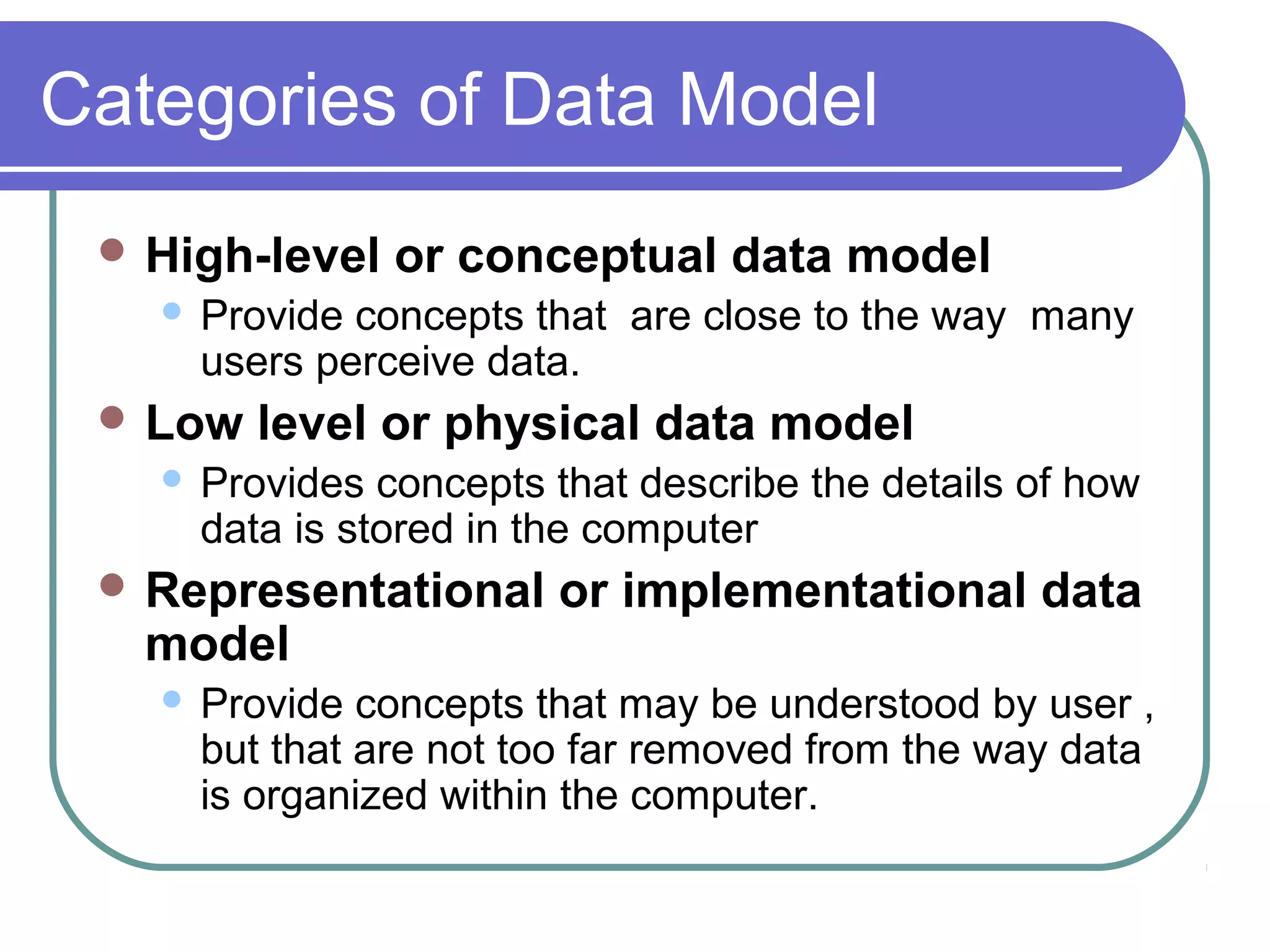
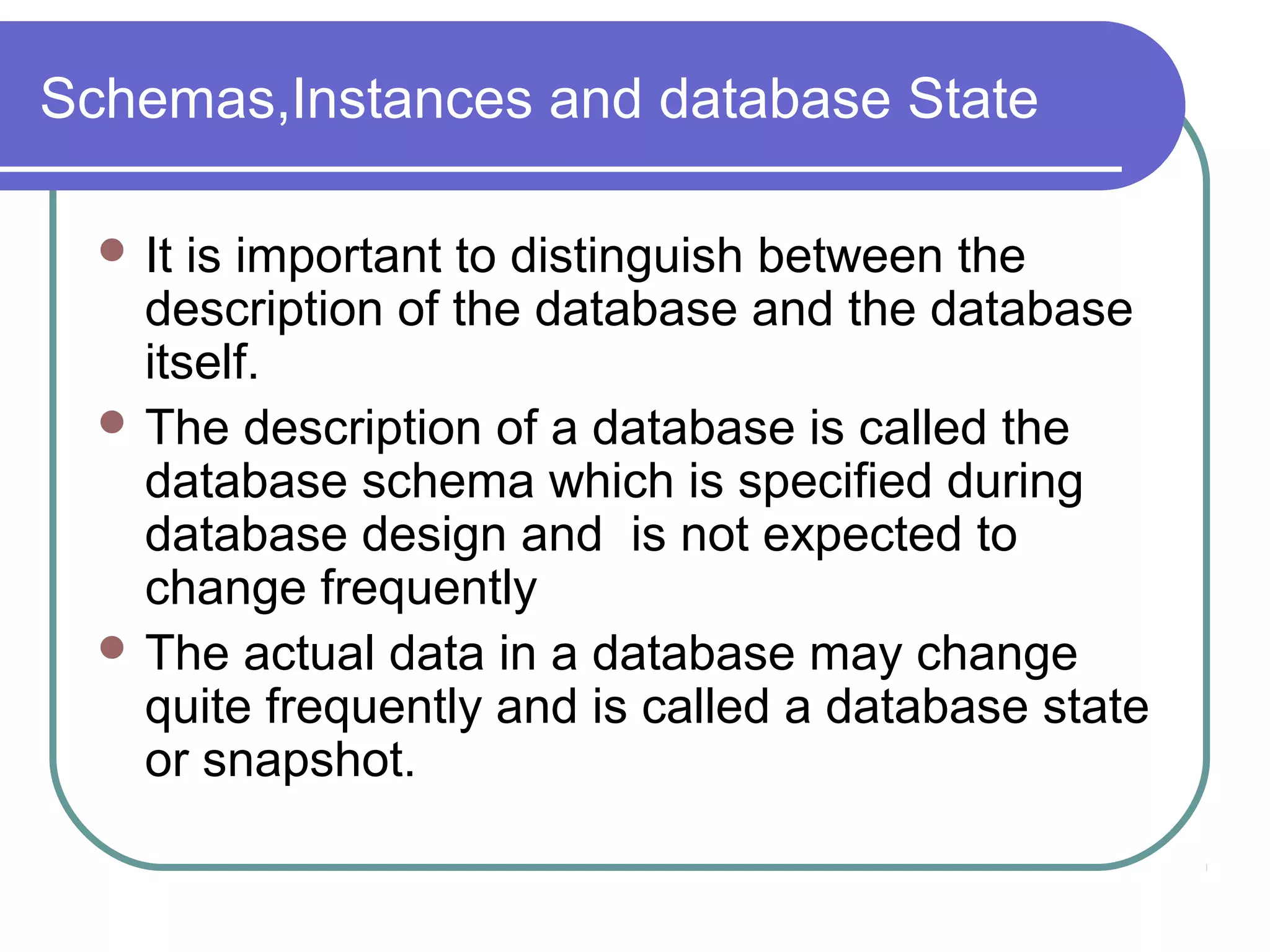
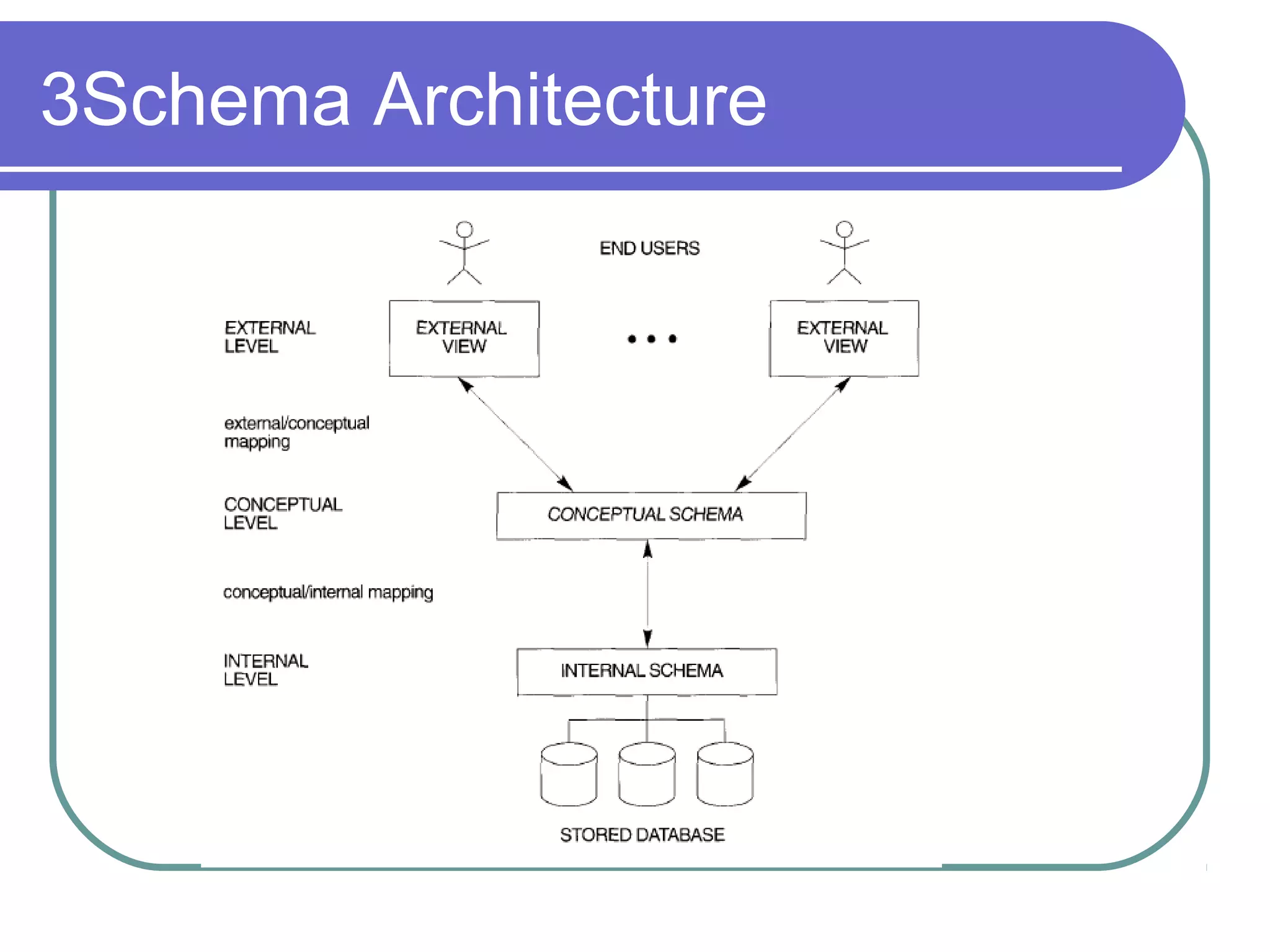
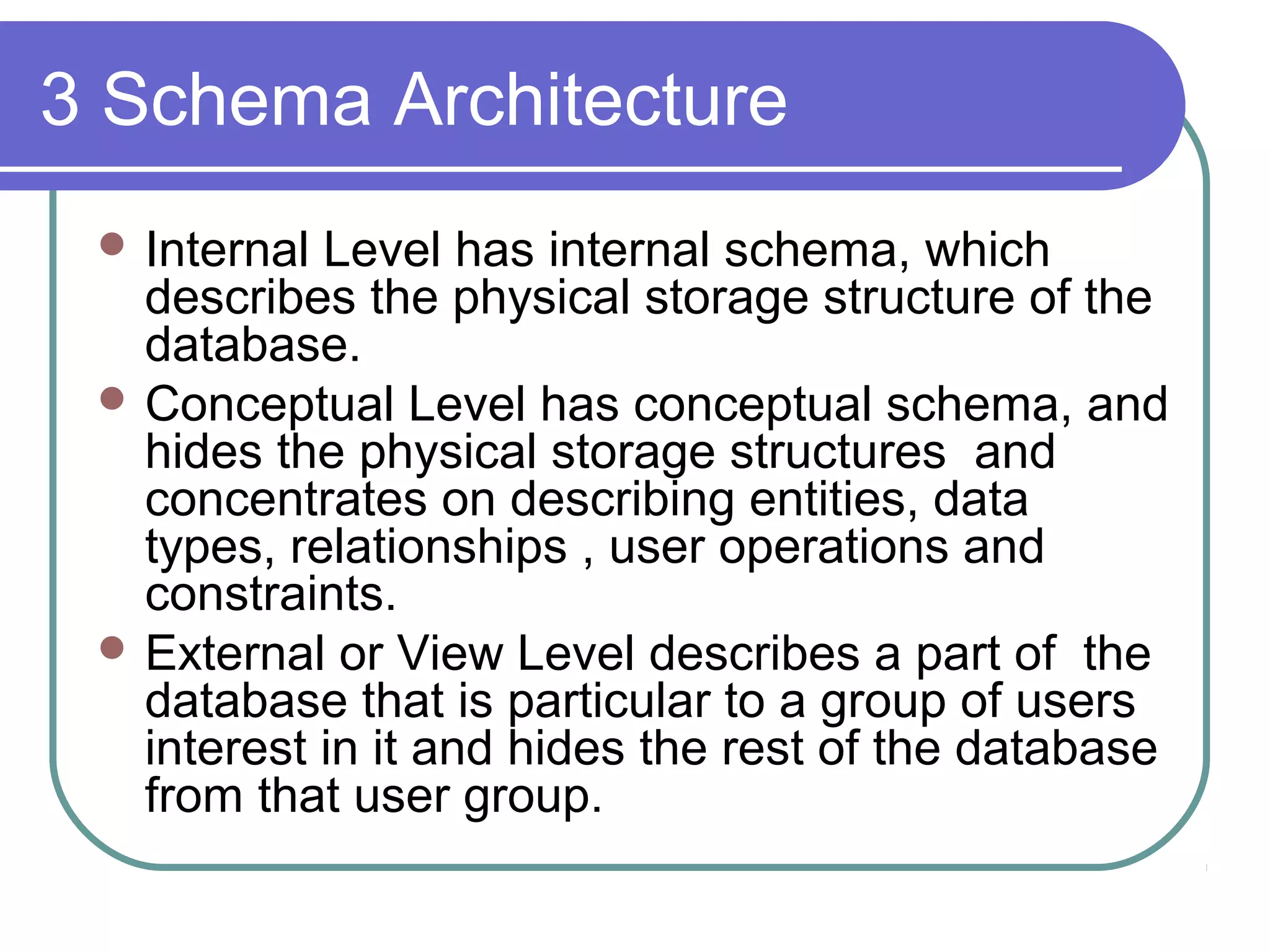
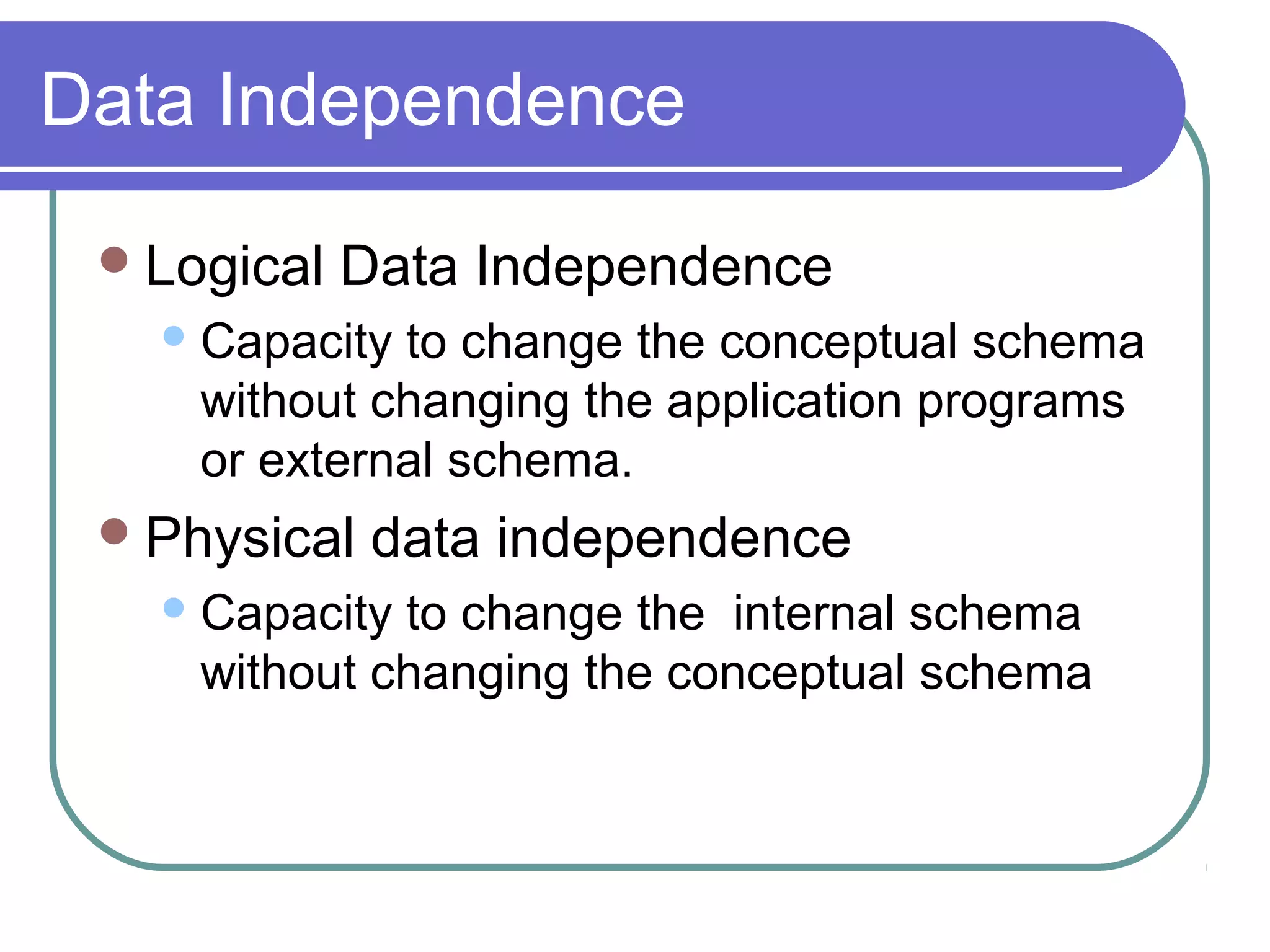
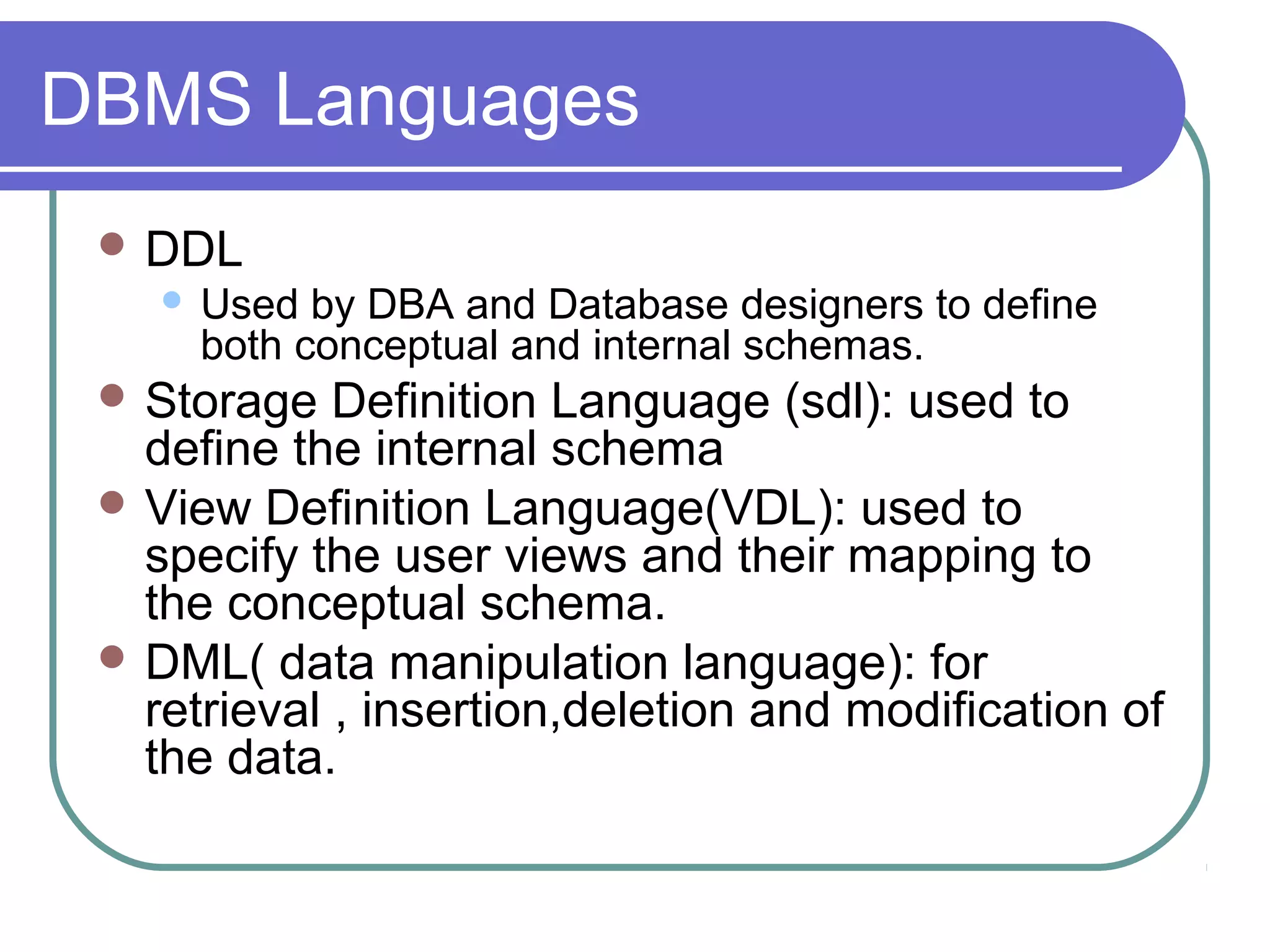
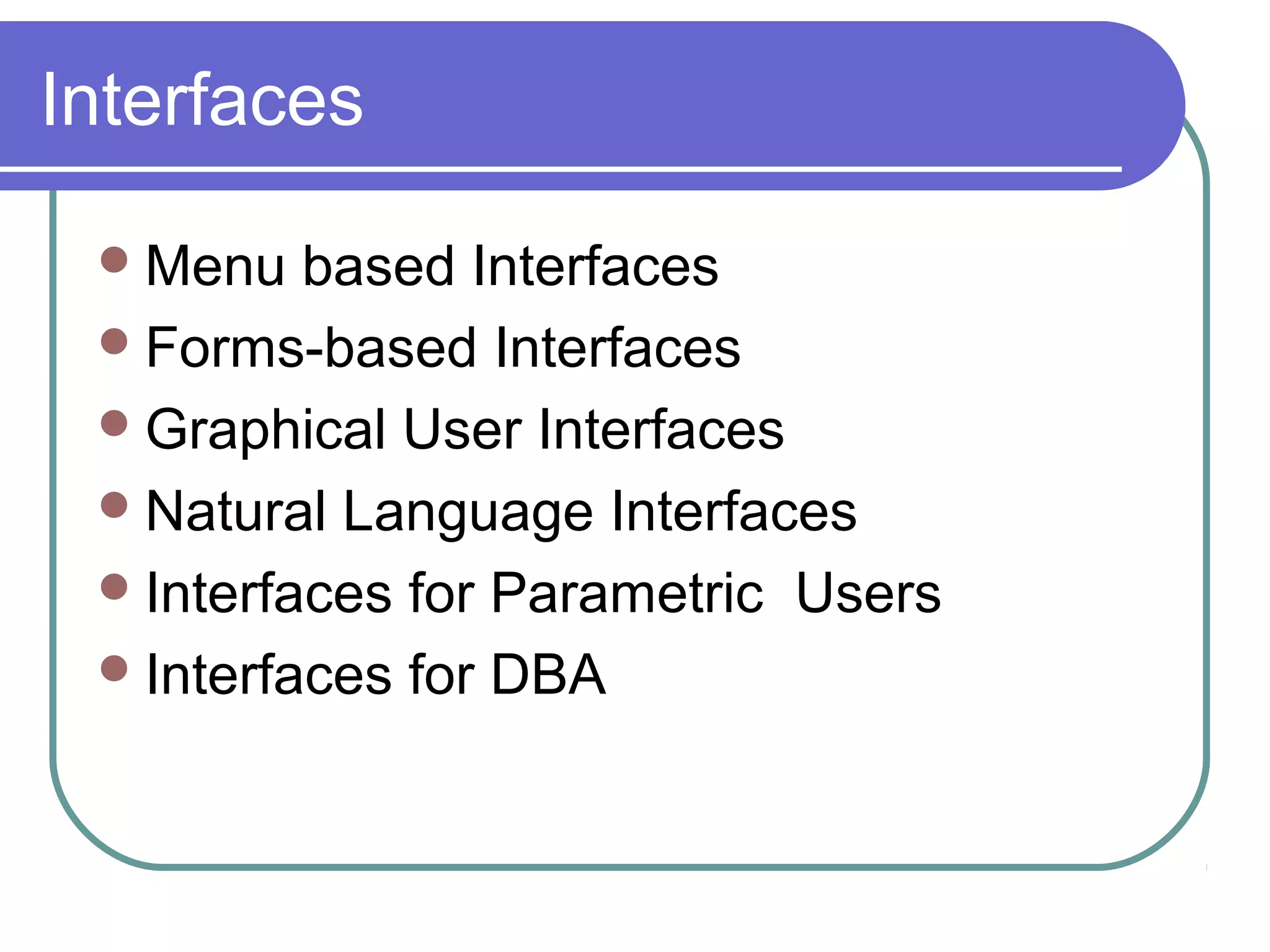
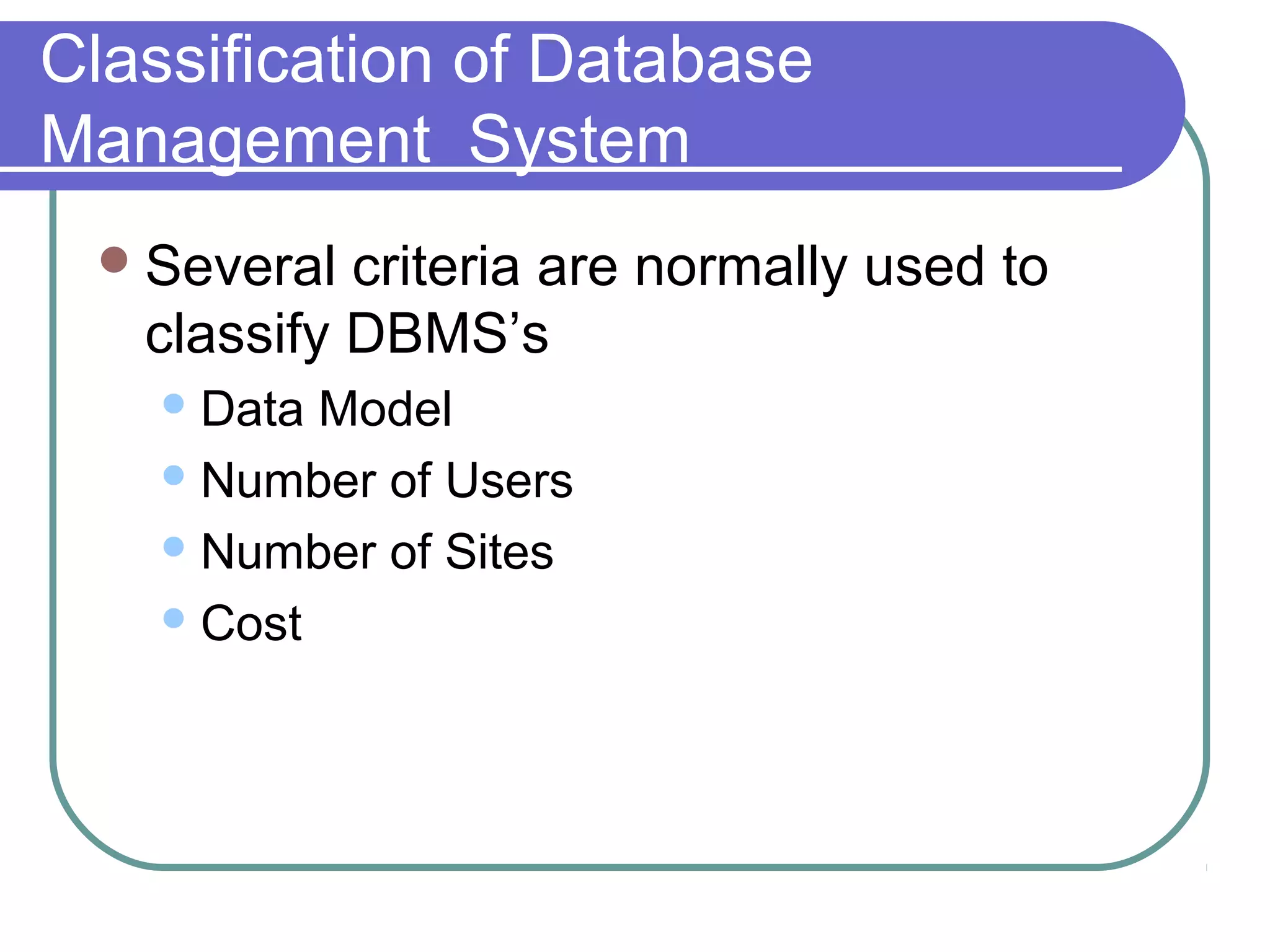
This document discusses database system concepts and architecture. It covers data models, schemas, and instances. There are three categories of data models: high-level conceptual models, low-level physical models, and representational models. Schemas describe the database design while instances represent the actual data. The three schema architecture separates the internal, conceptual, and external schemas. Database languages include DDL for design, DML for manipulation, and others. DBMSs provide various interfaces and operate within a database system environment.