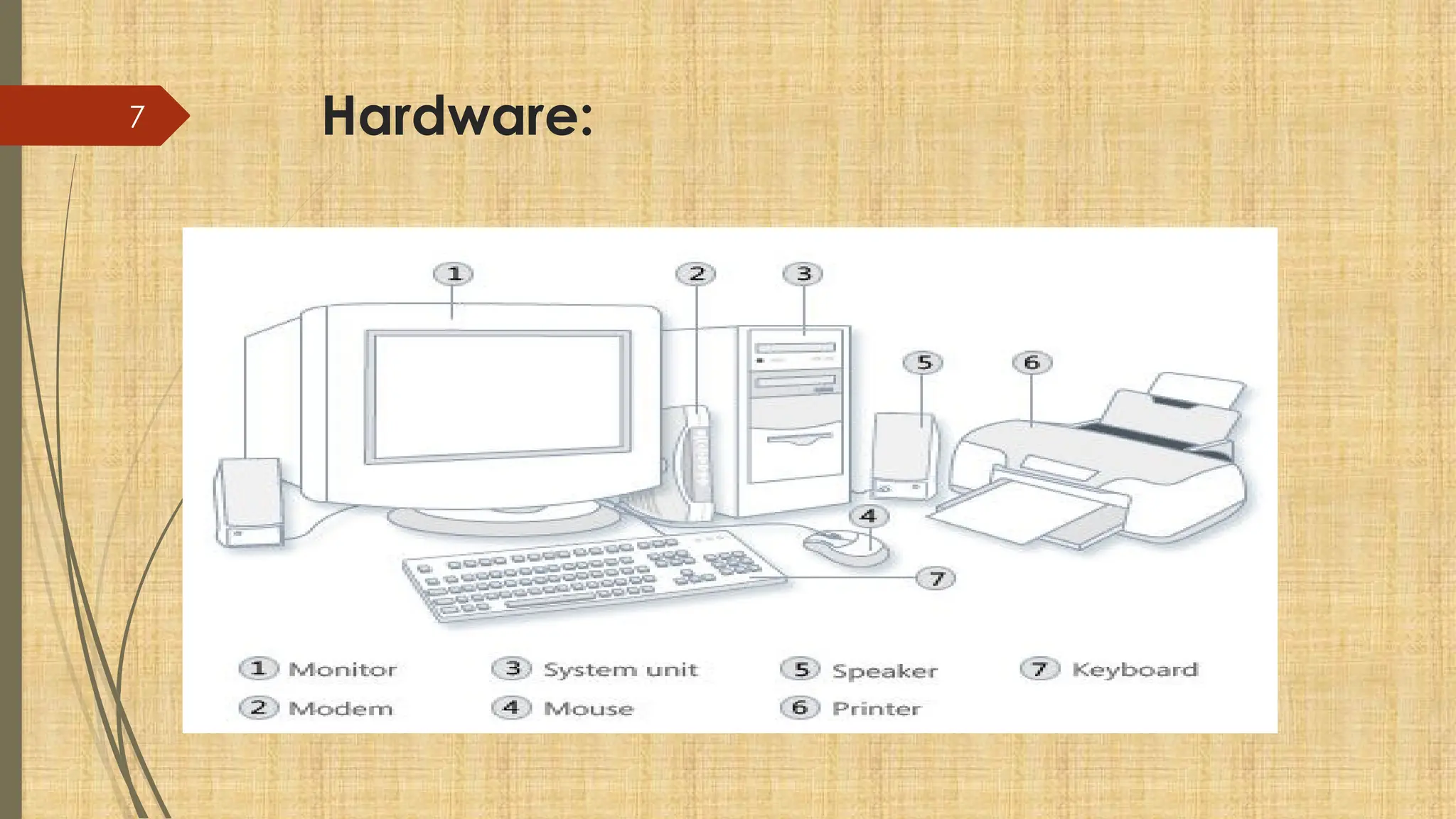
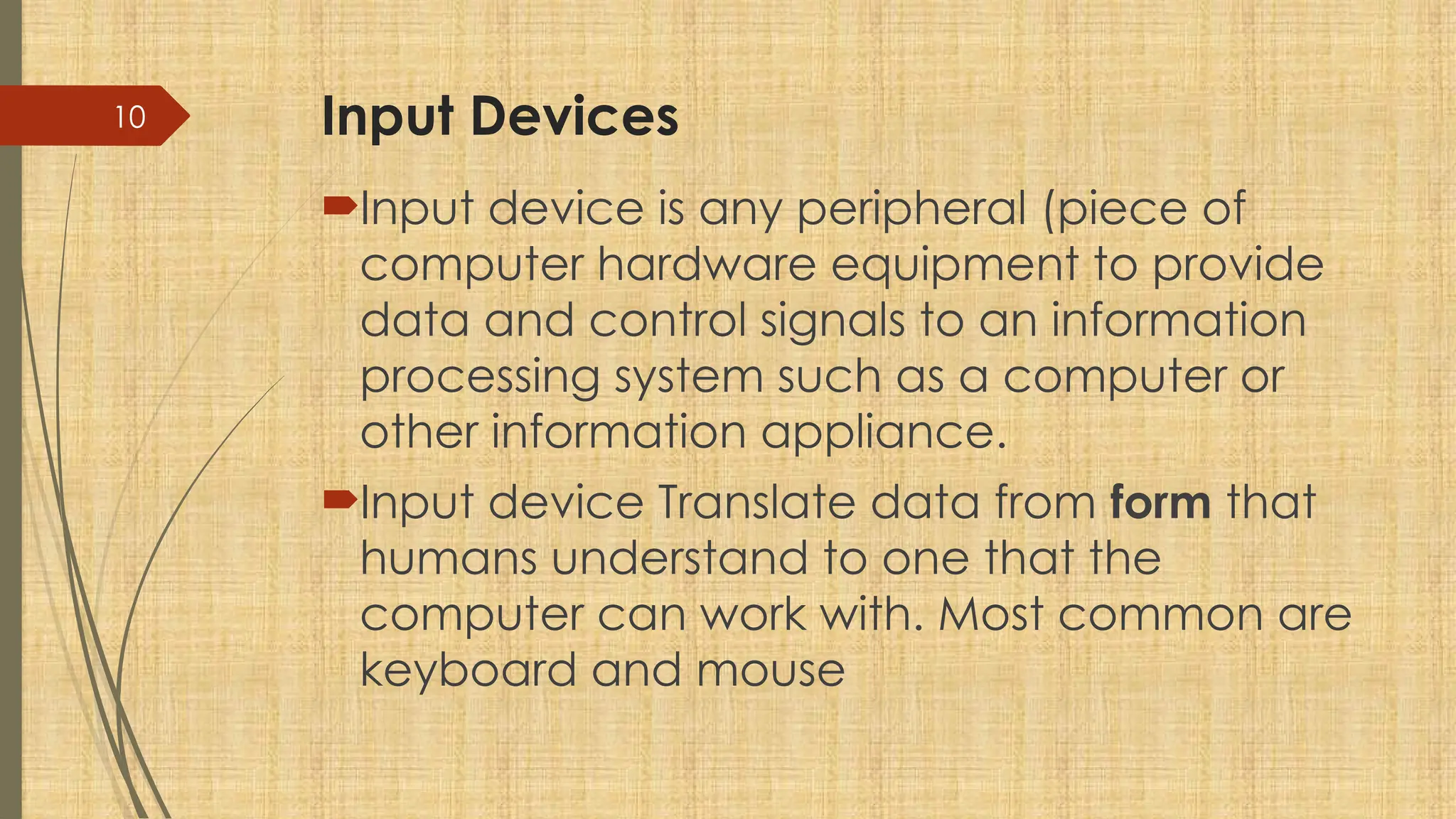
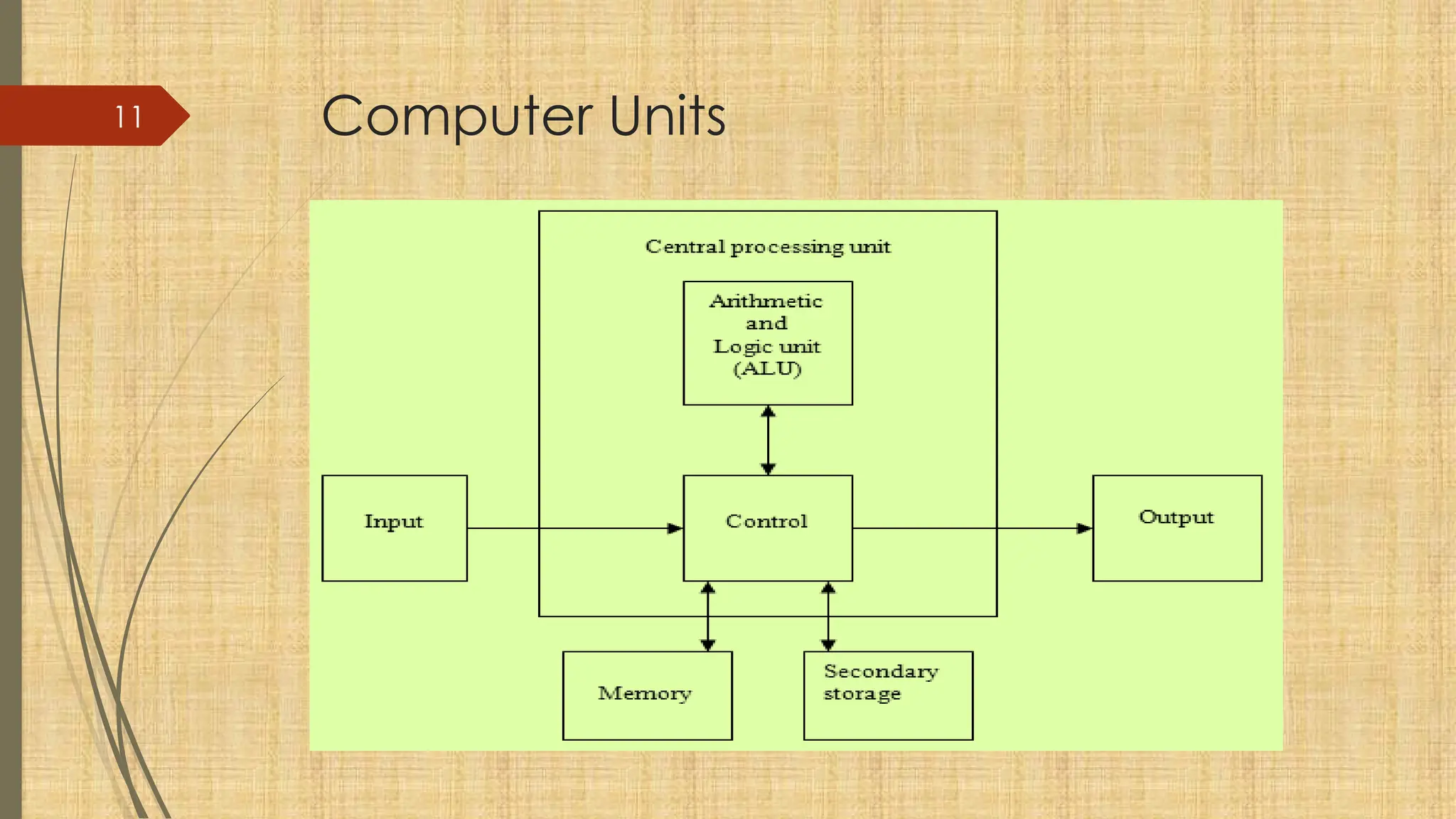
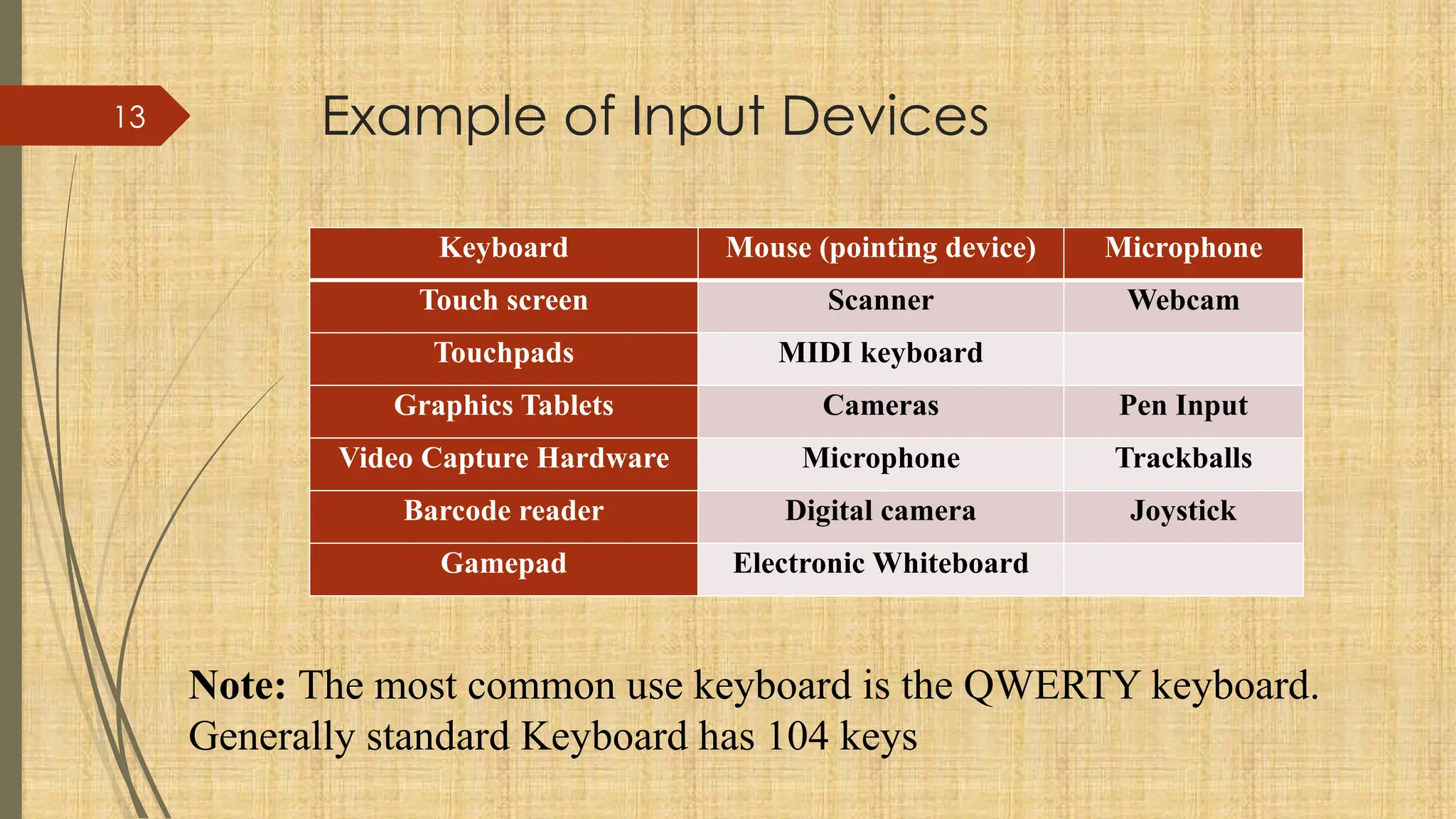
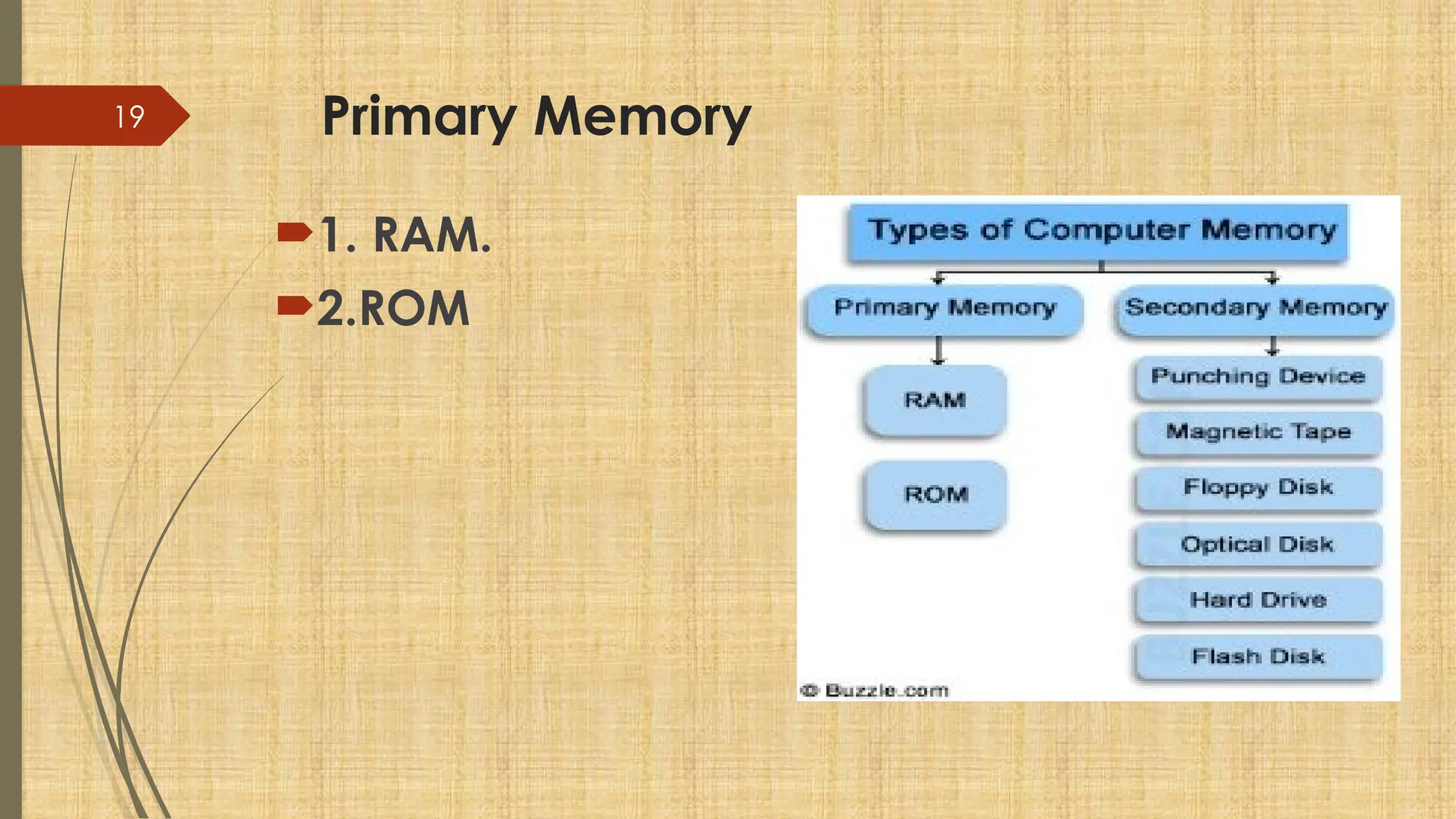
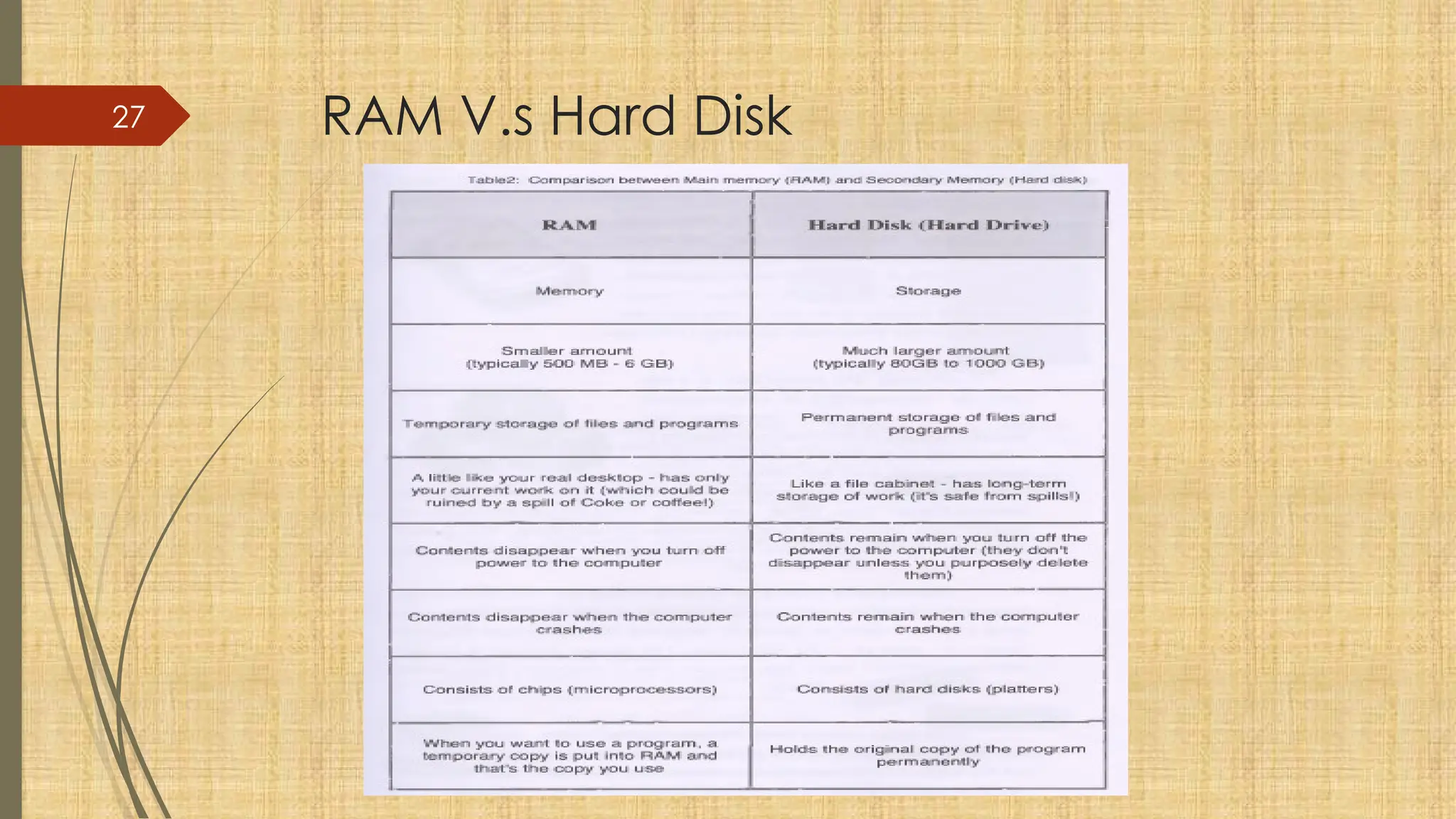
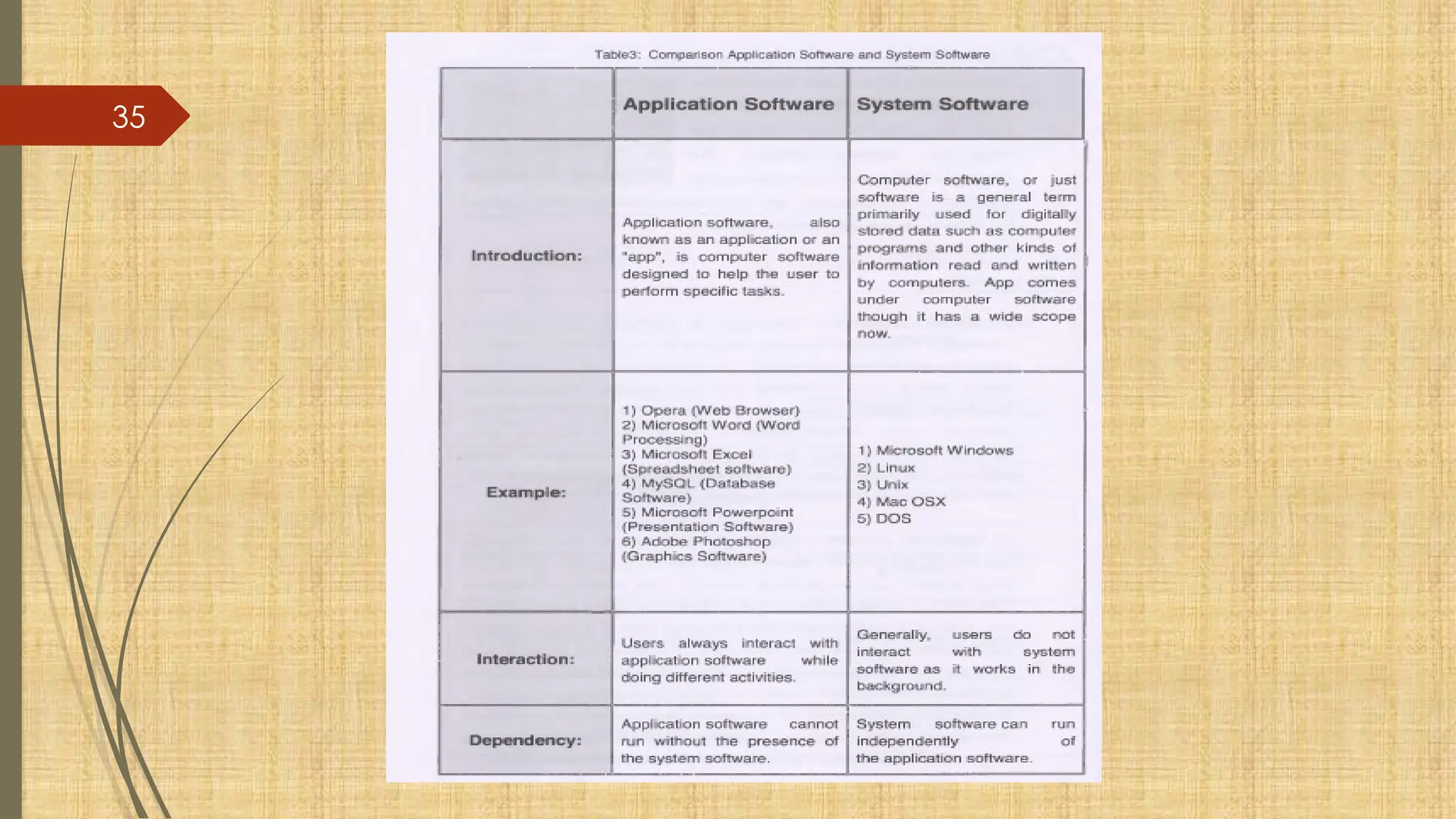
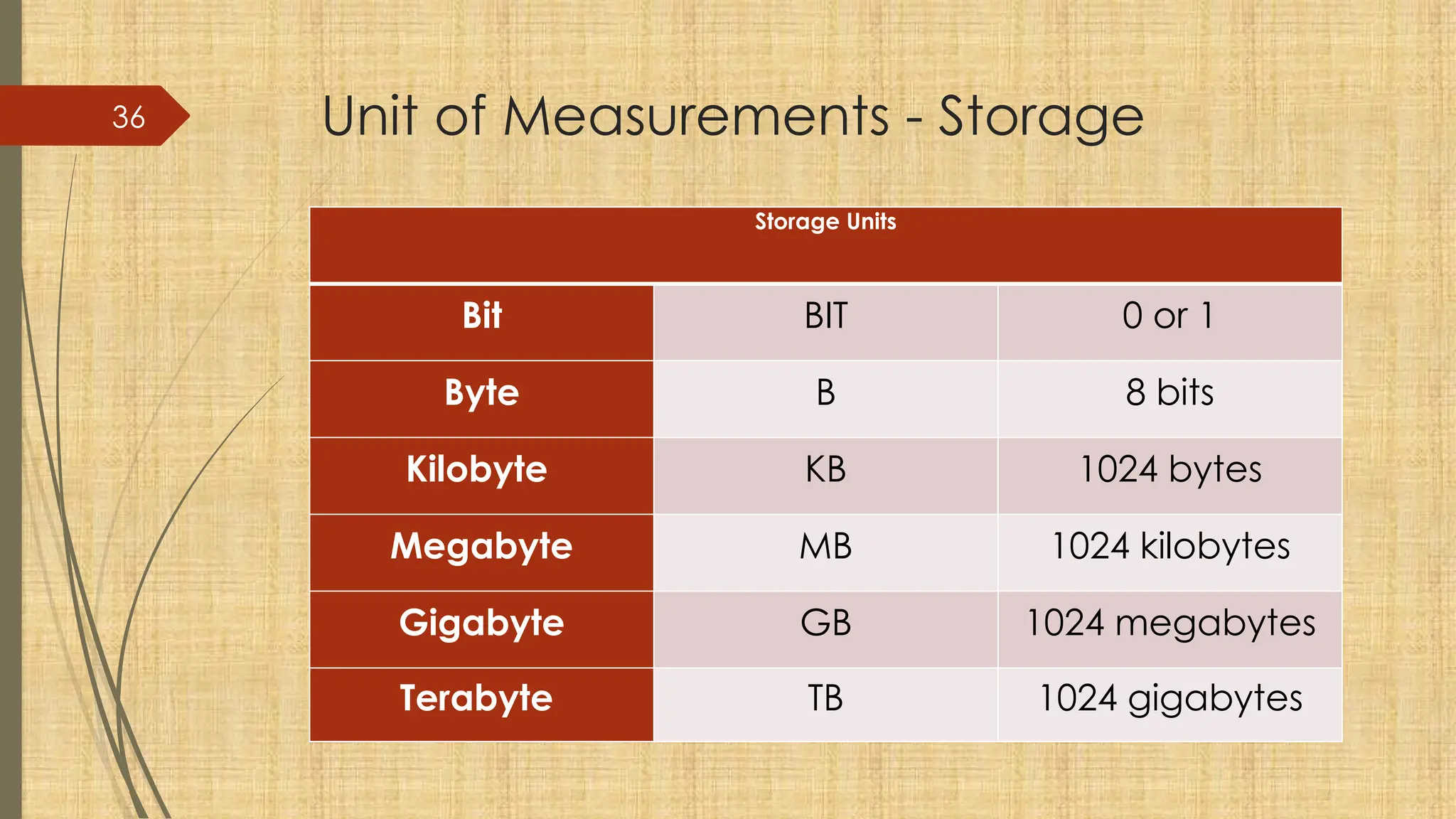
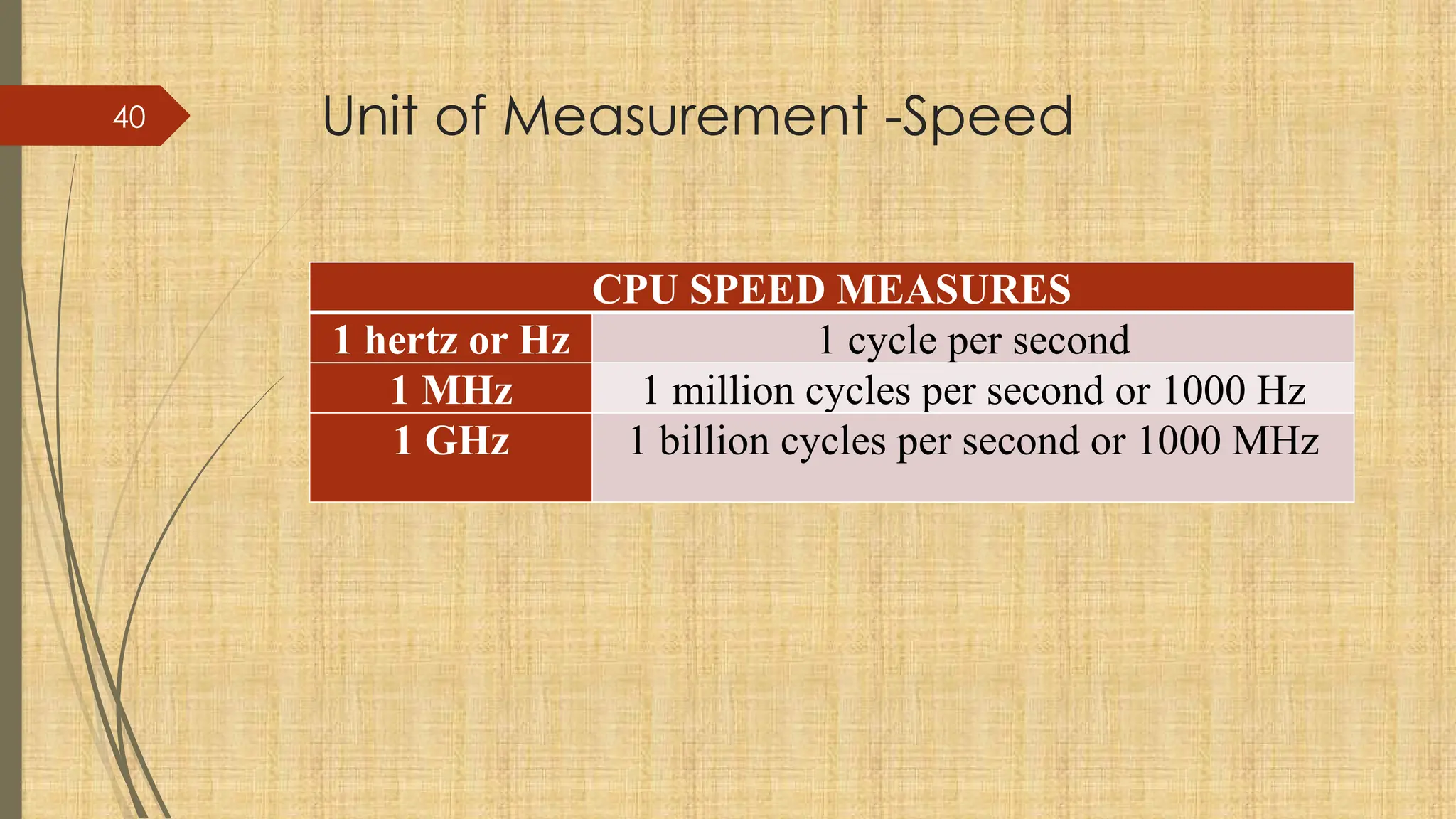
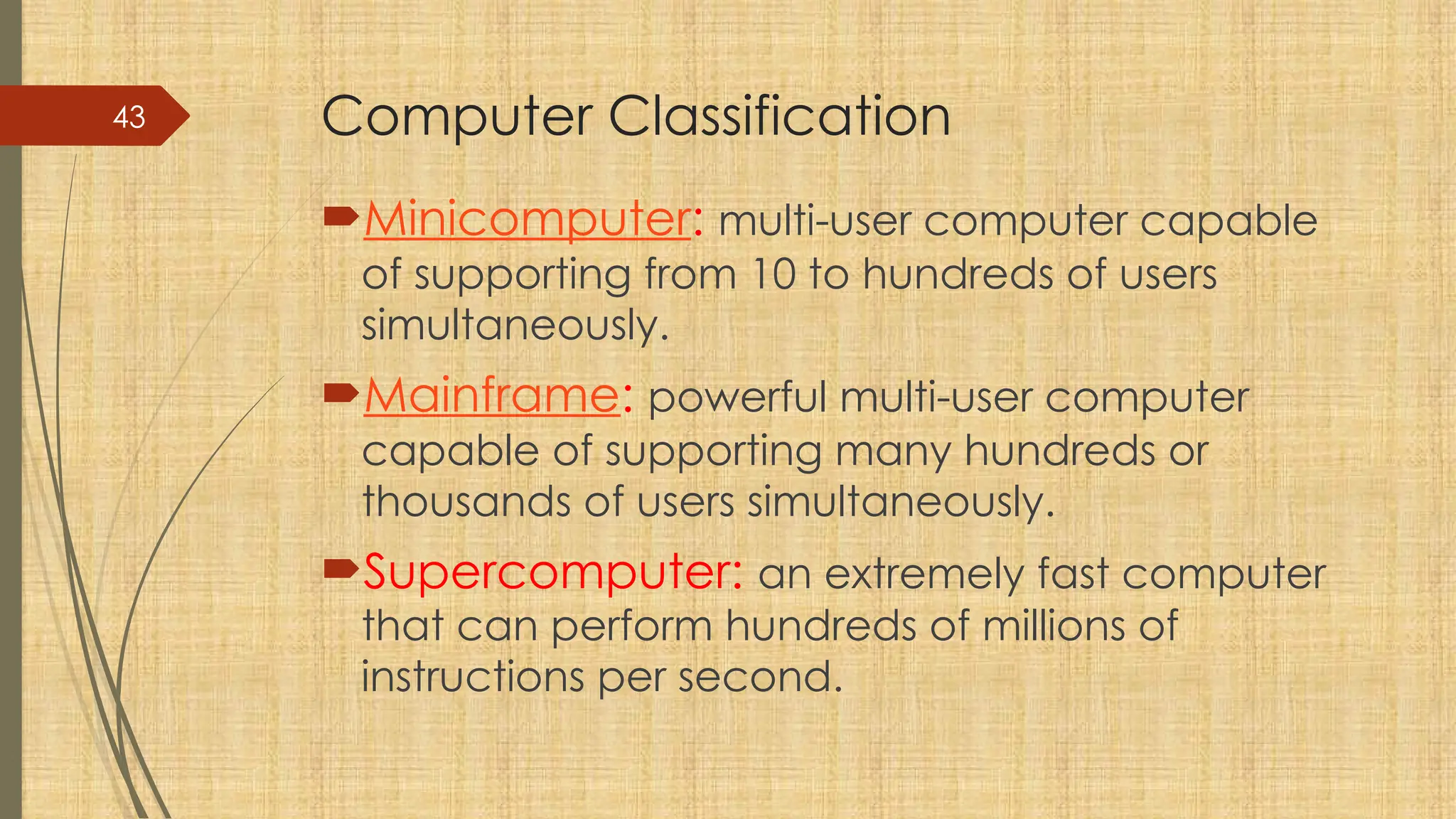
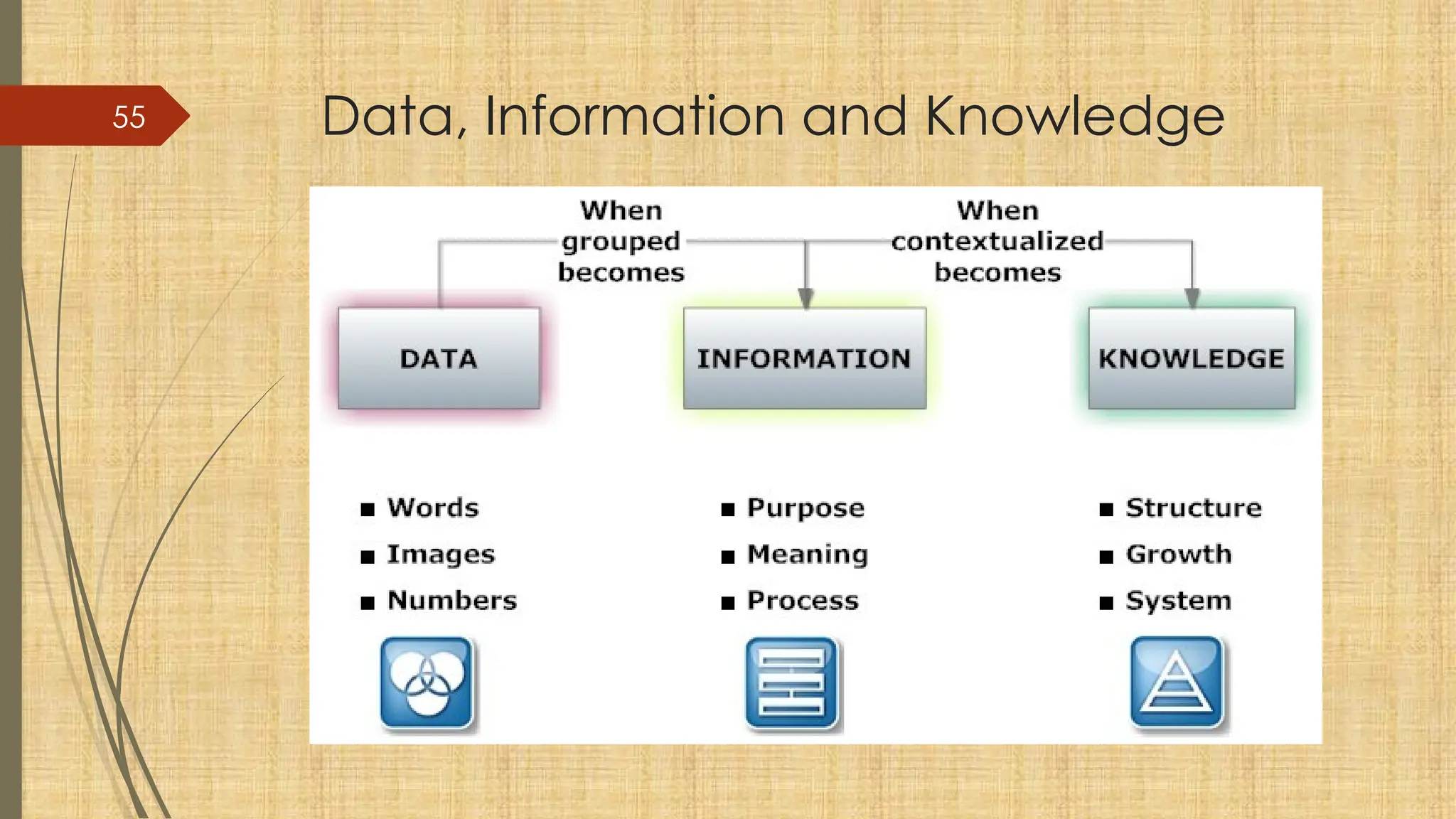
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer basics, including definitions, functions, components, and types of computers. It covers hardware and software distinctions, details about primary and secondary memory, and the roles of input and output devices. Additionally, it touches on data processing, computer characteristics, classifications, and security concerns such as viruses.