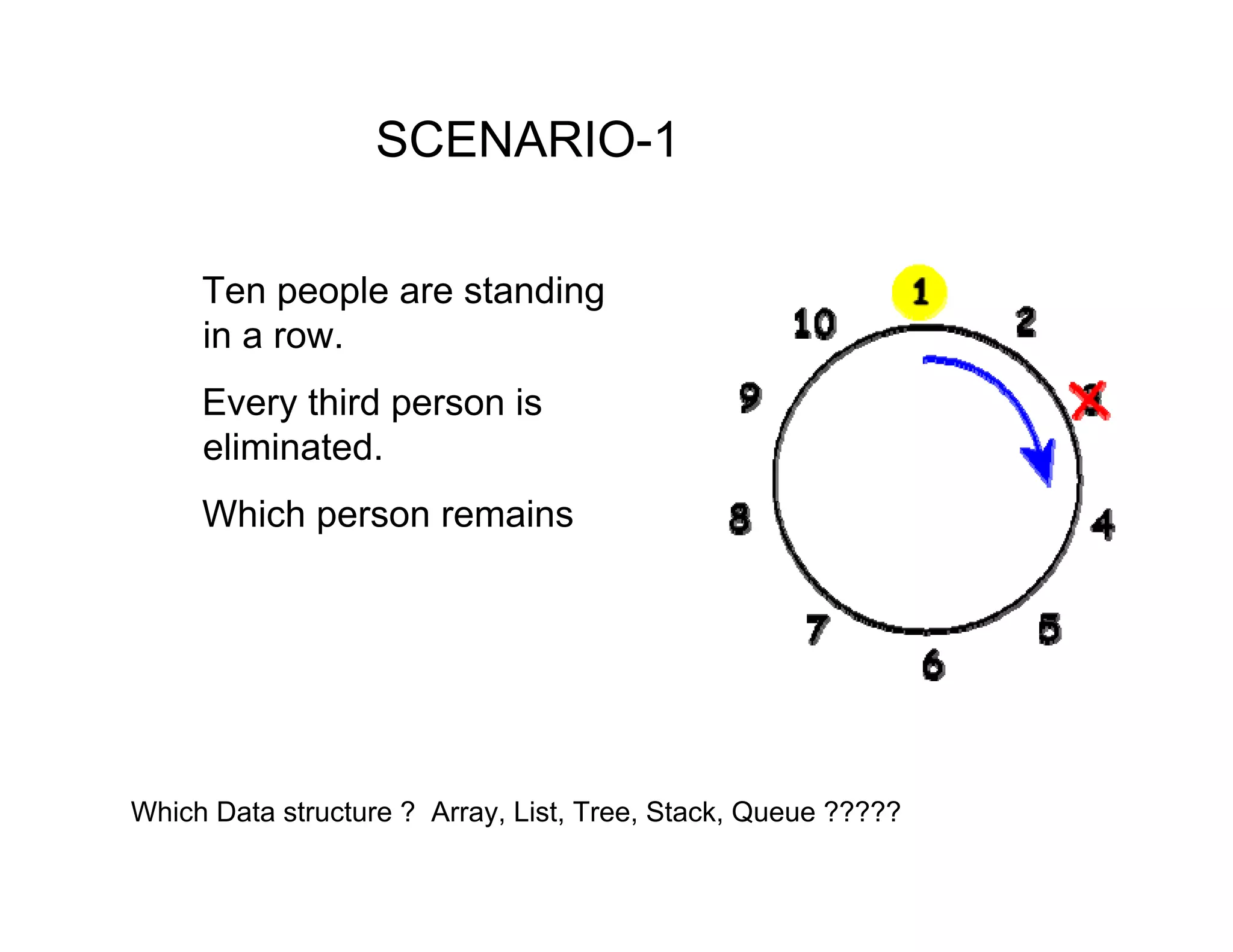
This document discusses different data structures and their uses. It describes arrays, linked lists, trees, stacks, queues, and hash tables. For each scenario presented, it asks which data structure would be best. Scenario 1 involves eliminating every third person in a row, scenario 2 displaying recent missed calls, scenario 3 maintaining a student database with various operations, and scenario 4 prioritizing people in an office. The document provides examples and explanations of different data structures and their pros and cons for accessing, inserting, and deleting data. It emphasizes choosing the right data structure based on the needed operations.






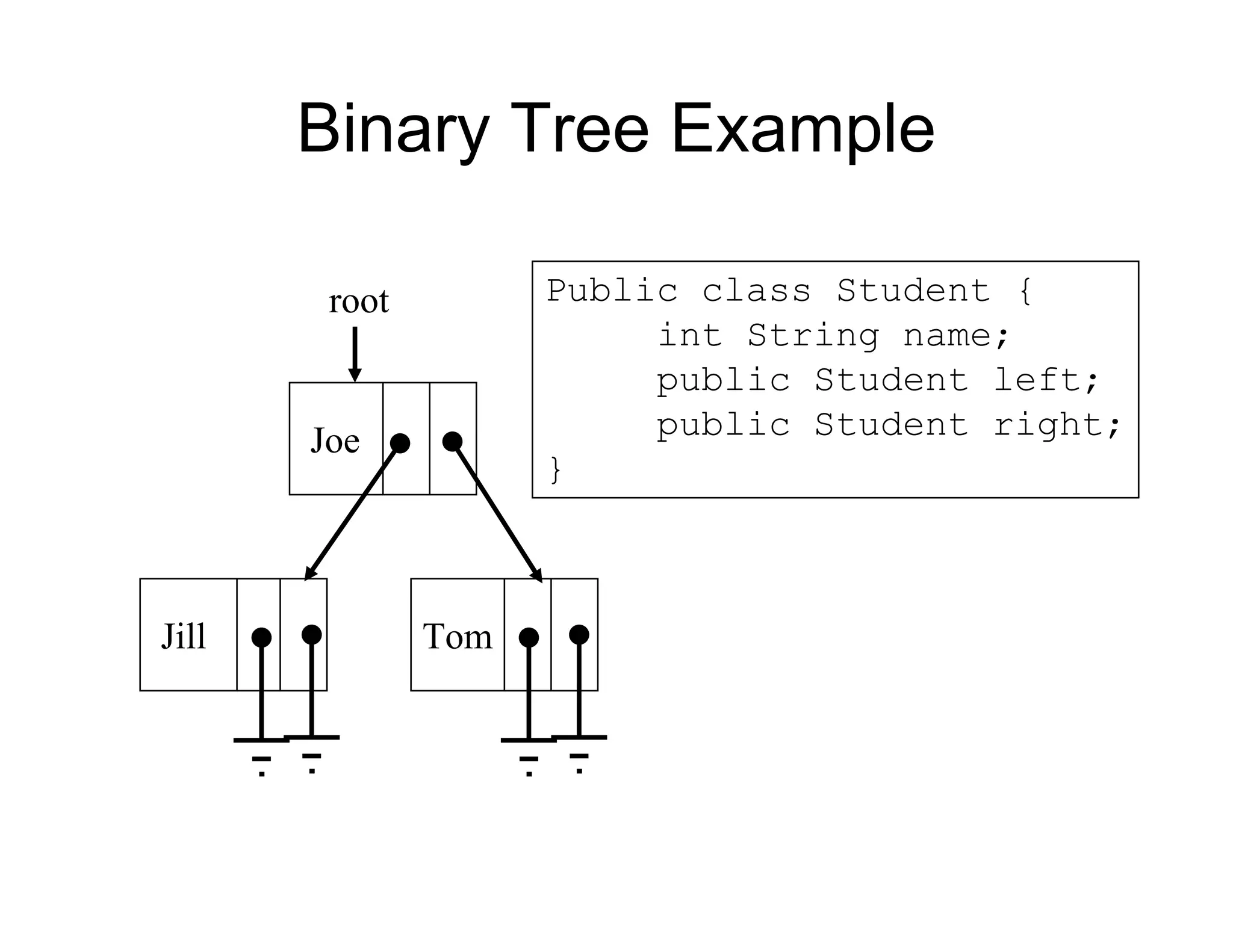
![Linked List Example
Jill Joe Tom
first
Public static main (String[] argv) {
Student first;
…
}
Public class Student {
String name;
public Student next;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructures-130922101455-phpapp01/75/Data-structures-introduction-9-2048.jpg)