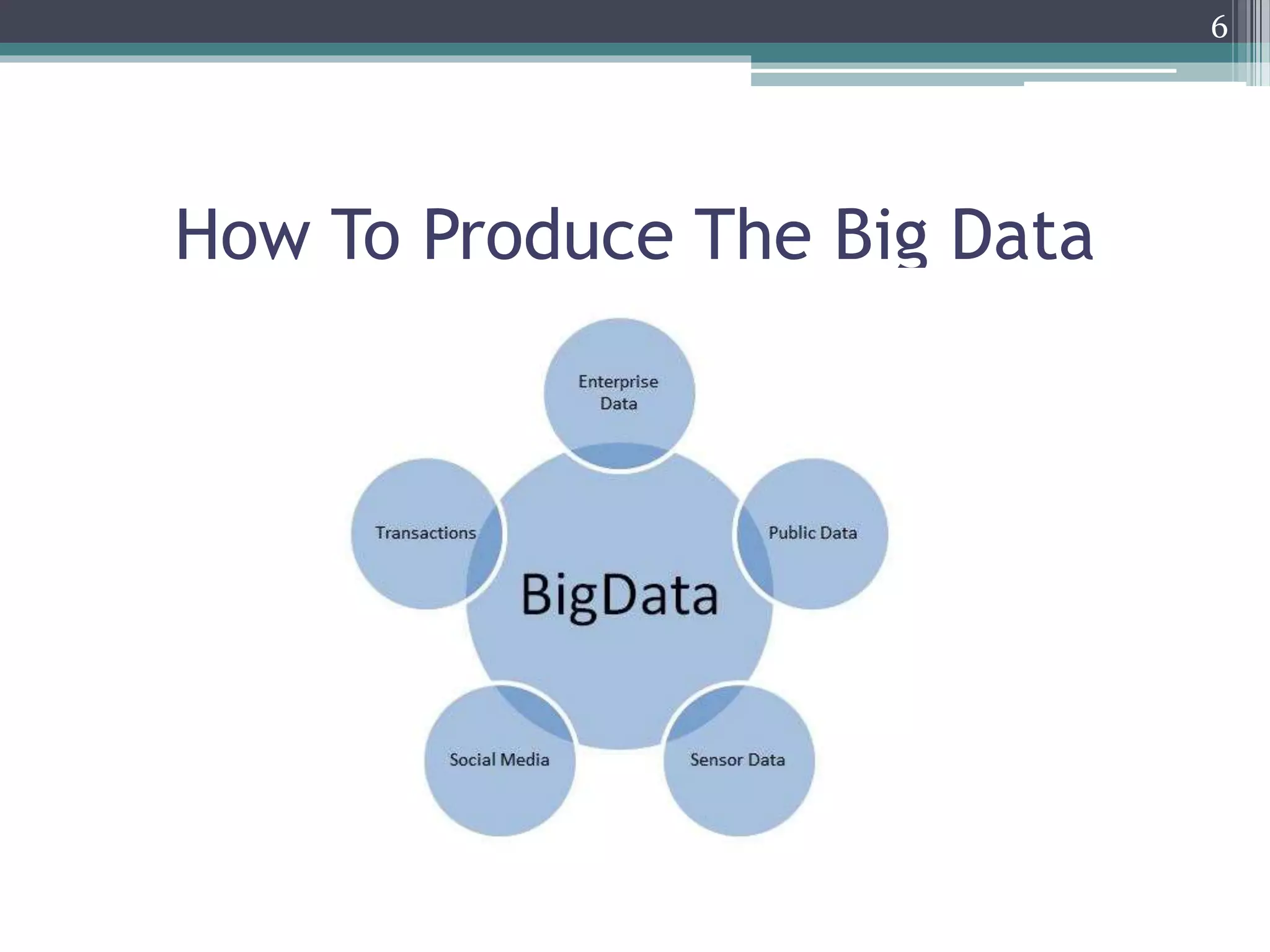
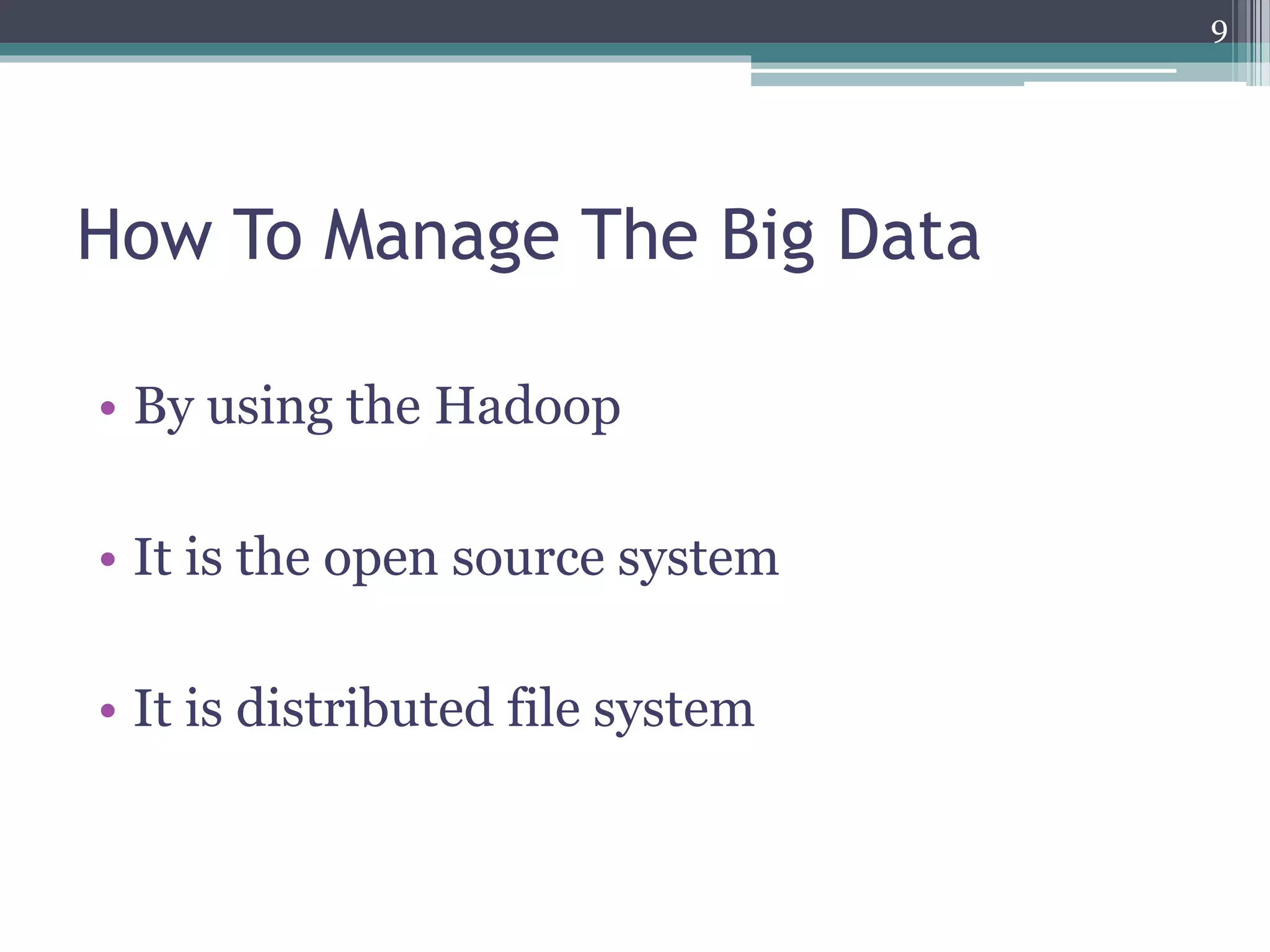
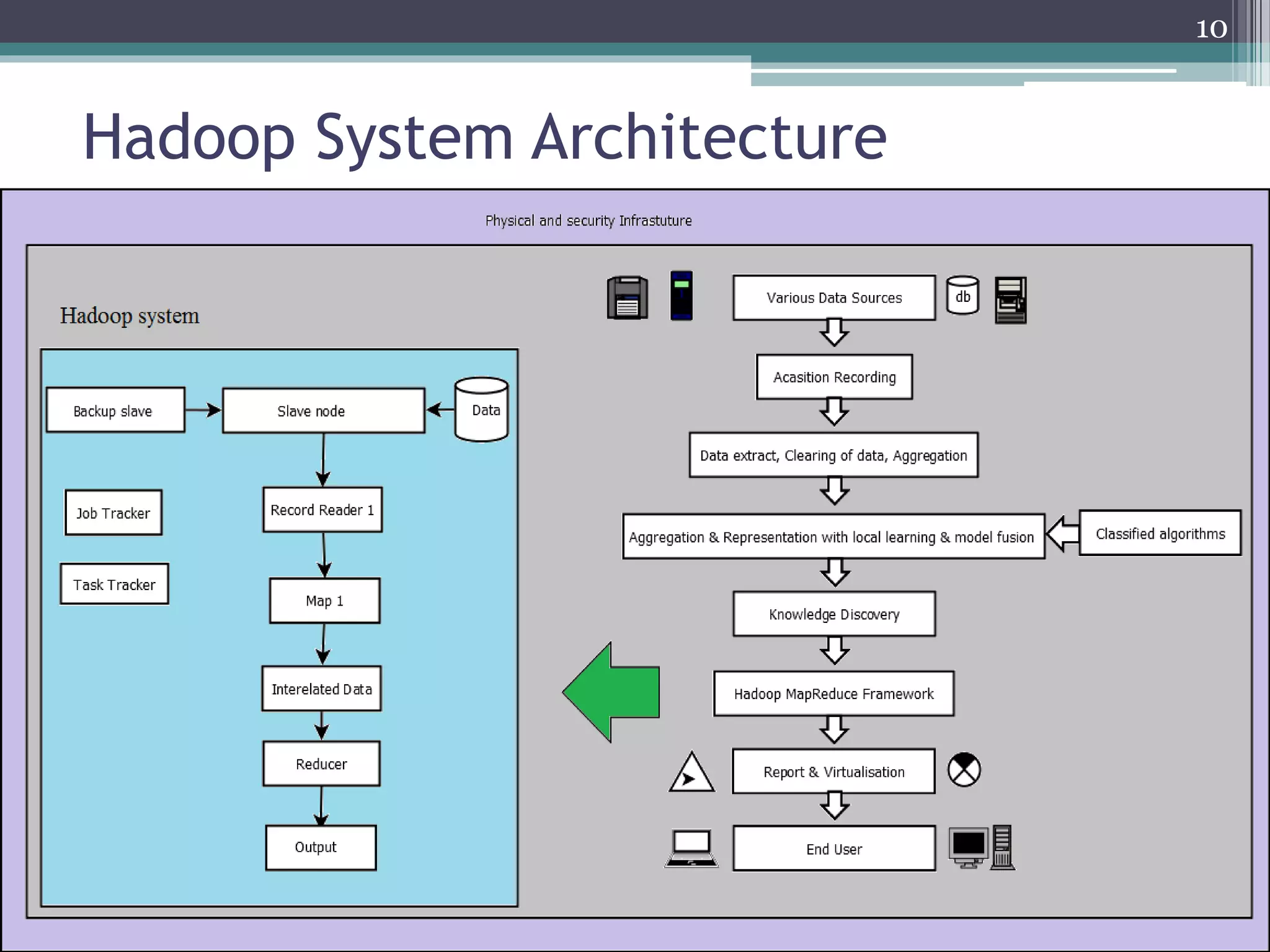
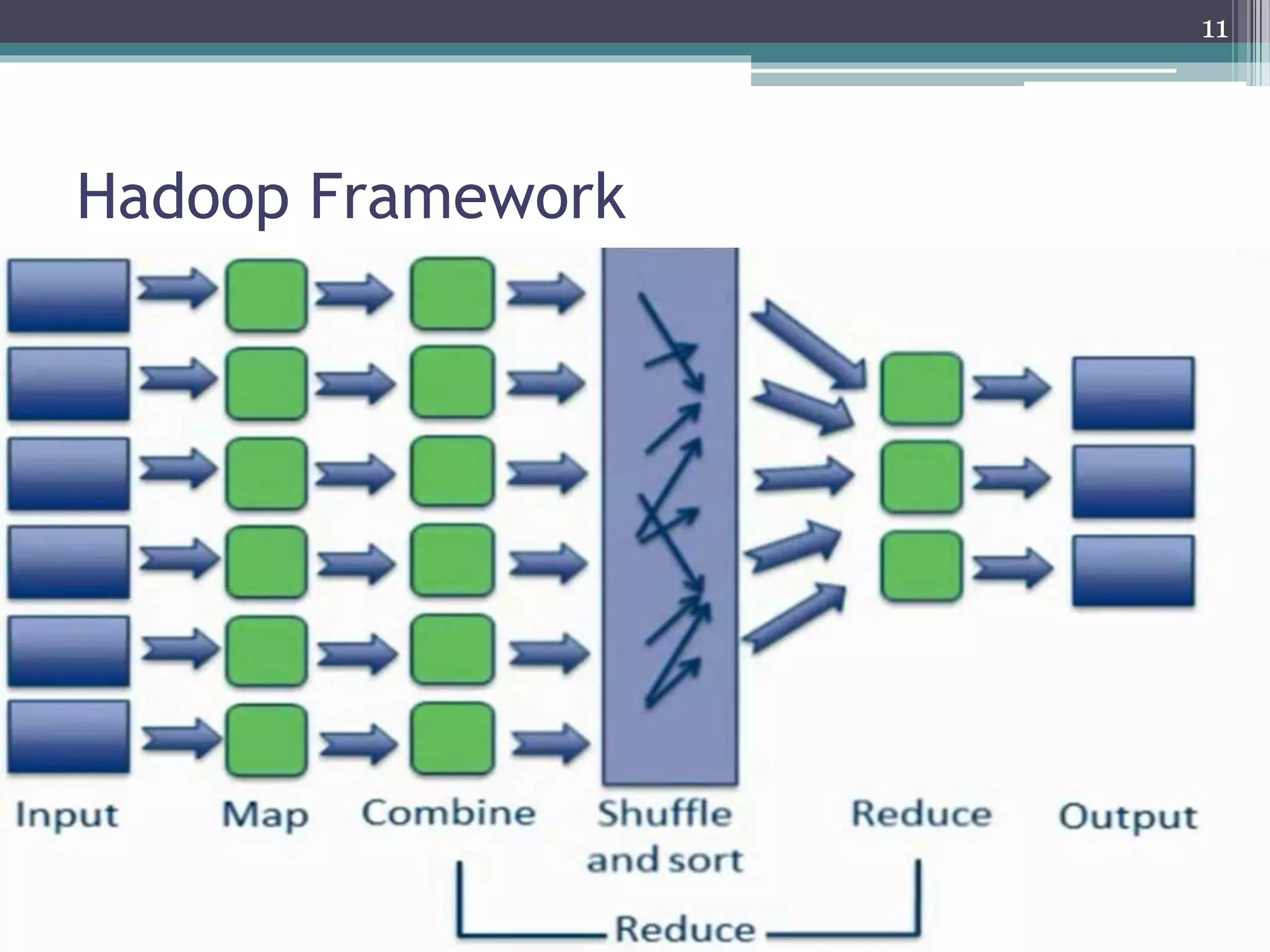
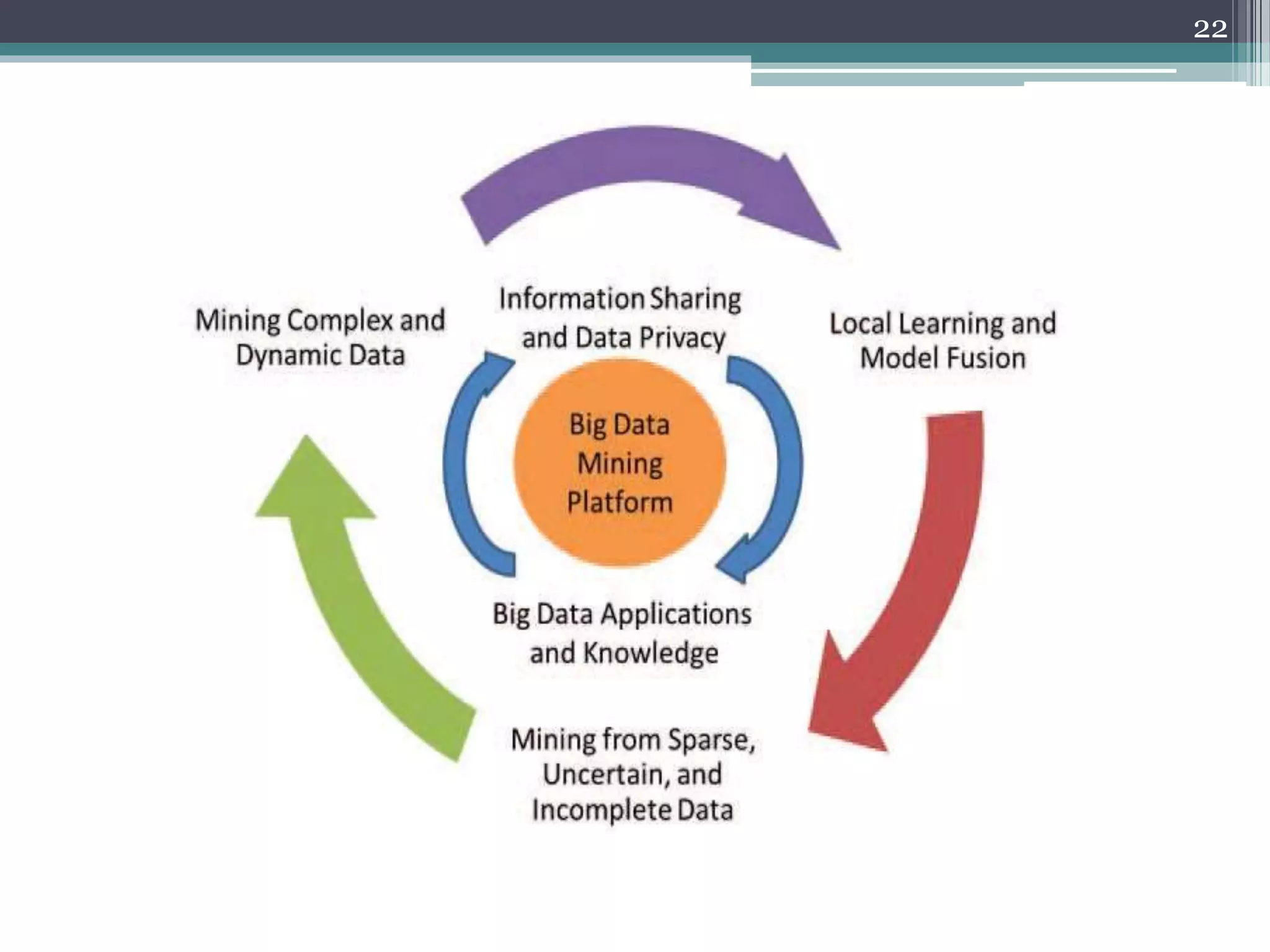
Data Mining With Big Data presents an overview of data mining techniques for large and complex datasets. It discusses how big data is produced and its characteristics including volume, velocity, variety, and variability. The document outlines challenges of big data mining such as platform and algorithm design, and solutions like distributed computing and privacy controls. Hadoop is presented as a framework for managing big data using its distributed file system and processing capabilities. The presentation concludes that big data technologies can provide more relevant insights by analyzing large and dynamic data sources.