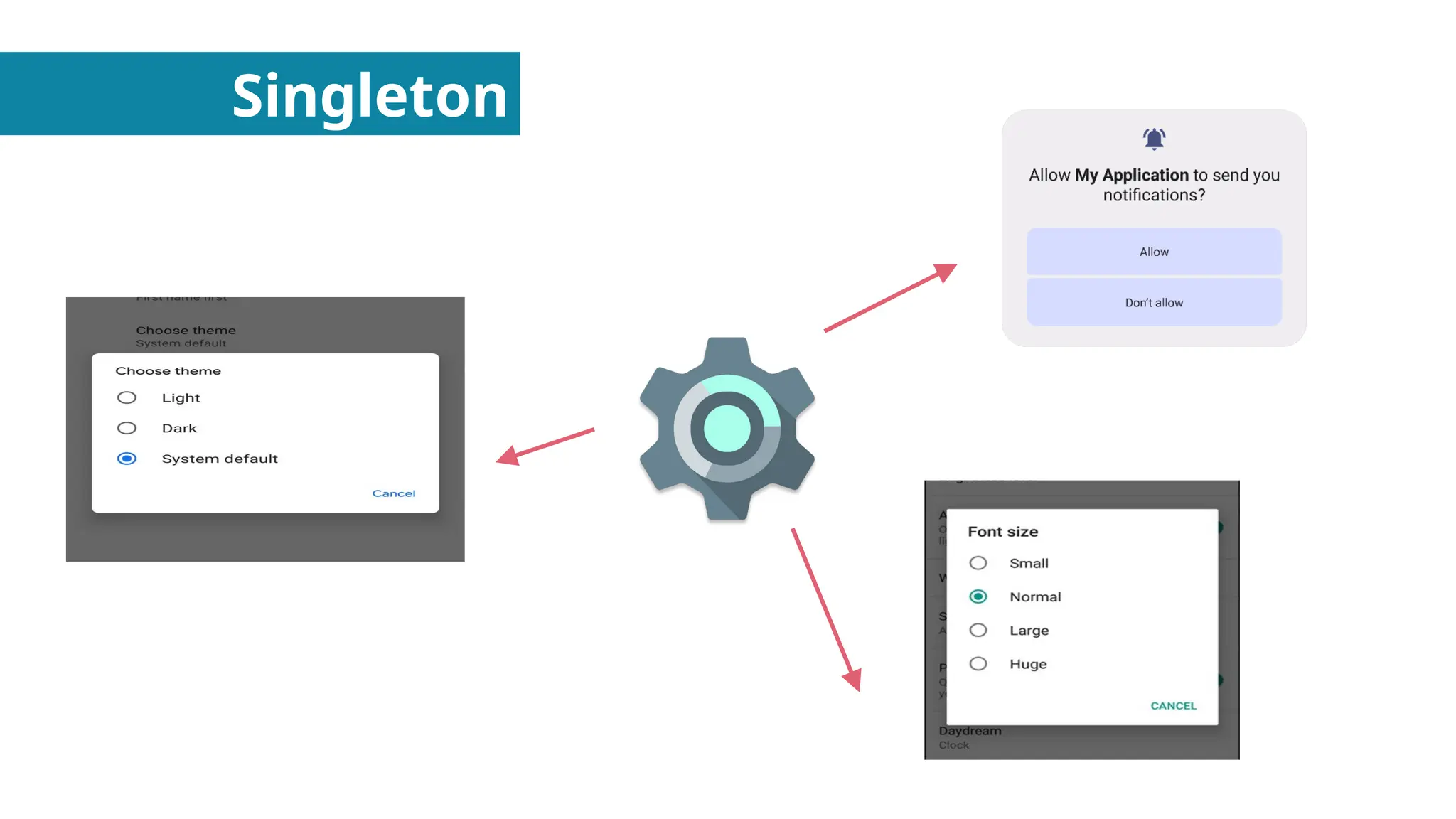
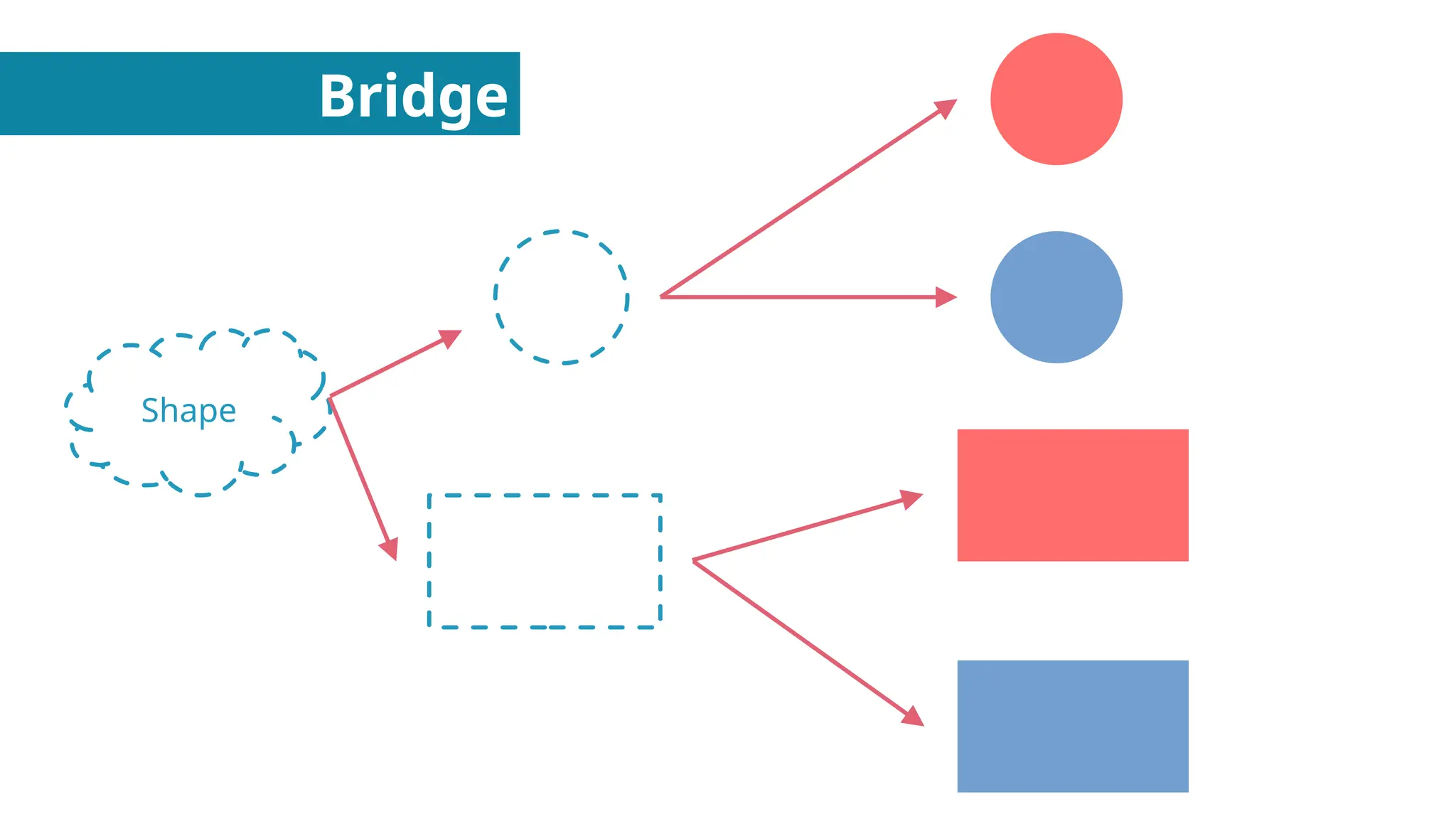
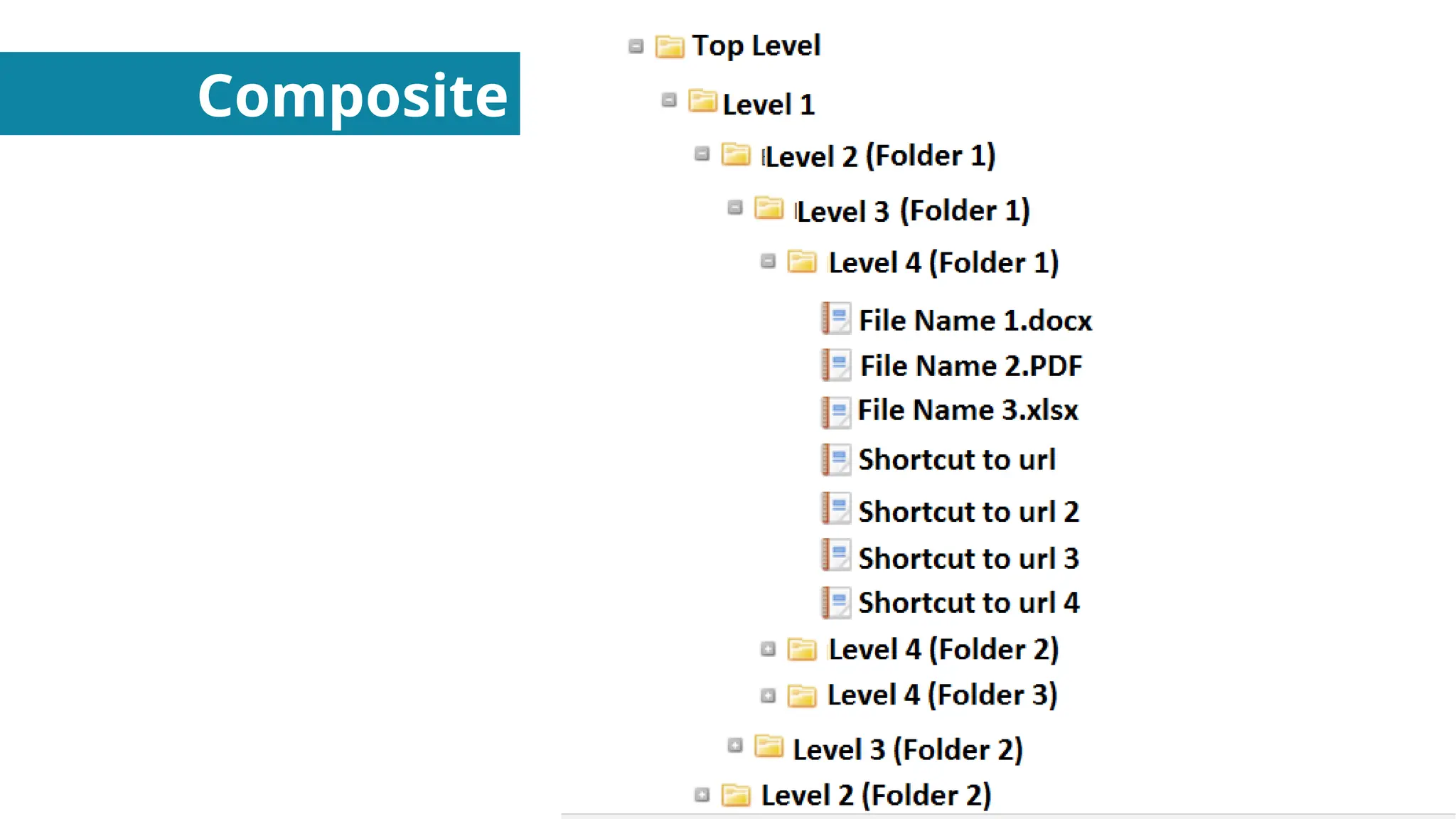
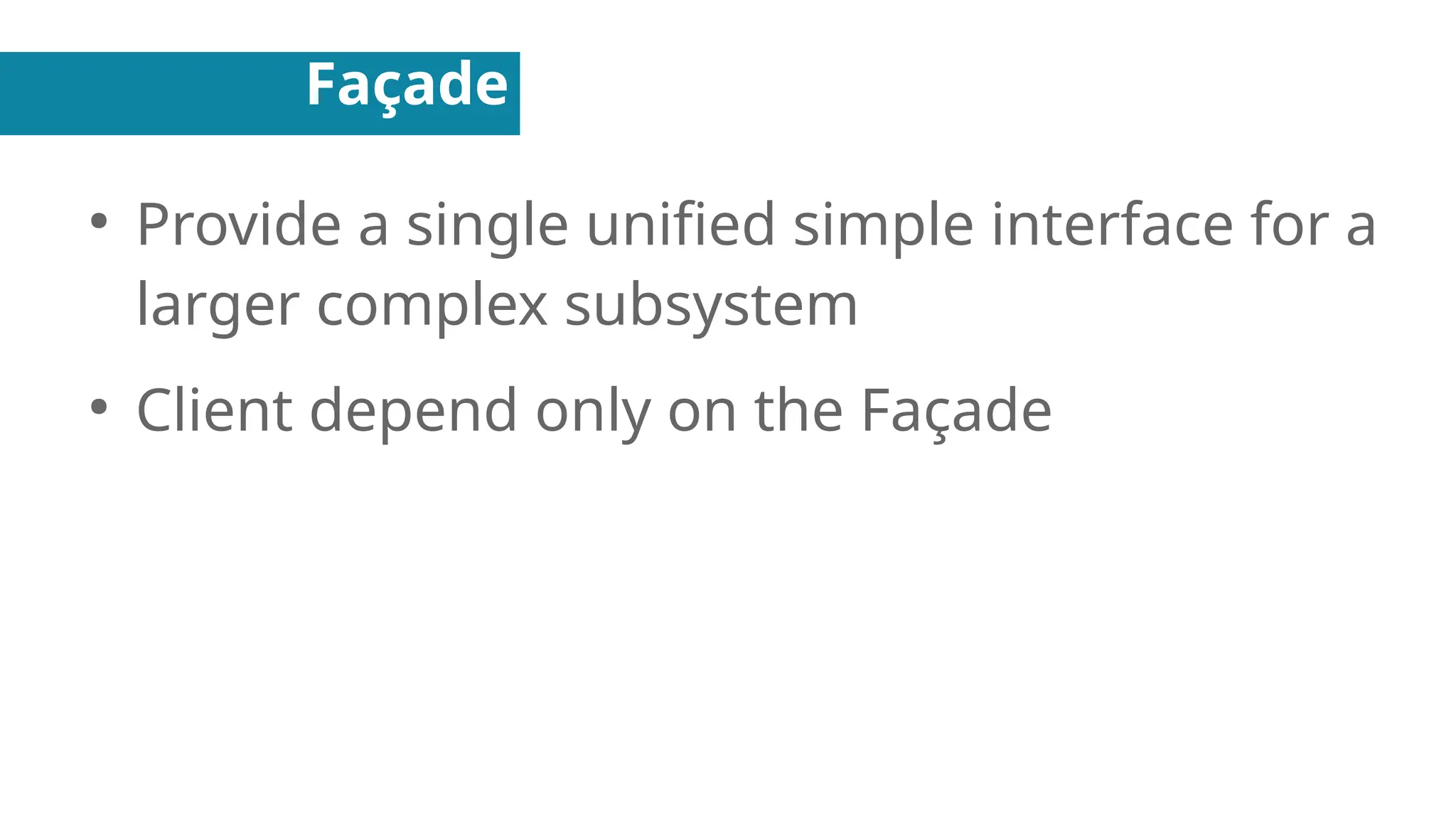
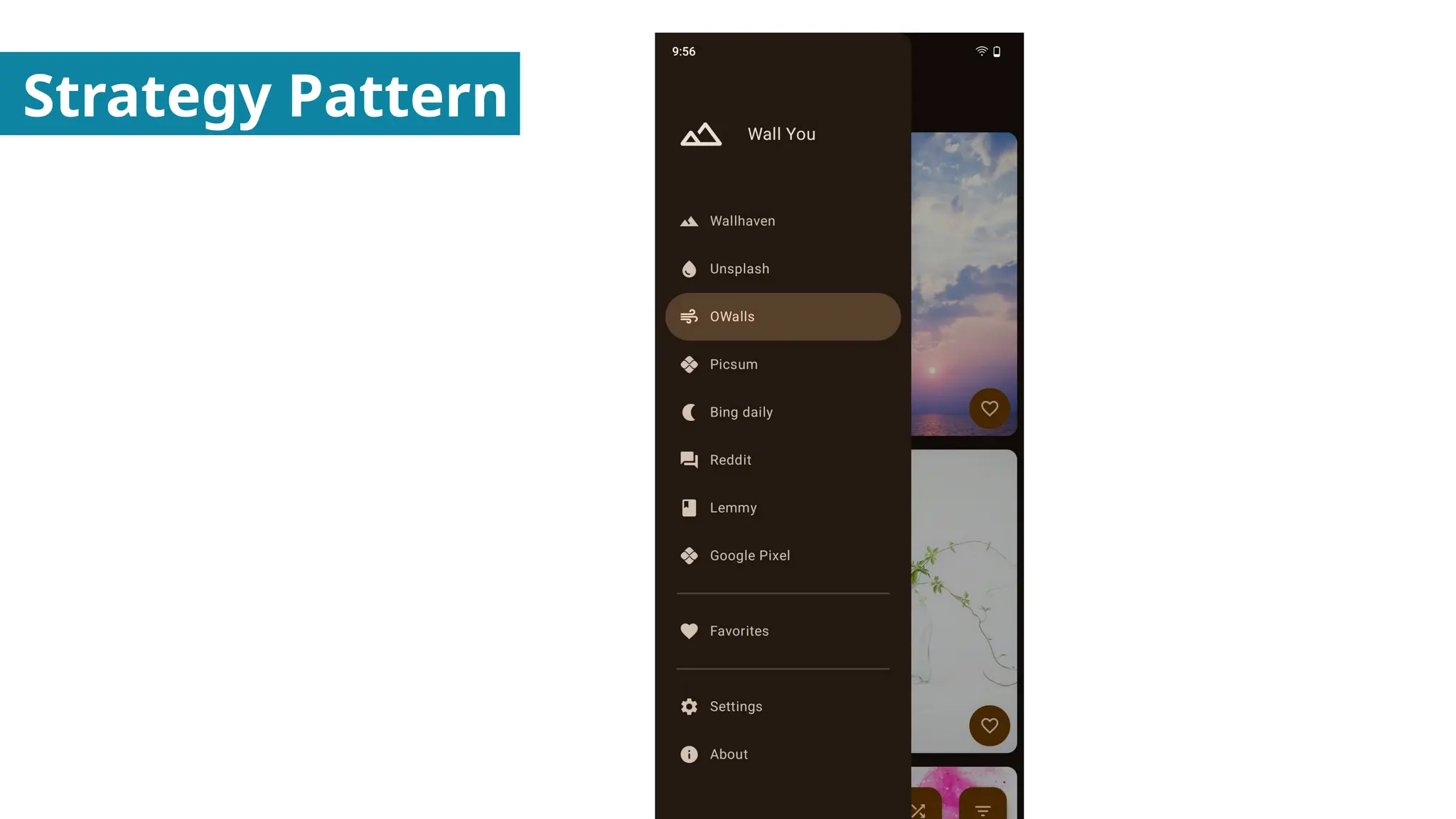
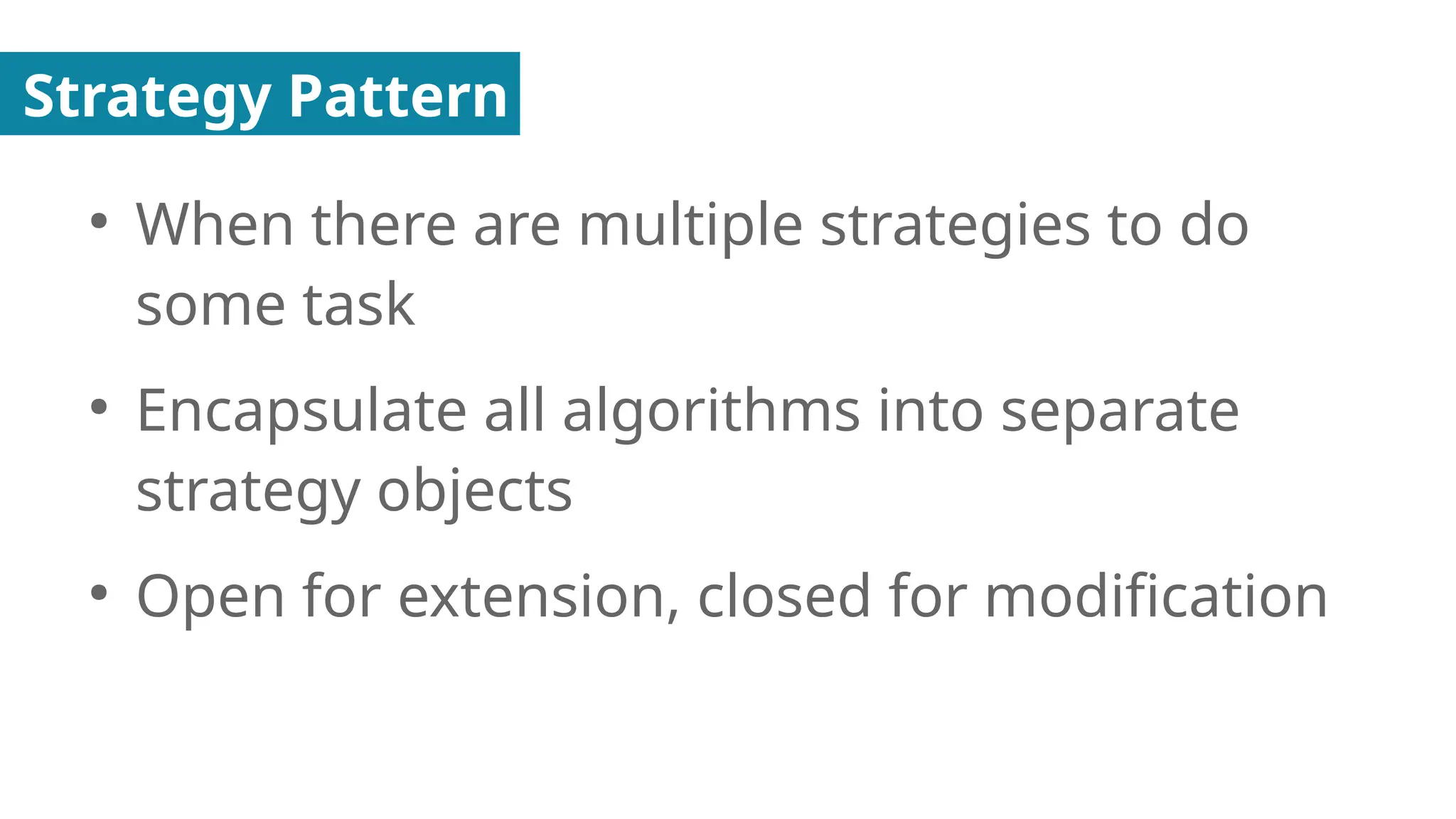
In this presentation I discuss about Design Patterns found in Object Oriented Programming.
Mainly there are 3 types of design patterns.
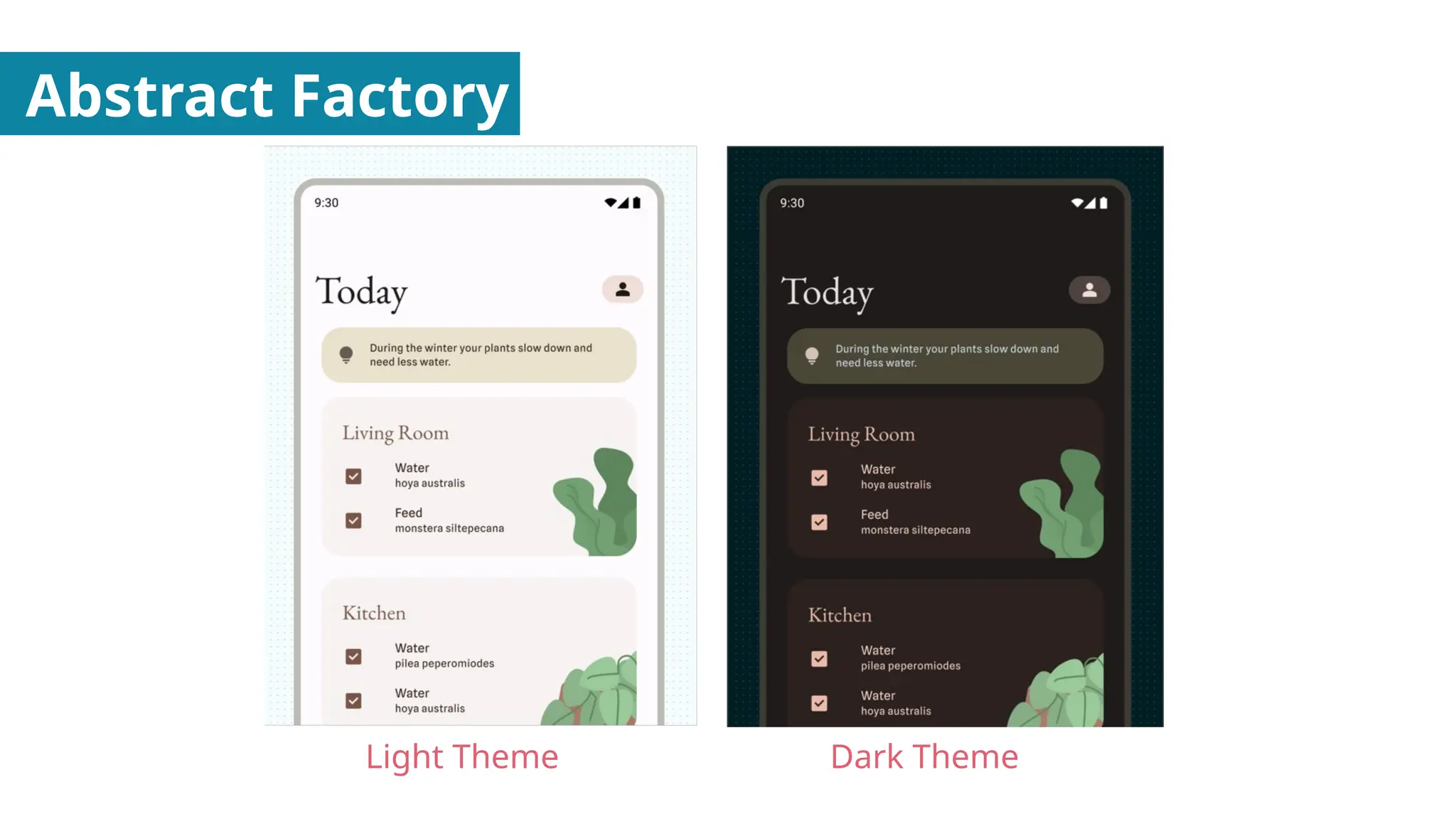
Creational Design Patterns - About the creation of objects
Structural Design Patterns - About Putting Objects together
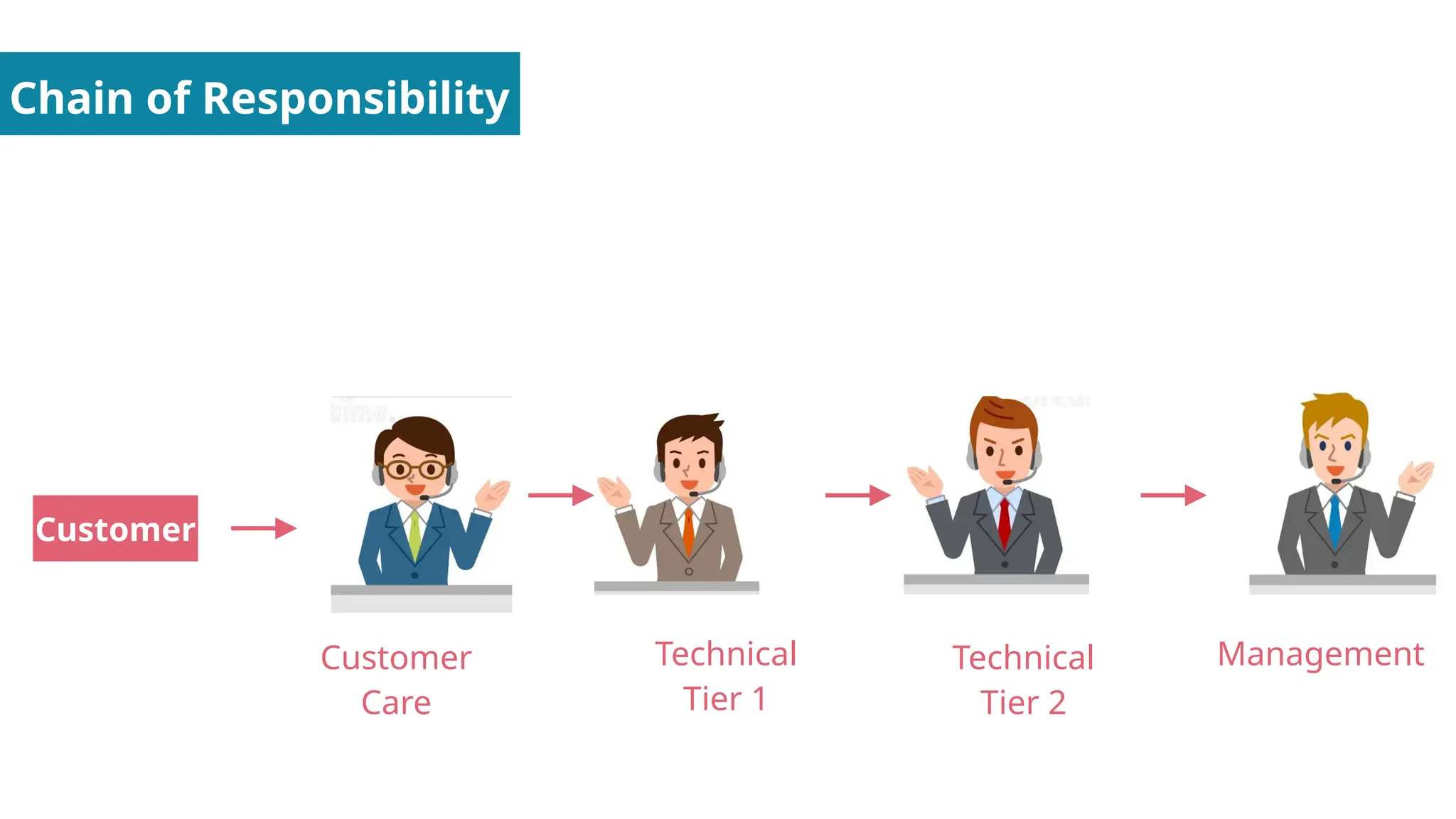
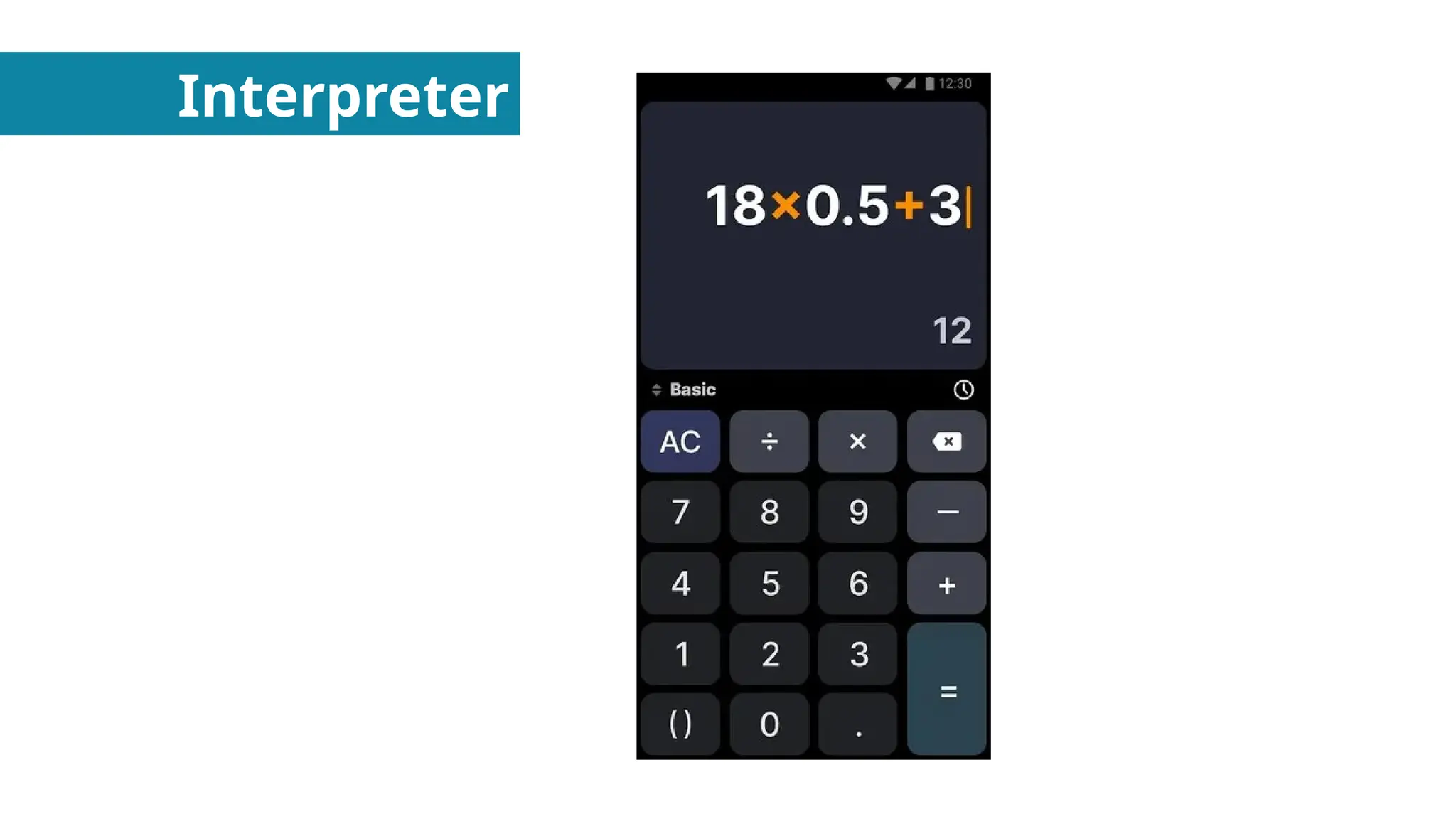
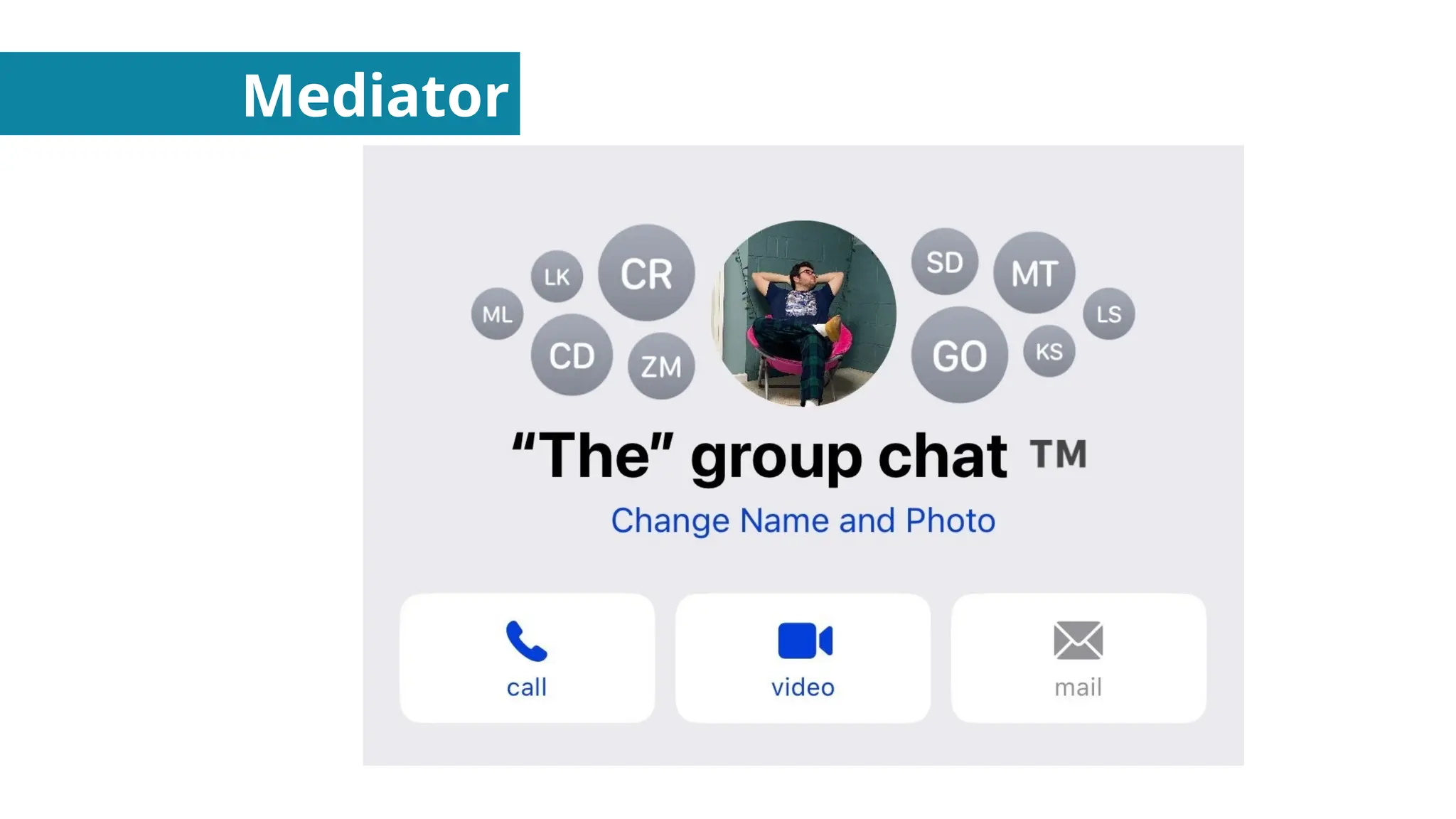
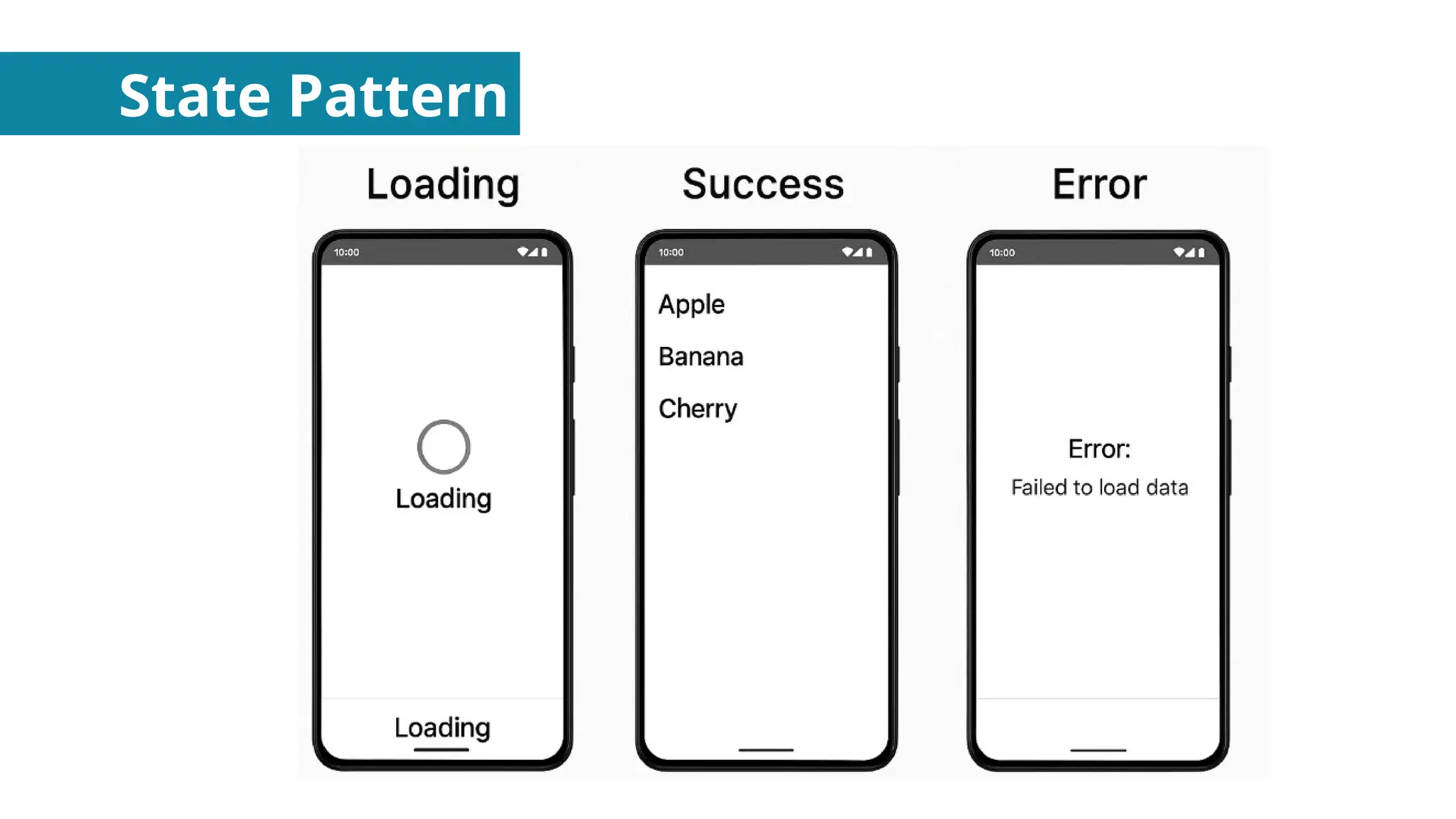
Behavioral Design Patterns - About how objects interact with each other