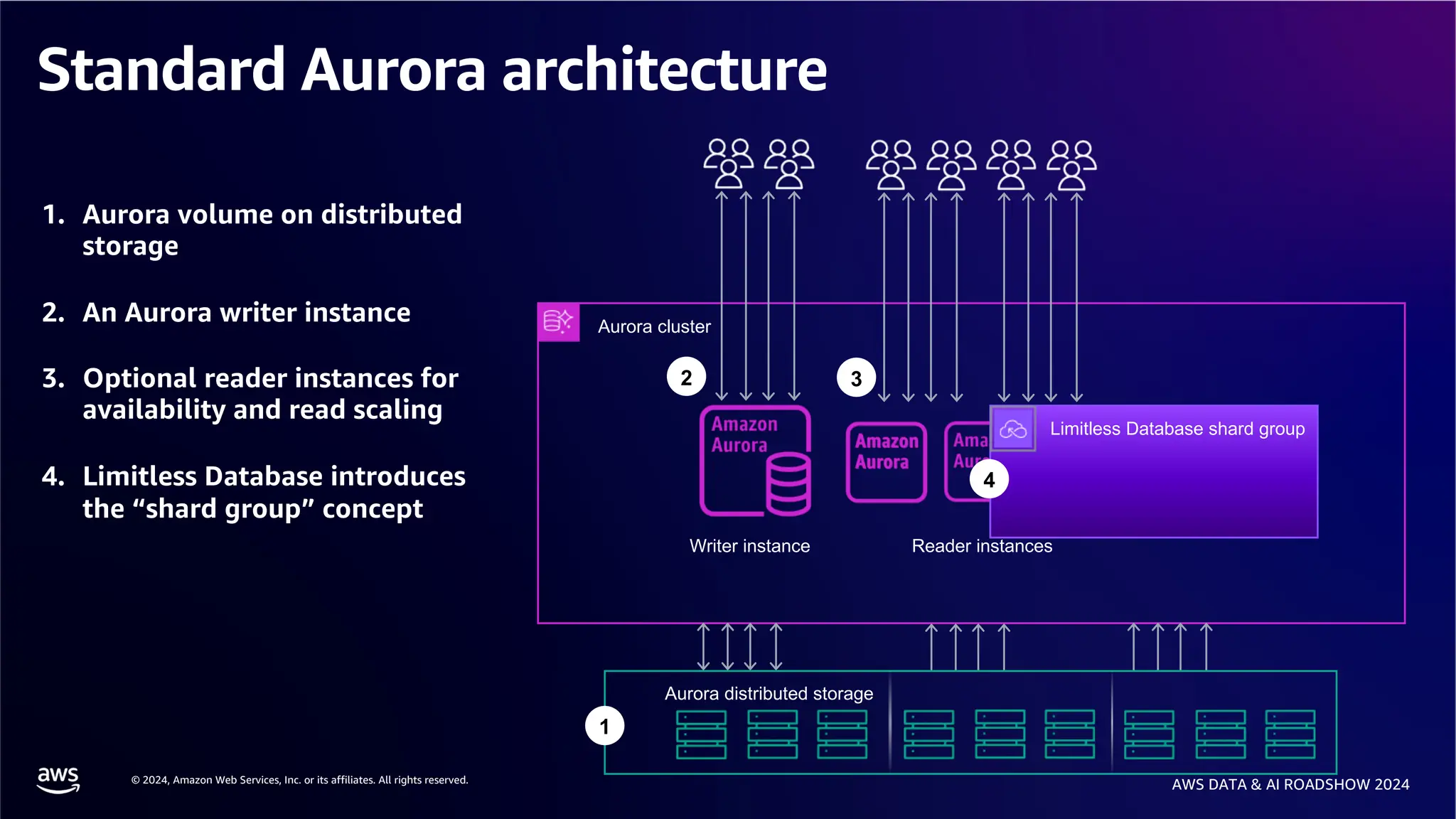
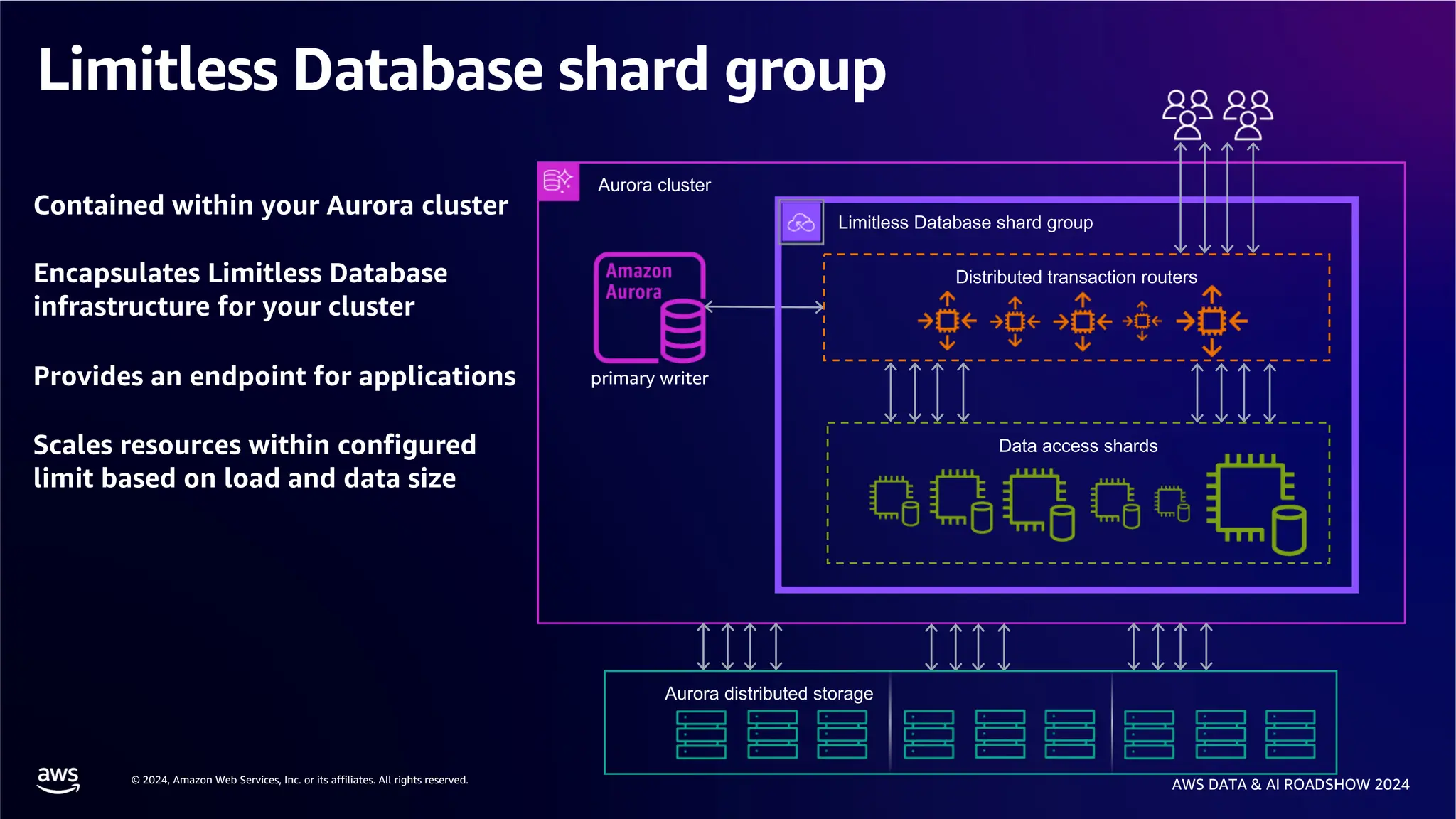
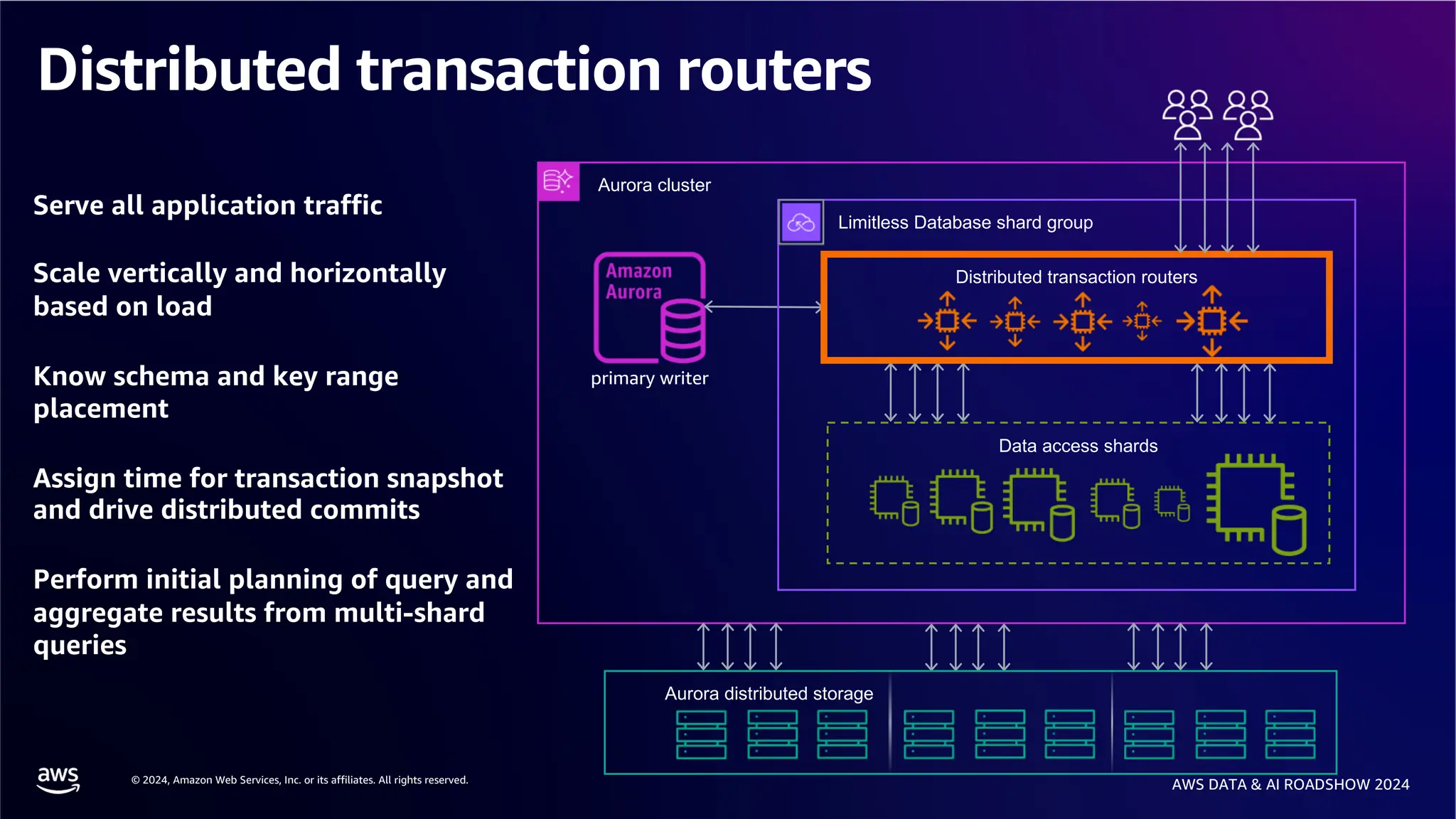
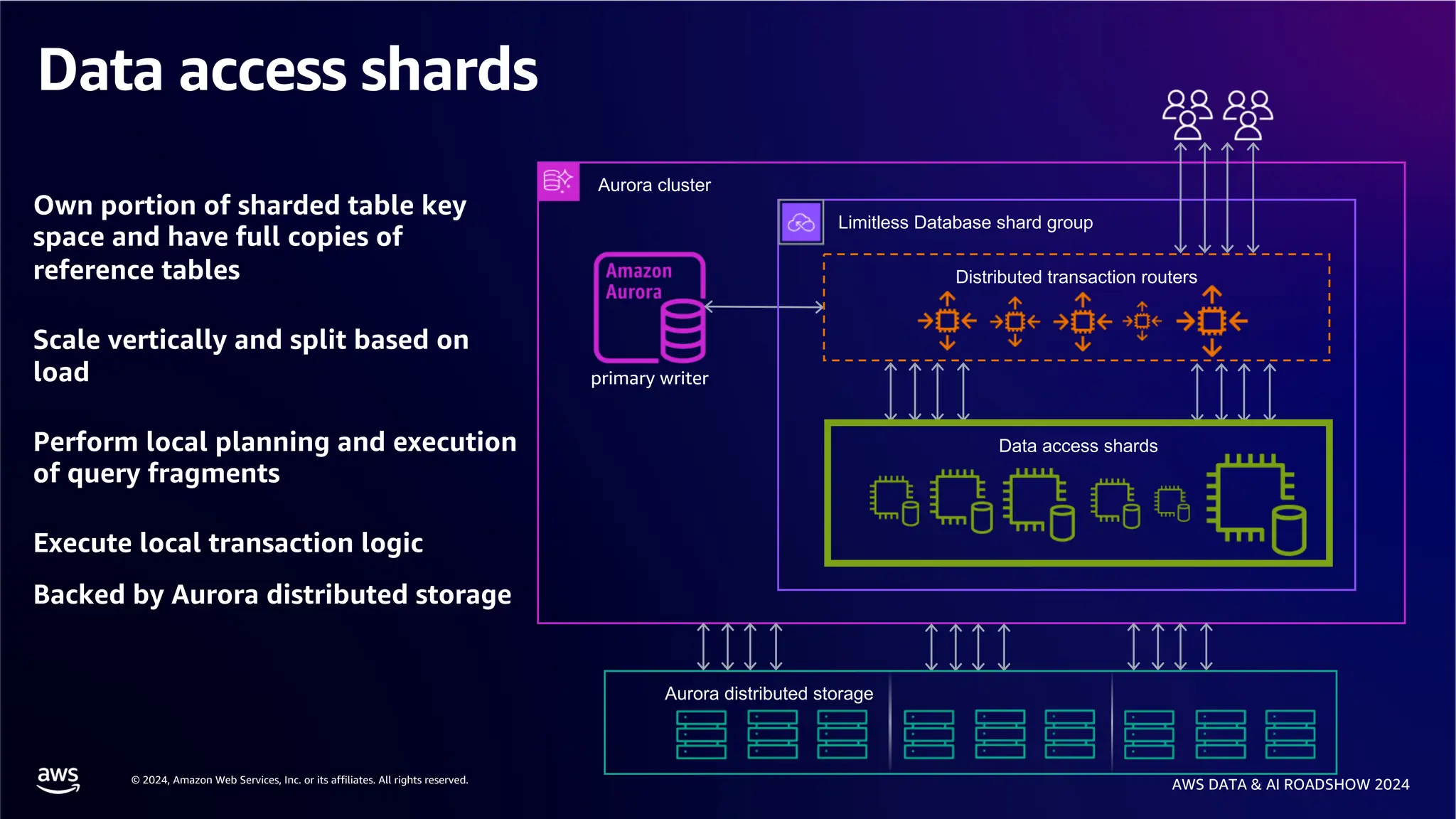
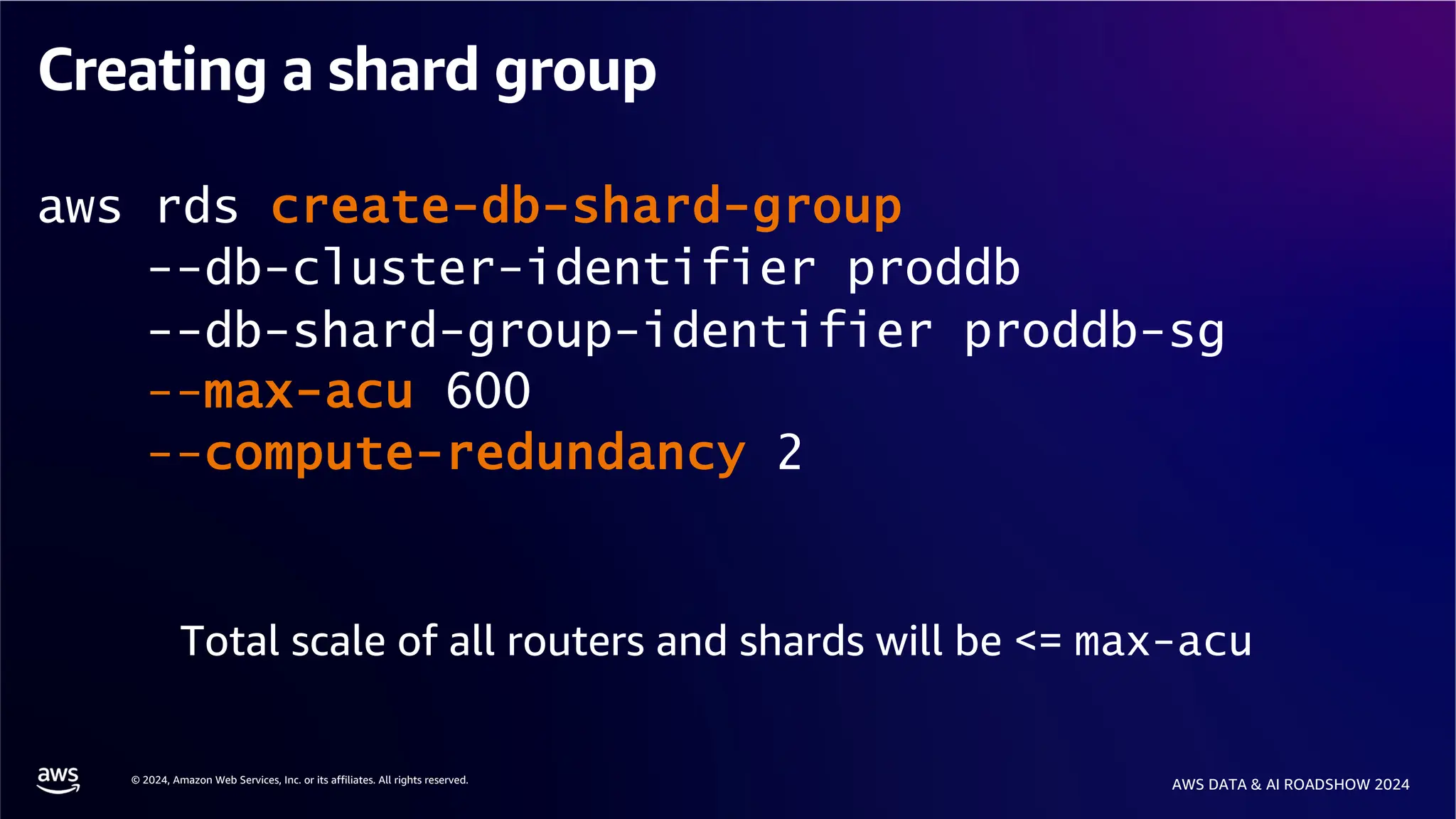
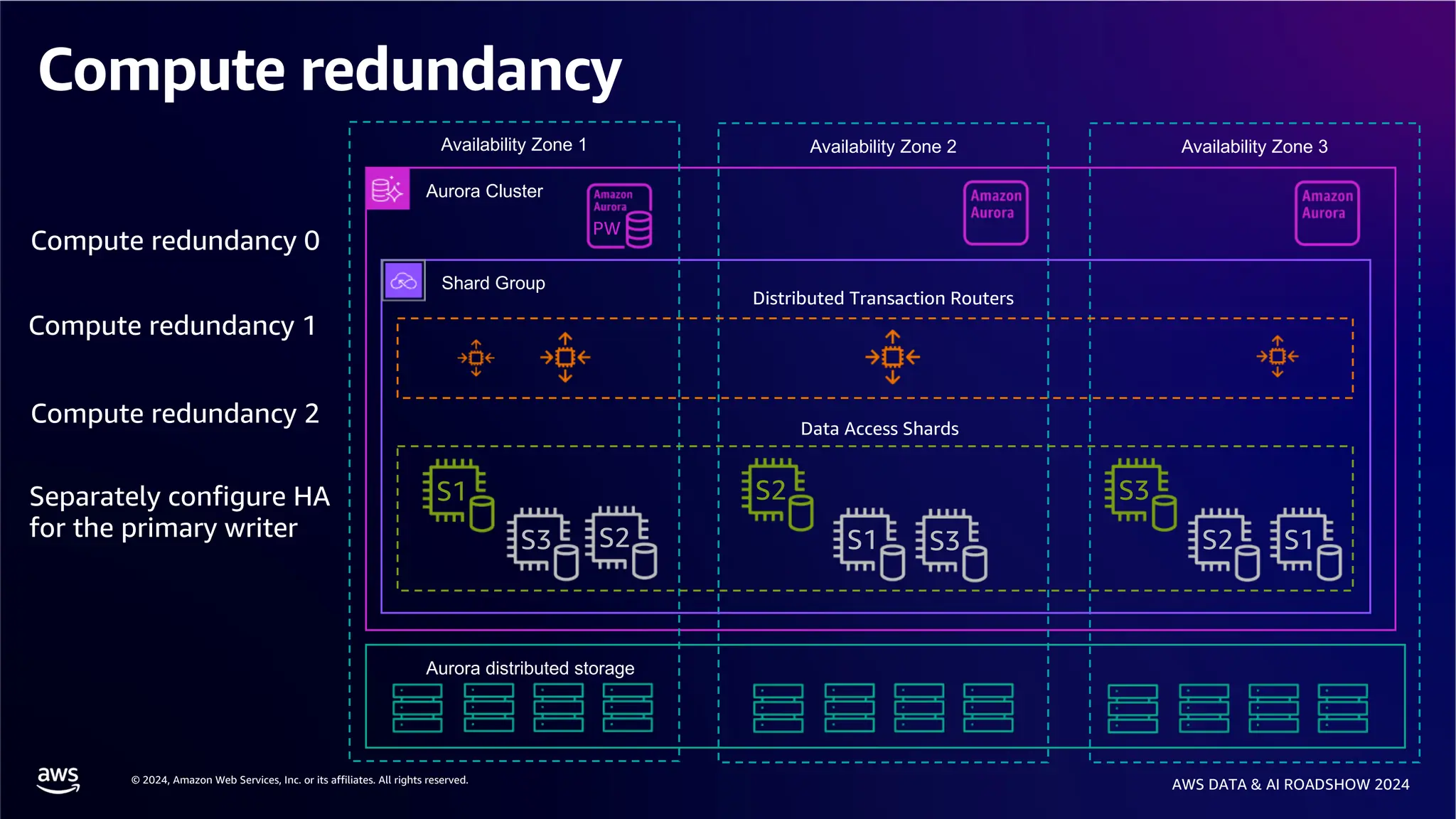
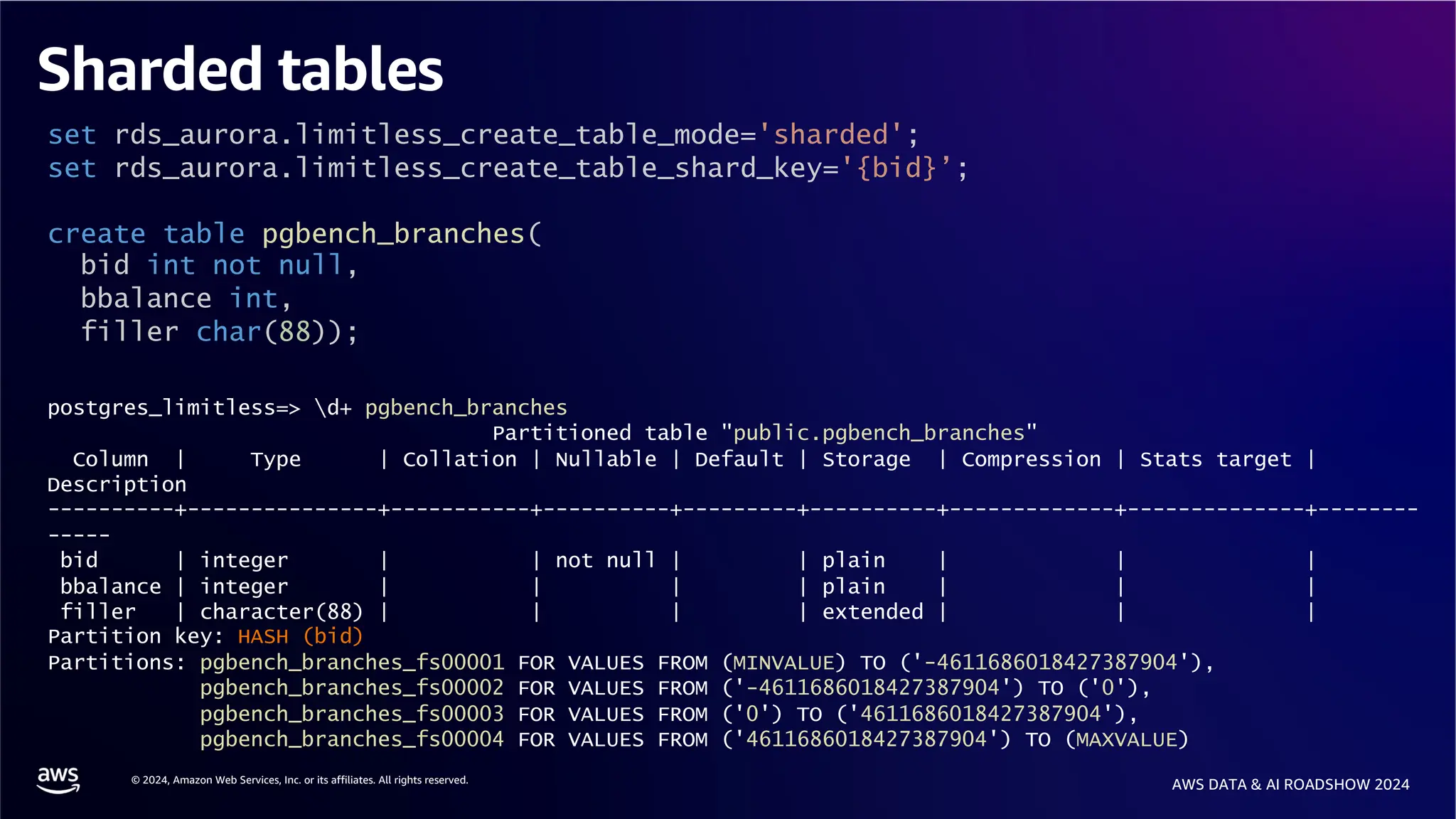
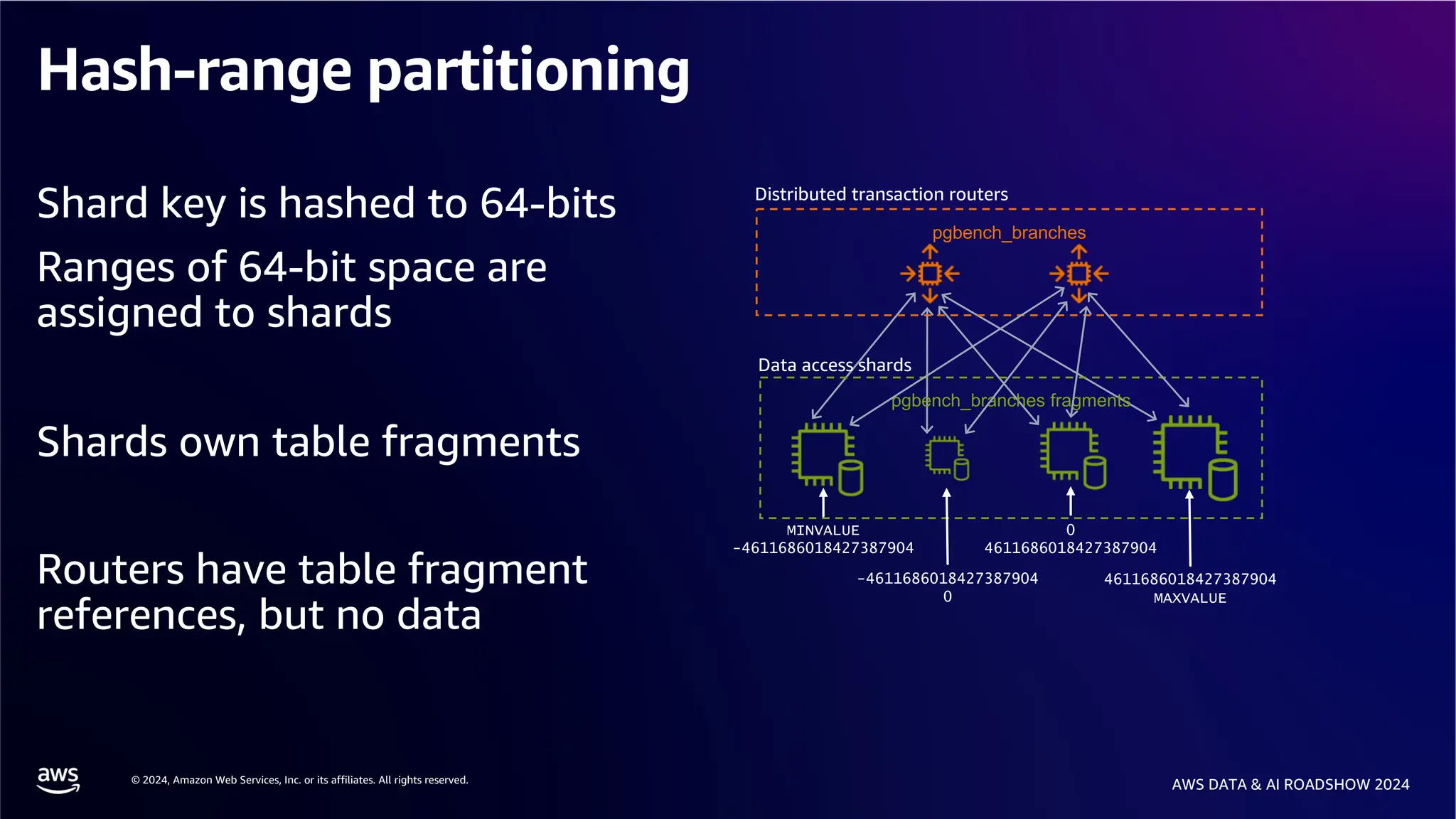
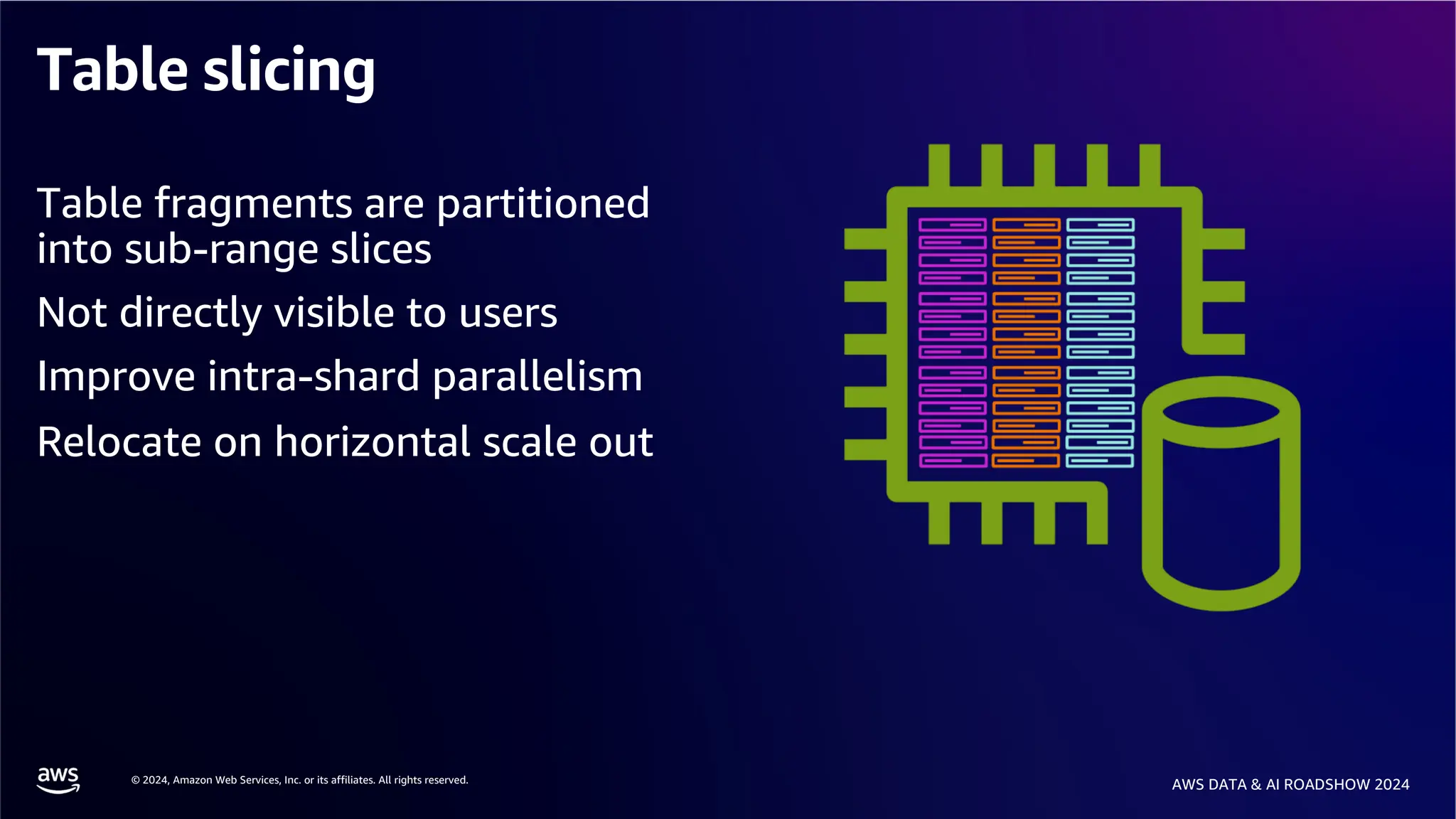
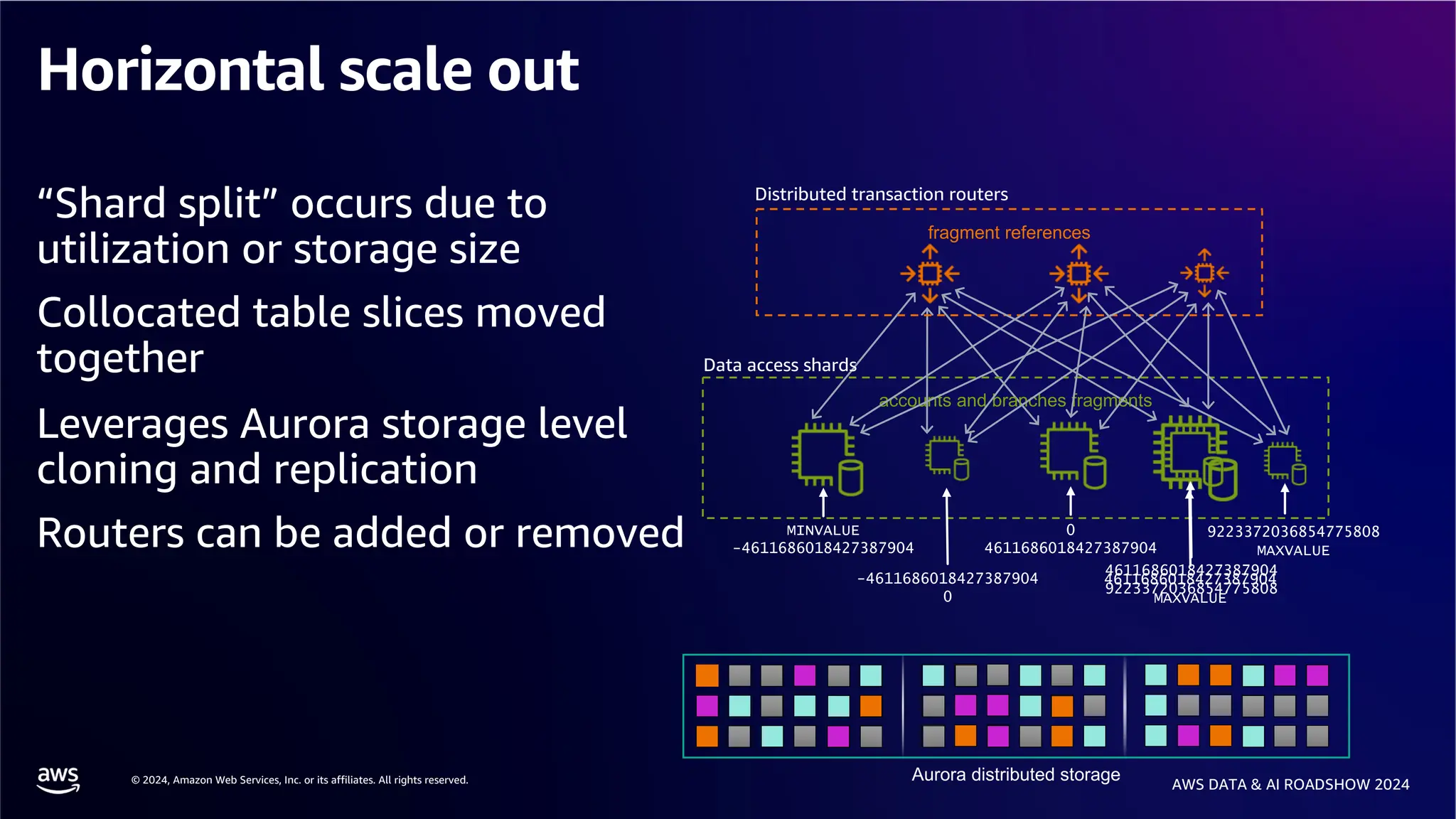
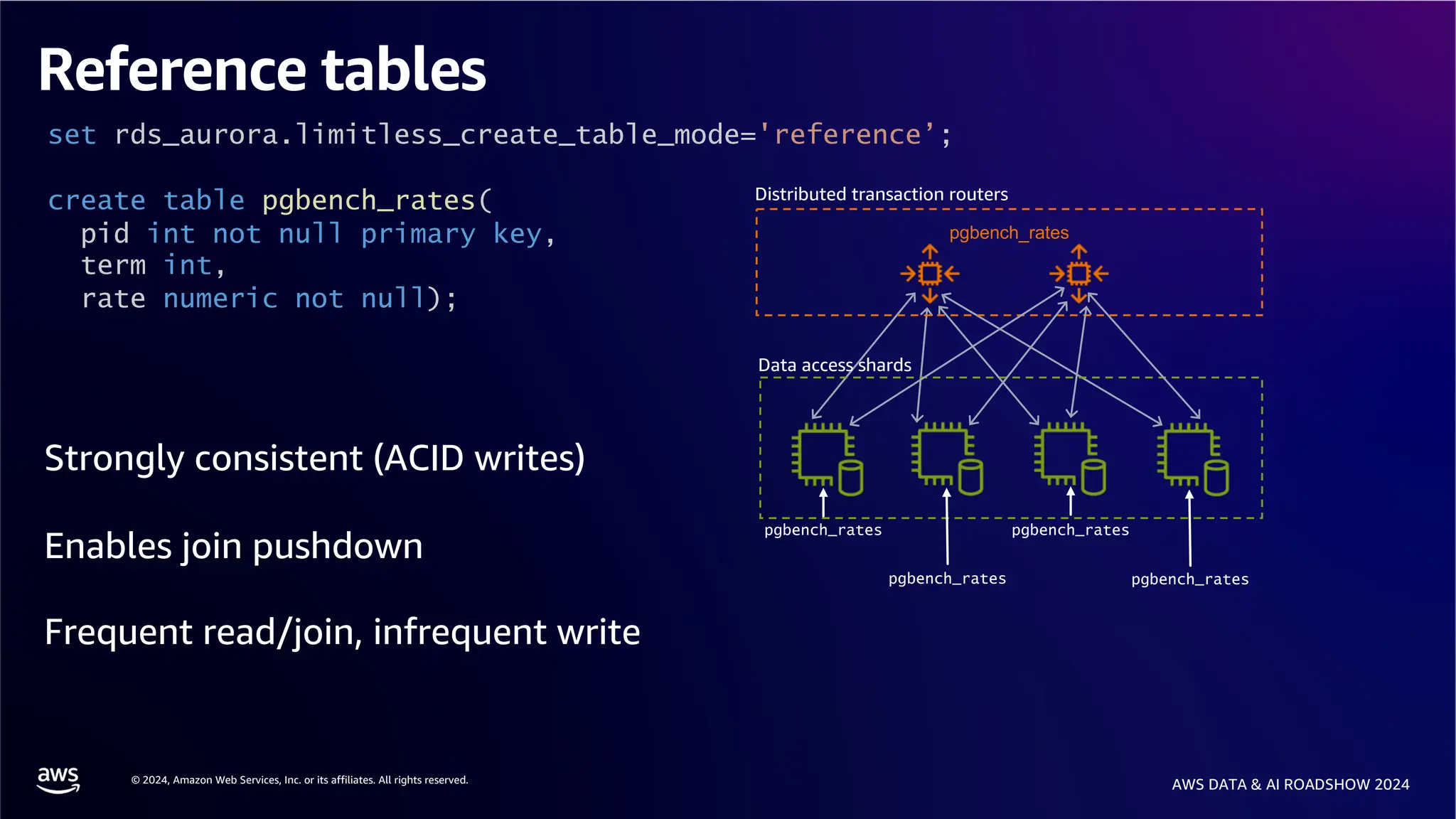
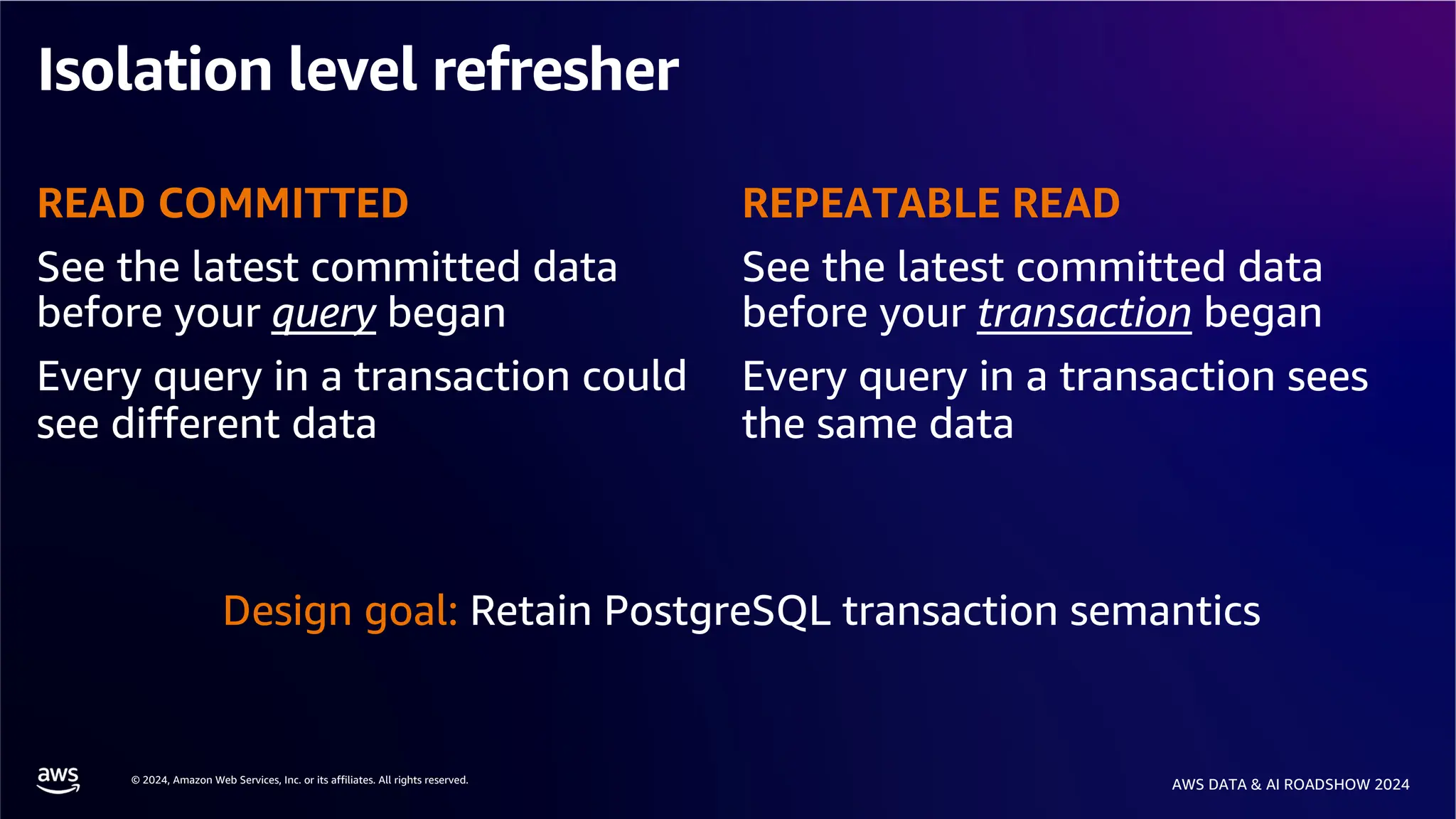
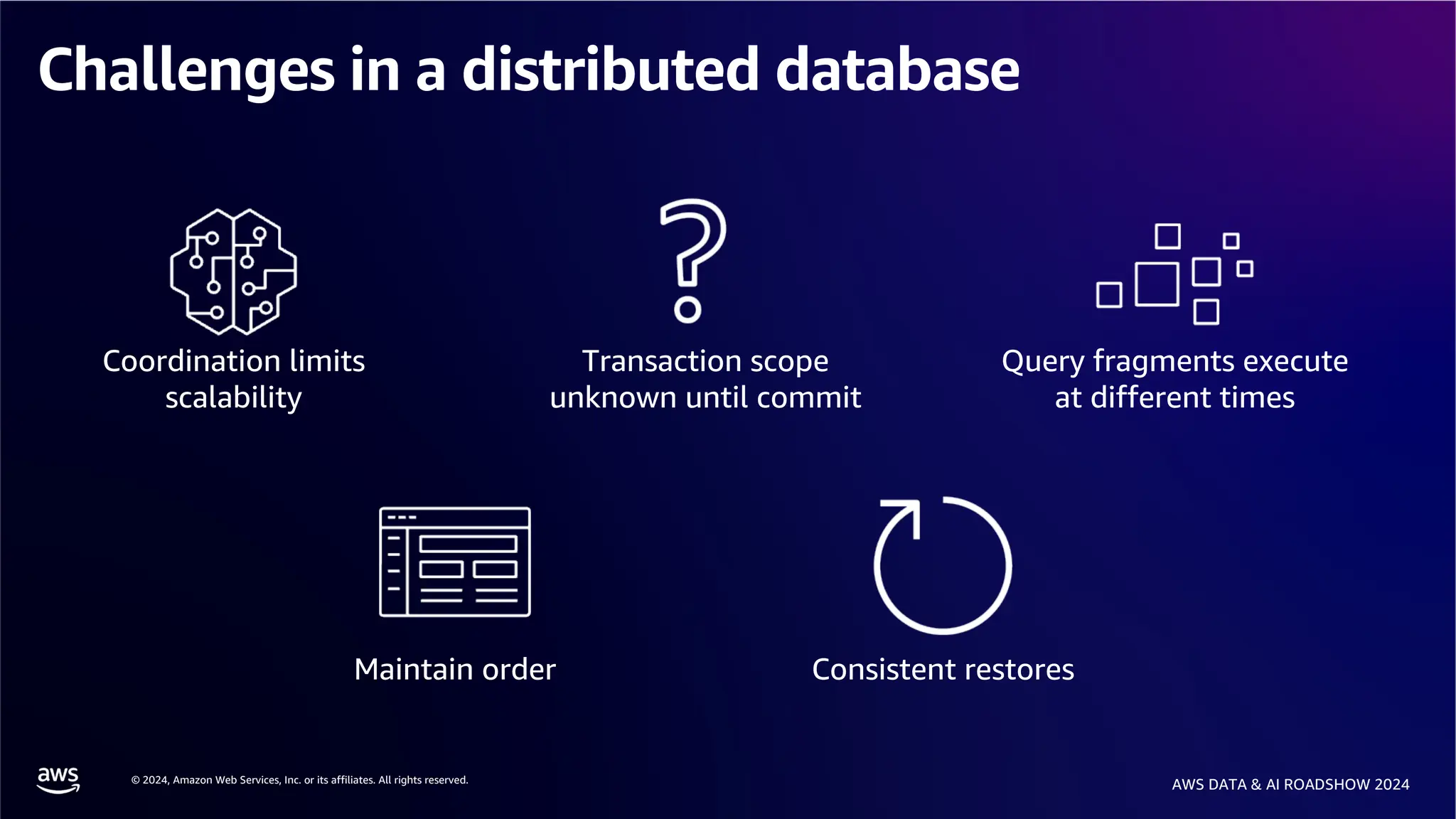
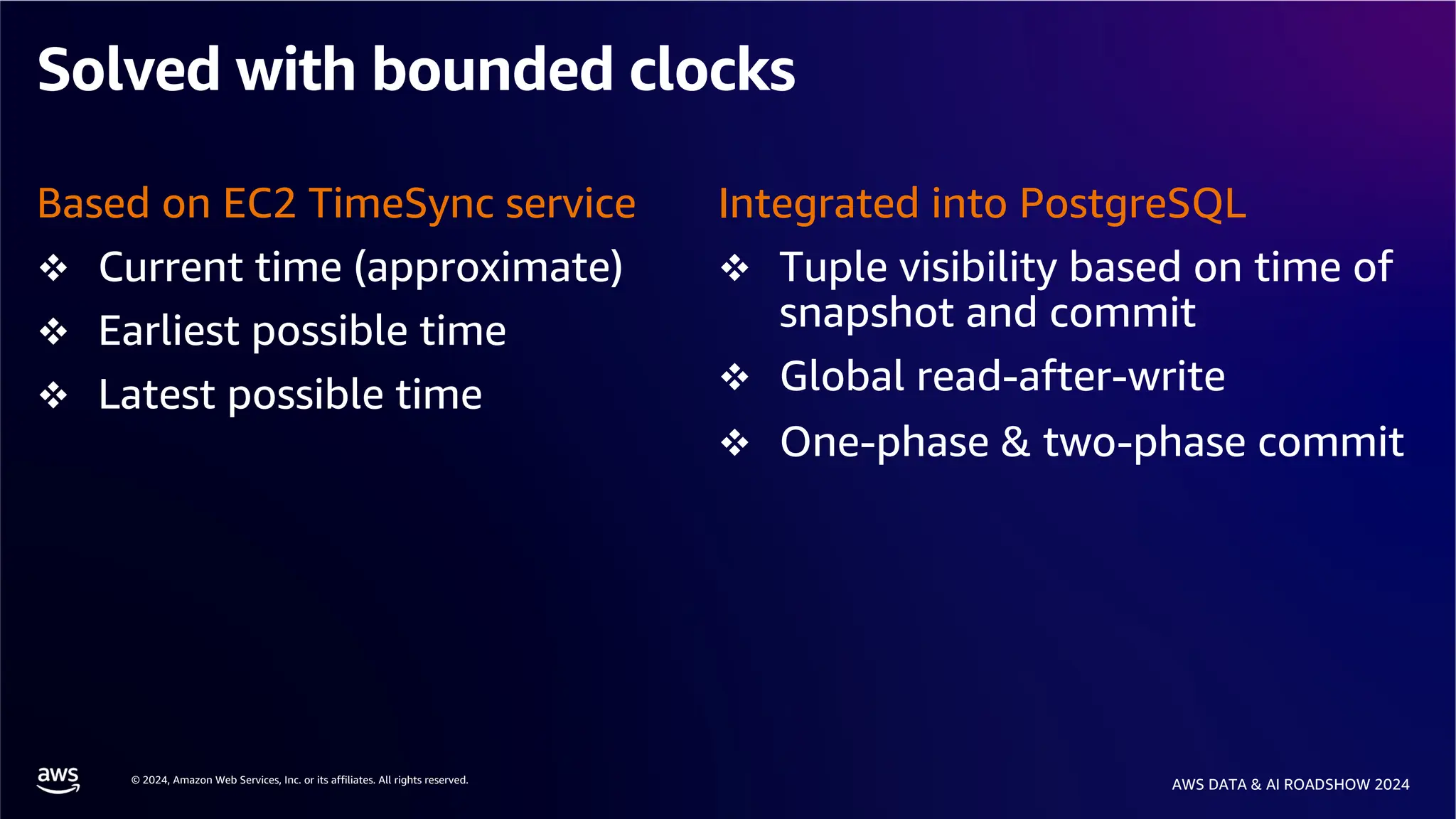
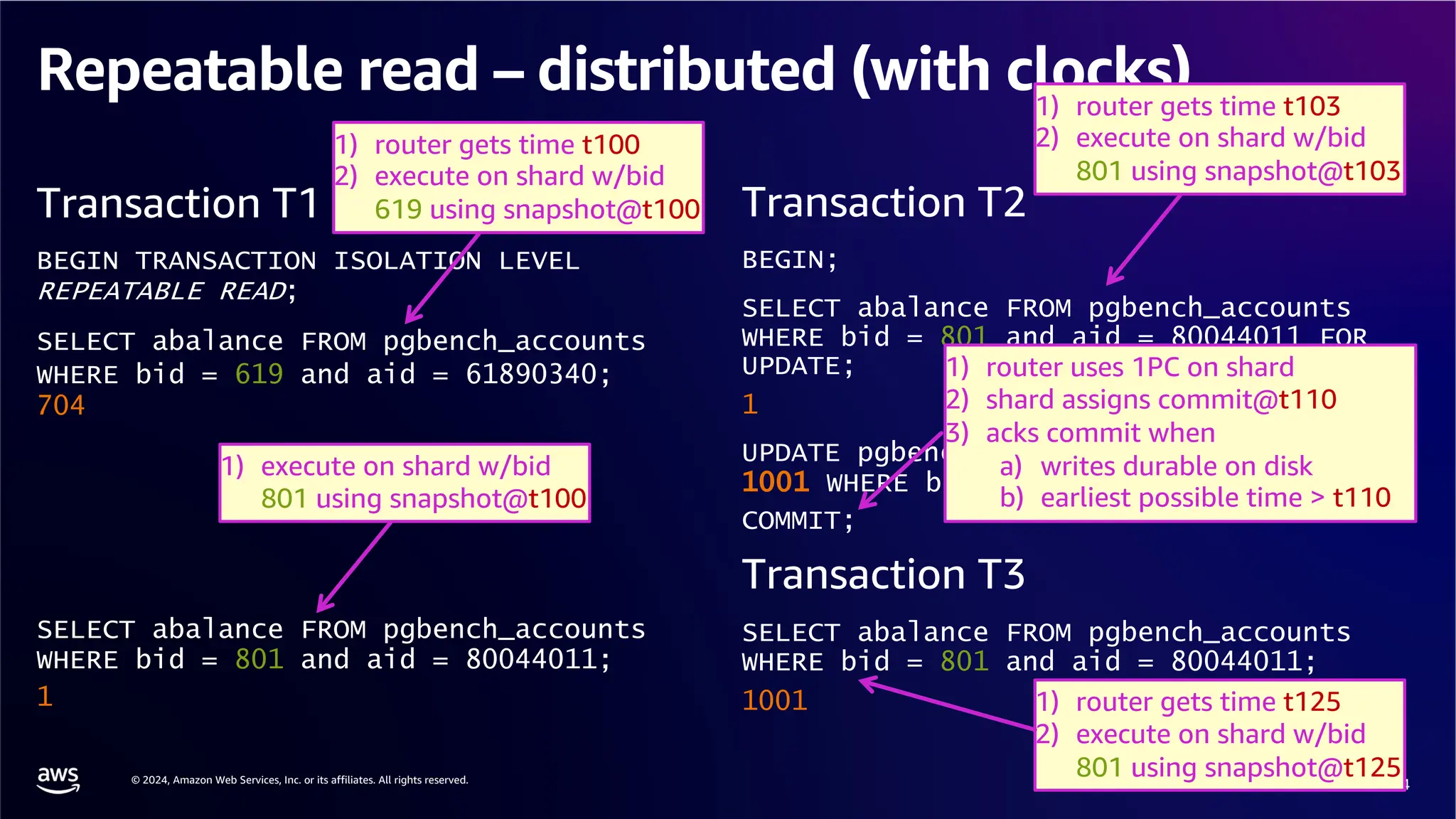
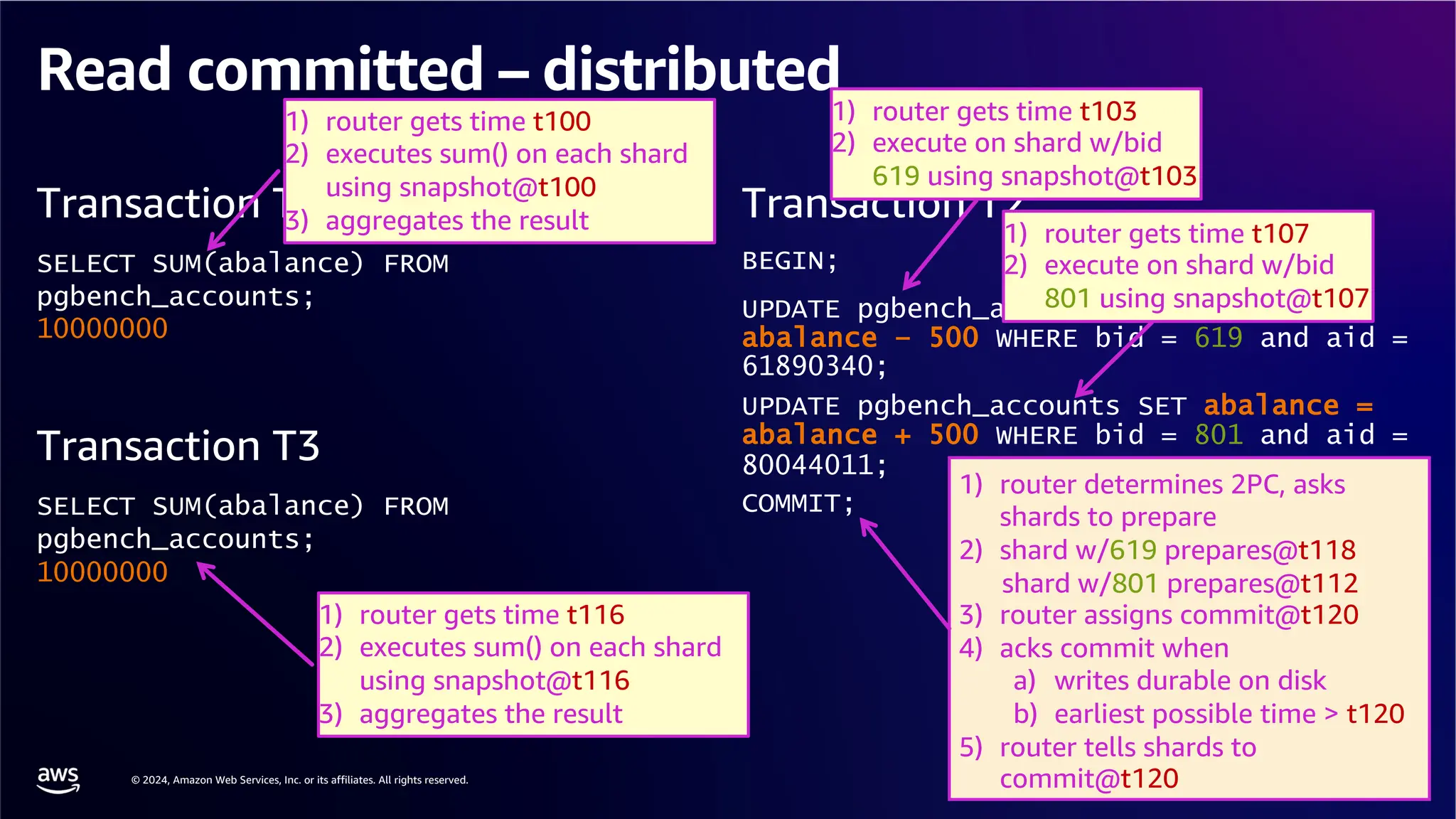
The document provides an overview of the AWS Data & AI Roadshow 2024, focusing on the features and architecture of Amazon Aurora's limitless database, including its sharding capabilities for scalability and enhanced performance. It discusses the creation and management of sharded tables, the role of distributed transaction routers, and transaction support while maintaining PostgreSQL semantics. Additionally, the document emphasizes the operational efficiency of queries over multiple shards and the handling of distributed transactions.