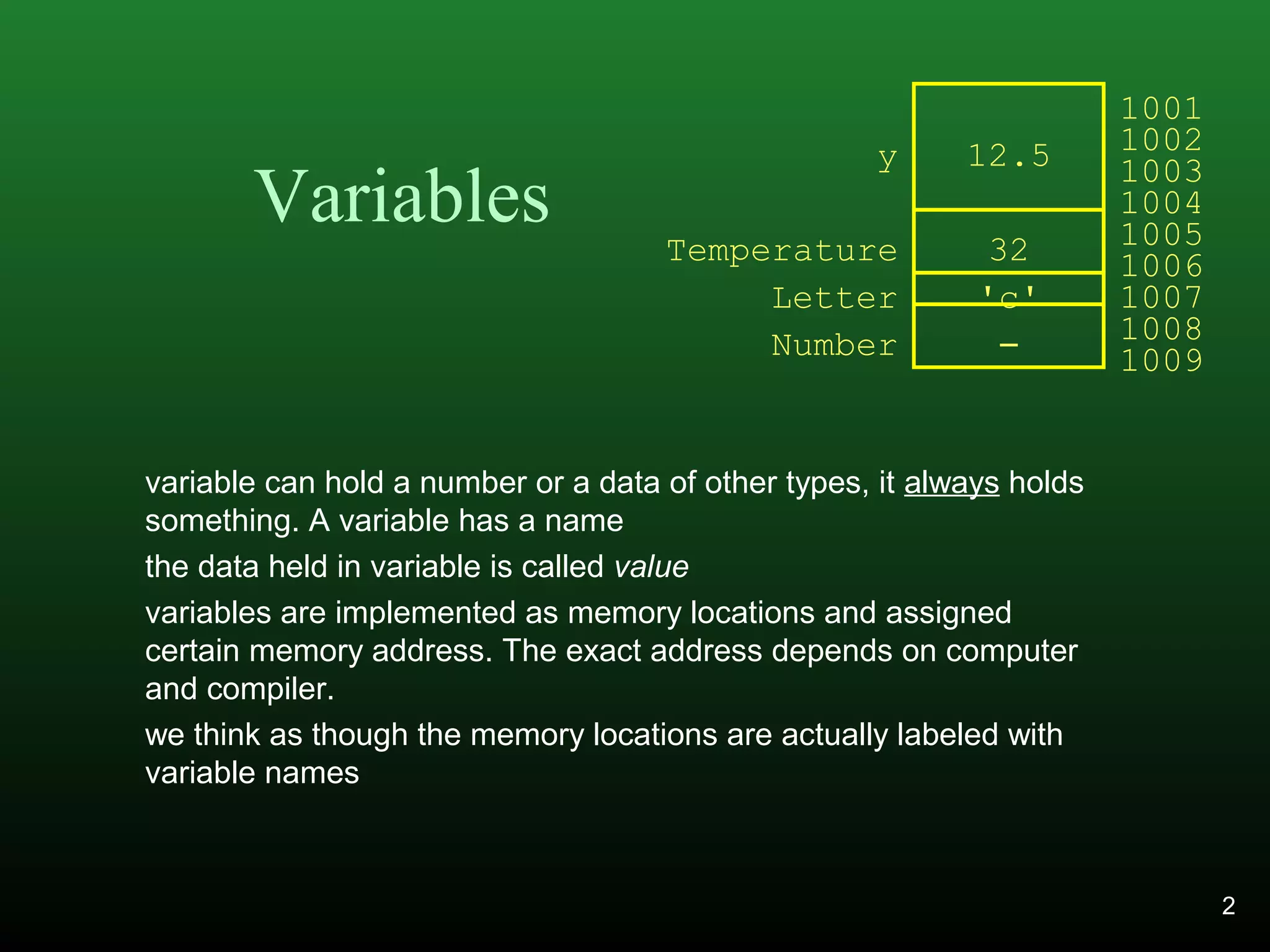
C++ variables can hold different data types like numbers and characters. Variables must be declared with a name and type before use and can be assigned values. Keywords like int and double are used to declare variable types for whole numbers and decimals. Variables are output using cout and input using cin. User input and output allows the program to display prompts and receive user-entered values.