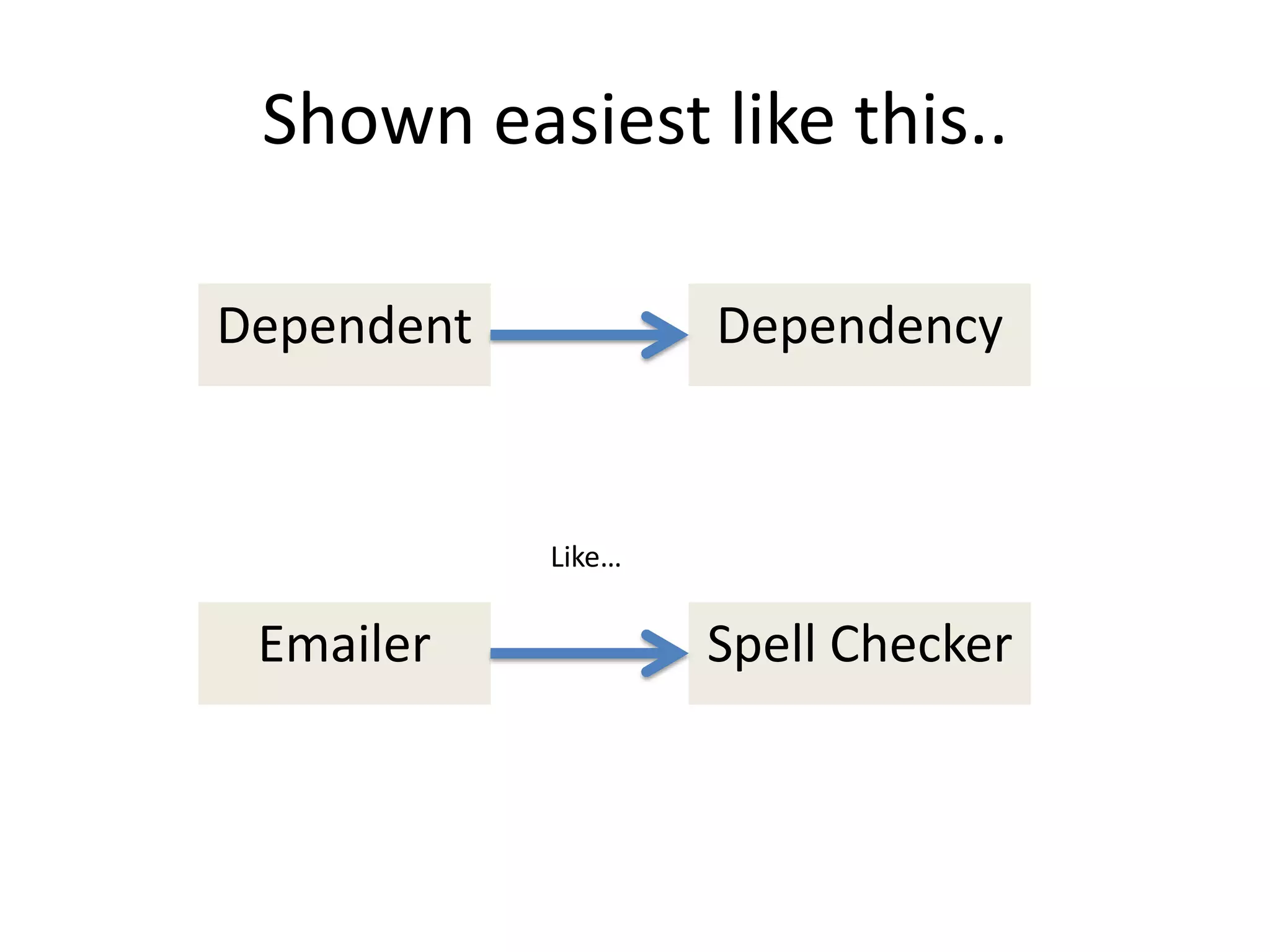
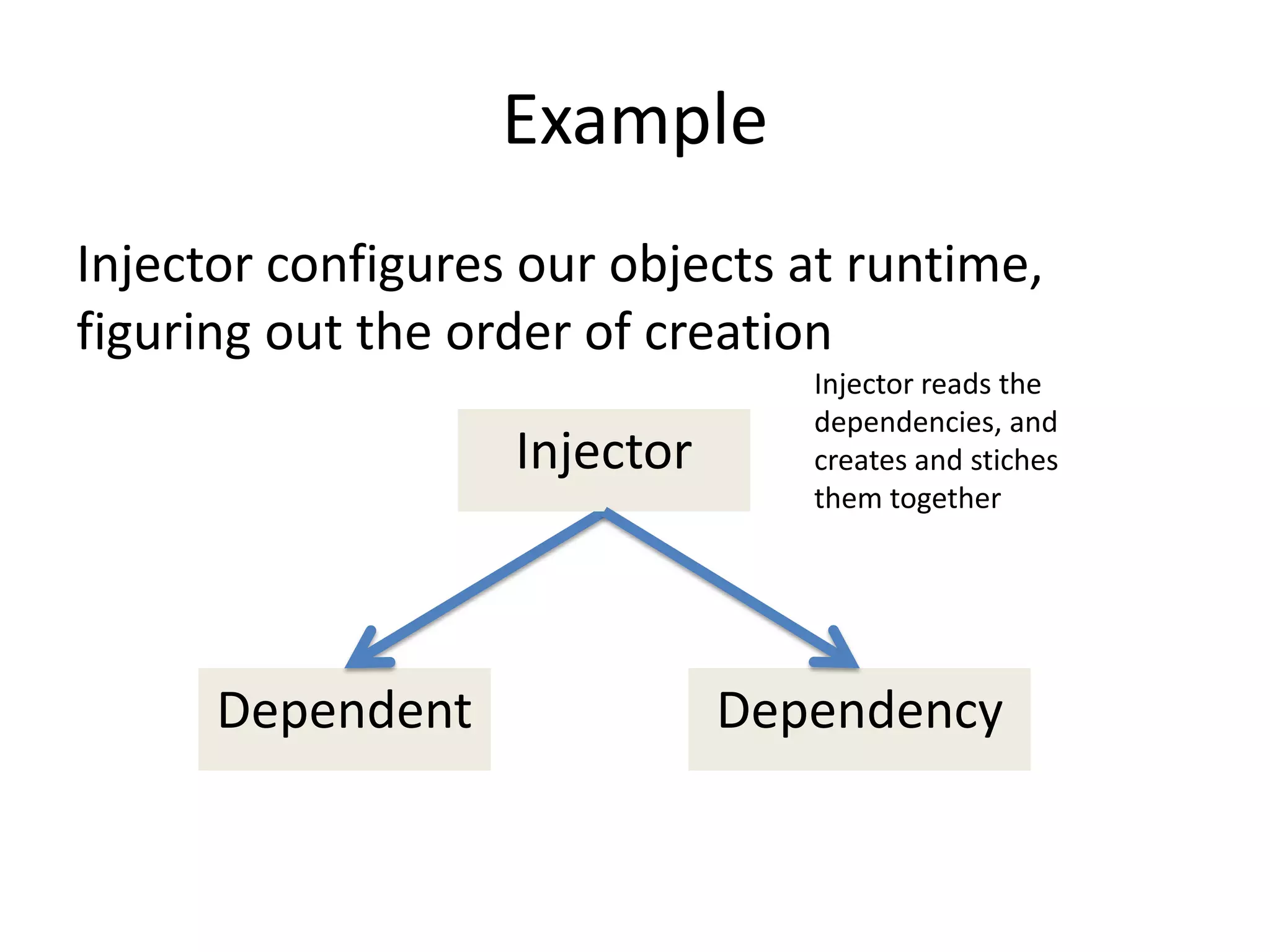
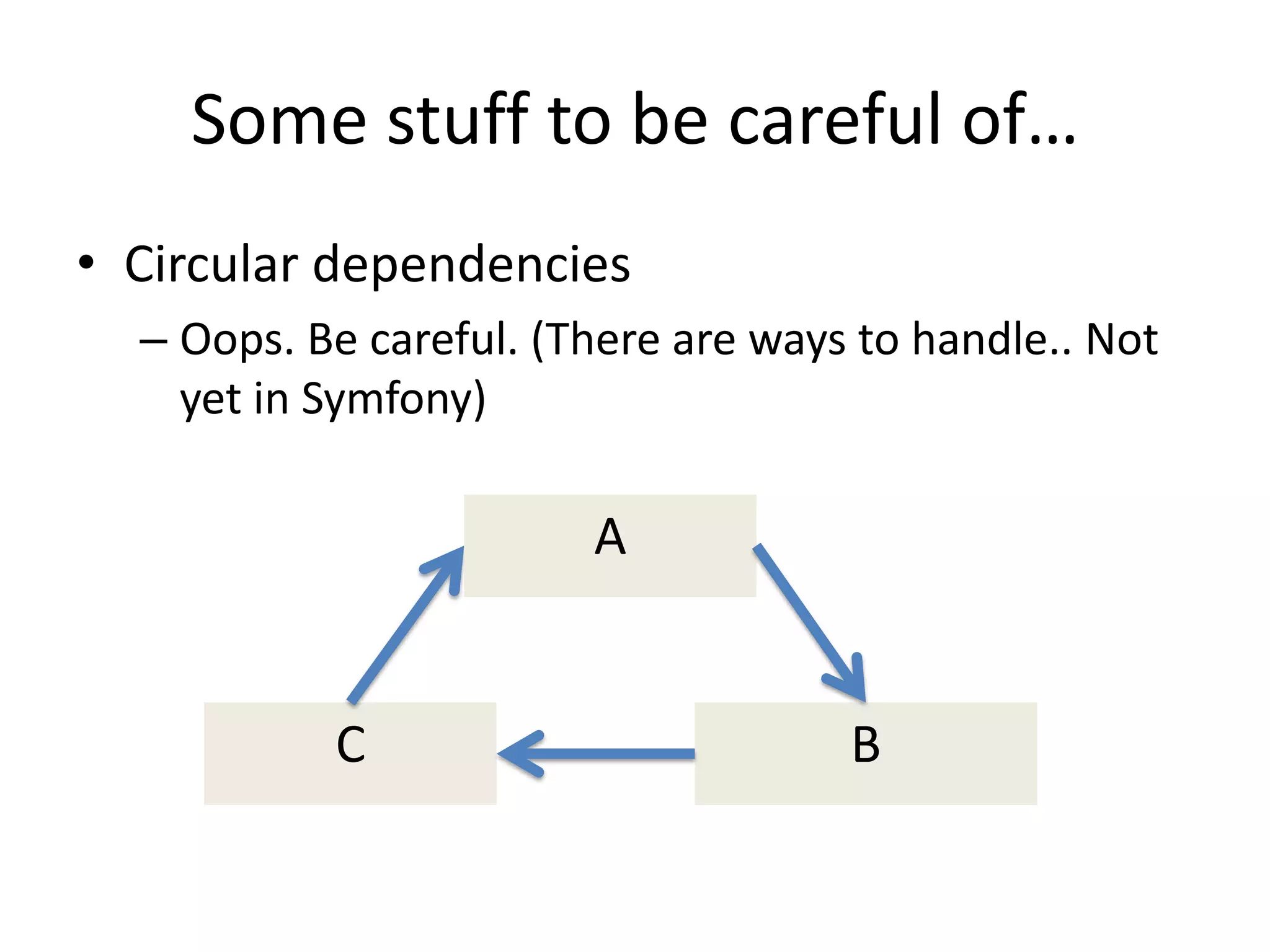
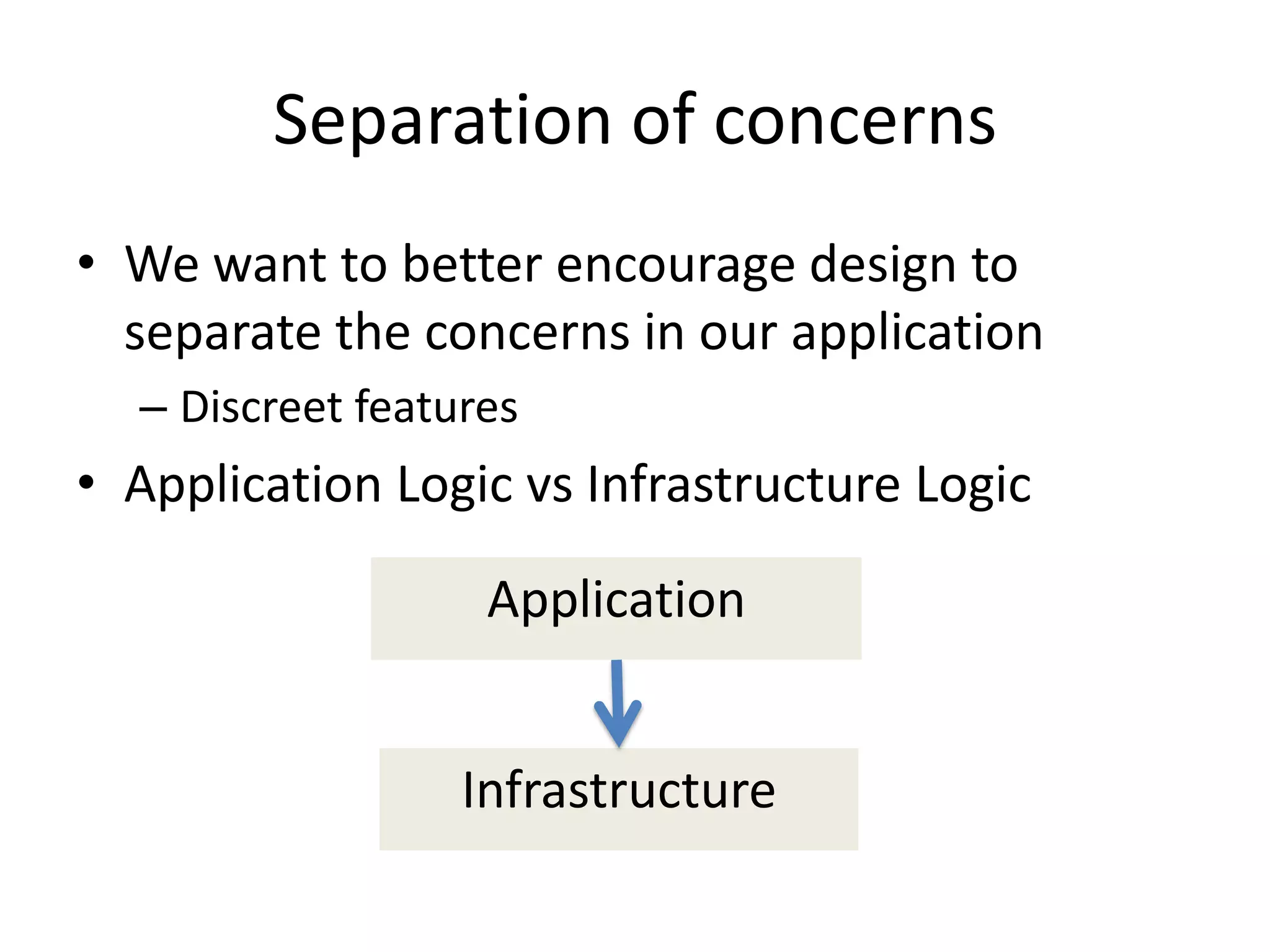
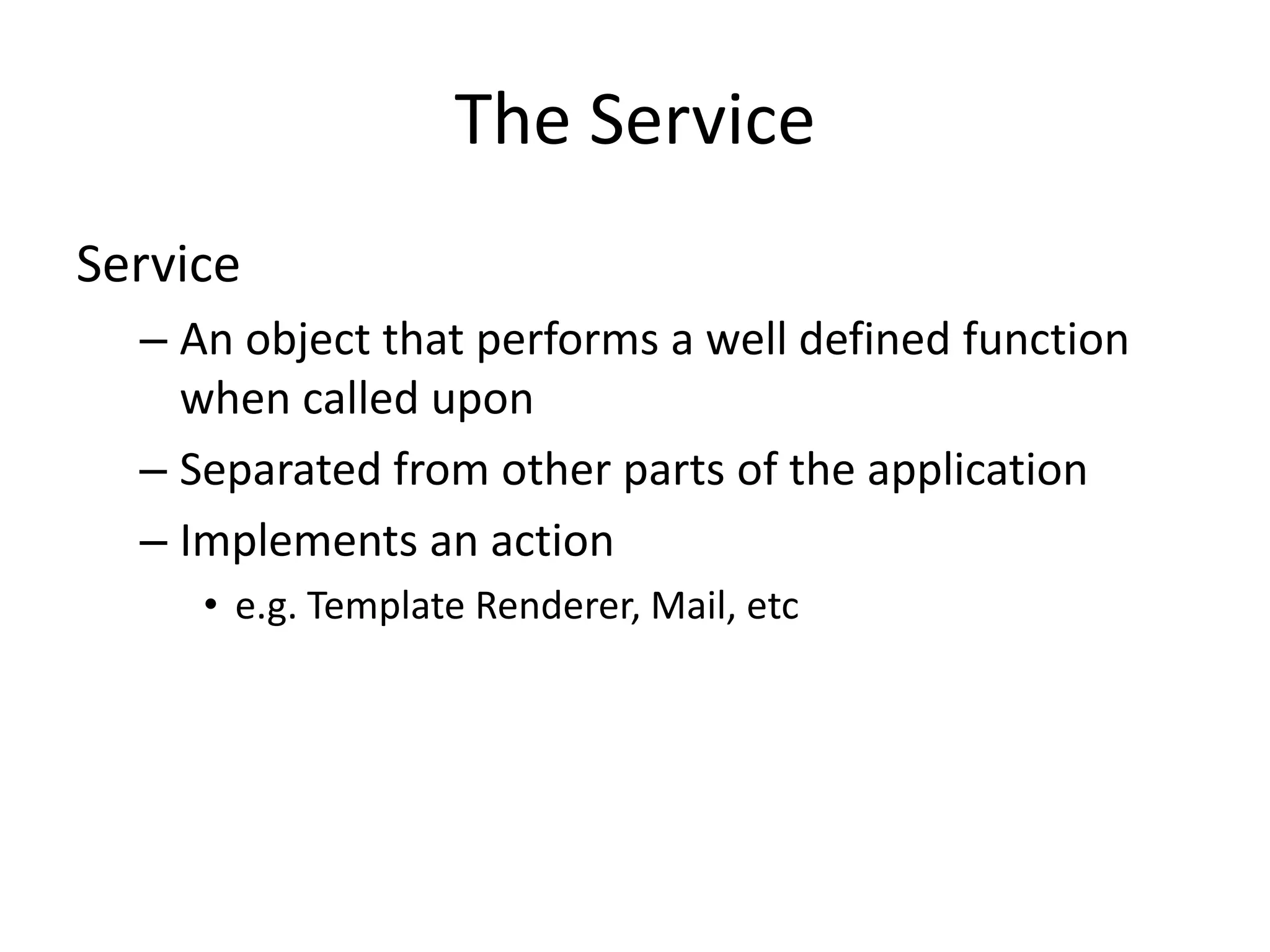
The document provides an introduction to dependency injection and its application in Symfony, highlighting its role in managing dependencies and improving modularity. It covers concepts such as constructor and setter injection, along with the benefits of decoupling and better testability in applications. The conclusion emphasizes the ease of implementation and management of dependencies through Symfony's service architecture.