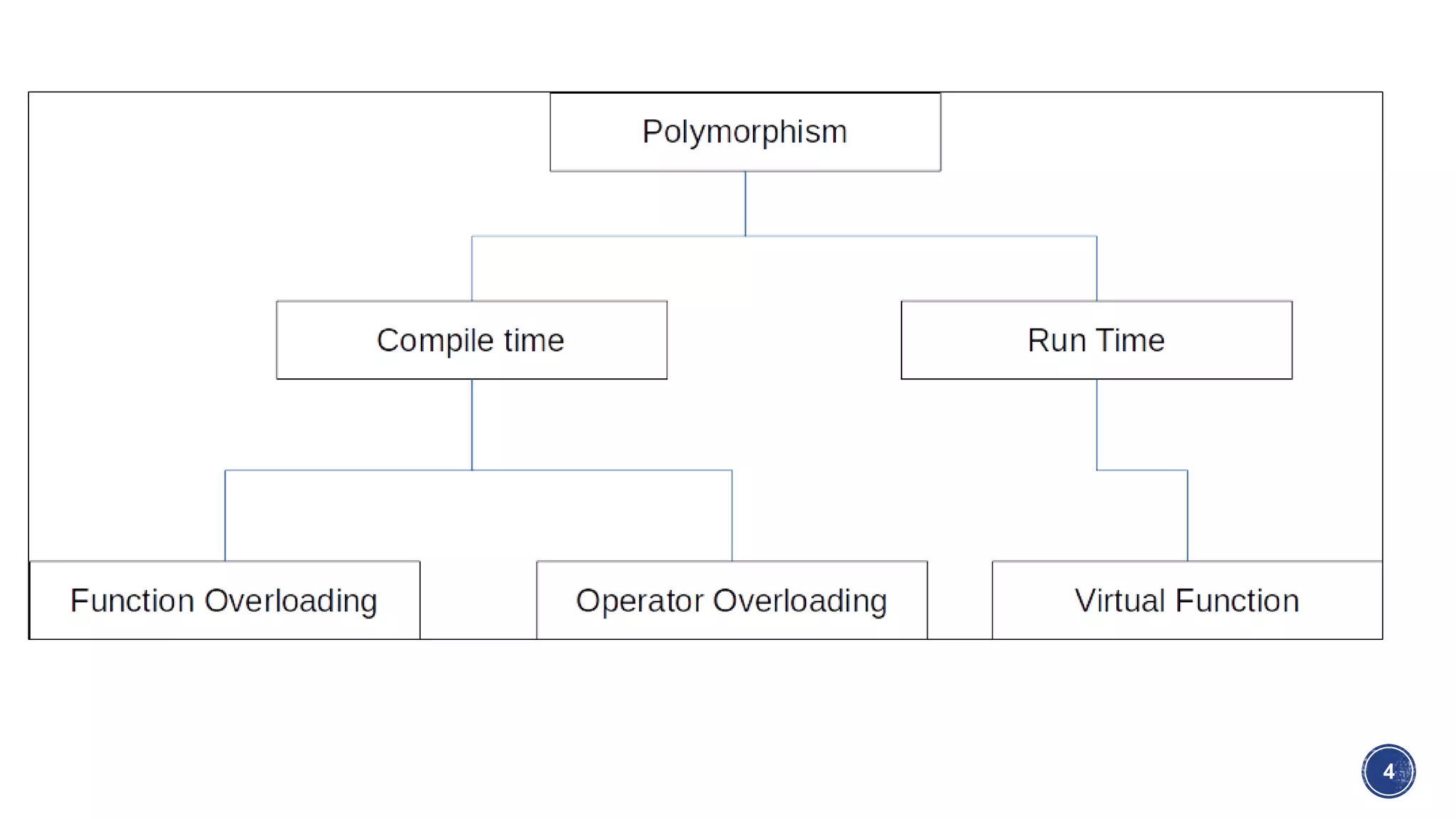
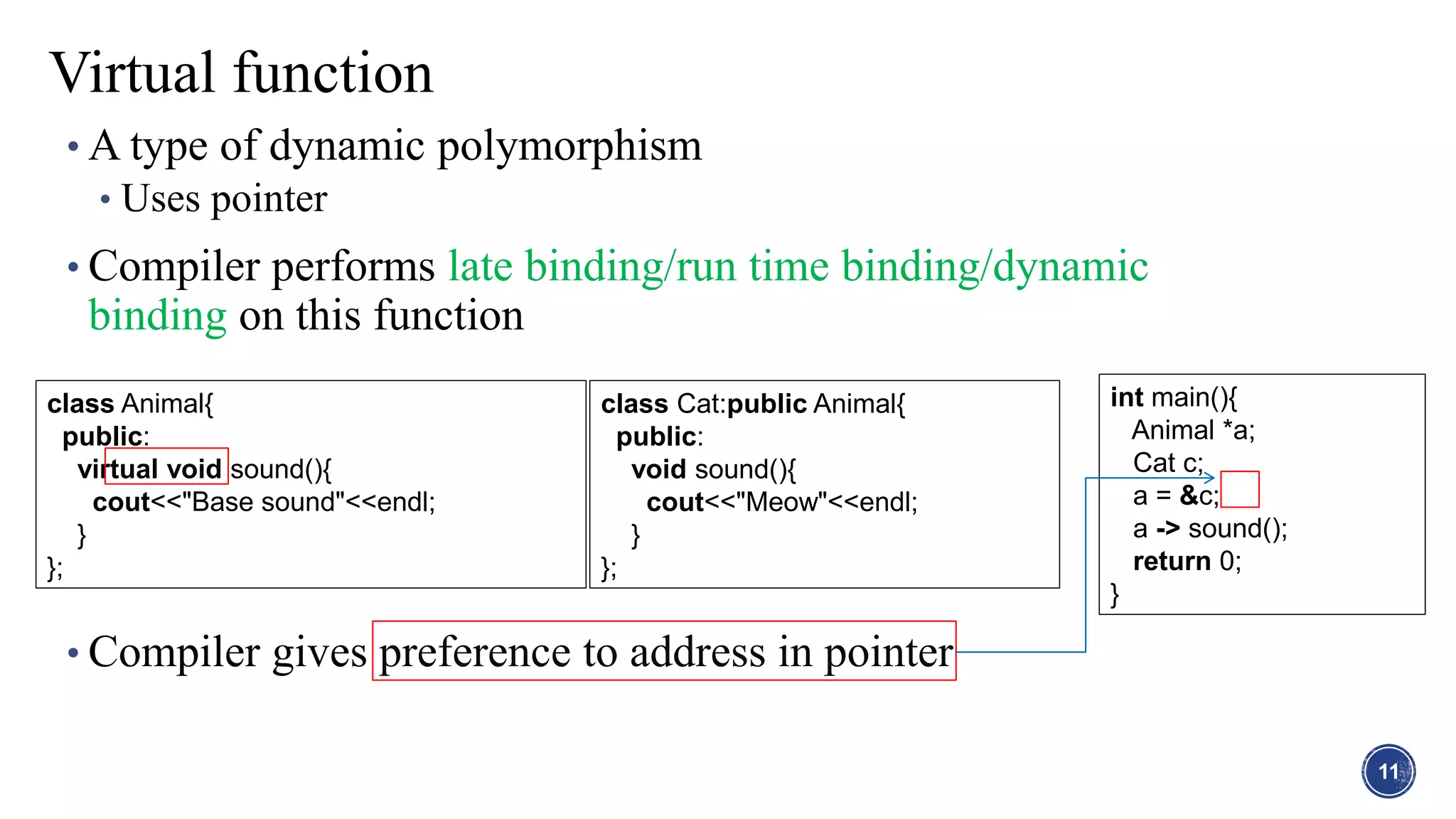
This document discusses polymorphism in C++. It defines static polymorphism as function overloading and overriding, where functions can have the same name but different parameters. Dynamic polymorphism uses virtual functions and runtime binding via pointers. Virtual functions allow overriding in derived classes. Pure virtual functions make a class abstract, requiring implementation in derived classes. Interface classes are like abstract classes but inheritance is not required.