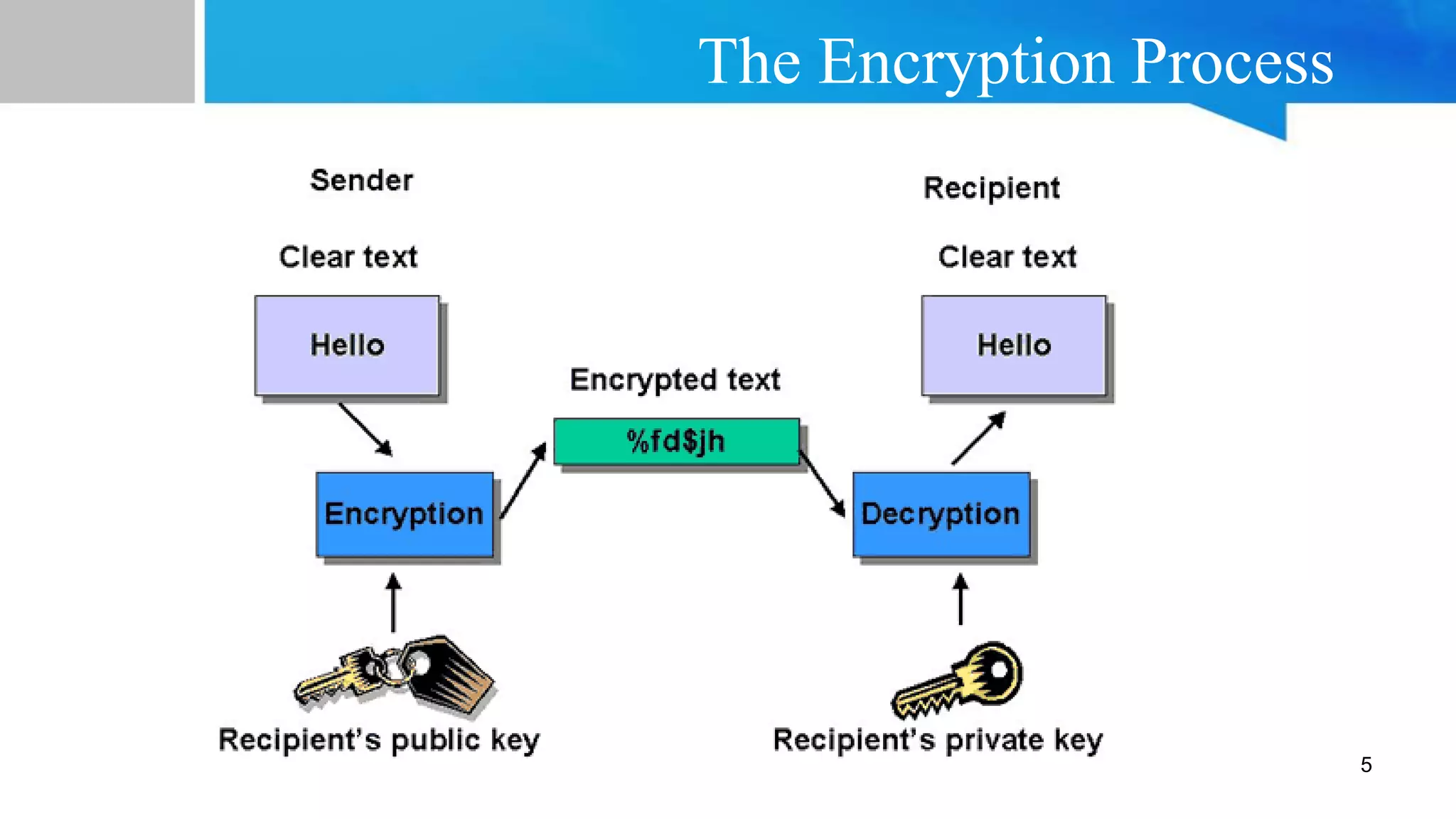
The document discusses data encryption in databases. It defines encryption as a process that transforms data into cipher text that can only be read by those with the decryption key. There are different levels of encryption, including transparent encryption of the entire database, column-level encryption of individual columns, and field-level encryption of specific data fields. Advantages of encryption include security of data at all times, maintaining data integrity and privacy, and protecting data across devices. Disadvantages include key management issues and potential performance impacts of encrypting database content.