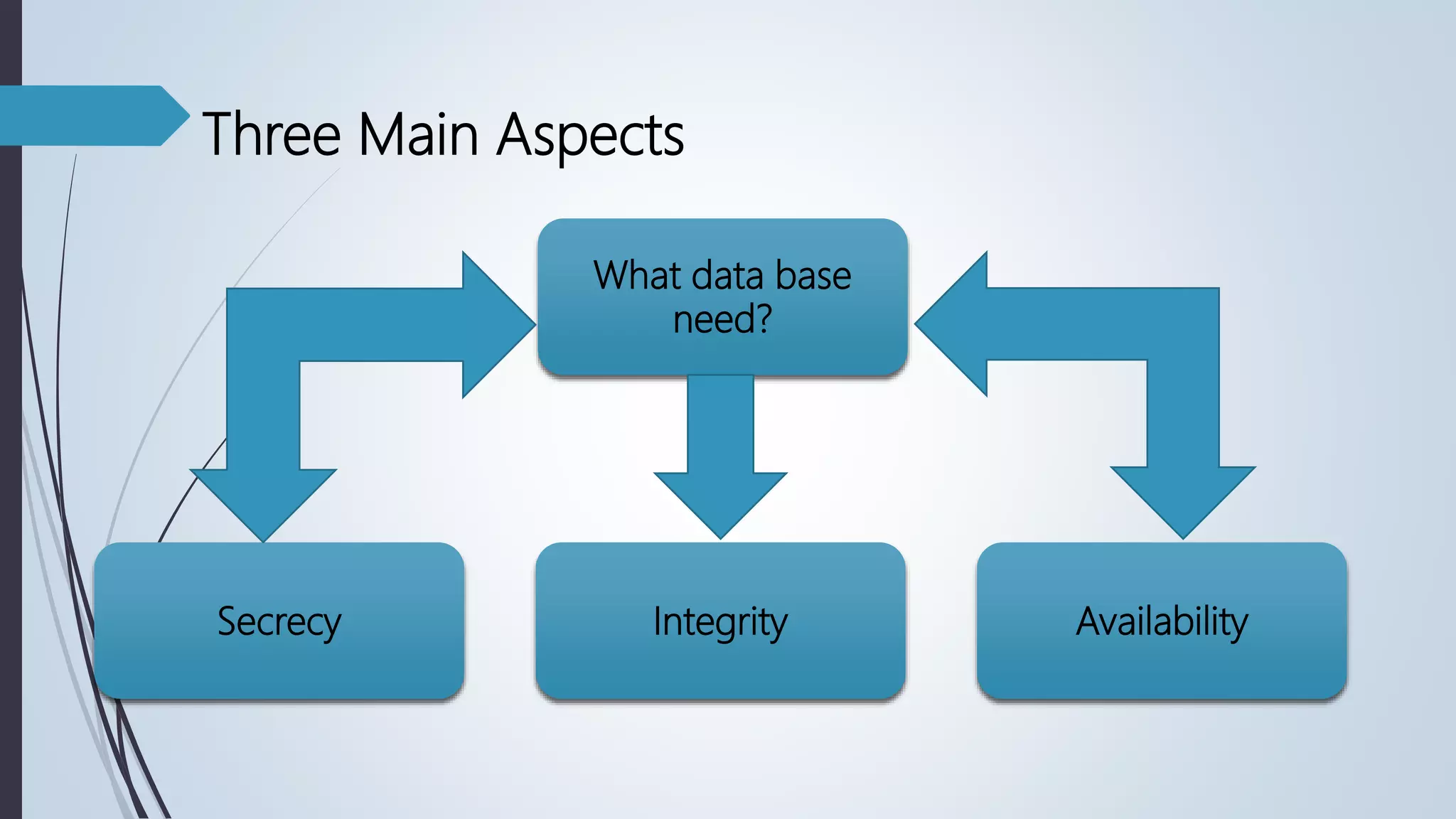
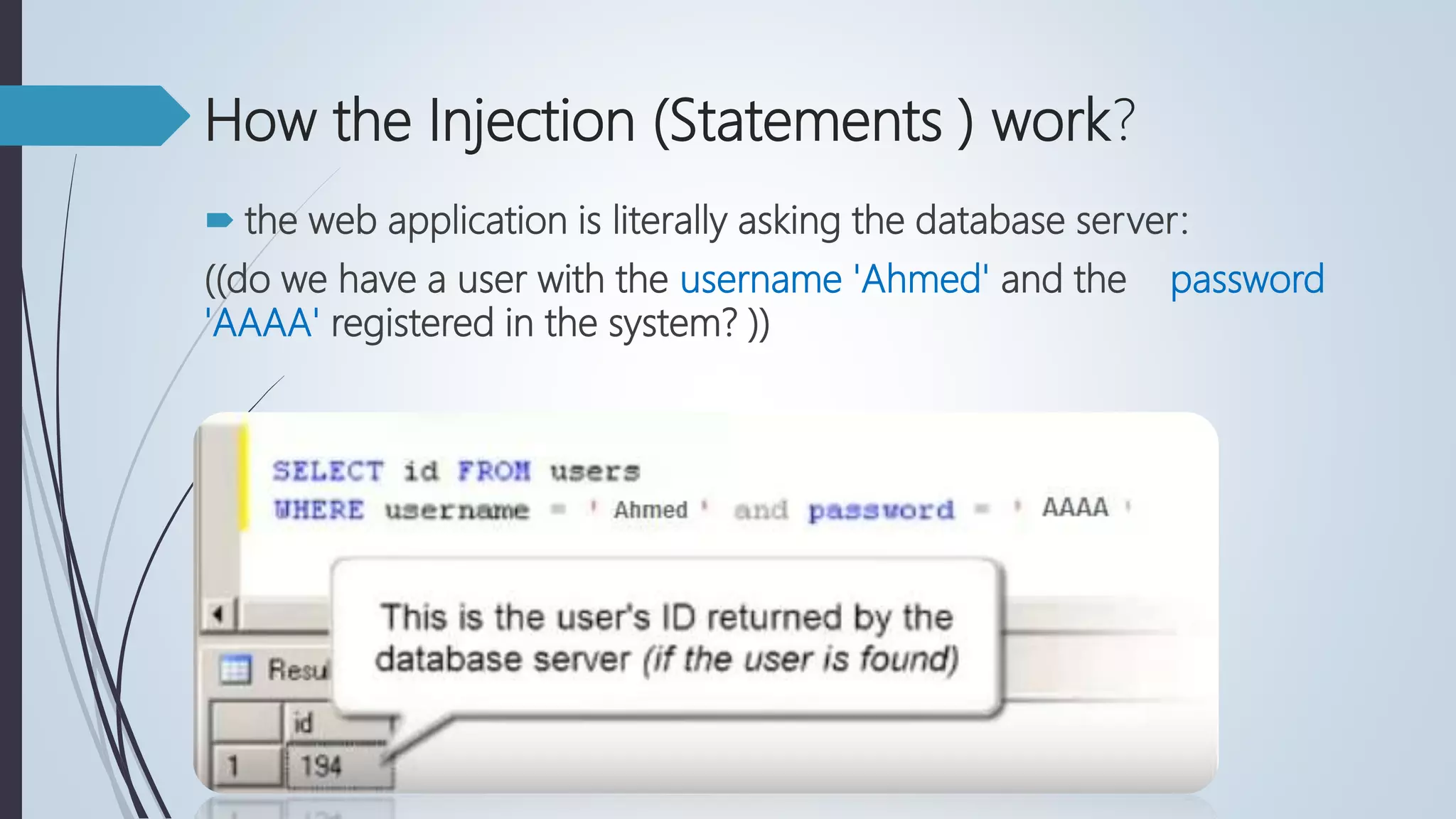
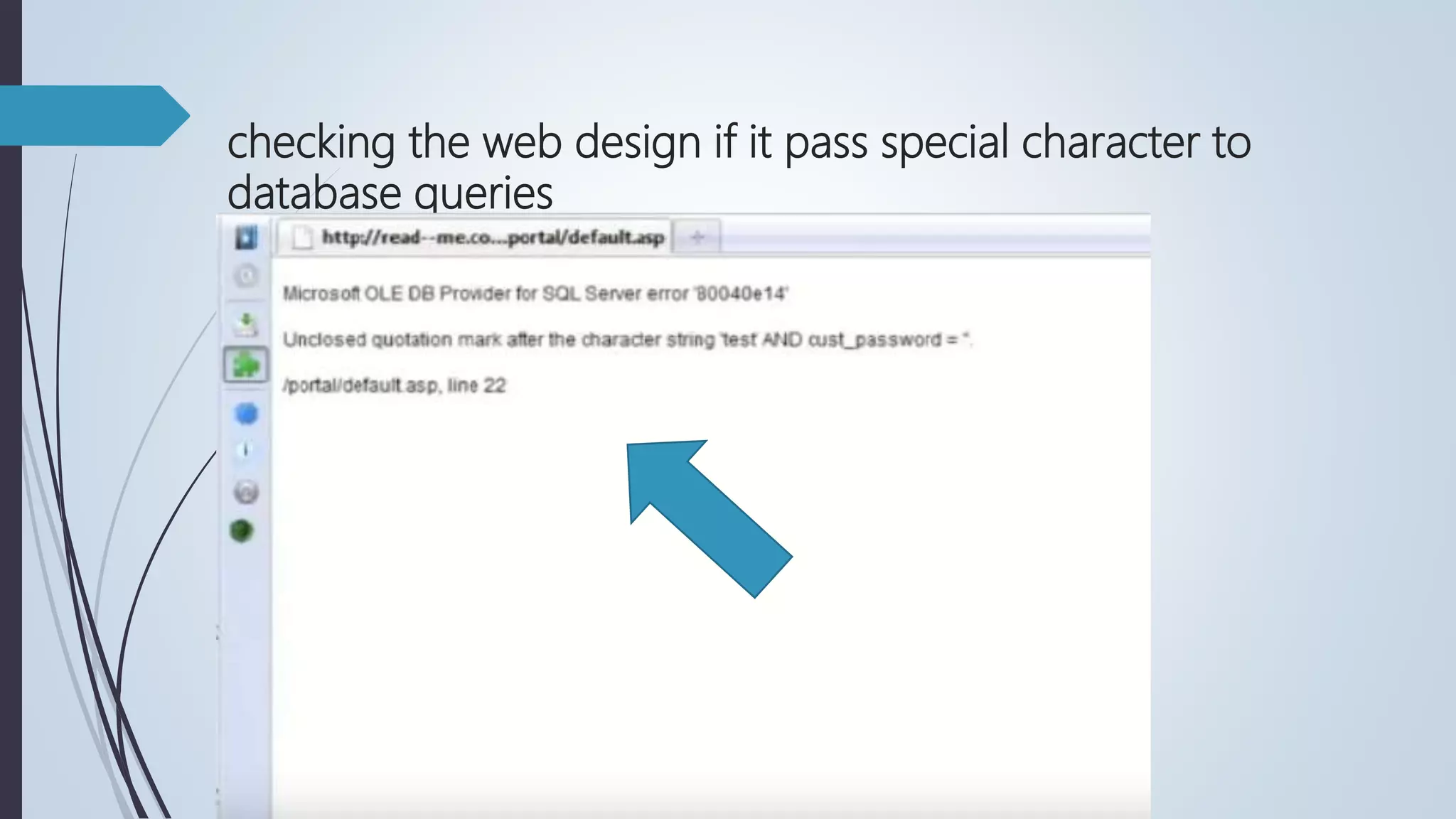
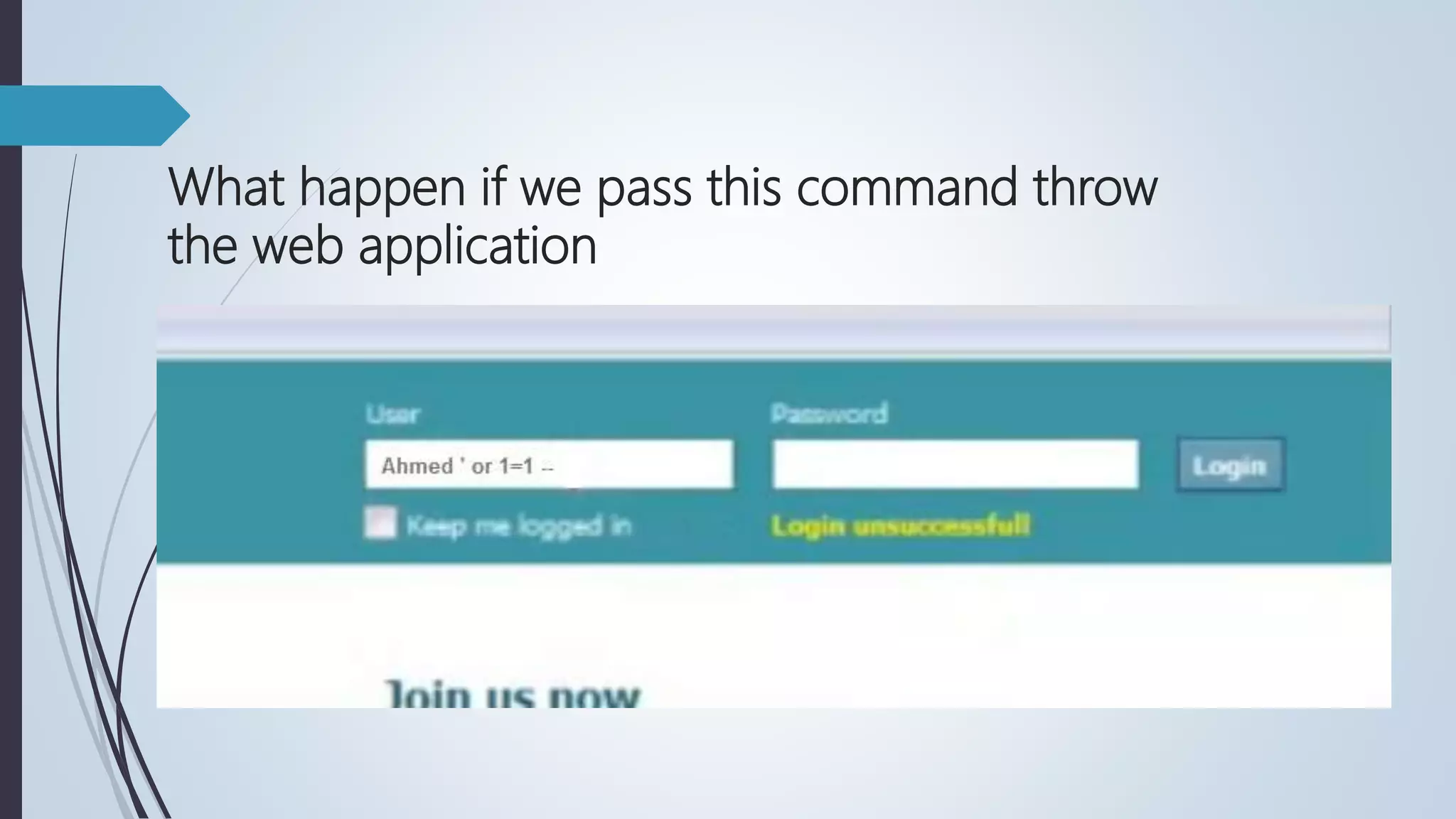
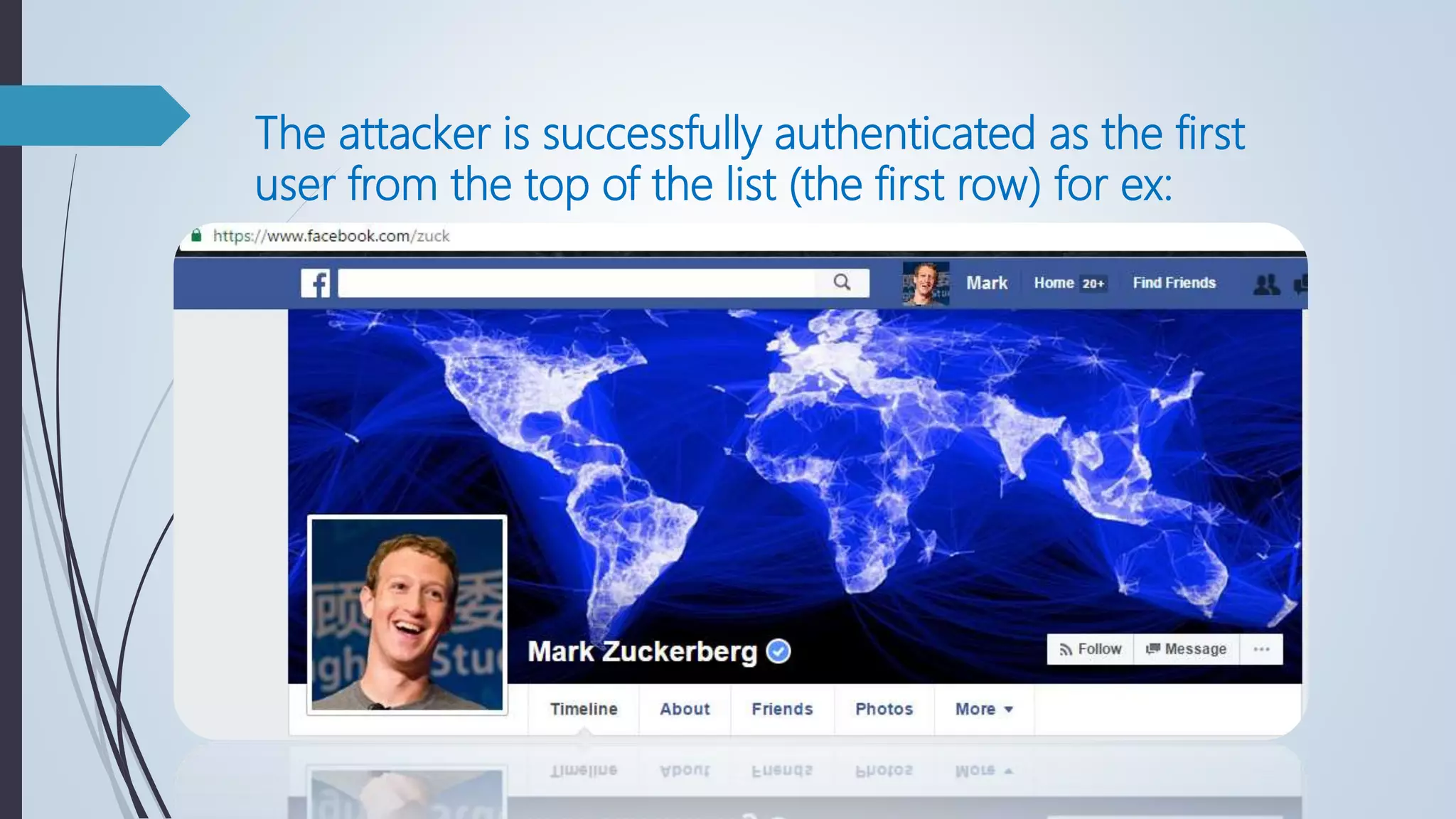
Database security involves protecting a database from both intentional and accidental threats. There are three main aspects of database security: secrecy, ensuring only authorized users can access data; integrity, ensuring data is not altered improperly; and availability, ensuring authorized users can access data when needed. One major threat is input injection attacks, such as SQL injection, where malicious SQL commands are injected into database queries, compromising security. Countermeasures include authorization, authentication, backups, encryption, and RAID technology to protect data and ensure continuous access.