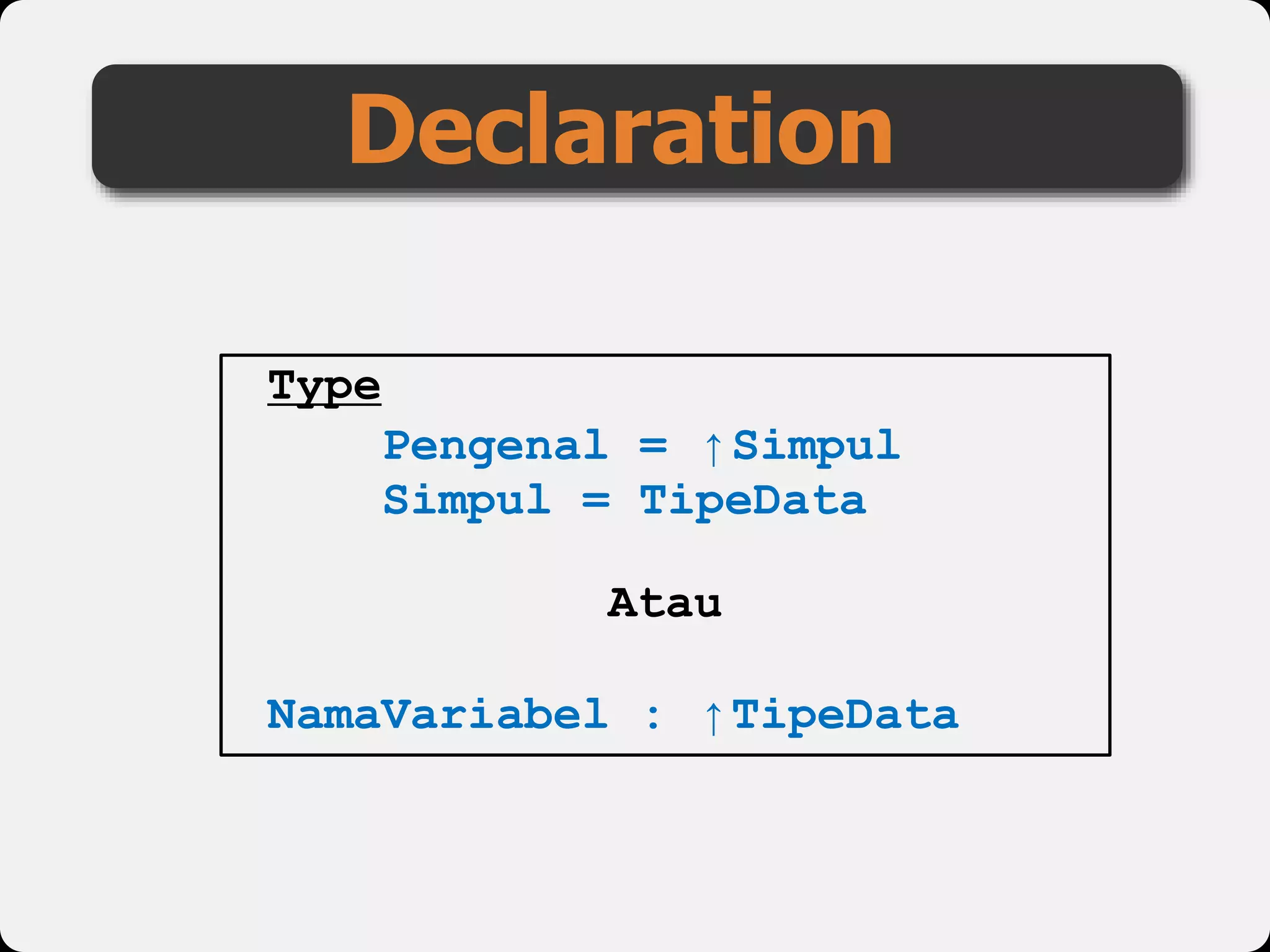
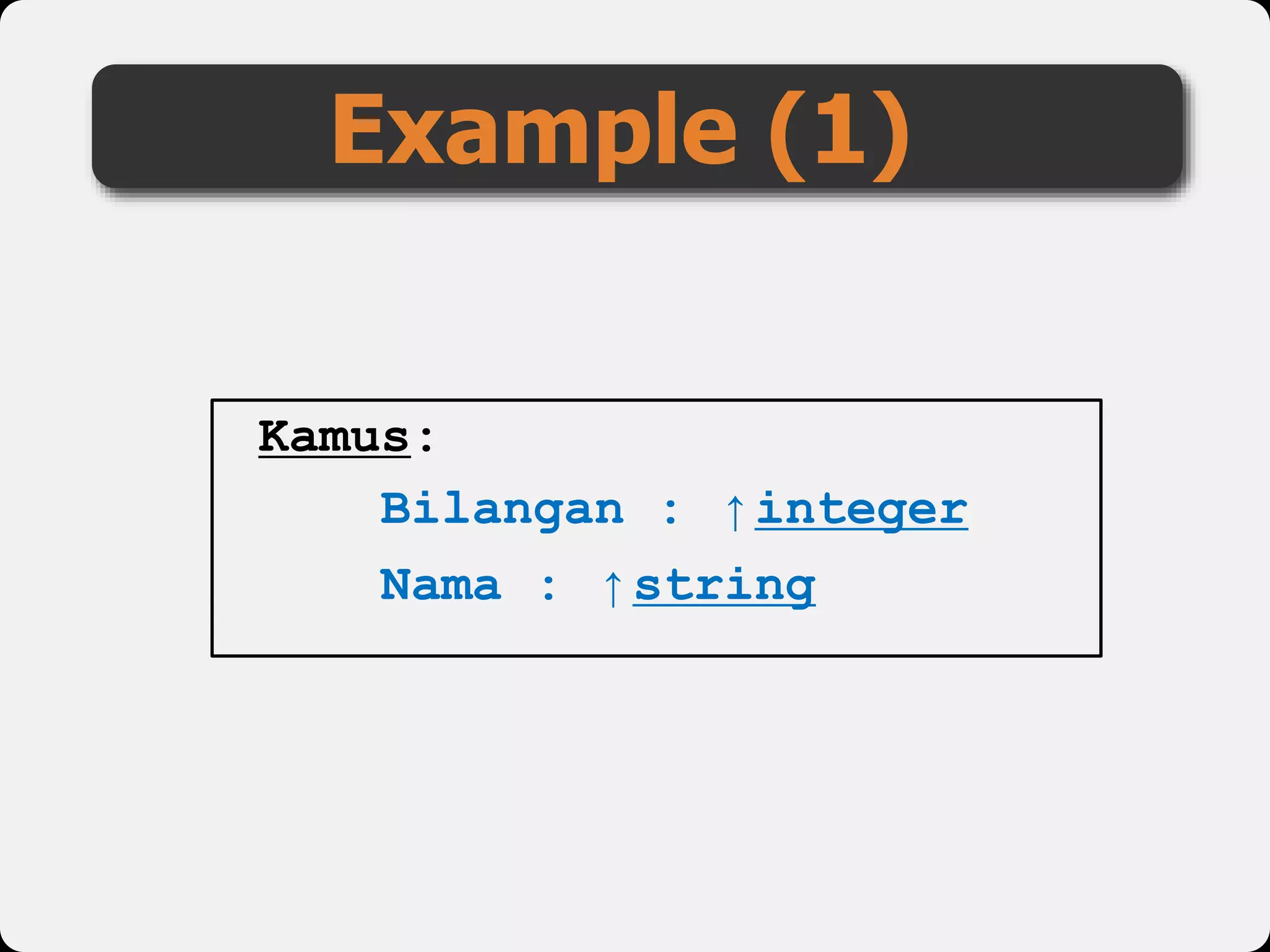
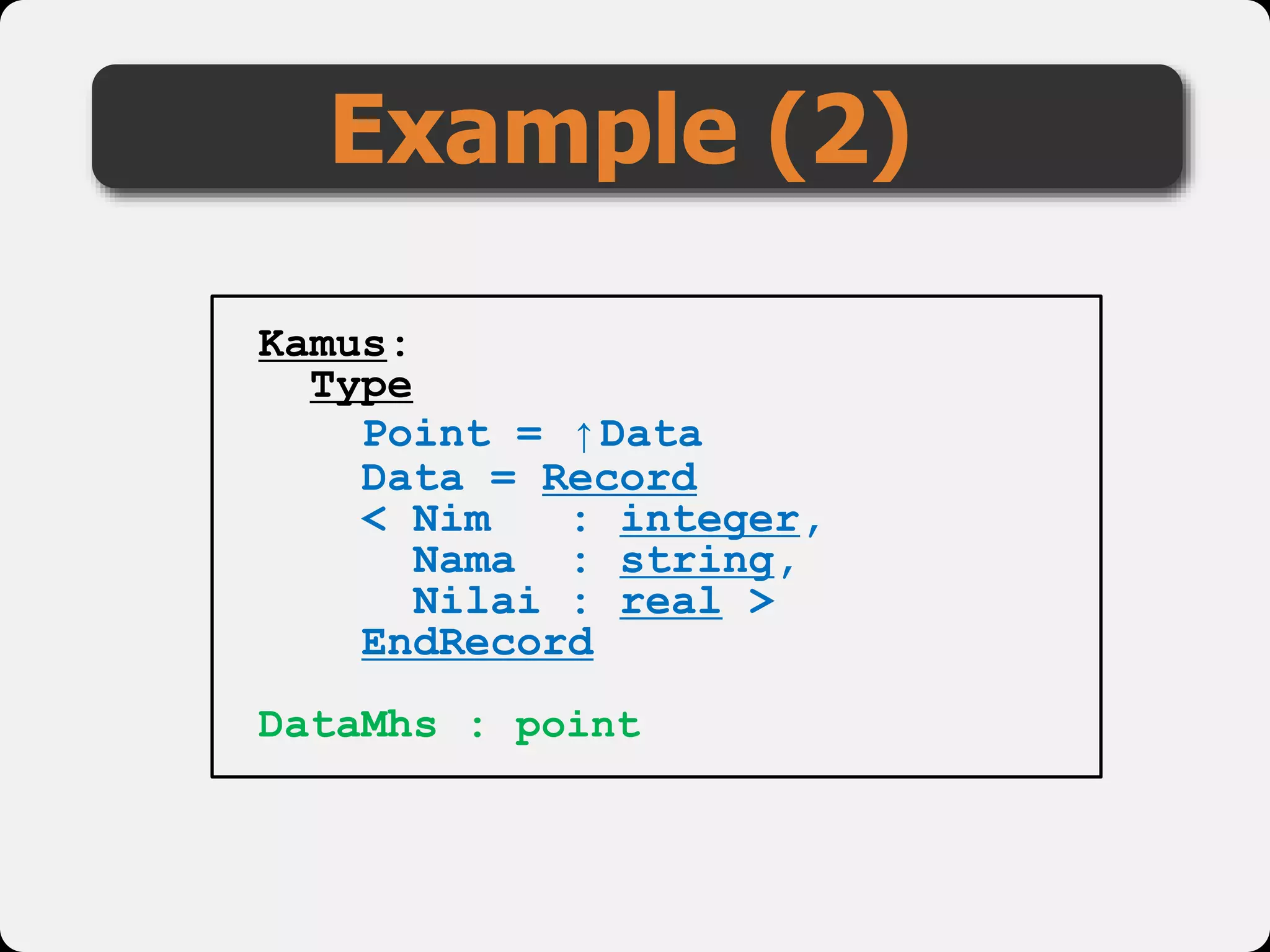
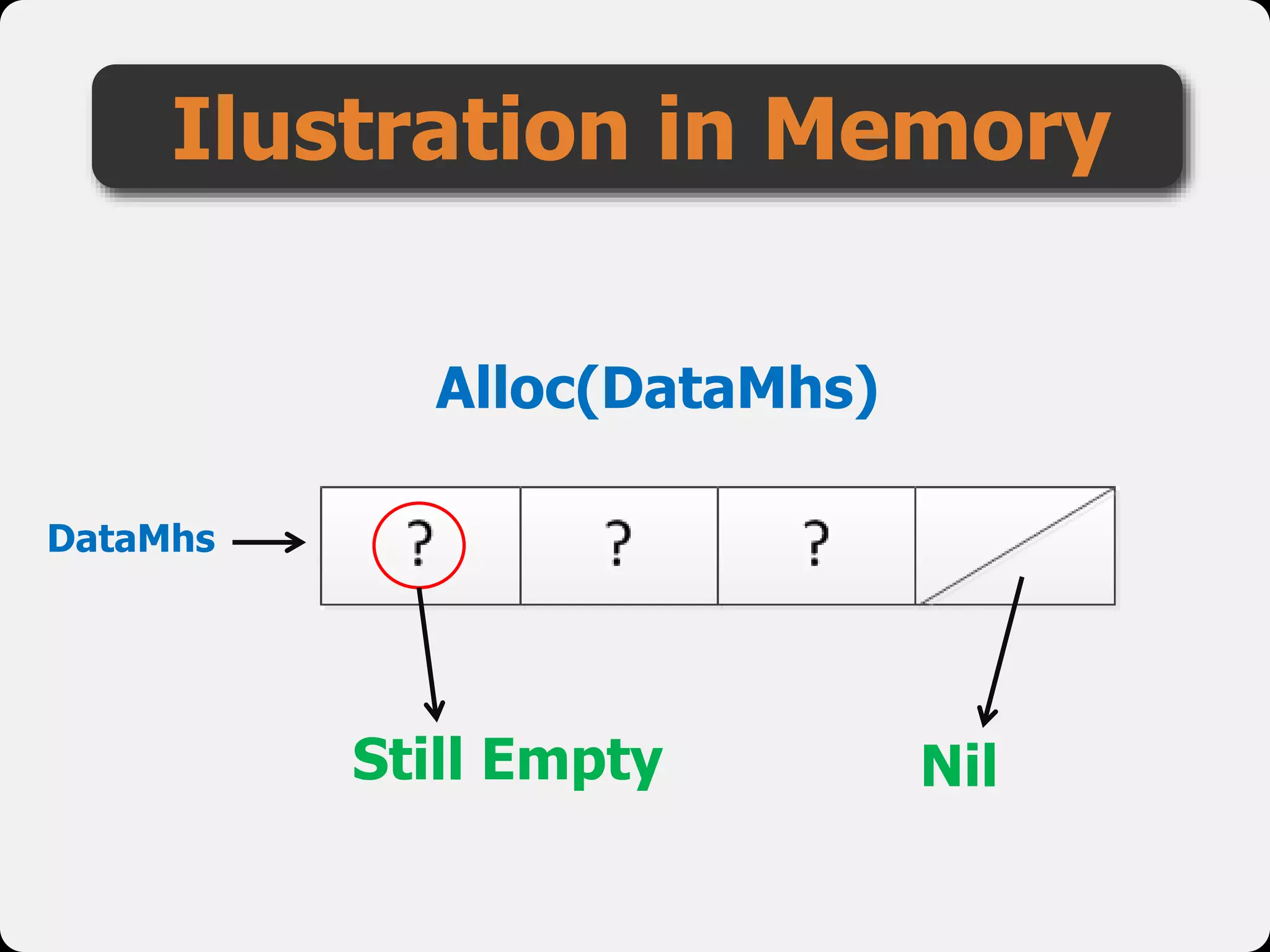
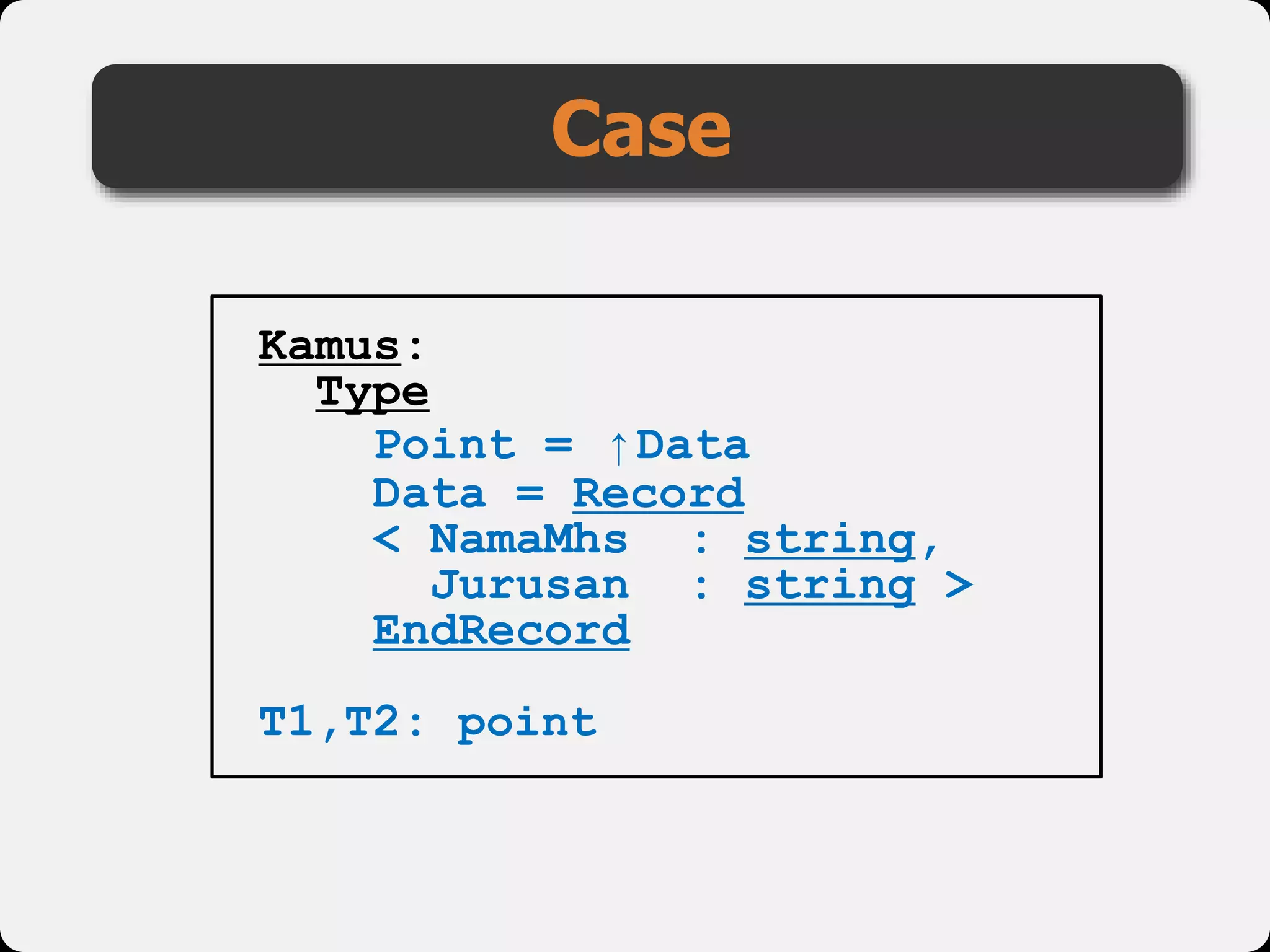
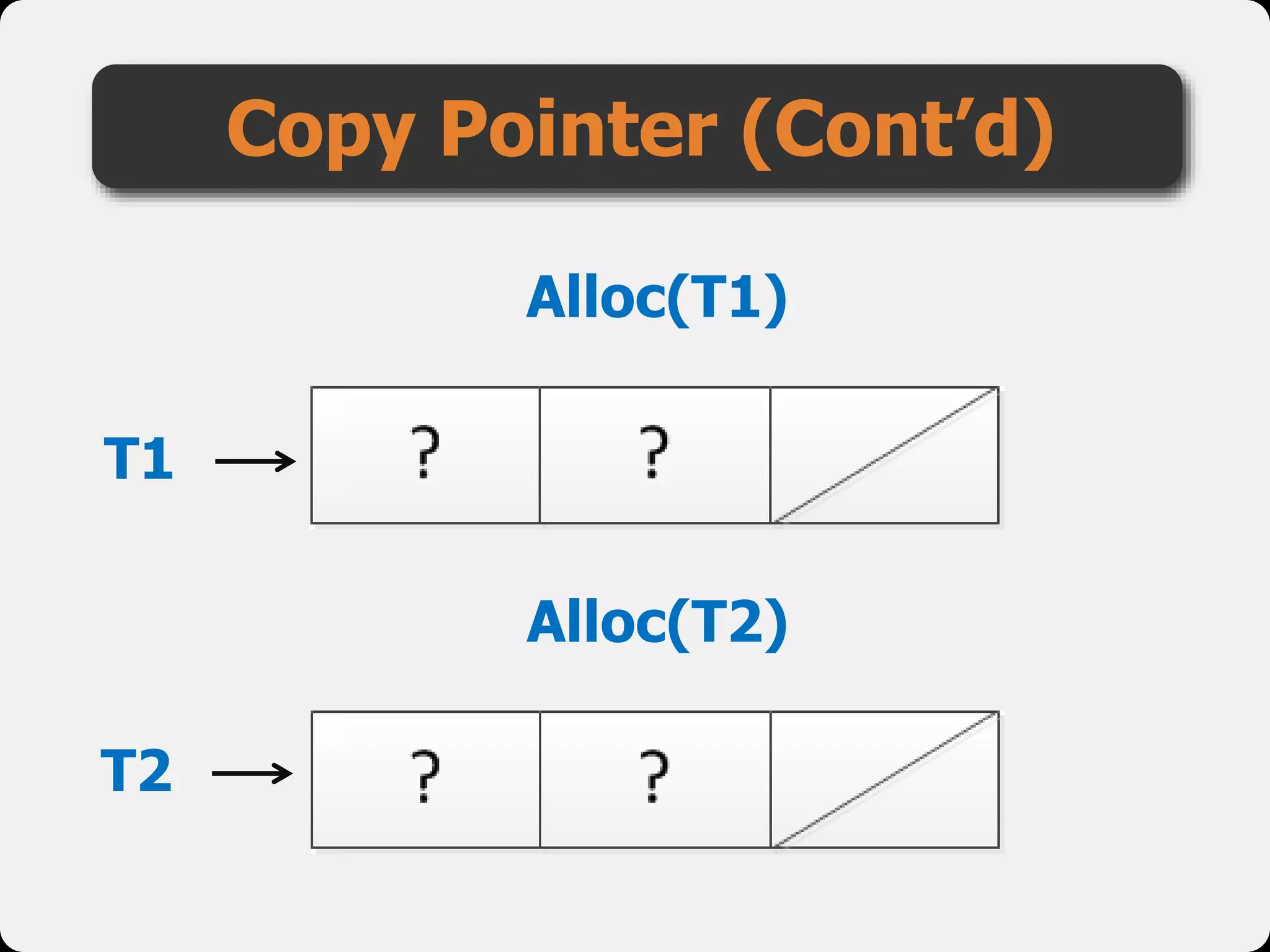
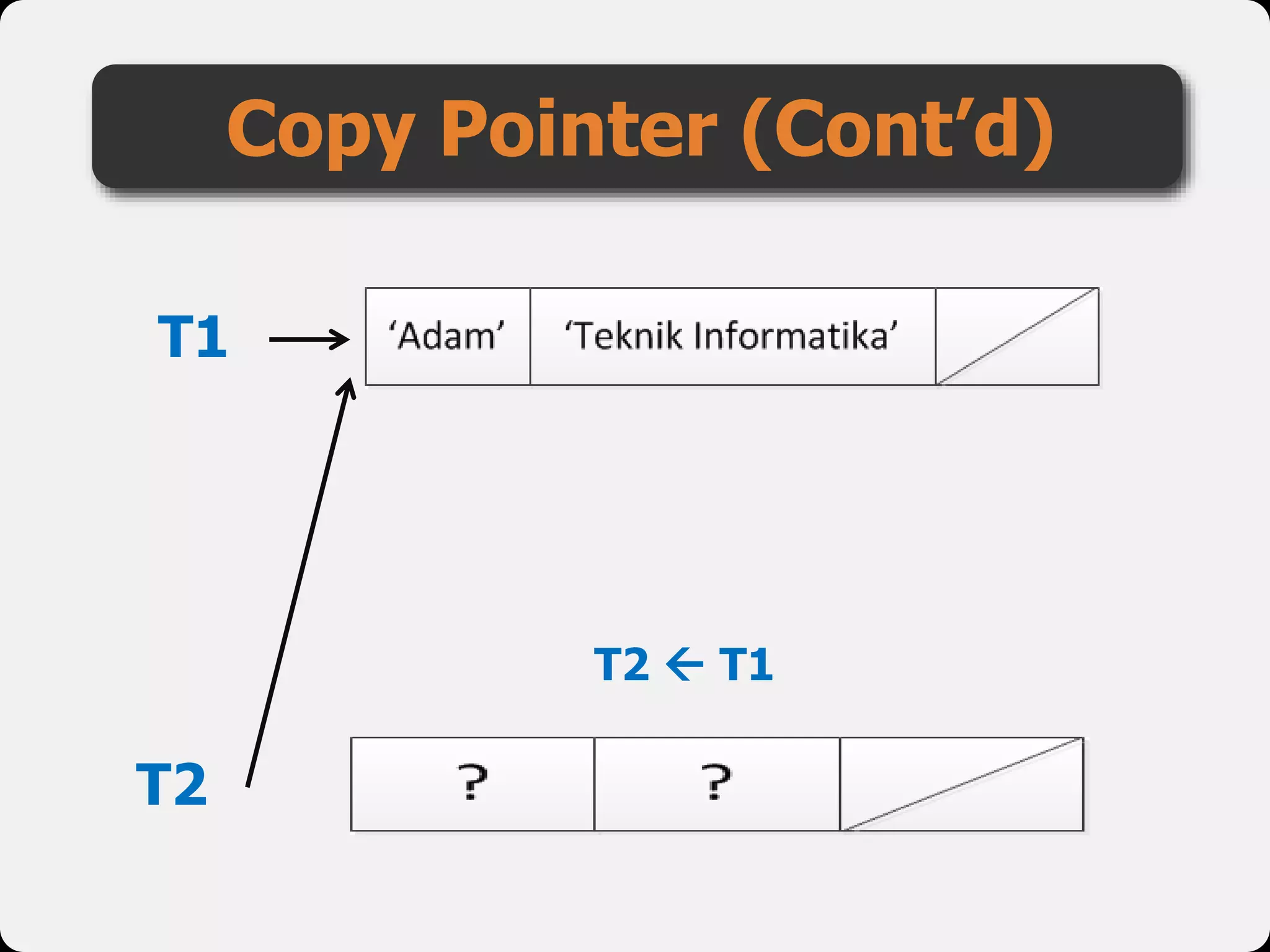
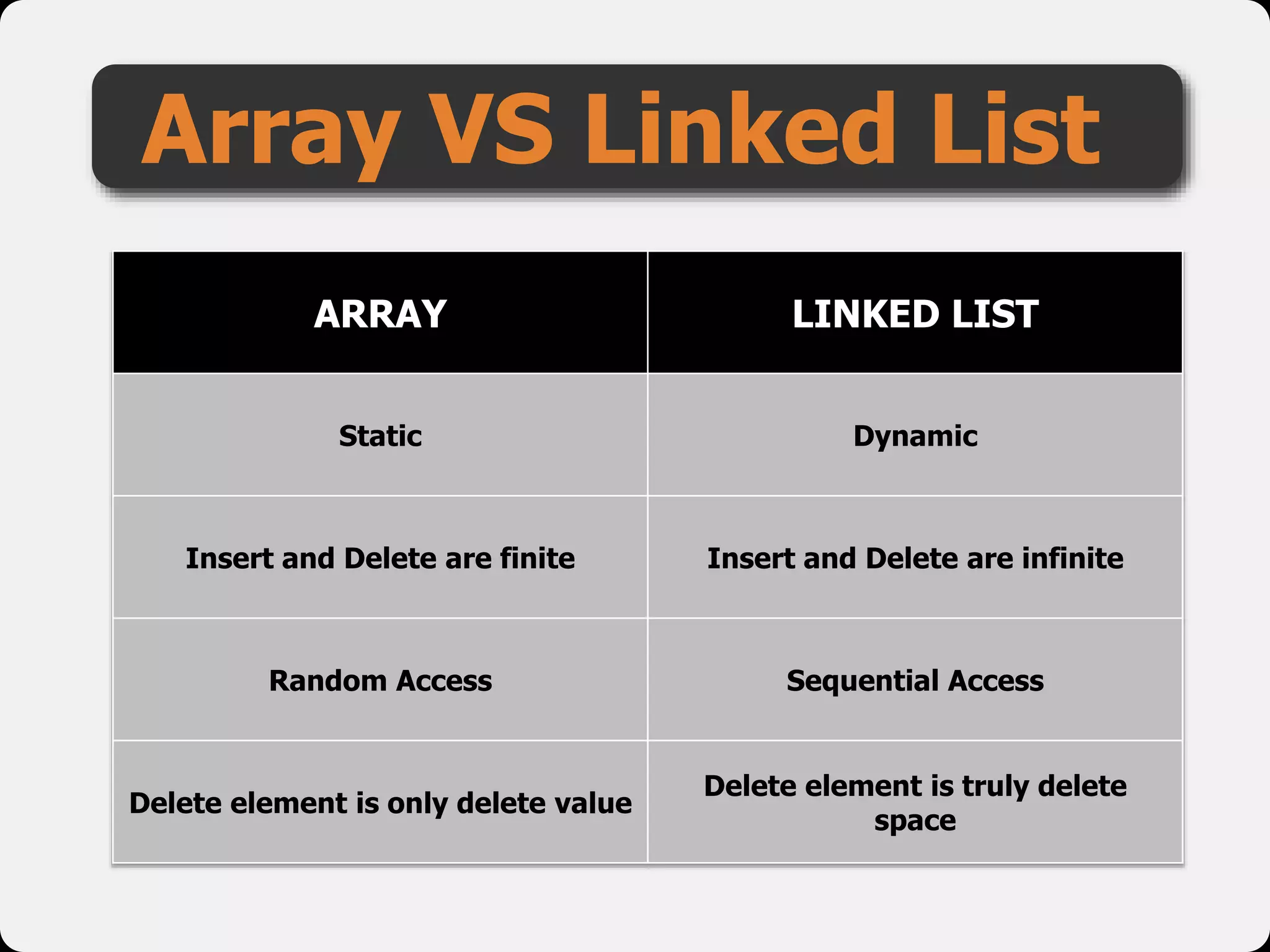
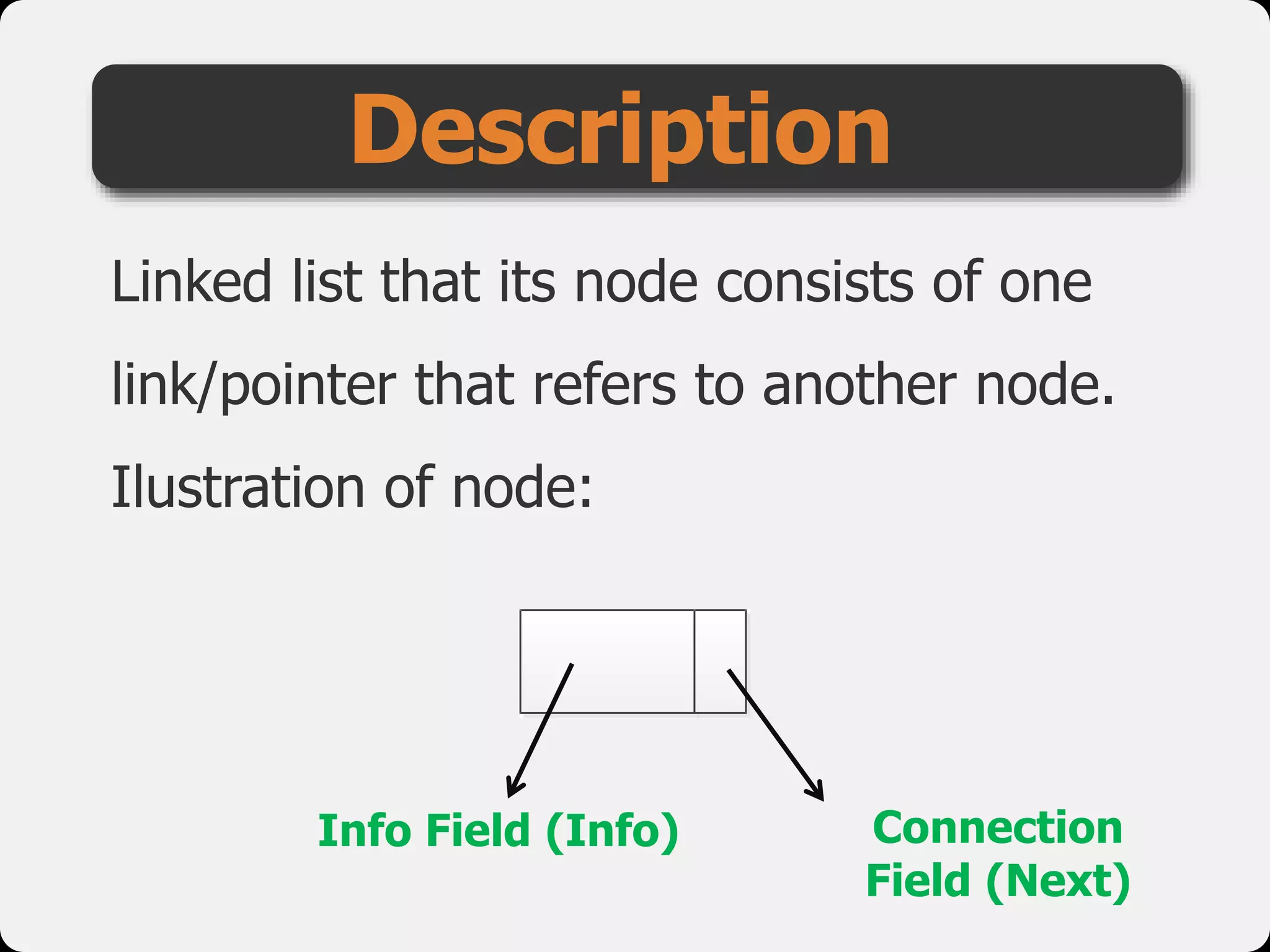
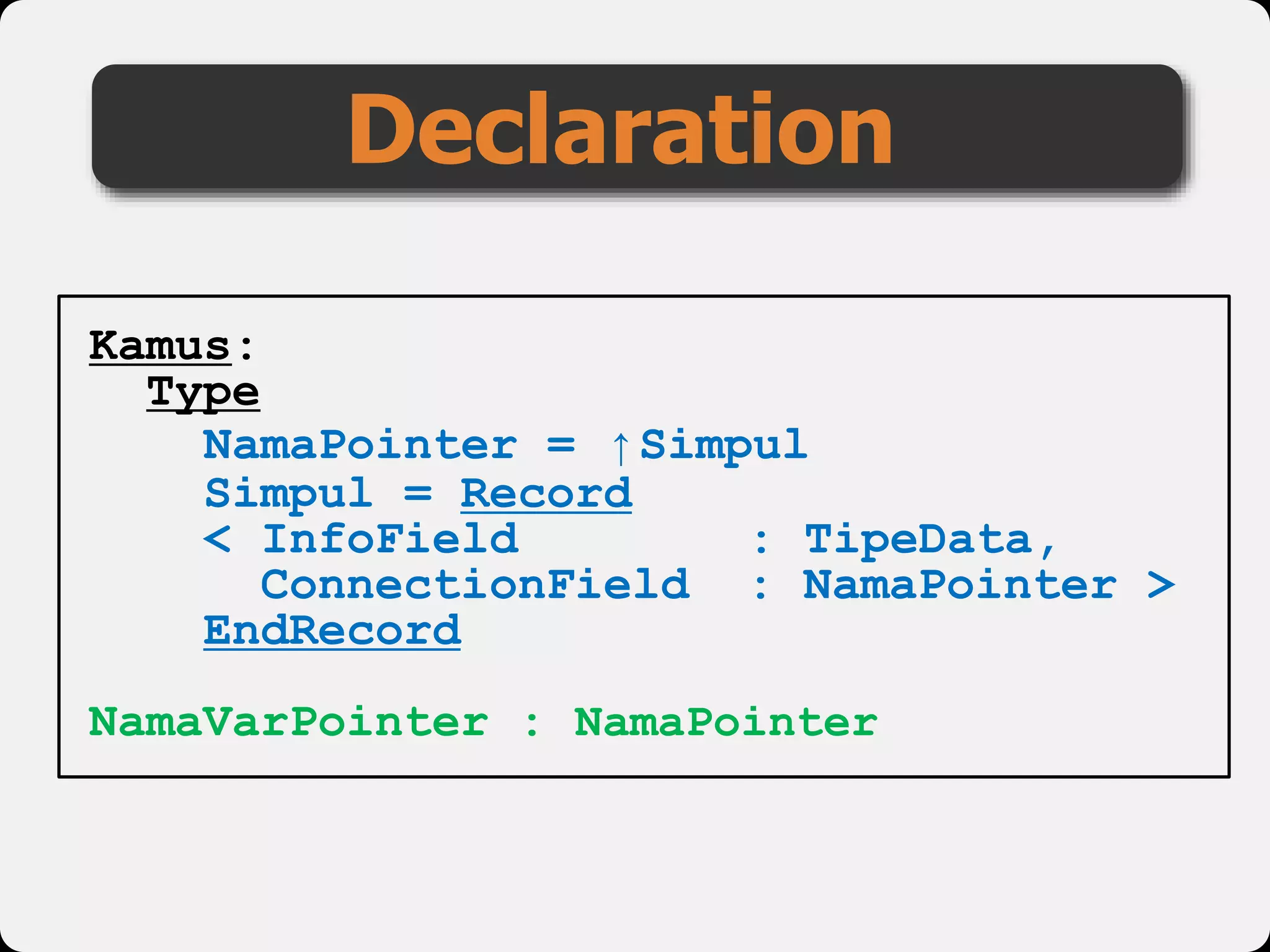
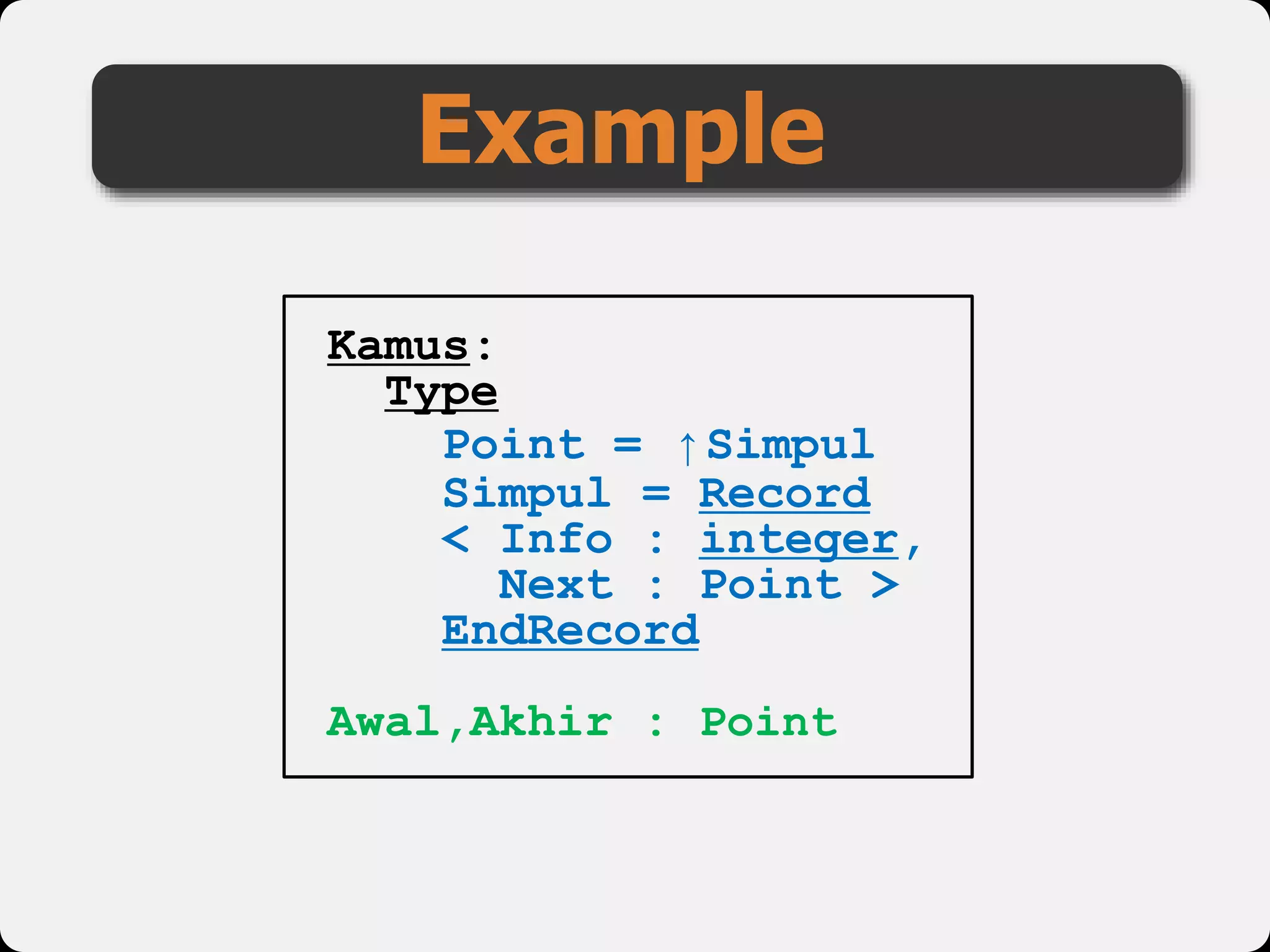
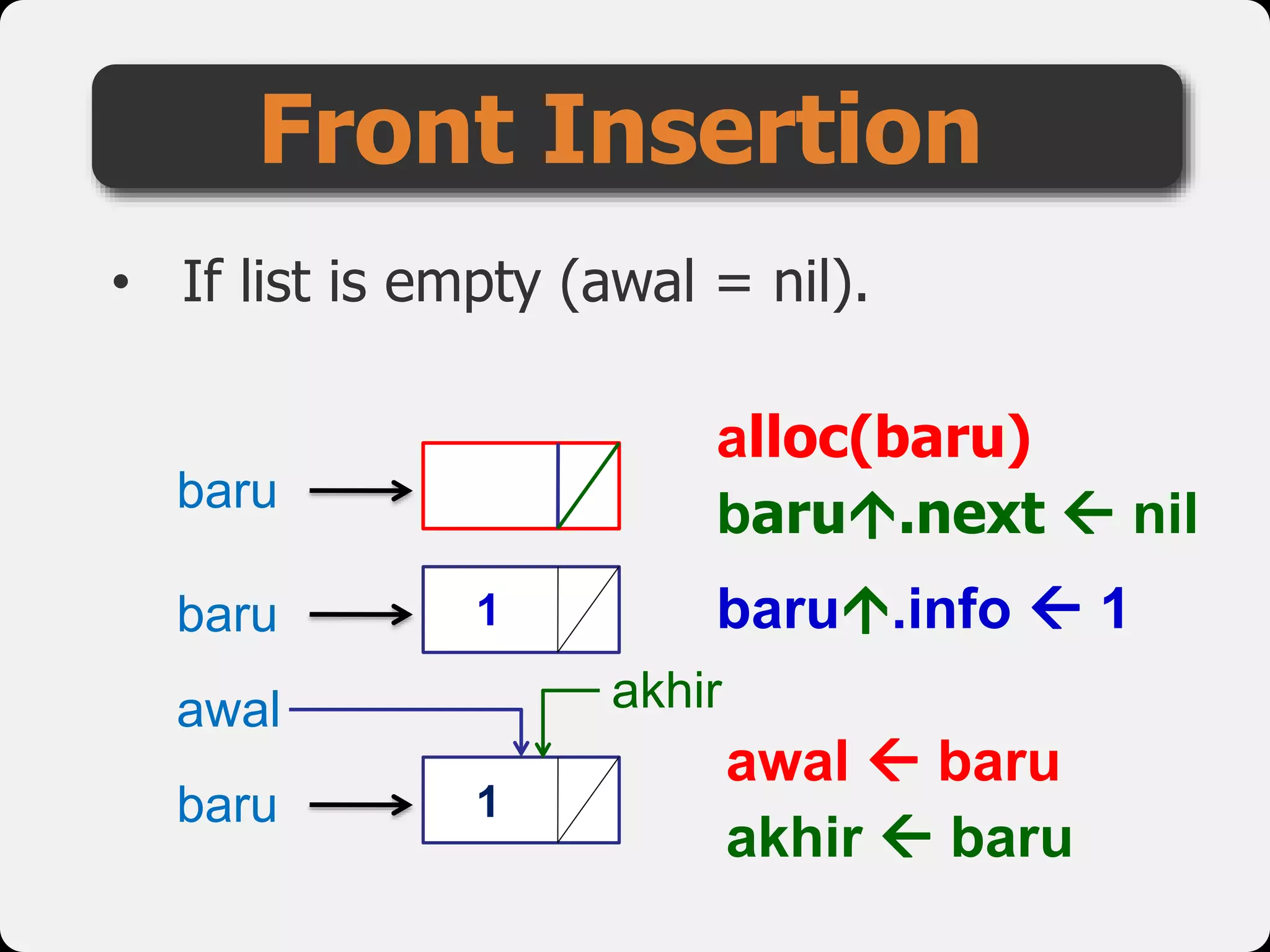
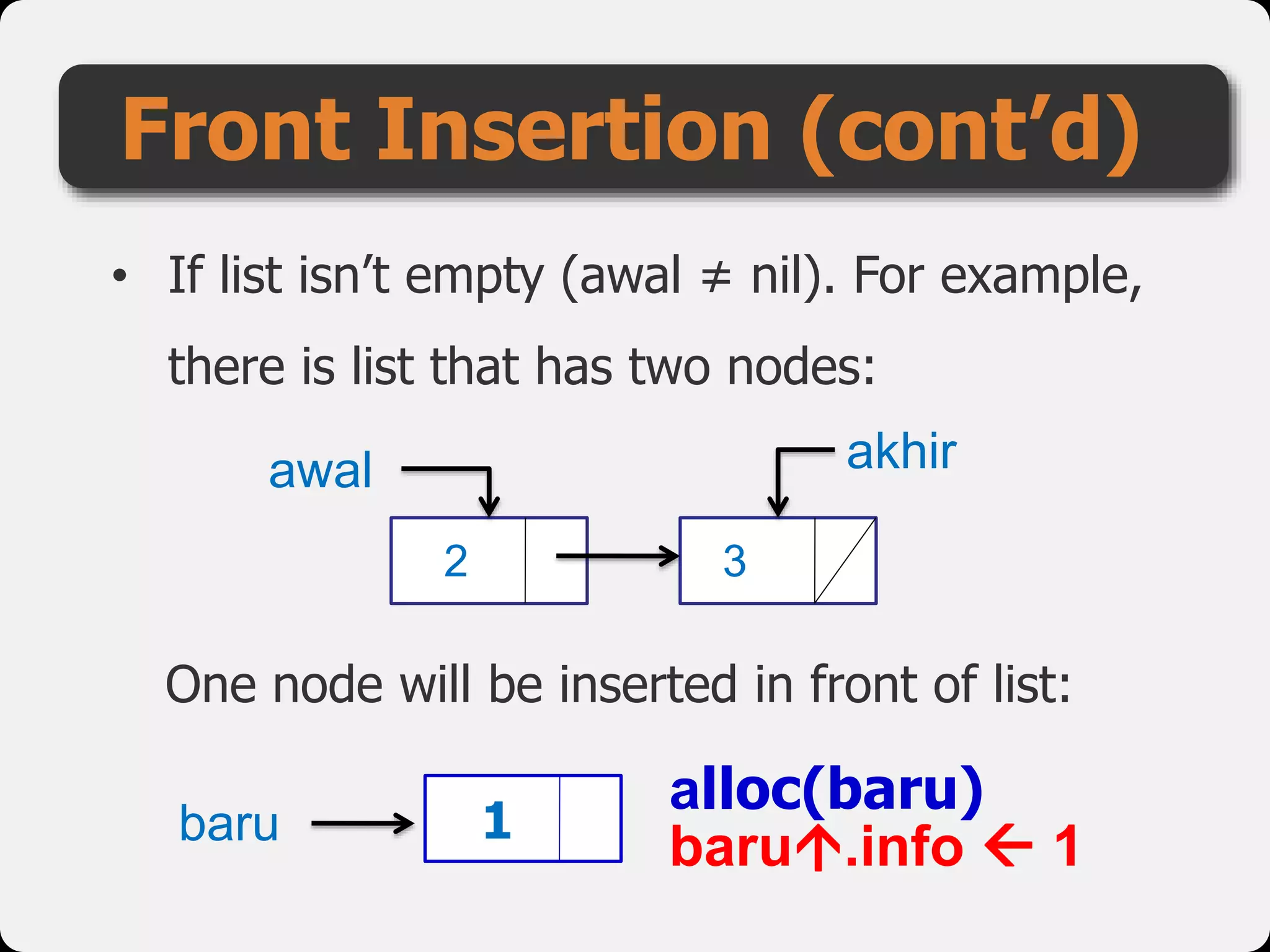
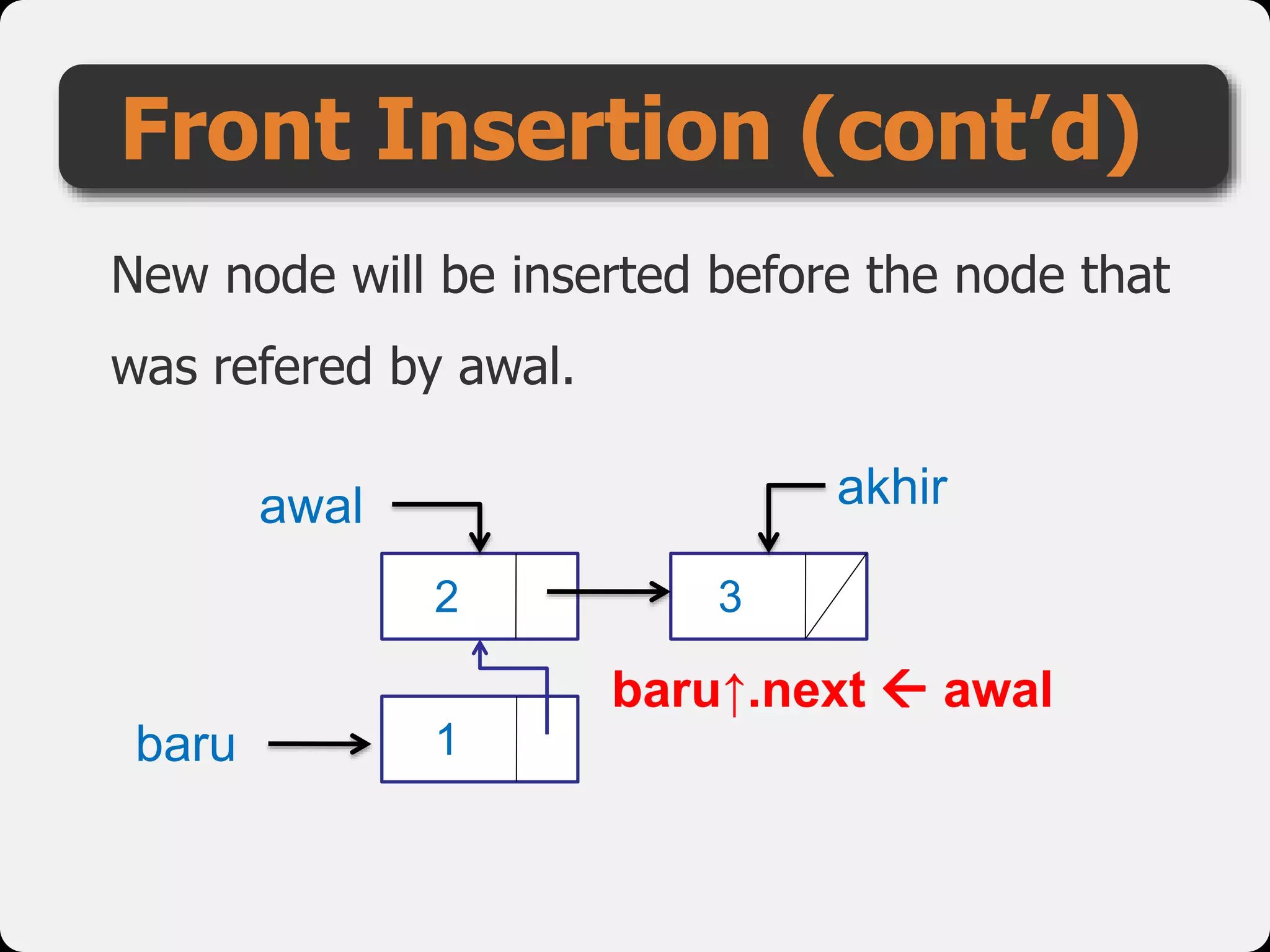
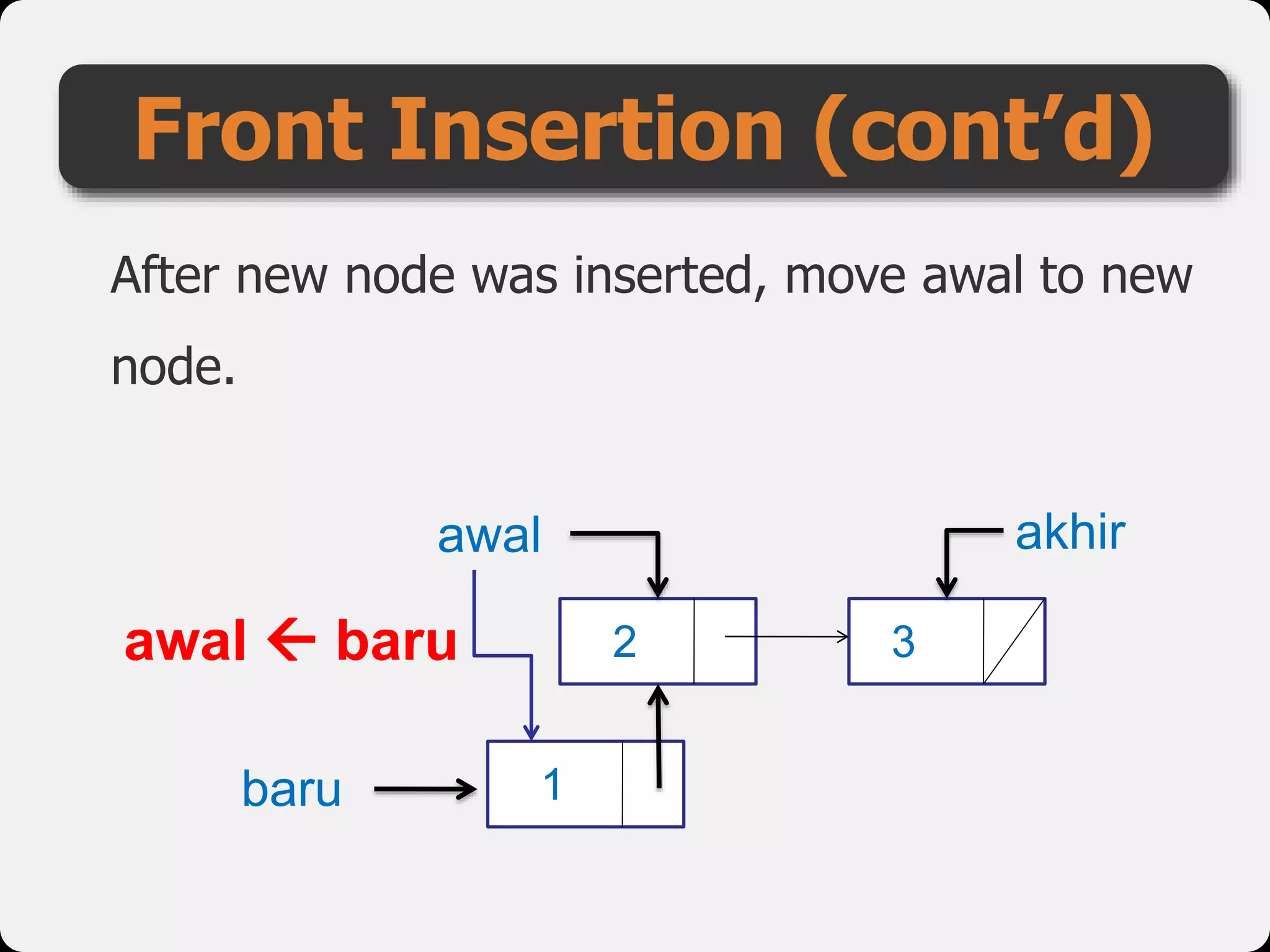
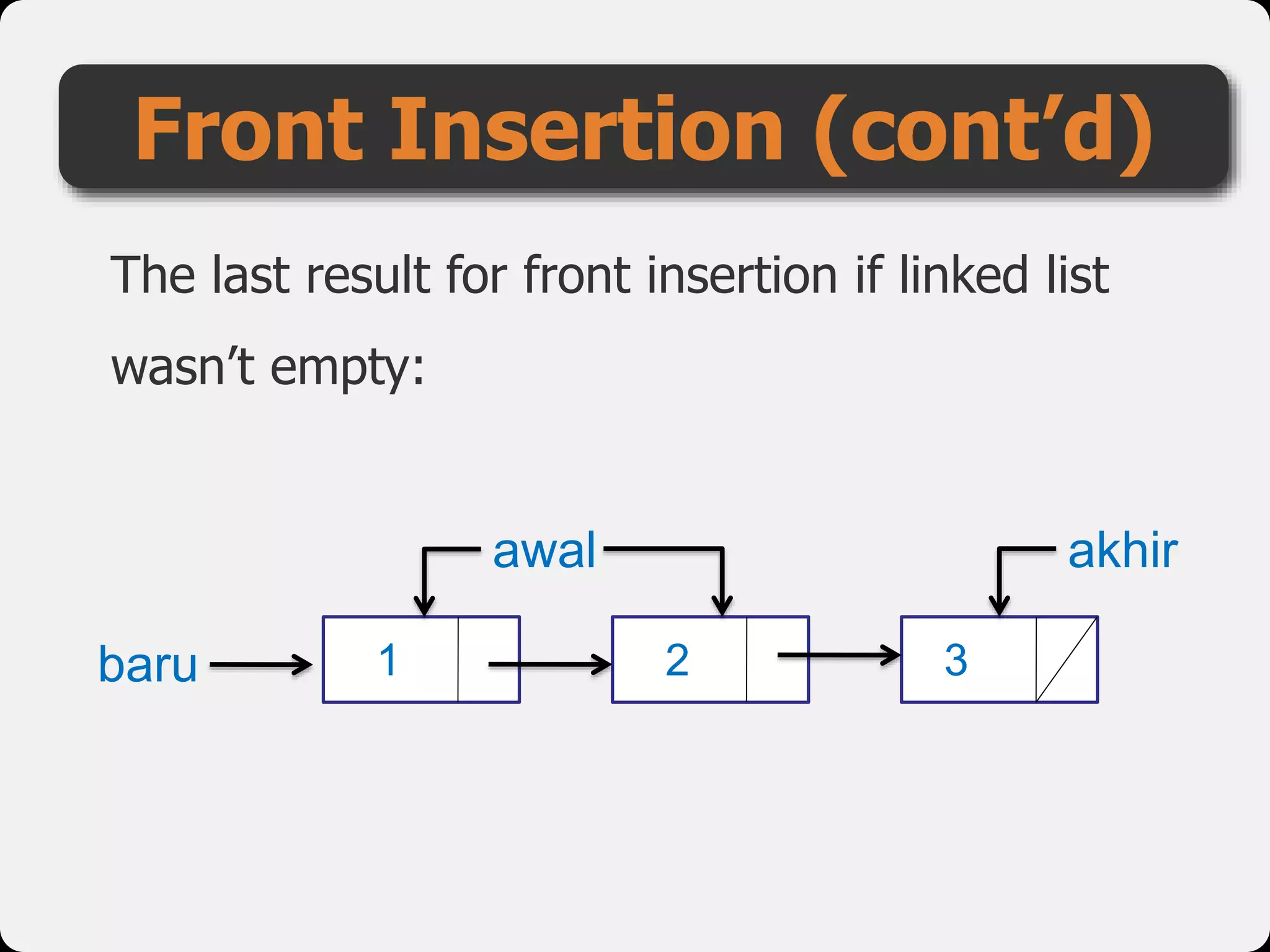
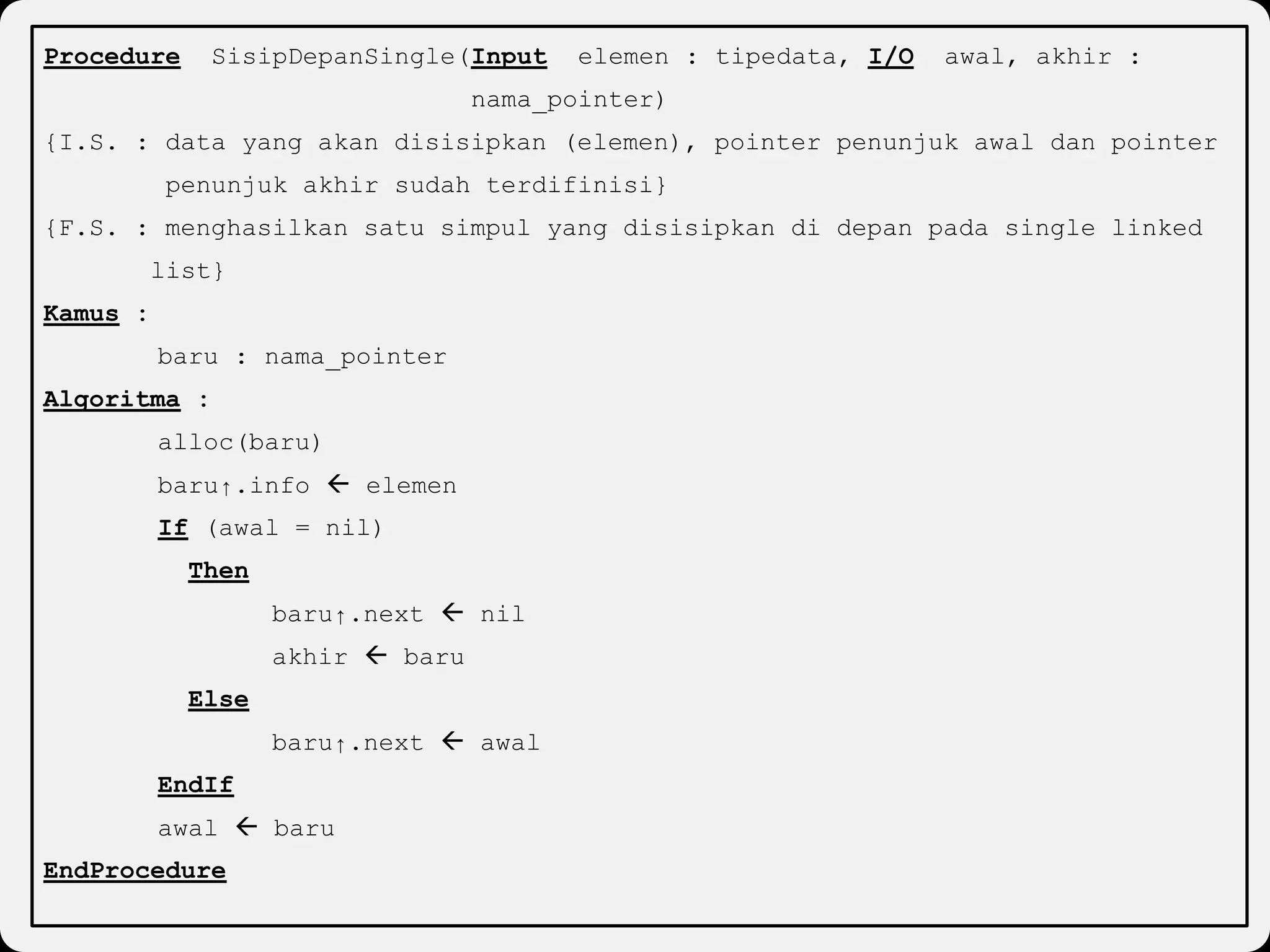
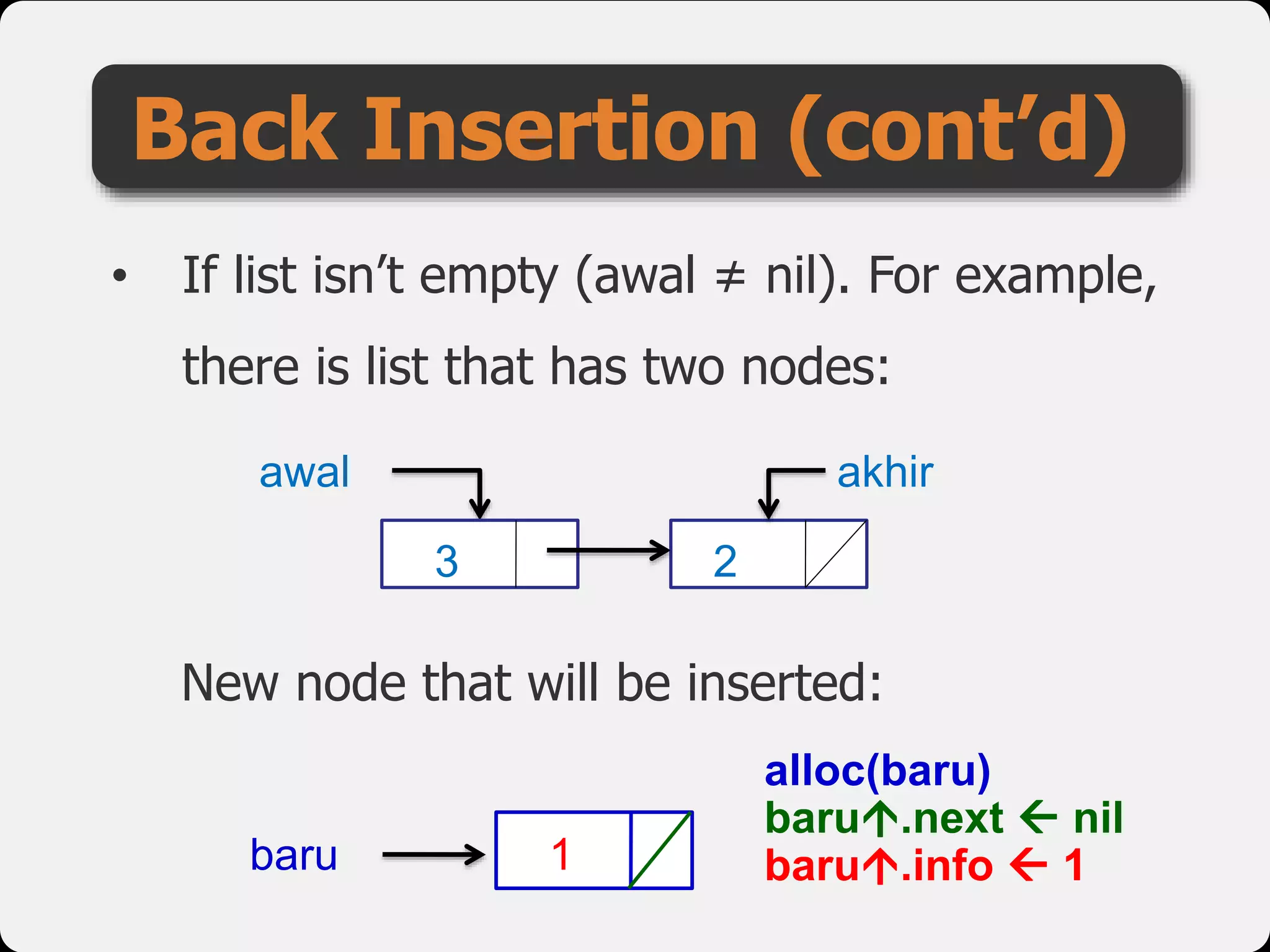
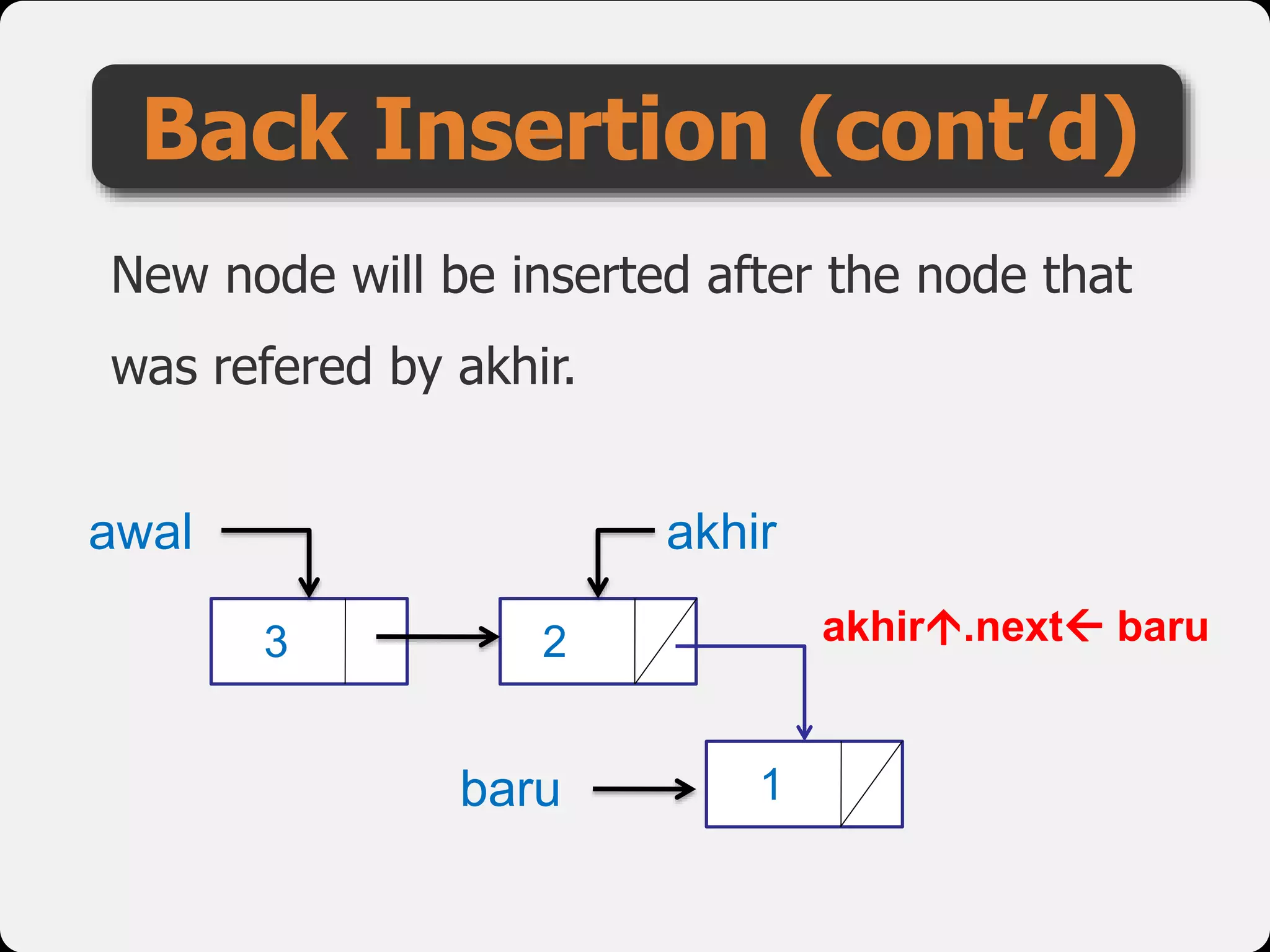
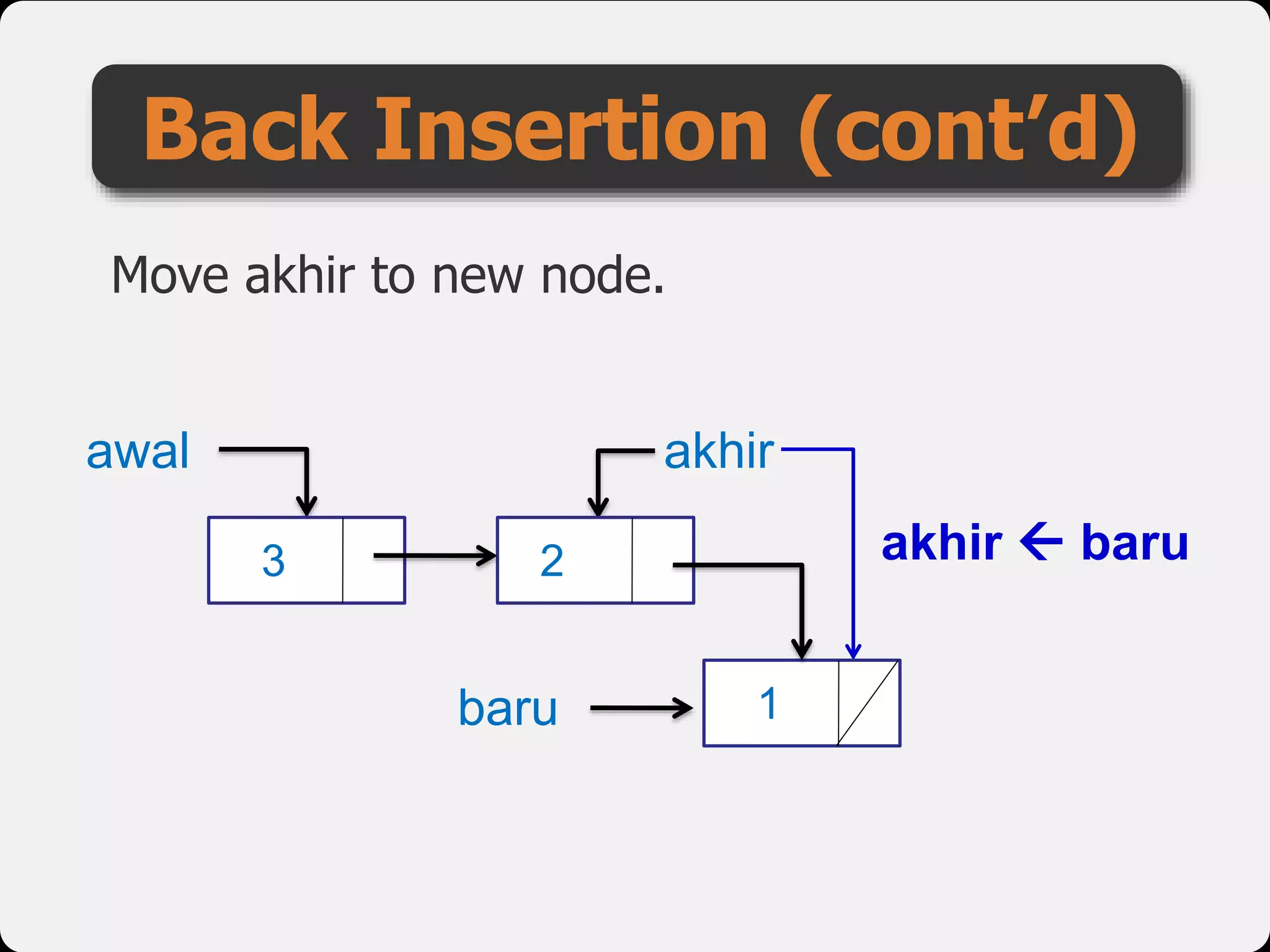
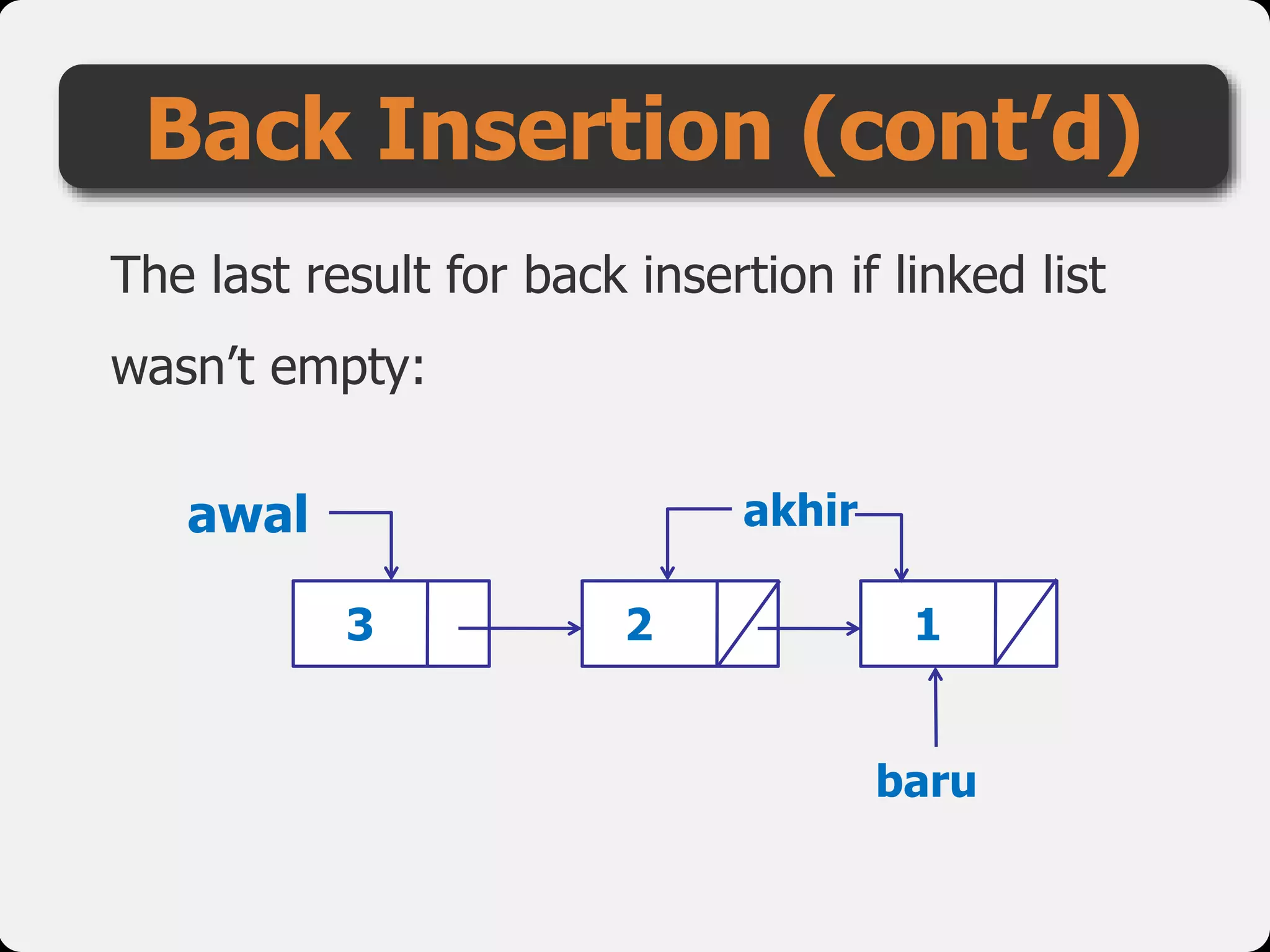
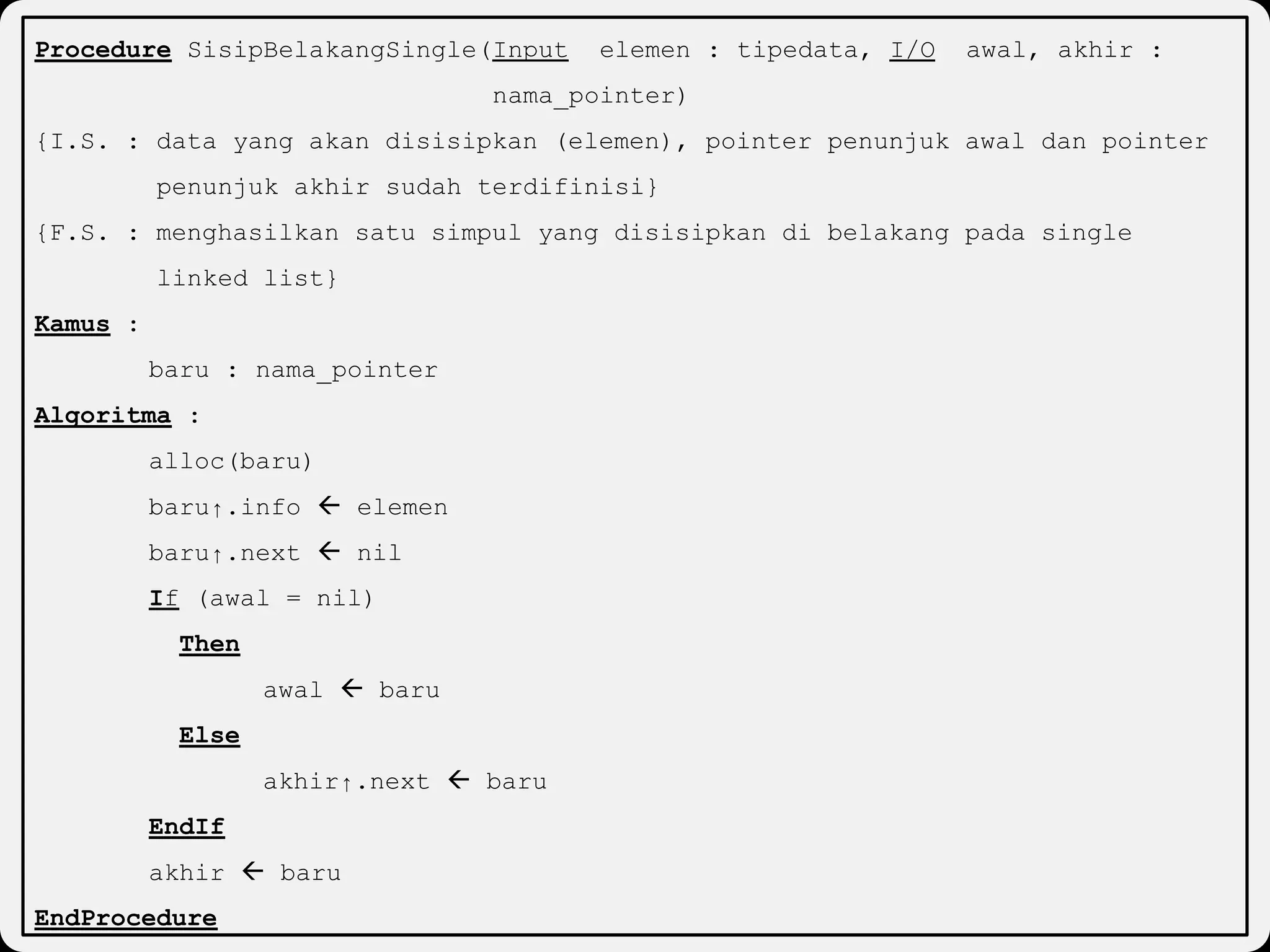
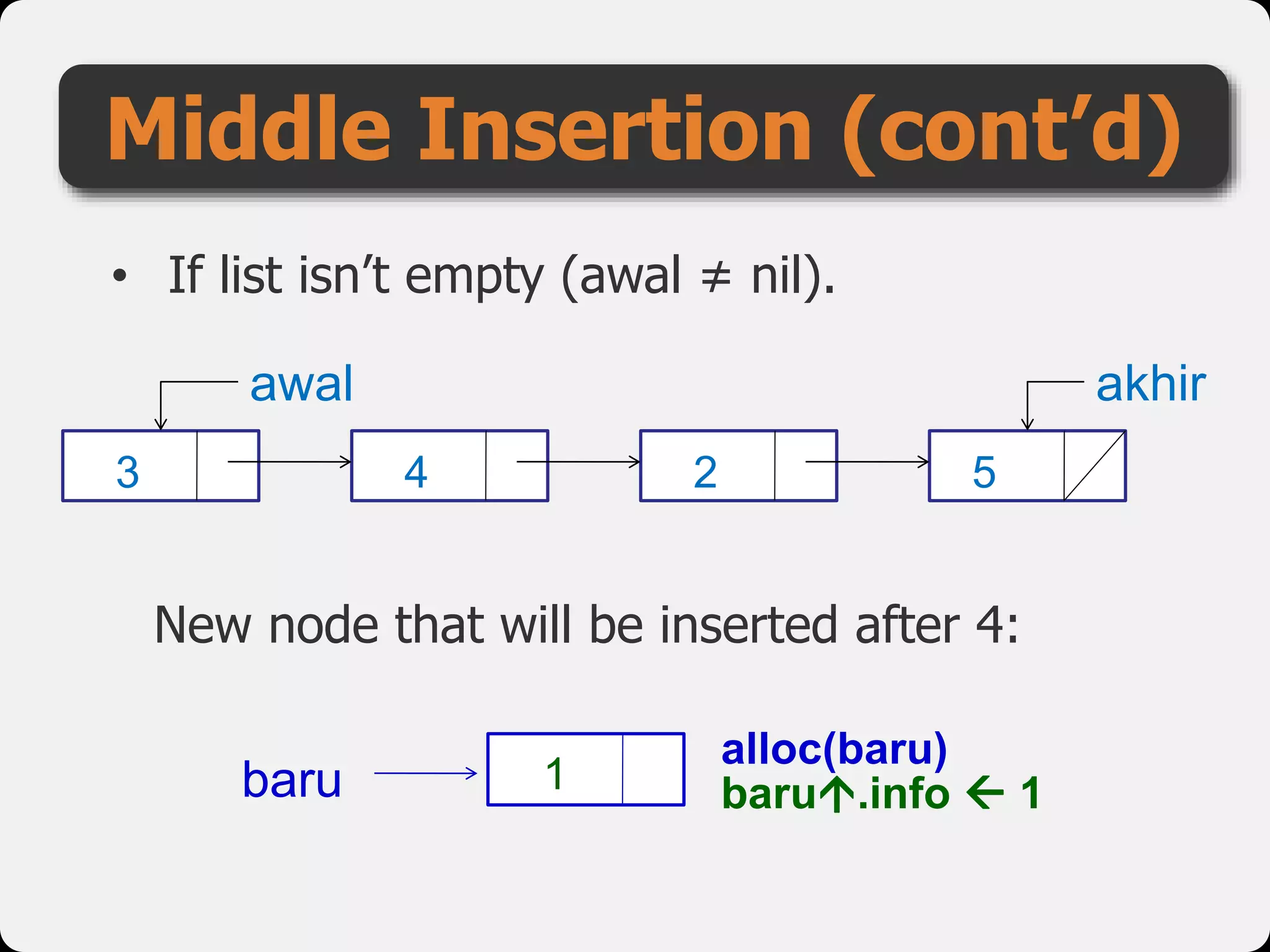
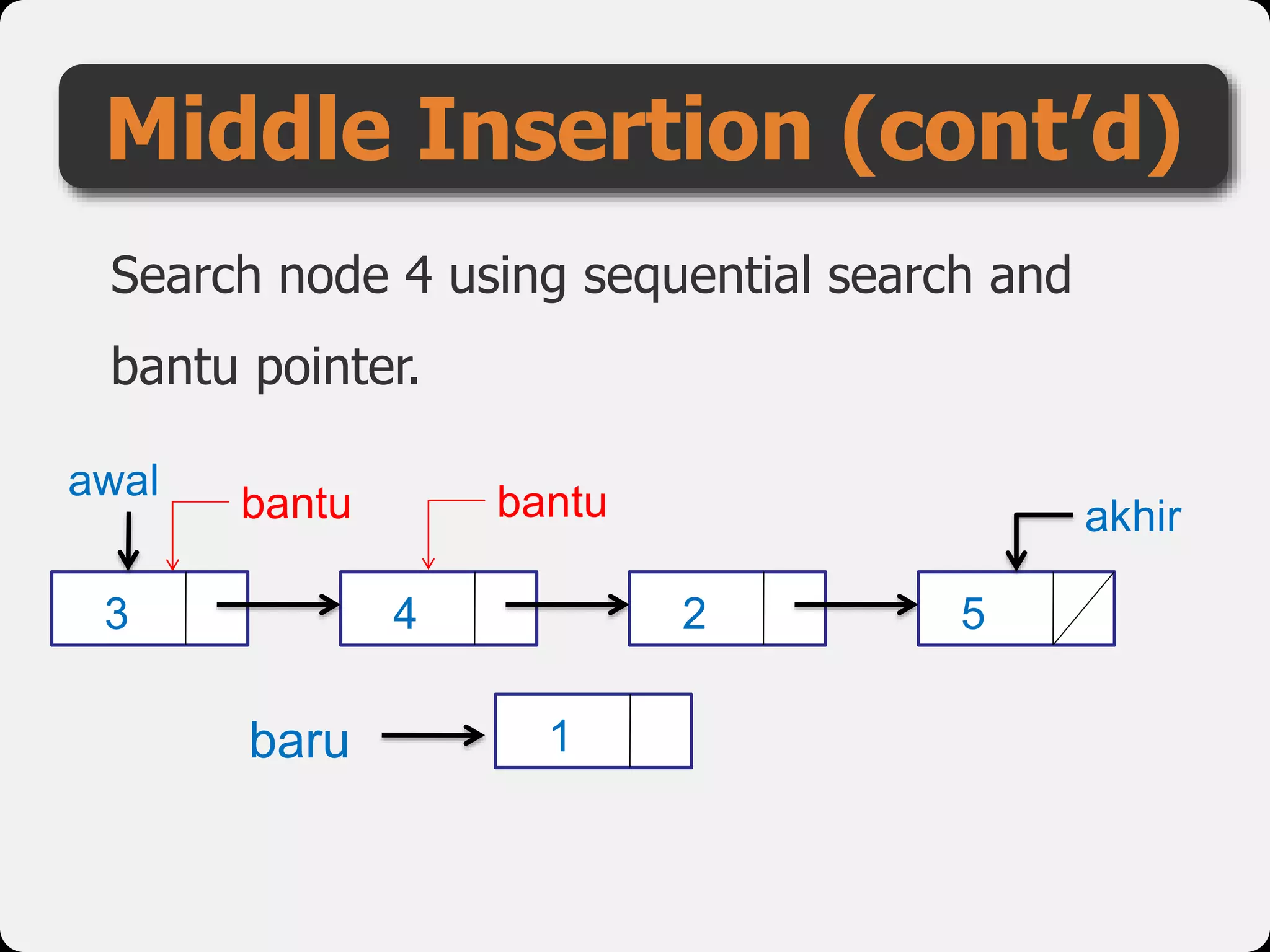
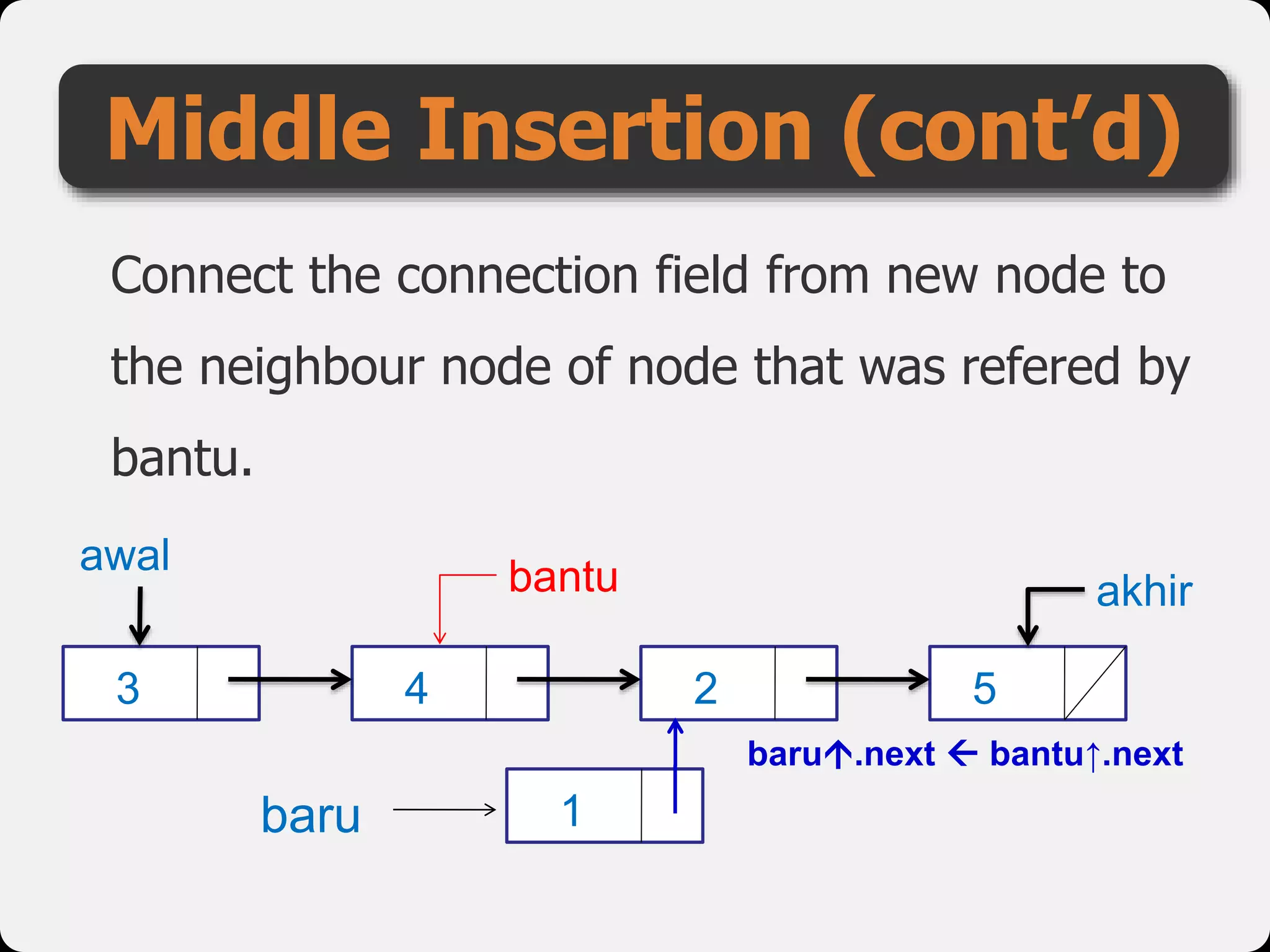
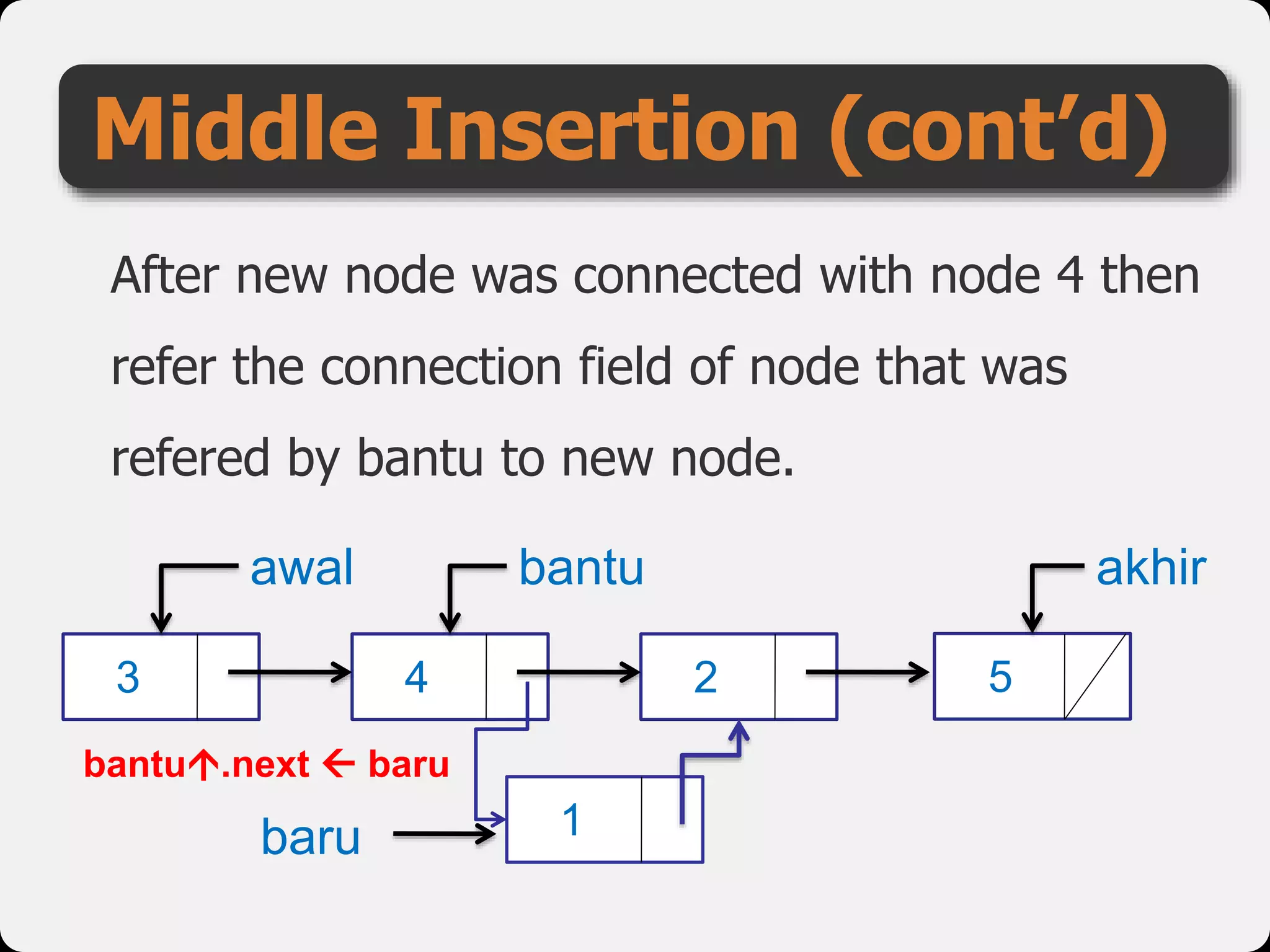
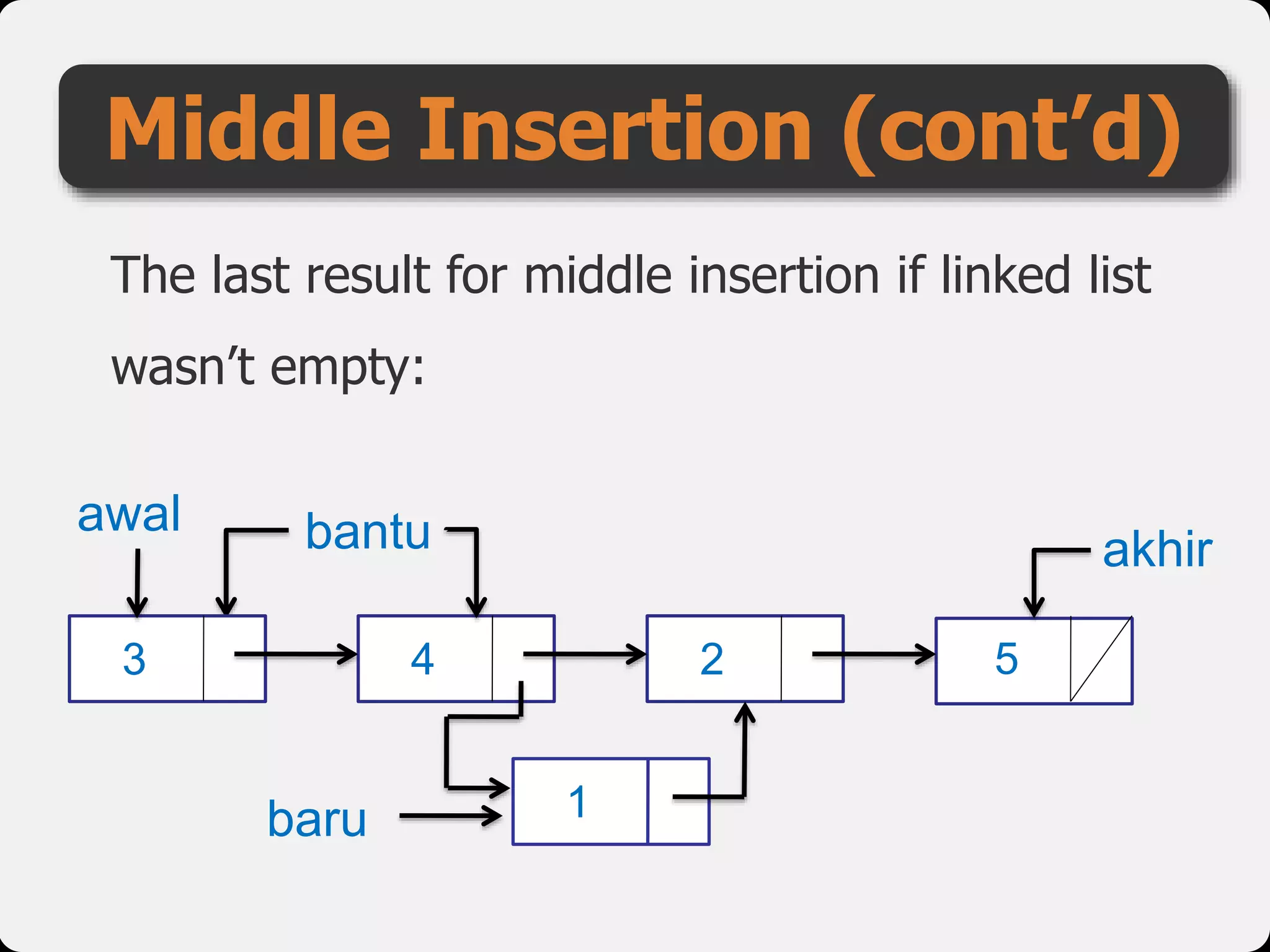
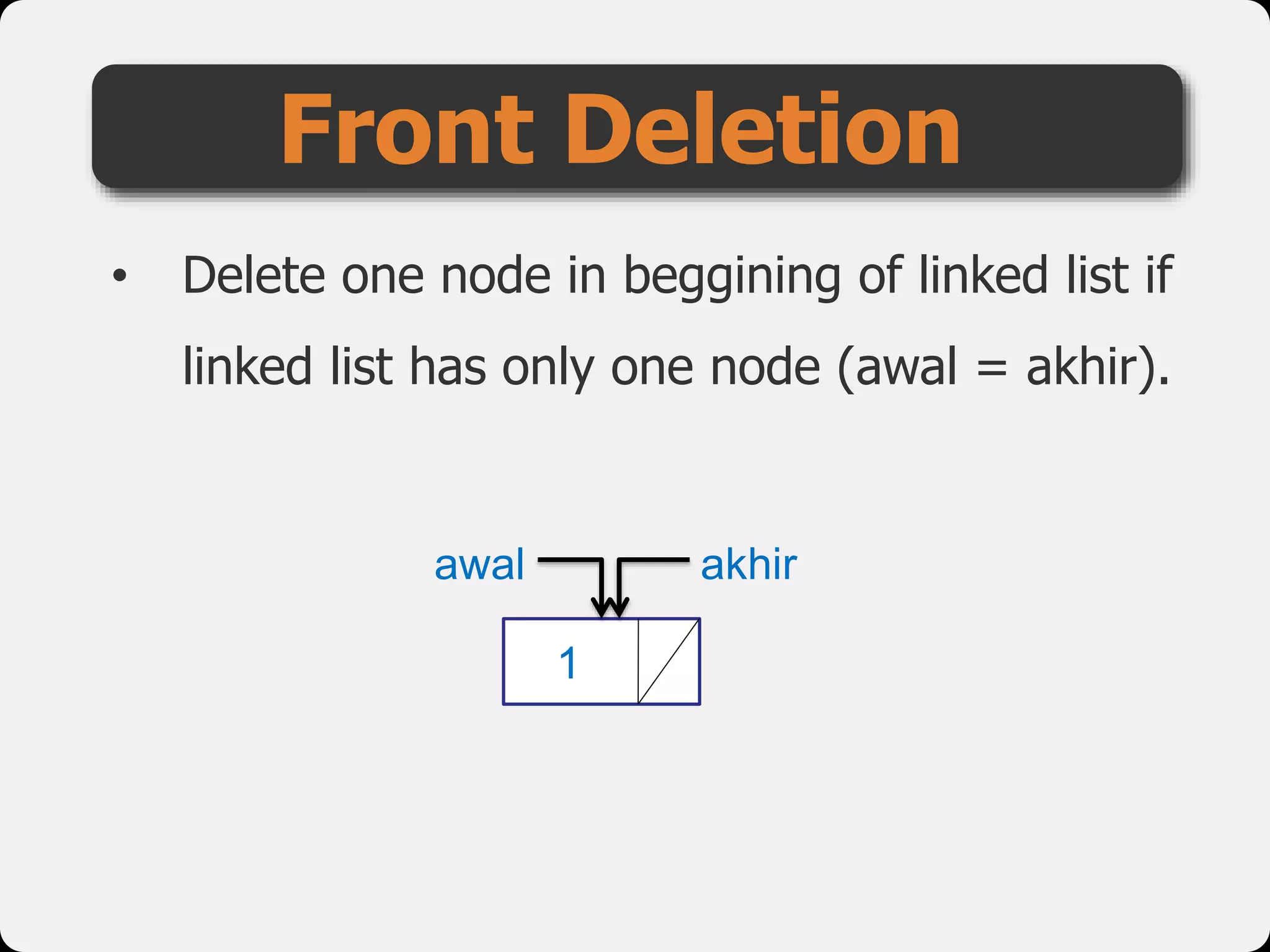
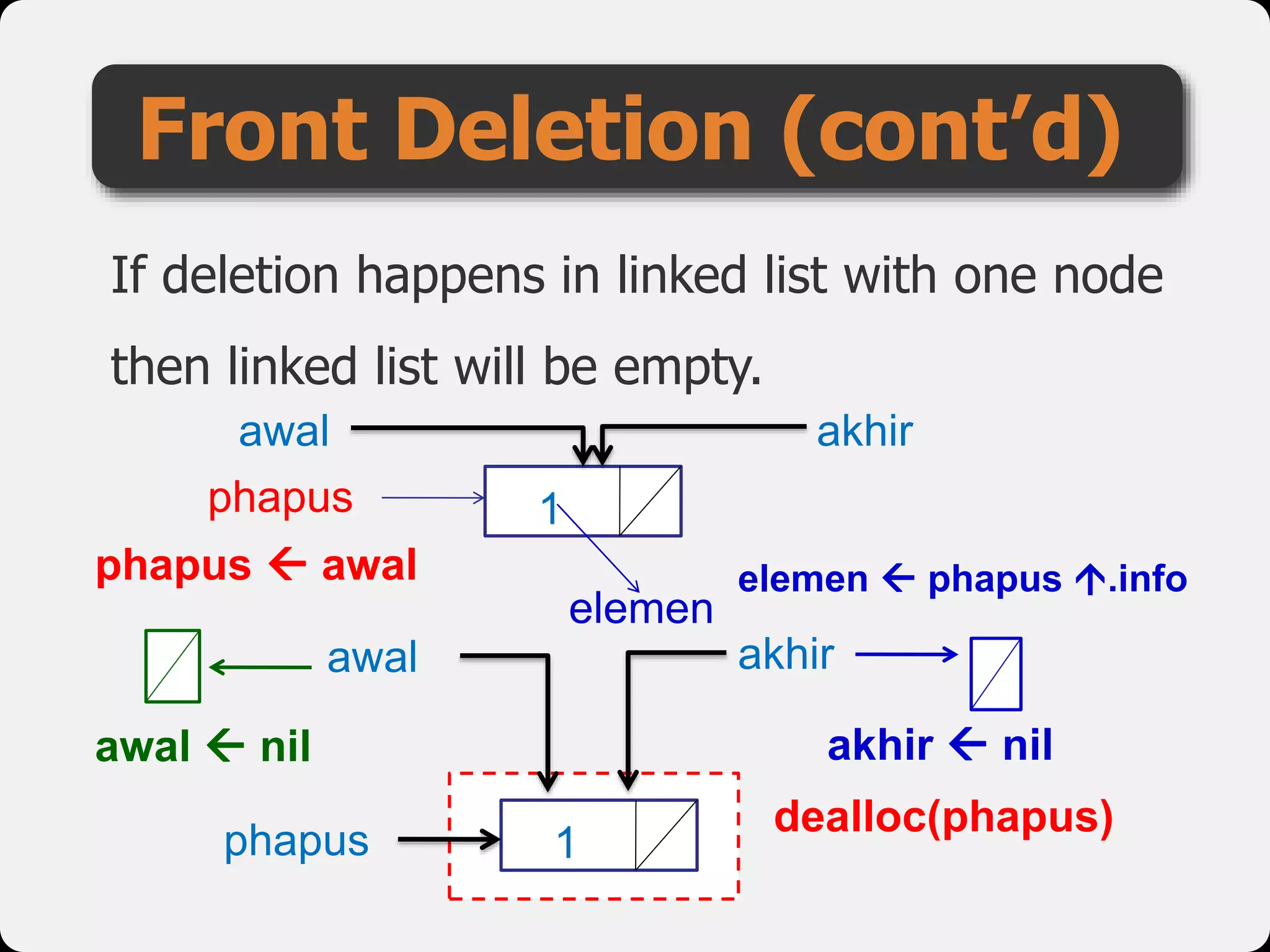
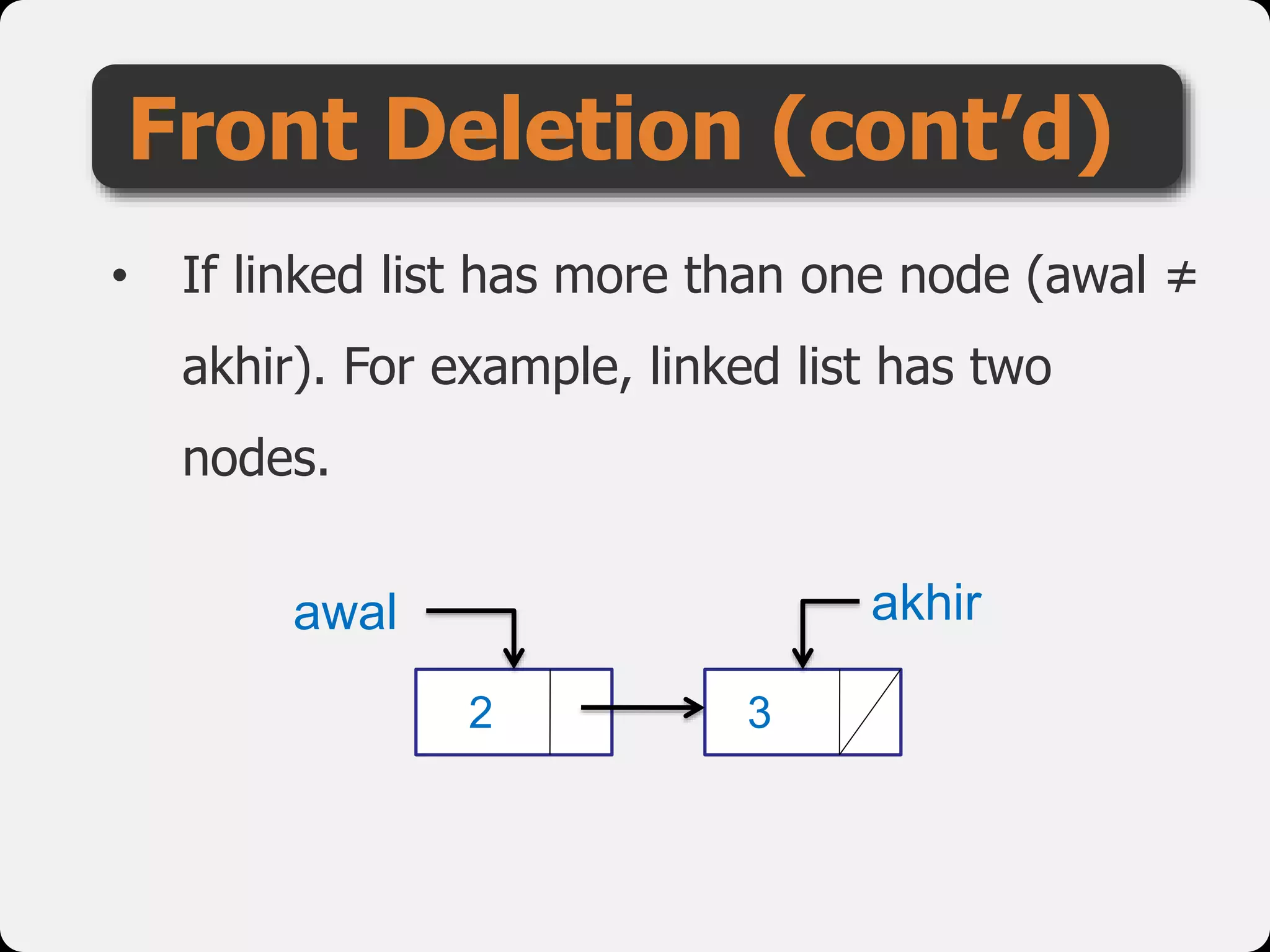
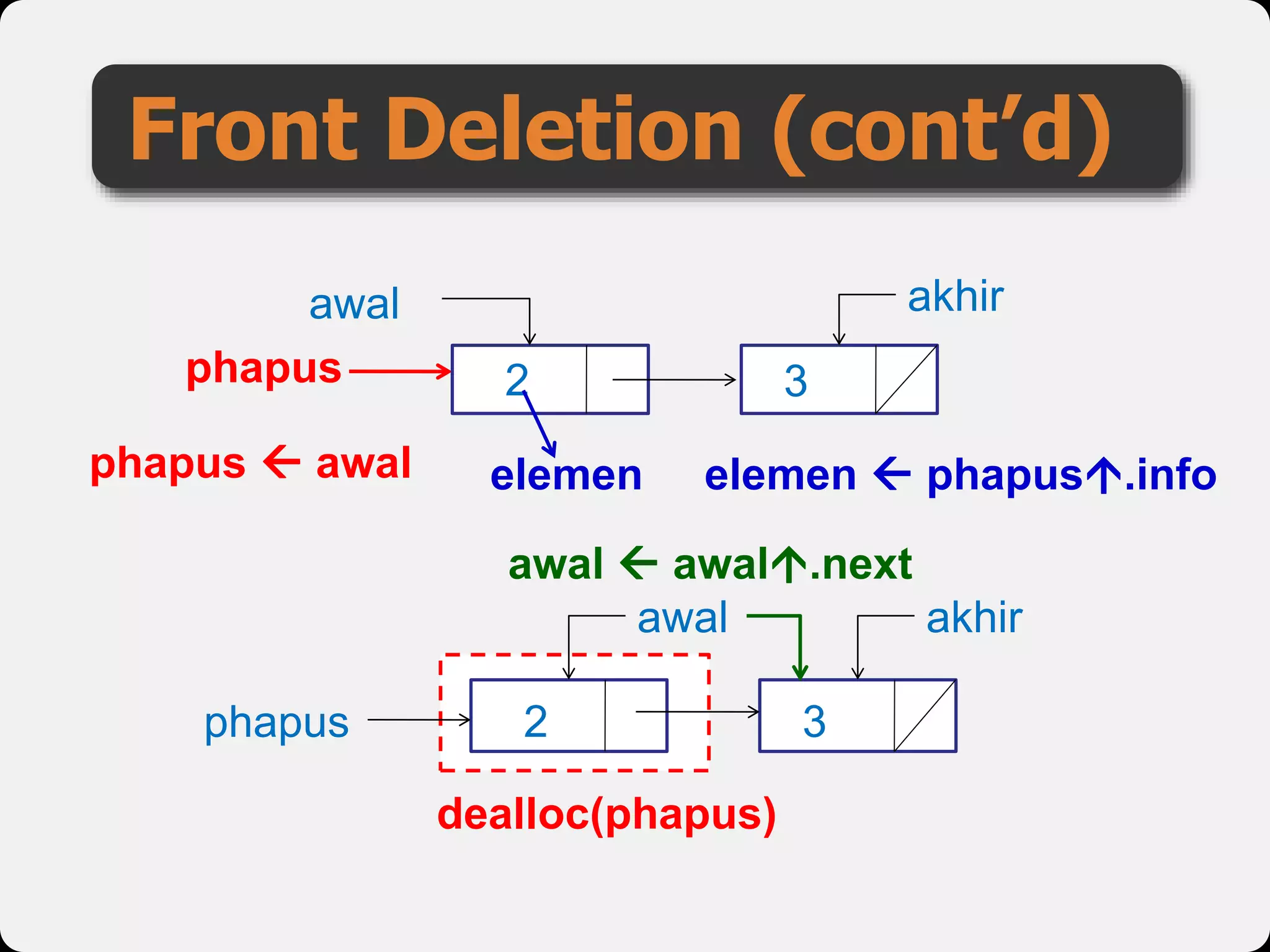
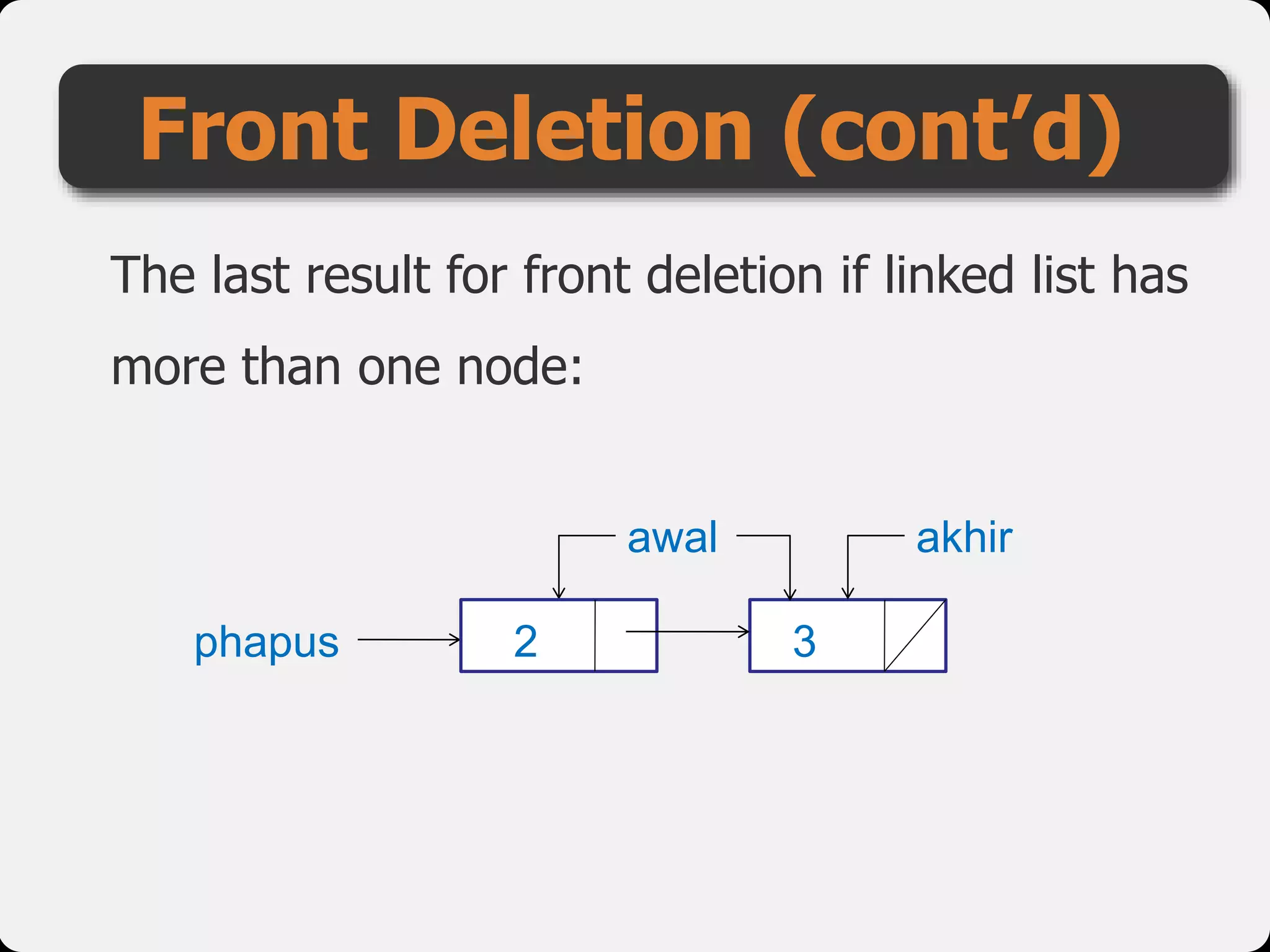
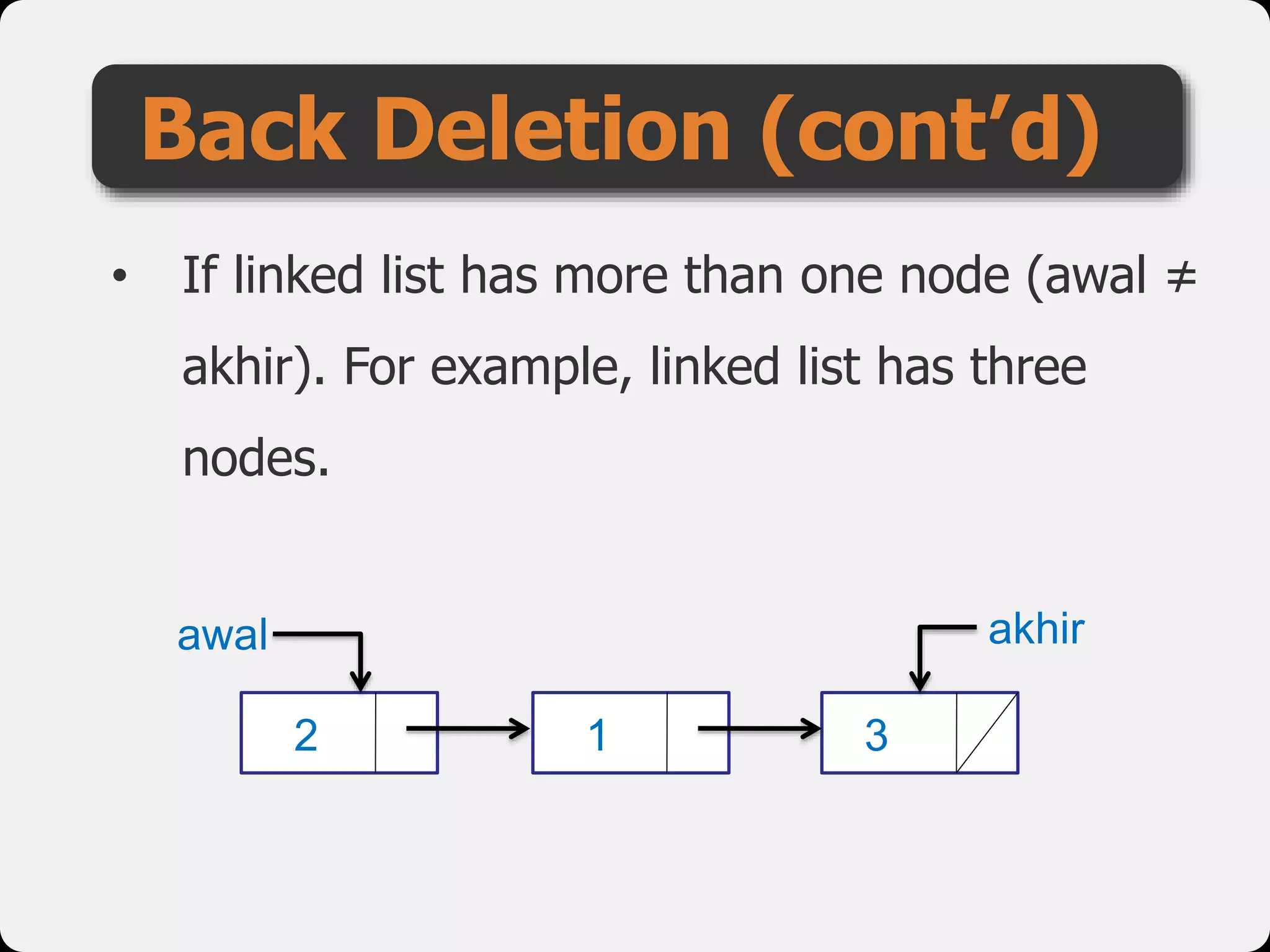
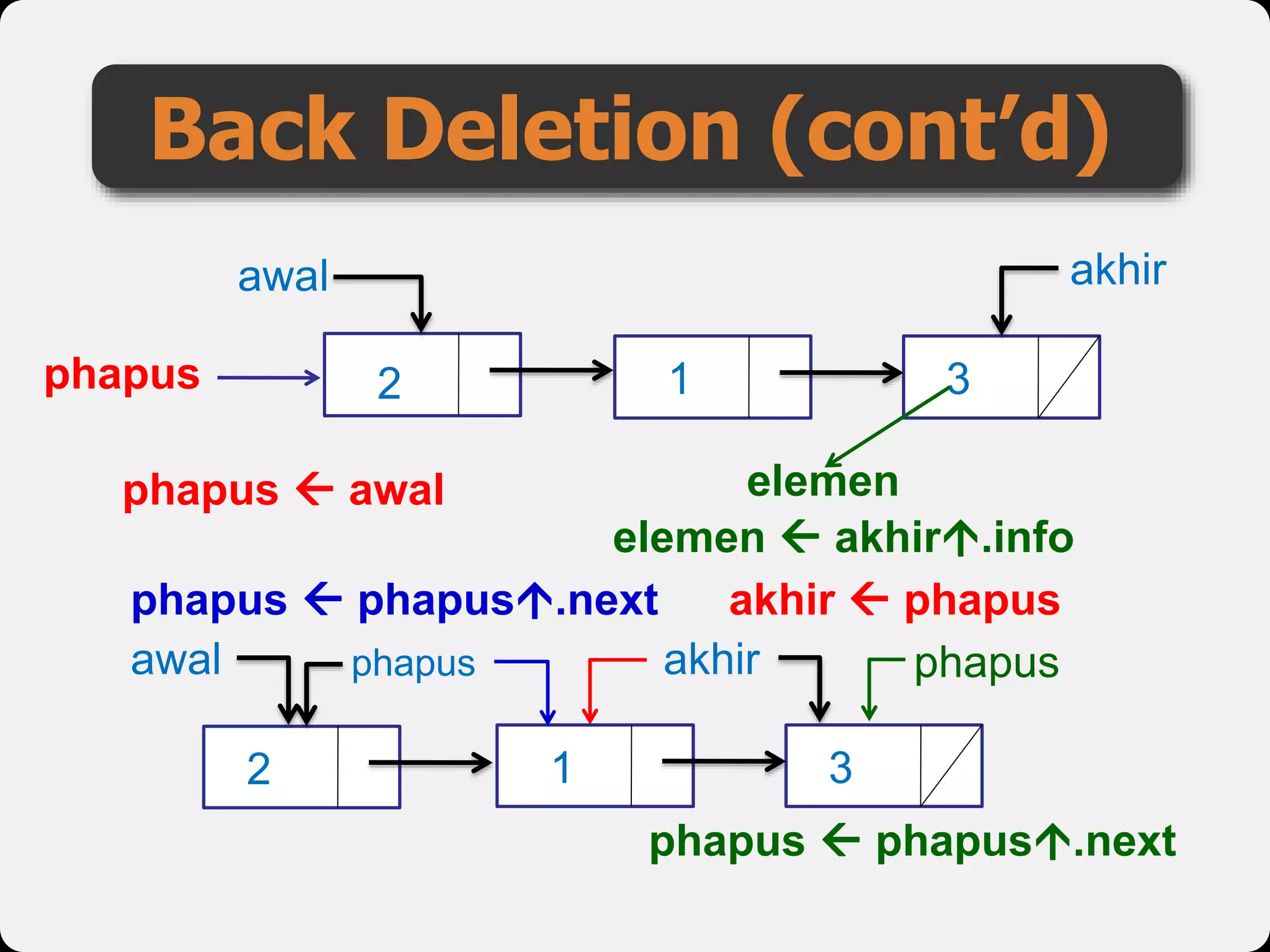
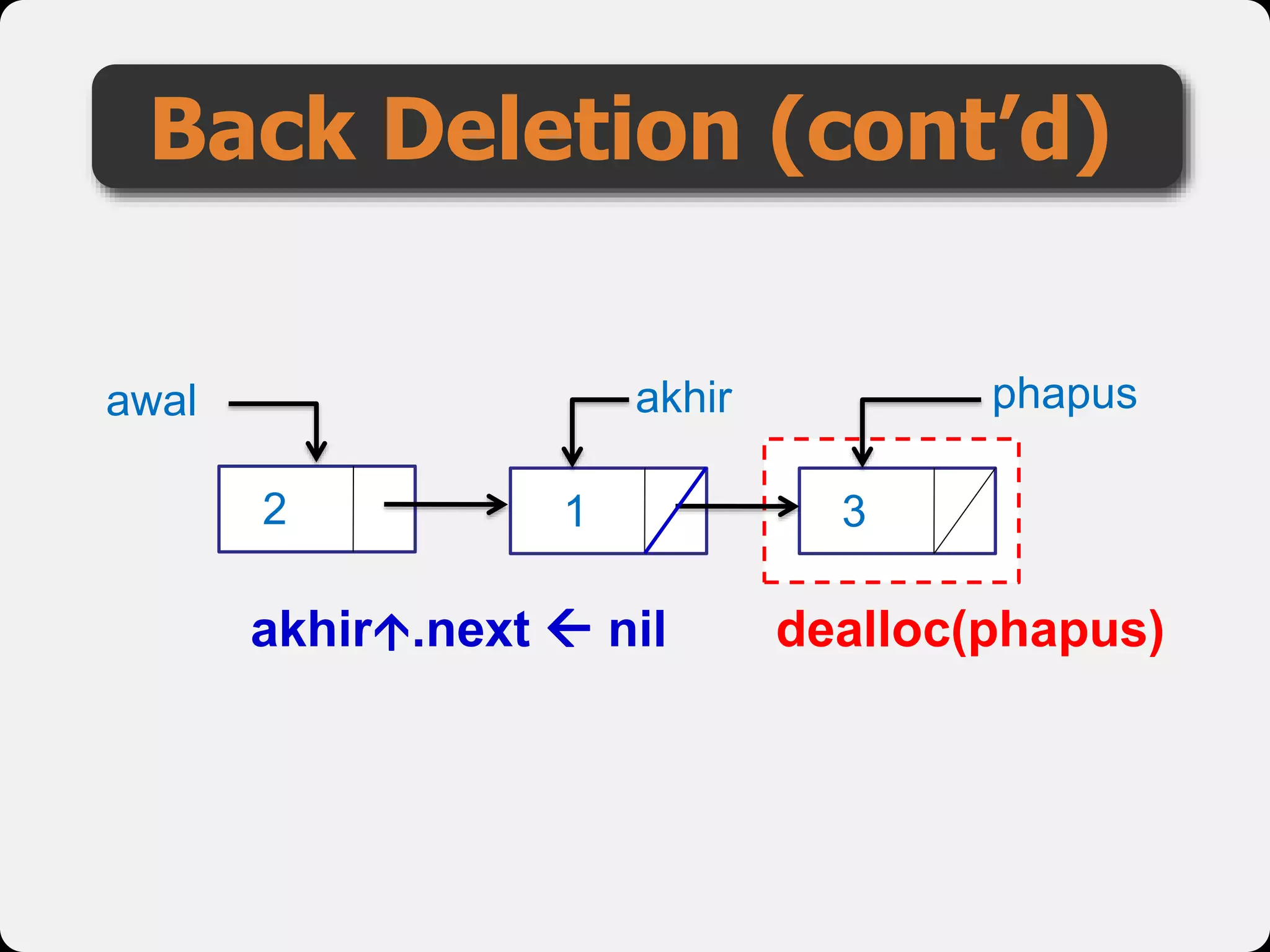
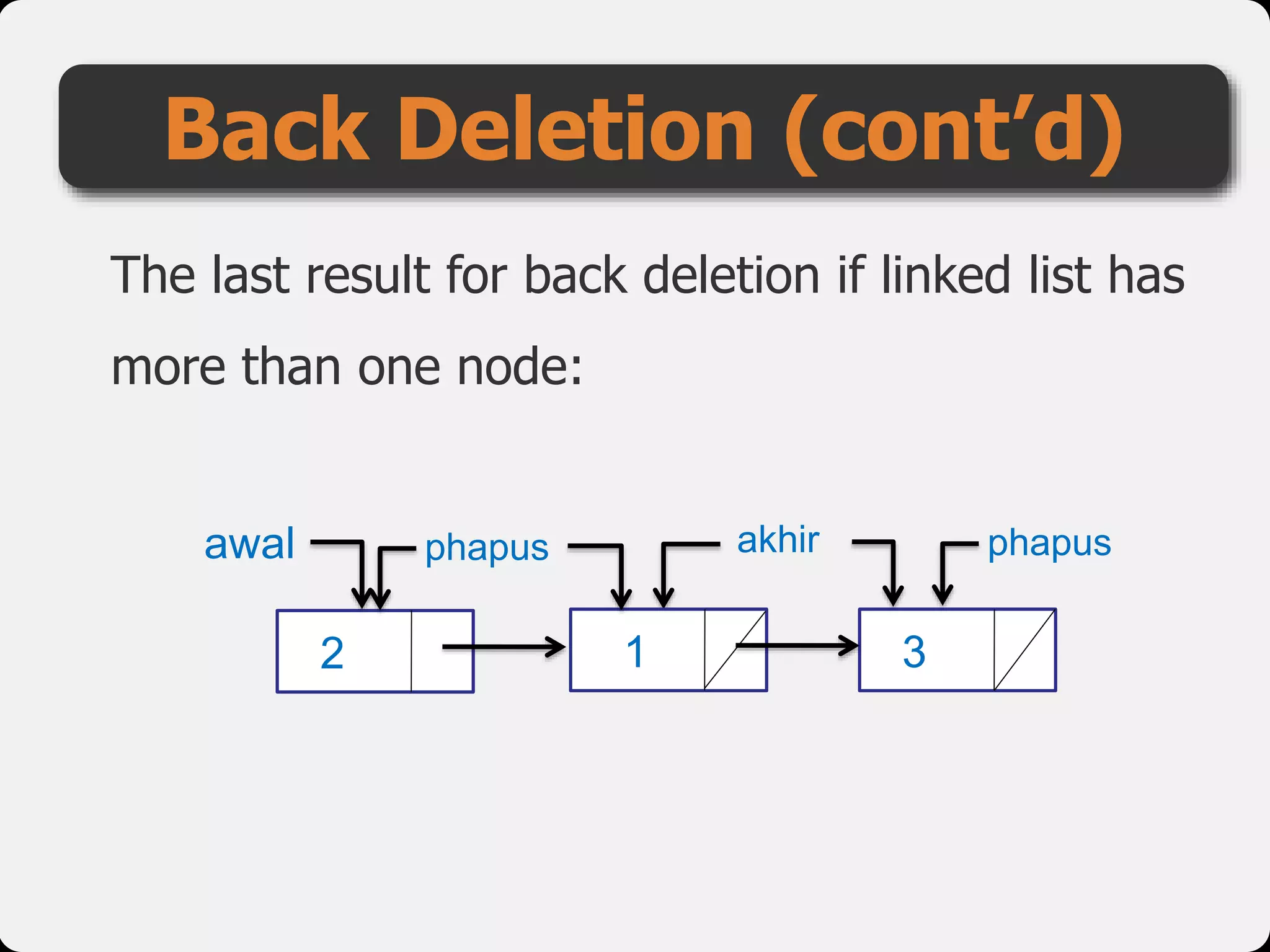
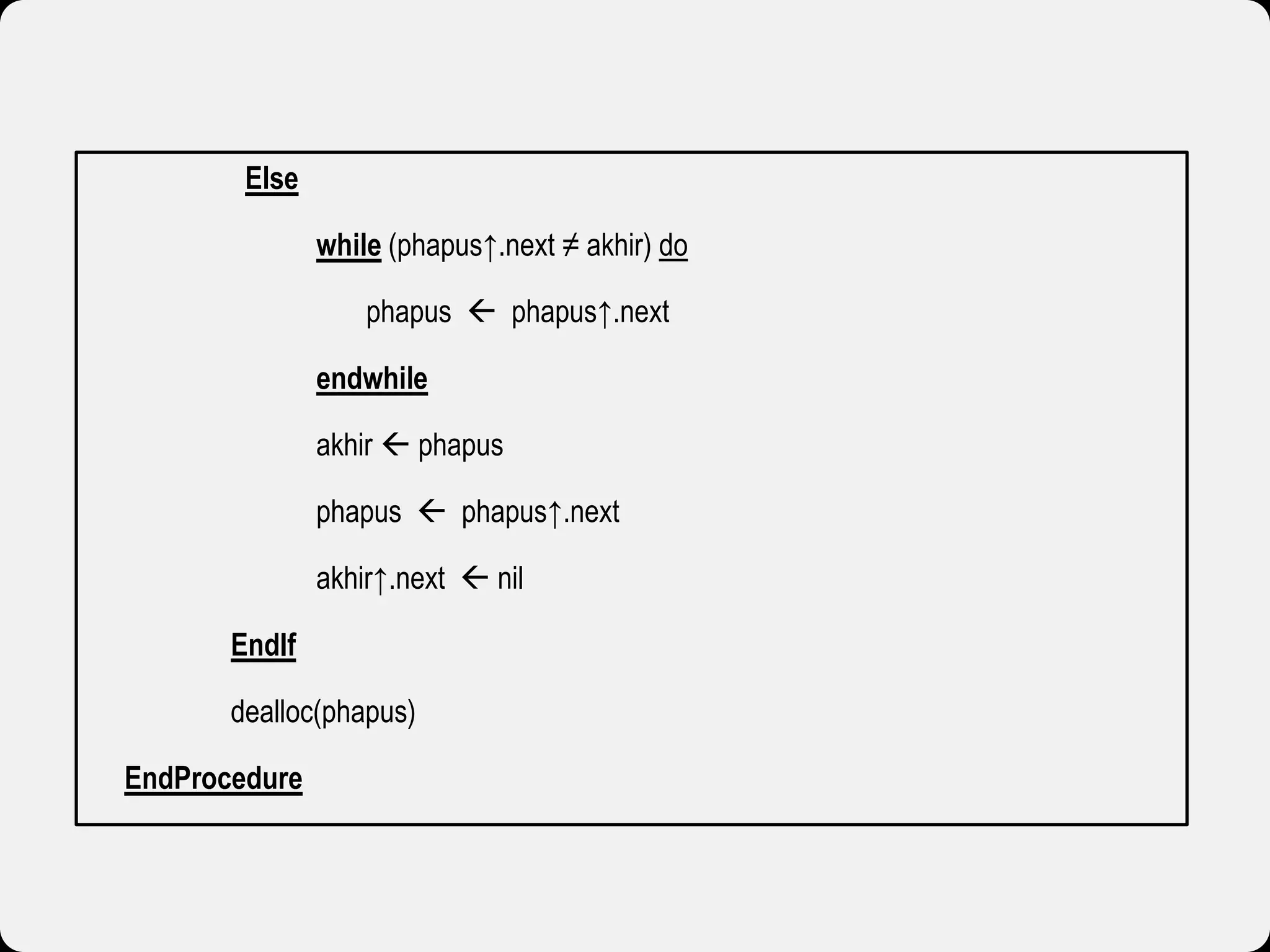
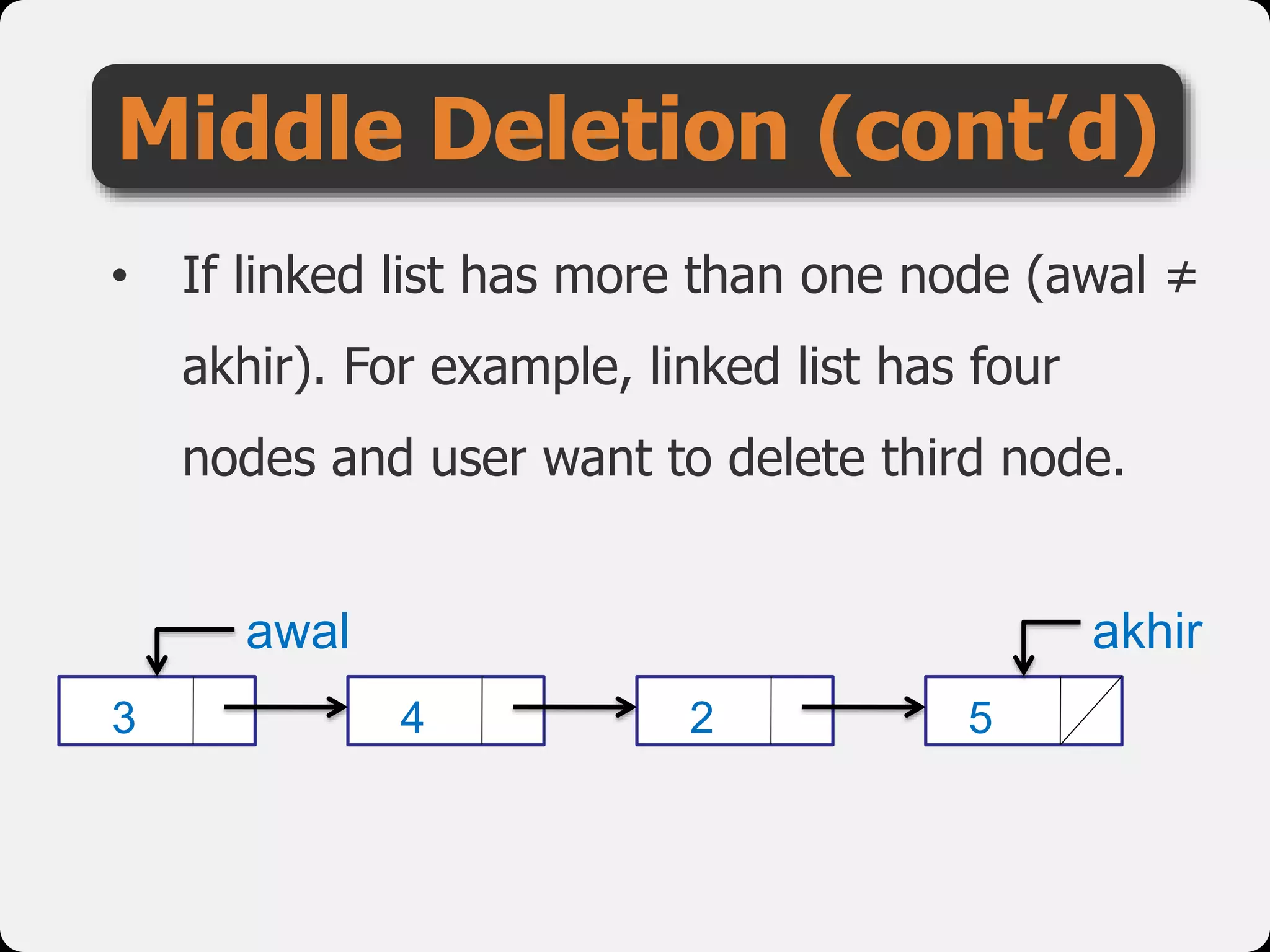
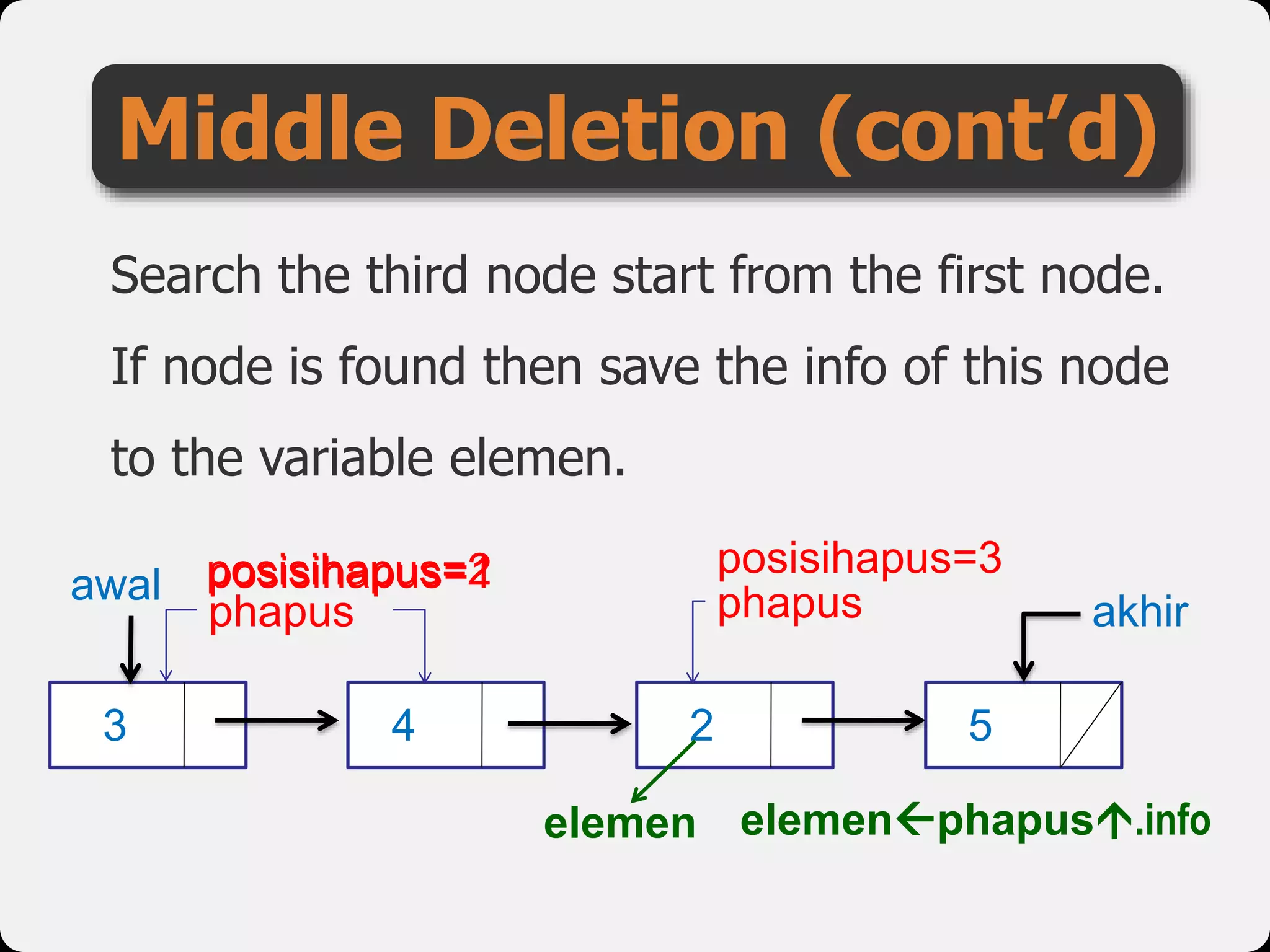
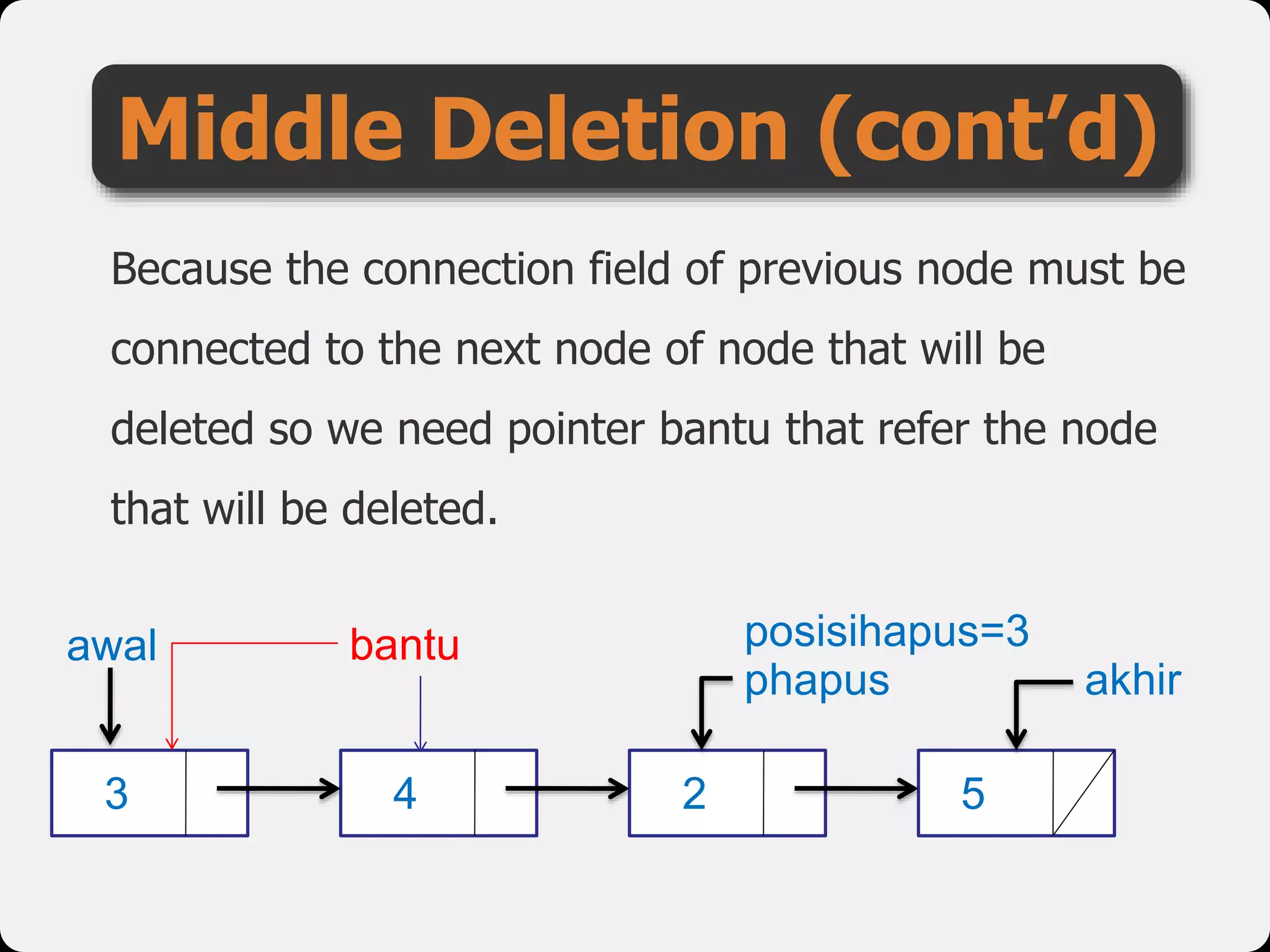
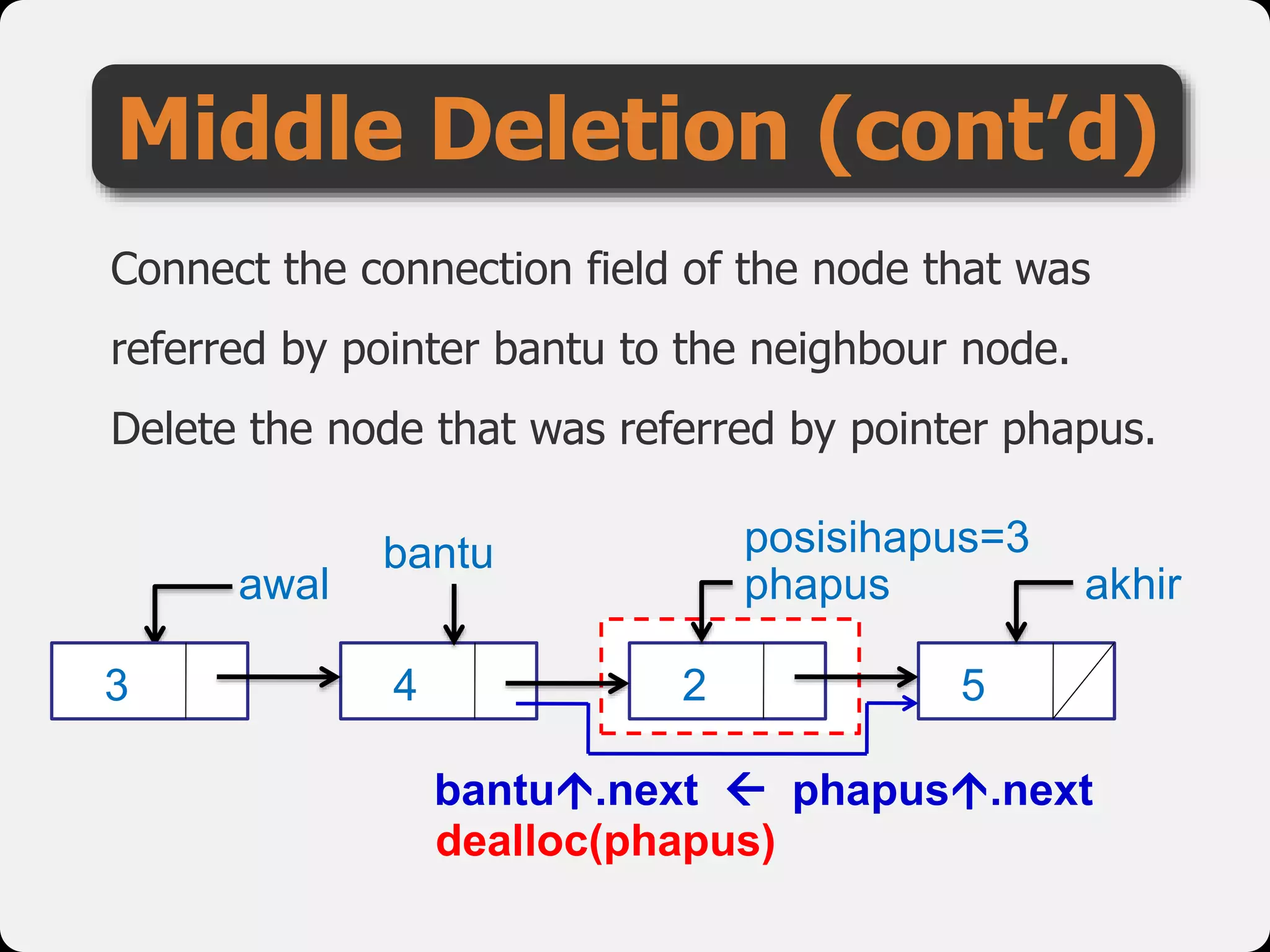
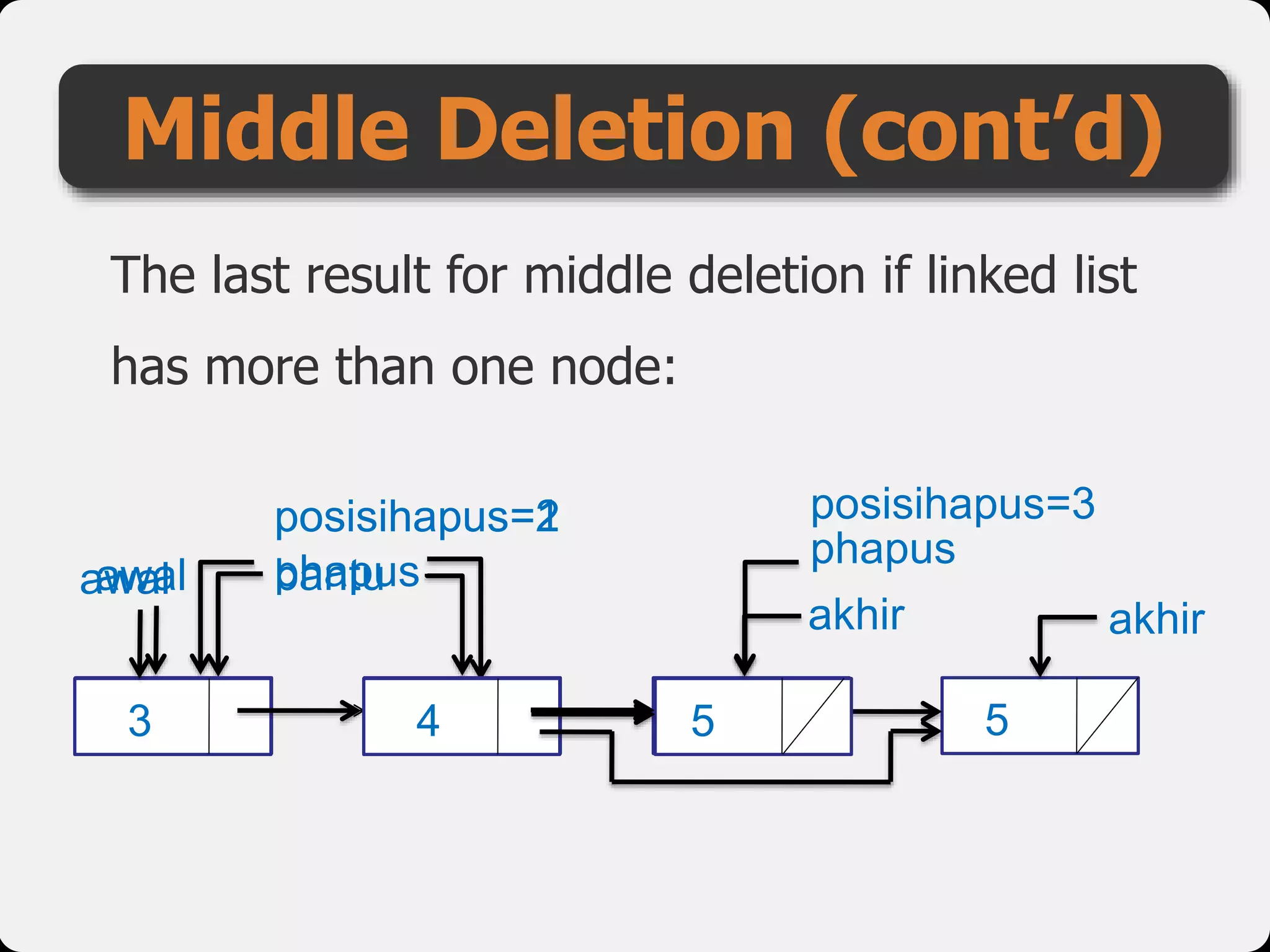
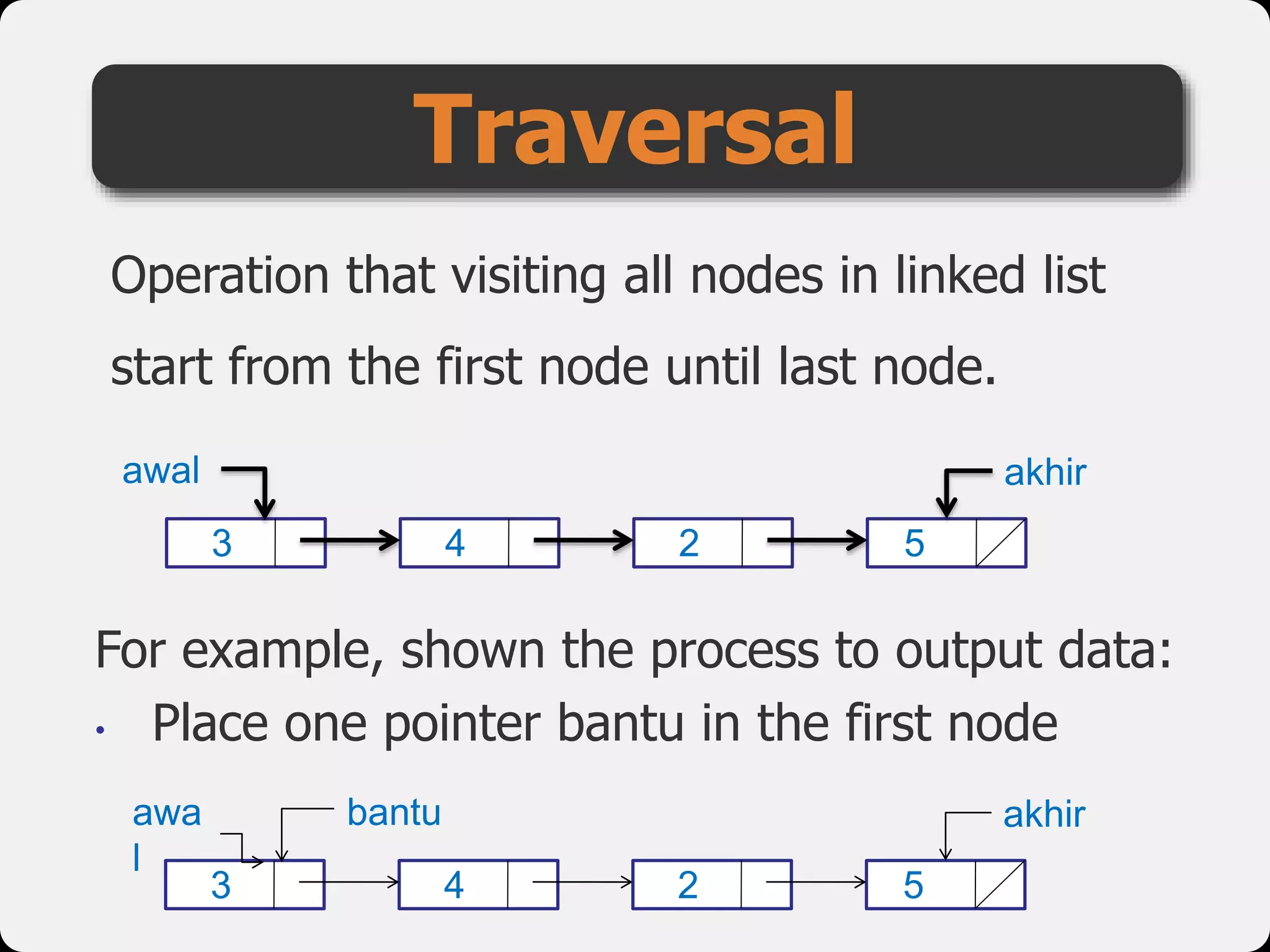
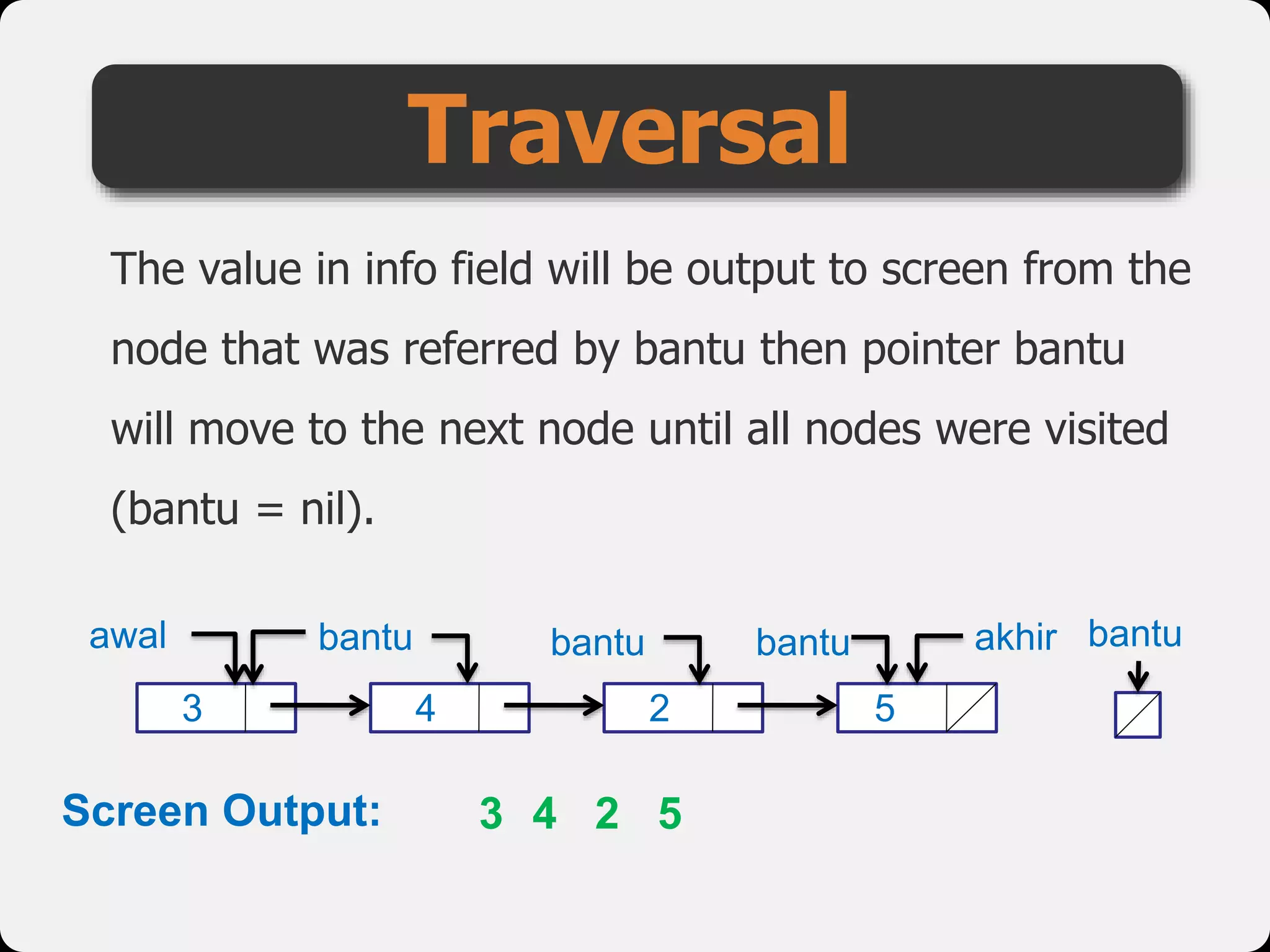
The document discusses dynamic arrays and linked lists, explaining their definitions and memory management functions such as allocation and deallocation. It also covers types of linked lists, operations such as insertion and deletion, and procedures for managing linked list nodes. Additionally, it includes examples and algorithms for various linked list operations like front, back, and middle insertions and deletions.