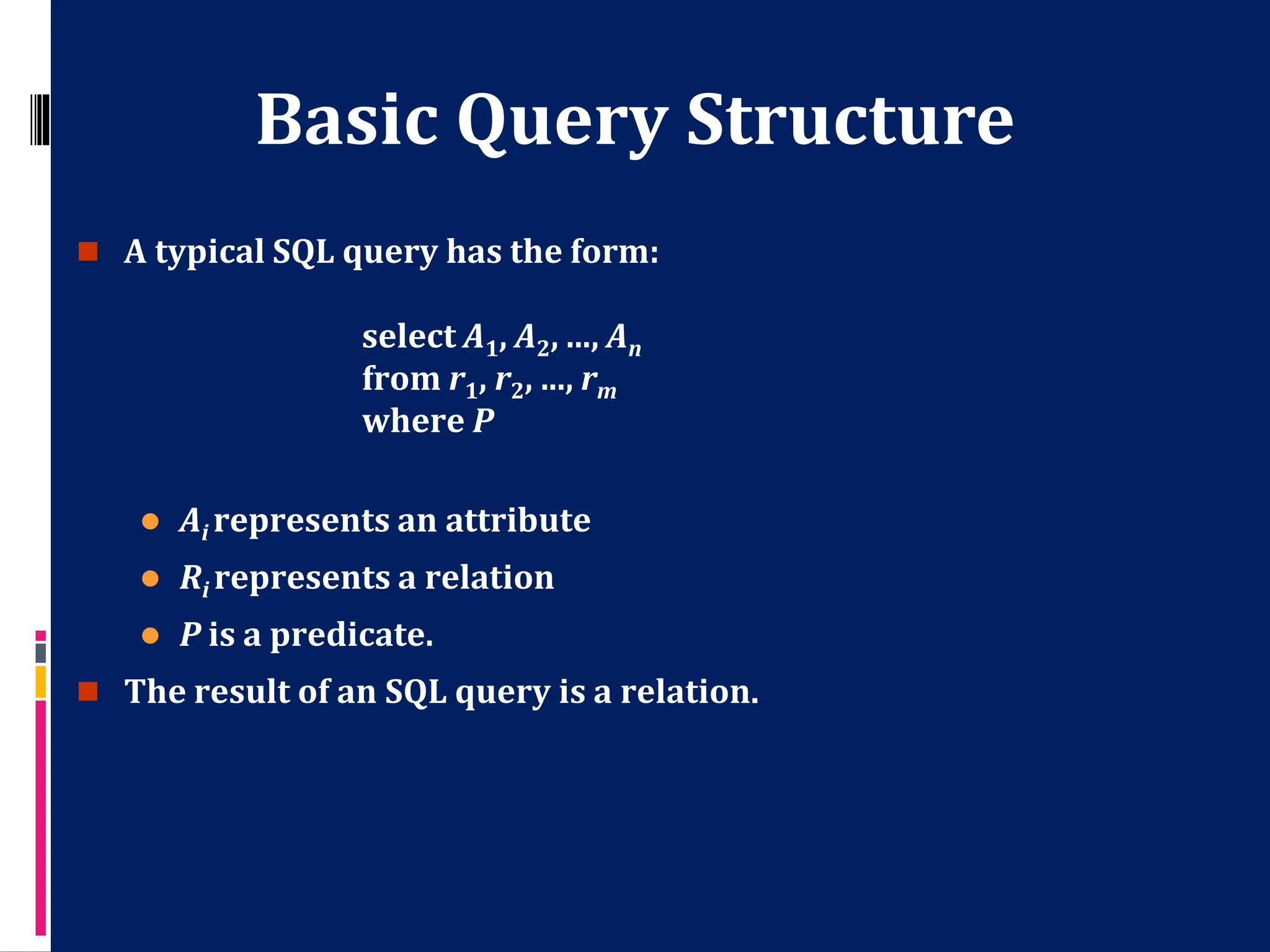
This document provides an overview of the basic structure of SQL queries. It discusses the main components of an SQL query, including the SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses. It also explains some basic SQL commands like CREATE, ALTER, DROP, SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE. Examples are provided to illustrate how to retrieve data from one or more tables and apply selection predicates to filter results.