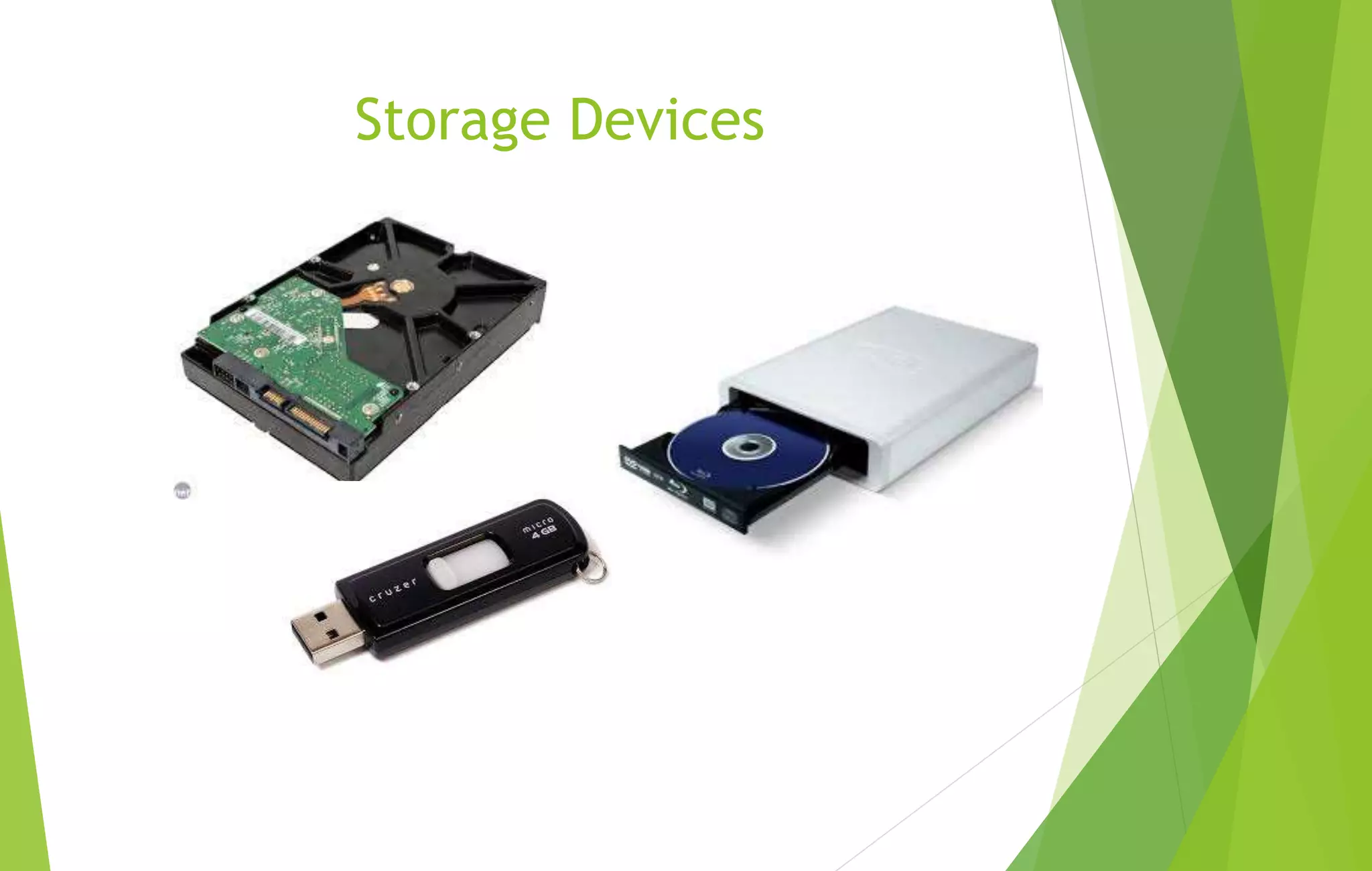
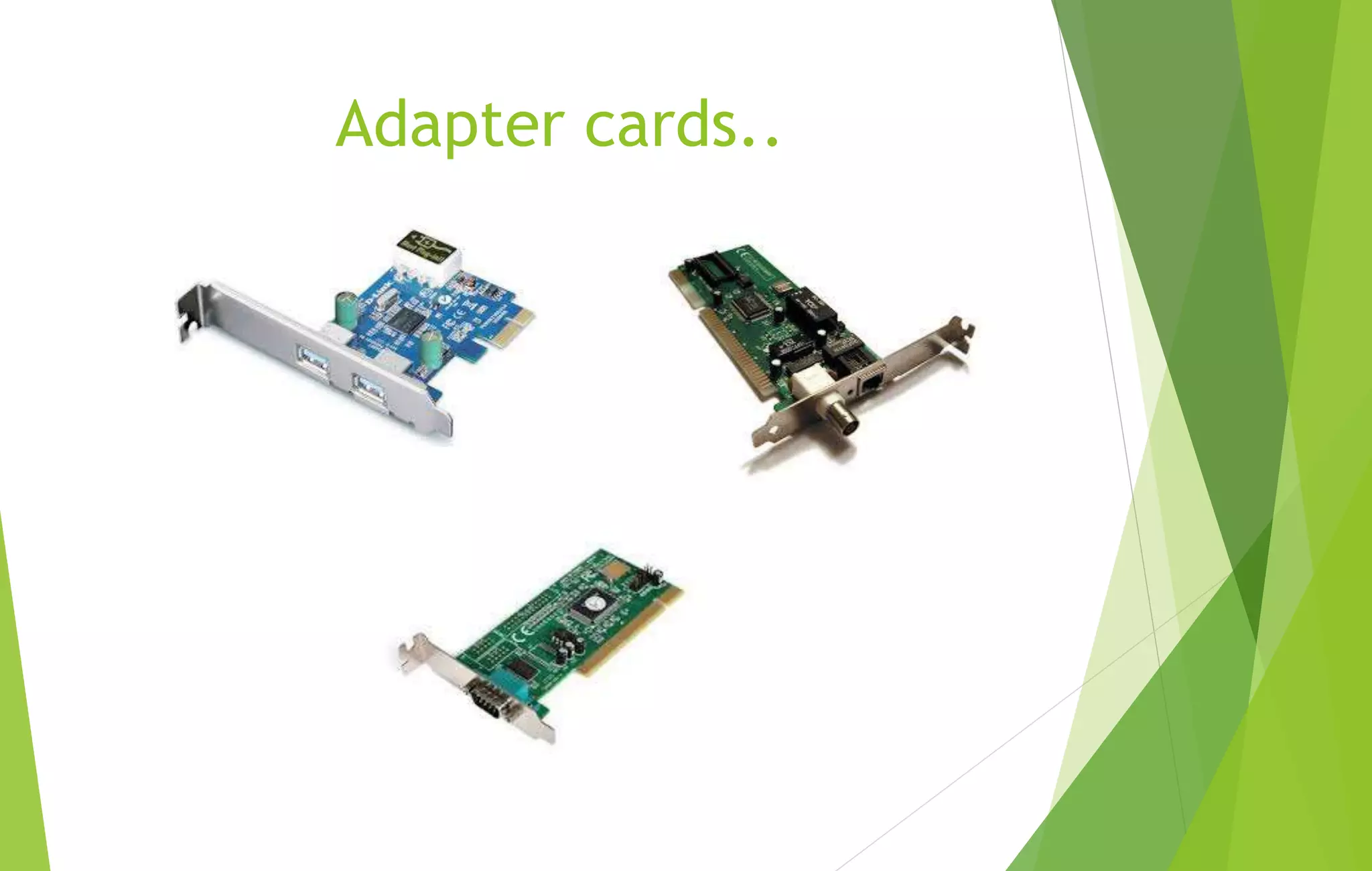
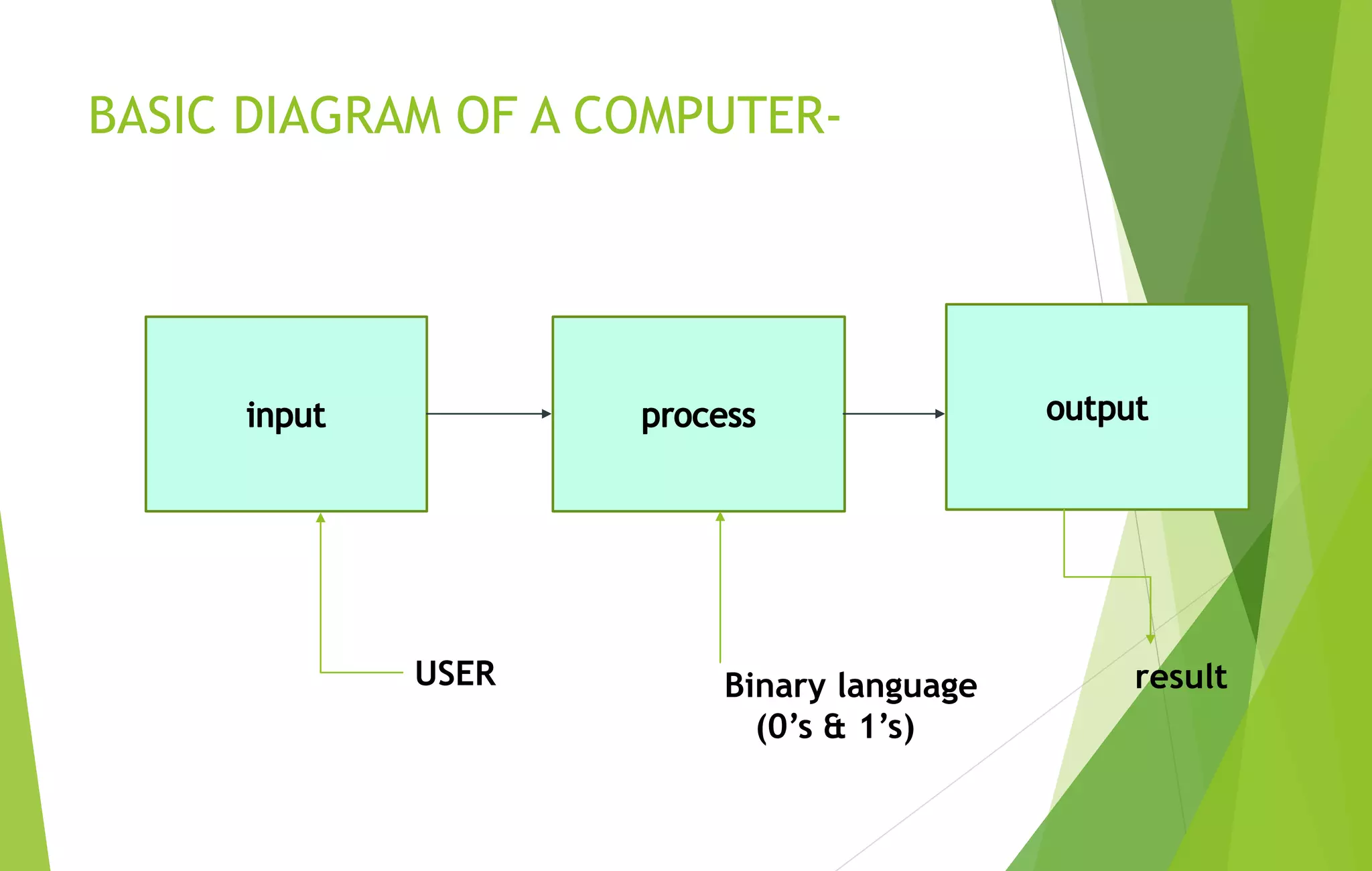
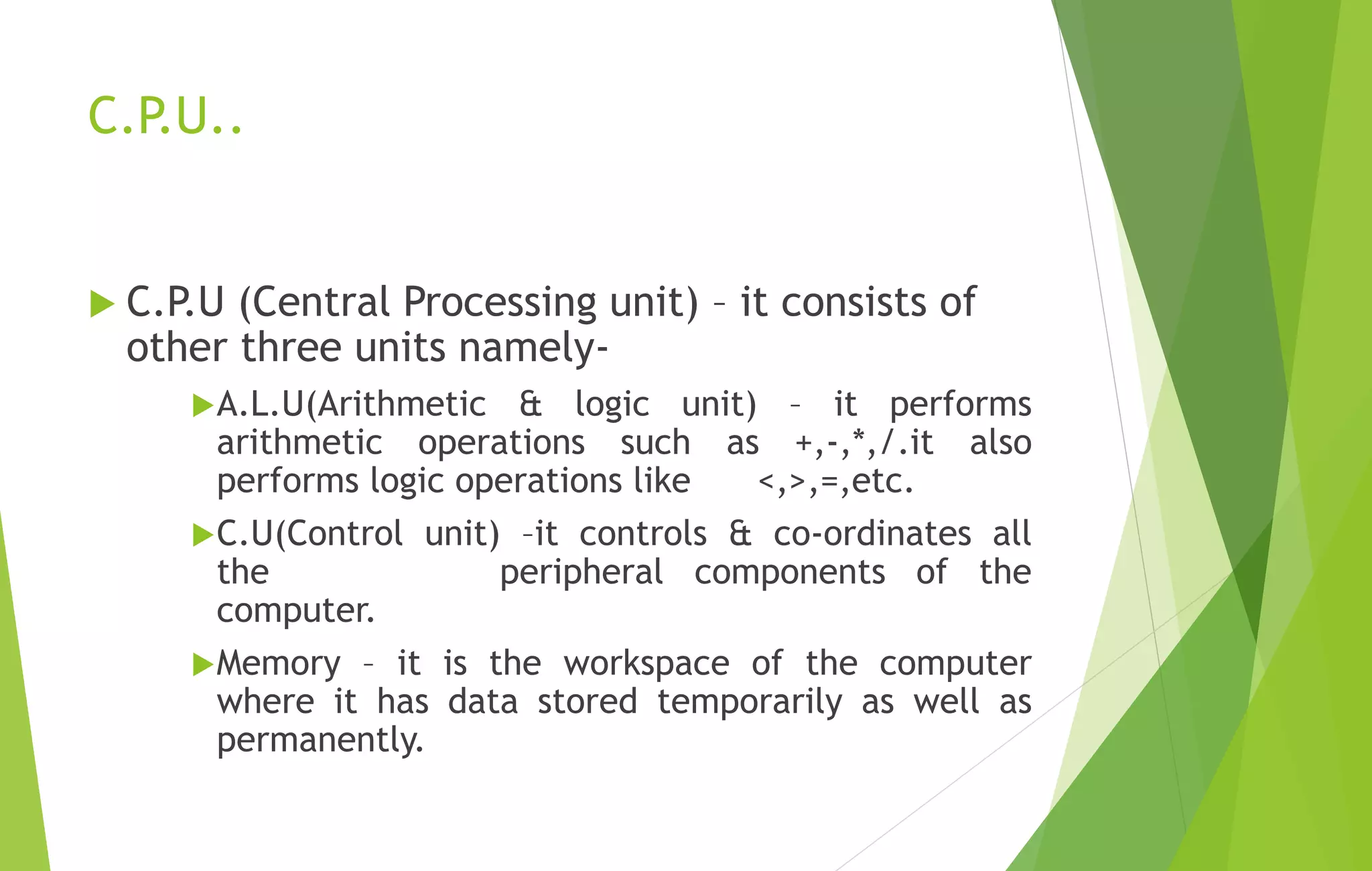
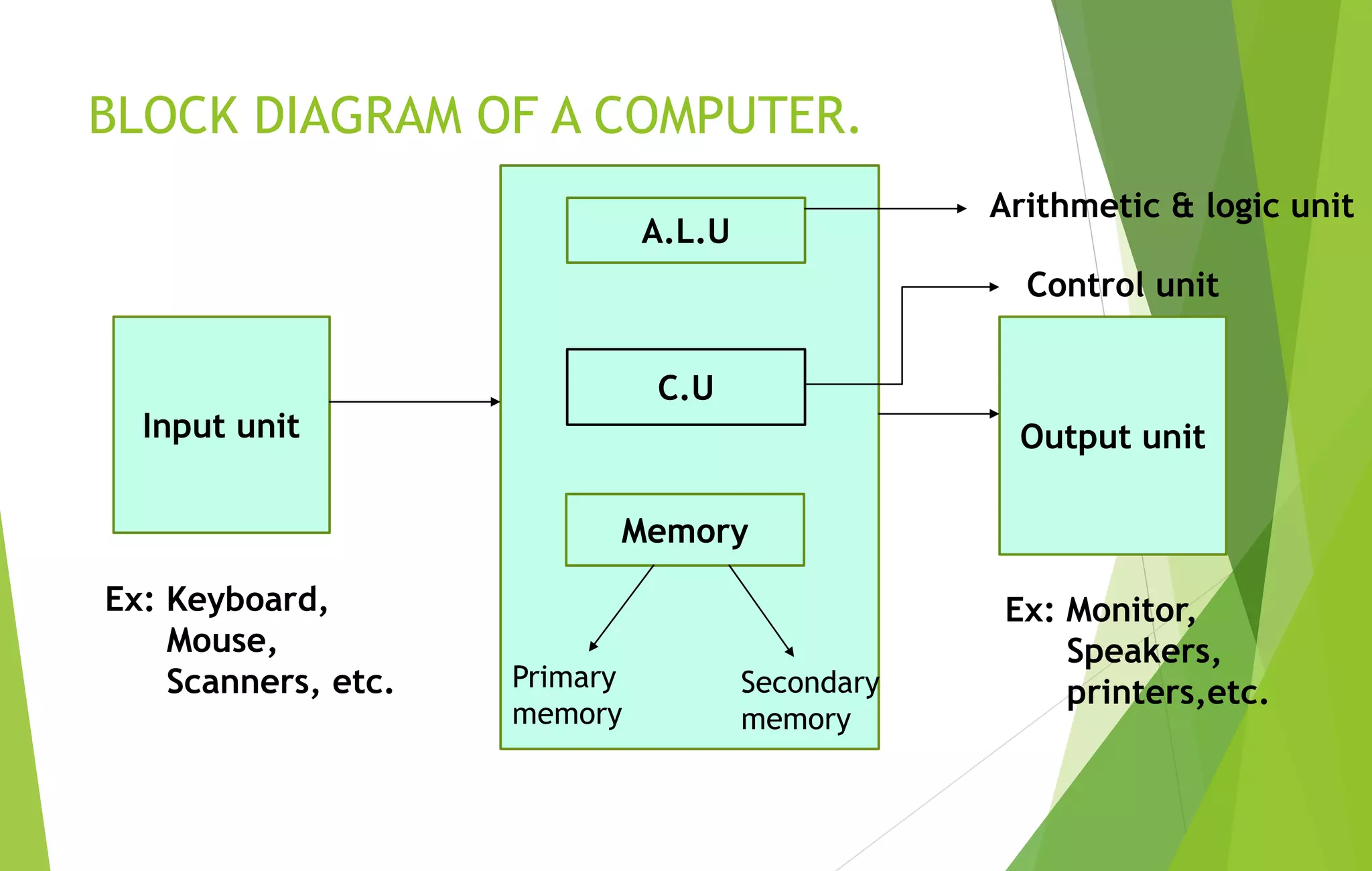
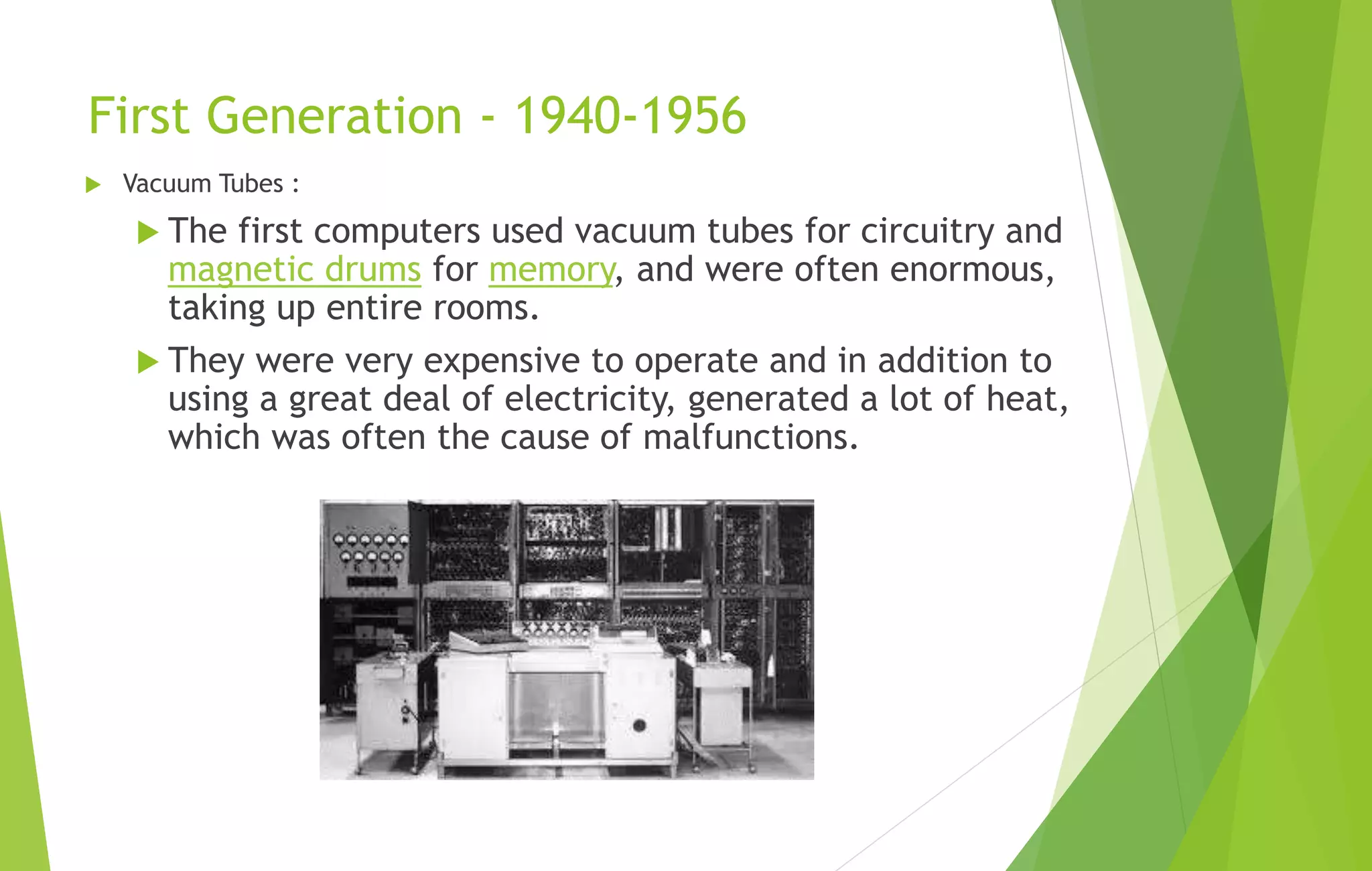
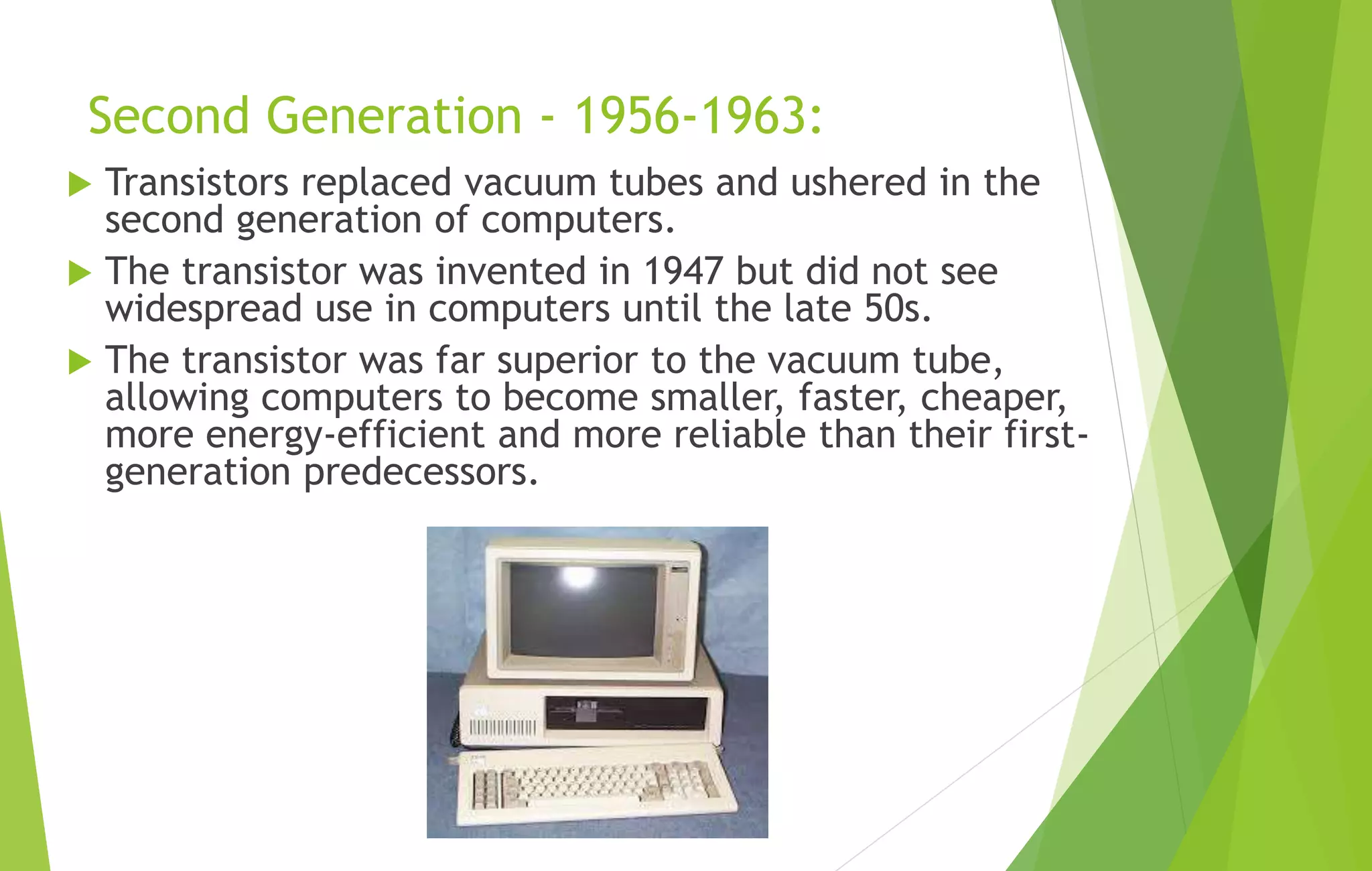
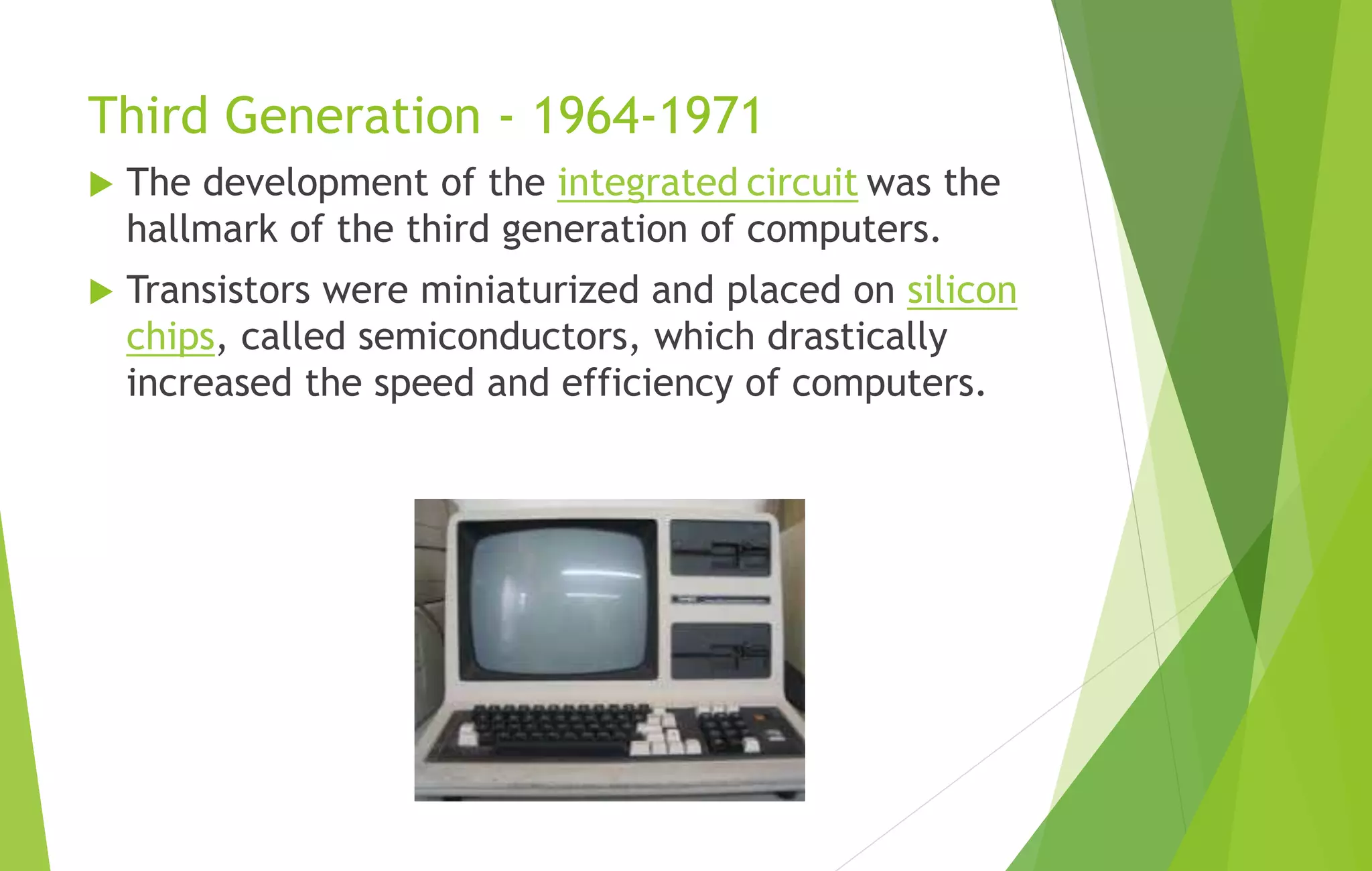
This document provides an overview of computer basics, including definitions of a computer, its components, and the history of computers. It discusses how a computer accepts data as input, processes it, and provides output. The main components are the input, output, and central processing units. It covers the five generations of computers from the first generation using vacuum tubes to the current fifth generation aiming for natural language processing. Different types of computers like analog and digital are also defined. The document concludes by identifying the common hardware components of a modern computer like the keyboard, mouse, power supply, motherboard, processor, memory, storage, display, and ports.